Abstract
The present study aimed to evaluate the cinnamic acid effect on memory impairment, oxidative stress, and cholinergic dysfunction in streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic model in mice. In this experimental study, 48 male Naval Medical Research Institute (NMRI) mice (30–35 g) were chosen and were randomly divided into six groups: control, cinnamic acid (20 mg/kg day, i.p. ), diabetic, and cinnamic acid-treated diabetic (10, 20 and 40 mg/kg day, i.p. ). Memory was impaired by administering an intraperitoneal STZ injection of 50 mg/kg. Cinnamic acid was injected for 40 days starting from the 21st day after confirming STZ-induced dementia to observe its therapeutic effect. Memory function was assessed using cross-arm maze, morris water maze and passive avoidance test. After the administration, biochemical parameters of oxidative stress and cholinergic function were estimated in the brain. Present data indicated that inducing STZ caused significant memory impairment, whereas administration of cinnamic acid caused significant and dose-dependent memory improvement. Assessment of brain homogenates indicated cholinergic dysfunction, increase in lipid peroxidation and reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels, and decrease in glutathione (GSH), superoxide dismutase (SOD), and catalase (CAT) activities in the diabetic group compared to the control animals, whereas cinnamic acid administration ameliorated these indices in the diabetic mice. The present study demonstrated that cinnamic acid improves memory by reducing the oxidative stress and cholinergic dysfunction in the brain of diabetic mice.
Keywords: Cinnamic acid, Diabetes, Memory, Oxidative stress, Streptozotocin
INTRODUCTION
The human brain is a very intricate system and several factors such as age and various diseases may affect its working [1]. Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease that can have worsening effects on many organs, including the brain. It adversely affects the central nervous system leading to cognitive impairments [2,3]. Although both diabetes types play a crucial role in memory weakening, their mode of action on memory and learning system remains unclear [4]. It is reported that factors such as improved apoptosis, reduced neuronal densities, metabolic impairments, and oxidative stress are crucial in the pathogenesis of cognitive impairment and memory deficiency [5]. Several studies recommended a significant role of oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of cognitive impairment [6]. The long-term hyperglycemia enhances glucose oxidation, which sequentially produces reactive oxygen species (ROS) causing increased oxidative stress; this leads to morphological and functional changes in the hippocampus due to the excessive production of malanoldehyde (MDA) and reduced efficacy of superoxide dismutase (SOD) [7]. Moreover, several evidences reported that dietary enrichment with nutritional antioxidants could improve the cognitive function not only in normal subjects but also in cognitive deficits after stroke [8,9,10,11].
Although many antioxidants are available, we used a natural approach to suppress the oxidative stress in the brain. Cinnamon (Cinnamomum cassia) is widely used for centuries as a natural spice and flavoring material throughout the world [12]. In some countries, it is used in traditional medicine as an antidiabetic agent. Cinnamon contains volatile oils such as cinnamaldehyde, eugenol, and cinnamic acid; phenolic compounds such as tannin, catechins, and proanthocyanidin; mono terpenes and sesquiterpenes; and trace coumarin [12,13,14]. Among these compounds, cinnamic acid and cinnamaldehyde form the major components of cinnamon aqueous extract. Moreover, it has been reported that in rats, cinnamaldehyde is partly metabolized into cinnamic acid in the stomach and small intestine, and is almost completely metabolized into cinnamic acid in the liver before it is absorbed into the blood [15]. Cinnamic acid moderates glycogenesis and gluconeogenesis and decreased blood glucose and glucose tolerance in diabetic rats [16]. Additionally, cinnamic acid increases the insulin secretion in isolated islets [12]. Furthermore, several studies have reported other pharmacological properties of cinnamic acid, including hepatoprotective [17] and antioxidant activity [18,19,20]. Cinnamic acid reveals high antioxidant activity due to the presence of vinyl fragments. This property develops our interest in studying this compound as a potential drug for the management of pathologies associated with the lipid peroxidation in cellular membranes [21]. The present study was designed to determine the therapeutic effect of cinnamic acid on memory impairment in diabetic mice, in addition to reducing the previously observed diabetic symptoms. Therefore, we planned to examine the therapeutic effect of cinnamic acid on memory and cognitive impairment, oxidative stress, and cholinergic dysfunction in streptozotocin (STZ)-induced model of diabetes in male mice.
METHODS
Chemicals and drugs
Cinnamic acid (99% pure), 4-(2-Hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazineethanesulfonic acid) (HEPES), mannitol, ethylene glycol tetra acetic acid (EGTA), bovine serum albumin (BSA), 2,7-di chloro fluorescein diacetate (DCFH-DA), 3,4 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2, 5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT), Rhodamine 123, thiobarbituric acid, trichloroacetic acid, 1,1,3,3-tetramethoxypropane, reduced glutathione, oxidized glutathione, Coomassie Brilliant Blue and STZ powder were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St Louis, Missouri, USA), and sucrose 5, 5′-dithiobis-2-nitrobenzoic acid (DTNB), dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), NaCl, KCl, CaCl2, MgCl2 and NaHCO3 were obtained from Merck company (Darmstadt, Germany).
Animals
48 males Naval Medical Research Institute (NMRI) mice (30–35 g) were obtained from the animal facility of Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Science (AJUMS), which is completely qualified by AJUMS animal care guidelines with an ethics committee grantee No. IR.AJUMS.REC.1396.261. After one week adaptation, the mice were housed eight per cage in polycarbonate cages with corncob bedding in 20±4℃ temperature with a 12 h light/12 h dark cycle and 10% humidity.
Induction and assessment of diabetes
Animals were rendered diabetic by a single intraperitoneal STZ injection of 50 mg/kg. STZ was dissolved in 0.05 M citrate buffer at pH 4.5, immediately before administration. The control mice (n=8) were injected with citrate buffer alone. Blood glucose levels were evaluated using a glucometer (ACON Laboratories, Inc., USA) 72 h later. The mice with glucose levels higher than 220 mg/dl were considered as diabetic. Accordingly, the animals exposed to chronic hyperglycemia revealed obvious pathological changes in the central nerve structure and function, three weeks after STZ injection; the blood glucose level was again determined and mice with final blood glucose levels above 220 mg/dl were considered diabetic [22].
The mice used in this study were randomly assigned into six groups:
(1) Control group (Con) (n=8); normal mice treated with saline, IP (physiological saline 0.1 ml/100 g), for 40 days
(2) Cinnamic group (cinn) (n=8); normal mice treated with cinnamic (20 mg/kg/day), for 40 days
(3) Control diabetic group (DM) (n=8); diabetic mice treated with saline, IP (physiological saline 0.1 ml/100 g), for 40 days
(4) DM+ cinnamic group1 (n=8); diabetic mice treated with cinnamic (10 mg/kg/day), for 40 days.
