ABSTRACT
Wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) collect wastewater from various sources for a multi-step treatment process. By mixing a large variety of bacteria and promoting their proximity, WWTPs constitute potential hotspots for the emergence of antibiotic resistant bacteria. Concerns have been expressed regarding the potential of WWTPs to spread antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) from environmental reservoirs to human pathogens. We utilized epicPCR (Emulsion, Paired Isolation and Concatenation PCR) to detect the bacterial hosts of ARGs in two WWTPs. We identified the host distribution of four resistance-associated genes (tetM, int1, qacEΔ1and blaOXA-58) in influent and effluent. The bacterial hosts of these resistance genes varied between the WWTP influent and effluent, with a generally decreasing host range in the effluent. Through 16S rRNA gene sequencing, it was determined that the resistance gene carrying bacteria include both abundant and rare taxa. Our results suggest that the studied WWTPs mostly succeed in decreasing the host range of the resistance genes during the treatment process. Still, there were instances where effluent contained resistance genes in bacterial groups not carrying these genes in the influent. By permitting exhaustive profiling of resistance-associated gene hosts in WWTP bacterial communities, the application of epicPCR provides a new level of precision to our resistance gene risk estimates.
Keywords: epicPCR, antibiotic resistance, wastewater treatment, horizontal gene transfer
epicPCR was utilized to link antibiotic resistance genes to bacterial host species in two wastewater purification plants.
INTRODUCTION
The emergence and spread of antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) among pathogenic and non-pathogenic bacteria has been a rising threat in recent decades. Among suspected sites for resistance transmission are wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) where wastewater from various sources, including municipalities, hospitals and industries, is mixed and treated in a multi-step purification process. As the microbes from different sources are in close contact during the purification process, WWTPs have been suggested to be hotspots for the emergence and dissemination of antibiotic-resistant bacteria (Rizzo et al. 2013a). The wastewater treatment process creates conditions that may favor horizontal gene transfer with high bacterial densities, stress caused by pollutants such as heavy metals and antibiotics, and biofilms formed during the purification process (Karkman et al. 2017).
Currently, studies evaluating the scope and frequency of antibiotic resistance in WWTPs are largely based on the use of quantitative PCR (qPCR) (Auerbach, Seyfried and McMahon 2007; Karkman et al. 2016; Karkman et al. 2017), metagenomics (Bengtsson-Palme et al. 2016) or cultivation. With qPCR, ARGs can be quantified in the studied environment, and recent advances in the use of high-throughput qPCR arrays (Stedtfeld et al. 2008) have enabled the detection and quantification of hundreds of genes simultaneously (Karkman et al. 2016; Muziasari et al. 2016; Muurinen et al. 2017). Nevertheless, the information about gene-carrying species is missing, and whether the ARG carriers are potential pathogens or harmless environmental bacteria remains unresolved. Cultivation-based approaches, although widely used in clinical microbiology, are limited as only a small fraction of microbes can be grown on laboratory media (Amann, Ludwig and Schleifer 1995). In recent years, the use of metagenomics in ARG research has increased (Yang et al. 2014; Bengtsson-Palme et al. 2016), but the approach still has several challenges. The relatively low abundance of resistance genes and their frequent presence on mobile genetic elements, which can be distributed in several different species, as well as difficulties in the assembly of mosaic genetic elements, complicate linking taxonomic information to specific ARGs. The application of Inverse-PCR (Pärnänen et al. 2016) has enabled circumventing problems in the assembly of ARGs and their genetic context. However, genes that are localized on mobile genetic elements are still difficult to assign to a specific species due to their distribution in more than one taxa.
Differences in the taxonomy of ARG carrying bacteria in WWTP influent and effluent could indicate potential transfer events during the wastewater purification process. To study this, we utilized epicPCR (Spencer et al. 2016) to gain a comprehensive understanding of the species carrying ARGs in the raw influent and purified effluent of WWTPs. epicPCR has been utilized so far for determining the bacterial host diversity of the dissimilatory sulfite reductase gene, dsrB (Spencer et al. 2016). epicPCR requires a priori knowledge of the sequences of the target genes of interest, provided for this study by prior qPCR experiments (Karkman et al 2016). epicPCR workflow begins by the encapsulation of a sufficient cell number (2 × 107) individually into hydrogel beads, after which a gene of interest (here, ARGs) is linked to the 16S rRNA gene of the host bacterium with the use of concatenating PCR. These concatenated amplicons are subsequently sequenced using high-throughput sequencing technologies, primarily Illumina MiSeq. Finally, the hosts of the ARG are identified bioinformatically based on 16S rRNA gene sequence.
For the selection of genes to be used in epicPCR, we utilized data gathered with qPCR (Laht et al. 2014) and qPCR array (Karkman et al. 2016) from the Viikinmäki WWTP over four seasons. The following genes abundant in the WWTPs were selected for the study: tetM encodes a protein protecting from inhibition of translation by tetracycline at the ribosome (Roberts 2005). Tetracycline resistance genes are common in feces (Hu et al. 2013) and thus found from WWTPs. blaOXA-58 is a beta-lactamase gene conferring resistance to carbapenems (Poirel et al. 2005) by hydrolyzing the compound, and it is clinically significant as carbapenems belong to last-resort antibiotics. It has been detected in WWTPs (Caucci et al. 2016; Karkman et al. 2016), and our interest was the host range of this ARG. int1 was chosen as antimicrobial resistance genes may be captured and thus spread via class I intergrons that recruit genes into a series of gene cassettes ensuring their expression and are frequently present in mobile elements (Gillings et al. 2008). Class 1 integrons have a broad host range and have been detected in both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria including a diverse array of obligatory and opportunistic human and zoonotic pathogens (Nandi et al. 2004; Gillings et al. 2015). Lastly, qacEΔ1, a biocide resistance gene, is linked to clinical class I integrons containing various ARGs (Gillings et al. 2008).
