Abstract
Degeneration or loss of inner ear hair cells (HCs) is irreversible and results in sensorineural hearing loss (SHL). Human-induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs) have been employed in disease modelling and cell therapy. Here, we propose a transcription factor (TF)-driven approach using ATOH1 and regulatory factor of x-box (RFX) genes to generate HC-like cells from hiPSCs. Our results suggest that ATOH1/RFX1/RFX3 could significantly increase the differentiation capacity of iPSCs into MYO7AmCherry-positive cells, upregulate the mRNA expression levels of HC-related genes and promote the differentiation of HCs with more mature stereociliary bundles. To model the molecular and stereociliary structural changes involved in HC dysfunction in SHL, we further used ATOH1/RFX1/RFX3 to differentiate HC-like cells from the iPSCs from patients with myoclonus epilepsy associated with ragged-red fibres (MERRF) syndrome, which is caused by A8344G mutation of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA), and characterised by myoclonus epilepsy, ataxia and SHL. Compared with isogenic iPSCs, MERRF-iPSCs possessed ~42–44% mtDNA with A8344G mutation and exhibited significantly elevated reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and CAT gene expression. Furthermore, MERRF-iPSC-differentiated HC-like cells exhibited significantly elevated ROS levels and MnSOD and CAT gene expression. These MERRF-HCs that had more single cilia with a shorter length could be observed only by using a non-TF method, but those with fewer stereociliary bundle-like protrusions than isogenic iPSCs-differentiated-HC-like cells could be further observed using ATOH1/RFX1/RFX3 TFs. We further analysed and compared the whole transcriptome of M1ctrl-HCs and M1-HCs after treatment with ATOH1 or ATOH1/RFX1/RFX3. We revealed that the HC-related gene transcripts in M1ctrl-iPSCs had a significantly higher tendency to be activated by ATOH1/RFX1/RFX3 than M1-iPSCs. The ATOH1/RFX1/RFX3 TF-driven approach for the differentiation of HC-like cells from iPSCs is an efficient and promising strategy for the disease modelling of SHL and can be employed in future therapeutic strategies to treat SHL patients.
Introduction
Degeneration or loss of inner ear hair cells (HCs) is irreversible and results in sensorineural hearing loss (SHL). In the regeneration of inner ear HCs in vitro, mouse bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) were the first cell type to be differentiated into HC-like cells1. Furthermore, mouse embryonic stem cells (ESCs) and induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) have been demonstrated to be differentiated into HC-like cells2,3. However, it has been suggested that using chicken utricle stromal cells as feeder cells for HC differentiation may make a subsequent examination problematic4. Notably, Ronaghi et al.5 reported a feeder cell-free method for the generation of human ESC-derived HC-like cells, which exhibited many features of nascent HCs.
Proneural Atoh1 is a basic helix–loop–helix transcription factor (TF) and regulates the differentiation of HCs6. The ectopic expression of Atoh1 in mouse bone marrow MSCs can result in the differentiation of HC-like cells with the expression of Myo7A and espin1. Atoh1 can directly transdifferentiate the supporting cells in chick cochlea to become HCs7. By contrast, the systemic loss of Atoh1 in mice does not result in HC differentiation8. However, the detection of some Myo7a and Fgf8-positive cells in Atoh1 conditional knockout mice also suggests that the expression of these HC markers can be regulated by other factors9. Furthermore, the ectopic expression of ATOH1 in human umbilical cord MSCs can lead to their differentiation to HC-like cells10. Notably, an increasing body of evidence has indicated that ATOH1 gene therapy is effective for the treatment of SHL in animals11–13 and is under evaluation in a phase I/II clinical trial14. However, the ATOH1-mediated differentiation of HCs was still immature in vivo15, evidencing the need for HC differentiation.
The regulatory factor for the x-box (RFX) gene family has seven members in mammals (RFX1 to 7), with a highly conserved DNA binding domain and a winged-helix structure16,17 from yeast18, Caenorhabditis elegans (daf-19)19, and Drosophila (dRfx, dRfx2)20 to mammals16. RFX1, RFX2 and RFX3 are suggested to activate the genes in the ciliogenic pathway and mediate the transcriptional rewiring of ciliary genes21. Notably, Rfx3 knockout mice demonstrated a differentiation defect in the multiciliated cells (ependymal cells) of the brain22. Rfx1 and Rfx3 conditional knockout mice are deaf due to the rapid loss of initially well-formed outer HCs (OHCs) and the deranged inner HCs (IHCs), indicating the essential roles of Rfx1 and Rfx3 in hearing function and the survival of terminally differentiating HCs23. We have previously reported that RFX1 is a negative regulator and RFX2 is a positive regulator of human FGF1 gene activation to confer the characteristics of neural stem/progenitor cells24–26. In addition, RFX1, RFX2 and RFX3 can regulate ALMS1, which encodes a centrosomal protein and is required for the proper function of primary cilia27. Mutations in ALMS1 cause Alström syndrome28, a disorder characterised by symptoms such as neurosensory degeneration and hearing loss29.
In this study, we hypothesised that ciliogenic RFX TFs may facilitate the generation of HC-like cells from human iPSCs for the disease modelling of SHL. Our findings demonstrated that ATOH1/RFX1/RFX3 TFs could promote the differentiation of iPSC-derived HCs and facilitate the disease modelling of SHL using iPSCs from MERRF patients with A8344G mutation of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA). The ATOH1/RFX1/RFX3 TF-driven differentiation of HC-like cells is a promising approach for the development of future therapeutic strategies for the treatment of SHL patients.
Results
Differentiation of inner ear HC-like cells from hiPSCs through a non-TF method
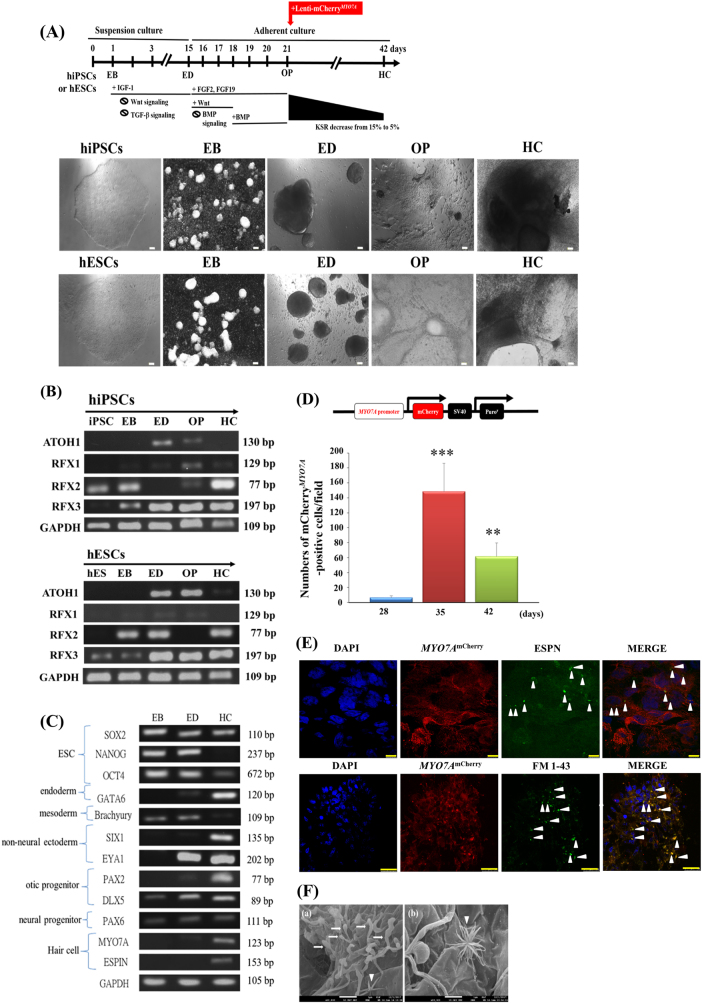
To differentiate human inner ear HC-like cells, we initially utilised the feeder cell-free otic guidance protocol developed by Ronaghi et al.5 (Fig. 1a, non-TF method). Furthermore, we analysed the messenger RNA (mRNA) expression levels of ATOH1, RFX1, RFX2 and RFX3 during the differentiation of hiPSCs or human ESCs (hESCs) to HC (Fig. 1b) through reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR). It has been suggested that the expression of Atoh1 mRNA can be detected in otic progenitors (OPs) and the early immature HC stage differentiated from hESCs5, but not in HCs differentiated from mouse ESCs3. In this study, we found that the mRNA expression of ATOH1 could be detected from the ectoderm differentiation (ED) to OP stages, but not at the late HC stage (day 42) (Fig. 1b). Furthermore, we revealed that different mRNA expression levels of RFX1, RFX2 and RFX3 were detected at the HC stage after the differentiation of hiPSCs or hESCs for 42 days. Notably, the mRNA expression levels of RFX1 and RFX3 could be detected at the OP stage (Fig. 1b), implying the crucial roles of RFX1 and RFX3 for inducing the OP into HC stage by the non-TF method.
