In the crystal, N—H⋯N hydrogen bonds link the molecules into the supramolecular chains propagating along the c-axis direction.
Keywords: crystal structure, Biginelli condensation, benzoxadiazocine, Hirshfeld surfaces
Abstract
The title compound, C19H19N5O2, was prepared by the reaction of 3-amino-5-(pyridin-3-yl)-1,2,4-triazole with acetone and 2-hydroxy-3-ethoxybenzaldehyde. It crystallizes from ethanol in a tetragonal space group, with one molecule in the asymmetric unit. The 1,2,4-triazole five-membered ring is planar (maximum deviation = 0.0028 Å). The pyridine and phenyl rings are also planar with maximum deviations of 0.0091 and 0.0094 Å, respectively. In the crystal, N—H⋯N hydrogen bonds link the molecules into supramolecular chains propagating along the c-axis direction. Hirshfeld surface analysis and two-dimensional fingerprint plots have been used to analyse the intermolecular interactions present in the crystal.
Chemical context
The title compound represents a conformationally restricted analogue of so-called Biginelli compounds known to exhibit multiple pharmacological activities. It was selected for a single-crystal X-ray analysis in order to probe the chemical and spatial requirements of some kinds of activity. 4-Aryl-3,4-dihydropyrimidine-2(1H)-ones and -thiones, known as Biginelli compounds, display a wide spectrum of significant pharmacological activities (Kappe, 2000 ▸). For example, these pyrimidine derivatives were assayed as antihypertensive agents, selective α1a-adrenergic receptor antagonists, neuropeptide Y antagonists and were used as a lead for the development of anticancer drugs (Kappe, 2000 ▸). The Biginelli products have also been found to be potent hepatitis B replication inhibitors (Deres et al., 2003 ▸).
Recently, the ability of oxygen-bridged azolopyrimidine derivatives to inhibit Eg5 activity has been examined (Svetlík et al., 2010 ▸). As each of the above activities originates from stereo-selective binding of the drug molecule to its specific receptor, it is of interest to design a conformationally restricted probe molecule in order to examine geometric requirements of the given receptor binding site.
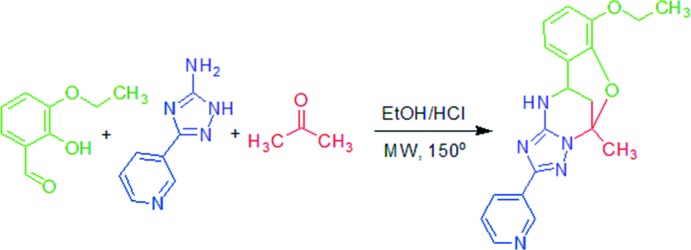
Since we had previously synthesized such a rigid type of oxygen-bridged triazolo-pyrimidine derivative, (I) (Gümüş et al., 2017 ▸), we decided to examine the structure of this heterocyclic system by X-ray analysis. A novel Biginelli-like assembly of 3-amino-5-(pyridin-3-yl)-1,2,4-triazole with acetone and 2-hydroxy-3-ethoxybenzaldehyde has been developed to enable easy access to 7-ethoxy-5-methyl-2-(pyridin-3-yl)-11,12-dihydro-5,11-methano[1,2,4]triazolo[1,5-c][1,3,5]benzoxadiazocine compounds as representatives of a new class of heterocycles.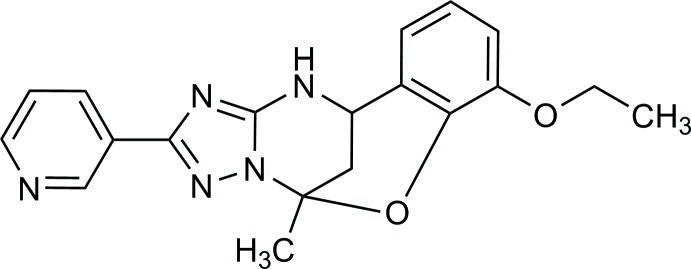
Structural commentary
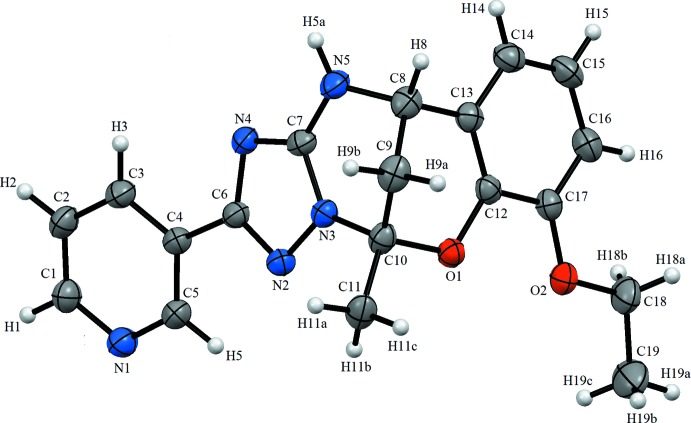
The asymmetric unit of the title compound contains one independent molecule (Fig. 1 ▸). In the 1,2,4-triazole ring, the average C=N and C—N bond lengths are 1.324 and 1.355 Å, respectively, while the N—N bond is 1.389 (4) Å. These values consistent with literature values (Şen et al., 2017a ▸,b ▸; Atalay et al., 2004 ▸). The 1,2,4-triazole ring is planar with a maximum deviation of 0.0028 Å. The N1/C1–C5 and C12–C17 rings are also planar with maximum deviations of 0.0091 and 0.0094 Å, respectively. The dihedral angle between the N1/C1–C5 and C6/N2/N3/C7/N4 rings is 13.1 (2)°, while the latter ring is inclined to the N3/C10–C8/N5/C7 plane by 6.87 (15)°. The C12–C17 and N3/C10–C8/N5/C7 planes form dihedral angles of 7.8 (2) and 88.82 (12)°, respectively, with the C9/C10/O1/C12/C13 plane.