(5) DM+ cinnamic group2 (n=8); diabetic mice treated with cinnamic (20 mg/kg/day), for 40 days
(6) DM+ cinnamic group1 (n=8); diabetic mice treated with cinnamic (40 mg/kg/day), for 40 days
Behavioral training
Passive avoidance test
The step-down passive avoidance task is used to evaluate the state-dependent learning and memory. The apparatus consisted of a box made of Plexiglas with dimensions of 40×30×30 cm with a floor of steel bars. Each of the steel bars was 4 mm. in diameter with a spacing of 13 mm. A wooden platform with dimensions of 4×4×4 cm at the bottom center of the floor was provided. Electric shocks with a frequency of 1 Hz at 15 V for 15 s using a stimulator connected to the floor bars transmitted a shock to the animals' hands and feet. When the animal was placed on the podium, the natural tendency of the animal was to get down on the floor bars; however, if the animal received a shock its innate desire to get down from on the platform was suppressed, in particular, an inhibitory avoidance learning occurred. The latency time of moving down from the safe podium (stepdown latency) was considered as memory retrieval [23], which involved two stages, namely training and testing. In the training phase, animals were slowly placed on the wooden platform in the middle of the device and the delay in moving down from the platform was recorded by a chronometer. When the mouse stepped down from the platform and placed all its paws on the grid floor, intermittent electric shocks were delivered continuously for 15 s. Before the final shock, the animal was removed [24,25]. This training procedure was performed between 9:00 and 15:00 h, and animals with latencies longer than 30 s were omitted from the study. The test phase was conducted for 24 h after the training phase and was similar to the training phase; however, in this phase the animal did not receive any shock treatment. Thus, each animal was slowly placed on the wooden platform again and the delay in coming down from the platform was considered as a memory retrieval. In these experiments, the time limit for retaining the mouse on the podium was of maximum 300 s [23]. The retention test was also conducted between 9:00 and 15:00 h. At the end of each test, the surface of the apparatus was thoroughly cleaned to avoid the presence of olfactory cues [25].
Spatial navigation memory test
This test was performed using cross-arm maze. The task was to test the navigation memory, which could be weakened by brain damage. This model was used to test the spatial navigation memory considering the spatial orientation and perception as described by Ragozzino et al. [26]. The maze was constructed of wood, painted gray, and comprised a central platform (25 cm diameter), which radiated four symmetrical arms (55 cm long×10 cm wide) with 12 cm walls. Briefly, mice were placed individually in a four-arm cross maze and were allowed to transverse the maze freely for 12 min. The number and arrangement of entries were noted; an alternation was defined as an entry into four different arms on an overlapping quadruple set. Four consecutive arm choices within the total set of arm choices made up a quadruple set. A quadruple set consisting of arm choices B, D, C, A comprised “actual alternation,” whereas the set with B, D, B, A did not (using this procedure, possible alternation sequences were equal to the number of total arm entries minus three). Percent alternation was calculated as follows:
Alternation percentage is an indicator of spatial navigation memory of the experimental mice and the number of total arm entries is the index of the locomotor activity in this maze [22].
Morris water maze test
The device comprised a round container, 100 cm in diameter and 50 cm in depth. The tank was filled with water (21–26℃) up to a height of 30 cm and the transparent escape platform made of Plexiglas (10 cm in diameter and 29 cm in height) was concealed at 1.5 cm under the surface of water at a fixed place. The water was turned milky with powdered nonfat milk or nontoxic white colored dye. The platform was not observable from just above the water level and removal trials have designated that escape on to the platform was not done by visual or other proximal signs [27,28]. The period spent by the animal to reach the concealed platform was used as the memory index. Before the test commencement, the mice were adapted to the maze location. The water maze test was conducted for all mice groups on 10th, 20th, 30th, and 40th days for all animals (n=5). For each trial, the time required (in seconds) for an individual mouse to find the concealed platform was recorded and the mean data from the tests were used for the statistical analyses.
Biochemical analysis
Determination of brain weight to body weight ratio
At the end of 40 days, the mice were decapitated under ether anesthesia. The skull was cut open and the brain was exposed from its dorsal side. The whole brain was quickly removed and weighed. Then the ratio of brain weight to body weight was calculated for each animal [29].
Brain tissue preparation
The whole brain was quickly removed and cleaned with normal saline on the ice. A 10% (w/v) homogenate of brain samples (0.03 M sodium phosphate buffer, pH-7.4) was prepared by using an Ultra-Turrax T25 (USA) homogenizer at a speed of 9500 rpm. The homogenized tissue preparation was used to measure AChE, ROS, Catalase, MDA, GSH and nitrite.
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) level in tissues of brain
The level of ROS in brain tissue was measured using 2, 7-dichlorofluorescindiacetate (DCFDA) that converted into highly fluorescent DCF by cellular peroxides. Briefly, 10% brain homogenate were prepared in phosphate buffer 1 mM, pH 7.4. For each test 2 ml homogenate tissue was mixed with 40 ml of 1.25 mM DCFDA in methanol for ROS estimation. All samples were incubated for 15 min in a water bath at 37℃. Fluorescence was calculated using a fluorimeter, at 488 nm excitation and 525 nm emission wavelength [30].
Glutathione (GSH) in tissue of brain
Glutathione content was measured according to the method described by Thomas and Skrinska. Brain homogenates were incubated whit 1 ml of 20% trichloroacetic acid (TCA) and 1 ml EDTA 1mM for 5 min, which was used as protein precipitant. The total homogenate was centrifuged at 10,000 g for 30 min at 4℃. 200 µl of supernatant was mixed with 1.8 ml of 0.1 mM 5.5′-dithio-bis (2-nitro benzoic acid) (DTNB). The GSH reacts with DTNB and forms a yellow-colored complex with DTNB. The absorbance was read at 412 nm. The result was expressed as µmoles of GSH/mg protein [31].
Thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS) in tissue of brain
The extent of lipid peroxidation in terms of malondialdehyde (MDA) formation was measured. Briefly homogenate brain sample containing 1 ml was mixed with 1 ml TCA (20%), 2 ml TBA (0.67%) and heated for 1 h in boiling water bath. After cooling, mixture centrifuged and absorbance of the supernatant measured at 532 nm against suitable blank. The amount of TBARS was calculated by using a molar extinction coefficient of ε=1.56×105/M/cm and expressed as mol/mg protein [31].
Catalase (CAT) in tissue of brain
Catalase activity was assayed according to the method used by L.Goth. 500 µl of 0.05 mmol Tris-HCl, 1 ml H2O2 and 50 µl of sample were mixed and incubated for 10 min, and then Reaction was stopped by adding 500 µl Ammonium molybdate solution 4%. The absorbance was read at 410 nm. The result was expressed as U/mg protein [32].