Here, our aim was to determine the bacterial hosts of the ARG of interest and find differences in the host distribution of the ARGs in raw inflow and effluent water at two municipal waste water treatment plants.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Sample collection
Samples were collected from two different municipal treatment plants in Helsinki and Espoo, Finland. Viikinmäki is the largest WWTP in Nordic countries processing wastewater from 800 000 residents and from the region's industry (annually 100 million m3 of wastewater). Approximately 15% of the wastewater is from industry and 85% is domestic wastewater. The Suomenoja WWTP processes the wastewaters of 310 000 residents (annually 35 million m3 of wastewater) and around 8% of the wastewater originates from industry. 24 h collection samples were taken on three subsequent days from influent and from effluent water in September 2016. The collection ended in the morning, and the samples were transported to the laboratory within 2 h.
Cells for epicPCR were collected from 2 ml of the influent wastewater by centrifuging for 5 min at 11 000 × g and from 200 ml of effluent wastewater by centrifuging for 40 min at 8000 × g. After discarding the supernatant, the remaining cell pellets were resuspended in 20% glycerol, flash frozen with liquid nitrogen and stored in –80°C.
For DNA extractions, 50 ml of influent wastewater and 200 ml of effluent water were filtered through 0.22 µm polycarbonate filters (diameter 47 mm, Whatman) in triplicate. The filters for influent water were cut in half with a sterile scalpel and forceps, and filters were transferred to Mobio PowerWater DNA Isolation Kit (Mobio Laboratories, CA, USA) bead beating tubes and stored in –20°C.
DNA extraction and 16S rRNA gene PCR
DNA from the filters was extracted with Mobio PowerWater DNA Isolation Kit following manufacturer's instructions. The DNA was quantified with Qubit Broad-Range Assay Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). PCR amplification of the V3–V4 region of the 16S rRNA gene was performed in two steps. The first round of amplification was done with the primers 341F1-4 and 785R1-4 that contain partial Illumina TruSeq adapter sequences in the 5΄ ends (Table 1) using Phusion polymerase with GC buffer and 2.5% DMSO (New England Biolab, MA, USA). The cycling conditions were as follows: initial denaturation at 98°C, followed by 15 cycles at 98°C for 10 s, 65°C for 30 s and 72°C for 10 s, and a final extension for 5 min at 72°C. The amount of template DNA used was approximately 25 ng. The PCR run included a PCR negative control without template DNA. The PCR products were purified with exonuclease I (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) and thermosensitive alkaline phosphatase (FastAP; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). A second PCR round was performed with full-length TruSeq P5 and Index containing P7 adapters. The cycling conditions were identical to the previous ones except that 18 instead of 15 cycles were run. The final PCR products were purified with Agencourt® AMPure® XP magnetic beads (Beckman Coulter, CA, USA), pooled and sequenced on the Illumina MiSeq platform at the Institute of Biotechnology, University of Helsinki, Finland. All 16S rRNA gene sequences have been deposited in the European Nucleotide Archive (accession no. PRJEB23695).
Table 1.
Primers used in the study.
| Gene name | sequence 5΄-3΄ a) b) | Target | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| 341F1 | ATCTACACTCTTTCCCTACACGACGCTCTTCCGATCTCCTACGGGNGGCWGCAG | 16S rRNA gene | Herlemann et al. (2011) |
| 341F2 | ATCTACACTCTTTCCCTACACGACGCTCTTCCGATCTgtCCTACGGGNGGCWGCAG | 16S rRNA gene | Herlemann et al. (2011) |
| 341F3 | ATCTACACTCTTTCCCTACACGACGCTCTTCCGATCTagagCCTACGGGNGGCWGCAG | 16S rRNA gene | Herlemann et al. (2011) |
| 341F4 | ATCTACACTCTTTCCCTACACGACGCTCTTCCGATCTtagtgtCCTACGGGNGGCWGCAG | 16S rRNA gene | Herlemann et al. (2011) |
| 785R1 | GTGACTGGAGTTCAGACGTGTGCTCTTCCGATCTGACTACHVGGGTATCTAATCC | 16S rRNA gene | Herlemann et al. (2011) |
| 785R2 | GTGACTGGAGTTCAGACGTGTGCTCTTCCGATCTaGACTACHVGGGTATCTAATCC | 16S rRNA gene | Herlemann et al. (2011) |
| 785R3 | GTGACTGGAGTTCAGACGTGTGCTCTTCCGATCTtctGACTACHVGGGTATCTAATCC | 16S rRNA gene | Herlemann et al. (2011) |
| 785R4 | GTGACTGGAGTTCAGACGTGTGCTCTTCCGATCTctgagtgGACTACHVGGGTATCTAATCC | 16S rRNA gene | Herlemann et al. (2011) |
| tetM_F1 | CATCATAGACACGCCAGGACA | tetM epic forward | Karkman et al. (2016) |
| tetM_R1_F2’ | GWATTACCGCGGCKGCTGCTGTTTGATTACAATTTCCGC | tetM epic linker | Tamminen et al. (2011) |
| TetM_F3_TS | ATCTACACTCTTTCCCTACACGACGCTCTTCCGATCTGCAATTCTACTGATTTCTGC | tetM epic nested | Tamminen et al. (2011) |
| qacEΔ1_F1 | TCGCAACATCCGCATTAAAA | qacEΔ1 epic forward | Eckert, Gautier and Arlet (,2006) |
| qacEΔ1_R1_F2’ | GWATTACCGCGGCKGCTGATGGATTTCAGAACCAGAGAAAGAAA | qacEΔ1 epic linker | Karkman et al. (2016) |
| qacEΔ1_F1_TS | ATCTACACTCTTTCCCTACACGACGCTCTTCCGATCTTCGCAACATCCGCATTAAAA | qacEΔ1 epic nested | Karkman et al. (2016) |
| int1-a_F1 | CGAAGTCGAGGCATTTCTGTC | int1 epic forward | Muziasari et al. (2014) |
| int1-a_R1_F2’ | GWATTACCGCGGCKGCTGGCCTTCCAGAAAACCGAGGA | int1 epic linker | Muziasari et al. (2014) |
