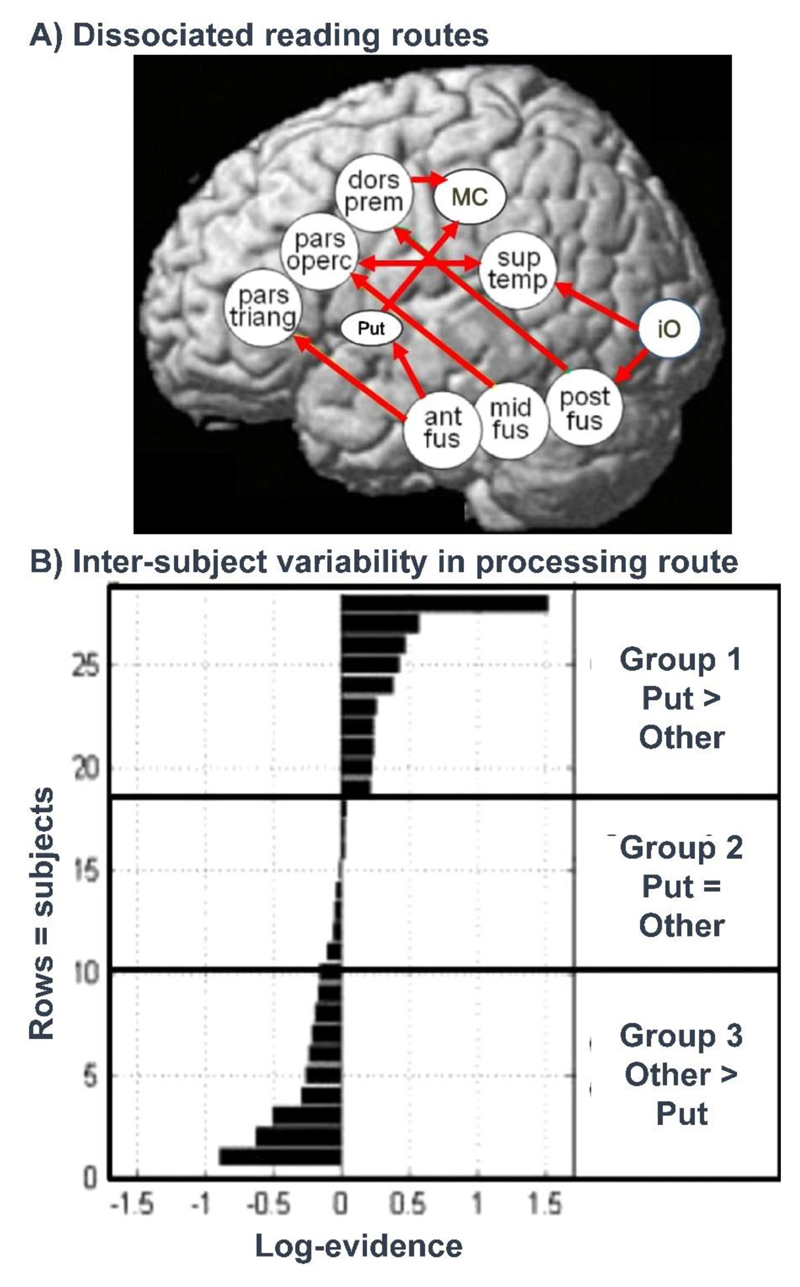
Figure 7. Neural pathways for reading outnumber predictions from cognitive models.
(A) Brain regions and functional connections for reading that have been shown to dissociate for different types of word stimuli (Mechelli et al., 2005) and in different subjects reading the same words (Seghier et al., 2010; 2014; Richardson et al., 2011). The dissociation of these pathways can be demonstrated by showing that as use of one pathway increases, use of the other pathway decreases. (B) shows inter-subject variability in the engagement of the putamen reading pathway. Group 1 used the putamen (put) reading pathway more than other pathways. Group 2 did not use the putamen pathway more or less than other pathways. Group 3 used the putamen pathway less than the other pathways. Data from Seghier et al., (2010).