Figure 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound, showing the atom labelling. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 30% probability level.
Supramolecular features
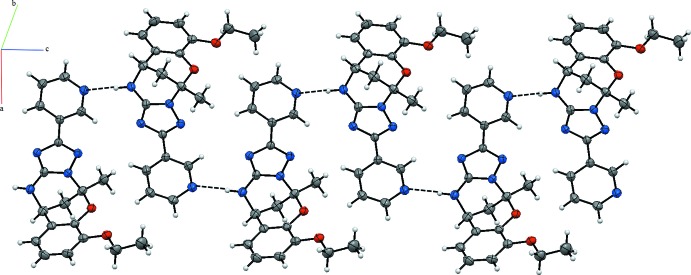
In the crystal, the N—H⋯N hydrogen bonds link the molecules, forming the supramolecular chains propagating along the c-axis direction (Table 1 ▸, Fig. 2 ▸).
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N5—H5A⋯N1i | 0.86 | 2.13 | 2.907 (4) | 149 |
Symmetry code: (i) 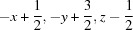 .
.
Figure 2.
A partial view of the crystal packing of the title compound. Dashed lines denote the intermolecular N—H⋯N hydrogen bonds.
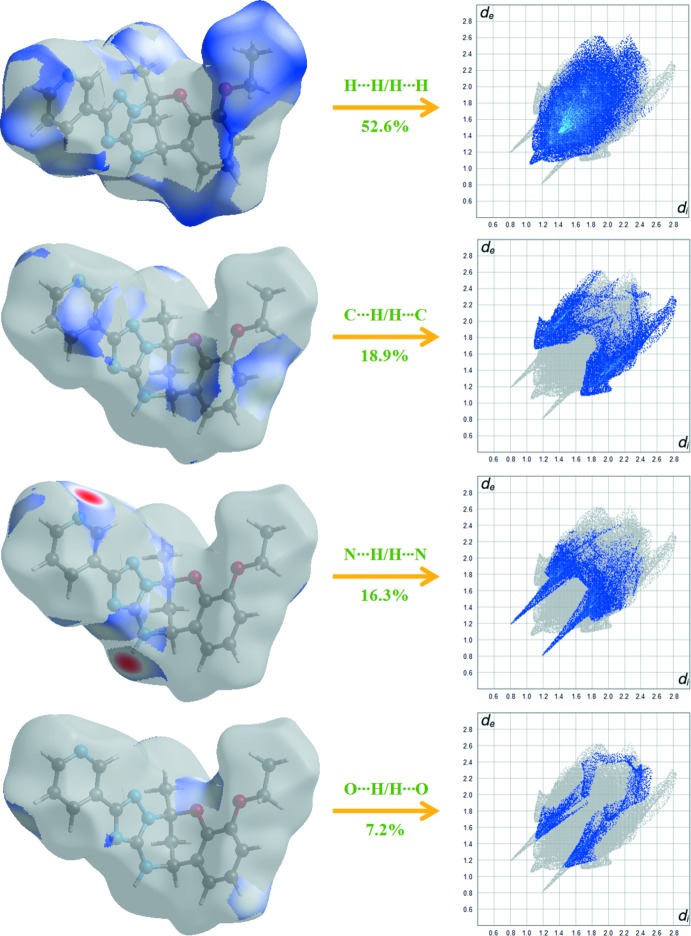
Hirshfeld surface analysis
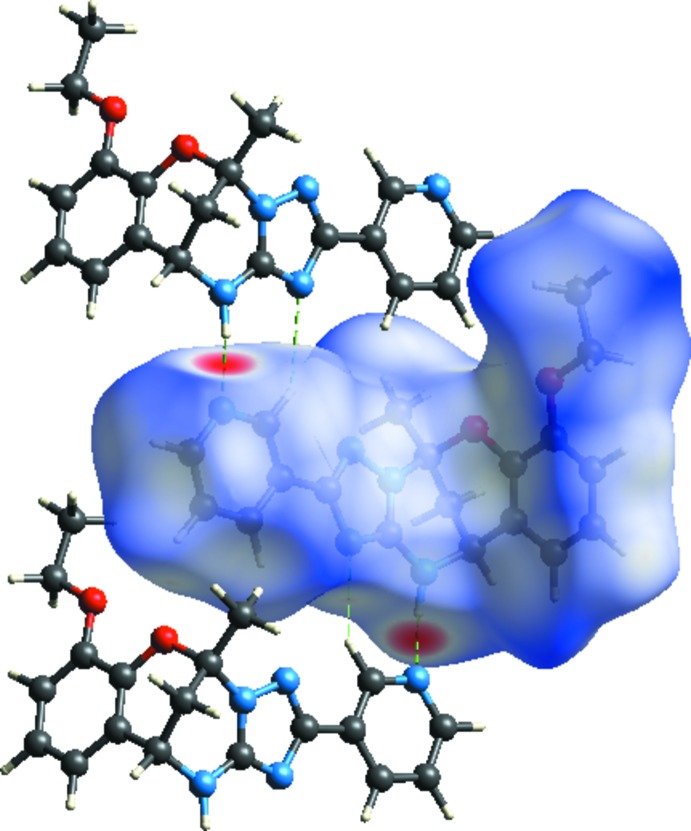
Crystal Explorer17.5 (Turner et al., 2017 ▸) was used to analyse the interactions in the crystal; fingerprint plots mapped over d norm (Figs. 3 ▸ and 4 ▸) were generated. The molecular Hirshfeld surfaces were obtained using a standard (high) surface resolution with the three-dimentional d norm surfaces mapped over a fixed colour scale of −0.484 (red) to 1.652 (blue). There are two red spots in the d norm surface (Fig. 3 ▸), which are on the N-acceptor atoms involved in the interactions listed in Table 1 ▸. The red spots indicate the regions of donor–acceptor interactions (Kansiz et al., 2018 ▸ ; Şen et al., 2017a ▸,b ▸, 2018 ▸; Yaman et al., 2018 ▸).
Figure 3.
The Hirshfeld surface of C19H19N5O2 mapped with d norm.
Figure 4.
d norm mapped on Hirshfeld surfaces to visualize the intermolecular interactions of C19H19N5O2.
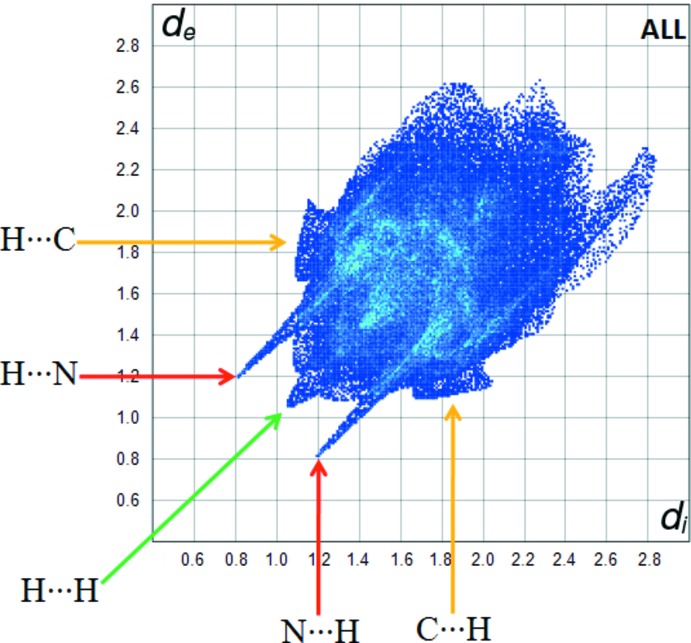