Superoxide dismutase (SOD) in tissue of brain
The SOD activity was determined using a xanthine/xanthine oxidase system for production of superoxide radical and subsequent measurement of cytochrome c as a scavenger of the radicals. Optical density was evaluated using a spectrometer (UV-1601, Shimadzu) at 550 nm. One unit of enzyme activity was defined as the quantity of SOD required to inhibit the reduction rate of cytochrome c by 50% [33]. SOD activity is presented as units per milligram of protein (U/mg protein).
Estimation of brain total protein
Total brain protein was estimated by the Lowry et al method using bovine serum albumin (BSA) (1 mg/ml) as standard. The absorption was read spectrophotometrically at 750 nm [34].
Nitrite estimation
Nitrite was estimated using Greiss reagent, which served as an indicator of nitric oxide production. An amount of 100 µL Greiss reagent (1:1 solution of 1% sulphanilamide in 5% phosphoric acid and 0.1% napthaylamine diamine dihydrochloric acid in water) was added to 100 µL of supernatant and absorbance was measured at 542 nm [35]. Nitrite concentration was calculated using a standard curve for sodium nitrite. Nitrite levels were expressed as of the control percentage.
Estimation of brain acetyl cholinesterase (AChE) activity
The whole brain AChE activity was measured by the Ellman method [36] and Voss and Sachsse method [37]. Change in the absorbance per min of the sample was read spectrophotometrically at 420 nm.
Blood glucose and serum insulin estimation
Twenty four hours after the last experimental day, the overnight fasting animals were anesthetized by ether. Fasting blood glucose levels (FBG) were measured using a glucometer (Elegance CT-X10, Convergent Technologies, Germany) by cutting the tail tip of mice. Furthermore, blood samples were directly collected by cardiac puncture and centrifuged at 3500 rpm for 20 min. Insulin level was measured by ELISA assay kits (Monobind, USA) (The sensitivity of hormone detection per assay tube was 0.182 µIU/ml).
Statistical analysis
Data were expressed as means±SE for three different experiments. All the results were analyzed using Graph Pad Prism (version 5.04). Statistical significance was determined using the oneway analysis of variance (ANOVA) with the Tukey's post hoc test. Statistical significance was set at p<0.05.
RESULTS
Effects of diabetes and cinnamic acid on state-dependent memory
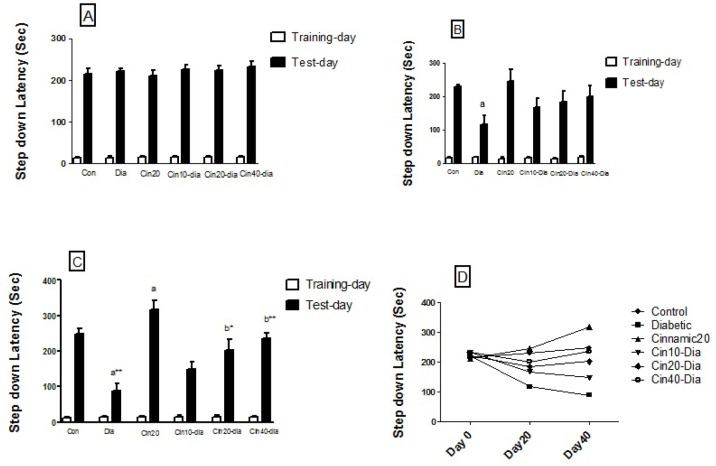
Step-down passive avoidance task assesses the ability of the animals to retain and recall information. The mean initial latency did not significantly differ among the various groups, whereas the retention latency significantly differed between the groups. Fig. 1A-D represents comparisons of step-down latency in different groups before treatment and after 20 and 40 days. The results revealed that the step-down latency significantly decreased in diabetic mice as compared to the controls after 20 (p<0.05) and 40 (p<0.01) days. Treatment of the diabetic mice with cinnamic acid caused significant (p<0.01, p<0.001) increase in the step-down latency compared to the diabetic group after 40 days. Cinnamic acid alone did not cause any significant change in the retention latency in the passive avoidance test before 20 days; however, the retention latency increased compared to control group (p<0.05) after 40 days (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1. Effects of diabetes and cinnamic acid on memory retention in mice.
(A) Step down latency before treat. (B) Step down latency after 20 days. (C) Step down latency after 40 days. Each value was presented as means±SEM (n=8). Letter a: Significantly different from control group (p<0.05), Letter b: Significantly different from diabetic group (p<0.05), a* and b*: p< 0.01, a** and b**: p< 0.001. p values were from one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey's test for multiple comparisons.
Effect of diabetes and cinnamic acid on spatial navigation memory
Fig. 2 represents the number of arm entries, as the locomotor activity index in cross-arm maze significantly (p<0.05) decreased in diabetic mice as compared to the controls. Treatment of diabetic mice with cinnamic acid significantly (p<0.05) increased the locomotor activity in dose-dependent manner compared to the diabetic group. No significant increase was observed in the number of arm entries in mice injected with cinnamic acid alone when compared to the control animals.
Fig. 2. Effect of diabetes and cinnamic acid on number of entries in the cross-arm maze in mice.
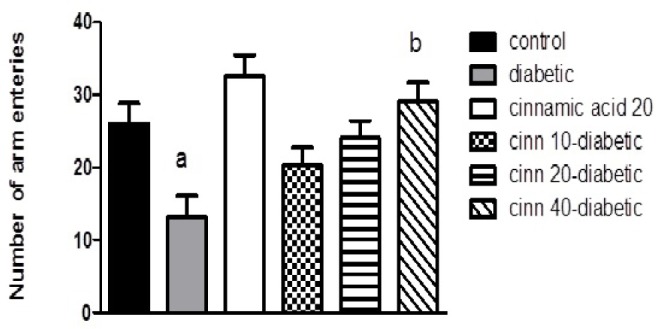
Letter a: indicates significant difference compared to control group (p<0.05). Letter b: indicates significant difference compared to diabetic group (p<0.05). p values were from oneway ANOVA, followed by Tukey's test for multiple comparisons.
Fig. 3 reveals the percent alternation in the cross-arm maze. Diabetes significantly decreased the actual alternation score, thereby decreasing the alternation percentage and the spatial navigation memory index in the cross-arm maze compared to the control group (p<0.01), whereas administration of cinnamic acid significantly (p<0.01) and in dose-dependent manner prevented the spatial memory debilitation in diabetic mice. Moreover, cinnamic acid injection significantly (p<0.05) increased the alternation percentage in intact animals compared to the control animals.
Fig. 3. Effect of diabetes and cinnamic acid on alternation percent in the cross-arm maze in mice.
