The structure of a coumarin ester is reported and compared with the results of a quantum chemical calculation. In the crystal, intermolecular C—H⋯O contacts generate an infinite C(6) chain along the b axis. C=O⋯π and π–π stacking interactions also occur. Hirshfeld surface analysis was used to confirm and quantify the supramolecular interactions.
Keywords: crystal structure, C—H⋯O hydrogen bond, coumarin, Hirshfeld surface analysis, quantum chemical calculations
Abstract
In the title compound, C20H18O4, the benzoate ring is oriented at an acute angle of 33.10 (12)° with respect to the planar (r.m.s deviation = 0.016 Å) coumarin ring system. An intramolecular C—H⋯O hydrogen bond closes an S(6) ring motif. In the crystal, C—H⋯O contacts generate infinite C(6) chains along the b-axis direction. Also present are π–π stacking interactions between neighbouring pyrone and benzene rings [centroid–centroid distance = 3.7034 (18) Å] and C=O⋯π interactions [O⋯centroid = 3.760 (3) Å]. The data obtained from quantum chemical calculations performed on the title compound are in good agreement with the observed structure, although the calculated C—O—C—C torsion angle between the coumarin ring system and the benzoate ring (129.1°) is somewhat lower than the observed value [141.3 (3)°]. Hirshfeld surface analysis has been used to confirm and quantify the supramolecular interactions.
Chemical context
Coumarins and their derivatives constitute one of the major classes of naturally occurring compounds and interest in their chemistry continues unabated because of their usefulness as biologically active agents. They also form the core of several molecules of pharmaceutical importance. Coumarin and its derivatives have been reported to serve as anti-bacterial (Basanagouda et al., 2009 ▸), anti-oxidant (Vukovic et al., 2010 ▸) and anti-inflammatory agents (Emmanuel-Giota et al., 2001 ▸). In view of their importance and as a continuation of our work on the crystal structure analysis of coumarin derivatives (Abou et al., 2012 ▸, 2013 ▸), we report herein the synthesis, crystal structure, geometry optimization and Hirshfeld surface analysis of the title coumarin derivative, (I).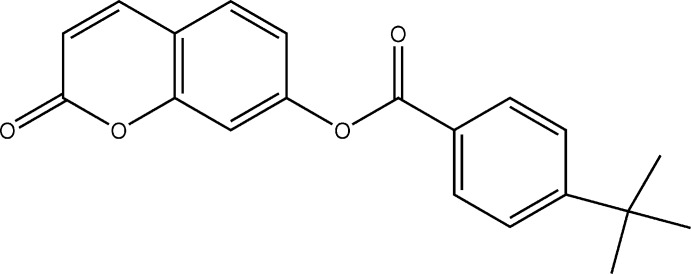
Structural commentary
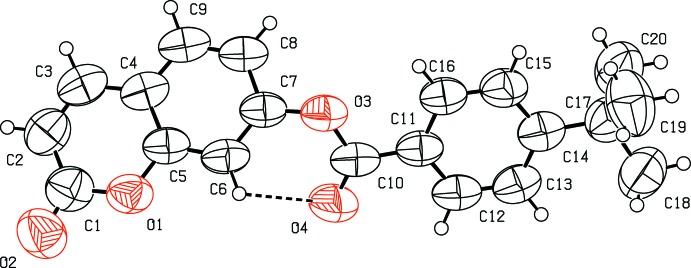
The molecular structure of the title coumarin derivative, (I), is illustrated in Fig. 1 ▸. An S(6) ring motif arises from an intramolecular C6—H6⋯O4 hydrogen bond, and generates a pseudo-tricyclic ring system (Fig. 1 ▸). The coumarin ring system is planar [r.m.s deviation = 0.016 Å] and is oriented at an acute angle of 33.10 (12)° with respect to the C11–C16 benzene ring while the pseudo-six-membered ring makes dihedral angles of 27.34 (11) and 13.98 (13)°, respectively, with the coumarin ring system and the benzene ring. An inspection of the bond lengths shows that there is a slight asymmetry of the electronic distribution around the pyrone ring: the C3—C2 [1.338 (5) Å] and C2—C1 [1.426 (5) Å] bond lengths are shorter and longer, respectively, than those excepted for a Car—Car bond. This suggests that the electron density is preferentially located in the C2—C3 bond of the pyrone ring, as seen in other coumarin derivatives (Gomes et al., 2016 ▸; Ziki et al., 2016 ▸).
Figure 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound and the atomic numbering scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level. H atoms are shown as spheres of arbitrary radius. The intramolecular hydrogen bond is indicated by dashed lines.