| int1-a_F1_TS | ATCTACACTCTTTCCCTACACGACGCTCTTCCGATCTCGAAGTCGAGGCATTTCTGTC | int1 epic nested | Muziasari et al. (2014) |
| blaOXA-58_F1 | ACAGGCACTGTAGATGCTTG | bla OXA-58 epic forward | Karkman et al. (2016) |
| blaOXA-58_R1_F2’ | GWATTACCGCGGCKGCTGTGTGCTGAGCATAGTATGAG | bla OXA-58 epic linker | Karkman et al. (2016) |
| blaOXA-58_F3_TS | ATCTACACTCTTTCCCTACACGACGCTCTTCCGATCTTCGGTCTAAATGCGTGCCAT | bla OXA-58 epic nested | Karkman et al. (2016) |
| pH’ | AAGGAGGTGATCCAGCCGCA | 16S rRNA gene | Edwards et al. (1989) |
Lower case nucleotides in primers 341F and 785R are introduced for mixing in sequencing.
Nucleotides in bold mark the 16S rRNA gene sequence (in R1_F2’) or the short Illumina TrueSeq adapter (in nested primers).
Primer design
ARGs were selected based on previous results (Karkman et al. 2016) and targeted using previously published primers (Table 1). Because of the melting temperatures of the targeted ARGs, the pH΄ primer (Table 1) was used as the reverse primer for amplifying the 16S rRNA gene, differing from the protocol used by Spencer et al. (2016), who used a primer with a lower melting temperature. Also, the primer 785R from the original protocol used in nested PCR was modified (Table 1), and short TrueSeq adapter sequences were added to the nested PCR primers.
epicPCR
The droplets for epicPCR were done for cells stored in glycerol as described by Spencer et al. (2016) with the following modifications: for bead formation, 100 µl autoclaved MilliQ water (Millipore), 100 µl 30% BIS/acrylamide (29:1, Bio Rad, CA, USA) and 25 µl 10% APS (Sigma, MO, USA) were used. A 35 µm cell strainer (Falcon, NY, USA) was used in bead straining. The prevalence of beads containing several cells and the distribution of beads containing a single bacterium versus empty beads were estimated by staining cells with SybrGreenII (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) and microscopied under a compound microscope (Zeiss Axioskop 2 plus, Oberkochen, Germany).
The first PCR was done as described in Spencer et al. (2016) with the following exceptions: Phusion Hot Start Flex DNA Polymerase (NEB) was used with the GC buffer and 55°C annealing temperature and without water, BSA or Tween-20 as in Spencer et al. (2016). After bead purification, nested PCR was conducted in quadruplicate. For some genes, a semi-nested approach was used with primers including TrueSeq adapters (Table 1). In nested PCR, the annealing temperature was set to 55°C. PCR reactions were purified with the Agencourt AMPure XP purification system (Beckman Coulter, Inc., CA, USA) followed by eight cycles of PCR with TruSeq P5 and Index primers containing P7 adapters to prepare the samples for sequencing. The samples were sequenced on the Illumina MiSeq platform at the Institute of Biotechnology, University of Helsinki, Finland. All epicPCR sequences have been deposited in the European Nucleotide Archive (accession no. PRJEB23695).
16S rRNA gene data analysis
For 16S rRNA reads were joined with Pear (Zhang et al. 2014) with default options and quality trimmed using USEARCH -fastq_filter command with -fastq_maxee 1 and -fastq_minlen 350 parameters. Unique sequences were identified with the UPARSE pipeline (Edgar 2013) with -derep_fulllength command. OTUs were clustered, chimeras removed and reads were mapped to reference sequences with the –cluster_otus command with –minsize 2 parameter and -usearch_global command with -id 0.97 parameter. Taxonomic classification of OTUs was done using the classify.seqs command in mothur (Schloss et al. 2009) using the RDP naïve Bayesian Classifier (Wang et al. 2007) against the Silva 128 database (Quast et al. 2013) with classifier cutoff = 60.
The community composition between the two plants and the two different stages were compared with permutational multivariate analysis of variance using the function Adonis from the vegan package (Oksanen et al. 2017) in R (R Core team 2017). Shannon index and inverse Simpson index describing the alpha diversity of the microbial communities were calculated with phyloseq (McMurdie and Holmes 2013) as well as beta diversity with the Bray–Curtis dissimilarity index.
epicPCR data analysis
The paired end reads were joined with Pear (Zhang et al. 2014) and binned based on the ARG of interest. Short reads (<400 bp) were removed with cutadapt (Martin 2011) and the good quality reads were split into 16S rRNA and ARG sequences with Prinseq (Schmieder and Edwards 2011) based on the functional gene sequence. 16S rRNA gene OTUs (97%) were identified using UPARSE with the –cluster_otus command with –minsize 2 parameter and -usearch_global command with -id 0.97 parameter. The OTUs were assigned taxonomies in mothur (Schloss et al. 2009) using the RDP naive Bayesian classifier (Wang et al. 2007) against Silva 128 database (Quast et al. 2013) with classifier cutoff = 60. ARGs were also clustered to OTUs but using 100% identity and annotated with BlastN (Altschul et al. 1990) to verify that the correct gene was amplified. Results for a gene in a sample were taken into consideration when there were >57 reads after quality filtering. The average number of reads was 17 888.
