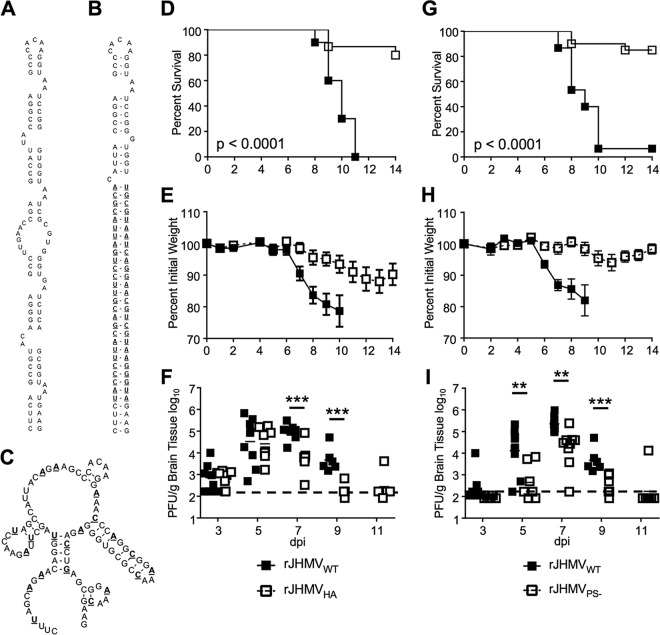
FIG 1 .
rJHMV packaging mutants are attenuated in vivo. (A) The RNA secondary structure of the MHV packaging signal (7). (B) Mfold predicted RNA secondary structure of rA59Nsp15-HA. HA epitope coding sequence and complement are boldfaced and underlined. (C) Mfold predicted RNA secondary structure of MHV PS−. Synonymous mutations are boldfaced and underlined. (D to F) Five- to 8-week-old male B6 mice were infected with 3 × 104 PFU of rJHMVNsp15-HA or rJHMVWT by intranasal inoculation. Infected mice were monitored for survival (D) and weight loss (E) for 14 dpi (rJHMVWT, n = 10; rJHMVNsp15-HA, n = 15). (F) Infected brains were harvested from mice at the indicated day postinfection. Brains were homogenized in PBS, and titers of infectious virus were determined by plaque assay on HeLa-MHVR cells. (G to I) Five- to 8-week-old male B6 mice were infected with 3 × 104 PFU of either rJHMVPS− or rJHMVWT by intranasal inoculation. Infected mice were monitored for survival (G) and weight loss (H) for 14 dpi (rJHMVWT, n = 15; rJHMVPS−, n = 20). (I) Infected brains were harvested from mice at the indicated day postinfection. Brains were homogenized in PBS, and titers of infectious virus were determined by plaque assay on HeLa-MHVR cells. The dashed line in panels F and I represents the limit of detection for the plaque assay. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001 by Mann-Whitney test.