Supramolecular features
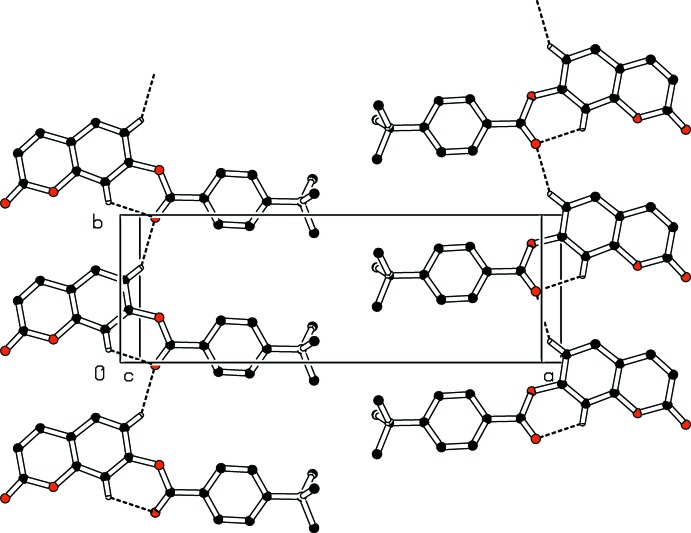
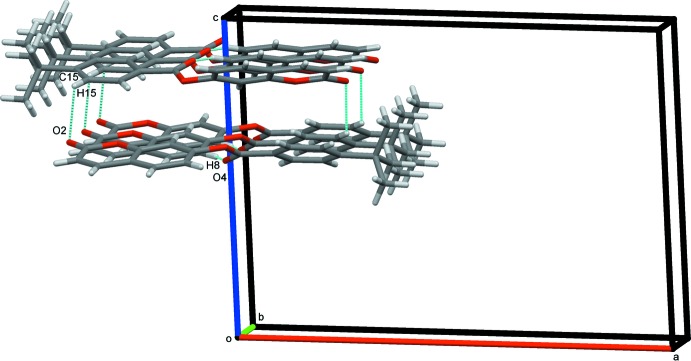
In the crystal, two types of intermolecular hydrogen-bonding interactions are present (Table 1 ▸). The C8—H8⋯O4 hydrogen bonds link molecules into infinite chains along the [010] direction (Fig. 2 ▸) while the C15—H15⋯O2 hydrogen-bonding interactions generate chains extending along the c-axis direction, as shown in Fig. 3 ▸. In addition, a close contact [H2⋯H19B(−x, − + y,
+ y,  − z) = 2.38 Å] is found at a distance shorter than the sum of the van der Waals radii. An unusual C10=O4⋯π interaction [O4⋯Cg2(−x,
− z) = 2.38 Å] is found at a distance shorter than the sum of the van der Waals radii. An unusual C10=O4⋯π interaction [O4⋯Cg2(−x,  + y,
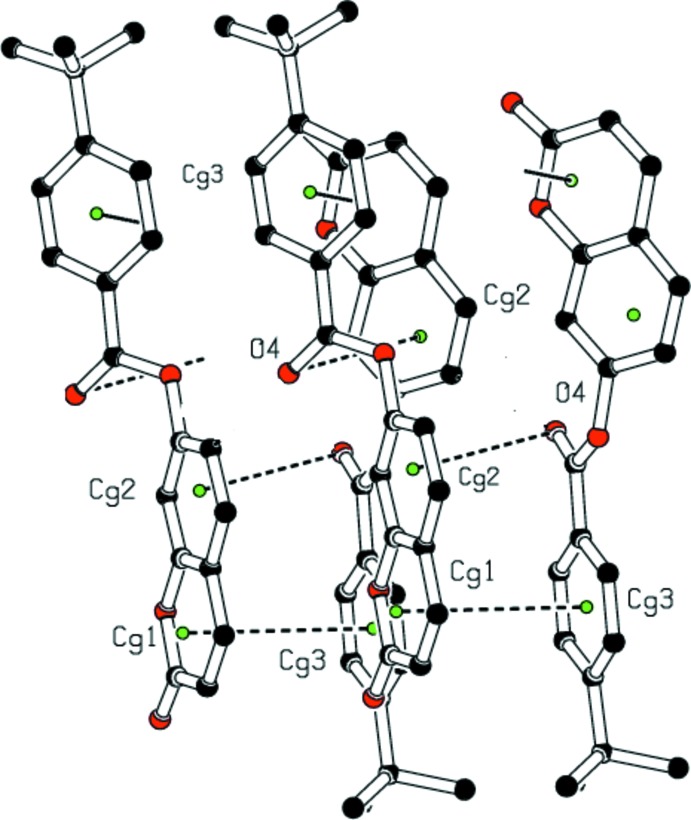
+ y,  − z) = 3.760 (3) Å, where Cg2 is the centroid of the C4–C9 benzene ring], is also present. The resulting supramolecular aggregation is completed by the presence of π–π stacking (Fig. 4 ▸) between the pyrone and benzene rings with centroid–centroid distances [Cg1⋯Cg3(−x, −
− z) = 3.760 (3) Å, where Cg2 is the centroid of the C4–C9 benzene ring], is also present. The resulting supramolecular aggregation is completed by the presence of π–π stacking (Fig. 4 ▸) between the pyrone and benzene rings with centroid–centroid distances [Cg1⋯Cg3(−x, − + y,
+ y,  − z) = 3.7035 (18) and Cg3⋯Cg1 (−x,
− z) = 3.7035 (18) and Cg3⋯Cg1 (−x,  + y,
+ y,  − z) = 3.7034 (18) Å, where Cg1 and Cg3 are the centroids of the pyrone and the C11–C16 benzene rings, respectively] that are less than 3.8 Å, the maximum regarded as suitable for an effective π–π interaction (Janiak, 2000 ▸). In these interactions, the perpendicular distances of Cg1 on ring 3 are 3.6144 (13) and 3.6143 (13) Å, respectively, and the distances between Cg1 and a perpendicular projection of Cg3 on ring 1 (slippage) are 0.726 and 0.807Å, respectively.
− z) = 3.7034 (18) Å, where Cg1 and Cg3 are the centroids of the pyrone and the C11–C16 benzene rings, respectively] that are less than 3.8 Å, the maximum regarded as suitable for an effective π–π interaction (Janiak, 2000 ▸). In these interactions, the perpendicular distances of Cg1 on ring 3 are 3.6144 (13) and 3.6143 (13) Å, respectively, and the distances between Cg1 and a perpendicular projection of Cg3 on ring 1 (slippage) are 0.726 and 0.807Å, respectively.
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
Cg2 is the centroid of the C4–C9 ring.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C8—H8⋯O4i | 0.93 | 2.32 | 3.114 (4) | 144 |
| C15—H15⋯O2ii | 0.93 | 2.65 | 3.310 (4) | 128 |
| C6—H6⋯O4 | 0.93 | 2.41 | 2.813 (4) | 106 |
| C10—O4⋯Cg2iii | 1.18 (1) | 3.76 (1) | 3.560 (3) | 71 (1) |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii) 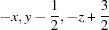 ; (iii)
; (iii) 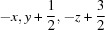 .
.
Figure 2.
Part of the crystal packing of the title compound showing the formation of an infinite C(6) chain along the b-axis direction. Dashed lines indicate hydrogen bonds. H atoms not involved in hydrogen-bonding interactions have been omitted for clarity.
Figure 3.
Crystal packing of (I) showing adjacent pairs of molecules along the b axis
Figure 4.
A view of the crystal packing, showing H⋯H contacts, C10=O4⋯π and π–π stacking interactions (dashed lines). The green dots are ring centroids. H atoms not involved in H⋯H interactions have been omitted for clarity.
