Abstract
Purpose of review
Environmental toxicants are increasingly implicated in the global decline in metabolic health. Focusing on diabetes, herein the molecular and cellular mechanisms by which metabolism disrupting chemicals (MDCs) impair energy homeostasis are discussed.
Recent findings
Emerging data implicate MDC perturbations in a variety of pathways as contributors to metabolic disease pathogenesis, with effects in diverse tissues regulating fuel utilization. Potentiation of traditional metabolic risk factors, such as caloric excess, and emerging threats to metabolism, such as disruptions in circadian rhythms, are important areas of current and future MDC research. Increasing evidence also implicates deleterious effects of MDCs on metabolic programming that occur during vulnerable developmental windows, such as in utero and early post-natal life as well as pregnancy.
Summary
Recent insights into the mechanisms by which MDCs alter energy homeostasis will advance the field’s ability to predict interactions with classical metabolic disease risk factors and empower studies utilizing targeted therapeutics to treat MDC-mediated diabetes.
Keywords: EDCs, MDCs, diabetes, obesity, metabolism, endocrine disruptor, glucose intolerance, insulin resistance, metabolic syndrome
Introduction
Diabetes and obesity rates have risen exponentially over the last several decades, and the impact of this on individual morbidity and societal costs are significant. In addition to the burden of disease in adults, metabolic disease in children has risen dramatically [1], and the impact of diabetes across the lifespan has been further compounded by increased rates of gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) in pregnant women [2]. Indeed, GDM has tripled in the past 20 years, affecting 9% of pregnancies in the United States [2], which is critical because GDM is linked to adverse pregnancy outcomes for both mother and child [3]. While traditional metabolic risk factors such as reduced physical activity, increased caloric intake, aging, and sleep deficits are undoubted contributors to this phenomenon, they insufficiently account for this upsurge. Indeed, for a given level of activity and caloric intake, individuals in today’s society weigh more than they did 20–30 years ago [4••]. Consequently, other factors are implicated in the global deterioration of metabolic health, including exposure to environmental factors that drive or facilitate metabolic dysfunction [5••. Over the last decade, abundant epidemiologic evidence has emerged linking an increasing number of endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) to the development of metabolic disease; however, our understanding of the mechanisms by which these exposures promote metabolic dysregulation remains relatively rudimentary. This report will integrate the current molecular and cellular evidence by which EDCs act as metabolism disrupting chemicals (MDCs) to dysregulate glucose homeostasis and increase diabetes risk (Table 1, Supplemental Table 1) in order to provide direction for future research aimed at mitigating the deleterious impact of environmental exposures on human metabolic health.
Table 1.
Summary of cellular and molecular effects of MDCs with common routes of exposure, nationally recommended safe exposure levels, and estimated elimination half-lives in humans
| Compound | Uses and Common Routes of Exposure | Recommended Safe Exposure Level in Humans | Cellular/Molecular Metabolic Effects | Elimination Half-life in Humans | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Organotins (TPT, TBT) | *Biocide in marine paints, fungicide, wood preservative, PVC stabilizer *Drinking water, seafood, PVC products |
0.1 mg/m3 air (OSHA/NI OSH) | General mechanisms: Activates PPARγ and RXR Whole animals: Increased weight, increased/reduced insulin levels, leptin, hepatic steatosis β-cells: Reduced GSIS, impaired Ca2+ signaling, reduced NAD(P)H and ATP, and PKA levels Insulin target cells: Increased adipogenesis |
Serum half-life 3 days (POP) | [11–13,75, 76,87,103, 125] | |
| Arsenic | *Pesticides, smelting, industrial waste *Drinking water, soil, seafood, rice, mushrooms, poultry |
10 ppb (water; EPA) | General mechanisms: Oxidative stress/Unknown Whole animals: Glucose intolerance Gestational exposure: Glucose intolerance, obesity in dams β-cells: Reduced GSIS, increased ROS, impaired Ca2+ signaling, insulin granule exocytosis, insulin gene expression. Induced autophagy, apoptosis. Insulin target cells: Reduced insulin signaling, ROS, reduced hepatic glycogen |
4–6 hours; 20–30 hours (methyl ated) | [14–17,30, 31,50,53, 68,104,126 ] | |
| Cadmium | *Byproduct of mining, combustion, waste incineration *Soil, water, air; leafy vegetables, peanuts, soybeans, sunflower seeds; inhalation |
0.005 mg/L (water; EPA); 5 μg/m3 per day (air; OSHA) | General mechanisms: Oxidative stress/Unknown Whole animals: Insulin resistance, increased insulin levels β-cells: Reduced GSIS, increased ROS, mitochondrial dysfunction, apoptosis, mediated by JNK Insulin target cells: Reduced GLUT4 |
4–38 years | [33,34,59,1–27] | |
| Mercury | *Mining, waste incineration, manufacturing *Fish, shellfish, medical/dental procedures |
2 ppb (water; EPA); 1 ppm (food; FDA); 0.1 mg/m3 (air; OSHA) | General mechanisms: Oxidative stress/Unknown β-cells: Reduced GSIS, increased ROS, PI3 kinase and Akt, induced apoptosis and necrosis. |
1–3 weeks to 1–3 months (depend s on route of exposur e, chronicit y) | [35,36] | |
| Alkylphenoli c Compounds (e.g. Octylphenol, Nonylphenol ) | *Surfactants, detergents, emulsifiers *Fish, drinking water, personal care products |
Undetermi ned | General mechanisms: Modulates estrogen signaling β-cells: Reduced GSIS, impaired mitochondrial structure and function. Insulin target cells: Impaired FA metabolism, reduced lipogenesis |
2–3 hours (POP) | [19,128] | |
| BPA | *Food packaging, toys, canned food liners *Ubiquitous exposure |
50 mcg/kg/da y (FDA) 4 mcg/kg/da y (European Food Safety Authority) | General mechanisms: Modulates estrogen signaling Whole animals: Glucose intolerance Gestational exposure: Glucose intolerance, increased weight in both dams and offspring. β-cells: Reduced GSIS, disrupted mitochondrial structure and function, increased ROS Insulin target cells: Reduced insulin action and signaling intermediates, increased adipose inflammation (JNK, NFκB) |
4–5 hours | [19,29,40,4–8, 51,52,77,7–8, 92,93,101, 102, 108] | |
| Phthalates/P hthalate esters (e.g. DEHP, MEHP) | *Liquid plasticizers; Lend flexibility to plastics (e.g. PVC); lubricants, perfumes, cosmetics, medical tubing, wood finishes, adhesives, paints, toys, emulsifiers in food. *Ubiquitous exposure |
DEHP: 6ppb (water; EPA); 5mg/m3/8 hour day (OSHA) | General mechanisms: Activates PPARγ signaling Whole animals: Insulin resistance, reduced hepatic glycogen, increased ROS. Gestational exposure: increased systemic inflammation and altered adipose development in offspring β–cells: Reduced GSIS, insulin content, increased ROS Insulin target cells: Reduced insulin signaling, glucose oxidation, increased ROS in muscle |
12 hours | [32,56,57,6–9, 105] | |
| PCBs (mix of >200 congeners) | *Plasticizers, in resins, carbonless copy paper, adhesives, paints, inks (banned 1979) *High fat food (dairy, meat, fish) |
0.0005 ppm (water; EPA) 0.2–3.0 ppm (food; FDA); 0.5– 1.0 mg/m3 (air; OSHA); 6.0 ug/kg/d (total) | General mechanisms: Unknown/Varied Whole animals: Glucose intolerance β-cells: increased insulin secretion and Ca2+ signaling |
6 months - >100 years (varies by exposur e; POP) | [20,129,130] | |
| Dioxins (e.g. TCDD, PCB126) | *Byproducts of smelting, paper manufacture, herbicides and pesticides, hospital waste. *Soil, dairy, meat, seafood. |
0.01- 1ng/L/day pg/kg/d (water; EPA) | General mechanisms: Activates AhR signaling, induces inflammation Whole animals: Glucose intolerance β-cells: Reduced GSIS, insulin content; increased basal insulin secretion, [Ca2+]IC Insulin target cells: Reduced insulin signaling, increased inflammation (JNK, ERK1/2), reduced hepatic glycogen |
7–11years (POP) | [54,55,65, 71–74] | |
| Perfluoroalk yl substances (e.g. PFOA, PFOS) | *Stain resistant coating in clothing, cookware, upholstery; food packaging *Food, drinking water |
70 ppt (water; EPA) | General mechanisms: Modulates estrogen signaling, activates PPARα signaling Whole animals: Altered lipid metabolism, steatosis Gestational exposure: increased weight, leptin, insulin levels, glucose intolerance Insulin target cells: Increased insulin signaling/sensitivity, reduced hepatic glycogen synthesis |
3–5 years | [66,106,107,131] | |
| Tolylfluanid | *Agricultural fungicide, biocide on ships, paints *Food, water; occupational exposures in shipping and agriculture |
0.1 mg/kg/day (FDA) | General mechanism: Activates GR signaling Whole animals: increased weight, adiposity, insulin resistance, glucose intolerance, altered circadian feeding patterns. Insulin target cells: reduced insulin signaling |
hours - days | [49,88,90] | |
| Atrazine | *Most widely used herbicide in the U.S.; used on corn, sorghum, sugar cane, Christmas trees, golf courses *Food, drinking water |
3 μg/L (water; EPA), 5 mg/m3/shif t (OSHA) | General mechanisms: Unknown Whole animals: Increased weight, insulin resistance Insulin target cells: Reduced insulin signaling, mitochondrial toxicity, impaired FA oxidation in liver |
10–11 hours | [67,112] | |
| Particulate Matter | *Aerosol particles with diameter less than 2.5 μm; combustion associated with traffic, mining, burning coal, oil, wood *Ubiquitous; Inhalation |
35 μg/m3 air daily average; 15 μg/m3 annual average. | General mechanisms: Inflammation/Unknown Whole animals: Increased visceral adiposity, insulin resistance Insulin target cells: Reduced insulin signaling, PKC activity, increased inflammation, ROS, NASH, reduced glycogen. |
Unknow n | [97,98,111] | |
Afflicting 415 million individuals globally with 642 million projected to suffer from the disease by 2040 [6], diabetes is a common, heterogeneous disorder defined by hyperglycemia arising from inadequate insulin production, impaired insulin action, or a combination of the two. Traditionally, type 2 diabetes (T2DM), the most common form of the disease, is thought to originate from the development of insulin resistance, which increases synthetic demand for insulin that eventually becomes unsustainable as pancreatic β-cells begin to decompensate, ultimately leading to overt T2DM [7]. In contrast, type 1 diabetes (T1DM) classically arises from the primary destruction of β-cells. Thus, factors that potentiate insulin resistance or promote β-cell failure augment diabetes risk. Importantly, mounting evidence demonstrates that MDCs affect multiple levels of glucose regulation from β-cell insulin secretion to insulin signaling in metabolically active tissues such as the liver, muscle, adipose, brain, and gastrointestinal (GI) tract (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
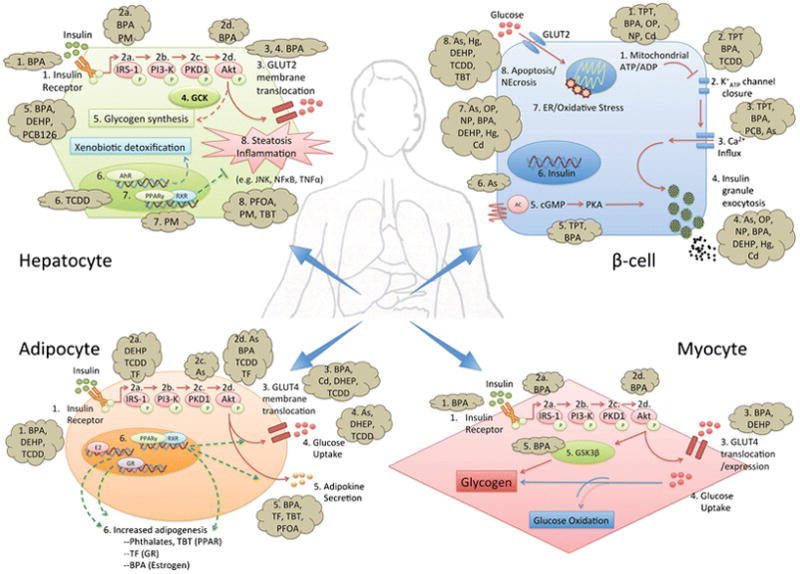
Overview of the molecular mechanisms by which MDCs disrupt energy homeostasis in the β-cell, myocyte, hepatocyte, and adipocyte.