Fig. 1. Morphological and mRNA expression analyses during hair cell (HC) differentiation from human iPSCs (hiPSCs) or human ESCs (hESCs) through a non-TF method.
a Schematic of the 42-day otic guidance protocol. hiPSCs and hESCs exhibited a round and flat morphology in the bright field. The spherical embryoid body (EB) formation was observed on day 1. Ectoderm differentiation (ED) was observed on day 15. Otic progenitor (OP) induction was observed on day 21. The hair cell (HC) differentiation stage was observed on day 42. Scale bar = 100 µm. b Semiquantitative reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR) analyses for the mRNA expression of ATOH1, RFX1, RFX2 and RFX3 genes at different stages (EB, ED, OP and HC) during HC differentiation from hiPSCs and hESCs. c ESC-specific gene transcripts (SOX2, OCT4 and NANOG) were expressed at the EB stage. Non-neural ectoderm-specific genes (SIX1 and EYA1) were expressed at the ED stage. OP-specific genes (PAX2 and DLX5), the neural progenitor-specific PAX6 gene and HC-specific genes (MYO7A and ESPN) were expressed at the HC stage. d mCherryMYO7A-positive cells were counted on days 28, 35 and 42. Data are presented as mean ± SD; ***p < 0.001, **p < 0.01. Positive cells were counted by randomly selecting five fields in the indicated time points. e Colocalisation of MYO7AmCherry with ESPN and FM1-43-positive cells. Scale bar in ESPN staining is 10 µm, scale bar in FM 1-43 staining is 25 µm. f Morphology of cilia on the surface of HC-like cells, as determined through SEM. The arrow indicates the single cilium and arrowhead indicates the clustered cilia. Scale bar = 1 µm. KSR knockout serum replacement
Data from RT-PCR analyses revealed that the mRNA expression levels of pluripotency markers SOX2, NANOG and OCT4 were downregulated during the inner ear HC differentiation process. SOX2, NANOG and OCT4 are suggested to be crucial TFs to confer pluripotency and self-renewal ability of hESCs30. It has been demonstrated that SOX2 is a marker for the prosensory identity of the otic lineage31. Notably, SOX2 mRNA was continuously expressed until the HC stage (Fig. 1c). Our finding suggest that the endothermal marker GATA632 was not expressed during embryoid body (EB) formation and ED, indicating that the mesodermal cells and endodermal cells derived from hiPSCs were suppressed by DKK-1 and SIS3. The expression of GATA6 was significantly upregulated at the HC stage, indicating the existence of endoderm-derived cells at this stage. By contrast, Brachyury, the mesodermal marker33, was detected from the EB to ED stages, but not at the HC stage while using the non-TF method. The formation of the preplacodal ectoderm is crucial for cranial development. Numerous marker genes have been demonstrated to be expressed in the preplacodal ectoderm, such as SIX134 and EYA135. Our data indicate that the expression levels of SIX1 and EYA1 were upregulated during the HC differentiation process (Fig. 1c).
The transcriptional regulators PAX2 and DLX5 are markers of otic lineage. They have been reported to be expressed during otic differentiation from mouse36 and human ESCs37. The co-expression of these markers can serve as an indication of OP identity. DLX5 was detectable from the EB stage to ED and HC stages. It has been revealed that the non-TF HC differentiation protocol5 is similar to the differentiation method of neural progenitor cells (NPCs)38,39. The upregulation of PAX2 was also detected from the ED to HC stages (Fig. 1c). The mRNA expression levels of sensory inner ear HC markers, MYO7A and ESPN, were upregulated after long-term HC differentiation, indicating the formation of HC-like cells (Fig. 1c).
Expression of HC markers in iPSC-differentiated HC-like cells through a non-TF method
The upregulation of HC markers can be used to monitor the differentiation of iPSCs to HC-like cells. We then used lentivirus carrying an MYO7A promoter fused with the mCherry reporter gene to infect cells at the OP stage and monitor the HC differentiation process of the hiPSCs or hESCs. The differentiated cells at the OP stage were infected with lenti-MYO7AmCherry virus on day 21 (Fig. 1a, d). In the present study, the number of MYO7AmCherry-positive cells was semiquantitatively counted by randomly selecting five different fields in which the MYO7AmCherry–positive cells were observed. After infecting the cells at the OP stage with the lenti-MYO7AmCherry virus on day 21, we discovered that the number of MYO7AmCherry-positive cells was significantly higher on days 35 and 42 than on day 28 (Fig. 1d). We then used immunofluorescence staining to demonstrate that MYO7AmCherry-positive cells were colocalised with the staining signal of ESPN or FM 1-43 staining (Fig. 1e). ESPN has been suggested as a critical structural marker for the actin filament cross-link in stereociliary bundles40. Notably, the mRNA expression levels of sensory inner ear HC markers such as MYO7A and ESPN were upregulated after long-term HC differentiation, indicating that the formation of HC-like cells occurred (Fig. 1c). In addition, it has been revealed that FM 1-43 fluorescent dye can permeate auditory HCs through ion channels. The dye rapidly and specifically labels inner ear HCs by permeating the mechanotransduction channels40.
Differentiated HC-like cells failed to acquire mature stereociliary bundles through a non-TF method
We examined the morphology of the stereociliary bundle or hair bundle on the surface of HC-like cells through scanning electron microscopy (SEM). In epithelium-like areas, we observed cilium-like protrusions extending from the surface of cells. In most cases, these protrusions displayed a single cilium (the arrow in Fig. 1f) or a cluster of cilia (arrowhead in Fig. 1f); however, the clustered cilia were splayed and did not resemble the typical morphology of the mechanosensory stereociliary bundles of inner ear HCs. The lack of a typical stereociliary bundle morphology suggested that these HC-like cells may have been at a nascent state of development and may fail to completely mature in an in vitro culture system. Our observations are in agreement with those reported in studies of cultures of mouse OP41 and human ESCs5. However, the HC-like cells did not exhibit a typical mature physiological morphology, most likely due to the absence of environmental cues.