Database survey
A CSD search (Web CSD version 5.39; March 9, 2018; Groom et al., 2016 ▸) found five coumarin ester structures with substituents at the 7 positions (Ramasubbu et al.,1982 ▸; Gnanaguru et al., 1985 ▸; Parveen et al., 2011 ▸; Ji et al., 2014 ▸, 2017 ▸). In these structures and those of meta-substituted coumarin esters (Abou et al., 2012 ▸, 2013 ▸; Bibila Mayaya Bisseyou et al., 2013 ▸; Yu et al., 2014 ▸; Gomes et al., 2016 ▸; Ziki et al., 2016 ▸, 2017 ▸), the pyrone rings all show three long (in the range 1.37–1.46 Å) and one short (1.32–1.34 Å) C—C distances, suggesting that the electronic density is preferentially located in the short C—C bond at the pyrone ring. This pattern is clearly repeated here with C2—C3 = 1.338 (5) Å while C1—C2 = 1.426 (5), C3—C4 = 1.436 (5) and C4—C5 = 1.375 (4) Å.
Hirshfeld surface analysis
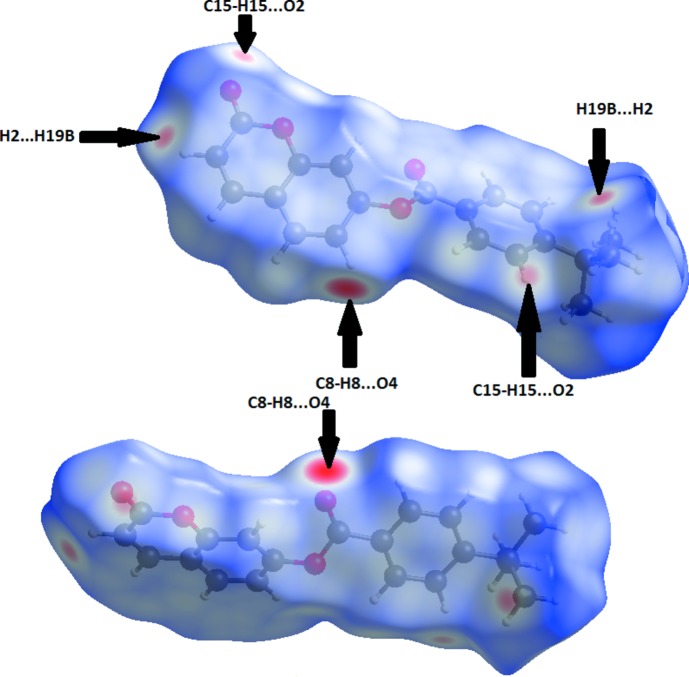
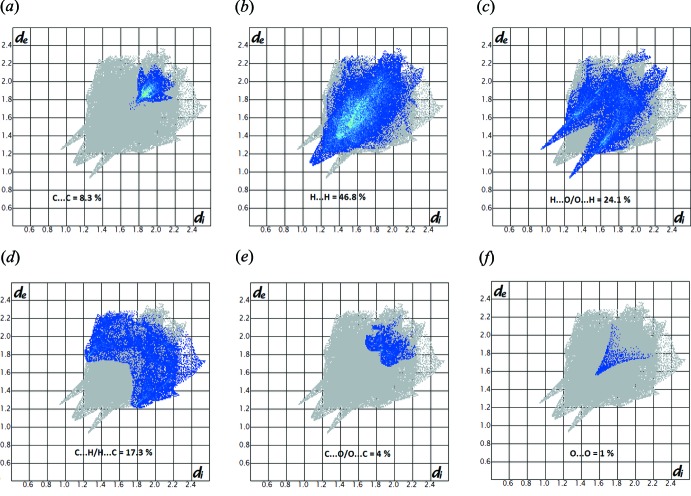
Molecular Hirshfeld surfaces of 2-oxo-2H-chromen-7-yl 4-tert-butylbenzoate, (I), were calculated using a standard (high) surface resolution, and with the three-dimensional d norm surfaces mapped over a fixed colour scale of −0.39 (red) to 1.4 Å (blue) with the program CrystalExplorer 3.1 (Wolff et al., 2012 ▸). The analysis of intermolecular interactions through the mapping of d norm is accomplished by considering the contact distances d i and d e from the Hirshfeld surface to the nearest atom inside and outside, respectively. In (I), the surface mapped over d norm highlights six red spots showing distances shorter than the sum of the van der Waals radii. These dominant interactions correspond to intermolecular C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, O⋯π and π–π stacking interactions between the surface and the neighbouring environment. The mapping also shows white spots with distances equal to the sum of the van der Waals radii and blue regions with distances longer than the sum of the van der Waals radii. The surfaces are transparent to allow visualization of the molecule (Fig. 5 ▸). Furthermore, the two-dimensional fingerprint plots (FP) in Fig. 6 ▸ highlight particular close contacts of atom pairs and the contributions from different contacts are provided. The red spots in the middle of the surface appearing near d e = d i ≃ 1.8–2 Å correspond to close C⋯C interplanar contacts. These contacts, which comprise 8.3% of the total Hirshfeld surface area, relate to π–π interactions (Fig. 6 ▸ a), as shown by the X-ray study. The most significant contribution to the Hirshfeld surface (46.8%) is from H⋯H contacts, which appear in the central region of the FP (Fig. 6 ▸ b). H⋯O/O⋯H interactions with a 24.1% contribution appear as blue spikes in Fig. 6 ▸ c and show the presence of O⋯H contacts, whereas the C⋯H/H⋯C plot (17.3%) gives information about intermolecular hydrogen bonds (Fig. 6 ▸ d). Other visible spots in the Hirshfeld surfaces show C⋯O/O⋯C and O⋯O contacts, which contribute only 4.0 and 1.0%, respectively (Fig. 6 ▸ e and 6f).
Figure 5.
A View of the Hirshfeld surfaces with the three-dimensional d norm surfaces mapped over a fixed colour scale of −0.39 (red) to 1.4 Å (blue) for compound (I).
Figure 6.
Decomposed two-dimensional fingerprint plots for compound (I). Various close contacts and their relative contributions are indicated.
Theoretical calculations
The geometry optimization of compound (I) was performed using the density functional theory (DFT) method with a 6-311++G(d,p) basis set. The crystal structure in the solid state was used as the starting structure for the calculations. The DFT calculations are performed with the GAUSSIAN09 program package (Frisch et al., 2013 ▸). The resulting geometrical parameters are compared with those obtained from the X-ray crystallographic study. An analysis of the computational bond lengths and bond angles and comparison with the crystallographic results shows a good agreement between them, with a root-mean-square deviation of 0.017 Å for bond lengths and 0.97° for bond angles (see Supplementary Tables S1 and S2). In addition, an inspection of the calculated torsion angles shows that the coumarin ring system and the benzene (C11–C16) ring are planar (Supplementary Table S3), which is in good agreement with the crystallographic prevision, although the calculated C10—O3—C7—C8 torsion angle between them (129.1°) is somewhat lower than the observed value [141.3 (3)°].