MDC Disruption of β-Cell Function
Classically, increased extracellular glucose concentrations increase glucose uptake into β-cells via glucose transporter 2 (GLUT2), followed by entry into glycolysis, oxidative phosphorylation, and ATP generation. Increases in the ATP/ADP ratio promote ATP-sensitive K+-channel (KATP) closure, membrane depolarization, and calcium influx. Increased intracellular calcium induces cytoskeletal rearrangements that result in transport and release of insulin-containing vesicles [8]. Defects in insulin secretion are central to diabetes pathogenesis [9]. Insulin secretion is also regulated by incretin hormones, such as glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and gastric inhibitory polypeptide (GIP), as well as estrogens, which modulate intracellular calcium flux and potentiate insulin secretion via a cAMP-mediated pathway (reviewed in [10]). Post-prandial incretin release from the GI tract augments insulin response, an effect that is attenuated in diabetes [10]. Importantly, multiple EDCs have been shown to disrupt β-cell function at various points in these pathways.
Triphenyltin (TPT) is a persistent organotin compound historically used as an antifouling agent. Islets from TPT-exposed hamsters exhibited impaired intracellular calcium flux and insulin secretion in response to known β-cell stimuli, including acetylcholine, GIP, and glucose [11]; and TPT exposure of primary islets in culture reduced NAD(P)H and ATP production [12]. These findings are consistent with TPT interference in β-cell function upstream of KATP channel closure, possibly via impaired mitochondrial ATP production [12]. Additionally, TPT reduced GIP and GLP-1 induced insulin release in a protein kinase A (PKA)-dependent manner [13], a pathway central to β-cell function.
A number of studies demonstrated that arsenic also impairs insulin secretion [14–17]. Arsenic is a ubiquitous environmental pollutant that contaminates drinking water above the current WHO safety standard of 10 μg/L for over 150 million individuals globally [18]. In a rat β-cell line, while high levels of arsenic reduced insulin gene expression [17], low micromolar concentrations impaired calpain-10 mediated proteolysis and activation of SNAP-25, a key step in insulin granule exocytosis [16]. The insulin exocytic machinery is similarly disrupted by phenolic compounds, widely used in adhesives and detergents. Exposure to low levels of phenolic estrogens reduced mRNA expression of Snap25 and Rab27a in rodent islets [19]. In contrast, polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB) treatment increased calcium influx and insulin secretion in a calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII)-dependent fashion [20]. Thus, MDCs can affect β-cell function both directly through altering calcium flux, and via modulation of downstream signaling.
Sex steroids play an important role in glucose homeostasis, regulating β-cell insulin secretion in both cGMP-dependent and -independent ways [21,22]. Physiologic fluctuations in estrogen balance are associated with increased vulnerability to metabolic stress [23]. Importantly, multiple EDCs have been shown to alter estrogen signaling, including PCBs, bisphenol A (BPA), phthalates, phytoestrogens, and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) [5], making this pathway a likely target of metabolic disruption by exogenous chemicals (discussed in [24,25]).
Endoplasmic Reticulum and Oxidative Stress in MDC Action
Under conditions of hyperglycemia, insulin biosynthesis accelerates and can account for half of all β-cell protein synthesis [26]. This high synthetic demand coupled with their relatively small size renders β-cells uniquely vulnerable to both endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and oxidative stress, and thus to chemicals that induce these reactions. Indeed, recent studies have implicated oxidative and ER stress as significant contributors to diabetes pathogenesis (reviewed in [27,28]). Mitochondria are critical regulators of the cellular redox balance, responsible for both ROS and antioxidant production; thus perturbations to mitochondrial integrity leads to increased cellular stress. Several MDCs promote oxidative stress in β-cells, including BPA [19,29], arsenic [30,31], and diethylhexylphthalate (DEHP) [32]. For example, rat islets exposed to the phenolic compounds octylphenol, nonylphenol, and BPA exhibited disruptions in islet mitochondrial architecture with alterations in mitochondrial gene expression [19]. Micromolar concentrations of BPA also induced reactive oxygen species (ROS) in INS-1 cells, causing glutathione depletion, DNA damage, and p53 induction, which was partially rescued by pretreatment with the antioxidant N-acetylcysteine (NAC) [29]. In INS-1 cells treatment with 0.25-1 μM sodium arsenite for 96 hours reduced thioredoxin reductase activity, increased pro-apoptotic gene expression, and reduced viability, possibly via a c-Jun-N-terminal kinase (JNK)-mediated pathway [31]. Importantly, arsenic toxicity was also attenuated by pretreatment with NAC [30], suggesting oxidative stress as a mechanism of toxicity and supporting trials of NAC as a potential treatment for arsenic-induced diabetes. Exposure to other heavy metals such as cadmium [33,34] and mercury [35,36] also impair insulin secretion and induce β-cell toxicity, although the epidemiologic evidence on a role for those metals in diabetes is inconsistent [37]. These effects have been presumed to occur via oxidative stress; however, the precise mechanisms by which these toxicants induce β-cell dysfunction require further study.
The role of ROS in β-cell function is complex as ROS also regulate insulin release [38]. Although arsenic has a well-documented ability to induce oxidative damage in multiple contexts, arsenic exposure has also been shown to reduce glucose-stimulated ROS generation [15]. This decrease in ROS coincides with a robust induction of an endogenous Nrf2-mediated antioxidant pathway, raising the hypothesis that chronic exposure to low levels of arsenic leads to an adaptive antioxidant response that indirectly dampens GSIS [15]. Taken together, these data indicate that MDCs may perturb insulin secretion through bidirectional alterations in β-cell ROS handling.
Increased cellular stress and resultant inflammation in β-cells have been implicated in the pathogenesis of T1DM as well [9], and are hallmarks of EDC toxicity. Chronic exposure to BPA accelerated spontaneous insulinitis in non-obese diabetic (NOD) mice, a model of immune-mediated diabetes [39]. In addition, NOD mice exposed to BPA in utero exhibited more severe insulinitis at 11 weeks of age and increased diabetes prevalence at 20 weeks [40•], suggesting that BPA may also play a role in accelerating the decline of β-cell reserve by promoting immune disruption of pancreatic islets, implicating MDCs as possible contributors to increasing T1DM prevalence.
MDC Disruption of Insulin Action
Insulin functions primarily in myocytes and adipocytes to promote glucose uptake, and in hepatocytes to promote glucose storage as glycogen. On a molecular level, insulin binds to its receptor triggering autophosphorylation and recruitment of the insulin receptor substrate (IRS) scaffolding proteins. This is followed by a series of iterative phosphorylation events that recruit and activate phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3-K), generate phosphatidylinositol triphosphate (PIP3), and activate phosphoinositide- dependent kinase 1 (PDK1), ultimately resulting in phosphorylation and activation of Akt/protein kinase B. Akt mediates many of the metabolic actions of insulin, including glucose uptake by promoting GLUT4 translocation to the plasma membrane, lipid biogenesis, hepatic glycogen synthesis, and suppression of gluconeogenesis [41]. Impairments in insulin action promote diabetes pathogenesis when insulin resistance outstrips the β-cell’s capacity for insulin secretion [7]. Global insulin resistance associated with MDC exposure is supported by epidemiologic, animal, and molecular studies [5]. Human exposures to a wide variety of chemicals have been associated with insulin resistance, including BPA [42,43], particulate matter (PM) [44], 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo dioxin (TCDD) [45], and phthalates [46,47]. The precise mechanisms by which these chemicals promote insulin resistance are discussed below.
Multiple MDCs can disrupt insulin action in target tissues by altering the expression or activity of insulin signaling intermediates including the insulin receptor [48], IRS-1 [49], PDK-1 [50], and Akt [48–53]. For example, rodents exposed to BPA exhibit global insulin resistance associated with defects in phosphorylation of both the insulin receptor [48] and Akt [48,52]. The phenylsulfamide fungicide tolylfluanid (TF) impaired insulin-stimulated Akt phosphorylation in primary rodent and human adipocytes, likely via down-regulation of IRS-1 expression and protein destabilization [49]. Similarly, insulin-stimulated Akt phosphorylation was attenuated and glucose uptake reduced following arsenite exposure in 3T3-L1 adipocytes [53]. Independent studies in this model showed that 4 hour exposure to either 50 μM arsenite or 2 μM methylarsonous acid also reduces Akt phosphorylation, inhibits PDK-1 activity, and prevents membrane GLUT4 translocation [50], the primary glucose transporter in adipocytes and myocytes. Dysregulation of GLUT proteins has been observed following exposure to multiple MDCs, including TCDD [54,55], DEHP [56-58], cadmium [59], and arsenic [53]. For example, mice injected with a single high dose of TCDD exhibited reduced GLUT4 and GLUT1 expression in adipose and neuronal tissue, respectively [55]. Similarly, DEHP exposure in L6 myotubes downregulated GLUT4 with concomitant impaired glucose utilization [56]. Importantly, while skeletal muscle is responsible for the majority of glucose disposal following nutrient intake [60], few studies have directly addressed MDC effects on muscle; further work on MDC-mediated alterations in skeletal muscle metabolism may illuminate the potential for exercise to antagonize MDC-associated diabetes risk.