Differentiation of HC-like cells from the iPSCs of patients with MERRF syndrome through a non-TF method
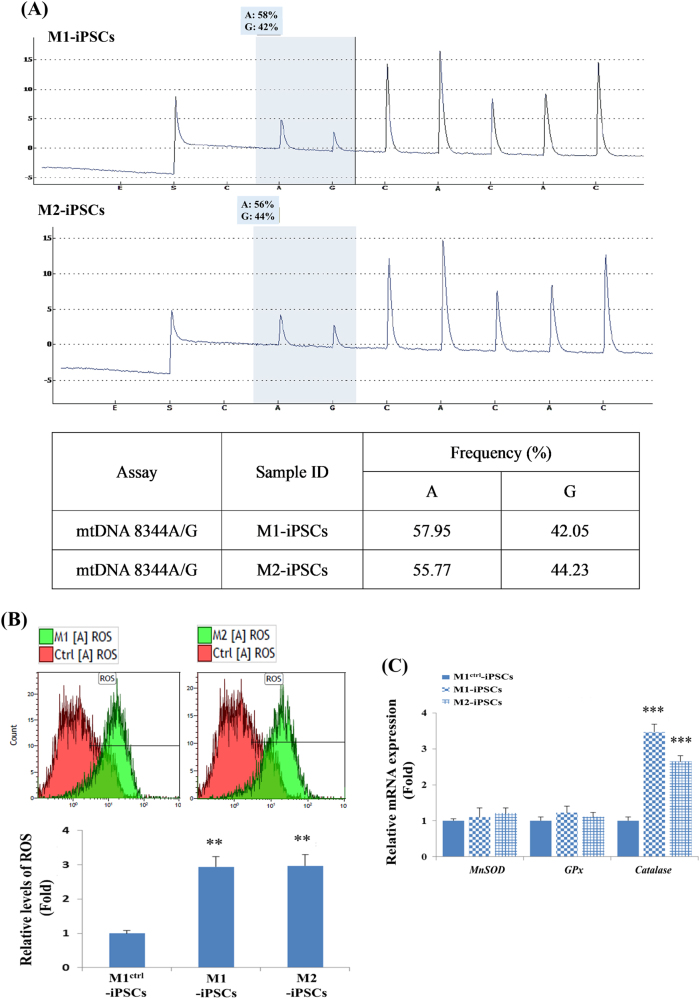
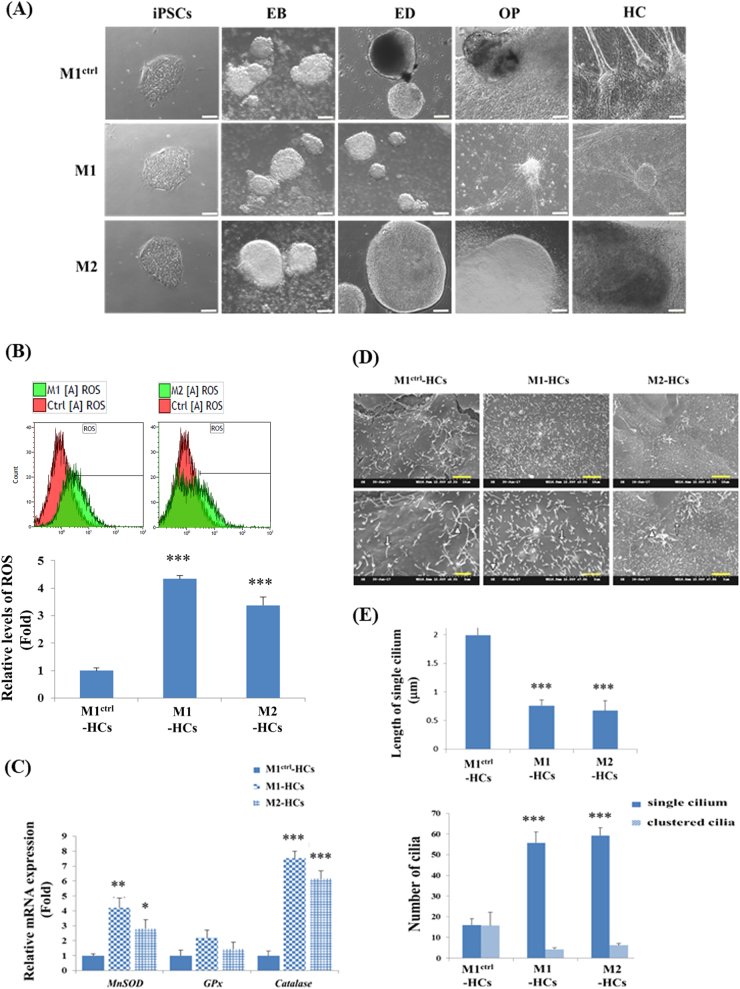
MERRF syndrome is characterised by A8344G mutation of mtDNA42. The mutation load of A8344G mutation of mtDNA in MERRF fibroblast-derived iPSCs were determined using a pyrosequencing assay conducted at the beginning of the otic guidance differentiation. Quantitative analysis revealed the proportions of A8344G mtDNA mutation were ~42.05% in M1-iPSCs and 44.23% in M2-iPSCs (Fig. 2a). M1ctrl-iPSCs are isogenic iPSCs without A8344G mutation of mtDNA due to heteroplasmy during iPSC reprograming42. It has been revealed that the A8344G mutation of mtDNA reduced cell proliferation in hiPSCs42. In the present study, we observed that the A8344G mutation of mtDNA did not affect the morphology of M1-iPSC and M2-iPSC colonies during iPSC culturing (Fig. 3a).
Fig. 2. Characterisation of hiPSCs harbouring the A8344G mutation of mtDNA.
a The proportion of mtDNA with A8344G mutation was quantified by pyrosequencing of MERRF iPSCs (M1-iPSCs and M2-iPSCs). b The reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels of M1-iPSCs and M2-iPSCs were higher than that of M1Ctrl, as indicated by flow cytometry. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, N = 3. c Quantitative RT-PCR (qRT-PCR) demonstrated that the expression level of the antioxidant enzyme gene CAT in M1- and M2-iPSCs was significantly higher than that in M1Ctrl-iPSCs. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, N = 3
Fig. 3. Morphological characterisation of HC-like cells from hiPSCs harbouring the A8344G mutation of mtDNA.
a Morphology of M1ctrl, M1 and M2 cells during HC differentiation: these iPSCs exhibited a round and flat morphology in the bright-field imaging. The whole HC differentiation process included embryoid body (EB) formation, ectoderm differentiation (ED), otic progenitor (OP) and HC differentiation. Scale bar = 100 µm. b The ROS levels of M1-HCs and M2-HCs were higher than that of M1Ctrl-HC-like cells, as revealed by flow cytometry. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, N = 3. c Quantitative RT-PCR (qRT-PCR) demonstrated that the expression levels of the antioxidant enzyme genes MnSOD and CAT in M1- and M2-HC-like cells were significantly higher than those in M1Ctrl HC-like cells. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, N = 3. d M1Ctrl, M1 and M2 HC-like cells obtained through a non-TF method exhibited cilia-like protrusions on the surface of cells. The arrow indicates the single cilium and arrowhead indicates the clustered cilia. Scale bar = 5 µm in the upper row of d, 2.5 µm in the lower row of d. e The length and number of cilia were measured from the cilia in the SEM image using ImageJ software. Data are presented as mean ± SD, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001., N=3.
A8344G mutation of mtDNA causes reactive oxygen species accumulation and alters expression of antioxidant genes in iPSCs and iPSC-derived HC-like cells
To investigate the levels of ROS in iPSCs and HC-like cells derived from MERRF-iPSCs, we stained iPSCs and HC-like cells with CellROX, a green fluorescent dye used for the detection of ROSs in living cells. We revealed that the intracellular ROS levels in M1-iPSCs and M2-iPSCs were significantly higher than those in M1Ctrl-iPSCs (Fig. 2b). Through a non-TF differentiation method, we also discovered that the intracellular ROS levels in M1-HC-like cells and M2-HC-like cells were significantly higher than the ROS levels in M1Ctrl-HC-like cells (Fig. 3b). Furthermore, we analysed the expression of antioxidant genes including MnSOD, GPx and CAT by using quantitative RT-PCR. Notably, the results revealed a significantly increased catalase expression in M1-iPSCs and M2-iPSCs (Fig. 2c); however, their expression levels of MnSOD and GPx remained similar to those in M1Ctrl-iPSCs (Fig. 2c), indicating the impaired hydrogen peroxide and hydroxyl radical scavenging capacities of MERRF-iPSCs. Using a non-TF differentiation method, the significantly upregulated expression of MnSOD and CAT was observed in the M1- and M2-HC-like cells, but the expression level of GPx in these cells remained similar to that in the M1Ctrl-HC-like cells (Fig. 3c), indicating the impaired hydroxyl radical scavenging capacity of the MERRF-HC-like cells. Collectively, our results were in agreement with the findings of Chou et al.42, indicating elevated ROS levels and impaired ROS scavenging capacities in the MERRF-iPSCs and their differentiated progenies.
In addition, it is noteworthy that the mRNA expression levels of ATOH1, RFX2 and RFX3 could be detected at the ED, OP and HC stages after the differentiation of M1 and M2-iPSCs (Supplementary Fig. 1). Notably, the mRNA expression level of RFX1 was reduced in the OP and HC stages after the differentiation of M1 and M2-iPSCs (Supplementary Fig. 1). By contrast, the mRNA expression of RFX1 was observed in the OP and HC stages after the differentiation of hESCs and M1ctrl-iPSCs (Supplementary Fig. 1), suggesting that the downregulation of mRNA expression of RFX1 in M1-HCs and M2-HCs might also account for the defects in the stereociliary bundles of M1-HCs and M2-HCs.