Synthesis and crystallization
To a solution of 4-tert-butylbenzoyl chloride (6.17 mmol; 1.3 g) in dry tetrahydrofuran (30 to 40 ml), was added dry trimethylamine (2.6 ml; 3 molar equivalents) and 7-hydroxycoumarin (6.17 mmol; 1g) in small portions over 30 min. The mixture was then refluxed for four h and poured into 40 ml of chloroform. The solution was acidified with diluted hydrochloric acid until the pH was 2–3. The organic layer was extracted, washed with water to neutrality, dried over MgSO4 and the solvent removed. The resulting precipitate (crude product) was filtered off with suction, washed with petroleum ether and recrystallized from chloroform. Colourless crystals of the title compound were obtained in a good yield: 90%; m.p. 406–408 K.
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 2 ▸. H atoms were placed in calculated positions [C—H = 0.93 (aromatic) or 0.96 Å (methyl group)] and refined using a riding-model approximation with U iso(H) constrained to 1.2 (aromatic) or 1.5 (methyl) times Ueq(C) of the respective parent atom.
Table 2. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | C20H18O4 |
| M r | 322.34 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, P21/c |
| Temperature (K) | 298 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 18.684 (2), 6.5431 (5), 13.6688 (14) |
| β (°) | 93.627 (11) |
| V (Å3) | 1667.7 (3) |
| Z | 4 |
| Radiation type | Cu Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.73 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.40 × 0.12 × 0.04 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Rigaku Oxford Diffraction SuperNova, Dual, Cu at zero, Atlas S2 |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Rigaku OD, 2015 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.714, 1.000 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 9647, 3005, 1710 |
| R int | 0.035 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.600 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.057, 0.202, 1.01 |
| No. of reflections | 3005 |
| No. of parameters | 217 |
| H-atom treatment | H-atom parameters constrained |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.14, −0.13 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018004188/sj5549sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018004188/sj5549Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018004188/sj5549Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 1828991
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Spectropôle Service of the Faculty of Sciences and Techniques of Saint Jérôme (France) for the use of the diffractometer.
supplementary crystallographic information
Crystal data
| C20H18O4 | F(000) = 680 |
| Mr = 322.34 | Dx = 1.284 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Melting point = 406–408 K |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cu Kα radiation, λ = 1.54184 Å |
| a = 18.684 (2) Å | Cell parameters from 1499 reflections |
| b = 6.5431 (5) Å | θ = 4.7–63.4° |
| c = 13.6688 (14) Å | µ = 0.73 mm−1 |
| β = 93.627 (11)° | T = 298 K |
| V = 1667.7 (3) Å3 | Prism, colorless |
| Z = 4 | 0.40 × 0.12 × 0.04 mm |
Data collection
| Rigaku Oxford Diffraction SuperNova, Dual, Cu at zero, Atlas S2 diffractometer | 3005 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: micro-focus sealed X-ray tube, SuperNova (Cu) X-ray Source | 1710 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Mirror monochromator | Rint = 0.035 |
| Detector resolution: 5.3048 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 67.7°, θmin = 4.7° |
| ω scans | h = −22→19 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Rigaku OD, 2015) | k = −7→7 |
| Tmin = 0.714, Tmax = 1.000 | l = −15→16 |
| 9647 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.057 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.202 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.01 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0981P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3005 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 217 parameters | Δρmax = 0.14 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.13 e Å−3 |
| 72 constraints |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O3 | 0.05338 (12) | 0.1955 (3) | 0.65709 (16) | 0.0967 (6) | |
| O1 | −0.19810 (13) | 0.3433 (3) | 0.65369 (16) | 0.1016 (7) | |
| O4 | 0.04152 (14) | 0.5177 (3) | 0.6031 (2) | 0.1233 (9) | |
