The conformations of the two free doxorubicin (DoxH+) cations present in the crystal structure of the title compound and (Dox) bound to proteins and DNA are compared.
Keywords: doxorubicin, anthracycline, conformation, intercalation, crystal structure
Abstract
Crystal structure determination of doxorubicin nitrate, (DoxH)NO3, systematic name (7S,9S)-7-{[(2R,4S,5S,6S)-4-azaniumyl-5-hydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxy}-6,9,11-trihydroxy-9-(2-hydroxyacetyl)-4-methoxy-8,10-dihydro-7H-tetracen-5,12-dione nitrate, shows two formula units present in the asymmetric unit. In the crystal lattice, hydrogen-bonded pairs of (DoxH+) cations and segregation of the aglycone and sugar moieties are observed. Inspection of molecular overlays reveals that the conformation of (DoxH)NO3 resembles that of DNA-intercalated, but not of protein-docked (DoxH)+. The structure was refined as a two-component twin.
Chemical context
Since its discovery and isolation by genetic mutation of Streptomyces peucetius in 1969 (Arcamone et al., 1969 ▸), the anthracycline antibiotic doxorubicin [(Dox); trade name adriamycin] has become one of the most potent and widely used drugs in cancer chemotherapy (Denel-Bobrowska & Marczak, 2017 ▸; Cagel et al., 2017 ▸; Cappetta et al., 2018 ▸). Extensive studies of the anticancer activities of doxorubicin (Weiss, 1992 ▸; Shafei et al., 2017 ▸) have led to FDA approval for the treatment of cancer forms, such as breast (Shafei et al., 2017 ▸), ovarian (Duggan & Keating, 2011 ▸) and small-cell lung cancer (López-González et al., 2013 ▸). The anticancer action of doxorubicin is a consequence of its intercalation into base pairs of double-stranded DNA and subsequent inhibition of human DNA topoisomerase II (Arcamone, 1981 ▸; Liu, 1989 ▸; Chaires, 1998 ▸; Yang & Wang, 1999 ▸; Jung & Reszka, 2001 ▸). Although a few crystal structures of doxorubicin bound to DNA, enzymes and proteins have been reported, to the best of our knowledge, there is no crystal structure determination of doxorubicin itself in the literature. A Cambridge Structural Database (CSD version 5.38; Groom et al., 2016 ▸) search for the doxorubicin skeleton structure gave only two hits for hydrochloride salts of N- and O-substituted variants [CSD entries ADRMVL (Eckle & Stezowski, 1980 ▸) and BUJZIP (Eckle & Stezowski, 1983 ▸)]. Even for daunorubicin (also known as daunomycin), a closely related anthracycline antibiotic, only the crystal structures of its hydrochloride solvates have been reported (Neidle & Taylor, 1977 ▸; Courseille et al., 1979 ▸). In the absence of a high-resolution crystal structure, researchers have so far relied on computational and solution studies to ascertain the preferred conformational geometry of (Dox) (Zhu et al., 2010 ▸; Agrawal et al., 2009 ▸; Barthwal et al., 2008 ▸).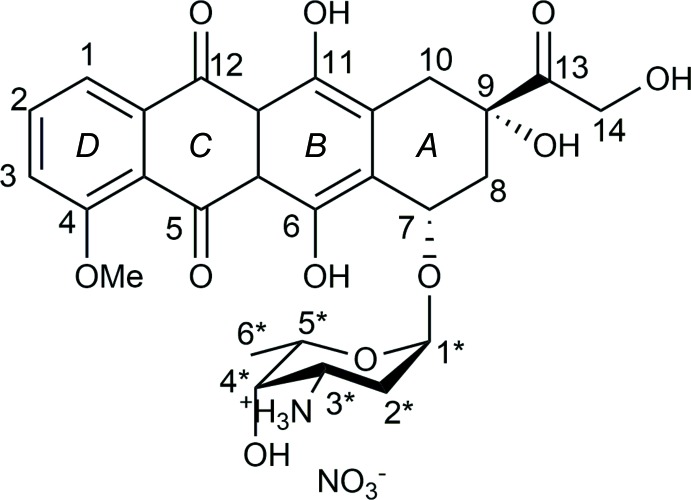
In order to probe and improve the activity of (Dox), several derivatives have been studied (Post et al., 2005 ▸). Metal complexation to doxorubicin is known to alter its pharmaceutical activity and several Fe, Mn, Pt and Sn derivatives of the anthracycline have been studied with regard to their anticancer activities (Ming, 2003 ▸). (DoxH)+-functionalized iron oxide nanoparticles have been studied as cancer theranostics (Yu et al., 2008 ▸). With a similar objective, we have attempted to coordinate Ag+ to (Dox). However, mixing stoichiometric amounts of (DoxH)Cl and AgNO3 in the presence of Et3N yielded only the nitrate derivative of (Dox) as (DoxH)NO3 in crystalline form. In this article, we report the 0.80 Å resolution crystal structure determination of doxorubicin nitrate and analyze and compare conformational details.