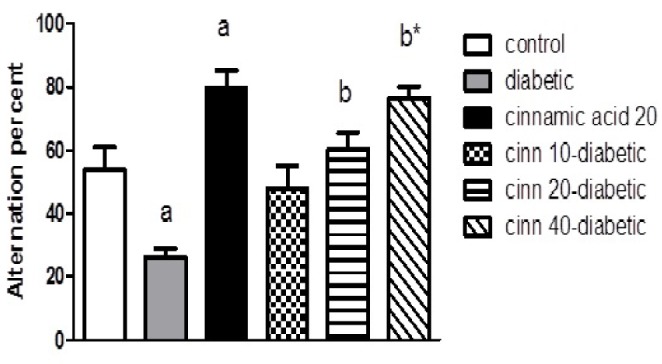
Letter a: indicates significant difference compared to control group (p <0.05). Letter b: indicates significant difference compared to diabetic group (p <0.05). a* and b*: p<0.01. p values were from one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey's test for multiple comparisons.
Effect of diabetes and cinnamic acid on spatial memory in morris water maze test
Our results on spatial memory abilities in mice revealed that, compared to the control mice, escape latency (time taken to reach the hidden platform) decreased from 130 to 80 s in cinnamic acid-treated mice, whereas in mice injected with STZ, the escape latency increased from 180 to 250 s throughout the total tenure of the test. One interesting observation on group IV mice treated with STZ and concurrently administered with cinnamic acid was that, even though the escape latency was more (170 s) than that of the control mice at the initial stages, after 40 days, it almost reached the normal levels (130 s) (Fig. 4).
Fig. 4. Effect of diabetes and cinnamic acid on spatial memory in morris water maze test.

p values were from one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey's test for multiple comparisons.
Effect of diabetics and cinnamic acid on oxidative stress in STZ treated mice
Effects on ROS formation in the brain tissue
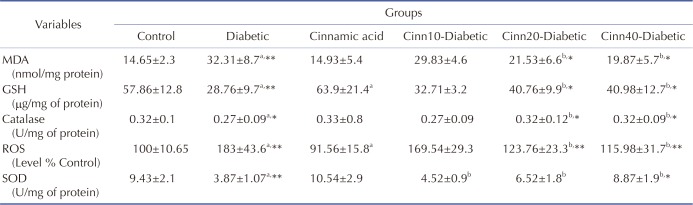
Increased ROS formation is expressed as DCF fluorescence intensity unit. As mentioned in Table 1, ROS level was significantly (p<0.001) elevated in the brain of diabetic animals as compared to the control. Cinnamic acid administration significantly (p<0.001) inhibited the ROS production in diabetic mice. Moreover, exposure to cinnamic acid resulted in significantly (p<0.05) lower ROS formation in nondiabetic mice when compared with the control (Table 1).
Table 1. Effect of diabetics and cinnamic acid on oxidative stress in STZ treated mice.
Data are Mean±SD; n=8. MDA, Malondialdehyde; ROS, reactive oxygen species; GSH, glutathione; SOD, superoxide dismutase. aSignificantly different from control group (p<0.05), bSignificantly different from diabetic group (p<0.05), a* and b*: p<0.01, a** and b**: p<0.001, p values were from one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey's test for multiple comparisons.
Effect on glutathione (GSH) level in the brain tissue
Glutathione assessment results reported a significant decrease in the diabetic group compared to the control mice (p<0.001). Cinnamic acid administration significantly (p<0.01) prevented this decrease in GSH level in diabetic mice. Moreover, exposure to cinnamic acid resulted in significantly (p<0.05) greater GSH level in nondiabetic mice when compared with the control mice (p<0.05) (Table 1).
Effects on thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS) in the brain tissue
The results of lipid peroxidation revealed that STZ treated group reported significant increase in the MDA level (p<0.001) in comparison to the control group. Cinnamic acid administration significantly (p<0.01) inhibited the MDA level in diabetic mice. No significant difference was observed between cinnamic acid-treated mice and control group (Table 1).
Effects on catalase enzyme level in the brain tissue
Assessment of brain homogenates indicated a significant (p<0.01) decrease in the CAT activities in diabetic group than the control animals, while cinnamic acid administration significantly (p<0.01) ameliorated these indices in diabetic mice. No significant difference was observed between the cinnamic acid-treated mice and the control group (Table 1).
Effect on SOD activity in the brain tissue
As shown in Table 1, the SOD production was significantly reduced in brains of the STZ treated mice (p<0.001). Administration of cinnamic acid significantly increased the SOD activity in the brain, when compared with the STZ-treated group (p<0.01).
Effect of cinnamic acid on STZ induced nitrosative stress
Nitrite levels were significantly (p<0.05) elevated in the brain of STZ treated animals as compared to the control group. Cinnamic acid administration significantly (p<0.05) inhibited the nitrite levels in STZ treated mice (Fig. 5).
Fig. 5. Effect of diabetes and cinnamic acid on nitrite level.
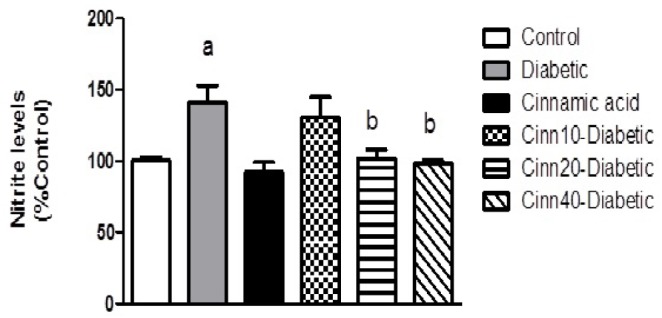
Letter a: indicates significant difference compared to control group (p<0.05). Letter b: indicates significant difference compared to diabetic group (p<0.05). a*: p<0.01. p values were from one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey's test for multiple comparisons.
Effect of cinnamic acid on STZ induced changes in acetylcholinesterase activity
Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) activity significantly (p<0.01) increased in STZ treated mice when compared with the control group. Cinnamic acid significantly (p<0.05) inhibited AChE activity in STZ treated mice (Fig. 6).
Fig. 6. Effect of diabetes and cinnamic acid on AChE activity.
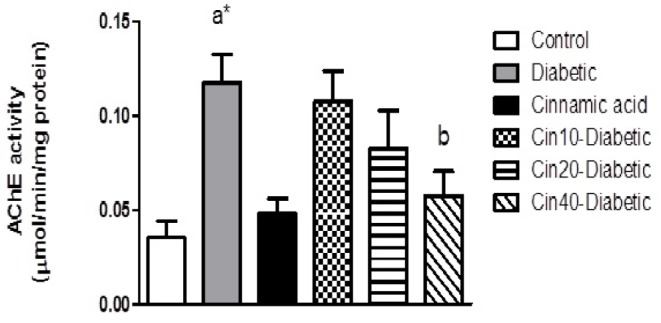
Data values are expressed as mean AChE activity (µmol/min/mg protein)±SEM. Letter a: indicates significant difference compared to control group (p<0.05). Letter b: indicates significant difference compared to diabetic group (p<0.05). a**: p<0.001. p values were from one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey's test for multiple comparisons.