| C7 | −0.01924 (18) | 0.1455 (4) | 0.64140 (19) | 0.0869 (8) | |
| C4 | −0.15790 (19) | 0.0068 (4) | 0.61057 (19) | 0.0905 (8) | |
| C6 | −0.07476 (18) | 0.2783 (4) | 0.6568 (2) | 0.0904 (8) | |
| H6 | −0.0662 | 0.4119 | 0.6776 | 0.108* | |
| C11 | 0.15865 (18) | 0.3838 (4) | 0.63538 (19) | 0.0860 (8) | |
| C5 | −0.14356 (18) | 0.2044 (4) | 0.63979 (19) | 0.0869 (8) | |
| C9 | −0.1001 (2) | −0.1235 (4) | 0.5982 (2) | 0.0974 (9) | |
| H9 | −0.1086 | −0.2586 | 0.5797 | 0.117* | |
| C10 | 0.0789 (2) | 0.3799 (4) | 0.6300 (2) | 0.0907 (8) | |
| C12 | 0.1920 (2) | 0.5629 (4) | 0.6107 (2) | 0.0974 (9) | |
| H12 | 0.1645 | 0.6774 | 0.5935 | 0.117* | |
| C14 | 0.3083 (2) | 0.4064 (5) | 0.6350 (2) | 0.0971 (9) | |
| C8 | −0.0311 (2) | −0.0549 (4) | 0.6129 (2) | 0.0933 (8) | |
| H8 | 0.0073 | −0.1419 | 0.6038 | 0.112* | |
| C3 | −0.2317 (2) | −0.0532 (5) | 0.5957 (2) | 0.1066 (10) | |
| H3 | −0.2432 | −0.1866 | 0.5774 | 0.128* | |
| O2 | −0.31255 (16) | 0.4209 (5) | 0.6509 (2) | 0.1421 (11) | |
| C13 | 0.2657 (2) | 0.5738 (5) | 0.6111 (2) | 0.1024 (10) | |
| H13 | 0.2872 | 0.6965 | 0.5950 | 0.123* | |
| C16 | 0.20033 (19) | 0.2163 (4) | 0.6614 (2) | 0.0957 (9) | |
| H16 | 0.1788 | 0.0951 | 0.6794 | 0.115* | |
| C15 | 0.2743 (2) | 0.2284 (5) | 0.6607 (2) | 0.1034 (10) | |
| H15 | 0.3018 | 0.1140 | 0.6781 | 0.124* | |
| C1 | −0.2694 (2) | 0.2881 (6) | 0.6378 (3) | 0.1124 (10) | |
| C2 | −0.2839 (2) | 0.0826 (6) | 0.6080 (3) | 0.1137 (11) | |
| H2 | −0.3314 | 0.0415 | 0.5968 | 0.136* | |
| C17 | 0.3902 (2) | 0.4102 (6) | 0.6331 (3) | 0.1112 (10) | |
| C18 | 0.4185 (3) | 0.6214 (7) | 0.6053 (4) | 0.1529 (18) | |
| H18A | 0.3973 | 0.6606 | 0.5423 | 0.229* | |
| H18B | 0.4062 | 0.7200 | 0.6535 | 0.229* | |
| H18C | 0.4697 | 0.6157 | 0.6028 | 0.229* | |
| C19 | 0.4251 (3) | 0.3551 (9) | 0.7329 (4) | 0.170 (2) | |
| H19A | 0.4763 | 0.3583 | 0.7302 | 0.256* | |
| H19B | 0.4107 | 0.4518 | 0.7807 | 0.256* | |
| H19C | 0.4103 | 0.2205 | 0.7508 | 0.256* | |
| C20 | 0.4126 (3) | 0.2572 (8) | 0.5546 (4) | 0.166 (2) | |
| H20A | 0.3901 | 0.2942 | 0.4920 | 0.249* | |
| H20B | 0.4638 | 0.2604 | 0.5512 | 0.249* | |
| H20C | 0.3979 | 0.1219 | 0.5717 | 0.249* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O3 | 0.1181 (17) | 0.0720 (10) | 0.0991 (14) | 0.0106 (10) | −0.0014 (11) | 0.0063 (9) |
| O1 | 0.1168 (17) | 0.0875 (13) | 0.0988 (14) | 0.0074 (11) | −0.0057 (12) | −0.0189 (10) |
| O4 | 0.129 (2) | 0.0812 (13) | 0.160 (2) | 0.0214 (13) | 0.0119 (16) | 0.0276 (13) |
| C7 | 0.119 (2) | 0.0684 (13) | 0.0726 (15) | 0.0089 (14) | −0.0013 (14) | 0.0037 (10) |
| C4 | 0.132 (2) | 0.0739 (14) | 0.0647 (14) | −0.0064 (15) | 0.0000 (14) | 0.0019 (10) |
| C6 | 0.128 (2) | 0.0655 (13) | 0.0764 (15) | 0.0065 (14) | −0.0047 (14) | −0.0088 (11) |
| C11 | 0.120 (2) | 0.0690 (13) | 0.0681 (14) | 0.0067 (13) | −0.0017 (14) | −0.0029 (10) |
| C5 | 0.121 (2) | 0.0732 (13) | 0.0660 (14) | 0.0058 (15) | −0.0021 (13) | −0.0042 (11) |
| C9 | 0.150 (3) | 0.0642 (13) | 0.0779 (16) | 0.0016 (16) | 0.0037 (17) | 0.0010 (11) |
| C10 | 0.133 (3) | 0.0646 (13) | 0.0730 (15) | 0.0115 (14) | −0.0011 (15) | −0.0031 (11) |
| C12 | 0.133 (3) | 0.0688 (14) | 0.0890 (18) | 0.0092 (15) | −0.0019 (17) | 0.0035 (12) |
| C14 | 0.124 (3) | 0.0839 (17) | 0.0813 (17) | −0.0018 (16) | −0.0056 (16) | −0.0001 (13) |
| C8 | 0.130 (3) | 0.0681 (14) | 0.0815 (16) | 0.0106 (15) | 0.0045 (16) | 0.0028 (12) |
| C3 | 0.143 (3) | 0.0864 (18) | 0.0893 (19) | −0.0144 (19) | 0.0001 (19) | −0.0027 (14) |
| O2 | 0.126 (2) | 0.149 (2) | 0.149 (2) | 0.0183 (18) | −0.0063 (17) | −0.0434 (19) |
| C13 | 0.132 (3) | 0.0772 (16) | 0.097 (2) | −0.0074 (16) | 0.0000 (18) | 0.0070 (14) |
| C16 | 0.121 (3) | 0.0740 (15) | 0.0915 (19) | 0.0033 (15) | 0.0038 (16) | 0.0098 (13) |
| C15 | 0.123 (3) | 0.0817 (17) | 0.104 (2) | 0.0078 (16) | −0.0040 (18) | 0.0128 (15) |
| C1 | 0.127 (3) | 0.114 (2) | 0.095 (2) | 0.003 (2) | −0.0028 (19) | −0.0183 (18) |
| C2 | 0.123 (3) | 0.115 (3) | 0.102 (2) | −0.016 (2) | 0.002 (2) | −0.0086 (19) |
| C17 | 0.115 (3) | 0.109 (2) | 0.108 (2) | −0.0068 (19) | −0.0027 (19) | −0.0005 (18) |
| C18 | 0.137 (4) | 0.133 (3) | 0.185 (5) | −0.031 (3) | −0.019 (3) | 0.017 (3) |
| C19 | 0.119 (3) | 0.246 (6) | 0.143 (4) | 0.016 (3) | −0.012 (3) | 0.050 (4) |
| C20 | 0.140 (4) | 0.166 (4) | 0.198 (5) | −0.026 (3) | 0.052 (4) | −0.048 (4) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O3—C10 | 1.357 (3) | C8—H8 | 0.9300 |