The intermolecular interactions of the title compound are shown in the 2D fingerprint plots shown in Fig. 5 ▸. The H⋯H interactions appear in the middle of the scattered points in the two-dimensional fingerprint plots with a contribution to the overall Hirshfeld surface of 52.6% (Fig. 6 ▸). The contribution from the N⋯H/H⋯N contacts, corresponding to the N—H⋯N interaction, is represented by a pair of sharp spikes characteristic of a strong hydrogen-bond interaction (16.3%). The whole fingerprint region and all other interactions, which are a combination of d e and d i, are displayed in Fig. 6 ▸.
Figure 5.
Fingerprint plot of the title compound.
Figure 6.
Two-dimensional fingerprint plots with a d norm view of the H⋯H/H⋯H (52.6%), C⋯H/H⋯C (18.9%), N⋯H/H⋯N (16.3%) and O⋯H/H⋯O (7.2%) contacts in the title compound.
Database survey
There are no direct precedents for the structure of (I) in the crystallographic literature (CSD Version 5.38; Groom et al., 2016 ▸). However, there are several precedents for the triazolobenzoxadiazocines, including the structures of 5-(2-hydroxyphenyl)-7-methyl-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro[1,2,4]triazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-7-ol (Gorobets et al., 2010 ▸), ethyl 7-chloromethyl-5-(2-chlorophenyl)-7-hydroxy-2-methylsulfanyl-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-1,2,4-triazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine-6-carboxylate (Huang, 2009 ▸) and methyl 5′-(2-hydroxyphenyl)-5′,6′-dihydro-4′H-spiro[chromene-2,7′-[1,2,4]triazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine]-3-carboxylate (Kettmann & Světlík, 2011 ▸).