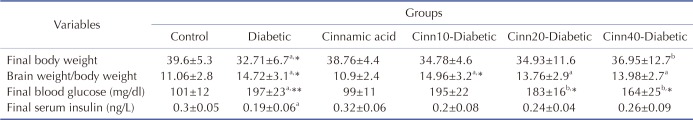
Effect of f diabetics and cinnamic acid on body weight, brain weight to body weight ratio, final blood glucose and serum insulin
As anticipated, diabetic mice weighed less than the control group (p<0.01). Furthermore, administration of cinnamic acid (40 mg/kg) in diabetic mice revealed a significant increase in weight than the diabetic control mice (p<0.05) (Table 2).
Table 2. Effect of diabetes and cinnamic acid on body weight, brain weight to body weight ratio, final blood glucose and serum insulin.
Data are Mean±SD; n=8. aSignificantly different from control group (p<0.05), bSignificantly different from diabetic group (p<0.05), a* and b*: p<0.01, a** and b**: p<0.001, p values were from one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey's test for multiple comparisons.
The average total brain to body weight ratio after 40 days training was significantly greater in diabetic mice than the control mice (p<0.01); however, no significant difference was observed between the cinnamic acid-treated diabetic mice and the diabetic control group (Table 2).
The results revealed that STZ treated group reported a significant increase in the FBG level (p<0.001) in comparison to the control group. Cinnamic acid administration significantly (p<0.01) inhibited the FBG level in diabetic mice. No significant difference was observed between the cinnamic acid-treated mice and the control group (Table 2).
As shown in Table 2, the insulin level was significantly reduced in the serum of the STZ treated mice (p<0.05). No significant difference was observed in the serum insulin level (mg/dl) among the STZ and cinnamic acid-treated STZ groups (10, 20 and 40 mg/kg).
DISCUSSION
The present study examined the effects of cinnamic acid treatment on memory impairment, oxidative stress, and cholinergic dysfunction in STZ-induced model of diabetes in mice. Previous studies have suggested that diabetes mellitus is connected with neurological difficulties in the central nervous system [38,39,40] such as weak learning and memory [41,42,43]. Based on the concentration, STZ can contribute to type 1 and type 2 diabetes. In this study, not only does the diabetes type matter but also a model of diabetes that can cause defects in memory is equally important. Previous study suggested that the STZ mice model is an applicable animal model used for studying the memory impairment [44,45,46,47]. STZ is a glucosamine-nitrosourea compound, which was known as an antibiotic. It is toxic to the beta cells of pancreas and was generally used to induce experimental diabetes in animals. STZ administration through the intracebroventricular or intraperitoneal route produces reduced cognition and increased cerebral aggregated Aβ fragments, total tau protein, and Aβ deposits [48]. Administering STZ in a rodent's brain is known to cause neuroinflammation, oxidative stress, and biochemical alterations, which is considered to be a valid experimental model for the early pathophysiological changes in the neurodegenerative diseases [49]. Furthermore, the STZ treated animals develop insulin resistant brains, which are associated with memory impairment, progressive cholinergic deficits, glucose hypometabolism, oxidative stress, and neurodegeneration that share many common features with dementia observed in humans [50]. Thus, from the aforementioned reports, it is inferred that STZ produces most prevalent type of memory impairment. In the present study, administration of STZ in mice showed a persistent memory deficit in passive avoidance test as evidenced by significantly reduced in step-down latencies and in Morris water maze test as proved by increased in escape latency.
Cognitive and memory deficits in diabetes mellitus can result from hyperglycemia [51,52]. Although the pathogenesis of these deficits is multifactorial, sufficient data is available for excess production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) [37,51]. STZ caused oxidative stress by significantly increasing the MDA level and decreasing the GSH level. Furthermore, the nitrite levels in brain of STZ treated mice significantly increased. This increase in the oxidative stress may be due to hyperglycemic disorder prevalent in brain after administration of STZ. The brain slices of STZ rats are known to display reduced glucose ingestion as compared to the control rats, leading to hyperglycemic condition in the brain [52]. Plaschke et al. [53] indicated increased extracellular concentration of glucose in the brain of STZ injected rats. This may lead to improved glucose auto-oxidation, resulting in production of advanced glycation end-products. In addition, improved free radicals, due to greater oxidative stress, increased the nitrite level. Hyperglycemia induces upregulation of iNOS and parallel increase of superoxide formation leads to the production of peroxynitrite, a potent pro-oxidant, which exaggerates the oxidative stress [54,55,56,57,58,59].
In the present study, administration of STZ significantly increased the malondialdehyde levels, an index of lipid peroxidation, in the brain. One reason for the raised lipid peroxidation in STZ-induced diabetes is the decrease of antioxidant enzymes such as glutathione peroxidase and catalase activities. In this experiment, we found that untreated diabetes initiated reduced function of glutathione peroxidase and catalase in the brain. Our findings are consistent with the previous reports, which suggest that the antioxidant enzyme functions decreased in the brain during chronic diabetic neuropathy [39,60,61]
In diabetic animal models, such as those induced by STZ, reduced synaptic plasticity and impaired performances on behavioral learning tasks, are common [61,62,63,64,65], and a reduction in diabetic animals performance has been shown in complex task, such as Morris water maze and T-maze [66,67,68].
In the present study, treatment by cinnamic acid, in STZ injected mice, improved spatial memory and condition avoidance memory. In passive avoidance test, administration of cinnamic acid for 40 days after STZ-induced memory deficit, reported memory improvement; however, the vehicle treated group exhibited memory impairment even after 20 days. Moreover, in this study we have examined the effects of cinnamic acid on spatial navigation memory in diabetic mice by cross-arm maze. We reported that diabetes could significantly decrease the actual alternation percent as a spatial navigation memory index; however, oxidative stress may contribute to spatial navigation deficit during hyperglycemia. Therefore, antioxidants could be preferred to prevent the memory damage associated with diabetes. Herein, we found that cinnamic acid as an antioxidant could increase the alternation percent during the cross-maze test. We observed that the number of arm entries, as a locomotors activity index, in cross-arm maze, decreased in diabetic mice. Treatment with cinnamic acid increased the locomotor activity and the alternation percent in diabetic mice; whereas, cinnamic acid increased the alternation percent but did not alter the locomotor activity in nondiabetic mice. This contradiction indicates that increasing effect of cinnamic acid on actual alternation score could not be a result from the locomotors activity in crescent in diabetics. Furthermore, the results of the Morris water maze test also confirm the effect of cinnamic acid on enhancing the spatial memory in diabetic and nondiabetic mice.