For 16S rRNA gene OTUs, a representative sequence from each bacterial family was aligned with PyNAST (Caporaso et al. 2010), and a phylogenetic tree of the representative sequences was built with Fasttree (Price, Dehal and Arkin 2009). The presence/absence of an ARG in the bacterial family of origin of OTUs was visualized in iTol (Letunic and Bork 2016). A gene was considered present in the OTU of interest when found in all samples passing the quality filtering step (2/2 or 3/3) from the influent/effluent in a plant of interest.
RESULTS
Microbial community composition in the WWTPs
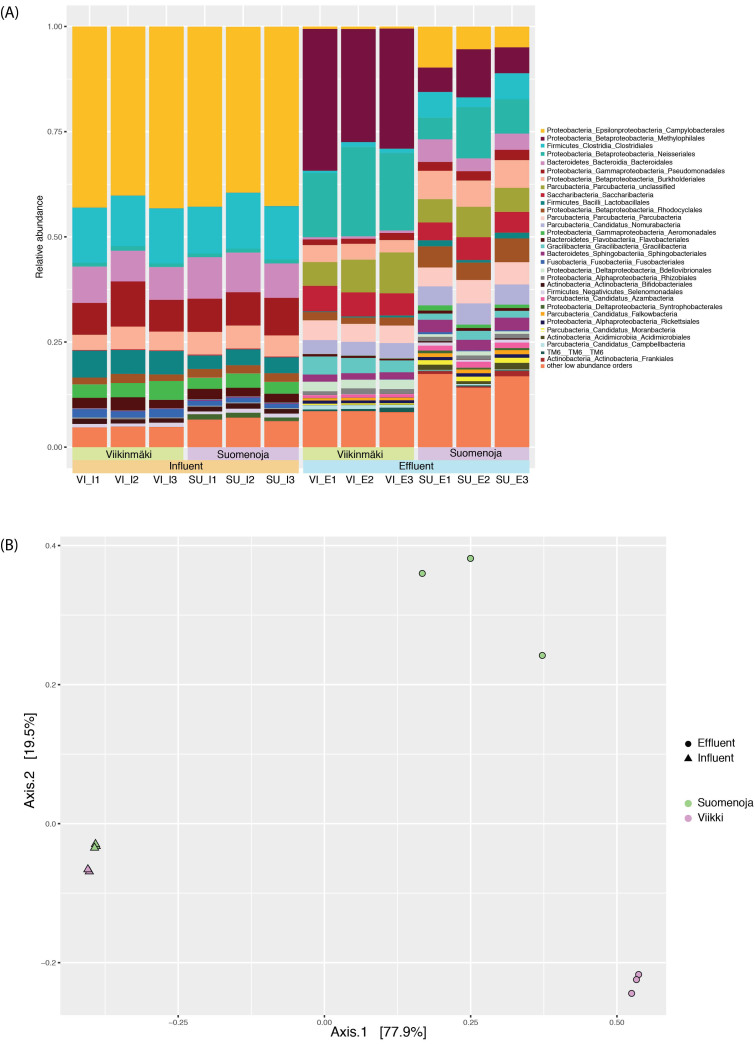
The bacterial community composition in the Viikimäki and Suomenoja WWTPs was characterized by similar influent composition. In contrast, the effluent communities of the two plants differed substantially (PERMANOVA with Bray–Curtis dissimilarity: plant P = 0.007, phase P = 0.0001, plant: phase P = 0.003; Fig. 1a and b). The main species in the influent belonged to the bacterial order Campylobacteriales with 39%–43% of the reads assigned to this order. Other orders with high relative abundance in the influent included Clostridia (12.55 ± 1.6%), Bacteroidales (8.53 ± 1.0%) and Pseudomonadales (8.43 ± 1.2%). However, the community profiles differed in the WWTP effluents (Fig. 1a): in Viikinmäki, the main orders were Methylophilales (29.70 ± 3.6%), Neisseriales (18.31 ± 3.0%) and unclassified Parcubacteria (7.72 ± 2.0%); in Suomenoja, there were no clear dominant species but the diversity was higher (Fig. S1, Supporting Information) and the orders with the highest relative abundance were Neisseriales (8.48 ± 3.5%), Methylophilales (7.8 ± 3.2%) and Campylobacteriales (6.68 ± 2.65%).
Figure 1.
(A) Order level classification of the 16S rRNA gene sequences. Microbial community composition was analyzed from both plants (VI = Viikinmäki, SU = Suomenoja) in the influent and effluent water on three subsequent days. (B) Principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) plot from the OTU relative abundance with the Bray–Curtis dissimilarity. The influent clusters from two plants clustered together, whereas the effluent samples were more distinct at the studied plants.
