IMMUNOLOGY Correction for “B and T lymphocyte attenuator inhibits LPS-induced endotoxic shock by suppressing Toll-like receptor 4 signaling in innate immune cells,” by Yoshihisa Kobayashi, Arifumi Iwata, Kotaro Suzuki, Akira Suto, Saki Kawashima, Yukari Saito, Takayoshi Owada, Midori Kobayashi, Norihiko Watanabe, and Hiroshi Nakajima, which was first published March 11, 2013; 10.1073/pnas.1222093110 (Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:5121–5126).
The authors note that Fig. 4 appeared incorrectly. The corrected figure and its legend appear below.
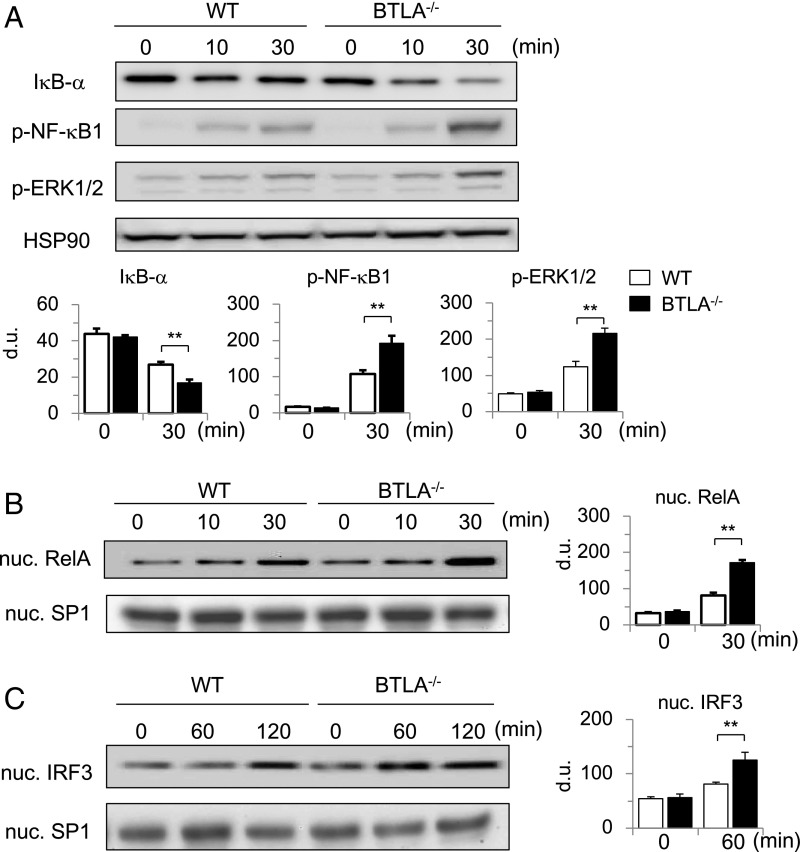
Fig. 4.
LPS-induced activation of NF-κB, MAPK, and IRF-3 pathways is enhanced in BTLA−/− DCs. (A and B) BTLA−/− BMDCs and WT BMDCs were stimulated with LPS (100 ng/mL) for indicated time periods. (A) Whole-cell lysates were subjected to immunoblotting with antibodies against IκB-α, p-NF-κB1, p-ERK1/2, and HSP90α/β (as a control). (B) Nuclear extracts were subjected to immunoblotting with antibodies against RelA and SP1 (as a control). Shown are representative blots and densitometric analyses of relative intensity of three independent experiments. (C) BTLA−/− BMDCs and WT BMDCs were stimulated with LPS (1 μg/mL) for indicated time periods. Nuclear extracts were subjected to immunoblotting with antibodies against IRF-3 and SP1. Shown are representative blots and densitometric analyses of relative intensity of three independent experiments. **P < 0.01.