Synthesis and crystallization
The synthesis of the title compound (Fig. 7 ▸) was described by Gümüş et al. (2017 ▸). 3-Amino-5-(pyridin-3-yl)-1,2,4-triazole(1.0 mmol), 2-hydroxy-3-ethoxybenzaldehyde (1.0 mmol), acetone (0.22 mL, 3.0 mmol), and abs. EtOH (2.0 mL) were mixed in a microwave process vial, and then a 4 N solution of HCl in dioxane (0.07 mL, 0.3 mmol) was added. The mixture was irradiated at 423 K for 30 min. The reaction mixture was cooled by an air flow and stirred for 24 h at room temperature for complete precipitation of the product. The precipitate was filtered off, washed with EtOH (1.0 mL) and Et2O (3 × 1.0 mL), and dried. Compound (I) was obtained in the form of a white solid. It was recrystallized from ethanol.
Figure 7.
Synthesis of the title compound.
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 2 ▸. H atoms were positioned geometrically [N—H = 0.86 Å, C—H = 0.93 (aromatic), 0.96 (methyl) and 0.97 (methylene) Å] and refined using a riding model, with U iso(H) = 1.2U eq(N, C) and 1.5U eq(methyl C).
Table 2. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | C19H19N5O2 |
| M r | 349.39 |
| Crystal system, space group | Tetragonal, I
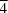
|
| Temperature (K) | 293 |
| a, c (Å) | 17.1509 (8), 11.9033 (7) |
| V (Å3) | 3501.4 (4) |
| Z | 8 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.09 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.54 × 0.34 × 0.16 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Stoe IPDS 2 |
| Absorption correction | Integration (X-RED32; Stoe & Cie, 2002 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.959, 0.984 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 8018, 3629, 2449 |
| R int | 0.053 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.628 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.042, 0.088, 0.90 |
| No. of reflections | 3629 |
| No. of parameters | 236 |
| H-atom treatment | H-atom parameters constrained |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.15, −0.12 |
| Absolute structure | Refined as an inversion twin. |
| Absolute structure parameter | −3 (2) |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018002621/xu5917sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018002621/xu5917Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018002621/xu5917Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 1820439
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the Faculty of Arts and Sciences, Ondokuz Mayıs University, Turkey, for the use of the Stoe IPDS 2 diffractometer (purchased under grant F.279 of the University Research Fund).
supplementary crystallographic information
Crystal data
| C19H19N5O2 | Dx = 1.326 Mg m−3 |
| Mr = 349.39 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Tetragonal, I4 | Cell parameters from 8727 reflections |
| a = 17.1509 (8) Å | θ = 1.7–27.6° |
| c = 11.9033 (7) Å | µ = 0.09 mm−1 |
| V = 3501.4 (4) Å3 | T = 293 K |
| Z = 8 | Prism, colorless |
| F(000) = 1472 | 0.54 × 0.34 × 0.16 mm |
Data collection
| Stoe IPDS 2 diffractometer | 3629 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: sealed X-ray tube, 12 x 0.4 mm long-fine focus | 2449 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Detector resolution: 6.67 pixels mm-1 | Rint = 0.053 |
| rotation method scans | θmax = 26.5°, θmin = 1.7° |
| Absorption correction: integration (X-RED32; Stoe & Cie, 2002) | h = −20→21 |
