Abstract
The use of Bt proteins in crops has revolutionized insect pest management by offering effective season-long control. However, field-evolved resistance to Bt proteins threatens their utility and durability. A recent example is field-evolved resistance to Cry1Fa and Cry1A.105 in fall armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda). This resistance has been detected in Puerto Rico, mainland USA, and Brazil. A S. frugiperda population with suspected resistance to Cry1Fa was sampled from a maize field in Puerto Rico and used to develop a resistant lab colony. The colony demonstrated resistance to Cry1Fa and partial cross-resistance to Cry1A.105 in diet bioassays. Using genetic crosses and proteomics, we show that this resistance is due to loss-of-function mutations in the ABCC2 gene. We characterize two novel mutant alleles from Puerto Rico. We also find that these alleles are absent in a broad screen of partially resistant Brazilian populations. These findings confirm that ABCC2 is a receptor for Cry1Fa and Cry1A.105 in S. frugiperda, and lay the groundwork for genetically enabled resistance management in this species, with the caution that there may be several distinct ABCC2 resistances alleles in nature.
Introduction
The fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda (J.E. Smith) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae), is one of the most significant crop pests across a vast area in North and South America. This polyphagous species feeds on major crops such as maize, soybean, cotton, and sugarcane, in addition to a wide variety of other plant species1. Severe infestations of S. frugiperda can be devastating, resulting in significant crop loss2. This species is also highly mobile, for example, in North America, populations overwinter in the southern United States and migrate as far north as Canada in the summer months. Moreover, S. frugiperda is highly adaptive and has developed resistance to numerous classes of chemical insecticides3, and more recently to plant-expressed Bt proteins4–6.
The use of plant-expressed Bt proteins (also known as Bt crops) is a significant advance in S. frugiperda control. These proteins are stably transformed into a crop genome and when expressed make the plant tissues toxic to target insects after feeding. In particular, certain Bt proteins belonging to the Cry1 and Cry2 families have proven to be highly effective in controlling S. frugiperda7, including in particular Cry1Fa, Cry1A.105 and Cry2Ab2, and to a lesser extent Cry1Ab. The use of these proteins for S. frugiperda control has become widespread in maize and cotton. With high utilization in Bt crops, the Bt proteins come under increased selection pressure and increased risk of resistance in target insects, including S. frugiperda. For example, reports of S. frugiperda resistance to Cry1Fa first surfaced in maize grown in Puerto Rico in 2006, and were later confirmed in 20105,6. This resistance issue was severe enough that it led to the removal of products containing the Cry1Fa expressing TC1507 transgenic event from the Puerto Rican market5. Additionally, Cry1Fa resistant insects were also found to be partially cross-resistant to other Cry1 family proteins, including Cry1Ab and Cry1Ac5, and Cry1Aa8, suggesting a shared mode of action for these Cry1 family proteins. This result has been verified biochemically, with the addition of Cry1A.105 as another protein with a high potential for cross-resistance with Cry1Fa9. More recently, selection experiments using purified Cry1A.105 also indicated that increased resistance to that protein lead to a coordinated increase in resistance to Cry1Fa10, again highlighting a potential for cross-resistance between Cry1Fa and Cry1A.105.
Following this initial discovery of resistance in Puerto Rico, additional studies have reported resistance to Cry1Fa in Brazil11 and the Southeastern US4. In both studies the resistance allele was found to be recessive and capable of delivering at least 84-fold resistance relative to a susceptible control population. The study by Huang et al.4 also demonstrated empirically that there is partial cross-resistance between Cry1Fa and Cry1A.105, as earlier biochemical assays had predicted9.
The development of resistance to members of the Cry1 family of toxins threatens their continued use in controlling S. frugiperda. Insect Resistance Management (IRM) programs have been implemented to fight the spread of resistance. IRM seeks to develop pest management practices that maintain low resistance allele frequency and minimize the probability of resistance spreading to new regions12. IRM is grounded in the principles of population genetics and benefits greatly from a basic understanding of the genetic mechanism of resistance13. For example, resistance allele frequency and the dominance of resistance can strongly shape the trajectory of the rise and spread of resistance12. Also, if the causal resistance gene(s) are known, genetic markers can be deployed to track resistance allele frequency across different regions and across time. This knowledge can lead to adaptive IRM strategies and better outcomes14. However, knowing these key facts requires a precise understanding of the gene(s) involved in resistance.
Fortunately, with respect to Cry1 family proteins, several studies have provided insights into their mode of action among lepidopteran insects. Early studies in Heliothis virescens demonstrated that Cry1Ac resistance was linked to mutations in a cadherin protein15. This receptor protein is embedded in the insect gut membrane and its wild-type form appears to interact with the Bt protein enabling toxicity16. Knockout mutations of this cadherin gene reduce or completely remove this interaction between Cry1Ac and its cadherin receptor, thereby conferring resistance17–19. More recently, mutations in ATP-binding cassette transporter proteins (ABC transporters) have also been shown to confer resistance to the Cry1 family proteins in Bombyx mori20, Helicoverpa armigera21, Heliothis virescens22,23, Ostrinia nubilalis24, Spodoptera exigua25, Plutella xylostella26, and Trichoplusia ni26. In each case resistance was linked to ABCC2, a member of the ABC transporter C family. In much the same way as with the cadherins, it is thought that Cry1 family proteins interact with ABCC2 to initiate pore formation in the insect gut membrane27. When different truncation mutations render the ABCC2 protein non-functional, the loss of this interaction leads to resistance23.
The goal of the current study was to find the gene responsible for Cry1Fa and Cry1A.105 resistance in S. frugiperda, which in turn can enhance IRM by providing genetic markers for monitoring, with the ultimate goal of combatting Bt resistance. Because of the phylogenetically widespread involvement of ABCC2 in resistance to the Cry1 family of proteins, we hypothesized that the reported resistance in S. frugiperda was likely due to a mutation in ABCC2. We tested this hypothesis on a Cry1Fa resistant colony collected from Puerto Rico, which also exhibits significant cross-resistance to Cry1A.105. We cloned the ABCC2 gene and discovered that the resistant colony harbored two mutant alleles of ABCC2, each resulting in a predicted truncation of the protein. We show that a) both mutant alleles co-segregated with resistance in a simple Mendelian fashion in a F2 mapping population, b) one allele conferred resistance in vitro in a cell-based assay for toxin activity, and c) ABCC2 peptides from resistant S. frugiperda could not be detected in the insect gut membrane in a quantitative proteomics assay. Finally, we screened several field populations from the Puerto Rico and Brazil for the presence of one ABCC2 mutant allele and detected its presence only in the populations from Puerto Rico.