In addition to skeletal muscle disruptions, understanding MDC effects on hepatic function is critical for predicting metabolic risk, a fact underscored by the liver’s dual role in energy and xenobiotic metabolism as well as the recent rise in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) [61••]. Multiple MDCs can disrupt hepatic function, leading to toxicity, altered gluconeogenesis, and impaired glycogen storage, including POPs [62], BPA [63,64], PCBs [65], perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) [66], atrazine [67], arsenic [68], and DEHP [69]. For example, rats exposed to lipophilic POPs contained in dietary fish oil exhibited insulin resistance, abdominal obesity, and hepatosteatosis [62]. Exposure of rodents to BPA led to impaired glucose oxidation and significantly reduced glycogen stores in primary hepatocytes [64]. Similarly, PCB 126 inhibited hepatic glycogen metabolism, cAMP-mediated gluconeogenesis, and expression of a key enzyme in this pathway, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK), in an aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR)-dependent fashion [65]. AhR is an orphan receptor that regulates hepatic detoxification of xenobiotic substances via controlling the activity of cytochrome P450 enzymes [70]. It has several known exogenous ligands including PAH, dioxin-like compounds (e.g. TCDD), and polyphenols [70]; thus, it is a likely mediator of MDC toxicity. Interestingly, RNA-Seq analysis of human hepatocytes exposed to PFOA and PFOS demonstrate altered expression of lipid metabolism genes, possibly by direct interference with and downregulation of hepatocyte nuclear factor 4α (HNF4α), a master regulator of hepatocyte development and metabolism [66]. Mutations in HNF4α also cause a form of familial diabetes, maturity onset diabetes of the young type 1 (MODY1), which is uniquely responsive to the insulin augmenting class of sulfonylurea drugs. Thus, MDC disruption of HNF4α may have effects on both β-cell and hepatocyte physiology. Integrating understanding of the genetic and environmental causes of metabolic disease may thus inform future therapy decisions. Collectively, these data demonstrate that disruption in hepatic energy metabolism is emerging as an important consequence of MDC exposure [61••].
Context-Dependent MDC Action
The impact of MDCs may be context-dependent. For example, TCDD [71–74], organotins [75,76], and BPA [48,51,64,77,78] differentially affect insulin levels and action depending on the experimental model. Acute TCDD exposure induces a wasting syndrome characterized by weight loss, adipose derangements, hyperlipidemia, ectopic lipid deposition, and hypoinsulinemia [79]. Conversely, multiple epidemiologic studies link TCDD to diabetes and hyperinsulinemia [80,81]. In β-cell models, TCDD effects are similarly conflicting. TCDD impaired GSIS in primary rodent islets [71] and INS-1 cells [72], and caused AhR-dependent reductions in second-phase insulin secretion in intact animals [74]; however, other studies using INS-1 cells exhibited persistently increased intracellular calcium levels and basal insulin secretion, an effect antagonized by calcium channel blockade [73]. Similarly, hamsters exposed to the organotin tributyltin (TBT) for 45 days exhibited hyperinsulinemia and insulin resistance [76]; however, continuing exposure to 60 days promoted β-cell apoptosis with concomitant reduction in insulin levels [75]. These findings suggest a model whereby acute MDC exposure may augment insulin secretion at the expense of subsequent β-cell exhaustion and diminished metabolic reserve later in life; however, this hypothesis requires further interrogation.
Adipose Disruption and Global Metabolic Dysfunction
Adipose tissue is an important regulator of metabolic health, as increased adiposity is a well-recognized risk factor for insulin resistance and diabetes, and impairments in adipose development and function are also associated with metabolic disease [82]. Adipose tissue performs several important functions for metabolic homeostasis, including controlling the storage and redistribution of lipids as well as secreting adipokines (e.g. leptin and adiponectin) that regulate food intake, insulin sensitivity, and β-cell health. Due to the lipophilic nature of many MDCs, adipose tissue is a toxicant depot and may determine their chemical persistence in vivo. MDCs that affect adipose function, termed obesogens, have been tied to alterations in adipocyte differentiation, insulin action, and nutrient handling (reviewed in [83]). The transcription factor peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-γ (PPARγ) is a key regulator of normal adipocyte development (reviewed in [82]). PPARγ null mice lack adipose tissue, and PPARγ ablation leads to adipocyte death within days. PPARγ also influences glucose homeostasis by controlling expression of GLUT4, adiponectin, leptin, TNFα, and resistin [82]. Humans with heterozygous loss of function PPARγ mutations have lipodystrophy and insulin resistance [84]. Thus, disruption of PPARγ activity has multiple negative consequences on adipocyte development and function. Several MDCs disrupt PPARγ signaling, including organotins and phthalates [85]. Importantly, the classical obesogen TBT, has been shown to promote adipogenesis in multiple model systems via PPARγ activation [86], while generating a dysfunctional adipocyte with reduced expression of the beneficial adipokine adiponectin [87]. In addition to MDCs that modulate PPARγ activity, several MDCs alter adipogenesis through other key regulatory pathways such as the glucocorticoid receptor (GR) and sex steroid nuclear receptor pathways. For example, TF promotes adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 cells [88], likely by activating GR signaling, as treatment of primary mouse adipocytes with TF led to GR activation, nuclear translocation, and enrichment at GR response elements in target genes [89]. Moreover, rodents exposed to TF developed increased visceral adiposity, impaired glucose tolerance, and reduced adiponectin levels [90•], mimicking the pathologic features of glucocorticoid excess in humans [91]. Disruptions in the balance of estrogens and androgens also impair adipocyte differentiation. Human adipocyte stem cells exposed to BPA demonstrated increased adipogenesis in an ER-dependent fashion [92]. Interestingly, prolonged exposure of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes to BPA led to development of a compromised adipocyte with increased lipid accumulation, impaired glucose utilization, and increased expression of inflammatory cytokines [93•]. Importantly, while many studies have emphasized the adipogenesis-promoting capacity of MDCs, more attention is required to understand the potential dysfunctional state of MDC-generated adipocytes. Moreover, MDCs that inhibit adipogenesis are likely to promote metabolic dysfunction since impaired adipose expansion shifts lipid storage to muscle and liver, resulting in metabolic dysregulation in these vital tissues, as seen in lipodystrophies [82].
Inflammation in MDC Action
In the obese state, adipocytes enlarge owing to increased triglyceride accumulation; this is accompanied by an increase in inflammatory markers, macrophage infiltration, and release of cytokines such as TNFα and IL-1β that further recruit immune cells and propagate the inflammatory cascade. Multiple molecular signaling pathways have been implicated in the pathogenesis of obesity-induced inflammation, including nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NFκB), mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), and JNK; conversely, targeted loss-of-function mutations in key pathway members is protective [82]. Increased inflammation shifts adipocytes away from lipogenesis and toward lipolysis, increasing circulating free fatty acids and promoting deleterious ectopic lipid deposition in muscle, liver, and β-cells [94]. Furthermore, inflammatory cytokines directly impair insulin action by exerting inhibitory effects on IRS proteins [95], and downregulating insulin receptor, IRS-1, and GLUT4 expression [96]. Many MDCs induce inflammation. For example, BPA treatment of 3T3-L1 cells increased IL-6 and IFNγ release in association with reduced glucose uptake [51]. Exposure of mice to particulate matter (PM) increased systemic inflammation with concomitant insulin resistance, impaired hepatic glycogen storage, and increased visceral adiposity [97•,98]. Thus, inflammation may mechanistically link poor air quality with diabetes and obesity [99]. TCDD also increased TNFα expression with an associated downregulation of insulin signaling intermediates, an effect partially rescued by disruption of key inflammatory mediators, including AhR, ERK, and JNK [54], highlighting their role in the negative metabolic effects of TCDD. Interestingly, microarray analysis of human adipose-derived stem cells treated with TCDD or PCB-126 identified genes regulating inflammation as the principal molecular alterations induced by these chemicals [100]. Collectively, these studies demonstrate that inflammation is a likely inducer of MDC-associated metabolic disease, and therapies directed at inflammatory responses should be investigated as potential interventions.
Developmental Origins of Metabolic Disease
Increasing evidence suggests that environmental exposures during key developmental windows program metabolic disease risk later in life; this includes the in utero and early post-natal period. For example, six-month old male offspring of dams exposed to BPA exhibited impairments in glucose tolerance, insulin sensitivity, and insulin secretion [101]. Earlier interrogation showed that these mice exhibited increased β-cell mass and hyperinsulinemia that preceded a subsequent decline in both parameters. This suggests that in utero BPA exposure may promote insulin-induced insulin resistance that is detrimental to long-term β-cell function [102••]. Additionally, the consequences of BPA exposure may synergize with traditional metabolic risk factors such as a high fat diet [63]. The metabolic disruptions in these offspring were associated with altered expression of genes regulating fatty acid metabolism, including the sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1, PPARα, and carnitine palmitoyltransferase [63], suggesting potential molecular disruptions in lipid handling. In utero exposures to several EDCs disrupts glucose homeostasis, including TCDD [103], arsenic [104], DEHP [58,105], PFOA [106], and PFOS [107]; however, the precise molecular defects remain largely undefined. In one study, however, in utero DEHP exposure induced inhibitory chromatin modifications at the GLUT4 promoter with reduced GLUT4 expression [58], suggesting that site-specific epigenetic alterations may mechanistically define links between early life stressors and later life metabolic disease; however, significant additional work is required to define the relevant mechanisms in this area.
In addition to being a sensitive period of development for the fetus, pregnancy is also a window of susceptibility for mothers. For example, pregnant mice exposed to BPA exhibit hyperinsulinemia [101] similar to women with GDM before the onset of overt diabetes [3]. Pregnant dams exposed to BPA exhibited increased weight, impaired glucose tolerance, and insulin resistance [108••], effects likely arising from defects in adipocyte and β-cell function as these mice exhibited increased periuterine fat mass as well as reduced β-cell mass resulting from both decreased proliferation and increased apoptosis [108••]. Importantly, β-cells from BPA-exposed dams exhibited persistent reductions in the expression of proliferative genes [cyclin D2 and cyclin-dependent kinase-4 (CDK4)] and increased expression of cell cycle inhibitors [p16 and p53] months after delivery [108••]. Collectively, these data suggest that MDC exposures during pregnancy may increase the risk of GDM while also predisposing to later life metabolic insults that augment diabetes risk (reviewed in [109]). To understand the impact of MDCs on metabolic risk in mothers and their offspring, further work into the underlying mechanisms responsible for these alterations are required, including efforts to precisely define causal epigenetic changes (e.g. DNA methylation and histone modifications) linked to energy physiology.
MDCs and Classical Metabolic Risk
Central to understanding how MDCs threaten metabolic health is a need to appreciate how this emerging metabolic risk intersects with traditional diabetes and obesity risk factors (e.g. caloric excess, physical inactivity, sleep disruption, and aging). Current evidence indicates that MDCs potentiate these risks. For example, in C57BL/6 mice, high fat diet-induced glucose intolerance and insulin resistance were exacerbated by BPA exposure [52]. Similarly, perinatal BPA exposure impaired glucose tolerance and promoted hyperinsulinemia, effects amplified with high fat feeding [110]. Particulate matter [111] and the herbicide atrazine [112] also promoted insulin resistance in rodents on high fat but not a standard chow diet. However, this potentiation of metabolic risk is not uniform. Offspring of CD-1 mice exposed to BPA did not exhibit glucose intolerance or increased adiposity when fed either normal chow or a high fat diet [113]. Furthermore, while high fat feeding worsened glucose tolerance in arsenic-exposed C57BL/6 mice, these animals also exhibited reduced fat mass, improved fasting blood glucose, and may have had enhanced insulin sensitivity [114]. Thus, there are likely toxicant- and strain-specific differences that impact metabolic outcomes. Importantly, exploring these differences as well as interactions with specific dietary components may illuminate the underlying biological mechanisms by which MDCs promote disease risk.