Resistance-associated gene hosts as determined by epicPCR
Two ARGs, the tetracycline resistance gene, tetM, and beta-lactamase gene, blaOXA-58, together with the class I integron integrase intI and biocide resistance gene, qacEΔ1 (Table 1), were analyzed with epicPCR from the two WWTPs. We modified the epicPCR protocol from the published one (Spencer et al. 2016) by using 16S rRNA gene primers with a higher melting temperature. All of the studied genes were detected in both influent and effluent. However, the OTUs carrying ARGs and ARG associated genes differed from the most abundant OTUs in the total community. There were also differences in the bacterial genera carrying ARGs between the two WWTPs (Figs 2 and 3; Tables S1 and S2, Supporting Information). Due to the inherent qualitative nature of epicPCR resulting from a large number of cycles in two PCR steps, we analyzed the epicPCR results using presence/absence data as opposed to a quantitative approach. When comparing the number of OTUs associated with the targeted ARGs and ARG associated genes detected in the epicPCR analyses to the total number of OTUs detected in the 16S rRNA sequence library, we found that the ratio (Table 2) of these two was generally higher in the raw influent wastewater than in the more diverse (Fig. S1, Supporting Information) effluent water.
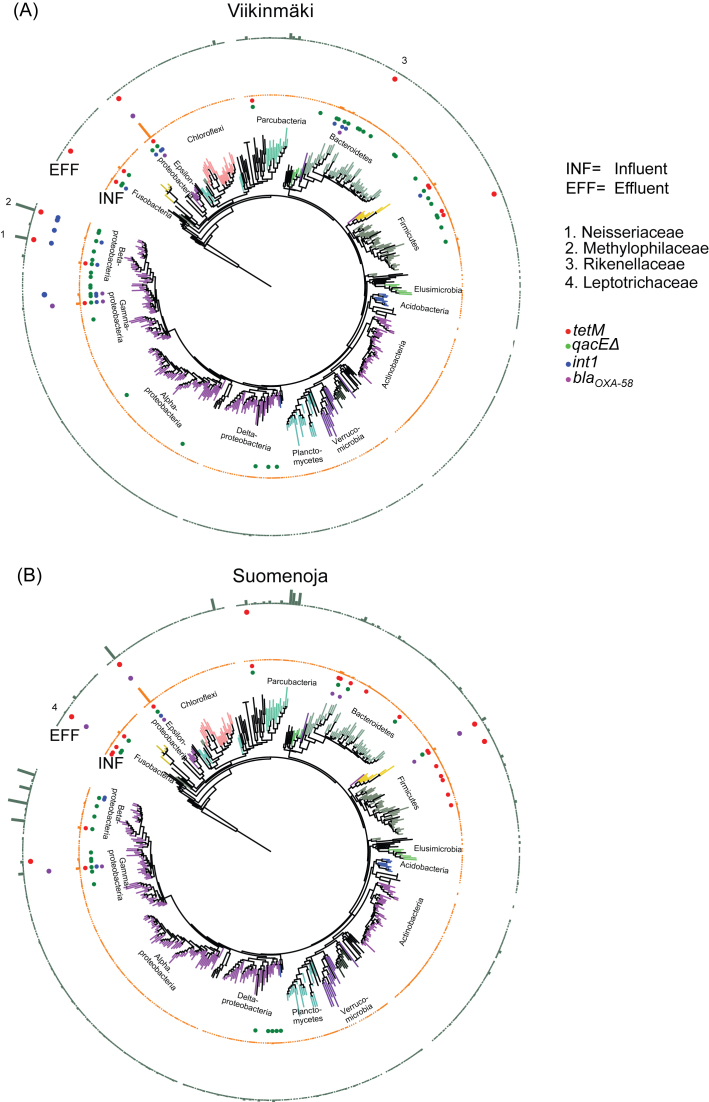
Figure 2.
Presence of ARGs in microbial families in the two wastewater purification plants. The phylogenetic tree was constructed from family-level OTUs based on 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequences. An ARG was considered to be present in a bacterial genus when found in 2/2 or 3/3 samples (depending on whether all three samples passed the QC step) from the influent or effluent water at the same plant. The inner circle (INF) denotes the influent and the outer circle (EFF) the effluent water. The results are presented at family level and bars in the INF and EFF rings display relative abundance.
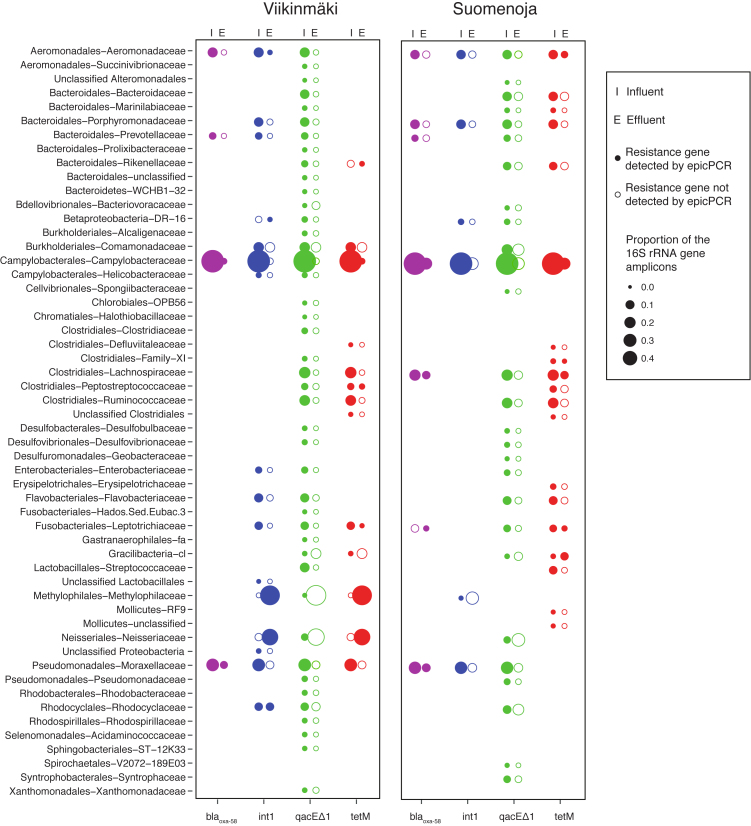
Figure 3.