Concurrent with this study, Banerjee et al.28, made many of the same discoveries, including the identification of one of the two resistance alleles we discovered. Our study also uncovered a unique resistance allele, making a total of two described alleles. Our work thus provides an immediate validation of the Banerjee et al.28 study, including arriving at the same conclusions using different methods. Our work is also complementary to Banerjee et al.28, because our geographic sampling differs from theirs and adds to our growing understanding of the nature of Cry1Fa and Cry1A.105 resistance in S. frugiperda.
Results
Establishment and characterization of a resistant colony
To understand the genetic mechanism of Cry1Fa and Cry1A.105 resistance in S. frugiperda, we first established a resistant colony. This colony was started with ~500 insects captured in non-Bt maize in Juana Diaz, Puerto Rico in 2010. Past reports indicated that S. frugiperda populations in Puerto Rico harbor high frequencies of resistance allele(s) to Cry1Fa and related Bt proteins5. The resistant colony (JuanaDiazR) was selected with the Cry1Fa toxin core (see Methods). After >50 generations of selection, characterization of the JuanaDiazR population suggested that it had >500-fold resistance to the Cry1Fa toxin core and 87-fold resistance to Cry1A.105, when compared to a susceptible colony (Supplementary Table S1).
Identification of candidate resistance mutations in S. frugiperda ABCC2
Test crosses between the JuanaDiazR resistant individuals and susceptible individuals obtained from Benzon Research (BenzonS) showed that the segregation of resistance among F1s was recessive and not sex linked (Supplementary Table S2). Moreover, after randomly mating F1s, their F2 progeny showed 3:1 susceptible:resistant phenotypic ratios, consistent with a recessive monogenic trait. Previous studies have shown that the ABCC2 gene is a strong candidate as the binding partner for members of the Cry1 family of toxins20,22–26. With this knowledge, we took a candidate gene approach and cloned and sequenced the S. frugiperda ABCC2 cDNA (SfABCC2) from the JuanaDiazR colony and compared it to a wild type allele from BenzonS. The JuanaDiazR population was found to harbor an allele with a two base pair + GC insertion 2,218 nucleotides from the start codon (Fig. 1). This mutation (referred to hereafter as R1) causes a frameshift which results in a premature stop codon 7 codons downstream from the insertion. The resulting protein is truncated to 747 amino acids, approximately half the length of the wild type SfABCC2 allele. This truncation removes the final 6 (of 12) transmembrane domains of the protein (Fig. 2), along with the second ATP binding cassette, and is identical to the SfABCC2mut allele described in Banerjee et al.28.
Figure 1.
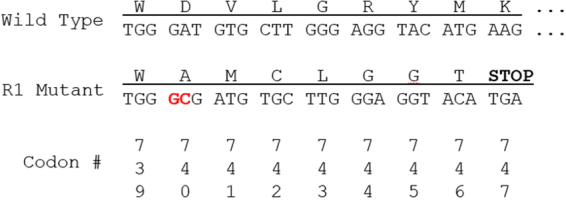
The diagram shows the amino acid (top) and codon (bottom) identities for the Wild Type and R1 mutant alleles of SfABCC2. The R1 mutant has a 2 bp GC insertion (highlighted in red) in the 740th codon, which causes a premature stop codon to arise at codon 747.
Figure 2.
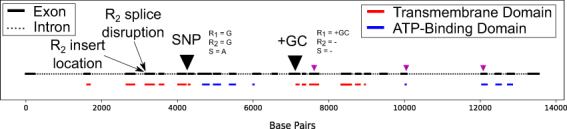
Schematic of representation of the SfABCC2 gene. The two-marker system (SNP and +GC) used to diagnose the three segregating haplotypes is presented on the structure of the SfABCC2 gene, along with the rubric used to identify each haplotype. This schematic applies to Family 1, however in Family 26 the S allele behaved dominantly, rather than codominantly, in R2S backgrounds, making it impossible to separate SS from R2S genotypes. The intron/exon structure of SfABCC2 is given, and the protein domains are color-coded and shown below their corresponding exons. The location of the R2 insert and splice disruption sites on exon 4 is also marked. Finally, three numbered magenta triangles mark the location of the putatively paralogous peptides detected in in the resistant individuals using LC-MS/MS. Their numbering is as follows 1) FFDTNPSGR, 2) SSLISALFR, and 3) SKISIIPQEPVLFSASLR.
We hypothesized that this large truncation of the SfABCC2 gene in the R1 allele would render the translated protein a non-functional Cry1Fa and Cry1A.105 toxin receptor. To test this hypothesis, we expressed both the truncated R1 allele and the wild type (WT) allele in S. frugiperda Sf9 cells and evaluated whether either conferred susceptibility to the Cry1Fa toxin core or Cry1A.105 using the SYTOX Green fluorescence assay (Table 1). This assay measures cell death, with greater fluorescence indicating greater cell death. In both assays, the WT allele conferred far greater susceptibility than the R1 allele (Welch’s t-test p-value 0.006 and 0.003, respectively, both with 4 df). This result provided preliminary evidence that the R1 allele may obstruct the Bt toxin mode of action, making it a candidate allele for Cry1Fa and Cry1A.105 toxin resistance.
Table 1.
SYTOX green fluorescence averages and standard deviations given in relative fluorescence units (RFU), for the wild type (WT) and R1 allele, and a GUS control.
| Toxin Core | Target Receptor | Average RFU | St. Dev. RFU | N |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cry1A.105 | WT | 14928 | 1352 | 3 |
| Cry1A.105 | R1 | 1225 | 98 | 3 |
| Cry1A.105 | GUS control | 493 | 108 | 3 |
| Cry1Fa | WT | 4283 | 550 | 3 |
| Cry1Fa | R1 | 260 | 44 | 3 |
| Cry1Fa | GUS control | 88 | 8 | 3 |
Increased SYTOX Green fluorescence is associated with greater cell death.
In the SYTOX Green fluorescence assay we also detect a difference between the R1 allele and the GUS control (Welch’s t-test p-values < 0.003 for Cry1Fa and Cry1A.105, both with 4 df), suggesting that he R1 allele confers a degree of susceptibility in this assay, though it is an order of magnitude less than the WT allele. Finally, we note that the resistance observed in the SYTOX Green fluorescence assay was only 16.5- and 12.1-fold, respectively, for Cry1Fa and Cry1A.105. This is lower than the >500- and 87-fold resistance observed in the larval bioassay for these toxins. However, we do not expect of proportional response between these assays, as they measure different phenotypes (cell death vs. organismal death) and likely have different sensitivities.