Recently, disruptions in circadian rhythms have emerged as novel metabolic risk factors. In human and mouse models, impaired sleep and disruptions in normal circadian patterns of food intake impair metabolic health [115], and MDCs are emerging as novel contributors to disease risk in this area. For example, TF was shown to deleteriously alter normal circadian feeding patterns in mice [90•]. Additionally, population studies have associated higher urinary BPA levels with shorter sleep duration [116]; a finding supported by studies in male zebrafish demonstrating BPA-induced alterations in circadian activity [117]. Exposure to estradiol, tamoxifen, BPA, and 4-tert-octylphenol in mangrove killifish also altered expression of circadian clock genes [118•]. A mechanistic basis for these associations is supported by genetic analysis of these circadian genes demonstrating conserved promoter binding sites for estrogen, the AhR, and the xenobiotic response element [118•], factors implicated in various MDC responses.
Conclusions: From Mechanisms to Interventions
As our mechanistic understanding of MDC action improves, a central challenge moving forward is translating this knowledge into interventions to improve human health. Clearly, preventing exposures and rapid remediation of environmental contaminants is critical to address MDC-induced metabolic dysfunction. Indeed, there may be promise in this as one study demonstrated that arsenic’s β-cell toxicity in cultured islets could be reversed by incubation in arsenic-free media, providing evidence for islet recovery [14]. Where exposure reduction is not possible or the effects of exposures are irreversible, employing mechanism-based therapeutics will be essential for improving human metabolic health. For those MDCs that interfere with β-cell insulin production, studies from neonatal diabetes may illuminate therapeutic approaches. The most common form of neonatal diabetes results from a heterozygous activating mutation in KCNJ11 that prevents closure of the KATP channel [119]. In these patients, sulfonylureas are highly effective. Several MDCs affect β-cell KATP channel function, suggesting that sulfonylureas may be beneficial in these contexts as suggested by one study of TPT’s metabolic effects [12]. Conversely, several MDCs promote insulin resistance that impairs insulin action in peripheral tissues and stresses β-cells by increasing synthetic demand for insulin. While insulin is a mainstay of diabetes treatment, newer therapies that reduce the glycemic burden such as the sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT-2) inhibitors, or that promote a more physiologic insulin release from the pancreas, such as dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP4) inhibitors and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists may be beneficial in treating MDC-mediated diabetes. Because of the central role of adipose tissue in regulating global energy metabolism and evidence that many MDCs target adipocyte function, another class of anti-diabetic therapies of interest are the thiazolidinediones (TZDs), which target PPARγ and inhibit hepatic gluconeogenesis, improve adipose function, reduce inflammation, and increase insulin sensitivity [120–123]. Where oxidative stress is implicated in MDC action, investigations into the utility of antioxidants are warranted. This approach is supported by studies showing that pre-treatment with NAC mitigates some of the β-cell toxicity induced by arsenic [30,124] and BPA [29]. As our appreciation of MDCs as metabolic risk factors increases, future work mandates investigations into the specific disease-promoting mechanisms by which these toxicants work in order to devise targeted interventions to stem the global tide of metabolic deterioration.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health (T32DK007011 to M.S.M.), the American Diabetes Association (Junior Faculty Development Award to R.M.S.), and the Ministerio de Economia y Competitividad (SAF2014-58335-P to A.N.) and Generalitat Valenciana (PROMETEOII/2015/016 to A.N.). CIBERDEM is an initiative of the Instituto de Salud Carlos III.
Abbreviations
- EDCs
endocrine disrupting chemicals
- GDM
gestational diabetes mellitus
- MDCs
metabolism disrupting chemicals
- T1DM
type 1 diabetes mellitus
- T2DM
type 2 diabetes mellitus
- GI
gastrointestinal
- ATP
adenosine triphosphate
- ADP
adenosine diphosphate
- KATP
potassium sensitive ATP channel
- TPT
triphenyltin
- GLP- 1
glucagon-like peptide-1
- GIP
gastric inhibitory polypeptide/glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide
- cAMP
cyclic AMP, NAD(P)H, Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate
- SNAP-25
Synaptosome Associated Protein 25kDa
- GPCR
G-protein coupled receptor
- TBT
tributyltin
- PKA
protein kinase A
- PCB
polychlorinated biphenyl
- CamKII
calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II
- BPA
bisphenol A
- GSIS
glucose-stimulated insulin secretion
- PAH
polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon
- ncmER
non-classical membrane estrogen receptor
- ER-β
estrogen receptor beta
- CREB
cAMP-response element binding
- ERα
estrogen receptor alpha
- ERK
extracellular signal–regulated kinase
- ER
endoplasmic reticulum
- DEHP
diethylhexylphthalate
- ROS
reactive oxygen species
- DNA
deoxyribonucleic acid
- NAC
N-acetyl cysteine
- JNK
c-Jun-N-terminal kinase
- NOD
non-obese diabetic
- IRS
insulin receptor substrate
- PI3-K
phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase
- PIP3
phosphatidylinositol triphosphate
- PDK1
phosphoinositide-dependent kinase 1
- PKB
Protein Kinase B
- PM
particulate matter
- TCDD
2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo dioxin
- TF
tolylfluanid
- POP
persistent organic pollutant
- PFOA
perfluorooctanoic acid
- PEPCK
phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase
- AhR
aryl hydrocarbon receptor
- PFOS
perfluorooctanesulfonic acid
- HNF4-α
hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 alpha
- PPARγ
peroxisome proliferator activated receptor gamma
- TNFα
tumor necrosis factor alpha
- AMPK
5' adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase
- IL-1β
interleukin 1 beta
- NFκB
nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells
- MAPK
mitogen-activated protein kinases
- IL-6
interleukin 6
- NEFA
non-esterified fatty acids
- Srebpc1
sterol regulatory element-binding proteins 1
- PPARα
peroxisome proliferator activated receptor alpha
- Cpt1b
carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1B
- CDK4
cyclin-dependent kinase-4
- SGLT-1
sodium-glucose cotransporter-2
- DPP4
dipeptidyl peptidase 4
- GLP-1
glucagon-like peptide-1
Footnotes
Compliance with Ethics Guidelines
Conflict of Interest
Mizuho S. Mimoto and Angel Nadal declare that they have no conflict of interest. Robert M. Sargis reports honoraria from CVS Health.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as:
• Of importance
• Of outstanding importance
- 1.Dabelea D, Mayer-Davis EJ, Saydah S, Imperatore G, Linder B, Divers J, et al. Prevalence of type 1 and type 2 diabetes among children and adolescents from 2001 to 2009. JAMA. 2014 May 7;311(17):1778–86. doi: 10.1001/jama.2014.3201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.DeSisto CL, Kim SY, Sharma AJ. Prevalence estimates of gestational diabetes mellitus in the United States, Pregnancy Risk Assessment Monitoring System (PRAMS), 2007–2010. Prev Chronic Dis. 2014 Jun 19;11:E104. doi: 10.5888/pcd11.130415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Damm P, Houshmand-Oeregaard A, Kelstrup L, Lauenborg J, Mathiesen ER, Clausen TD. Gestational diabetes mellitus and long-term consequences for mother and offspring: a view from Denmark. Diabetologia. 2016 Jul;59(7):1396–9. doi: 10.1007/s00125-016-3985-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4••.Brown RE, Sharma AM, Ardern CI, Mirdamadi P, Mirdamadi P, Kuk JL. Secular differences in the association between caloric intake, macronutrient intake, and physical activity with obesity. Obesity Research & Clinical Practice. 2016 May;10(3):243–55. doi: 10.1016/j.orcp.2015.08.007. This study provides evidence that increasing rates of obesity are not accounted for by changes in diet or activity, supporting the need to pursue alternate etiologies. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5••.Gore AC, Chappell VA, Fenton SE, Flaws JA, Nadal A, Prins GS, et al. EDC-2: The Endocrine Society's Second Scientific Statement on Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals. Endocrine Reviews. 2015 Dec;36(6):E1–E150. doi: 10.1210/er.2015-1010. Comprehensive review of endocrine disrupting chemicals across all organ systems. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.da Rocha Fernandes J, Ogurtsova K, Linnenkamp U, Guariguata L, Seuring T, Zhang P, et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas estimates of 2014 global health expenditures on diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2016 Jul;117:48–54. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2016.04.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kahn SE, Hull RL, Utzschneider KM. Nature. 7121. Vol. 444. Nature Publishing Group; 2006. Dec 14, Mechanisms linking obesity to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes; pp. 840–6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Fu Z, Gilbert ER, Liu D. Regulation of insulin synthesis and secretion and pancreatic Beta-cell dysfunction in diabetes. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2013 Jan 1;9(1):25–53. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Schwartz SS, Epstein S, Corkey BE, Grant SFA, Gavin JR, Aguilar RB. The Time Is Right for a New Classification System for Diabetes: Rationale and Implications of the β-Cell-Centric Classification Schema. Dia Care. 2016 Feb;39(2):179–86. doi: 10.2337/dc15-1585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Yabe D, Seino Y. Two incretin hormones GLP-1 and GIP: Comparison of their actions in insulin secretion and β cell preservation. Progress in Biophysics and Molecular Biology. 2011 Nov;107(2):248–56. doi: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2011.07.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Miura Y, Kato M, Ogino K, Matsui H. Impaired cytosolic Ca2+ response to glucose and gastric inhibitory polypeptide in pancreatic beta-cells from triphenyltin-induced diabetic hamster. Endocrinology. 1997 Jul;138(7):2769–75. doi: 10.1210/endo.138.7.5234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Miura Y, Hori Y, Kimura S, Hachiya H, Sakurai Y, Inoue K, et al. Triphenyltin impairs insulin secretion by decreasing glucose-induced NADP(H) and ATP production in hamster pancreatic β-cells. Toxicology. 2012 Sep 28;299(2–3):165–71. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2012.05.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Miura Y, Matsui H. Triphenyltin impairs a protein kinase A (PKA)-dependent increase of cytosolic Na+ and Ca2+ and PKA-independent increase of cytosolic Ca2+ associated with insulin secretion in hamster pancreatic beta-cells. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology. 2006 Nov 1;216(3):363–72. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2006.05.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Douillet C, Currier J, Saunders J, Bodnar WM, Matoušek T, Stýblo M. Methylated trivalent arsenicals are potent inhibitors of glucose stimulated insulin secretion by murine pancreatic islets. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology. 2013 Feb 15;267(1):11–5. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2012.12.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Fu J, Woods CG, Yehuda-Shnaidman E, Zhang Q, Wong V, Collins S, et al. Low-level arsenic impairs glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in pancreatic beta cells: involvement of cellular adaptive response to oxidative stress. Environ Health Perspect. 2010 Jun;118(6):864–70. doi: 10.1289/ehp.0901608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Díaz-Villaseñor A, Burns AL, Salazar AM, Sordo M, Hiriart M, Cebrián ME, et al. Arsenite reduces insulin secretion in rat pancreatic beta-cells by decreasing the calcium-dependent calpain-10 proteolysis of SNAP-25. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology. 2008 Sep 15;231(3):291–9. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2008.05.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Díaz-Villaseñor A, Sánchez-Soto MC, Cebrián ME, Ostrosky-Wegman P, Hiriart M. Sodium arsenite impairs insulin secretion and transcription in pancreatic beta-cells. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology. 2006 Jul 1;214(1):30–4. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2005.11.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Shankar S, Shanker U, Shikha Arsenic contamination of groundwater: a review of sources, prevalence, health risks, and strategies for mitigation. ScientificWorldJournal. 2014;2014:304524. doi: 10.1155/2014/304524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Song L, Xia W, Zhou Z, Li Y, Lin Y, Wei J, et al. Low-level phenolic estrogen pollutants impair islet morphology and β-cell function in isolated rat islets. Journal of Endocrinology. 2012 Nov;215(2):303–11. doi: 10.1530/JOE-12-0219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Fischer LJ, Wagner MA, Madhukar BV. Potential involvement of calcium, CaM kinase II, and MAP kinases in PCB-stimulated insulin release from RINm5F cells. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology. 1999 Sep 15;159(3):194–203. doi: 10.1006/taap.1999.8728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Ropero AB, Fuentes E, Rovira JM, Ripoll C, Soria B, Nadal A. Non-genomic actions of 17beta-oestradiol in mouse pancreatic beta-cells are mediated by a cGMP-dependent protein kinase. J Physiol (Lond) 1999 Dec 1;521(Pt 2):397–407. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1999.00397.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Soriano S, Ropero AB, Alonso-Magdalena P, Ripoll C, Quesada I, Gassner B, et al. Rapid Regulation of K ATPChannel Activity by 17β-Estradiol in Pancreatic β-Cells Involves the Estrogen Receptor β and the Atrial Natriuretic Peptide Receptor. Molecular Endocrinology. 2009 Dec;23(12):1973–82. doi: 10.1210/me.2009-0287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Mauvais-Jarvis F, Clegg DJ, Hevener AL. The role of estrogens in control of energy balance and glucose homeostasis. Endocrine Reviews. 2013 Jun;34(3):309–38. doi: 10.1210/er.2012-1055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Alonso-Magdalena P, Ropero AB, Soriano S, García-Arévalo M, Ripoll C, Fuentes E, et al. Bisphenol-A acts as a potent estrogen via non-classical estrogen triggered pathways. Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology. 2012 May;355(2):201–7. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2011.12.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Nadal A, Alonso-Magdalena P, Soriano S, Quesada I, Ropero AB. The pancreatic beta-cell as a target of estrogens and xenoestrogens: Implications for blood glucose homeostasis and diabetes. Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology. 2009 May 25;304(1–2):63–8. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2009.02.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Schuit FC, In't Veld PA, Pipeleers DG. Glucose stimulates proinsulin biosynthesis by a dose-dependent recruitment of pancreatic beta cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1988 Jun;85(11):3865–9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Hasnain SZ, Prins JB, McGuckin MA. Oxidative and endoplasmic reticulum stress in β-cell dysfunction in diabetes. J Mol Endocrinol. 2016 Feb;56(2):R33–54. doi: 10.1530/JME-15-0232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Eizirik DL, Cardozo AK, Cnop M. The role for endoplasmic reticulum stress in diabetes mellitus. Endocrine Reviews. 2008 Feb;29(1):42–61. doi: 10.1210/er.2007-0015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Xin F, Jiang L, Liu X, Geng C, Wang W, Zhong L, et al. Bisphenol A induces oxidative stress-associated DNA damage in INS-1 cells. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen. 2014 Jul 15;769:29–33. doi: 10.1016/j.mrgentox.2014.04.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Zhu X-X, Yao X-F, Jiang L-P, Geng C-Y, Zhong L-F, Yang G, et al. Sodium arsenite induces ROS-dependent autophagic cell death in pancreatic β-cells. Food Chem Toxicol. 2014 Aug;70:144–50. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2014.05.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Yao X-F, Zheng B-L, Bai J, Jiang L-P, Zheng Y, Qi B-X, et al. Low-level sodium arsenite induces apoptosis through inhibiting TrxR activity in pancreatic β-cells. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology. 2015 Sep;40(2):486–91. doi: 10.1016/j.etap.2015.08.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Sun X, Lin Y, Huang Q, Shi J, Qiu L, Kang M, et al. Di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate-induced apoptosis in rat INS-1 cells is dependent on activation of endoplasmic reticulum stress and suppression of antioxidant protection. J Cell Mol Med. 2015 Mar;19(3):581–94. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Muayed El M, Raja MR, Zhang X, MacRenaris KW, Bhatt S, Chen X, et al. Accumulation of cadmium in insulin-producing β cells. Islets. 2012 Nov;4(6):405–16. doi: 10.4161/isl.23101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Chang K-C, Hsu C-C, Liu S-H, Su C-C, Yen C-C, Lee M-J, et al. Cadmium induces apoptosis in pancreatic β-cells through a mitochondria-dependent pathway: the role of oxidative stress-mediated c-Jun N-terminal kinase activation. PLoS ONE. 2013;8(2):e54374. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Chen Y-W, Huang C-F, Yang C-Y, Yen C-C, Tsai K-S, Liu S-H. Inorganic mercury causes pancreatic beta-cell death via the oxidative stress-induced apoptotic and necrotic pathways. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology. 2010 Mar 15;243(3):323–31. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2009.11.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Chen Y-W, Huang C-F, Tsai K-S, Yang R-S, Yen C-C, Yang C-Y, et al. The role of phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt signaling in low-dose mercury-induced mouse pancreatic beta-cell dysfunction in vitro and in vivo. Diabetes. 2006 Jun;55(6):1614–24. doi: 10.2337/db06-0029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Kuo C-C, Moon K, Thayer KA, Navas-Acien A. Environmental Chemicals and Type 2 Diabetes: An Updated Systematic Review of the Epidemiologic Evidence. Curr Diab Rep. 2013 Oct 11;13(6):831–49. doi: 10.1007/s11892-013-0432-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Pi J, Bai Y, Zhang Q, Wong V, Floering LM, Daniel K, et al. Reactive oxygen species as a signal in glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. Diabetes. 2007 Jul;56(7):1783–91. doi: 10.2337/db06-1601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Bodin J, Bølling AK, Samuelsen M, Becher R, Løvik M, Nygaard UC. Long-term bisphenol A exposure accelerates insulitis development in diabetes-prone NOD mice. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2013 Jun;35(3):349–58. doi: 10.3109/08923973.2013.772195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40•.Bodin J, Bolling AK, Becher R, Kuper F, Lovik M, Nygaard UC. Transmaternal Bisphenol A Exposure Accelerates Diabetes Type 1 Development in NOD Mice. Toxicological Sciences. 2014 Jan 31;137(2):311–23. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kft242. This study demonstrates that in utero BPA exposure can exacerbate β-cell decline in a mouse model of Type 1 diabetes. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Boucher J, Kleinridders A, Kahn CR. Insulin Receptor Signaling in Normal and Insulin-Resistant States. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology. 2014 Jan 2;6(1):a009191–1. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a009191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Wang T, Li M, Chen B, Xu M, Xu Y, Huang Y, et al. Urinary bisphenol A (BPA) concentration associates with obesity and insulin resistance. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012 Feb;97(2):E223–7. doi: 10.1210/jc.2011-1989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Beydoun HA, Khanal S, Zonderman AB, Beydoun MA. Sex differences in the association of urinary bisphenol-A concentration with selected indices of glucose homeostasis among U.S. adults. Ann Epidemiol. 2014 Feb;24(2):90–7. doi: 10.1016/j.annepidem.2013.07.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Pearson JF, Bachireddy C, Shyamprasad S, Goldfine AB, Brownstein JS. Dia Care. 10. Vol. 33. American Diabetes Association; 2010. Sep 28, Association Between Fine Particulate Matter and Diabetes Prevalence in the U.S; pp. 2196–201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Cranmer M. Exposure to 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) Is Associated with Hyperinsulinemia and Insulin Resistance. Toxicological Sciences. 2000 Aug 1;56(2):431–6. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/56.2.431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Stahlhut RW, van Wijngaarden E, Dye TD, Cook S, Swan SH. Concentrations of urinary phthalate metabolites are associated with increased waist circumference and insulin resistance in adult U.S. males. Environ Health Perspect. 2007 Jun;115(6):876–82. doi: 10.1289/ehp.9882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.James-Todd TM, Meeker JD, Huang T, Hauser R, Ferguson KK, Rich-Edwards JW, et al. Pregnancy urinary phthalate metabolite concentrations and gestational diabetes risk factors. Environ Int. 2016 Sep 17;96:118–26. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2016.09.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Batista TM, Alonso-Magdalena P, Vieira E, Amaral MEC, Cederroth CR, Nef S, et al. Short-term treatment with bisphenol-A leads to metabolic abnormalities in adult male mice. PLoS ONE. 2012;7(3):e33814. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0033814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Sargis RM, Neel BA, Brock CO, Lin Y, Hickey AT, Carlton DA, et al. The novel endocrine disruptor tolylfluanid impairs insulin signaling in primary rodent and human adipocytes through a reduction in insulin receptor substrate-1 levels. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Basis of Disease. 2012 Jun;1822(6):952–60. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2012.02.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Paul DS, Harmon AW, Devesa V, Thomas DJ, Stýblo M. Molecular mechanisms of the diabetogenic effects of arsenic: inhibition of insulin signaling by arsenite and methylarsonous acid. Environ Health Perspect. 2007 May;115(5):734–42. doi: 10.1289/ehp.9867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Valentino R, D’Esposito V, Passaretti F, Liotti A, Cabaro S, Longo M, et al. PLoS ONE. 12. Vol. 8. Public Library of Science; 2013. Dec 9, Bisphenol-A Impairs Insulin Action and Up-Regulates Inflammatory Pathways in Human Subcutaneous Adipocytes and 3T3-L1 Cells; p. e82099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Moon MK, Jeong I-K, Jung Oh T, Ahn HY, Kim HH, Park YJ, et al. Long-term oral exposure to bisphenol A induces glucose intolerance and insulin resistance. Journal of Endocrinology. 2015 Jul;226(1):35–42. doi: 10.1530/JOE-14-0714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Xue P, Hou Y, Zhang Q, Woods CG, Yarborough K, Liu H, et al. Prolonged inorganic arsenite exposure suppresses insulin-stimulated AKT S473 phosphorylation and glucose uptake in 3T3-L1 adipocytes: involvement of the adaptive antioxidant response. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 2011 Apr 8;407(2):360–5. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.03.024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Nishiumi S, Yoshida M, Azuma T, Yoshida KI, Ashida H. 2,3,7,8- Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-Dioxin Impairs an Insulin Signaling Pathway through the Induction of Tumor Necrosis Factor- in Adipocytes. Toxicological Sciences. 2010 May 17;115(2):482–91. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfq052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Liu PC, Matsumura F. Mol Pharmacol. 