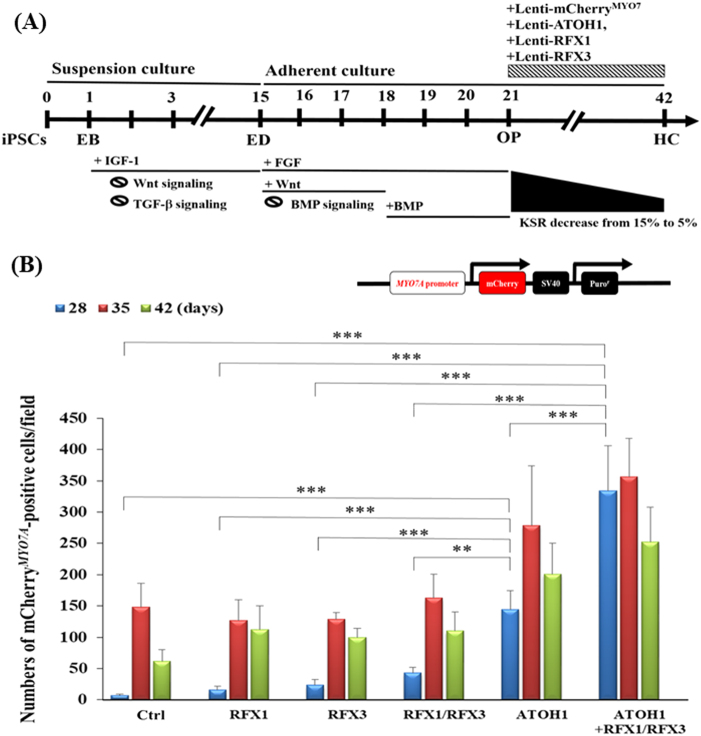
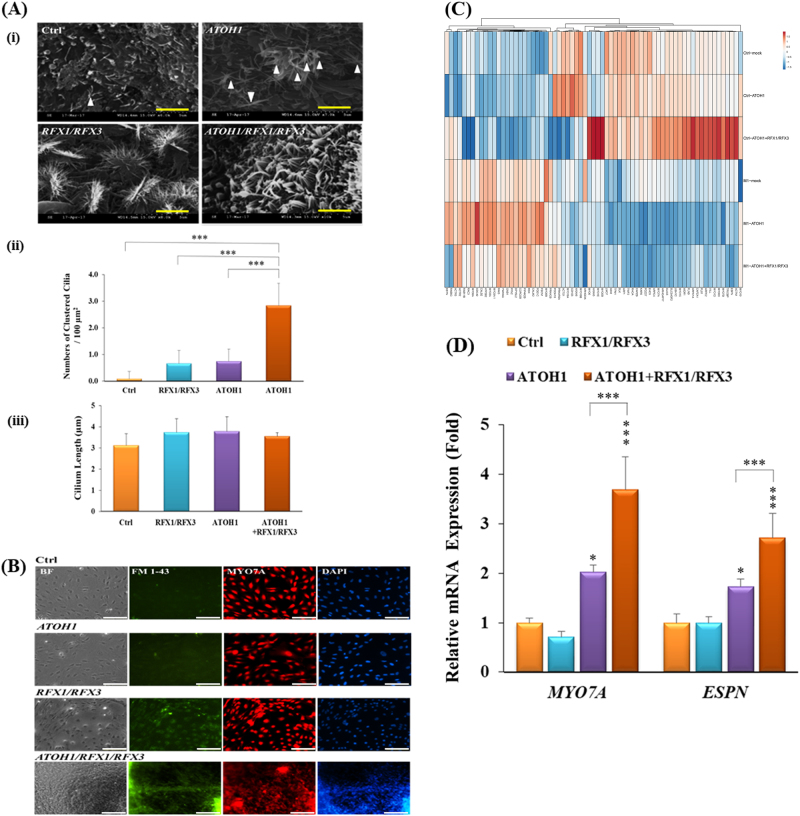
ATOH1, RFX1and RFX3 promote the differentiation of HC-like cells and the formation of stereociliary bundles
We hypothesised that in addition to ATOH1, RFX TFs might be involved in HC differentiation. Our hypothesis was based not only on the expression profile of RFX TFs during the course of differentiation of iPSCs to HC (Fig. 1b), but also on observations in previous studies23–26,43 that have revealed that RFX1 and RFX3 TFs are essential for ciliogenesis and for the hearing function of mice. Therefore, to investigate whether RFX1 and RFX3 promote HC differentiation, we designed the following experiments: control (Ctrl), ATOH1, RFX1, RFX3, RFX1/RFX3 and ATOH1/RFX1/RFX3. The MYO7AmCherry reporter gene was used to monitor the process of HC differentiation (Fig. 4a). Notably, ATOH1/RFX1/RFX3 efficiently promoted the differentiation of iPSCs into MYO7AmCherry-positive cells more than ATOH1 in the early stage of HC differentiation (day 28) (Fig. 4b). Furthermore, ATOH1 and ATOH1/RFX1/RFX3 treatments resulted in significantly higher numbers of MYO7AmCherry-positive cells than in the Ctrl condition on day 28 (Fig. 4b); however, the RFX1/RFX3 condition did not significantly increase the number of MYO7AmCherry-positive cells. By contrast, we found that ATOH1 gene infection alone or in combination with RFX1/RFX3 at the OP stage could significantly increase the number of MYO7AmCherry-positive cells on day 28, implying that the decline of ATOH1 mRNA expression from the OP to HC stage (Fig. 1b) could be compensated by the infection of lenti-ATOH1 at the OP stage (Fig. 4b).
Fig. 4. Differentiation of HC-like cells from human iPSCs (hiPSCs) through the ATOH1/RFX1/RFX3 TF method.
a Schematic of the HC differentiation protocol with lentiviral infections (MYO7AmCherry reporter gene, ATOH1, RFX1/RFX3 and ATOH1/RFX1/RFX3) on day 21. b The number of MYO7AmCherry-positive cells in the ATOH1/RFX1/RFX3 and ATOH1 conditions was higher than that in the control (Ctrl) condition. The number of MYO7AmCherry-positive cells in the ATOH1/RFX1/RFX3 and ATOH1 conditions was higher than those in the RFX1/RFX3 and ATOH1 conditions. Positive cells were counted by randomly selecting five fields in each experimental condition. Data are presented as mean ± SD, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001
We then investigated whether ATOH1/RFX1/RFX3 could promote the differentiation of HC-like cells. We examined the morphology of HC-like cells derived from hiPSCs under four experimental conditions through SEM. In the Ctrl condition, we observed a few single cilia on the surface of the cells. We discovered that HC-like cells in the ATOH1 condition harboured tightly squeezed cilia on the cell surface, and a considerable number of cilia were observed. In addition, the morphology of the cilia in HC-like cells in the RFX1/RFX3 condition was more clustered, but the clustered cilia were splayed. In particular, the cilium morphology of HC-like cells in the ATOH1/RFX1/RFX3 condition exhibited stereociliary bundle-like protrusions (Fig. 5a-i and Supplementary Fig. 2). The density of the clustered stereocilia in iPSC-derived HC-like cells was 0.1 ± 0.3/100 μm2 in the Ctrl condition, 0.7 ± 0.5/100 μm2 in the RFX1/RFX3 condition, 0.8 ± 0.5/100 μm2 in the ATOH1 condition and 2.8 ± 0.8/100 μm2 in the ATOH1/RFX1/RFX3 condition (Fig. 5a-ii). However, the cilium lengths in each condition were similar (Fig. 5a-iii): 3.1 ± 0.5 μm in the Ctrl condition, 3.7 ± 0.7 μm in the RFX1/RFX3 condition, 3.8 ± 0.7 μm in the ATOH1 condition and 3.5 ± 0.2 μm in the ATOH1/RFX1/RFX3 condition.
Fig. 5. Stereociliary structure and molecular characterisation of HC-like cells differentiated from hiPSCs through the ATOH1/RFX1/RFX3 TF differentiation method.
a(i) HC-like cells acquired numerous cilia on the cell surfaces in the ATOH1 condition, mostly acquired through clustered cilia in the RFX1/RFX3 condition, and more mature stereociliary bundles were acquired in the ATOH1/RFX1/RFX3 condition. Scale bar = 2.5 µm in the control (Ctrl), ATOH1 and RFX1/RFX3, and 1.5 µm in ATOH1/RFX1/RFX3. (ii) The number of clustered cilia in an area of 100 μm2 was measured in 10 fields of the SEM image. Data are presented as mean ± SD, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. (iii) Stereocilium length was measured from the cilia in 10 fields of the SEM image using ImageJ software. The average stereocilium lengths of HC-like cells in the Ctrl, ATOH1, RFX1/RFX3 and ATOH1/RFX1/RFX3 conditions were 3.52 ± 0.29, 3.41 ± 0.24 and 3.05 ± 0.23 μm, respectively. Data are presented as mean ± SD, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. b Immunofluorescent staining for the expression of ESPN and MYO7A in the iPSC-differentiated HCs by ATOH1, RFX1/RFX3 and ATOH1/RFX1/RFX3. c Whole-transcriptome analyses for the genes involved in stereociliary bundles of HC-like cells differentiated from human iPSCs through RNA sequencing. The genes involved in the characteristics of stereociliary bundles were chosen for the cluster analyses, following the procedure of Liu et al.44 d Quantitative RT-PCR analyses revealed significantly higher mRNA expression levels of MYO7A and ESPN in the ATOH1/RFX1/RFX3 and ATOH1 conditions than in the Ctrl condition. Furthermore, mRNA expression levels of MYO7A and ESPN in the ATOH1/RFX1/RFX3 condition were significantly higher than those in the ATOH1 condition. Data are presented as mean ± SD. N = 3, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001
Furthermore, we analysed the expression of HC marker proteins including MYO7A and ESPN through immunofluorescence staining. Notably, the expression levels of ESPN in the RFX1/RFX3 and ATOH1/RFX1/RFX3 conditions were markedly higher than those in the Ctrl and ATOH1 conditions, and the expression levels of MYO7A and ESPN in the ATOH1/RFX1/RFX3 condition were higher than those in the Ctrl, ATOH1 and RFX1/RFX3 conditions (Fig. 5b).