Bacterial families with resistance gene detected by epicPCR in influent and/or effluent of the two plants (Viikinmäki and Suomenoja). Relative abundance of the family in total 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing is shown with the size of the sphere. Open sphere: gene not detected with epicPCR, closed sphere: gene detected with epicPCR.
Table 2.
Number of OTUs detected in epicPCR versus 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing.
| sample | tetM | bla OXA-58 | int1 | qacEΔ1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VI_I1 | 1.14% | 0.69% | 0.55% | 6.57% |
| VI_I2 | 1.04% | 0.52% | 1.51% | – |
| VI_I3 | 2.95% | 0.73% | 1.77% | 7.04% |
| VI_O1 | 0.68% | 0.22% | 0.00% | 0.19%a |
| VI_O2 | – | 0.24% | 0.34% | 0.64% |
| VI_O3 | 0.32% | – | 0.45% | – |
| Sample | tetM | bla OXA-58 | int1 | qacEΔ1 |
| SU_I1 | 2.90% | 0.40% | – | 2.78% |
| SU_I2 | – | 0.36% | 0.32% | – |
| SU_I3 | 3.89% | 2.22% | 0.59% | 5.31% |
| SU_O1 | 0.65% | – | – | – |
| SU_O2 | – | 0.23% | – | 0.36%a |
| SU_O3 | 1.62% | 0.29% | – | – |
In Viikinmäki, tetM was found in 13 bacterial genera in the influent (Table S1, Supporting Information), whereas it was observed in six genera in the effluent. A similar profile was observed in Suomenoja, although the number of tetM carrying genera was higher in Suomenoja than in Viikinmäki with 28 genera in the influent and nine in the effluent wastewater (Table S1, Supporting Information). These genera were distributed in families of the phyla Bacteroidetes, Firmicutes, Proteobacteria, Tenericutes, Fusobacteria and Gracilibacteria (Fig. 2). The host range of tetM was broader than that of blaOXA-58. In Viikinmäki five and in Suomenoja seven genera were observed to carry the gene in the influent, and two and eight, respectively, in the effluent. The phyla containing the genera carrying blaOXA-58 included members of Bacteroidetes, Firmicutes, Fusobacteria and Proteobacteria (Fig. 2). The gene qacEΔ1 had the broadest host range observed with epicPCR: in the influent qacEΔ1 was found in 84 and 44 genera in Viikinmäki and Suomenoja, respectively, and in the effluent in four genera in both treatment plants (Table S1, Supporting Information). For the intI gene in the Viikinmäki WWTP, there was larger diversity in the influent than in the effluent, with 17 genera associated with the gene in the influent and only six in the effluent. In Suomenoja, there were seven genera carrying intI in the influent but we were not able to detect the gene in the effluent water with epicPCR.
DISCUSSION
EpicPCR was originally used to profile the host distribution of the dissimilatory sulfite reductase gene, dsrB, in linker PCR with the 16S rRNA gene in the protocol by Spencer et al. (2016). Here, for the first time, we applied epicPCR to link ARGs and class I integron associated genes with the taxonomic information of the bacteria carrying them. We were able to detect differences in ARG and integron carrying bacterial genera in the wastewater influent and treated effluent at the two purification plants studied. We also analyzed the total bacterial communities in the studied samples and found that both the total community and the observed ARG and integron carrying genera changed during the wastewater treatment process.
We were able to observe putative HGT events using epicPCR. In the Suomenoja effluent water, blaOXA-58 gene was found to be associated with a Leptotrichiaceae OTU belonging to Fusobacteria, while the gene was not detected in this phylum in the influent. Similarly, tetM was observed in the effluent in an uncultured member of Rikennellacea with low relative abundance in the total community and two abundant members of Methylophilaceae and Neisseriaceae families, while tetM was not detected in these families in the raw influent (Figs 2 and 3; Table S2, Supporting Information). Due to the highly variable OTU abundances in the samples, we cannot definitively conclude whether the differences in the host species distribution were due to horizontal gene transfer or the detection limit of the method. Clearly, the abundance of reads attained in 16S rRNA gene sequencing does not limit the detection of hosts in epicPCR (Fig. 2) as bacterial families with both low and high relative abundance were linked to the four studied genes. However, mechanistic proof of gene transfer during the treatment process would require further methodological advancements in in situ HGT studies.
The total relative abundance of ARGs has been shown to decline during the wastewater purification process (Yang et al. 2014; Bengtsson-Palme et al. 2016; Karkman et al. 2016) but the relative abundance of some genes is enriched in the effluent bacterial community (Mao et al. 2015; Munck et al. 2015). The conditions in the purification process are often considered to favor horizontal gene transfer (Rizzo et al. 2013b). However, actual data supporting active HGT in WWTPs is rather scarce. It remains unknown whether the species carrying ARGs are the same before and after the treatment process but are at low abundance and thus below detection limit, or whether the wastewater treatment process favors horizontal gene transfer of ARGs. The latter is observed when the taxa that carry ARGs are different in the effluent from those in the influent. However, reliable association of ARG carriage with horizontal gene transfer events requires that all the cases of ARG carriage are detected. This warrants further investigation into factors influencing the detection limit of epicPCR.