| Tmin = 0.959, Tmax = 0.984 | k = −21→21 |
| 8018 measured reflections | l = −14→13 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| Least-squares matrix: full | H-atom parameters constrained |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.042 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0372P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| wR(F2) = 0.088 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| S = 0.90 | Δρmax = 0.15 e Å−3 |
| 3629 reflections | Δρmin = −0.12 e Å−3 |
| 236 parameters | Absolute structure: Refined as an inversion twin. |
| 0 restraints | Absolute structure parameter: −3 (2) |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refined as a 2-component inversion twin. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C1 | 0.0390 (2) | 0.7259 (2) | 0.4925 (3) | 0.0581 (10) | |
| H1 | −0.014021 | 0.716332 | 0.501878 | 0.070* | |
| C2 | 0.0662 (2) | 0.7372 (2) | 0.3863 (3) | 0.0597 (10) | |
| H2 | 0.032912 | 0.733641 | 0.324888 | 0.072* | |
| C3 | 0.1444 (2) | 0.7541 (2) | 0.3716 (3) | 0.0558 (9) | |
| H3 | 0.164641 | 0.761427 | 0.299904 | 0.067* | |
| C4 | 0.19186 (19) | 0.76002 (19) | 0.4641 (3) | 0.0451 (8) | |
| C5 | 0.1594 (2) | 0.7450 (2) | 0.5683 (3) | 0.0524 (9) | |
| H5 | 0.191757 | 0.746889 | 0.630959 | 0.063* | |
| C6 | 0.27446 (19) | 0.78337 (18) | 0.4538 (3) | 0.0433 (8) | |
| C7 | 0.3820 (2) | 0.81015 (19) | 0.3807 (3) | 0.0452 (8) | |
| C8 | 0.5188 (2) | 0.8326 (2) | 0.3714 (3) | 0.0530 (9) | |
| H8 | 0.557656 | 0.853590 | 0.319160 | 0.064* | |
| C9 | 0.5062 (2) | 0.8898 (2) | 0.4669 (4) | 0.0575 (10) | |
| H9A | 0.555879 | 0.903724 | 0.500282 | 0.069* | |
| H9B | 0.481787 | 0.936913 | 0.438785 | 0.069* | |
| C10 | 0.4545 (2) | 0.85180 (19) | 0.5536 (3) | 0.0484 (8) | |
| C11 | 0.4295 (2) | 0.9041 (2) | 0.6485 (4) | 0.0620 (11) | |
| H11A | 0.401451 | 0.947929 | 0.618728 | 0.093* | |
| H11B | 0.396382 | 0.875548 | 0.698823 | 0.093* | |
| H11C | 0.474656 | 0.922184 | 0.688324 | 0.093* | |
| C12 | 0.53691 (18) | 0.74016 (18) | 0.5322 (3) | 0.0432 (8) | |
| C13 | 0.54834 (18) | 0.75667 (19) | 0.4207 (3) | 0.0460 (8) | |
| C14 | 0.5883 (2) | 0.7029 (2) | 0.3536 (3) | 0.0557 (10) | |
| H14 | 0.596039 | 0.713003 | 0.277630 | 0.067* | |
| C15 | 0.6162 (2) | 0.6352 (2) | 0.4004 (4) | 0.0631 (11) | |
| H15 | 0.642215 | 0.599352 | 0.355389 | 0.076* | |
| C16 | 0.6062 (2) | 0.6195 (2) | 0.5133 (3) | 0.0576 (10) | |
| H16 | 0.625672 | 0.573495 | 0.543568 | 0.069* | |
| C17 | 0.56737 (19) | 0.6719 (2) | 0.5813 (3) | 0.0471 (8) | |
| C18 | 0.5850 (3) | 0.5943 (3) | 0.7453 (4) | 0.0716 (12) | |
| H18A | 0.641332 | 0.593704 | 0.738080 | 0.086* | |
| H18B | 0.564269 | 0.547848 | 0.709738 | 0.086* | |
| C19 | 0.5622 (3) | 0.5965 (3) | 0.8665 (4) | 0.1006 (17) | |
| H19A | 0.582492 | 0.551306 | 0.903941 | 0.151* | |
| H19B | 0.583133 | 0.642681 | 0.900739 | 0.151* | |
| H19C | 0.506407 | 0.597026 | 0.872521 | 0.151* | |
| N1 | 0.08383 (17) | 0.72774 (19) | 0.5838 (3) | 0.0572 (8) | |
| N2 | 0.31602 (16) | 0.80437 (15) | 0.5418 (2) | 0.0458 (7) | |
| N3 | 0.38723 (15) | 0.82148 (16) | 0.4920 (2) | 0.0442 (7) | |
| N4 | 0.31108 (15) | 0.78598 (17) | 0.3519 (2) | 0.0467 (7) | |
| N5 | 0.44380 (16) | 0.82375 (18) | 0.3130 (2) | 0.0542 (8) | |
| H5A | 0.439554 | 0.826988 | 0.241203 | 0.065* | |
| O1 | 0.49588 (12) | 0.78802 (13) | 0.60565 (18) | 0.0468 (6) | |