Whole-transcriptome analysis through RNA sequencing
A total of 16,272 mRNA were identified as being differentially expressed (DE) when a significance threshold of p ≤ 0.05 was exclusively considered. Notably, 70 of these 16,272 mRNA-encoding genes were identified as being be involved in the formation of stereociliary bundles of HCs, as suggested by Liu et al.44 (Fig. 5c). Our results indicate that ATOH1/RFX1/RFX3 could enhance the mRNA expression of a cluster of genes involved in stereociliary bundles, including ESPN and MYO7A (Fig. 5c). Furthermore, we used quantitative RT-PCR to demonstrate that the expression levels of MYO7A and ESPN genes in the ATOH1/RFX1/RFX3 condition were significantly higher than those in the Ctrl condition (Fig. 5d). Taken together, these findings suggest that ATOH1/RFX1/RFX3 could upregulate HC marker gene expression and promote the differentiation of HC-like cells.
Disease modelling of HC-like cells in patients with MERRF syndrome
We analysed the HC differentiation capacities of M1-iPSCs and M2-iPSCs with the A8344G mutation of mtDNA. To differentiate the HC-like cells from MERRF-iPSCs, M1-iPSCs and M2-iPSCs were initially subjected to HC differentiation through a non-TF method. During the differentiation process, we observed that at the EB formation, ED induction, OP induction and HC differentiation stages, M1-iPSCs and M2-iPSCs exhibited no significant differences compared with those in M1Ctrl-iPSCs (Fig. 3a). The HC-like cells in the Ctrl condition also exhibited a single cilium (arrows) or a cluster of cilia (arrowheads); however, the clustered cilia were splayed and did not closely resemble the typical morphology of the stereociliary bundles of HCs (Fig. 3d). MERRF-HC-like cells that had more single cilia with shorter lengths could be observed using the non-TF method (Fig. 3e) and those with fewer stereociliary bundle-like protrusions than the control HC-like cells could be further observed using ATOH1/RFX1/RFX3 TFs (Fig. 6a, b).
Fig. 6. Stereociliary structure and molecular characterisation of HC-like cells differentiated from MERRF-iPSCs through an ATOH1/RFX1/RFX3 TF-driven approach.
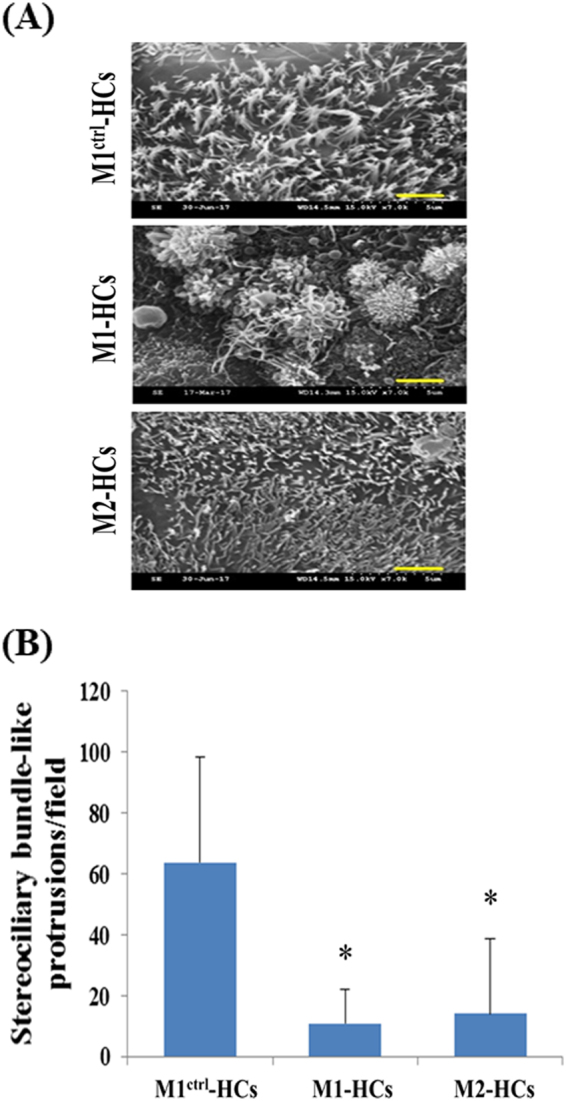
a Through ATOH1/RFX1/RFX3 TF-driven HC differentiation, M1Ctrl-HC-like cells acquired more mature stereociliary bundles than M1 and M2 HC-like cells. Scale bar = 2.5 µm. b The number of stereociliary bundle-like protrusions in a field was measured in four different fields of the SEM image. Data are presented as mean ± SD. N = 3, *p < 0.05
Discussion
In this study, we developed an efficient HC differentiation protocol with ATOH1/RFX1/RFX3 TFs by using the feeder cells-free method. The ATOH1/RFX1/RFX3 TF-driven approach will be useful for the differentiation of HC-like cells for disease modelling and drug screening for SHL. We found that the A8344G mutation of mtDNA did not interfere with the morphology of M1- and M2-iPSCs (Fig. 3a). Furthermore, we performed RNA-sequencing experiments to analyse the whole-transcriptome levels between M1ctrl-HCs and M1-HCs after ATOH1 or ATOH1/RFX1/RFX3 treatments. Our results suggested that the HC differentiation of M1ctrl-iPSCs has a significantly higher tendency to be activated by ATOH1/RFX1/RFX3 than M1-iPSCs (Fig. 5c, supplementary Figures 3 and 4). Although Chou et al.42 revealed that the differentiation capacities of M1-iPSCs, M2-iPSCs and isogenic M1Ctrl-iPSCs towards cardiomyocyte and NPCs were similar, the discrepancy in differentiation capacities among cardiomyocytes, NPCs, and HC-like cells may be due to divergent lineage differentiation protocols and the growth factors and signalling inhibitors used.
For the disease modelling of SHL, Tang et al.45 generated a diseased iPSC line with compound heterozygous MYO7A c.1184G>A and c.4118C>T mutations from deaf patients. Their results revealed that the MYO7A mutation did not influence the pluripotency of iPSCs. They further adopted a HC differentiation protocol for human ESCs and observed stereocilia-like protrusions after 3 weeks of culture on mitotically inactivated chicken utricle stromal cells. Although the differentiation capacities of MYO7A-mutation-iPSC-derived OPs were not significantly different than those of non-MYO7A-mutation-iPSC-derived OPs, the morphology of the stereocilia-like protrusions of the HC-like cells differentiated from MYO7A-mutation iPSCs was distinct from that of the protrusions in cells induced from non-MYO7A-mutation iPSCs. Notably, Tang et al.45 observed that the MYO7A-mutation-HC-like cells exhibited less FM1-43 uptake, abnormal electrophysiological properties and deranged stereocilia-like protrusions. These MYO7A-mutation-HC-like cells were curved, dishevelled and scattered, and exhibited no bonding with each other. Tang et al.45 corrected one of the MYO7A-mutation sites (c.4118C>T) in the MYO7A-mutation iPSCs with CRISPR/Cas9, and the HC-like cells from the corrected iPSCs exhibited a restored organisation of stereocilia-like protrusions. In addition, Chen et al.46 generated MYO15A-mutation iPSCs (c.4642G>A and c.8374G>A mutations), and demonstrated that the abnormal HC morphology, including disorganisation of F-actin bundles, abnormally short stereocilia and syncytia, and dysfunction (lower current density) of the HC-like cells from the MYO15A-mutation iPSCs can be corrected with CRISPR/Cas9. It is worth noting that they used the same HC differentiation protocol as Tang et al.45 with chicken utricle stromal cells. The stereocilium length was 3.52 ± 0.29 μm in the HC-like cells differentiated from non-MYO15A-mutation iPSCs, whereas the stereocilium length was 0.94 ± 0.22 μm in the HC-like cells differentiated from the MYO15A-mutation iPSCs. In our ATOH1/RFX1/RFX3-driven HC differentiation protocol, we also observed that the stereocilium length in iPSC-derived HC-like cells was 3.5 ± 0.2 μm in the ATOH1/RFX1/RFX3 differentiation condition (Fig. 5a-iii), indicating that the stereocilium length in the HC-like cells from our ATOH1/RFX1/RFX3-driven HC differentiation protocol was comparable to that in the previous protocol with chicken utricle stromal cells5. ATOH1/RFX1/RFX3-differentiated HC-like cells possessed more mature stereociliary bundles than the cells obtained using the protocol involving chicken utricle stromal cells.