The gene tetM was carried in partly different bacterial families in the influent and effluent wastewater. Members from the families Methylophilaceae, Neisseriaceae and Rikenellaceae harbored tetM in effluent water, although they were not observed to carry the gene in the influent suggesting possible HGT events. Of these families, Neisseriaceae is known to contain pathogenic species (Rotman and Seifert 2014), whereas Rikenellaceae and Methylophilaceae are typical bacteria in the wastewater purification process. The tetM gene is commonly localized on a conjugative transposon, Tn916, with a broad host range (Roberts and Mullany 2009) possibly explaining the observed diversity of the tetM carrying taxa in effluents.
The gene blaOXA-58, a plasmid-borne gene providing resistance to carbapenem, is commonly detected in Acinetobacter baumannii. A. baumannii is an opportunistic pathogen responsible for a range of nosocomial infections, especially in intensive care units (Heritier et al. 2005). Here, the gene was linked to Acinetobacter, but also to gammaproteobacterial genera including Tolumonas, Aeromonas and Enhydrobacter. In addition, blaOXA-58 was linked to Arcobacter, the family Lachnospiraceae belonging to Clostridia, the family Leptotrichiaceae belonging to Fusobacteria and several Bacteroidales families. These groups contain bacteria found in feces and include pathogenic species as well as environmental bacteria. Although the blaOXA-58 gene has been considered to be affiliated with A. baumannii and a few other Acinetobacter species (Coelho et al. 2006), it was recently characterized in the enterobacterium Proteus mirabilis isolated from a plasmid in clinical samples (Lange et al. 2017). In P. mirabilis, the gene was found in a plasmid with a different genetic context than in A. baumannii. epicPCR linked the gene to several genera, suggesting the possibility of this gene having been transferred to more taxa than originally thought. However, the number of species the gene was linked to decreased during the wastewater treatment process. Despite the decrease in genera, we observed blaOXA-58 to be associated with the family Leptotrichiaceae in the effluent in Suomenoja WWTP, although the gene was not associated to the family in the influent.
The four studied genes had differences in their host range, but interestingly, Arcobacter was found to carry all of the investigated genes in the effluent water. Arcobacter belongs to Campylobacteria and species of the genus are considered to be emergent pathogens (Miller et al. 2007). The species in this genus have been found to carry several ARGs in their genome, and in our study, the genus harbored the widest range of genes. Recently, a member of this genus common in WWTPs has been found to carry several ARGs (Millar and Raghavan 2017). However, there are only 14 genome sequences of Arcobacter in the NCBI genome database (2017–11-22) and their diversity in the environment is largely unknown. The results suggest that Arcobacter species might be important carriers of ARGs in WWTP environments.
This study demonstrates that epicPCR can be used to determine the host range of ARGs in complex environmental samples. Adding more primers to the used set is straightforward, enabling the analysis of the host ranges of multiple ARGs in complex communities at single cell level in a high-throughput manner.
Supplementary Material
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors wish to acknowledge CSC—IT Center for Science, Finland, for computational resources and thank Helsinki Region Environmental Services Authority (HSY) for providing the wastewater samples.
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA
Supplementary data are available at FEMSEC online.
FUNDING
This work was supported by the Academy of Finland [Grant Numbers 268643, 288897] and the Water JPI [Pilot Call project StARE], University of Helsinki [three year grant to JH] and Doctoral Programme in Microbiology and Biotechnology to KP and JC.
Conflict of interest. None declared.
REFERENCES
- Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W et al. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990;215:403–10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amann RI, Ludwig W, Schleifer KH. Phylogenetic identification and in situ detection of individual microbial cells without cultivation. Microbiol Rev. 1995;59:143–69. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auerbach EA, Seyfried EE, McMahon KD. Tetracycline resistance genes in activated sludge wastewater treatment plants. Water Res. 2007;41:1143–51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bengtsson-Palme J, Hammaren R, Pal C et al. Elucidating selection processes for antibiotic resistance in sewage treatment plants using metagenomics. Sci Total Environ. 2016;572:697–712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caporaso JG, Bittinger K, Bushman FD et al. PyNAST: a flexible tool for aligning sequences to a template alignment. Bioinformatics. 2010;26:266–7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caucci S, Karkman A, Cacace D et al. Seasonality of antibiotic prescriptions for outpatients and resistance genes in sewers and wastewater treatment plant outflow. FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 2016;92:fiw060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coelho J, Woodford N, Afzal-Shah M et al. Occurrence of OXA-58-like carbapenemases in Acinetobacter spp. collected over 10 years in three continents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006;50:756–8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckert C, Gautier V, Arlet G. DNA sequence analysis of the genetic environment of various blaCTX-M genes. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2006;57:14–23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgar RC. UPARSE: highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat Methods. 2013;10:996–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards U, Rogall T, Blocker H et al. Isolation and direct complete nucleotide determination of entire genes. Characterization of a gene coding for 16S ribosomal. RNA Nucleic Acids Res. 1989;17:7843–53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillings M, Boucher Y, Labbate M et al. The evolution of class 1 integrons and the rise of antibiotic resistance. J Bacteriol. 2008;190:5095–100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillings MR, Gaze WH, Pruden A et al. Using the class 1 integron-integrase gene as a proxy for anthropogenic pollution. ISME J. 2015;9:1269–79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heritier C, Poirel L, Lambert T et al. Contribution of acquired carbapenem-hydrolyzing oxacillinases to carbapenem resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005;49:3198–202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herlemann DP, Labrenz M, Jurgens K et al. Transitions in bacterial communities along the 2000 km salinity gradient of the Baltic. Sea ISME J. 2011;5:1571–9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu Y, Yang X, Qin J et al. Metagenome-wide analysis of antibiotic resistance genes in a large cohort of human gut microbiota. Nat Commun. 