| O2 | 0.55363 (14) | 0.66252 (14) | 0.6933 (2) | 0.0567 (7) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.045 (2) | 0.071 (3) | 0.058 (3) | −0.0032 (17) | −0.0068 (19) | −0.002 (2) |
| C2 | 0.055 (2) | 0.077 (3) | 0.048 (2) | −0.0014 (19) | −0.0144 (18) | −0.001 (2) |
| C3 | 0.055 (2) | 0.070 (2) | 0.042 (2) | 0.0003 (18) | −0.0024 (18) | 0.0043 (18) |
| C4 | 0.0452 (19) | 0.051 (2) | 0.0389 (19) | 0.0027 (15) | −0.0019 (16) | −0.0025 (16) |
| C5 | 0.050 (2) | 0.065 (2) | 0.043 (2) | 0.0048 (17) | −0.0047 (17) | −0.0016 (18) |
| C6 | 0.0474 (19) | 0.0454 (19) | 0.0370 (19) | 0.0039 (14) | −0.0035 (16) | −0.0014 (16) |
| C7 | 0.052 (2) | 0.046 (2) | 0.037 (2) | 0.0000 (16) | −0.0011 (17) | 0.0026 (16) |
| C8 | 0.050 (2) | 0.054 (2) | 0.055 (2) | −0.0108 (17) | −0.0034 (18) | 0.0068 (19) |
| C9 | 0.062 (2) | 0.0416 (19) | 0.069 (3) | −0.0079 (16) | −0.012 (2) | 0.0020 (19) |
| C10 | 0.052 (2) | 0.0433 (18) | 0.050 (2) | 0.0020 (15) | −0.0100 (17) | −0.0025 (17) |
| C11 | 0.070 (3) | 0.051 (2) | 0.064 (3) | 0.0125 (18) | −0.020 (2) | −0.0181 (19) |
| C12 | 0.0350 (17) | 0.0465 (19) | 0.048 (2) | −0.0012 (14) | −0.0029 (15) | −0.0062 (17) |
| C13 | 0.0388 (19) | 0.050 (2) | 0.049 (2) | −0.0059 (15) | −0.0008 (16) | −0.0023 (17) |
| C14 | 0.048 (2) | 0.066 (2) | 0.054 (2) | −0.0040 (18) | 0.0081 (18) | −0.0043 (19) |
| C15 | 0.056 (2) | 0.065 (3) | 0.068 (3) | 0.0102 (19) | 0.014 (2) | −0.013 (2) |
| C16 | 0.048 (2) | 0.056 (2) | 0.069 (3) | 0.0077 (17) | 0.0038 (19) | −0.001 (2) |
| C17 | 0.0395 (19) | 0.048 (2) | 0.053 (2) | 0.0002 (15) | −0.0013 (16) | 0.0001 (17) |
| C18 | 0.070 (3) | 0.072 (3) | 0.073 (3) | 0.020 (2) | −0.002 (2) | 0.020 (2) |
| C19 | 0.101 (4) | 0.119 (4) | 0.082 (3) | 0.032 (3) | 0.009 (3) | 0.039 (3) |
| N1 | 0.0495 (18) | 0.075 (2) | 0.0473 (19) | −0.0042 (15) | −0.0009 (15) | 0.0003 (16) |
| N2 | 0.0471 (17) | 0.0498 (16) | 0.0404 (17) | 0.0034 (12) | −0.0027 (14) | −0.0044 (13) |
| N3 | 0.0414 (16) | 0.0491 (16) | 0.0422 (18) | −0.0011 (12) | −0.0038 (13) | −0.0030 (13) |
| N4 | 0.0436 (17) | 0.0571 (18) | 0.0393 (17) | 0.0005 (14) | −0.0050 (13) | 0.0033 (13) |
| N5 | 0.0486 (18) | 0.073 (2) | 0.0410 (16) | −0.0050 (15) | −0.0034 (14) | 0.0104 (16) |
| O1 | 0.0494 (13) | 0.0459 (13) | 0.0451 (13) | 0.0082 (10) | −0.0054 (11) | −0.0044 (11) |
| O2 | 0.0557 (15) | 0.0585 (16) | 0.0559 (16) | 0.0140 (12) | −0.0017 (13) | 0.0087 (13) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| C1—N1 | 1.331 (5) | C10—C11 | 1.504 (5) |
| C1—C2 | 1.362 (5) | C11—H11A | 0.9600 |
| C1—H1 | 0.9300 | C11—H11B | 0.9600 |
| C2—C3 | 1.384 (5) | C11—H11C | 0.9600 |
| C2—H2 | 0.9300 | C12—C13 | 1.372 (5) |
| C3—C4 | 1.373 (5) | C12—O1 | 1.390 (4) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9300 | C12—C17 | 1.409 (5) |
| C4—C5 | 1.383 (5) | C13—C14 | 1.399 (5) |
| C4—C6 | 1.477 (4) | C14—C15 | 1.374 (5) |
| C5—N1 | 1.343 (4) | C14—H14 | 0.9300 |
| C5—H5 | 0.9300 | C15—C16 | 1.380 (6) |
| C6—N2 | 1.317 (4) | C15—H15 | 0.9300 |
| C6—N4 | 1.367 (4) | C16—C17 | 1.380 (5) |
| C7—N4 | 1.330 (4) | C16—H16 | 0.9300 |
| C7—N3 | 1.342 (4) | C17—O2 | 1.364 (4) |
| C7—N5 | 1.352 (4) | C18—O2 | 1.428 (4) |
| C8—N5 | 1.469 (4) | C18—C19 | 1.495 (6) |
| C8—C13 | 1.515 (5) | C18—H18A | 0.9700 |
| C8—C9 | 1.517 (5) | C18—H18B | 0.9700 |
| C8—H8 | 0.9800 | C19—H19A | 0.9600 |
| C9—C10 | 1.509 (5) | C19—H19B | 0.9600 |
| C9—H9A | 0.9700 | C19—H19C | 0.9600 |
| C9—H9B | 0.9700 | N2—N3 | 1.389 (4) |
| C10—O1 | 1.443 (4) | N5—H5A | 0.8600 |