We also investigated if the SfABCC2 protein was expressed in the larval brush border membrane-bound protein fraction from both the JuanaDiazR and BenzonS colonies. Brush border membrane proteins were subjected to tryptic digestion and LC-MS/MS analysis to identify candidate peptides matching SfABCC2. Table 2 lists all peptides identified in susceptible and resistant samples. Our hypothesis was that the truncated R1 allele from the JuanaDiazR strain would be unable to insert in the brush border membrane. This was true for 28 of the 31 peptides we detected (Table 2). Unexpectedly, three peptides were identified in JuanaDiazR (FFDTNPSGR, SSLISALFR, and SKISIIPQEPVLFSASLR). However, all three peptides occur after the R1 mutation in the JuanaDiazR strain (Table 2 and Fig. 2), and should not be expressed. This suggests they may come from another gene. In support of this hypothesis, we found two closely related genes (GSSPFP00023863001_OGS1.0 and GSSPFP00033000001_OGS1.0) residing on different genomic contigs of the corn variant S. frugiperda genome29. The latter of these two genes is a near perfect match for our translated clone of the wild type SfABCC2 gene. Thus, the genome sequence provides evidence that the unexpected appearance of these three peptides in JuanaDiazR can be explained by expression from a closely related paralog in the ABCC family. A representative spectrum which shows the signal for the peptides that can be detected in the susceptible colony but not in the resistant colony is shown in Supp. Figure S1. The sequence map highlights the peptides which can be detected in the SfABCC2 protein. These results support the hypothesis that the truncated R1 allele is either absent from the brush border membrane or present at a level below LC-MS/MS detection.
Table 2.
Proportion among eight individuals from the BenzonS and JuanaDiazR population that were positive for 31 peptides from the SfABCC2 protein.
| Annotated Sequence | Susceptible Proportion Pos. | Resistant Proportion Pos. |
|---|---|---|
| [R].MSQVSVGDVAGGK.[L] | 0.75 | 0 |
| [K].YSPDDPPVLK.[D] | 0.25 | 0 |
| [K].VSEGGTNFSMGQR.[Q] | 0.875 | 0 |
| [R].ALEQVELKESIPALDYK.[V] | 0.75 | 0 |
| [R].ALEQVELK.[E] | 0.625 | 0 |
| [K].MYAWEKPFQLVVK.[A] | 1 | 0 |
| [K].DMGAMDELLPR.[S] | 0.375 | 0 |
| [R].SKISIIPQEPVLFSASLR.[Y] | 1 | 0.125 |
| [R].ENILFGLEYNVAK.[Y] | 0.75 | 0 |
| [R].QSGSLKWDVLGR.[Y] | 0.25 | 0 |
| [R].AYEMSALR.[K] | 0.625 | 0 |
| [K].SSLISALFR.[L] | 0.75 | 0.875 |
| [R].YWFEEVAIAEREDRDPSLWK.[A] | 1 | 0 |
| [R].IKLMSEIINGIQVIK.[M] | 0.5 | 0 |
| [R].IQGFLLLDER.[S] | 0.75 | 0 |
| [K].TSLLQLLLR.[E] | 0.75 | 0 |
| [R].SDIQITPK.[V] | 0.375 | 0 |
| [K].LMSEIINGIQVIK.[M] | 0.625 | 0 |
| [R].LSDITGSIKIDGLDTQGIAK.[K] | 0.25 | 0 |
| [R].FFDTNPSGR.[V] | 0.875 | 0.5 |
| [R].DVEEDDLIVPSK.[K] | 0.75 | 0 |
| [K].IAASSLLFR.[K] | 0.625 | 0 |
| [K].ILIMDEATANVDPQTDALIQK.[T] | 0.125 | 0 |
| [K].DLNFAIK.[S] | 0.5 | 0 |
| [K].IDGLDTQGIAK.[K] | 0.5 | 0 |
| [R].GVSLSGGQR.[AX] | 0.625 | 0 |
| [R].ASENLHNTIYEK.[L] | 0.75 | 0 |
| [K].VNATWADLNDNKEMTLK.[N] | 0.25 | 0 |
| [R].ILFEVAK.[T] | 1 | 0 |
| [K].SDDEEGEEKVQVLEAEER.[Q] | 0.75 | 0 |
| [K].LVNLLSNDVAR.[F] | 0.25 | 0 |
R1 mutation is not fixed in JuanaDiazR population
To determine the frequency of the R1 allele in the JuanaDiazR population, we developed a genetic marker assay to distinguish it from wild type and genotyped 48 randomly selected individuals from the JuanaDiazR colony. We found 2 WT/WT, 18 R1/WT, and 28 R1/R1 individuals. This results in an estimated R1 allele frequency of 77%, indicating that the R1 allele was not fixed in the JuanaDiazR population. If we assume R1 was the only resistance allele in the JuanaDiazR population and that it was recessive, then given the R1 allele frequency we would predict that approximately 41% of the individuals in the JuanaDiazR colony would be susceptible (i.e. either WT/WT or R1/WT genotypes) under Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. This prediction was inconsistent with the results of our test crosses, and with the many generations of selection the JuanaDiazR colony had been through. We hypothesized that the JuanaDiazR population harbored two (or more) distinct resistance alleles, including the R1 allele we first identified and a second resistance allele (R2), which had not yet been functionally characterized. Moreover, if the hypothesized R2 allele is observed at approximately 23% allele frequency in the JuanaDiazR population, then the R1 and R2 alleles would be in Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium (χ2 = 0.18, df = 2, p-value = 0.91), which would further support the existence of R2.
Co-segregation of R1 and R2 alleles with Bt Protein resistance
To test if the R1 allele and the hypothesized R2 allele were genetically linked with resistance, we constructed segregating populations through single pair matings by crossing a single JuanaDiazR resistant parent with a susceptible BenzonS parent (Fig. 3). In total 30 crosses were initiated and 16 successfully mated. After mating, the resistant colony parents from the 16 successful crosses were genotyped. For 14 pairs the resistant parent was the R1R1 genotype, and these pairs were discarded. We identified two pairs (#1 and #26) where the resistant parent was heterozygous for the R1 allele. These two resistant parents were putatively the R1R2 genotype. Within both families, F1 siblings were randomly bulk-mated to produce a segregating F2 population. The expected genotypic ratios of the F2 population can be found in Fig. 3. The key feature of this mating design is that it will produce R1R1, R1R2, and R2R2 genotypes, which allows us to determine if either allele co-segregates with resistance, and whether the alleles complement one another.
Figure 3.