| O3—C7 | 1.399 (4) | C3—C2 | 1.338 (5) |
| O1—C1 | 1.383 (4) | C3—H3 | 0.9300 |
| O1—C5 | 1.387 (3) | O2—C1 | 1.206 (4) |
| O4—C10 | 1.184 (3) | C13—H13 | 0.9300 |
| C7—C6 | 1.379 (4) | C16—C15 | 1.385 (5) |
| C7—C8 | 1.382 (4) | C16—H16 | 0.9300 |
| C4—C5 | 1.375 (4) | C15—H15 | 0.9300 |
| C4—C9 | 1.395 (5) | C1—C2 | 1.426 (5) |
| C4—C3 | 1.436 (5) | C2—H2 | 0.9300 |
| C6—C5 | 1.379 (4) | C17—C19 | 1.517 (5) |
| C6—H6 | 0.9300 | C17—C18 | 1.536 (5) |
| C11—C16 | 1.378 (4) | C17—C20 | 1.545 (5) |
| C11—C12 | 1.379 (4) | C18—H18A | 0.9600 |
| C11—C10 | 1.488 (5) | C18—H18B | 0.9600 |
| C9—C8 | 1.369 (5) | C18—H18C | 0.9600 |
| C9—H9 | 0.9300 | C19—H19A | 0.9600 |
| C12—C13 | 1.380 (5) | C19—H19B | 0.9600 |
| C12—H12 | 0.9300 | C19—H19C | 0.9600 |
| C14—C13 | 1.381 (4) | C20—H20A | 0.9600 |
| C14—C15 | 1.383 (4) | C20—H20B | 0.9600 |
| C14—C17 | 1.531 (5) | C20—H20C | 0.9600 |
| C10—O3—C7 | 121.3 (2) | C14—C13—H13 | 119.3 |
| C1—O1—C5 | 121.1 (3) | C11—C16—C15 | 120.1 (3) |
| C6—C7—C8 | 122.2 (3) | C11—C16—H16 | 120.0 |
| C6—C7—O3 | 124.1 (3) | C15—C16—H16 | 120.0 |
| C8—C7—O3 | 113.7 (3) | C14—C15—C16 | 121.7 (3) |
| C5—C4—C9 | 118.2 (3) | C14—C15—H15 | 119.2 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 117.8 (3) | C16—C15—H15 | 119.2 |
| C9—C4—C3 | 124.0 (3) | O2—C1—O1 | 115.8 (3) |
| C5—C6—C7 | 117.1 (3) | O2—C1—C2 | 127.2 (4) |
| C5—C6—H6 | 121.5 | O1—C1—C2 | 117.0 (4) |
| C7—C6—H6 | 121.5 | C3—C2—C1 | 122.3 (4) |
| C16—C11—C12 | 118.8 (3) | C3—C2—H2 | 118.8 |
| C16—C11—C10 | 123.2 (3) | C1—C2—H2 | 118.8 |
| C12—C11—C10 | 118.0 (3) | C19—C17—C14 | 110.7 (3) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 122.8 (3) | C19—C17—C18 | 107.5 (4) |
| C4—C5—O1 | 121.6 (3) | C14—C17—C18 | 112.2 (3) |
| C6—C5—O1 | 115.6 (2) | C19—C17—C20 | 110.6 (4) |
| C8—C9—C4 | 120.8 (3) | C14—C17—C20 | 108.4 (3) |
| C8—C9—H9 | 119.6 | C18—C17—C20 | 107.3 (4) |
| C4—C9—H9 | 119.6 | C17—C18—H18A | 109.5 |
| O4—C10—O3 | 123.5 (3) | C17—C18—H18B | 109.5 |
| O4—C10—C11 | 124.8 (3) | H18A—C18—H18B | 109.5 |
| O3—C10—C11 | 111.7 (2) | C17—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| C11—C12—C13 | 120.6 (3) | H18A—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| C11—C12—H12 | 119.7 | H18B—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| C13—C12—H12 | 119.7 | C17—C19—H19A | 109.5 |
| C13—C14—C15 | 117.4 (4) | C17—C19—H19B | 109.5 |
| C13—C14—C17 | 123.0 (3) | H19A—C19—H19B | 109.5 |
| C15—C14—C17 | 119.6 (3) | C17—C19—H19C | 109.5 |
| C9—C8—C7 | 119.0 (3) | H19A—C19—H19C | 109.5 |
| C9—C8—H8 | 120.5 | H19B—C19—H19C | 109.5 |
| C7—C8—H8 | 120.5 | C17—C20—H20A | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 120.1 (3) | C17—C20—H20B | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 119.9 | H20A—C20—H20B | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 119.9 | C17—C20—H20C | 109.5 |
| C12—C13—C14 | 121.4 (3) | H20A—C20—H20C | 109.5 |
| C12—C13—H13 | 119.3 | H20B—C20—H20C | 109.5 |
| C10—O3—C7—C6 | −41.5 (4) | C6—C7—C8—C9 | 0.8 (4) |
| C10—O3—C7—C8 | 141.3 (3) | O3—C7—C8—C9 | 178.1 (3) |
| C8—C7—C6—C5 | −1.7 (4) | C5—C4—C3—C2 | 1.5 (5) |
| O3—C7—C6—C5 | −178.7 (2) | C9—C4—C3—C2 | −179.2 (3) |
| C9—C4—C5—C6 | 0.3 (4) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | 0.8 (5) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 179.7 (3) | C15—C14—C13—C12 | −1.5 (5) |
| C9—C4—C5—O1 | 180.0 (2) | C17—C14—C13—C12 | 177.9 (3) |
| C3—C4—C5—O1 | −0.6 (4) | C12—C11—C16—C15 | −1.1 (5) |
| C7—C6—C5—C4 | 1.2 (4) | C10—C11—C16—C15 | 177.2 (3) |
| C7—C6—C5—O1 | −178.5 (2) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | 0.9 (5) |
| C1—O1—C5—C4 | −0.5 (4) | C17—C14—C15—C16 | −178.5 (3) |
| C1—O1—C5—C6 | 179.2 (3) | C11—C16—C15—C14 | 0.4 (5) |
| C5—C4—C9—C8 | −1.3 (4) | C5—O1—C1—O2 | −179.1 (3) |
| C3—C4—C9—C8 | 179.4 (3) | C5—O1—C1—C2 | 0.8 (5) |
| C7—O3—C10—O4 | 9.6 (4) | C4—C3—C2—C1 | −1.2 (5) |
| C7—O3—C10—C11 | −168.7 (2) | O2—C1—C2—C3 | 180.0 (4) |
| C16—C11—C10—O4 | −175.9 (3) | O1—C1—C2—C3 | 0.1 (6) |
| C12—C11—C10—O4 | 2.4 (5) | C13—C14—C17—C19 | 122.1 (4) |
| C16—C11—C10—O3 | 2.3 (4) | C15—C14—C17—C19 | −58.5 (5) |
| C12—C11—C10—O3 | −179.4 (2) | C13—C14—C17—C18 | 1.9 (5) |
| C16—C11—C12—C13 | 0.6 (4) | C15—C14—C17—C18 | −178.7 (4) |
| C10—C11—C12—C13 | −177.8 (3) | C13—C14—C17—C20 | −116.5 (4) |
| C4—C9—C8—C7 | 0.7 (4) | C15—C14—C17—C20 | 62.9 (4) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
Cg2 is the centroid of the C4–C9 ring.