| C10—N3 | 1.463 (4) | ||
| N1—C1—C2 | 123.7 (3) | H11A—C11—H11C | 109.5 |
| N1—C1—H1 | 118.1 | H11B—C11—H11C | 109.5 |
| C2—C1—H1 | 118.1 | C13—C12—O1 | 124.0 (3) |
| C1—C2—C3 | 118.7 (4) | C13—C12—C17 | 121.3 (3) |
| C1—C2—H2 | 120.7 | O1—C12—C17 | 114.7 (3) |
| C3—C2—H2 | 120.7 | C12—C13—C14 | 119.1 (3) |
| C4—C3—C2 | 119.2 (3) | C12—C13—C8 | 120.3 (3) |
| C4—C3—H3 | 120.4 | C14—C13—C8 | 120.6 (3) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 120.4 | C15—C14—C13 | 119.7 (4) |
| C3—C4—C5 | 117.8 (3) | C15—C14—H14 | 120.1 |
| C3—C4—C6 | 121.4 (3) | C13—C14—H14 | 120.1 |
| C5—C4—C6 | 120.7 (3) | C14—C15—C16 | 121.1 (4) |
| N1—C5—C4 | 123.5 (3) | C14—C15—H15 | 119.5 |
| N1—C5—H5 | 118.2 | C16—C15—H15 | 119.5 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 118.2 | C17—C16—C15 | 120.3 (4) |
| N2—C6—N4 | 116.6 (3) | C17—C16—H16 | 119.9 |
| N2—C6—C4 | 121.8 (3) | C15—C16—H16 | 119.9 |
| N4—C6—C4 | 121.5 (3) | O2—C17—C16 | 125.5 (3) |
| N4—C7—N3 | 111.2 (3) | O2—C17—C12 | 116.0 (3) |
| N4—C7—N5 | 128.1 (3) | C16—C17—C12 | 118.5 (3) |
| N3—C7—N5 | 120.7 (3) | O2—C18—C19 | 107.4 (4) |
| N5—C8—C13 | 112.8 (3) | O2—C18—H18A | 110.2 |
| N5—C8—C9 | 107.2 (3) | C19—C18—H18A | 110.2 |
| C13—C8—C9 | 108.2 (3) | O2—C18—H18B | 110.2 |
| N5—C8—H8 | 109.5 | C19—C18—H18B | 110.2 |
| C13—C8—H8 | 109.5 | H18A—C18—H18B | 108.5 |
| C9—C8—H8 | 109.5 | C18—C19—H19A | 109.5 |
| C10—C9—C8 | 108.5 (3) | C18—C19—H19B | 109.5 |
| C10—C9—H9A | 110.0 | H19A—C19—H19B | 109.5 |
| C8—C9—H9A | 110.0 | C18—C19—H19C | 109.5 |
| C10—C9—H9B | 110.0 | H19A—C19—H19C | 109.5 |
| C8—C9—H9B | 110.0 | H19B—C19—H19C | 109.5 |
| H9A—C9—H9B | 108.4 | C1—N1—C5 | 116.8 (3) |
| O1—C10—N3 | 109.5 (3) | C6—N2—N3 | 101.2 (3) |
| O1—C10—C11 | 105.7 (3) | C7—N3—N2 | 109.4 (3) |
| N3—C10—C11 | 111.3 (3) | C7—N3—C10 | 126.8 (3) |
| O1—C10—C9 | 109.4 (3) | N2—N3—C10 | 123.7 (3) |
| N3—C10—C9 | 105.9 (3) | C7—N4—C6 | 101.6 (3) |
| C11—C10—C9 | 115.1 (3) | C7—N5—C8 | 115.0 (3) |
| C10—C11—H11A | 109.5 | C7—N5—H5A | 122.5 |
| C10—C11—H11B | 109.5 | C8—N5—H5A | 122.5 |
| H11A—C11—H11B | 109.5 | C12—O1—C10 | 115.3 (2) |
| C10—C11—H11C | 109.5 | C17—O2—C18 | 117.1 (3) |
| N1—C1—C2—C3 | −2.2 (6) | C2—C1—N1—C5 | 2.8 (6) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −0.9 (6) | C4—C5—N1—C1 | −0.4 (5) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 3.0 (5) | N4—C6—N2—N3 | −0.8 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—C6 | −175.7 (3) | C4—C6—N2—N3 | −179.3 (3) |
| C3—C4—C5—N1 | −2.5 (5) | N4—C7—N3—N2 | −0.2 (4) |
| C6—C4—C5—N1 | 176.2 (3) | N5—C7—N3—N2 | 179.3 (3) |
| C3—C4—C6—N2 | 166.1 (3) | N4—C7—N3—C10 | −176.5 (3) |
| C5—C4—C6—N2 | −12.5 (5) | N5—C7—N3—C10 | 3.0 (5) |
| C3—C4—C6—N4 | −12.4 (5) | C6—N2—N3—C7 | 0.5 (3) |
| C5—C4—C6—N4 | 169.0 (3) | C6—N2—N3—C10 | 177.0 (3) |
| N5—C8—C9—C10 | 68.7 (3) | O1—C10—N3—C7 | −101.2 (4) |
| C13—C8—C9—C10 | −53.3 (4) | C11—C10—N3—C7 | 142.3 (4) |
| C8—C9—C10—O1 | 67.4 (3) | C9—C10—N3—C7 | 16.6 (4) |
| C8—C9—C10—N3 | −50.5 (3) | O1—C10—N3—N2 | 83.0 (4) |
| C8—C9—C10—C11 | −173.8 (3) | C11—C10—N3—N2 | −33.5 (4) |
| O1—C12—C13—C14 | −177.8 (3) | C9—C10—N3—N2 | −159.2 (3) |
| C17—C12—C13—C14 | 2.6 (5) | N3—C7—N4—C6 | −0.2 (4) |
| O1—C12—C13—C8 | 2.9 (5) | N5—C7—N4—C6 | −179.7 (3) |
| C17—C12—C13—C8 | −176.7 (3) | N2—C6—N4—C7 | 0.7 (4) |
| N5—C8—C13—C12 | −98.3 (4) | C4—C6—N4—C7 | 179.2 (3) |
| C9—C8—C13—C12 | 20.1 (4) | N4—C7—N5—C8 | −166.6 (3) |
| N5—C8—C13—C14 | 82.4 (4) | N3—C7—N5—C8 | 14.0 (5) |