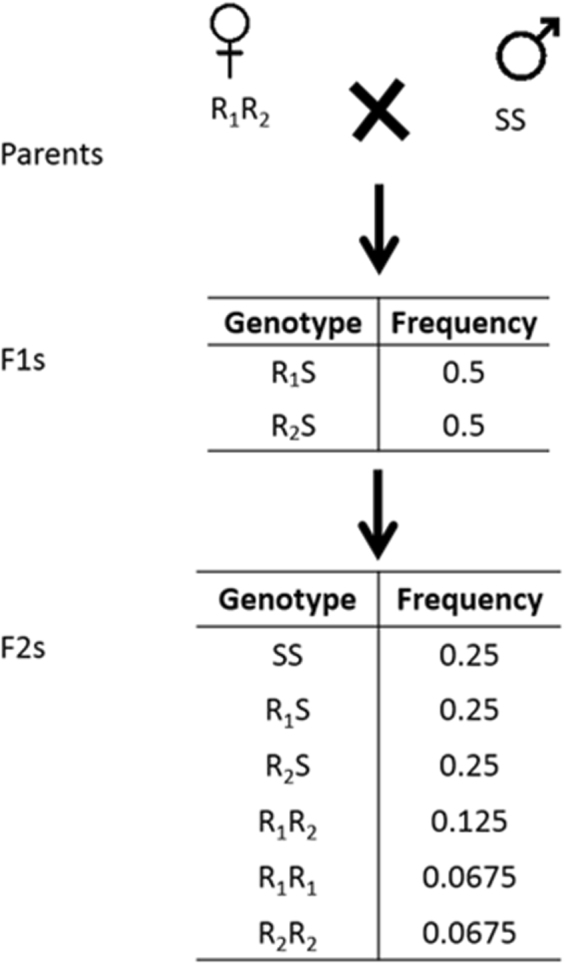
Mating scheme and expected genotype frequencies for Family 1 and 26, which had a heterozygous R1R2 resistant parent.
We lacked a genetic marker for the R2 allele, so we sampled both the susceptible and resistant parents and found a diagnostic SNP in SfABCC2 gene. We do not believe that this SNP is itself associated with resistance, however, it allowed us to differentiate the R2 allele from the susceptible wild type allele. Also, because this SNP was only approx. 2,700 base pairs from the GC insertion site (Fig. 2), we can reasonably assume that it is unlikely for a recombination event to occur between these markers within the F2 mapping populations. This assumption allowed us to use these two codominant markers to diagnose the three allelic haplotypes (R1, R2, and S) segregating in the F2 mapping population (Fig. 2). The R1 haplotype was inferred present when an individual tested positive for the GC insertion at the R1 marker and had the G allele at the R2 marker. The R2 allele haplotype was inferred as the combination of the wild type allele at the R1 marker and the G allele for the R2 marker. Finally, the wild type susceptible (S) haplotype was inferred when the wild type allele was detected at R1 and the A allele at the R2 marker (Fig. 2). A further complication arose in family 26, where the marker assay for the S genotype was functionally dominant to the R2 genotype. For this family, we found an absence of the R2/S genotype. At the same time, we found a complementary excess of the S/S genotype (Table 3). A simple explanation for this result is that the S marker behaves dominantly in the R2/S background in family 26, confounding these genotypes. However, because this confounded class is highly susceptible (Table 3), there is no need to differentiate them into genotypic classes to interpret the experiment.
Table 3.
F2 genotype and phenotype results for family #1 (top panel) and #26 (bottom panel).
| Observed Genotype | Family 1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resistant Individuals | Susceptible Individuals | Expected Freq | Observed Freq | |
| R1R1 | 40 | 0 | 0.0625 | 0.0917 |
| R1R2 | 57 | 0 | 0.125 | 0.1307 |
| R2R2 | 24 | 0 | 0.0625 | 0.0550 |
| R1S | 5 | 125 | 0.25 | 0.2982 |
| R2S | 1 | 89 | 0.25 | 0.2064 |
| SS | 0 | 95 | 0.25 | 0.2179 |
| Total | 127 | 309 | ||
| Observed Genotype | Family 26 | |||
| Resistant Individuals | Susceptible Individuals | Expected Freq | Observed Freq | |
| R1R1 | 34 | 0 | 0.0625 | 0.0658 |
| R1R2 | 61 | 2 | 0.125 | 0.1219 |
| R2R2 | 40 | 1 | 0.0625 | 0.0793 |
| R1S | 1 | 107 | 0.25 | 0.2089 |
| R2S | 0 | 0 | 0.25 | 0 |
| SS | 2 | 269 | 0.25 | 0.5242 |
| Total | 138 | 379 | ||
The genotype categories are listed on the rows, while phenotypic results are given in the second and third columns. The fourth and fifth columns list the Hardy-Weinberg expected genotype frequencies and the observed frequencies, respectively, for each genotype.
For families 1 and 26 we phenotyped 436 and 517 F2s, respectively, for their sensitivity to the Cry1Fa toxin core. As anticipated for a recessive trait, both F2 families segregated at approximately 3:1 susceptible:resistant ratios (Table 3). All individuals were genotyped and the R1, R2, and S haplotypes were inferred. In both families, the co-segregation of either allele with resistance was highly significant (Chi-Squared p-value < 0.001). Moreover, the R1R2 heterozygote class was resistant in both families, indicating that the R1 and R2 are complementary recessive resistance alleles of the SfABCC2 gene.
In both families we see a small number of apparently misclassified individuals (e.g. R1S individuals who were phenotypically resistant). The most likely explanation for these individuals is that they are genotyping or phenotyping errors, similar to those seen by Coates and Siegfried24. However, in the diamondback moth (Plutella xylostella), Cry1Ac resistance was mapped to a locus containing several tightly linked candidate genes including five ABCC genes, and three MAP kinases, and two P450 genes30. Functional analyses were required to rule out the ABCC genes, and to implicate one of the MAP kinases. Analogous to this result, it is possible that resistance in S. frugiperda is conferred by a gene tightly linked to SfABCC2. Under this scenario, if all the misclassified individuals are taken at face-value, then we can infer that the true resistance gene must be approximately 0.63 cM from SfABCC2. There is strong evidence that SfABCC2 is itself the likely resistance gene for Cry1Fa and Cry1A.105, however further work would be needed to rule out very closely linked genes24.