Structural commentary
The title compound crystallizes in the chiral monoclinic P21 space group with two protonated doxorubicin cations (DoxH+) and two nitrate anions in the asymmetric unit. The (DoxH)+ cations consist of an aglycone, containing three approximately planar fused rings (the root-mean-square deviations of the six rings in the asymmetric unit are between 0.009 and 0.027 Å, B–D; the atom-numbering scheme and ring labels are shown in the scheme), and a sugar moiety in a chair conformation attached to ring A. Two nitrate ions hold pairs of cations with their fused rings at an approximately right angle to each other [86.4 (4)° between C1–C20 and N62(O64–O66)]. The two cations present in the asymmetric unit are rather similar, exhibiting insignificant differences (Fig. 1 ▸).
Figure 1.
Molecular structure of (DoxH)+ showing the atom-labeling scheme. Only one of the molecules present in the asymmetric unit is shown, with displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 40% probability level. H atoms are not presented for clarity. Inset: Molecular overlay of the two crystallographically independent (DoxH)+ moieties present in the asymmetric unit. The molecular overlay was performed using the function available within the Discovery Studio Visualizer Suite. The target chosen was one of the (Dox) units from the crystal structure, with the H atoms ignored.
In 2010, Zhu and co-workers published a detailed conformational analysis of anthracycline antibiotics, including doxorubicin, based on previously published (Dox)–protein and (Dox)–DNA complexes as well as DFT calculations (Zhu et al., 2010 ▸). The analysis identified three important doxorubicin conformational domains: (1) the aromatic ring system, (2) the functional group at C9 and (3) at C7 relating to the aminal linkage:
(1) The aromatic anthracycline ring system does not vary significantly in any of the DNA-bound (Dox) structures and in the structure in this study. A somewhat more pronounced variation is encountered in protein-bound-(Dox), such as the one in 4dx7 or 4mra (vide infra). Based on the B3LYP level of theory, Zhu et al. have proposed four types of stable conformational isomers, with type I tautomer – forming two hydrogen bonds between C5—O and C6—OH and between C12—O and C11—OH – being the preferred one. The crystal structure in the present report confirms this prediction.
(2) The C8 carbon can either be above or below the anthracycline planes; in this structure, C8 is above the plane and the C19—C20—C7—C8 torsion angles are 16.6 (6)° and 17.5 (7)° (Table 1 ▸). This is in the expected range for an intercalating (Dox), but significantly deviates from that found in a protein-bound (Dox). The conformation at C9 is similar to that at C8, as C9 is almost coplanar the anthracycline plane [C20—C19—C10—C9 torsion angles are 18.9 (6) and 19.2 (6)°]. More dramatic variations between the conformations of C8 and C9 are observed in the protein-bound (Dox) (5mra), where their torsion angles are 47.75 and −49.70°, respectively. According to a study based on resonant molecular dynamic calculations and NMR experiments, the conformation with a C7—O7—C1*—C2* torsion angle of 142–143° was found to be biologically relevant (Barthwal et al., 2008 ▸; Agrawal et al., 2009 ▸). However, this seems to be only applicable to DNA-intercalated (Dox). Protein-bound (Dox) have a wider range of torsion angles, for example, 88.43° in sorcin-bound (Dox), to 150.82° in AcrB-bound (Dox). The (Dox) structure in the present study has torsion angles of 161.6 (5) and 162.6 (4)°.
Table 1. Conformational parameters (°) of one of the (DoxH)+ cations present in the title compound, (DoxH)NO3, and representative examples from the literature.
| (DoxH)NO3 | AcrB-(Dox) (4dx7)a | Sorcin-(Dox) (5mra)b | DNA-(Dox) (1p20)c | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C7—O7—C1*—C2* | 161.6 (5), 162.6 (4) | 150.82 | 88.43 | 144.36 |
| C8 conformation C19—C20—C7—C8 | 16.6 (6), 17.5 (7) | −18.93 | 47.75 | 8.92 |
| C9 conformation C20—C19—C10—C9 | 18.9 (6), 19.2 (6) | −9.27 | −49.70 | 22.91 |
| O7—N3* | 7.947 (1), 8.042 (1) | 7.636 | 6.433 | 6.481 |
(3) The C7-connected daunosamine is the most flexible conformational entity in (Dox). The N3*—O7(C5) distance (2.74–8.50 Å) determines the conformational diversity. In the present structure, the corresponding distances are 7.947 (1) and 8.042 (2) Å, which are on the longer end of the spectrum. The presence of the nitrate ions between the two (Dox) fragments of the asymmetric unit influences this distance greatly.