This memory enhancement by cinnamic acid has been attributed to its act as an effective antioxidant that results from its direct free radicals scavenging activity and inducing antioxidant enzymes [69]. In our study, the treatment of diabetic animals with cinnamic acid significantly decreased the lipid peroxidation in the brain. Furthermore, we demonstrated an increase in the glutathione peroxidase, SOD, and catalase activities in the brain by administering the cinnamic acid; sufficient evidence identifies cinnamic acid as a potent antioxidant [18,70]. Our results also indicated a decrease in ROS and nitrite level in cinnamic acidtreated mice. The reduction in nitrite level by cinnamic acid may be due to its effect on the inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) expression and downregulation of its expression in the brain.
Beside oxidative stress, there is decreased activity of glycolytic enzymes in the STZ model of memory deficit mice resulting in decreased acetylcholine level [53,71,72], which is associated with cognition. Acetylcholine is metabolized by the enzyme acetyl cholinesterase (AChE); hence, AChE inhibitors are the most effective pharmacological resources for the treatment of cognition impairment [73]. In the present study, we reported increased AChE activity in the brain of STZ treated mice. This result is in accordance with the previous studies displaying rise in the AChE expression [74] and activity after STZ injection [47,75,76]. Additionally, it is reported that the activity of AChE increased in the cerebral cortex of STZ-induced diabetic rats [37,77]. Therefore, the modifications in AChE action may be a result of hyperglycemia like situation in the brain produced by STZ administration [78]. The restoration of AChE activity by cinnamic acid may be due to the enhancement of disturbed glucose metabolism and insulin signaling induced by STZ [78].
CONCLUSION
In conclusion, the present study reported that cinnamic acid treatment in diabetic mice revealed memory enhancement, which may be a result of its effective antioxidant activity. Hence, the use of cinnamic acid as a nutritional supplement should be encouraged to prevent diabetes and age associated memory disorders.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This study was labeled Student Research Project No. 95s104, and was supported financially by the Student Research Committee of Ahvaz Jundishapur Medical Sciences University, Ahvaz, Iran.
Footnotes
Author contributions: H.A.A.: study design, A.S.: completion of experiments and data analysis, A.A.: observation and design study.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST: The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- 1.Kumar R, Jaggi AS, Singh N. Effects of erythropoietin on memory deficits and brain oxidative stress in the mouse models of dementia. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2010;14:345–352. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2010.14.5.345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Yki-Järvinen H. Thiazolidinediones. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:1106–1118. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra041001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Liu X, Liu M, Mo Y, Peng H, Gong J, Li Z, Chen J, Xie J. Naringin ameliorates cognitive deficits in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2016;19:417–422. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Moghadamnia AA, Hakiminia S, Baradaran M, Kazemi S, Ashrafpour M. Vitamin D improves learning and memory impairment in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Arch Iran Med. 2015;18:362–366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Hasanein P, Shahidi S. Effects of combined treatment with vitamins C and E on passive avoidance learning and memory in diabetic rats. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2010;93:472–478. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2010.01.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Modi KK, Roy A, Brahmachari S, Rangasamy SB, Pahan K. Cinnamon and its metabolite sodium benzoate attenuate the activation of p21rac and protect memory and learning in an animal model of alzheimer's disease. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0130398. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0130398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Good M. Spatial memory and hippocampal function: where are we now. Psicológica. 2002;23:109–138. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Wattanathorn J, Jittiwat J, Tongun T, Muchimapura S, Ingkaninan K. Zingiber officinale mitigates brain damage and improves memory impairment in focal cerebral ischemic rat. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2011;2011:429505. doi: 10.1155/2011/429505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Koo BS, Lee WC, Chang YC, Kim CH. Protective effects of alpinae oxyphyllae fructus (Alpinia oxyphylla MIQ) water-extracts on neurons from ischemic damage and neuronal cell toxicity. Phytother Res. 2004;18:142–148. doi: 10.1002/ptr.1382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Suk K, Kim SY, Leem K, Kim YO, Park SY, Hur J, Baek J, Lee KJ, Zheng HZ, Kim H. Neuroprotection by methanol extract of Uncaria rhynchophylla against global cerebral ischemia in rats. Life Sci. 2002;70:2467–2480. doi: 10.1016/s0024-3205(02)01534-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Calapai G, Crupi A, Firenzuoli F, Marciano MC, Squadrito F, Inferrera G, Parisi A, Rizzo A, Crisafulli C, Fiore A, Caputi AP. Neuroprotective effects of Ginkgo biloba extract in brain ischemia are mediated by inhibition of nitric oxide synthesis. Life Sci. 2000;67:2673–2683. doi: 10.1016/s0024-3205(00)00858-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Hafizur RM, Hameed A, Shukrana M, Raza SA, Chishti S, Kabir N, Siddiqui RA. Cinnamic acid exerts anti-diabetic activity by improving glucose tolerance in vivo and by stimulating insulin secretion in vitro. Phytomedicine. 2015;22:297–300. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2015.01.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Anderson RA, Broadhurst CL, Polansky MM, Schmidt WF, Khan A, Flanagan VP, Schoene NW, Graves DJ. Isolation and characterization of polyphenol type-A polymers from cinnamon with insulinlike biological activity. J Agric Food Chem. 2004;52:65–70. doi: 10.1021/jf034916b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Jiao L, Zhang X, Huang L, Gong H, Cheng B, Sun Y, Li Y, Liu Q, Zheng L, Huang K. Proanthocyanidins are the major anti-diabetic components of cinnamon water extract. Food Chem Toxicol. 2013;56:398–405. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2013.02.049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Chen Y, Ma Y, Ma W. Pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of cinnamic acid after oral administration of Ramulus Cinnamomi in rats. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2009;34:51–56. doi: 10.1007/BF03191384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Huang DW, Shen SC. Caffeic acid and cinnamic acid ameliorate glucose metabolism via modulating glycogenesis and gluconeogenesis in insulin-resistant mouse hepatocytes. J Funct Food. 2012;4:358–366. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Lee EJ, Kim SR, Kim J, Kim YC. Hepatoprotective phenylpropanoids from Scrophularia buergeriana roots against CCl(4)-induced toxicity: action mechanism and structure-activity relationship. Planta Med. 2002;68:407–411. doi: 10.1055/s-2002-32081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Natella F, Nardini M, Di Felice M, Scaccini C. Benzoic and cinnamic acid derivatives as antioxidants: structure-activity relation. J Agric Food Chem. 1999;47:1453–1459. doi: 10.1021/jf980737w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Adisakwattana S, Sompong W, Meeprom A, Ngamukote S, Yibchok-Anun S. Cinnamic acid and its derivatives inhibit fructose-mediated protein glycation. Int J Mol Sci. 2012;13:1778–1789. doi: 10.3390/ijms13021778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Yuan HD, Huang B, Chung SH. Protective effect of cinnamaldehyde on streptozotocin-induced damage in rat pancreatic β-cells. Food Sci Biotechnol. 2011;20:1271–1276. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Sharma P. Cinnamic acid derivatives: a new chapter of various pharmacological activities. J Chem Pharm Res. 2011;3:403–423. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Babaei-Balderlou F, Zare S. Melatonin improves spatial navigation memory in male diabetic rats. Vet Res Forum. 2012;3:187–192. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Nootarki ZS, Kesmati M, Borujeni MP. Effect of magnesium oxide nanoparticles on atropine-induced memory impairment in adult male mice. Avicenna J Neuro Psycho Physiol. 2015;2:e36924 [Google Scholar]