After establishing that R2 is a candidate resistance allele, we next investigated the mutational mechanism behind this allele. To do this we first isolated 10 F2 individuals with the R2/R2 genotype, along with 10 control individuals with the S/S and R1/R1 genotypes from family #1 and family #26. We then extracted RNAs, converted to cDNA, and cloned and sequenced the SfABCC2 transcripts. cDNAs from all R2/R2 individuals exhibited a unique form of aberrant splicing approximately 600 nucleotides into the transcript (Figs 2 and S2). Most clones from the R2/R2 individuals were spliced slightly differently, but all cDNAs clones had a deletion of coding sequence relative to the wild type S/S individuals that created a missense mutation downstream (Supp. Figure S2). We next extracted genomic DNA from these same R2/R2 individuals, along with the S/S and R1/R1 controls, and identified an insertion near the start of the fourth exon unique to R2 (Figs 2 and S3). We were only able to gene walk 60 bp into this insertion before we hit a highly repetitive sequence and could no longer design unique PCR primers. Thus, we do not know the full size of the unique R2 insertion, but all S/S and R1/R1 control individuals lack it and we think it is likely that it is responsible for the aberrant splicing of R2. Similar to this scenario, aberrant splicing in a cadherin gene has been linked to Cry1Ac resistance in pink bollworm (Pectinophora gossypiella) in India31.
Frequency of the R1 mutation in natural populations
Using the R1 marker described above, we genotyped several Puerto Rican and Brazilian S. frugiperda populations. In total, we screened 461 individuals (922 alleles) for presence of the +GC mutation that characterizes the R1 allele using the Taqman marker described above (Table 4). The R1 allele was only found in Puerto Rico, where it was at an intermediate to high frequency depending on location. The R1 allele was completely absent in the Brazilian populations tested, despite sampling 144 individuals, many coming from populations with appreciable phenotypic resistance to Cry1A.105 (Table 4). The absence of the R1 allele in Brazilian populations could indicate that either these populations have distinct, and yet undiscovered, mutations in SfABCC2, or possibly that resistance is not mediated by the mutations in the SfABCC2 there. Further studies will be needed to determine which of these possibilities is correct.
Table 4.
Geographic sampling of +GC allele. All Brazilian populations of S. frugiperda were subjected to Cry1A.105 assays and their survivorship is given. The column labled N gives the number of individuals genotyped.
| Country | Location (State) | Year | N | +GC Allele Freq. | % Survivorship (Cry1A.105) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brazil | Campo Grande (MS) | 2016 | 10 | 0 | 57.5 |
| Brazil | Campo Verde (MT) | 2016 | 10 | 0 | 43.6 |
| Brazil | Casa Branca (SP) | 2016 | 10 | 0 | 7.8 |
| Brazil | Casa Branca (SP) | 2016 | 10 | 0 | 18.9 |
| Brazil | Ivatuba (PR) | 2016 | 10 | 0 | 15.0 |
| Brazil | Londrina (PR) | 2016 | 10 | 0 | 52.6 |
| Brazil | Não-me-Toque (RS) | 2016 | 10 | 0 | 4.0 |
| Brazil | Palotina (PR) | 2016 | 10 | 0 | 25.3 |
| Brazil | Ponta Grossa (PR) | 2016 | 10 | 0 | 31.2 |
| Brazil | Rio Verde (GO) | 2016 | 10 | 0 | 25.9 |
| Brazil | Santa Helena de Goiás (GO) | 2016 | 10 | 0 | 19.0 |
| Brazil | Santo Ângelo (RS) | 2016 | 10 | 0 | 56.3 |
| Brazil | Sapezal (MT) | 2016 | 4 | 0 | 46.0 |
| Brazil | Seara (SC) | 2016 | 10 | 0 | 0.0 |
| Brazil | Água Fria de Goiás (GO) | 2016 | 10 | 0 | 38.8 |
| USA | Benzon-JuanaDiazR (PR) | 2010 | 48 | 0.77 | NA |
| USA | Juana Diaz (PR) | 2015 | 177 | 0.88 | NA |
| USA | Isabella (PR) | 2015 | 49 | 0.48 | NA |
| USA | Unknown (PR)* | 2011 | 43 | 0.32 | NA |
*Samples provided by Fengneng Huang4.
Discussion
Bt crops represent one of the most rapidly adopted technologies for managing insect pests in maize, cotton, and soybean. The evolution of insect resistance to these crops is a major threat to their sustainability. Indeed, in two decades of Bt crop of cultivation, several insect species have developed resistance resulting in field control failures32,33. S. frugiperda is one such insect. It has developed resistance to Bt maize expressing the Cry1Fa protein in Puerto Rico5, the US mainland4, and Brazil11, with cross-resistance to Cry1A.105. Many studies have been conducted on various aspects of resistance to Cry1 family proteins in S. frugiperda, including inheritance, fitness costs, frequency of resistant alleles, resistance mechanism, allelic variation, and cross resistance to other Bt proteins4–6,8,9,11,34–36. Recently, Banerjee et al.28 performed competitive binding assays demonstrating that SfABCC2 is a receptor for Cry1F1. Here, we report confirmation of SfABCC2 as a receptor protein for Cry1Fa and Cry1A.105, and identify mutations causing resistance in a population collected from Juana Diaz, Puerto Rico.
Receptors play a significant role in mode of action of Bt proteins. Several classes of proteins (cadherins, ABC transporters, aminopeptidases, alkaline phosphatase) have been reported as Bt protein receptors in insects23. Mutations in these receptor proteins leading to reduced or no Bt protein binding have been reported to cause resistance in many insects22–25,28. Previous studies by Jakka et al.34 with Cry1Fa resistant S. frugiperda reported reduced binding of Cry1Fa, Cry1Ab and Cry1Ac but not Cry1Ca compared to a susceptible colony. They also observed an associated reduction in a membrane-bound alkaline phosphatase (ALP), which suggested that this gene might be a candidate for the Cry1Fa and Cry1A.105 resistance locus.
In addition to ALP, the ABCC2 gene was a strong candidate due to its involvement in Cry1 protein family resistance in diverse lepidopteran species20–24,26, including S. exigua24,25, a close relative of S. frugiperda. Because of this strong prior evidence, we decided to focus first on SfABCC2, and as demonstrated above, we found compelling evidence that when mutated it is responsible for Cry1Fa and Cry1A.105 resistance.
Concurrent to our studies, researchers from J. L. Jurat-Fuentes’ laboratory have reported the identification of SfABCC2 as a receptor protein for Cry1Fa and mutations resulting in field resistance28. These authors also discovered a mutant allele called SfABCC2mut, which is the same as our R1 allele, (i.e. a two base pair GC insertion at nucleotide 2,218). Consistent with our findings, these authors established that this mutation disrupts translation, creating a partial protein which does not function as a Cry1Fa or Cry1A.105 receptor. The results from our work and those of Banerjee et al.28 have come to the same conclusion, despite working with populations collected at different times, selected/maintained differently and studied with different methods.