Interestingly, the generation of tissue-specific organoids has been suggested to be important in the modelling of cell–cell interactions in the three-dimensional level during organ development47. Koehler et al.48 reported the generation of inner ear organoids from human ESCs and iPSCs and demonstrated that inner ear organoids can have sensory epithelial cells due to the expression of HC markers, such as ESPN and MYO7A. These sensory epithelial cells are also innervated by sensory neurons. Furthermore, their electrophysiological data suggested that hESCs and hiPSC-derived organoids adopted vestibular type I and type II HCs, but not cochlear HCs. By using ATOH1/RFX1/RFX3 TF-driven approach, the RNA-sequencing data suggested that ATOH1/RFX1/RFX3 could significantly upregulate many genes involved in cochlear OHCs (Supplementary Figure 3) and IHCs (Supplementary Figure 4). Future studies should investigate whether the combination of ATOH1/RFX1/RFX3 with the inner ear organoid system could facilitate the differentiation of cochlear OHCs and IHCs. In conclusion, our ATOH1/RFX1/RFX3 TF-driven approach to generate HC-like cells from hiPSCs was efficient and promising for disease modelling. It can be employed in the development of future therapeutic strategies for the treatment of SHL patients.
Materials and methods
Human iPSCs and ESCs
MERRF syndrome is characterised by A8344G mutation of mtDNA, resulting in changes in the nucleotide that is normally present at the anticodon wobble nucleotide in mitochondrial tRNALys and impairment of the synthesis of mitochondrial proteins that are fundamental for oxidative phosphorylation. Two patients, a 15-year-old Chinese girl (M1-iPSCs) and her 13-year-old sister (M2-iPSCs), were selected42. hiPSCs were generated from human fibroblasts derived from the patients with MERRF syndrome. MERRF-iPSCs (M1- and M2-iPSCs) were reprogrammed using four TFs, SOX2, OCT4, KLF4 and GLIS1, with retroviral vectors at Taipei Veterans General Hospital, Taiwan42. This study was approved by the by Institutional Review Board (IRB) of Mackay Memorial Hospital, Mackay Medical College and Taipei Veterans General Hospital. The IRB waived the informed consent requirement for the use of hiPSCs cell lines. hiPSCs were cultured on Geltrex (ThermoFisher Scientific, USA)-coated dishes in mTeSRTM1 medium (Stemcell Technologies, Canada). hiPSCs were generated from human fibroblasts derived from patients with MERRF syndrome. Both MERRF-iPSCs and human ESCs were generously provided by Prof. Shih-Hwa Chiou at Taipei Veterans General Hospital, Taiwan42. The pluripotency of M1ctrl-iPSCs, M1-iPSCs and M2-iPSCs was demonstrated by the expression of pluripotent markers, such as OCT4 and Nanog. The ability of M1ctrl-iPSCs, M1-iPSCs and M2-iPSCs to differentiate into three germ layers in vitro and form teratoma and three germ layers in vivo was also confirmed42. Chou et al.42 also characterised the expression of these markers in iPSCs-derived cardiomyocyte and NPCs in their publication. Notably, changes such as the elevation of ROS levels and impaired antioxidant catalase gene expression in M1ctrl-iPSCs/M1-iPSCs/M2-iPSCs and M1ctrl-HCs/M1-HCs/M2-HCs (Figs. 2 and 3) were similar to the previous findings in cardiomyocytes and NPCs differentiated from M1ctrl -iPSCs, M1-iPSCs and M2-iPSCs42,57.
HC differentiation from iPSCs
To differentiate human inner ear HC-like cells, we initially utilised the feeder cell-free otic guidance protocol developed by Ronaghi et al.5 (non-TF method). First, we generated EBs from hiPSCs or hESCs through a suspension cell culture with the addition of insulin growth factor-1 (IGF-1), which is an inhibitor of WNT and TGF-β signalling (Fig. 1a). Following EB formation, the EBs were treated with the inhibitors of TGF-β and WNT signalling pathways to suppress the differentiation of endodermal and mesodermal lineages and promote cells towards the formation of the cranial ectoderm3. The downregulation of WNT and TGF-β signalling can result in the formation of a primitive streak by the treatment of DKK-1 (Wnt inhibitor) and the selective inhibitor of Smad3 (SIS3, interference with TGF-β signalling), thus increasing the ED during EB formation. In addition, it has been revealed that IGF-1 and IGF signalling are crucial for the differentiation of the cranial ectoderm49. After treatment of EBs with IGF-1, DKK-1 and SIS3, the otic induction phase was initiated in an adherent cell culture. These EBs were then treated to induce the activation of the FGF signalling pathway, which was followed by an initial period of BMP inhibition with noggin, and then WNT activation with R-spondin 1. These EBs were then differentiated to the stage of presumptive OPs. It has been demonstrated that OPs independently differentiate into the surrounding tissues and do not require external signalling for correct differentiation50,51. Therefore, a long-term culture with a decreasing concentration of knockout serum replacement (KSR) was used in this study for the differentiation of HC-like cells (Fig. 1a)57.
Embryoid body formation
For EB formation, hiPSCs or hESCs were dissociated with dispase (Stemcell Technologies) and transferred to ultralow attachment surface plates (Corning, USA) containing the mTeSR™1 medium. EBs were cultured in ultralow attachment surface plates containing mTeSR™1 medium supplemented with 100 ng/mL of recombinant human DKK-1 (R&D Systems, USA), 3 μM of SIS3 and 10 ng/mL of IGF1 (both were from Sigma-Aldrich Chemical Co., USA) for 15 days5,57.
Induction of otic progenitors
For OP induction, the EBs were transferred into a plate coated with a poly-l-ornithine and laminin (both were from Sigma-Aldrich Chemical Co.)-coated plate and cultured for 3 days in an advanced Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM)/nutrient mixture F12 supplemented with 20% KSR, N2, B27 (ThermoFisher Scientific), human basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF; 25 ng/mL; R&D Systems), human FGF19 (25 ng/mL; R&D Systems), human noggin (30 ng/mL; R&D Systems), human R-spondin1 (R&D Systems; 50 ng/mL), heparan sulphate (50 ng/mL; Sigma, USA) and ampicillin (50 µg/mL). However, the medium was replaced with the advanced DMEM/F12 supplemented with 15% KSR, N2, B27, bFGF (25 ng/mL), human FGF19 (25 ng/mL), human BMP4 (20 ng/mL; R&D Systems), heparan sulphate (50 ng/mL) and ampicillin (50 µg/mL) and cultured for 3 days5,57.
Inner ear HC-like cells differentiation
For inner ear HC-like cell differentiation, the medium was replaced with the advanced DMEM/F12 supplemented with 15% KSR, N2 and B27, and ampicillin (50 mg/mL). The concentration of KSR progressively decreased until day 42. We used the lentivirus vector pEZX-LvPM02 (GeneCopoeia, Rockville, MD, USA) that carried the MYO7A promoter-driven mCherry as a reporter gene to infect differentiated cells on day 21 of the OP stage for the monitoring of the HC differentiation5,57. The lentiviral construct of MYO7AmCherry reporter used in this study was purchased from GeneCopoeia™ (HPRM25722-PG02, GeneCopoeia). The promoter details are as follows: >HPRM25722, NM_000260, NM_001127179; Entrez_ID = 4647; chr11+:76837906-76839534; −1404 to +224, length = 1629. We followed the method that Boëda et al.52 previously reported in the generation of human MYO7A promoter-GFP transgenic mice for targeting the MYO7A-positive cells in vivo. The expression of the GFP reporter gene was under the control of the human MYO7A promoter region −2109 to +2370. Notably, the promoter region (−1404 to +224) of the MYO7AmCherry reporter gene used in our study was within the MYO7A promoter (−2109 to +2370) in MYO7A promoter-GFP transgenic mice. These GFP transgenic mice were found to have the following characteristics: (1) GFP expression was specifically restricted to HCs in the inner ear and cochlear and (2) GFP expression was not observed in other organs52. To confirm the specificity of the MYO7AmCherry reporter gene, we used immunofluorescence double-staining experiments to demonstrate the colocalisation of MYO7AmCherry signal with mature HC markers (ESPN and FM1-43) (Fig. 1e). We attempted to dissociate the HC-like cells from human iPSCs and quantify the mCherry-positive cells through flow cytometry after HC differentiation. However, the HC-like cells formed a tissue-like structure and were difficult to dissociate into single cells to quantify the percentage of MYO7AmCherry-positive cells through flow cytometry. We therefore chose to semiquantitatively count the number of MYO7AmCherry-positive cells in the tissue-culture wells of iPSC-derived HC-like cells under a florescent microscope (Fig. 1d, e). Consistently, the number of MYO7AmCherry-positive cells was positively correlated with the mRNA expression of MYO7A in the HC stage at day 42 after differentiation (Fig. 1c, d).