1. Vol. 47. American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics; 1995. Jan 1, Differential effects of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin on the "adipose- type" and “brain-type” glucose transporters in mice; pp. 65–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Rajesh P, Balasubramanian K. Di(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate exposure impairs insulin receptor and glucose transporter 4 gene expression in L6 myotubes. Human & Experimental Toxicology. 2014 Jul;33(7):685–700. doi: 10.1177/0960327113506238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Rajesh P, Sathish S, Srinivasan C, Selvaraj J, Balasubramanian K. Phthalate is associated with insulin resistance in adipose tissue of male rat: role of antioxidant vitamins. J Cell Biochem. 2013 Mar;114(3):558–69. doi: 10.1002/jcb.24399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Rajesh P, Balasubramanian K. Phthalate exposure in utero causes epigenetic changes and impairs insulin signalling. Journal of Endocrinology. 2014 Oct;223(1):47–66. doi: 10.1530/JOE-14-0111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Han JC, Park SY, Hah BG, Choi GH, Kim YK, Kwon TH, et al. Cadmium induces impaired glucose tolerance in rat by down-regulating GLUT4 expression in adipocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2003 May 15;413(2):213–20. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(03)00120-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Shulman GI, Rothman DL, Jue T, Stein P, DeFronzo RA, Shulman RG. Quantitation of Muscle Glycogen Synthesis in Normal Subjects and Subjects with Non-Insulin-Dependent Diabetes by 13C Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. N Engl J Med. 1990 Jan 25;322(4):223–8. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199001253220403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61••.Heindel JJ, Blumberg B, Cave M, Machtinger R, Mantovani A, Mendez MA, et al. Metabolism Disrupting Chemicals and Metabolic Disorders. Reprod Toxicol. 2016 Oct 16; doi: 10.1016/j.reprotox.2016.10.001. Recent comprehensive review of metabolism disrupting chemicals. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Ruzzin J, Petersen R, Meugnier E, Madsen L, Lock E-J, Lillefosse H, et al. Persistent organic pollutant exposure leads to insulin resistance syndrome. Environ Health Perspect. 2010 Apr;118(4):465–71. doi: 10.1289/ehp.0901321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.García-Arévalo M, Alonso-Magdalena P, Rebelo Dos Santos J, Quesada I, Carneiro EM, Nadal A. Exposure to bisphenol-A during pregnancy partially mimics the effects of a high-fat diet altering glucose homeostasis and gene expression in adult male mice. PLoS ONE. 2014;9(6):e100214. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0100214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Jayashree S, Indumathi D, Akilavalli N, Sathish S, Selvaraj J, Balasubramanian K. Effect of Bisphenol-A on insulin signal transduction and glucose oxidation in liver of adult male albino rat. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology. 2013 Mar;35(2):300–10. doi: 10.1016/j.etap.2012.12.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Zhang W, Sargis RM, Volden PA, Carmean CM, Sun XJ, Brady MJ. PCB 126 and Other Dioxin-Like PCBs Specifically Suppress Hepatic PEPCK Expression via the Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor. In: Andrabi SA, editor. PLoS ONE. 5. Vol. 7. 2012. May 16, p. e37103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Beggs KM, McGreal SR, McCarthy A, Gunewardena S, Lampe JN, Lau C, et al. The role of hepatocyte nuclear factor 4-alpha in perfluorooctanoic acid- and perfluorooctanesulfonic acid-induced hepatocellular dysfunction. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology. 2016 Aug 1;304:18–29. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2016.05.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Jin Y, Lin X, Miao W, Wang L, Wu Y, Fu Z. Oral exposure of pubertal male mice to endocrine-disrupting chemicals alters fat metabolism in adult livers. Environ Toxicol. 2015 Dec;30(12):1434–44. doi: 10.1002/tox.22013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Huang C-F, Yang C-Y, Chan D-C, Wang C-C, Huang K-H, Wu C-C, et al. Arsenic Exposure and Glucose Intolerance/Insulin Resistance in Estrogen-Deficient Female Mice. Environ Health Perspect. 2015 Nov;123(11):1138–44. doi: 10.1289/ehp.1408663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Martinelli MI, Mocchiutti NO, Bernal CA. Dietary di(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate-impaired glucose metabolism in experimental animals. Human & Experimental Toxicology. 2006 Sep;25(9):531–8. doi: 10.1191/0960327106het651oa. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Beischlag TV, Luis Morales J, Hollingshead BD, Perdew GH. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor complex and the control of gene expression. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2008;18(3):207–50. doi: 10.1615/critreveukargeneexpr.v18.i3.20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Novelli M, Piaggi S, De Tata V. 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin-induced impairment of glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in isolated rat pancreatic islets. Toxicol Lett. 2005 Apr 10;156(2):307–14. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2004.12.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Piaggi S, Novelli M, Martino L, Masini M, Raggi C, Orciuolo E, et al. Cell death and impairment of glucose-stimulated insulin secretion induced by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) in the β-cell line INS-1E. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology. 2007 May;220(3):333–40. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2007.01.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Kim Y-H, Shim Y-J, Shin Y-J, Sul D, Lee E, Min B-H. 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) induces calcium influx through T-type calcium channel and enhances lysosomal exocytosis and insulin secretion in INS-1 cells. Int J Toxicol. 2009 May;28(3):151–61. doi: 10.1177/1091581809336885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Kurita H, Yoshioka W, Nishimura N, Kubota N, Kadowaki T, Tohyama C. Journal of Applied Toxicology. 8. Vol. 29. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd; 2009. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor- mediated effects of 2,3,7,8- tetrachlorodibenzo- p- dioxin on glucose- stimulated insulin secretion in mice; pp. 689–94. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Zuo Z, Wu T, Lin M, Zhang S, Yan F, Yang Z, et al. Chronic exposure to tributyltin chloride induces pancreatic islet cell apoptosis and disrupts glucose homeostasis in male mice. Environ Sci Technol. 2014 May 6;48(9):5179–86. doi: 10.1021/es404729p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Zuo Z, Chen S, Wu T, Zhang J, Su Y, Chen Y, et al. Tributyltin causes obesity and hepatic steatosis in male mice. Environ Toxicol. 2011 Feb;26(1):79–85. doi: 10.1002/tox.20531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Indumathi D, Jayashree S, Selvaraj J, Sathish S, Mayilvanan C, Akilavalli N, et al. Effect of bisphenol-A on insulin signal transduction and glucose oxidation in skeletal muscle of adult male albino rat. Human & Experimental Toxicology. 2013 Aug 9;32(9):960–71. doi: 10.1177/0960327112470273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Sakurai K, Kawazuma M, Adachi T, Harigaya T, Saito Y, Hashimoto N, et al. British Journal of Pharmacology. 2. Vol. 141. Blackwell Publishing Ltd; 2004. Bisphenol A affects glucose transport in mouse 3T3- F442A adipocytes; pp. 209–14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Seefeld MD, Corbett SW, Keesey RE, Peterson RE. Characterization of the wasting syndrome in rats treated with 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology. 1984 Apr;73(2):311–22. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(84)90337-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Warner M, Mocarelli P, Brambilla P, Wesselink A, Samuels S, Signorini S, et al. Diabetes, metabolic syndrome, and obesity in relation to serum dioxin concentrations: the Seveso women's health study. Environ Health Perspect. 2013 Aug;121(8):906–11. doi: 10.1289/ehp.1206113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Kern PA, Said S, Jackson WG, Michalek JE. Insulin sensitivity following agent orange exposure in Vietnam veterans with high blood levels of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004 Sep;89(9):4665–72. doi: 10.1210/jc.2004-0250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Guilherme A, Virbasius JV, Puri V, Czech MP. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 5. Vol. 9. Nature Publishing Group; 2008. May, Adipocyte dysfunctions linking obesity to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes; pp. 367–77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Janesick AS, Blumberg B. Obesogens: an emerging threat to public health. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2016 May;214(5):559–65. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2016.01.182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Agarwal AK, Garg A. A novel heterozygous mutation in peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma gene in a patient with familial partial lipodystrophy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002 Jan;87(1):408–11. doi: 10.1210/jcem.87.1.8290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Desvergne B, Feige JN, Casals-Casas C. PPAR-mediated activity of phthalates: A link to the obesity epidemic? Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology. 2009 May 25;304(1–2):43–8. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2009.02.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Grün F, Blumberg B. Endocrinology. 6. Vol. 147. Endocrine Society; 2006. Jun, Environmental Obesogens: Organotins and Endocrine Disruption via Nuclear Receptor Signaling; pp. s50–5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Regnier SM, El-Hashani E, Kamau W, Zhang X, Massad NL, Sargis RM. Tributyltin differentially promotes development of a phenotypically distinct adipocyte. Obesity. 2015 Aug 4;23(9):1864–71. doi: 10.1002/oby.21174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Sargis RM, Johnson DN, Choudhury RA, Brady MJ. Environmental endocrine disruptors promote adipogenesis in the 3T3-L1 cell line through glucocorticoid receptor activation. Obesity. 2010 Jul;18(7):1283–8. doi: 10.1038/oby.2009.419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Neel BA, Brady MJ, Sargis RM. The Endocrine Disrupting Chemical Tolylfluanid Alters Adipocyte Metabolism via Glucocorticoid Receptor Activation. Molecular Endocrinology. 2013 Mar;27(3):394–406. doi: 10.1210/me.2012-1270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90•.Regnier SM, Kirkley AG, Ye H, El-Hashani E, Zhang X, Neel BA, et al. Dietary Exposure to the Endocrine Disruptor Tolylfluanid Promotes Global Metabolic Dysfunction in Male Mice. Endocrinology. 2015 Mar;156(3):896–910. doi: 10.1210/en.2014-1668. This study investigates the role of TF in disrupting glucocorticoid signaling, an understudied area of MDC disruption. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Nieman LK, Biller BMK, Findling JW, Newell-Price J, Savage MO, Stewart PM, et al. The diagnosis of Cushing's syndrome: an Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline. The Journal of clinical endocrinology and metabolism. 2008;93:1526–40. doi: 10.1210/jc.2008-0125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Ohlstein JF, Strong AL, McLachlan JA, Gimble JM, Burow ME, Bunnell BA. Bisphenol A enhances adipogenic differentiation of human adipose stromal/stem cells. J Mol Endocrinol. 2014 Dec;53(3):345–53. doi: 10.1530/JME-14-0052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93•.Ariemma F, D’Esposito V, Liguoro D, Oriente F, Cabaro S, Liotti A, et al. Low-Dose Bisphenol-A Impairs Adipogenesis and Generates Dysfunctional 3T3-L1 Adipocytes. PLoS ONE. 2016;11(3):e0150762. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0150762. This study demonstrates that BPA exposure can promote the genesis of dysfunctional adipocytes which are detrimental to metabolic health, an understudied area of MDC effects. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.van Herpen NA, Schrauwen-Hinderling VB. Lipid accumulation in non-adipose tissue and lipotoxicity. Physiology & Behavior. 