Figure 4. Pitch-Contingent Inhibition of VTA-Area X Terminals is Sufficient to Aversively Guide Pitch Learning.
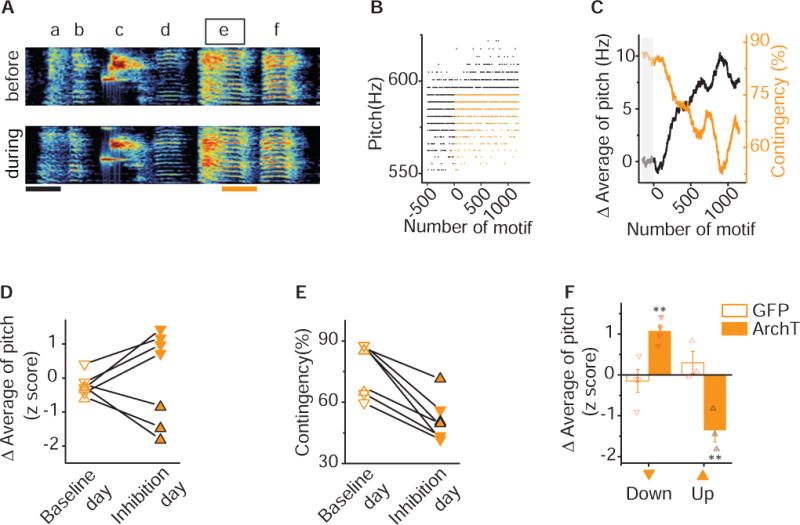
A) Sonogram from the bird used in the closed-loop optical inhibition experiment illustrated in figures 4B – 4C. Pitch contingent optical inhibition does not induce systematic changes in either song or syllable structure. Spectrograms of a song before (top) and during (bottom) an experiment in which light pulse (~520nm, 100ms, orange line) was delivered over syllable ‘e’ during lower pitch variants. Scale bar, 100ms. B) Plot of the pitch of syllable ‘e’ across 1,701 motifs before and during optical inhibition, each point corresponds to one rendition of syllable. Closed-loop optical inhibition of target syllables ’e’ to lower pitch variants (orange dots) but not higher pitch variants (black dots) resulted in a decrease in the number of ‘hit’ trials. C) Plot of the running average of the pitch and hit rate (contingency) during the day of close-looped optical inhibition illustrates the rapid increases in running average of pitch (black line) and concomitant decreases in contingency percentage (orange line). Each point corresponds to one rendition of the syllable; gray box indicates the baseline period before optical inhibition. D) Changes in running average of pitch during baseline day (open) and inhibition day (filled) for experiments in which optical inhibition was delivered to variants with higher pitch (upward pointing triangles with black outline, n=3) or lower pitch (downward pointing triangles, n=4), resulting in significant upward or downward shift in pitch (p=0.016, n=7, Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed-rank test). Changes in running average of pitch are expressed in units of the standard deviation of the last baseline session (z score). E) Closed-loop optical inhibition of syllables with either higher pitch (upward pointing triangles with black outline, n=3) or lower pitch (downward pointing triangles, n=4) elicited increases in contingency (p= 0.016, n=7, Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed-rank test). Contingency on baseline day (open) and stimulation day (filled) was determined according to the same preset threshold for each individual experiment. F) Closed-loop optical illumination of syllables with either higher pitch (up) or lower pitch (down) elicited downward (p=0.014) or upward (p=0.014, Unpaired t test with Welch’s correction) shift in running average of pitch in axArchT birds (filled, up n=3, down n=4) but not in GFP+ birds (open, up n=3, down n=4). Error bars indicate standard error of the mean. See also Figure S3.