Production of viruses
Lentiviral vectors lenti-RFX1 and lenti-RFX3 composed from the pSG5-RFX1 and pSG5-RFX3 constructs were provided by Shaul53 and Iwama54. The lenti-ATOH1 vector was purchased from GeneCopoeia. Lenti-ATOH1, lenti-RFX1, lenti-RFX3 and lenti- MYO7AmCherry vectors were transfected into HEK293T cells. After 48 h, viruses were collected. Viral supernatants were concentrated using an ultracentrifuge for 2 h at 100,000×g. A Global UltraRapid Lentiviral Titer Kit (System Biosciences Inc., Mountain View, CA, USA) was used to determined viral titres57.
Reverse transcription PCR
Total RNA was isolated using FavorPrep Tissue Total RNA Extraction Mini Kit (Favorgen, Ping-Tung, Taiwan). Afterwards, Tri-Reagent RNA clean-up kit (Favorgen, Ping-Tung, Taiwan) was applied, and complementary DNA (cDNA) was synthesised using the iScript cDNA synthesis kit (Bio-Rad, USA). A PCR was performed using the KAPA2G ReadyMix PCR kit (Kapa Biosystems, Cape Town, South Africa)57. The gene-specific primer sequences are presented in Supplementary Table 1.
RNA isolation and library construction and sequencing
The total RNA samples were first treated with DNase I to degrade any possible DNA contamination. Then, the mRNA was then enriched using the oligo (dT) magnetic beads. Mixed with the fragmentation buffer, the mRNA was fragmented into short fragments. Then, the first strand of cDNA was synthesised using random hexamer primer. Buffer, dNTPs, RNase H and DNA polymerase I were added to synthesise the second strand. The double-strand cDNA was purified with magnetic beads. End reparation and 3′-end single-nucleotide A (adenine) addition was then performed. Finally, sequencing adaptors were ligated to the fragments. The fragments were enriched through PCR amplification. During the quality control (QC) step, Agilent 2100 Bioanaylzer and ABI StepOnePlus Real-Time PCR System were used to qualify and quantify the sample library. The library products were then ready for sequencing through Illumina HiSeq TM 2000 or other sequencers. The RNA-sequencing experiments were performed by Genomics Inc. (New Taipei City, Taiwan).
Bioinformatic analyses
Primary sequencing data produced by Illumina Nextseq TM 500, called raw reads, was subjected to QC to determine if a resequencing step is was required. After QC, raw reads were filtered into clean reads, which are for alignment to the reference sequences. A QC of the alignment was performed to determine if resequencing was required. The alignment data was utilised to calculate the distribution of reads on reference genes and the mapping ratio. If alignment result passed the QC, we proceeded with the downstream analysis including gene expression and a deep analysis based on gene expression (e.g., principal component analysis (PCA)/correlation/screening DE genes). The bioinformatic analyses were performed by Genomics Inc.
Quantitative PCR
Total RNA was isolated using the FavorPrep RNA clean-up kit (Favorgen), and cDNA was synthesised using the iScript cDNA synthesis kit (Bio-Rad) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. PCR was performed using the KAPA SYBR FAST qPCR kit (Kapa Biosystems) and the 7900HT fast real-time PCR system57. The gene-specific primer sequence is presented in Supplementary Table 1.
Immunofluorescent staining
The cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 15 min at room temperature. Nonspecific binding sites were blocked, and an additional permeabilisation step was performed for 1 h in 0.2% Triton X-100 and 1% bovine serum albumin. The cells were incubated overnight with a primary antibody at 4 °C. Following this incubation, the fluorescein isothiocyanate- and tetramethylrhodamine-conjugated species secondary antibodies (1:500, Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) were used to detect the primary antibodies. The primary antibodies used in this study were anti-MyosinVIIa (1:500, Abcam, Cambridge, MA, USA) and anti-Espin (1:500, Abcam). Nuclei were visualised using the Hoechst stain (Invitrogen). For FM1-43 staining (Invitrogen), the cells were immersed in the stain solution on ice for 1 min according to the manufacturer’s instructions. We used FM 1-43 staining to demonstrate that the iPSC-derived differentiated HC-like cells exhibit the expression of not only HC markers (MYO7A and ESPN) but also specific ion channels in HCs57. It was reported that FM 1-43 can be used to characterise HCs55 and examine the recycling of synaptic vesicle-associated activities56.
Scanning electron microscopy
The cells were fixed with 4% glutaraldehyde for 1 h, dehydrated in a graded ethanol series and dried using critical point drying with liquid CO2. Specimens were sputter-coated with 100 Å Au/Pd and viewed using a Hitachi S-3500N variable pressure SEM operated under a high vacuum of 5–10 kV. The SEM experiments were performed in the Core Facility of SEM in Mackay Memorial Hospital57.
Statistics analyses
Data are expressed as means ± SD. Independent t test was used for comparison of two groups. One-way analysis of variance was used for comparison of multi-groups. The difference of data was considered statistically significant at p < 0.05.
Electronic supplementary material
Acknowledgements
We thank Professor Shih-Hwa Chiou for providing the hESCs and MERRF-iPSC line (M1ctrl, M1 and M2). We thank Dr. Shih-Jie Chou for sharing his experience on hiPSC culture and maintenance. Part of this article was prepared on the basis of our studies supported by grants from the Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST) of Taiwan Government (MOST104-2314-B-715-003-MY3 and MOST104-2320-B-715-006-MY2), intramural research grants from Mackay Medical College (RD1050179 and RD1050227) and Mackay Memorial Hospital (MMH-MM-10610).
Authors’ contributions
Y.-C.C.: manuscript writing, data analysis and interpretation, collection and/or assembly of data. C.-L.T.: manuscript writing, collection and/or assembly of data, data interpretation. Y.-H.W.: provide MERRF patients cell cultures and data interpretation. Y.-T.W.: provide MERRF patients cell cultures and data interpretation. W.-T.H.: data interpretation. H.-C.L.: data interpretation. Y.-C.H.: conception and design, collection and/or assembly of data, data analysis and interpretation, manuscript writing, and administrative support.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Footnotes
These authors contributed equally: Yen-Chun Chen, Chia-Ling Tsai.
Edited by I Amelio.
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper at 10.1038/s41419-018-0488-y.
Publisher's note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Jeon SJ, Oshima K, Heller S, Edge AS. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells are progenitors in vitro for inner ear hair cells. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2007;34:59–68. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2006.10.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Beisel K, Hansen L, Soukup G, Fritzsch B. Regenerating cochlear hair cells: quo vadis stem cell. Cell Tissue Res. 2008;333:373–379. doi: 10.1007/s00441-008-0639-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Oshima K, et al. Mechanosensitive hair cell-like cells from embryonic and induced pluripotent stem cells. Cell. 2010;141:704–716. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.03.035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Ding J, et al. Induction of differentiation of human embryonic stem cells into functional hair-cell-like cells in the absence of stromal cells. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2016;8:208–222. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2015.11.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Ronaghi M, et al. Inner ear hair cell-like cells from human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2014;23:1275–1284. doi: 10.1089/scd.2014.0033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Schimmang T. Transcription factors that control inner ear development and their potential for transdifferentiation and reprogramming. Hear. Res. 2013;297:84–90. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2012.11.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Cotanche DA, Kaiser CL. Hair cell fate decisions in cochlear development and regeneration. Hear. Res. 2010;266:18–25. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2010.04.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Fritzsch B, et al. Atoh1 null mice show directed afferent fiber growth to undifferentiated ear sensory epithelia followed by incomplete fiber retention. Dev. Dyn. 2005;233:570–583. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.20370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Pan N, et al. Conditional deletion of Atoh1 using Pax2-Cre results in viable mice without differentiated cochlear hair cells that have lost most of the organ of Corti. Hear. Res. 2011;275:66–80. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2010.12.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Devarajan K, Forrest ML, Detamore MS, Staecker H. Adenovector-mediated gene delivery to human umbilical cord mesenchymal stromal cells induces inner ear cell phenotype. Cell Reprogram. 2013;15:43–54. doi: 10.1089/cell.2011.0097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Atkinson PJ, Wise AK, Flynn BO, Nayagam BA, Richardson RT. Hair cell regeneration after ATOH1 gene therapy in the cochlea of profoundly deaf adult guinea pigs. PLoS ONE. 2014;9:e102077. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0102077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Yang SM, et al. Regeneration of stereocilia of hair cells by forced Atoh1 expression in the adult mammalian cochlea. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:e46355. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0046355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Izumikawa M, et al. Auditory hair cell replacement and hearing improvement by Atoh1 gene therapy in deaf mammals. Nat. Med. 2005;11:271–276. doi: 10.1038/nm1193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.A. Three-part, multicenter, open label, single dose study to assess the safety, tolerability, and efficacy of intra labyrinthine (IL) CGF166 in patients with severe-to-profound hearing loss: Novartis Pharmaceuticals https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02132130 (2017).