2008 May;94(2):231–41. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2007.11.049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Hotamisligil GS, Shargill NS. Adipose Expression of Tumor Necrosis Factor-α: Direct Role in Obesity-Linked Insulin Resistance. Science. 1993 Jan;259(5091):87–91. doi: 10.1126/science.7678183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.de Luca C, Olefsky JM. Inflammation and insulin resistance. FEBS Lett. 2008 Jan 9;582(1):97–105. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2007.11.057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97•.Zheng Z, Xu X, Zhang X, Wang A, Zhang C, Hüttemann M, et al. Exposure to ambient particulate matter induces a NASH-like phenotype and impairs hepatic glucose metabolism in an animal model. Journal of Hepatology. 2013 Jan;58(1):148–54. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2012.08.009. This study showed that air pollution can trigger hepatic steatosis and impair glucose metabolism, providing evidence for population studies linking metabolic disease to air quality. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Sun Q, Yue P, Deiuliis JA, Lumeng CN, Kampfrath T, Mikolaj MB, et al. Ambient Air Pollution Exaggerates Adipose Inflammation and Insulin Resistance in a Mouse Model of Diet-Induced Obesity. Circulation. 2009 Jan 19;119(4):538–46. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.108.799015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Yitshak Sade M, Kloog I, Liberty IF, Schwartz J, Novack V. The Association Between Air Pollution Exposure and Glucose and Lipids Levels. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2016 Jun;101(6):2460–7. doi: 10.1210/jc.2016-1378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Kim MJ, Pelloux V, Guyot E, Tordjman J, Bui L-C, Chevallier A, et al. Inflammatory pathway genes belong to major targets of persistent organic pollutants in adipose cells. Environ Health Perspect. 2012 Apr;120(4):508–14. doi: 10.1289/ehp.1104282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Alonso-Magdalena P, Vieira E, Soriano S, Menes L, Burks D, Quesada I, et al. Bisphenol A exposure during pregnancy disrupts glucose homeostasis in mothers and adult male offspring. Environ Health Perspect. 2010 Sep;118(9):1243–50. doi: 10.1289/ehp.1001993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102•.García-Arévalo M, Alonso-Magdalena P, Servitja J-M, Boronat-Belda T, Merino B, Villar-Pazos S, et al. Maternal Exposure to Bisphenol-A During Pregnancy Increases Pancreatic β-Cell Growth During Early Life in Male Mice Offspring. Endocrinology. 2016 Nov;157(11):4158–71. doi: 10.1210/en.2016-1390. This study provides evidence that in utero BPA exposure leads to impaired glucose tolerance later in life, which is exacerbated by high fat feeding, demonstrating the interaction between traditional metabolic risk factors and gestational MDC exposure. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Grün F, Watanabe H, Zamanian Z, Maeda L, Arima K, Cubacha R, et al. Endocrine-disrupting organotin compounds are potent inducers of adipogenesis in vertebrates. Mol Endocrinol. 2006 Sep;20(9):2141–55. doi: 10.1210/me.2005-0367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Rodriguez KF, Ungewitter EK, Crespo-Mejias Y, Liu C, Nicol B, Kissling GE, et al. Effects of in Utero Exposure to Arsenic during the Second Half of Gestation on Reproductive End Points and Metabolic Parameters in Female CD-1 Mice. Environ Health Perspect. 2016 Mar;124(3):336–43. doi: 10.1289/ehp.1509703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Campioli E, Martinez-Arguelles DB, Papadopoulos V. In utero exposure to the endocrine disruptor di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate promotes local adipose and systemic inflammation in adult male offspring. Nutr Diabetes. 2014;4:e115. doi: 10.1038/nutd.2014.13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Hines EP, White SS, Stanko JP, Gibbs-Flournoy EA, Lau C, Fenton SE. Phenotypic dichotomy following developmental exposure to perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) in female CD-1 mice: Low doses induce elevated serum leptin and insulin, and overweight in mid-life. Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology. 2009 May 25;304(1–2):97–105. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2009.02.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Wan HT, Zhao YG, Leung PY, Wong CKC. Perinatal exposure to perfluorooctane sulfonate affects glucose metabolism in adult offspring. PLoS ONE. 2014;9(1):e87137. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0087137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108••.Alonso-Magdalena P, García-Arévalo M, Quesada I, Nadal A. Bisphenol-A treatment during pregnancy in mice: a new window of susceptibility for the development of diabetes in mothers later in life. Endocrinology. 2015 May;156(5):1659–70. doi: 10.1210/en.2014-1952. This study demonstrates BPA exposure during pregnancy promotes diabetes development later in life and demonstrates that in addition to being a vulnerable window for the fetus, pregnancy is also a vulnerable window for mothers. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Alonso-Magdalena P, Quesada I, Nadal A. Prenatal Exposure to BPA and Offspring Outcomes: The Diabesogenic Behavior of BPA. Dose Response. 2015 Apr;13(2):1559325815590395. doi: 10.1177/1559325815590395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Wei J, Lin Y, Li Y, Ying C, Chen J, Song L, et al. Perinatal exposure to bisphenol A at reference dose predisposes offspring to metabolic syndrome in adult rats on a high-fat diet. Endocrinology. 2011 Aug;152(8):3049–61. doi: 10.1210/en.2011-0045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Yan Y-H, Chou CC, Lee C-T, Liu J-Y, Cheng T-J. Enhanced insulin resistance in diet-induced obese rats exposed to fine particles by instillation. Inhal Toxicol. 2011 Aug;23(9):507–19. doi: 10.3109/08958378.2011.587472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Lim S, Ahn SY, Song IC, Chung MH, Jang HC, Park KS, et al. Chronic exposure to the herbicide, atrazine, causes mitochondrial dysfunction and insulin resistance. PLoS ONE. 2009;4(4):e5186. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0005186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Ryan KK, Haller AM, Sorrell JE, Woods SC, Jandacek RJ, Seeley RJ. Perinatal exposure to bisphenol-a and the development of metabolic syndrome in CD-1 mice. Endocrinology. 2010 Jun;151(6):2603–12. doi: 10.1210/en.2009-1218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Paul DS, Walton FS, Saunders RJ, Stýblo M. Characterization of the impaired glucose homeostasis produced in C57BL/6 mice by chronic exposure to arsenic and high-fat diet. Environ Health Perspect. 2011 Aug;119(8):1104–9. doi: 10.1289/ehp.1003324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Longo VD, Panda S. Fasting, circadian rhythms, and time-restricted feeding in healthy lifespan. Cell Metabolism. 2016 doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2016.06.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Beydoun HA, Beydoun MA, Jeng HA, Zonderman AB, Eid SM. Bisphenol-A and Sleep Adequacy among Adults in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys. Sleep. 2016 Feb 1;39(2):467–76. doi: 10.5665/sleep.5466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Weber DN, Hoffmann RG, Hoke ES, Tanguay RL. Bisphenol A exposure during early development induces sex-specific changes in adult zebrafish social interactions. J Toxicol Environ Health Part A. 2015;78(1):50–66. doi: 10.1080/15287394.2015.958419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118•.Rhee J-S, Kim B-M, Lee B-Y, Hwang U-K, Lee YS, Lee J-S. Cloning of circadian rhythmic pathway genes and perturbation of oscillation patterns in endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs)-exposed mangrove killifish Kryptolebias marmoratus. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2014 Aug;164:11–20. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpc.2014.04.001. This study demonstrates the links between MDCs and circadian biology. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Pearson ER, Flechtner I, Njølstad PR, Malecki MT, Flanagan SE, Larkin B, et al. Switching from insulin to oral sulfonylureas in patients with diabetes due to Kir6.2 mutations. N Engl J Med. 2006 Aug 3;355(5):467–77. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa061759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Grossman SL, Lessem J. Mechanisms and clinical effects of thiazolidinediones. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 1997 Aug;6(8):1025–40. doi: 10.1517/13543784.6.8.1025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Joseph GY, Javorschi S, Hevener AL. The effect of thiazolidinediones on plasma adiponectin levels in normal, obese, and type 2 diabetic subjects. Diabetes. 2002 doi: 10.2337/diabetes.51.10.2968. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Boden G, Homko C, Mozzoli M, Showe LC, Nichols C, Cheung P. Thiazolidinediones upregulate fatty acid uptake and oxidation in adipose tissue of diabetic patients. Diabetes. 2005 Mar;54(3):880–5. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.54.3.880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.de Souza CJ, Eckhardt M, Gagen K, Dong M, Chen W, Laurent D, et al. Diabetes. 8. Vol. 50. American Diabetes Association; 2001. Aug 1, Effects of Pioglitazone on Adipose Tissue Remodeling Within the Setting of Obesity and Insulin Resistance; pp. 1863–71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Hill DS, Wlodarczyk BJ, Mitchell LE, Finnell RH. Arsenate-induced maternal glucose intolerance and neural tube defects in a mouse model. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology. 2009 Aug 15;239(1):29–36. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2009.05.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Kirchner S, Kieu T, Chow C, Casey S, Blumberg B. Prenatal exposure to the environmental obesogen tributyltin predisposes multipotent stem cells to become adipocytes. Molecular Endocrinology. 2010 Mar;24(3):526–39. doi: 10.1210/me.2009-0261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Dávila-Esqueda ME, Morales JMV, Jiménez-Capdeville ME, la Cruz De E, Falcón-Escobedo R, Chi-Ahumada E, et al. Low-level subchronic arsenic exposure from prenatal developmental stages to adult life results in an impaired glucose homeostasis. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2011 Nov;119(10):613617–617. doi: 10.1055/s-0031-1287782. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Treviño S, Waalkes MP, Flores Hernández JA, León-Chavez BA, Aguilar-Alonso P, Brambila E. Chronic cadmium exposure in rats produces pancreatic impairment and insulin resistance in multiple peripheral tissues. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2015 Oct 1;583:27–35. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2015.07.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Kim J, Kang E-J, Park M-N, Kim J-E, Kim S-C, Jeung E-B, et al. The adverse effect of 4-tert-octylphenol on fat metabolism in pregnant rats via regulation of lipogenic proteins. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology. 2015 Jul;40(1):284–91. doi: 10.1016/j.etap.2015.06.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Baker NA, Karounos M, English V, Fang J, Wei Y, Stromberg A, et al. Coplanar polychlorinated biphenyls impair glucose homeostasis in lean C57BL/6 mice and mitigate beneficial effects of weight loss on glucose homeostasis in obese mice. Environ Health Perspect. 2013 Jan;121(1):105–10. doi: 10.1289/ehp.1205421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Gray SL, Shaw AC, Gagne AX, Chan HM. Chronic exposure to PCBs (Aroclor 1254) exacerbates obesity-induced insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia in mice. J Toxicol Environ Health Part A. 2013;76(12):701–15. doi: 10.1080/15287394.2013.796503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Yan S, Zhang H, Zheng F, Sheng N, Guo X, Dai J. Perfluorooctanoic acid exposure for 28 days affects glucose homeostasis and induces insulin hypersensitivity in mice. Sci Rep. 2015 doi: 10.1038/srep11029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Kern PA, Dicker-Brown A, Said ST, Kennedy R, Fonseca VA. The stimulation of tumor necrosis factor and inhibition of glucose transport and lipoprotein lipase in adipose cells by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Metabolism. 