- 24.Jafari-Sabet M. Involvement of dorsal hippocampal muscarinic cholinergic receptors on muscimol state-dependent memory of passive avoidance in mice. Life Sci. 2011;88:1136–1141. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2011.04.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Guan H, Li S, Guo Y, Liu X, Yang Y, Guo J, Li S, Zhang C, Shang L, Piao F. Subchronic exposure to arsenic represses the TH/TRβ1-CaMK IV signaling pathway in mouse cerebellum. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17:E157. doi: 10.3390/ijms17020157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Ragozzino ME, Pal SN, Unick K, Stefani MR, Gold PE. Modulation of hippocampal acetylcholine release and spontaneous alternation scores by intrahippocampal glucose injections. J Neurosci. 1998;18:1595–1601. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-04-01595.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Morris R. Developments of a water-maze procedure for studying spatial learning in the rat. J Neurosci Methods. 1984;11:47–60. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(84)90007-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Morris RGM. Spatial location does not require the presence of local cues. Learn Motiv. 1981;12:239–260. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Chaudhuri AN, Basu S, Chattopadhyay S, Das Gupta S. Effect of high arsenic content in drinking water on rat brain. Indian J Biochem Biophys. 1999;36:51–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Jain A, Yadav A, Bozhkov AI, Padalko VI, Flora SJ. Therapeutic efficacy of silymarin and naringenin in reducing arsenic-induced hepatic damage in young rats. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2011;74:607–614. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2010.08.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Sinha M, Manna P, Sil PC. Arjunolic acid attenuates arsenicinduced nephrotoxicity. Pathophysiology. 2008;15:147–156. doi: 10.1016/j.pathophys.2008.03.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Sokolovic D, Djindjic B, Nikolic J, Bjelakovic G, Pavlovic D, Kocic G, Krstic D, Cvetkovic T, Pavlovic V. Melatonin reduces oxidative stress induced by chronic exposure of microwave radiation from mobile phones in rat brain. J Radiat Res. 2008;49:579–586. doi: 10.1269/jrr.07077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Kakkar P, Das B, Viswanathan PN. A modified spectrophotometric assay of superoxide dismutase. Indian J Biochem Biophys. 1984;21:130–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951;193:265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Green LC, Wagner DA, Glogowski J, Skipper PL, Wishnok JS, Tannenbaum SR. Analysis of nitrate, nitrite, and [15N]nitrate in biological fluids. Anal Biochem. 1982;126:131–138. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90118-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Ellman GL, Courtney KD, Andres V, Jr, Featherstone RM. A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol. 1961;7:88–95. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(61)90145-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Sánchez-Chávez G, Salceda R. Effect of streptozotocin-induced diabetes on activities of cholinesterases in the rat retina. IUBMB Life. 2000;49:283–287. doi: 10.1080/15216540050033140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Feldman EL, Stevens MJ, Greene DA. Pathogenesis of diabetic neuropathy. Clin Neurosci. 1997;4:365–370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Baynes JW, Thorpe SR. Role of oxidative stress in diabetic complications: a new perspective on an old paradigm. Diabetes. 1999;48:1–9. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.48.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Babaei-Balderlou F, Zare S, Heidari R, Farrokhi F. Effects of melatonin and vitamin E on peripheral neuropathic pain in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2010;13:1–8. [Google Scholar]
- 41.Tuzcu M, Baydas G. Effect of melatonin and vitamin E on diabetesinduced learning and memory impairment in rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 2006;537:106–110. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2006.03.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Nedzvetsky VS, Nerush PA, Kirichenko SV. Effect of melatonin on cognitive ability of rats and expression of NCAM in the brain structures in streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Neurophysiol. 2003;35:422–427. [Google Scholar]
- 43.Parihar MS, Chaudhary M, Shetty R, Hemnani T. Susceptibility of hippocampus and cerebral cortex to oxidative damage in streptozotocin treated mice: prevention by extracts of Withania somnifera and Aloe vera. J Clin Neurosci. 2004;11:397–402. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2003.09.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Nitsch R, Hoyer S. Local action of the diabetogenic drug, streptozotocin, on glucose and energy metabolism in rat brain cortex. Neurosci Lett. 1991;128:199–202. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(91)90260-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Lannert H, Hoyer S. Intracerebroventricular administration of streptozotocin causes long-term diminutions in learning and memory abilities and in cerebral energy metabolism in adult rats. Behav Neurosci. 1998;112:1199–1208. doi: 10.1037//0735-7044.112.5.1199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Sharma M, Gupta YK. Intracerebroventricular injection of streptozotocin in rats produces both oxidative stress in the brain and cognitive impairment. Life Sci. 2001;68:1021–1029. doi: 10.1016/s0024-3205(00)01005-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Agrawal R, Tyagi E, Shukla R, Nath C. A study of brain insulin receptors, AChE activity and oxidative stress in rat model of ICV STZ induced dementia. Neuropharmacology. 2009;56:779–787. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2009.01.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Chen S, An FM, Yin L, Liu AR, Yin DK, Yao WB, Gao XD. Glucagon-like peptide-1 protects hippocampal neurons against advanced glycation end product-induced tau hyperphosphorylation. Neuroscience. 2014;256:137–146. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.10.038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Gao C, Liu Y, Jiang Y, Ding J, Li L. Geniposide ameliorates learning memory deficits, reduces tau phosphorylation and decreases apoptosis via GSK3β pathway in streptozotocin-induced alzheimer rat model. Brain Pathol. 2014;24:261–269. doi: 10.1111/bpa.12116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Kamat PK, Rai S, Swarnkar S, Shukla R, Nath C. Mechanism of synapse redox stress in Okadaic acid (ICV) induced memory impairment: role of NMDA receptor. Neurochem Int. 2014;76:32–41. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2014.06.