Dear Editor in Chief
Micronuclei (MN) are fragments of chromosomes that fail to encompass into the nucleus and remains in the cytoplasm in cell division course (1). Monitoring MN in oral exfoliated epithelial cells for detecting exposed individuals to genotoxic agents was proposed by Stich et al. in 1982 for the first time (2).
The genotoxic agents of tobacco, waterpipe and even environmental contaminants are recognized as initiator factors in producing the aberrations that results in MN production (3-5). Assessing the frequency of MN in oral exfoliated cells is a non-invasive reliable indicator of genotoxic damage in human (6).
Among different staining methods to demonstrate the nuclear abnormalities, Feulgen is one of the most reliable method. The Feulgen staining is a specific and sensitive method for evaluating DNA damages. It has been shown that using non-DNA specific stains to monitor nuclear anomalies lead to false-positive or false-negative results (7).
In a routine Feulgen staining technique, slides are immersed in 5 mol/L HCl for 15 minutes, rinsed with distilled water for 3 minutes, stained with Schiff's reagent for 90 minutes, washed for 10 minutes and finally stained with 1% light green for 15 minutes (7-8). Using the Feulgen staining, nucleus and micronuclei appear magenta and cytoplasm seems green.
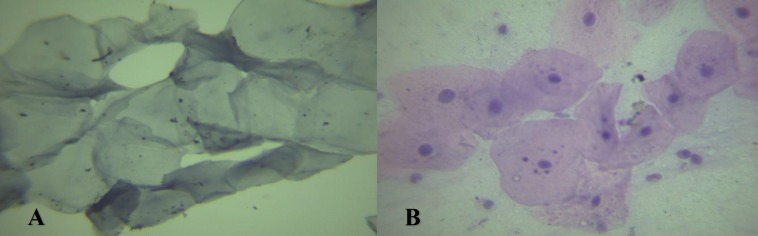
From self-experience, immersing the stained slides in hematoxylin for 3-5 minutes and eosin for few seconds in the final step after staining the slides with light green, provides a greater ground contrast and very better visualizing of nucleus (Fig1).
Fig 1.
Comparison of Feulgen Stained Slides (A) With Hematoxylin-eosin staining after Routine Feulgen Staining Technique (B
Using this method, the shape and outline of nucleus appear very clear and precise. Nuclear changes as karyorrhexis, karyolysis and pyknosis appear very characteristic and distinctive. By this method, a clear distinction can be made between micronuclei and other structures suggestive of a micronucleus. This experience of using hematoxylin-eosin stain in routine Feulgen staining protocol can be a modified method for Feulgen staining technique for better visualization of nucleus.
References
- 1.Cerqueira EM, Santoro CL, Donozo NF, Freitas BA, Pereira CA, Bevilacqua RG, etal Genetic damage in exfoliated cells of the uterine cervix Association and interaction between cigarette smoking and progression to malignant transformation? Acta Cytol . 1998;42(3):639–649. doi: 10.1159/000331820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Stich HF, Curtis JR, Parida BB. Application of the micronucleus test to exfoliated cells of high cancer risk groups: tobacco chewers. Int J Cancer. 1982;30(5):553–559. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910300504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Naderi NJ, Farhadi S, Sarshar S. Micronucleus assay of buccal mucosa cells in smokers with the history of smoking less and more than 10 years. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2012;55(4):433–438. doi: 10.4103/0377-4929.107774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.El-Setouhy M, Loffredo CA, Radwan G, Abdel Rahman R, Mahfouz E, Israel E, etal Genotoxic effects of waterpipe smoking on the buccal mucosa cells. Mutat Res. 2008;655(1-2):36–40. doi: 10.1016/j.mrgentox.2008.06.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Salama SA, Serrana M, Au WW. Biomonitoring using accessible human cells for exposure and health risk assessment. Mutat Res. 1999;436(1):99–112. doi: 10.1016/s1383-5742(98)00021-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Mr P, Guruprasad Y, Jose M, Saxena K, Deepa K, Prabhu V. Comparative study of genotoxicity in different tobacco related habits using micronucleus assay in exfoliated buccal epithelial cells. J Clin Diagn Res. 2014;8(5):ZC21–24. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2014/8733.4357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Nersesyan A, Kundi M, Atefie K, Schulte-Hermann R, Knasmüller S. Effect of staining procedures on the results of micronucleus assays with exfoliated oral mucosa cells. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2006;15:1835–1840. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-06-0248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Thomas P, Hecker J, Faunt J, Fenech M. Buccal micronucleus cytome biomarkers may be associated with Alzheimer's disease. Mutagenesis . 2007;22(6):371–379. doi: 10.1093/mutage/gem029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]