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C8—H8···O4i | 0.93 | 2.32 | 3.114 (4) | 144 |
| C15—H15···O2ii | 0.93 | 2.65 | 3.310 (4) | 128 |
| C6—H6···O4 | 0.93 | 2.41 | 2.813 (4) | 106 |
| C10—O4···Cg2iii | 1.18 (1) | 3.76 (1) | 3.560 (3) | 71 (1) |
Symmetry codes: (i) x, y−1, z; (ii) −x, y−1/2, −z+3/2; (iii) −x, y+1/2, −z+3/2.
S1
Experimental and calculated bond lengths (Å)
| Bond | X-ray | 6-311++G(d,p) |
| O3—C10 | 1.357 (3) | 1.381 |
| O3—C7 | 1.399 (4) | 1.387 |
| O1—C1 | 1.383 (4) | 1.399 |
| O1—C5 | 1.387 (3) | 1.363 |
| O4—C10 | 1.184 (3) | 1.203 |
| C7—C6 | 1.379 (4) | 1.387 |
| C7—C8 | 1.382 (4) | 1.399 |
| C4—C5 | 1.375 (4) | 1.406 |
| C4—C9 | 1.395 (5) | 1.405 |
| C4—C3 | 1.436 (5) | 1.438 |
| C6—C5 | 1.379 (4) | 1.392 |
| C11—C16 | 1.378 (4) | 1.401 |
| C11—C12 | 1.379 (4) | 1.397 |
| C11—C10 | 1.488 (5) | 1.482 |
| C9—C8 | 1.369 (5) | 1.383 |
| C12—C13 | 1.380 (5) | 1.391 |
| C14—C13 | 1.381 (4) | 1.401 |
| C14—C15 | 1.383 (4) | 1.405 |
| C14—C17 | 1.531 (5) | 1.537 |
| C3—C2 | 1.338 (5) | 1.350 |
| O2—C1 | 1.206 (4) | 1.202 |
| C16—C15 | 1.385 (5) | 1.388 |
| C1—C2 | 1.426 (5) | 1.457 |
| C17—C19 | 1.517 (5) | 1.547 |
| C17—C18 | 1.536 (5) | 1.540 |
| C17—C20 | 1.545 (5) | 1.547 |
S2
Experimental and calculated bond angles (°)
| Bond angle | X-ray | 6-311++G(d,p) |
| C10—O3—C7 | 121.3 (2) | 120.5 |
| C1—O1—C5 | 121.1 (3) | 122.9 |
| C6—C7—C8 | 122.2 (3) | 121.8 |
| C6—C7—O3 | 124.1 (3) | 121.7 |
| C8—C7—O3 | 113.7 (3) | 116.5 |
| C5—C4—C9 | 118.2 (3) | 118.3 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 117.8 (3) | 117.5 |
| C9—C4—C3 | 124.0 (3) | 124.3 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 117.1 (3) | 118.2 |
| C16—C11—C12 | 118.8 (3) | 118.9 |
| C16—C11—C10 | 123.2 (3) | 123.1 |
| C12—C11—C10 | 118.0 (3) | 118.0 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 122.8 (3) | 121.7 |
| C4—C5—O1 | 121.6 (3) | 121.2 |
| C6—C5—O1 | 115.6 (2) | 117.0 |
| C8—C9—C4 | 120.8 (3) | 120.8 |
| O4—C10—O3 | 123.5 (3) | 123.0 |
| O4—C10—C11 | 124.8 (3) | 125.7 |
| O3—C10—C11 | 111.7 (2) | 111.4 |
| C11—C12—C13 | 120.6 (3) | 120.5 |
| C13—C14—C15 | 117.4 (4) | 117.3 |
| C13—C14—C17 | 123.0 (3) | 122.8 |
| C15—C14—C17 | 119.6 (3) | 119.9 |
| C9—C8—C7 | 119.0 (3) | 119.2 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 120.1 (3) | 120.9 |
| C12—C13—C14 | 121.4 (3) | 121.4 |
| C11—C16—C15 | 120.1 (3) | 120.1 |
| C14—C15—C16 | 121.7 (3) | 121.8 |
| O2—C1—O1 | 115.8 (3) | 117.7 |
| O2—C1—C2 | 127.2 (4) | 126.4 |
| O1—C1—C2 | 117.0 (4) | 115.9 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 122.3 (4) | 121.6 |
| C19—C17—C14 | 110.7 (3) | 109.3 |
| C19—C17—C18 | 107.5 (4) | 108.2 |
| C14—C17—C18 | 112.2 (3) | 112.4 |
| C19—C17—C20 | 110.6 (4) | 109.4 |
| C14—C17—C20 | 108.4 (3) | 109.3 |
| C18—C17—C20 | 107.3 (4) | 108.2 |
S3
Experimental and calculated torsion angles (°)
| Torsion angle | X-ray | 6-311++G(d,p) |
| C10—O3—C7—C6 | -41.5 (4) | -54.7 |
| C10—O3—C7—C8 | 141.3 (3) | 129.1 |
| C8—C7—C6—C5 | -1.7 (4) | -0.3 |
| O3—C7—C6—C5 | -178.7 (2) | -176.3 |
| C9—C4—C5—C6 | 0.3 (4) | 0.1 |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 179.7 (3) | -180.0 |
| C9—C4—C5—O1 | 180.0 (2) | -179.7 |
| C3—C4—C5—O1 | -0.6 (4) | 0.3 |
| C7—C6—C5—C4 | 1.2 (4) | 0.2 |
| C7—C6—C5—O1 | -178.5 (2) | 179.9 |
| C1—O1—C5—C4 | -0.5 (4) | -0.0 |
| C1—O1—C5—C6 | 179.2 (3) | -179.8 |
| C5—C4—C9—C8 | -1.3 (4) | -0.2 |
| C3—C4—C9—C8 | 179.4 (3) | 179.9 |
| C7—O3—C10—O4 | 9.6 (4) | -2.1 |
| C7—O3—C10—C11 | -168.7 (2) | 178.3 |
| C16—C11—C10—O4 | -175.9 (3) | 178.9 |
| C12—C11—C10—O4 | 2.4 (5) | -1.0 |
| C16—C11—C10—O3 | 2.3 (4) | -1.6 |
| C12—C11—C10—O3 | -179.4 (2) | 178.6 |
| C16—C11—C12—C13 | 0.6 (4) | 0.1 |
| C10—C11—C12—C13 | -177.8 (3) | 179.9 |
| C4—C9—C8—C7 | 0.7 (4) | 0.0 |
| C6—C7—C8—C9 | 0.8 (4) | 0.2 |
| O3—C7—C8—C9 | 178.1 (3) | 176.4 |
| C5—C4—C3—C2 | 1.5 (5) | -0.23 |
| C9—C4—C3—C2 | -179.2 (3) | 179.7 |
| C11—C12—C13—C14 | 0.8 (5) | -0.1 |
| C15—C14—C13—C12 | -1.5 (5) | 0.0 |
| C17—C14—C13—C12 | 177.9 (3) | -180.0 |
| C12—C11—C16—C15 | -1.1 (5) | 0.0 |
