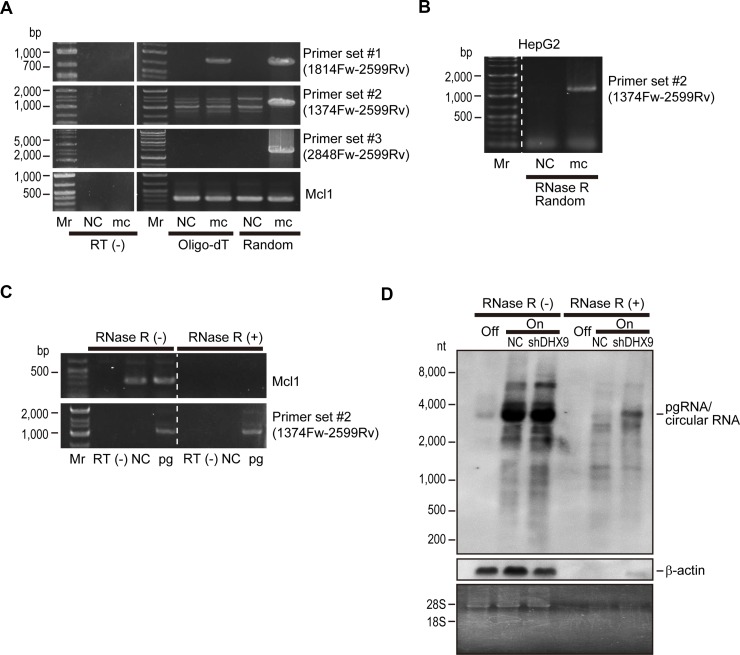
Figure 2. Viral circular RNA is produced during HBV replication.
(A) HepG2 cells were transfected with HBV minicircle construct (mc). Three days after transfection, RNAs were extracted and subjected to complementary DNA (cDNA) synthesis by reverse transcription using oligo-dT (Oligo-dT) or random (Random) primers as indicated. Cells without transfection were used as negative controls (NC). PCR was performed using the indicated primer sets. Primer set #1 was used to amplify the core region, and set #2 and set #3 were outward facing primers, which would theoretically result in no amplification. Mcl1 amplification was used as an internal control. RNAs that were not reverse transcribed (RT(−)) were included as negative controls for the PCR to confirm no DNA contamination. Mr, DNA marker. A representative image of two independent experiments is shown. (B) RNAs extracted from HepG2 cells transfected with HBV minicircle construct (mc) for 3 days were treated with RNase R and subjected to RT-PCR using random primers and primer set #2. Untransfected cells were used as a negative control (NC). (C) HepG2 cells were transfected with HBV pgRNA expressing plasmid (pg). Two days after transfection, extracted RNA was treated with or without RNase R and reverse transcribed using random primers. PCR was performed using primer set #2 and primers for Mcl1 gene amplification as a control. RNAs that were not reverse transcribed (RT(−)) were used as negative controls. Mr, DNA marker. A representative image of two independent experiments is shown. (D) DHX9 knockdown leads to increased viral circular RNA production. HepAD38 cells with HBV shut off (Off), HBV continuous expression (On), and HBV continuous expression with shDHX9 expression (On + shDHX9) were subjected to northern blotting with or without RNase R treatment. Probes against HBV RNA primarily spanning the core region and β-actin were used. Gel staining with ethidium bromide is shown to confirm RNA integrity (bands of 28S and 18S ribosomal RNA) and the effects of RNase treatment (disappearance of ribosomal RNA bands). A representative image of two independent experiments is shown.