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Wolff SP, Dean RT. Glucose autoxidation and protein modification. The potential role of ‘autoxidative glycosylation’ in diabetes. Biochem J. 1987;245:243–250. doi: 10.1042/bj2450243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Pathan AR, Viswanad B, Sonkusare SK, Ramarao P. Chronic administration of pioglitazone attenuates intracerebroventricular streptozotocin induced-memory impairment in rats. Life Sci. 2006;79:2209–2216. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2006.07.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Plaschke K, Hoyer S. Action of the diabetogenic drug streptozotocin on glycolytic and glycogenolytic metabolism in adult rat brain cortex and hippocampus. Int J Dev Neurosci. 1993;11:477–483. doi: 10.1016/0736-5748(93)90021-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Cosentino F, Hishikawa K, Katusic ZS, Lüscher TF. High glucose increases nitric oxide synthase expression and superoxide anion generation in human aortic endothelial cells. Circulation. 1997;96:25–28. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.96.1.25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Spitaler MM, Graier WF. Vascular targets of redox signalling in diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia. 2002;45:476–494. doi: 10.1007/s00125-002-0782-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Ceriello A, Quagliaro L, D'Amico M, Di Filippo C, Marfella R, Nappo F, Berrino L, Rossi F, Giugliano D. Acute hyperglycemia induces nitrotyrosine formation and apoptosis in perfused heart from rat. Diabetes. 2002;51:1076–1082. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.51.4.1076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Nash DT, Fillit H. Cardiovascular disease risk factors and cognitive impairment. Am J Cardiol. 2006;97:1262–1265. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2005.12.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Fisher ND, Sorond FA, Hollenberg NK. Cocoa flavanols and brain perfusion. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2006;47(Suppl 2):S210–S214. doi: 10.1097/00005344-200606001-00017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Ganguli M, Chandra V, Kamboh MI, Johnston JM, Dodge HH, Thelma BK, Juyal RC, Pandav R, Belle SH, DeKosky ST. Apolipoprotein E polymorphism and Alzheimer disease: the Indo-US Cross-National Dementia Study. Arch Neurol. 2000;57:824–830. doi: 10.1001/archneur.57.6.824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Anwar MM, Meki AR. Oxidative stress in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats: effects of garlic oil and melatonin. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol. 2003;135:539–547. doi: 10.1016/s1095-6433(03)00114-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Baydas G, Sonkaya E, Tuzcu M, Yasar A, Donder E. Novel role for gabapentin in neuroprotection of central nervous system in streptozotocine-induced diabetic rats. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2005;26:417–422. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-7254.2005.00072.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Alvarez EO, Beauquis J, Revsin Y, Banzan AM, Roig P, De Nicola AF, Saravia F. Cognitive dysfunction and hippocampal changes in experimental type 1 diabetes. Behav Brain Res. 2009;198:224–230. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2008.11.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Moazedi AA, Parsa M, Rashidi SH, Chinipardaz R. The effect of diatery butter on spatial learning using T-maze in mal rats. Physiol Pharmacol. 2002;5:179–188. [Google Scholar]
- 64.Lupien SB, Bluhm EJ, Ishii DN. Systemic insulin-like growth factor-I administration prevents cognitive impairment in diabetic rats, and brain IGF regulates learning/memory in normal adult rats. J Neurosci Res. 2003;74:512–523. doi: 10.1002/jnr.10791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Magariños AM, McEwen BS. Experimental diabetes in rats causes hippocampal dendritic and synaptic reorganization and increased glucocorticoid reactivity to stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000;97:11056–11061. doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.20.11056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Flood JF, Mooradian AD, Morley JE. Characteristics of learning and memory in streptozocin-induced diabetic mice. Diabetes. 1990;39:1391–1398. doi: 10.2337/diab.39.11.1391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Grzeda E, Wiśniewska RJ, Wiśniewski K. Effect of an NMDA receptor agonist on T-maze and passive avoidance test in 12-week streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Pharmacol Rep. 2007;59:656–663. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Zare K, Tabatabaei SR, Shahriari A, Jafari RA. The effect of butter oil on avoidance memory in normal and diabetic rats. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2012;15:983–989. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Bogdashev NN, Tukhovskaya NA, Pogrebnyak AV. Physicochemical characterization of cinnamic acid derivatives. Part 1. Relationship between antioxidant activity and physicochemical properties. Pharm Chem J. 1998;32:86–88. [Google Scholar]
- 70.Chen JH, Ho CT. Antioxidant activities of caffeic acid and its related hydroxycinnamic acid compounds. J Agric Food Chem. 1997;45:2374–2378. [Google Scholar]
- 71.Welsh B, Wecker L. Effects of streptozotocin-induced diabetes on acetylcholine metabolism in rat brain. Neurochemical Research. 1991;16:453–460. doi: 10.1007/BF00965566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Weinstock M, Kirschbaum-Slager N, Lazarovici P, Bejar C, Youdim MB, Shoham S. Neuroprotective effects of novel cholinesterase inhibitors derived from rasagiline as potential anti-Alzheimer drugs. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2001;939:148–161. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2001.tb03622.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Racchi M, Mazzucchelli M, Porrello E, Lanni C, Govoni S. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors: novel activities of old molecules. Pharmacol Res. 2004;50:441–451. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2003.12.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Lester-Coll N, Rivera EJ, Soscia SJ, Doiron K, Wands JR, de la Monte SM. Intracerebral streptozotocin model of type 3 diabetes: relevance to sporadic Alzheimer's disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 2006;9:13–33. doi: 10.3233/jad-2006-9102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Saxena G, Singh SP, Pal R, Singh S, Pratap R, Nath C. Gugulipid, an extract of Commiphora whighitii with lipid-lowering properties, has protective effects against streptozotocin-induced memory deficits in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2007;86:797–805. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2007.03.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Tota S, Kamat PK, Awasthi H, Singh N, Raghubir R, Nath C, Hanif K. Candesartan improves memory decline in mice: involvement of AT1 receptors in memory deficit induced by intracerebral streptozotocin. Behav Brain Res. 2009;199:235–240. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2008.11.044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Kuhad A, Chopra K. Curcumin attenuates diabetic encephalopathy in rats: behavioral and biochemical evidences. Eur J Pharmacol. 2007;576:34–42. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2007.08.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Isik AT, Celik T, Ulusoy G, Ongoru O, Elibol B, Doruk H, Bozoglu E, Kayir H, Mas MR, Akman S. Curcumin ameliorates impaired insulin/ IGF signalling and memory deficit in a streptozotocin-treated rat model. Age (Dordr) 2009;31:39–49. doi: 10.1007/s11357-008-9078-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]