| C10—C11—C16—C15 | 177.2 (3) | -179.8 |
| C13—C14—C15—C16 | 0.9 (5) | 0.1 |
| C17—C14—C15—C16 | -178.5 (3) | -179.9 |
| C11—C16—C15—C14 | 0.4 (5) | -0.1 |
| C5—O1—C1—O2 | -179.1 (3) | 179.7 |
| C5—O1—C1—C2 | 0.8 (5) | -0.3 |
| C4—C3—C2—C1 | -1.2 (5) | -0.1 |
| O2—C1—C2—C3 | 180.0 (4) | -179.6 |
| O1—C1—C2—C3 | 0.1 (6) | 0.4 |
| C13—C14—C17—C19 | 122.1 (4) | 119.9 |
| C15—C14—C17—C19 | -58.5 (5) | -60.1 |
| C13—C14—C17—C18 | 1.9 (5) | -0.3 |
| C15—C14—C17—C18 | -178.7 (4) | 179.7 |
| C13—C14—C17—C20 | -116.5 (4) | -120.4 |
| C15—C14—C17—C20 | 62.9 (4) | 59.6 |
References
- Abou, A., Djandé, A., Danger, G., Saba, A. & Kakou-Yao, R. (2012). Acta Cryst. E68, o3438–o3439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Abou, A., Djandé, A., Kakou-Yao, R., Saba, A. & Tenon, A. J. (2013). Acta Cryst. E69, o1081–o1082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Basanagouda, M., Kulkarni, M. V., Sharma, D., Gupta, V. K., Pranesha, Sandhyarani, P. & Rasal, V. P. (2009). J. Chem. Sci. 121, 485–495.
- Bibila Mayaya Bisseyou, Y., Abou, A., Djandé, A., Danger, G. & Kakou-Yao, R. (2013). Acta Cryst. E69, o1125–o1126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Burla, M. C., Caliandro, R., Carrozzini, B., Cascarano, G. L., Cuocci, C., Giacovazzo, C., Mallamo, M., Mazzone, A. & Polidori, G. (2015). J. Appl. Cryst. 48, 306–309.
- Emmanuel-Giota, A. A., Fylaktakidou, K. C., Litinas, K. E., Nicolaides, D. N. & Hadjipavlou-Litina, D. J. (2001). Heterocycl. Chem. 38, 717–722.
- Farrugia, L. J. (2012). J. Appl. Cryst. 45, 849–854.
- Frisch, M. J., et al. (2013). GAUSSIAN09. Gaussian, Inc., Wallingford, CT, USA.
- Gnanaguru, K., Ramasubbu, N., Venkatesan, K. & Ramamurthy, V. (1985). J. Org. Chem. 50, 2337–2346.
- Gomes, L. R., Low, J. N., Fonseca, A., Matos, M. J. & Borges, F. (2016). Acta Cryst. E72, 926–932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Groom, C. R., Bruno, I. J., Lightfoot, M. P. & Ward, S. C. (2016). Acta Cryst. B72, 171–179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Janiak, C. (2000). J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. pp. 3885–3896.
- Ji, W., Li, L., Eniola-Adefeso, O., Wang, Y., Liu, C. & Feng, C. (2017). J. Mater. Chem. B, 5, 7790–7795. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Ji, W., Liu, G., Xu, M., Dou, X. & Feng, C. (2014). Chem. Commun. 50, 15545–15548. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Macrae, C. F., Bruno, I. J., Chisholm, J. A., Edgington, P. R., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Rodriguez-Monge, L., Taylor, R., van de Streek, J. & Wood, P. A. (2008). J. Appl. Cryst. 41, 466–470.
- Parveen, M., Mehdi, S. H., Ghalib, R. M., Alam, M. & Pallepogu, R. (2011). Pharma Chemica, 3, 22–30.
- Ramasubbu, N., Gnanaguru, K., Venkatesan, K. & Ramamurthy, V. (1982). Can. J. Chem. 60, 2159–2161.
- Rigaku OD (2015). CrysAlis PRO. Rigaku Oxford Diffraction, Yarnton, England.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Vukovic, N., Sukdolak, S., Solujic, S. & Niciforovic, N. (2010). Arch. Pharm. Res. 33, 5–15. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Westrip, S. P. (2010). J. Appl. Cryst. 43, 920–925.
- Wolff, S. K., Grimwood, D. J., McKinnon, J. J., Turner, M. J., Jayatilaka, D. & Spackman, M. A. (2012). Crystal Explorer. The University of Western Australia.
- Yu, J., Gao, L.-L., Huang, P. & Wang, D.-L. (2014). Acta Cryst. E70, m369–m370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Ziki, E., Sosso, S., Mansilla-Koblavi, F., Djandé, A. & Kakou-Yao, R. (2017). Acta Cryst. E73, 45–47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Ziki, E., Yoda, J., Djandé, A., Saba, A. & Kakou-Yao, R. (2016). Acta Cryst. E72, 1562–1564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018004188/sj5549sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018004188/sj5549Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018004188/sj5549Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 1828991
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report