2002 Jan;51(1):65–8. doi: 10.1053/meta.2002.28088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Fried KW, Guo GL, Esterly N, Kong B, Rozman KK. 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) reverses hyperglycemia in a type II diabetes mellitus rat model by a mechanism unrelated to PPARγ. Drug and Chemical Toxicology. 2010 Apr 30;33(3):261–8. doi: 10.3109/01480540903390026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Enan E, Matsumura F. Journal of Biochemical and Molecular Toxicology. 2. Vol. 9. Wiley Subscription Services, Inc., A Wiley Company; 1994. 2,3,7,8- tetrachlorodibenzo- p- dioxin (TCDD) - induced changes in glucose transporting activity in guinea pigs, mice, and rats in vivo and in vitro; pp. 97–106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Ogino K, Inukai T, Miura Y, Matsui H, Takemura Y. Triphenyltin chloride induces glucose intolerance by the suppression of insulin release from hamster pancreatic beta-cells. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 1996;104(5):409–11. doi: 10.1055/s-0029-1211476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Liu S, Guo X, Wu B, Yu H, Zhang X, Li M. Arsenic induces diabetic effects through beta-cell dysfunction and increased gluconeogenesis in mice. Sci Rep. 2014;4:6894. doi: 10.1038/srep06894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Paul DS, Hernandez-Zavala A, Walton FS, Adair BM, Dedina J, Matoušek T, et al. Examination of the effects of arsenic on glucose homeostasis in cell culture and animal studies: development of a mouse model for arsenic-induced diabetes. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology. 2007 Aug 1;222(3):305–14. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2007.01.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.DW, MW, CL Ultrastructure of beta-cells of the endocrine pancreas in rats receiving polychlorinated biphenyls. Environ Physiol Biochem. 1975 Jan 1;5(5):322–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Wang J, Lv X, Du Y. Inflammatory response and insulin signaling alteration induced by PCB77. Journal of Environmental Sciences. 2010 Jul;22(7):1086–90. doi: 10.1016/s1001-0742(09)60221-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Quesada I, Fuentes E, Viso-León MC, Soria B, Ripoll C, Nadal A. Low doses of the endocrine disruptor bisphenol-A and the native hormone 17beta-estradiol rapidly activate transcription factor CREB. The FASEB Journal. 2002 Oct;16(12):1671–3. doi: 10.1096/fj.02-0313fje. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Soriano S, Alonso-Magdalena P, García-Arévalo M, Novials A, Muhammed SJ, Salehi A, et al. Rapid insulinotropic action of low doses of bisphenol-A on mouse and human islets of Langerhans: role of estrogen receptor β. PLoS ONE. 2012;7(2):e31109. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0031109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Alonso-Magdalena P, Laribi O, Ropero AB. Low doses of bisphenol A and diethylstilbestrol impair Ca2+ signals in pancreatic α-cells through a nonclassical membrane estrogen receptor within intact islets of …. Environmental health …. 2005 doi: 10.1289/ehp.8002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Alonso-Magdalena P, Morimoto S, Ripoll C, Fuentes E, Nadal A. The estrogenic effect of bisphenol A disrupts pancreatic beta-cell function in vivo and induces insulin resistance. Environ Health Perspect. 2006 Jan;114(1):106–12. doi: 10.1289/ehp.8451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Alonso-Magdalena P, Ropero AB, Carrera MP, Cederroth CR, Baquié M, Gauthier BR, et al. Pancreatic insulin content regulation by the estrogen receptor ER alpha. PLoS ONE. 2008;3(4):e2069. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0002069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Perreault L, McCurdy C, Kerege AA, Houck J, Færch K, Bergman BC. Bisphenol A impairs hepatic glucose sensing in C57BL/6 male mice. PLoS ONE. 2013;8(7):e69991. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0069991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Ma Y, Xia W, Wang DQ, Wan YJ, Xu B, Chen X, et al. Hepatic DNA methylation modifications in early development of rats resulting from perinatal BPA exposure contribute to insulin resistance in adulthood. Diabetologia. 2013 Sep;56(9):2059–67. doi: 10.1007/s00125-013-2944-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Angle BM, Do RP, Ponzi D, Stahlhut RW, Drury BE, Nagel SC, et al. Metabolic disruption in male mice due to fetal exposure to low but not high doses of bisphenol A (BPA): evidence for effects on body weight, food intake, adipocytes, leptin, adiponectin, insulin and glucose regulation. Reprod Toxicol. 2013 Dec;42:256–68. doi: 10.1016/j.reprotox.2013.07.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Li G, Chang H, Xia W, Mao Z, Li Y, Xu S. F0 maternal BPA exposure induced glucose intolerance of F2 generation through DNA methylation change in Gck. Toxicol Lett. 2014 Aug 4;228(3):192–9. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2014.04.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Mackay H, Patterson ZR, Khazall R, Patel S, Tsirlin D, Abizaid A. Organizational effects of perinatal exposure to bisphenol-A and diethylstilbestrol on arcuate nucleus circuitry controlling food intake and energy expenditure in male and female CD-1 mice. Endocrinology. 2013 Apr;154(4):1465–75. doi: 10.1210/en.2012-2044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Hao C-J, Cheng X-J, Xia H-F, Ma X. The endocrine disruptor 4-nonylphenol promotes adipocyte differentiation and induces obesity in mice. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2012;30(2):382–94. doi: 10.1159/000339032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Lee MJ, Lin H, Liu CW, Wu MH, Liao WJ, Chang HH, et al. AJP: Cell Physiology. 6. Vol. 294. American Physiological Society; 2008. Apr 9, Octylphenol stimulates resistin gene expression in 3T3-L1 adipocytes via the estrogen receptor and extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathways; pp. C1542–51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Lv Z, Li G, Li Y, Ying C, Chen J, Chen T, et al. Glucose and lipid homeostasis in adult rat is impaired by early-life exposure to perfluorooctane sulfonate. Environ Toxicol. 2013 Sep;28(9):532–42. doi: 10.1002/tox.20747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Ibrahim MM, Fjære E, Lock E-J, Naville D, Amlund H, Meugnier E, et al. Chronic consumption of farmed salmon containing persistent organic pollutants causes insulin resistance and obesity in mice. PLoS ONE. 2011;6(9):e25170. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0025170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Gayathri NS, Dhanya CR, Indu AR, Kurup PA. Changes in some hormones by low doses of di (2-ethyl hexyl) phthalate (DEHP), a commonly used plasticizer in PVC blood storage bags & medical tubing. Indian J Med Res. 2004 Apr;119(4):139–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.Lin Y, Wei J, Li Y, Chen J, Zhou Z, Song L, et al. Developmental exposure to di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate impairs endocrine pancreas and leads to long-term adverse effects on glucose homeostasis in the rat. AJP: Endocrinology and Metabolism. 2011 Sep;301(3):E527–38. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00233.2011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Rajesh P, Balasubramanian K. Gestational exposure to di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP) impairs pancreatic β-cell function in F1 rat offspring. Toxicol Lett. 2015 Jan 5;232(1):46–57. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2014.09.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Rengarajan S, Parthasarathy C, Anitha M, Balasubramanian K. Diethylhexyl phthalate impairs insulin binding and glucose oxidation in Chang liver cells. Toxicology in Vitro. 2007 Feb;21(1):99–102. doi: 10.1016/j.tiv.2006.07.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158.Hao C, Cheng X, Xia H, Ma X. The endocrine disruptor mono-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate promotes adipocyte differentiation and induces obesity in mice. Biosci Rep. 2012 Dec;32(6):619–29. doi: 10.1042/BSR20120042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159.Boberg J, Metzdorff S, Wortziger R, Axelstad M, Brokken L, Vinggaard AM, et al. Impact of diisobutyl phthalate and other PPAR agonists on steroidogenesis and plasma insulin and leptin levels in fetal rats. Toxicology. 2008 Sep 4;250(2–3):75–81. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2008.05.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160.Smith BE, Hsu WH, Yang PC. Amitraz-induced glucose intolerance in rats: antagonism by yohimbine but not by prazosin. Arch Toxicol. 1990;64(8):680–3. doi: 10.1007/BF01974698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161.Somm E, Schwitzgebel VM, Vauthay DM, Camm EJ, Chen CY, Giacobino J-P, et al. Prenatal nicotine exposure alters early pancreatic islet and adipose tissue development with consequences on the control of body weight and glucose metabolism later in life. Endocrinology. 2008 Dec;149(12):6289–99. doi: 10.1210/en.2008-0361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 162.Dunn JS, Duffy E, Gilmour MK, Kirkpatrick J, McLetchie NG. Further observations on the effects of alloxan on the pancreatic islets. J Physiol (Lond) 1944 Sep 29;103(2):233–43. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1944.sp004072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 163.Yau ET, Mennear JH. The inhibitoty effect of DDT on insulin secretion in mice. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology. 1977 doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(77)90179-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 164.Panahi P, Vosough-Ghanbari S, Pournourmohammadi S, Ostad SN, Nikfar S, Minaie B, et al. Stimulatory effects of malathion on the key enzymes activities of insulin secretion in langerhans islets, glutamate dehydrogenase and glucokinase. Toxicol Mech Methods. 2006;16(4):161–7. doi: 10.1080/15376520500191623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 165.Abdollahi M, Donyavi M, Pournourmohammadi S, Saadat M. Hyperglycemia associated with increased hepatic glycogen phosphorylase and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase in rats following subchronic exposure to malathion. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2004 Apr;137(4):343–7. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2004.03.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 166.Ueyama J, Kamijima M, Asai K, Mochizuki A, Wang D, Kondo T, et al. Effect of the organophosphorus pesticide diazinon on glucose tolerance in type 2 diabetic rats. Toxicol Lett. 2008 Nov 10;182(1–3):42–7. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2008.08.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 167.Kamath V, Rajini PS. Altered glucose homeostasis and oxidative impairment in pancreas of rats subjected to dimethoate intoxication. Toxicology. 2007 Mar 7;231(2–3):137–46. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2006.11.072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 168.Hoppe AA, Carey GB. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers as endocrine disruptors of adipocyte metabolism. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2007 Dec;15(12):2942–50. doi: 10.1038/oby.2007.351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 169.Naville D, Pinteur C, Vega N, Menade Y, Vigier M, Le Bourdais A, et al. Low-dose food contaminants trigger sex-specific, hepatic metabolic changes in the progeny of obese mice. The FASEB Journal. 2013 doi: 10.1096/fj.13-231670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 170.Naville D, Labaronne E, Vega N, Pinteur C, Canet-Soulas E, Vidal H, et al. PLoS ONE. 4. Vol. 10. Public Library of Science; 2015. Apr 24, Metabolic Outcome of Female Mice Exposed to a Mixture of Low-Dose Pollutants in a Diet-Induced Obesity Model; p. e0124015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