Furthermore, where Banerjee et al.28 explore the temporal and spatial distribution of resistance alleles in North America, our study explores their spatial distribution in both North and South America, adding additional geographical data. Similar to the conclusions from Banerjee et al.28 in North America, our results show an absence of the SfABCC2mut/R1 resistance allele in samples from Brazil. Together these results suggest that Cry1Fa and Cry1A.105 resistance in S. frugiperda may develop repeatedly in local populations, rather than infrequently and spread to new areas via long distance migration4. The resistance alleles found in Puerto Rico may be private alleles that came to high frequency in this island population. This is consistent with results from other species. For example, there are three known mutations in the ABCa2 gene which cause resistance to Cry2Ab in Helicoverpa armigera37, and cadherin mutations observed in laboratory developed Cry1Ac-resistant Pectinophora gossypiella in Arizona38 were different from those observed in field resistant colonies in India31. Consistent with these past studies, our work, and that of Banerjee et al.28, demonstrates that strong resistance to Cry1Fa and Cry1A.105 can evolve through simple loss-of-function mutations to SfABCC2. There are likely a large number of mutations that can render SfABCC2 nonfunctional as a Bt receptor, so it is not surprising to have new resistance alleles being created at a steady rate in nature. The occurrence of many resistant alleles, even in the same gene, limits the utility of DNA marker-based detection methods for resistance monitoring. Therefore, alternative methods, such as protein-based assays to identify disrupted receptor proteins or whole gene sequencing techniques to identify new mutations should be explored.
Methods
Insects
Eggs from a susceptible laboratory population were received from Benzon Research Laboratory (Carlisle, PA). A resistant colony was established in 2010 through larvae collected on non-Bt maize from Juana Diaz, Puerto Rico (JuanaDiazR). This colony was crossed with the susceptible colony (BenzonS) and selected using TIC842, a Cry1Fa-like Bt protein consisting of toxin domains I-III from Cry1Fa and a protoxin domain from Cry1Ac. Although this is a chimeric protein, insects are effectively selected against the activated Cry1Fa toxin core as the Cry1Ac protoxin domain is cleaved within in the insect gut. Similarly, the Bt event TC1507 expresses a truncated Cry1Fa, exposing insects to only activated Cry1Fa toxin core39, meaning that TIC842 presents the same Cry1Fa toxin core to the insect gut as does TC1507 and represents an equivalent selection pressure. For these reasons we refer to TIC842 as the Cry1Fa toxin core throughout this manuscript. The bouts of selection were conducted in alternative generations through exposing larvae to diet surface-treated with TIC842 at 2.0 µg/cm2 concentration for 7 D and rearing surviving second instar larvae to the pupal stage on non-treated diet. Characterization of this strain indicated >579-fold resistance to TIC842 (i.e. the Cry1Fa toxin core) and >87-fold cross-resistance to Cry1A.105 (Supplemental Table S1). Resistance was stable when insects were removed from selection for up to two generations (Supplemental Figure S4) and showed recessive inheritance (Supplementary Table S2).
Cloning and Sequencing ABCC2 from BenzonS and JuanaDiazR Colony
Gut tissues were dissected from 5 third instar S. frugiperda larvae from both populations (JuanaDiazR and BenzonS) and pooled within population. RNA was extracted from each pool following the AllPrep DNA/RNA mini kit manual from Qiagen (Hilden, Germany). First strand cDNA was synthesized using the GeneRacerTM Kit from Invitrogen. ABCC2 coding sequence was amplified from cDNA with primers given in Supp. Table S3. PCR products were cloned into the pIEx/BacTM-3 vector from Novagen (Damstadt, Germany). Plasmid DNA was extracted by following QIAprep Spin Miniprep Kit manual (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), and sequenced by Sanger sequencing. Sequences were translated into amino acids and manually inspected for mutations. These cDNA sequences can be found on Genbank under accessions MG387043-MG387070.
Recombinant Baculovirus Generation and Cell-Based Assay
Recombinant baculovirus for mutant and wildtype ABCC2 expression in Sf9 cells were generated using the BacMagicTM-3 DNA kit (Novagen, Damstadt, Germany). Sf9 cells were cultured in SF900III SFM medium in a refrigerated incubator/shaker at 27 °C and 150 rpm. The culture was diluted to a cell density of 5 × 105 cells/ml in growth medium and were seeded on 96 well black cell culture plates (catalog# 165305, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) with 100 ul/well. The seeded plates were incubated in a 27 °C incubator for cell recovery. To express ABCC2, the growth medium was removed after cell recovery, and 100 ul recombinant baculovirus (1 µl virus plus 99 ul SF900III SFM) was added to each well. After 48 h expression in 27 °C incubator, the medium was changed to the toxin mixture (50 ppm toxin + 2 µM SYTOX Green (catalog # S7020, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA)) in unsupplemented Grace’s medium (catalog # 11595030, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). Cells were incubated with toxins for 4 h in 27 °C incubator, and then SYTOX Green fluorescence intensity was read by a CLARIOstar microplate reader (BMG Labtech, Offenburg, Germany). Recombinant baculovirus expressing β-glucuronidase (GUS) was used as virus control.
Taqman Marker Design
To genotype ABCC2 alleles, we used Taqman genotyping assays (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA). Genotyping primer sets are given in Supp. Table S3. All genotype assays were carried out following the manufacturers instructions.
Cloning R2 allele
We extracted RNA from 10 individuals from the F2 mapping population with the R2R2 genotype and converted to cDNA as described above. cDNAs were then cloned and sequenced using Sanger sequencing. These cDNA sequences can be found on Genbank under accessions MG387043-MG387070.
Phenotypic assay for resistance
Lepidopteran larvae typically have alkaline gut pH which will change to acidic pH when midgut epithelial cells are damaged (e.g. Bt protein interaction with receptors) leading to exchange of cell contents with gut lumen. We developed a highly sensitive phenotyping assay using thymol blue, an indicator dye to measure midgut pH in S. frugiperda. The larvae are fed on the diet containing thymol blue and those that have intact midguts will maintain alkaline pH and retain the blue color in the midgut while larvae that have a compromised gut will lose the blue color and appear to have clear midguts. Using this assay one can identify resistant and susceptible larvae based on their response to given Bt protein.
Preliminary experiments were conducted to identify a diagnostic concentration to separate resistant and susceptible larvae. In this study, larvae were first exposed to diet containing thymol blue for 24 h and then transferred to diet containing thymol blue and surface treated with 11 concentrations of TIC842 ranging from 5.26 to 5.26 × 10−20 µg/cm2 for 4 h. Larvae were scored visually for the midgut coloration and the experiment was continued for 5 D, and scored for mortality to correlate early and endpoint responses. Based on these results (Supp. Figure 5), 0.526 µg/cm2 was selected as a diagnostic concentration. Following this protocol, F2 larvae from mapping populations were exposed to diet containing thymol blue for 24 h and then to diet containing thymol blue and surface treated with TIC842 at 0.526 µg/cm2 for 4 h. Phenotyped larvae were transferred to untreated diet, reared until third instar and used for genetic studies.