2013;4:2151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karkman A, Do TT, Walsh F et al. Antibiotic-resistance genes in waste water. Trends Microbiol. 2017;26:220–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karkman A, Johnson TA, Lyra C et al. High-throughput quantification of antibiotic resistance genes from an urban wastewater treatment plant. FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 2016;92, DOI: 10.1093/femsec/fiw014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laht M, Karkman A, Voolaid V et al. Abundances of tetracycline, sulphonamide and Beta-Lactam antibiotic resistance genes in conventional wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) with different waste load. PLoS One. 2014;9:e103705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange F, Pfennigwerth N, Gerigk S et al. Dissemination of blaOXA-58 in Proteus mirabilis isolates from Germany. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2017;72:1334–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letunic I, Bork P. Interactive tree of life (iTOL) v3: an online tool for the display and annotation of phylogenetic and other trees. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016;44:W242–5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mao D, Yu S, Rysz M et al. Prevalence and proliferation of antibiotic resistance genes in two municipal wastewater treatment plants. Water Res. 2015;85:458–66. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnetjournal. 2011;17:10–12. [Google Scholar]
- McMurdie PJ, Holmes S. phyloseq: an R package for reproducible interactive analysis and graphics of microbiome census data. PLoS One. 2013;8: e61217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millar JA, Raghavan R. Accumulation and expression of multiple antibiotic resistance genes in Arcobacter cryaerophilus that thrives in sewage. Peer J. 2017;5:e3269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller WG, Parker CT, Rubenfield M et al. The complete genome sequence and analysis of the epsilonproteobacterium Arcobacter butzleri. PLoS One. 2007;2:e1358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munck C, Albertsen M, Telke A et al. Limited dissemination of the wastewater treatment plant core resistome. Nat Commun. 2015;6:8452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muurinen J, Stedtfeld R, Karkman A et al. Influence of manure application on the environmental resistome under finnish agricultural practice with restricted antibiotic use. Environ Sci Technol. 2017;51:5989–99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muziasari WI, Managaki S, Parnanen K et al. Sulphonamide and trimethoprim resistance genes persist in sediments at Baltic Sea aquaculture farms but are not detected in the surrounding environment. PLoS One. 2014;9:e92702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muziasari WI, Parnanen K, Johnson TA et al. Aquaculture changes the profile of antibiotic resistance and mobile genetic element associated genes in Baltic Sea sediments. FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 2016;92:fiw052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nandi S, Maurer JJ, Hofacre C et al. Gram-positive bacteria are a major reservoir of Class 1 antibiotic resistance integrons in poultry litter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101:7118–22. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oksanen J, Blanchet FG, Friendly M et al. Vegan: Community Ecology Package. R package version 2.4-3. 2017. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan. [Google Scholar]
- Poirel L, Marque S, Heritier C et al. OXA-58, a novel class D {beta}-lactamase involved in resistance to carbapenems in Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005;49:202–8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price MN, Dehal PS, Arkin AP. FastTree: computing large minimum evolution trees with profiles instead of a distance matrix. Mol Biol Evol. 2009;26:1641–50. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pärnänen K, Karkman A, Tamminen M et al. Evaluating the mobility potential of antibiotic resistance genes in environmental resistomes without metagenomics. Sci Rep. 2016;6:35790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quast C, Pruesse E, Yilmaz P et al. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013;41:D590–6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing. Vienna, Austria, 2017. URL https://www.R-project.org/. [Google Scholar]
- Rizzo L, Manaia C, Merlin C et al. Urban wastewater treatment plants as hotspots for antibiotic resistant bacteria and genes spread into the environment: a review. Sci Total Environ. 2013a;447:345–60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizzo L, Manaia C, Merlin C et al. Urban wastewater treatment plants as hotspots for antibiotic resistant bacteria and genes spread into the environment: a review. Sci Total Environ. 2013b;447:345–60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts AP, Mullany P. A modular master on the move: the Tn916 family of mobile genetic elements. Trends Microbiol. 2009;17:251–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts MC. Update on acquired tetracycline resistance genes. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2005;245:195–203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotman E, Seifert HS. The genetics of Neisseria species. Annu Rev Genet. 2014;48:405–31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schloss PD, Westcott SL, Ryabin T et al. Introducing mothur: open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2009;75:7537–41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmieder R, Edwards R. Quality control and preprocessing of metagenomic datasets. Bioinformatics. 2011;27:863–4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer SJ, Tamminen MV, Preheim SP et al. Massively parallel sequencing of single cells by epicPCR links functional genes with phylogenetic markers. ISME J. 2016;10:427–36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stedtfeld RD, Baushke SW, Tourlousse DM et al. Development and experimental validation of a predictive threshold cycle equation for quantification of virulence and marker genes by high-throughput nanoliter-volume PCR on the OpenArray platform. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2008;74:3831–8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamminen M, Karkman A, Lohmus A et al. Tetracycline resistance genes persist at aquaculture farms in the absence of selection pressure. Environ Sci Technol. 2011;45:386–91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Q, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM et al. Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2007;73:5261–7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Y, Li B, Zou S et al. Fate of antibiotic resistance genes in sewage treatment plant revealed by metagenomic approach. Water Res. 2014;62:97–106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J, Kobert K, Flouri T et al. PEAR: a fast and accurate Illumina Paired-End reAd mergeR. Bioinformatics. 2014;30:614–20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.