| C9—C8—C13—C14 | −159.2 (3) | C13—C8—N5—C7 | 70.4 (4) |
| C12—C13—C14—C15 | −0.7 (5) | C9—C8—N5—C7 | −48.7 (4) |
| C8—C13—C14—C15 | 178.6 (3) | C13—C12—O1—C10 | 9.4 (4) |
| C13—C14—C15—C16 | −0.7 (6) | C17—C12—O1—C10 | −171.0 (3) |
| C14—C15—C16—C17 | 0.3 (6) | N3—C10—O1—C12 | 71.7 (3) |
| C15—C16—C17—O2 | 179.6 (4) | C11—C10—O1—C12 | −168.4 (3) |
| C15—C16—C17—C12 | 1.5 (5) | C9—C10—O1—C12 | −43.9 (4) |
| C13—C12—C17—O2 | 178.7 (3) | C16—C17—O2—C18 | 2.8 (5) |
| O1—C12—C17—O2 | −0.9 (4) | C12—C17—O2—C18 | −179.0 (3) |
| C13—C12—C17—C16 | −3.0 (5) | C19—C18—O2—C17 | −179.6 (4) |
| O1—C12—C17—C16 | 177.4 (3) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N5—H5A···N1i | 0.86 | 2.13 | 2.907 (4) | 149 |
Symmetry code: (i) −x+1/2, −y+3/2, z−1/2.
References
- Atalay, Ş., Yavuz, M., Kahveci, B., Ağar, E. & Şaşmaz, S. (2004). Acta Cryst. E60, o2119–o2121.
- Deres, K., Schröder, C. H., Paessens, A., Goldmann, S., Hacker, H. J., Weber, O., Krämer, T., Niewöhner, U., Pleiss, U., Stoltefuss, J., Graef, E., Koletzki, D., Masantschek, R. N. A., Reimann, A., Jaeger, R., Gross, R., Beckermann, B., Schlemmer, K. H., Haebich, D. & Rübsamen-Waigmann, H. (2003). Science, 299, 893–896. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Farrugia, L. J. (2012). J. Appl. Cryst. 45, 849–854.
- Gorobets, N. Y., Sedash, Y. V., Ostras, K. S., Zaremba, O. V., Shishkina, S. V., Baumer, V. N., Shishkin, O. V., Kovalenko, S. M., Desenko, S. M. & Van der Eycken, E. V. (2010). Tetrahedron Lett. 51, 2095–2098.
- Groom, C. R., Bruno, I. J., Lightfoot, M. P. & Ward, S. C. (2016). Acta Cryst. B72, 171–179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Gümüş, M. K., Gorobets, N. Y., Sedash, Y. V., Chebanov, V. A. & Desenko, S. M. (2017). Chem. Heterocycl. Compd, 53, 1261–1267.
- Huang, S. (2009). Acta Cryst. E65, o2671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Kansiz, S., Almarhoon, Z. M. & Dege, N. (2018). Acta Cryst. E74, 217–220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Kappe, C. O. (2000). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 35, 1043–1052. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Kettmann, V. & Světlík, J. (2011). Acta Cryst. E67, o92. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Şen, F., Çapan, İ., Dinçer, M. & Çukurovalı, A. (2018). J. Mol. Struct. 1155, 278–287.
- Şen, F., Dinçer, M., Yilmaz, I. & Cukurovali, A. (2017a). J. Mol. Struct. 1137, 193–205.
- Şen, F., Kansiz, S. & Uçar, İ. (2017b). Acta Cryst. C73, 517–524. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Stoe & Cie (2002). IPDS 2 User Manual. Stoe & Cie GmbH, Darmstadt, Germany.
- Svetlík, J., Veizerová, L., Mayer, T. U. & Catarinella, M. (2010). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 20, 4073–4076. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Turner, M. J., MacKinnon, J. J., Wolff, S. K., Grimwood, D. J., Spackman, P. R., Jayatilaka, D. & Spackman, M. A. (2017). Crystal Explorer17.5. University of Western Avustralia.
- Yaman, M., Almarhoon, Z. M., Çakmak, Ş., Kütük, H., Meral, G. & Dege, N. (2018). Acta Cryst. E74, 41–44. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018002621/xu5917sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018002621/xu5917Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018002621/xu5917Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 1820439
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report