Brush Border Membrane Preparation for Mass Spectrometry
Brush border membrane vesicles were isolated from neonates following Wolfersberger et al.40. Neonates were homogenized with a polytron mister in buffer containing 5 mM TRIS (pH 7.4), 50 mM sucrose with lipase inhibitor, PMSF and protease inhibitor cocktail at 16,000 rpm for three 10 sec pulses. In presence of CaCl2, the samples were transferred and centrifuged at 4300 g and 4 °C for 30 min. The supernatant was filtered through 4 layers of cheese cloth and centrifuged at 27,000 g and 4 °C for 30 min. The pellet was dried and resuspended in sucrose buffer. Protein concentration of the 6 BBM samples was determined by Bradford assay (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA) according to manufacturer’s protocol. The BBM were quality tested using alkaline phosphatase and leucine aminopeptidase enzyme assays. 50ug brush border membrane protein sample was reduced and digested with trypsin using proteome CEM Discover Proteomics System (Matthews, NC, USA). The resulting peptides were acidified with formic acid to pH < 3 to stop the reaction.
Data Acquisition by Nano-Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry and Protein Identification. Peptides were analyzed on an Ultimate 3000 nanoLC system connected with nanospray Q-Exactive HF Orbitrap MS (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) operated in Full MS/ddMS2 mode. The data were collected with the installed Xcalibur software (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). The binary mobile phase was used consisting of 0.1% formic acid in water or 80% acetonitrile. A flow rate of 5 µl/min was used to load the sample onto a C18 PepMap trap column (300 μm ID × 5 mm, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). The peptides were eluted from the trap column and separated at a flow rate of 300 nL/min on a C18 Tip column (75 μm ID × 150 mm, Acclaim PepMap@RSLC, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) with a spray voltage of 1.9 kV. The gradient was run with 10−30% B in 40 min for elution. Full-scan mass spectra were acquired in the Orbitrap over a mass range of 400−1,600 m/z with a resolution of 120,000 at AGC target 3 × 106. A lock mass function was used to obtain high mass accuracy. The 12 most intense precursor ions were selected for collision-induced fragmentation with normalized collision energy of 27% with a resolution of 15,000 with AGC target as 1 × 105. For each sample, the injection volume was adjusted per the protein assay to load 1 µg on column. Three technical replicates were applied with each sample.
Proteins were identified by the Proteome Discoverer (version 1.4; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). The S. frugiperda protein database (1,786 sequences) from uniport was combined with a S. frugiperda ABCC2 (SfABCC2) protein sequence (Supp. Figure S1) and a reversed decoy database was used for comparison. Data files were generated from acquired raw data files with Thermo Xcalibur. The protein identifications were filtered in Proteome Discoverer retaining only proteins that contained at least three peptides with XCorr scores above the threshold. The data include only rank 1 peptides and peptides in the top scored proteins. Parameters used in searches were as follows: Carbamidomethylation of cysteine and oxidation of methionine were set as modifications. Trypsin was specified as the proteolytic enzyme, and one missed cleavage was allowed. Peptide mass tolerance was set at 10 ppm, fragment mass tolerance was set at 0.6 Da, and peptide charge was set at + 2, +3, and +4. False discovery rates for peptide identification of all searches were less than 5.0%. For three biological samples each, three technical replicates were applied.
Electronic supplementary material
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Prof. Juan Luis Jurat-Fuentes for sharing prepublication results, and Prof. Fengneng Huang for providing access to a resistant colony. Dedicated to the memory of John Greenplate. This work would not have been possible without John’s intelligence, experience, and friendship.
Author Contributions
L.F., Y.W.L., J.H., J.G., A.G., and G.H. designed the research plan. L.F. and Y.W.L. devised insect mating designs. L.F., Y.W.L., H.W., S.S., and A.B. designed and implemented the genotyping assays. J.G., J.S., and N.A. performed insect rearing and crosses. A.G. performed insect phenotyping assays. J.W. and E.K. cloned SfABCC2 and performed cell-based assays. Y.W. and J.H. designed and performed proteomic assays. S.M., A.G., and G.H. collected insect populations. L.F., Y.W.L., J.H., A.G., and G.H. drafted the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Competing Interests
The authors are employed by Monsanto Company, or were employed by Monsanto Company while the work on this project was conducted. Monsanto Company manufactures maize containing the Cry1Fa and Cry1A.105 proteins. Some authors are also shareholders in Monsanto Company, although individually or collectively in no way represent any controlling interest in the affairs of Monsanto Company. Results described in the manuscript are the product of work financed by Monsanto Company and the publication fees were paid by Monsanto Company.
Footnotes
Lex Flagel and Young Wha Lee contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary information accompanies this paper at 10.1038/s41598-018-25491-9.
Publisher's note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Sparks AN. A review of the biology of the Fall Armyworm. Fla Entomol. 1979;62:82–87. doi: 10.2307/3494083. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Cruz I, Turpin FT. Yield Impact of Larval Infestations of the Fall Armyworm (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) to Midwhorl Growth Stage of Corn 1. J Econ Entomol. 1983;5:1052–1054. doi: 10.1093/jee/76.5.1052. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Yu SJ. Insecticide resistance in the fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda (J. E. Smith) Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology. 1991;39:84–91. doi: 10.1016/0048-3575(91)90216-9. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Huang F, et al. Cry1F resistance in Fall Armyworm Spodoptera frugiperda: single gene versus pyramided Bt maize. PLoS ONE. 2014;9:e112958. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0112958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Storer NP, et al. Discovery and characterization of field resistance to Bt maize: Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in Puerto Rico. J Econ Entomol. 2010;103:1031–1038. doi: 10.1603/EC10040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Storer, N. P., Kubiszak, M. E., Ed King, J., Thompson, G. D. & Santos, A. C. Status of resistance to Bt maize in Spodoptera frugiperda: Lessons from Puerto Rico. Journal of Invertebrate Pathology110, 294–300, (2012). [DOI] [PubMed]
- 7.Buntin GD, Lee RD, Wilson DM, McPherson RM. Evaluation of Yieldgard Transgenic Resistance for Control of Fall Armyworm and Corn Earworm (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) on Corn. The Florida Entomologist. 2001;84:37–42. doi: 10.2307/3496660. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Monnerat R, et al. Evidence of field-evolved resistance of Spodoptera frugiperda to Bt corn expressing Cry1F in Brazil that is still sensitive to modified Bt toxins. PLoS ONE. 2015;10:e0119544. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Hernández-Rodríguez CS, Hernández-Martínez P, Van Rie J, Escriche B, Ferré J. Shared Midgut Binding Sites for Cry1A.105, Cry1Aa, Cry1Ab, Cry1Ac and Cry1Fa Proteins from Bacillus thuringiensis in Two Important Corn Pests, Ostrinia nubilalis and Spodoptera frugiperda. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e68164. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0068164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Santos-Amaya, O. F. et al. Resistance to dual-gene Bt maize in Spodoptera frugiperda: selection, inheritance, and cross-resistance to other transgenic events. 5, 18243 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 11.Farias JR, et al. Field-evolved resistance to Cry1F maize by Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in Brazil. Crop Protection. 2014;64:150–158. doi: 10.1016/j.cropro.2014.06.019. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Head GP, Greenplate J. The design and implementation of insect resistance management programs for Bt crops. GM crops & food. 2012;3:144–153. doi: 10.4161/gmcr.20743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Roush, R. T. & Daly, J. C. The role of population genetics in resistance research and management. In Pesticide resistance in arthropods. Ch. 5, 97–152 (Chapman and Hall, 1990).