- 15.Liu Z, Fang J, Dearman J, Zhang L, Zuo J. In vivo generation of immature inner hair cells in neonatal mouse cochleae by ectopic Atoh1 expression. PLoS ONE. 2014;9:e89377. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0089377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Aftab S, Semenec L, Chu JS, Chen N. Identification and characterization of novel human tissue-specific RFX transcription factors. BMC Evol. Biol. 2008;8:226–237. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-8-226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Gajiwala KS, et al. Structure of the winged-helix protein hRFX1 reveals a new mode of DNA binding. Nature. 2000;403:916–921. doi: 10.1038/35002634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Emery P, Durand B, Mach B, Reith W. RFX proteins, a novel family of DNA binding proteins conserved in the eukaryotic kingdom. Nucleic Acids Res. 1996;24:803–807. doi: 10.1093/nar/24.5.803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Senti G, Swoboda P. Distinct isoforms of the RFX transcription factor DAF-19 regulate ciliogenesis and maintenance of synaptic activity. Mol. Biol. Cell. 2008;19:5517–5528. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e08-04-0416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Dubruille R, et al. Drosophila regulatory factor X is necessary for ciliated sensory neuron differentiation. Development. 2002;129:5487–5498. doi: 10.1242/dev.00148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Piasecki BP, Burghoorn J, Swoboda P. Regulatory factor X (RFX)-mediated transcriptional rewiring of ciliary genes in animals. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2010;107:12969–12974. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0914241107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Baas D, et al. A deficiency in RFX3 causes hydrocephalus associated with abnormal differentiation of ependymal cells. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2006;24:1020–1030. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2006.05002.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Elkon R, et al. RFX transcription factors are essential for hearing in mice. Nat. Commun. 2015;6:8549. doi: 10.1038/ncomms9549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Hsu YC, Kao CY, Chung YF, Chen MS, Chiu IM. Ciliogenic RFX transcription factors regulate FGF1 gene promoter. J. Cell. Biochem. 2012;113:2511–2522. doi: 10.1002/jcb.24127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Hsu YC, Liao WC, Kao CY, Chiu IM. Regulation of FGF1 gene promoter through transcription factor RFX1. J. Biol. Chem. 2010;285:13885–13895. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.081463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Kao CY, et al. The mood stabilizer valproate activates human FGF1 gene promoter through inhibiting HDAC and GSK-3 activities. J. Neurochem. 2013;126:4–18. doi: 10.1111/jnc.12292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Purvis TL, et al. Transcriptional regulation of the Alstrom syndrome gene ALMS1 by members of the RFX family and Sp1. Gene. 2010;460:20–29. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2010.03.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Collin GB, et al. The Alstrom syndrome protein, ALMS1, interacts with alpha-actinin and components of the endosome recycling pathway. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:e37925. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0037925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Alstrom CH, Hallgren B, Nilsson LB, Asander H. Retinal degeneration combined with obesity, diabetes mellitus and neurogenous deafness: a specific syndrome (not hitherto described) distinct from the Laurence-Moon-Bardet-Biedl syndrome: a clinical, endocrinological and genetic examination based on a large pedigree. Acta Psychiatr. Neurol. Scand. Suppl. 1959;129:1–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Boyer LA, et al. Core transcriptional regulatory circuitry in human embryonic stem cells. Cell. 2005;122:947–956. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.08.020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Kiernan AE, et al. Sox2 is required for sensory organ development in the mammalian inner ear. Nature. 2005;434:1031–1035. doi: 10.1038/nature03487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Morrisey EE, et al. GATA6 regulates HNF4 and is required for differentiation of visceral endoderm in the mouse embryo. Genes Dev. 1998;12:3579–3590. doi: 10.1101/gad.12.22.3579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Vidricaire G, Jardine K, McBurney MW. Expression of the Brachyury gene during mesoderm development in differentiating embryonal carcinoma cell cultures. Development. 1994;120:115–122. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.1.115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Brugmann SA, Pandur PD, Kenyon KL, Pignoni F, Moody SA. Six1 promotes a placodal fate within the lateral neurogenic ectoderm by functioning as both a transcriptional activator and repressor. Development. 2004;131:5871–5881. doi: 10.1242/dev.01516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Kwon HJ, Bhat N, Sweet EM, Cornell RA, Riley BB. Identification of early requirements for preplacodal ectoderm and sensory organ development. PLoS Genet. 2010;6:e1001133. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1001133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Li H, Roblin G, Liu H, Heller S. Generation of hair cells by stepwise differentiation of embryonic stem cells. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2003;100:13495–13500. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2334503100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Chen W, et al. Restoration of auditory evoked responses by human ES-cell-derived otic progenitors. Nature. 2012;490:278–282. doi: 10.1038/nature11415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Zhang X, et al. Pax6 is a human neuroectoderm cell fate determinant. Cell Stem Cell. 2010;7:90–100. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2010.04.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Curto GG. Pax6 is essential for the maintenance and multi-lineage differentiation of neural stem cells, and for neuronal incorporation into the adult olfactory bulb. Stem Cells Dev. 2014;23:2813–2830. doi: 10.1089/scd.2014.0058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Li H, et al. Correlation of expression of the actin filament-bundling protein espin with stereociliary bundle formation in the developing inner ear. J. Comp. Neurol. 2004;468:125–134. doi: 10.1002/cne.10944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Sinkkonen ST, et al. Intrinsic regenerative potential of murine cochlear supporting cells. Sci. Rep. 2011;1:26. doi: 10.1038/srep00026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Chou SJ, et al. Impaired ROS scavenging system in human induced pluripotent stem cells generated from patients with MERRF syndrome. Sci. Rep. 2016;6:23661. doi: 10.1038/srep23661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Wang J, Schwartz HT, Barr MM. Functional specialization of sensory cilia by an RFX transcription factor isoform. Genetics. 2010;186:1295–1307. doi: 10.1534/genetics.110.122879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Liu H, et al. Characterization of transcriptomes of cochlear inner and outer hair cells. J. Neurosci. 2014;34:11085–11095. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1690-14.2014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Tang ZH, et al. Genetic correction of induced pluripotent stem cells from a deaf patient with MYO7A mutation results in morphologic and functional recovery of the derived hair cell-like cells. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2016;5:561–571. doi: 10.5966/sctm.2015-0252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Chen JR, et al. Effects of genetic correction on the differentiation of hair cell-like cells from iPSCs with MYO15A mutation. Cell Death Differ. 2016;23:1347–1357. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2016.16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Camp JG, Treutlein B. Human organomics: a fresh approach to understanding human development using single-cell transcriptomics. Development. 2017;144:1584–1587. doi: 10.1242/dev.150458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Koehler KR, et al. Generation of inner ear organoids containing functional hair cells from human pluripotent stem cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 2017;35:583–589. doi: 10.1038/nbt.3840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Pera EM, Wessely O, Li SY, De Robertis EM. Neural and head induction by insulin-like growth factor signals. Dev. Cell. 2001;21:655–665. doi: 10.1016/S1534-5807(01)00069-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Corwin JT, Cotanche DA. Development of location-specific hair cell stereocilia in denervated embryonic ears. J. Comp. Neurol. 1989;288:529–537. doi: 10.1002/cne.902880402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Swanson GJ, Howard M, Lewis J. Epithelial autonomy in the development of the inner ear of a bird embryo. Dev. Biol. 1990;137:243–257. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(90)90251-D. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Boëda B, Weil D, Petit C. A specific promoter of the sensory cells of the inner ear defined by transgenesis. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2001;10:1581–1589. doi: 10.1093/hmg/10.15.1581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Lubelsky Y, Reuven N, Shaul Y. Autorepression of rfx1 gene expression: functional conservation from yeast to humans in response to DNA replication arrest. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005;25:10665–10673. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.23.10665-10673.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Iwama A, et al. Dimeric RFX proteins contribute to the activity and lineage specificity of the interleukin-5 receptor alpha promoter through activation and repression domains. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1999;19:3940–3950. doi: 10.1128/MCB.19.6.3940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Meyers JR, et al. Lighting up the senses: FM1-43 loading of sensory cells through nonselective ion channels. J. Neurosci. 2003;23:4054–4065. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-10-04054.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Iwabuchi S, Kakazu Y, Koh JY, Goodman KM, Harata NC. Examination of synaptic vesicle recycling using FM dyes during evoked, spontaneous, and miniature synaptic activities. J. Vis. Exp. 2014;85:e50557. doi: 10.3791/50557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Y.C Chen, Effects of Mitochondrial DNA A8344G Mutation on the Differentiation of Inner Ear Hair Cell-like Cells from Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells, Institute of Biomedical Sciences, Mackay Medical College, 2017, Master.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.