- 14.Bates SL, Zhao J-Z, Roush RT, Shelton AM. Insect resistance management in GM crops: past, present and future. Nat Biotech. 2005;23:57–62. doi: 10.1038/nbt1056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Gahan LJ, Gould F, Heckel DG. Identification of a Gene Associated with Bt Resistance in Heliothis virescens. Science. 2001;293:857–860. doi: 10.1126/science.1060949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Fabrick JA, Tabashnik BE. Binding of Bacillus thuringiensis toxin Cry1Ac to multiple sites of cadherin in pink bollworm. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. 2007;37:97–106. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2006.10.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Morin S, et al. Three cadherin alleles associated with resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis in pink bollworm. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 2003;100:5004–5009. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0831036100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Yang Y, Chen H, Wu Y, Yang Y, Wu S. Mutated Cadherin Alleles from a Field Population of Helicoverpa armigera Confer Resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis Toxin Cry1Ac. Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 2007;73:6939–6944. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01703-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Zhao J, Jin L, Yang Y, Wu Y. Diverse cadherin mutations conferring resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis toxin Cry1Ac in Helicoverpa armigera. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. 2010;40:113–118. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2010.01.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Atsumi S, et al. Single amino acid mutation in an ATP-binding cassette transporter gene causes resistance to Bt toxin Cry1Ab in the silkworm. Bombyx mori. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2012;109:E1591–E1598. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1120698109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Xiao Y, et al. Mis-splicing of the ABCC2 gene linked with Bt toxin resistance in Helicoverpa armigera. Scientific Reports. 2014;4:6184. doi: 10.1038/srep06184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Gahan LJ, Pauchet Y, Vogel H, Heckel DG. An ABC transporter mutation is correlated with insect resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Ac toxin. PLoS Genet. 2010;6:e1001248. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1001248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Heckel DG. Learning the ABCs of Bt: ABC transporters and insect resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis provide clues to a crucial step in toxin mode of action. Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology. 2012;104:103–110. doi: 10.1016/j.pestbp.2012.05.007. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Coates BS, Siegfried BD. Linkage of an ABCC transporter to a single QTL that controls Ostrinia nubilalis larval resistance to the Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Fa toxin. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. 2015;63:86–96. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2015.06.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Park Y, et al. ABCC transporters mediate insect resistance to multiple Bt toxins revealed by bulk segregant analysis. BMC Biology. 2014;12:46. doi: 10.1186/1741-7007-12-46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Baxter SW, et al. Parallel Evolution of Bacillus thuringiensis Toxin Resistance in Lepidoptera. Genetics. 2011;189:675–679. doi: 10.1534/genetics.111.130971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Bravo A, Gill SS, Soberón M. Mode of action of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry and Cyt toxins and their potential for insect control. Toxicon. 2007;49:423–435. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2006.11.022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Banerjee R, et al. Mechanism and DNA-based detection of field-evolved resistance to transgenic Bt corn in fall armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda) Scientific Reports. 2017;7:10877. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-09866-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Gouin A, et al. Two genomes of highly polyphagous lepidopteran pests (Spodoptera frugiperda, Noctuidae) with different host-plant ranges. Scientific Reports. 2017;7:11816. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-10461-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Guo Z, et al. MAPK Signaling Pathway Alters Expression of Midgut ALP and ABCC Genes and Causes Resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Ac Toxin in Diamondback Moth. PLoS Genet. 2015;11:e1005124. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Fabrick JA, et al. Alternative splicing and highly variable cadherin transcripts associated with field-evolved resistance of pink bollworm to Bt cotton in India. PLOS ONE. 2014;9:e97900. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0097900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Tabashnik BE, Brevault T, Carriere Y. Insect resistance to Bt crops: lessons from the first billion acres. Nat Biotech. 2013;31:510–521. doi: 10.1038/nbt.2597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Tabashnik BE, Gassmann AJ, Crowder DW, Carriere Y. Insect resistance to Bt crops: evidence versus theory. Nat Biotech. 2008;26:199–202. doi: 10.1038/nbt1382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Jakka SRK, Knight VR, Jurat-Fuentes JL. Fitness costs associated with field-evolved resistance to Bt maize in Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) Journal of Economic Entomology. 2014;107:342–351. doi: 10.1603/EC13326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Santos-Amaya OF, et al. Genetic basis of Cry1F resistance in two Brazilian populations of fall armyworm. Spodoptera frugiperda. Crop Protection. 2016;81:154–162. doi: 10.1016/j.cropro.2015.12.014. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Vélez AM, et al. Inheritance of Cry1F resistance, cross-resistance and frequency of resistant alleles in Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) Bulletin of Entomological Research. 2013;103:700–713. doi: 10.1017/S0007485313000448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Tay WT, et al. Insect resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis toxin Cry2Ab is conferred by mutations in an ABC transporter subfamily A protein. PLOS Genetics. 2015;11:e1005534. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Tabashnik BE, et al. DNA screening reveals pink bollworm resistance to Bt cotton remains rare after a decade of exposure. Journal of Economic Entomology. 2006;99:1525–1530. doi: 10.1093/jee/99.5.1525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Dow AgroSciences L. L. C. Petition for the determination of non-regulated status B.t. Cry1F insect resistant, glufosinate tolerant maize line. http://www.aphis.usda.gov/brs/aphisdocs/00_13601p.pdf (2000).
- 40.Wolfersberger M, et al. Preparation and partial characterization of amino acid transporting brush border membrane vesicles from the larval midgut of the cabbage butterfly (Pieris brassicae) Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part A: Physiology. 1987;86:301–308. doi: 10.1016/0300-9629(87)90334-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