Supramolecular features
The ammonium group forms hydrogen bonds with nitrate counter-ions with N⋯O distances of 2.836 (8), 2.876 (9) and 2.865 (8) Å (Table 2 ▸). The crystal structure is further stabilized by an extensive network of inter- and intramolecular O—H⋯O and N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds (Table 2 ▸), in addition to two intermolecular π–π interactions between the C and D rings of the aglycone moiety [centroid-to-centroid distances: 3.526 (3) and 3.694 (4) Å, Figs. 2 ▸ and 3 ▸] and a C—H⋯π interaction with Cg2 [Cg2 is the centroid of the C1–C4/C15/C16 ring; C⋯Cg distance 3.556 (7) Å].
Table 2. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
Cg2 is the centroid of the C1–C4/C15/C16 ring.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O6—H6⋯O5 | 0.82 | 1.81 | 2.526 (6) | 146 |
| O11—H11⋯O12 | 0.82 | 1.80 | 2.526 (6) | 146 |
| O14—H14⋯O65i | 0.82 | 2.07 | 2.779 (9) | 145 |
| N3*—H3*A⋯O13ii | 0.89 | 2.00 | 2.874 (7) | 167 |
| N3*—H3*C⋯O63 | 0.89 | 1.99 | 2.865 (8) | 168 |
| O41—H41⋯O42 | 0.82 | 1.82 | 2.537 (6) | 146 |
| O44—H44⋯O14iii | 0.82 | 2.08 | 2.888 (6) | 168 |
| O55—H55⋯O4* | 0.82 | 1.93 | 2.724 (6) | 163 |
| N54—H54A⋯O43iv | 0.89 | 2.18 | 2.890 (7) | 136 |
| N54—H54A⋯O44iv | 0.89 | 2.05 | 2.843 (7) | 147 |
| N54—H54B⋯O62 | 0.89 | 1.99 | 2.836 (8) | 159 |
| N54—H54C⋯O64 | 0.89 | 2.05 | 2.876 (9) | 155 |
| C38—H38B⋯Cg2v | 0.97 | 2.64 | 3.556 (7) | 157 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  ; (iv)
; (iv)  ; (v)
; (v)  .
.
Figure 2.
Molecular packing diagram of (DoxH)NO3 viewed parallel to the crystallographic a axis.
Figure 3.
Representation highlighting the π–π interactions between C and D rings of the aglycone moieties. Turquoise spheres indicate centroids.
Database survey
Table 3 ▸ lists the published crystal structures of macromolecules with (Dox) as the ligand (DM2 ligand code in PDB; Berman et al., 2000 ▸). To analyze the significance of the new (DoxH)NO3 crystal structure, structural comparisons were made by performing molecular overlays (Dassault Systèmes BIOVIA, 2017 ▸) of the current structure with published (Dox)-bound protein/DNA structures, which resulted in the following observations: (1) The most important functional groups are, understandably, the amino group of the daunosamine moiety and the hydroxyl group of the glycolic site; (2) (Dox) binds in the DNA minor groove and (3) while the crystal structure reported here is by and large quite similar to the one of (Dox) bound in DNA, significant conformational differences are prominent in comparison to protein-bound (Dox), mainly because of differences in hydrogen-bond donors present in proteins.
Table 3. Selected RCSB-PDB entries with (Dox) (DM2) as the ligand.
| PDB accession (Reference) | Macromolecule(s) | Resolution (Å) |
|---|---|---|
| 5MRA (Genovese et al., 2017 ▸) | Sorcin (protein) | 3.74 |
| 4ZVM (Leung & Shilton, 2015 ▸) | Ribsyldihydronicotinamide dehydrogenase | 1.97 |
| 4DX7 (Eicher et al., 2012 ▸) | Acriflavine resistance protein B (protein) DARPIN (protein) | 2.25 |
| 2DR6 (Murakami et al., 2006 ▸) | AcrB (protein) | 3.3 |
| 1P20 (Howerton et al., 2003 ▸) | DNA | 1.34 |
| 1I1E (Eswaramoorthy et al., 2001 ▸) | Botulinium Neurotoxin Type B (protein) | 2.5 |
| 151D (Lipscomb et al., 1994 ▸) | DNA | 1.4 |
| 1DA9 (Leonard et al., 1993 ▸) | DNA | 1.7 |
| 1D12 (Frederick et al., 1990 ▸) | DNA | 1.7 |
Binding of (Dox) to sorcin, a calcium-binding protein that causes multidrug resistance (MDR) in human tumors, impairs cell death. Sorcin is overexpressed in human tumors and MDR cancers. Two sites, designated as pocket 1 and pocket 2, were found to bind (Dox), which was modeled satisfactorily at pocket 1, but not at pocket 2. The molecular overlay in Fig. 4 ▸ a shows the significant differences in the conformation: methoxy and the glycolic units are significantly rotated from their native state. On the contrary, DNA-bound (intercalated) (Dox) and (Dox) in this study do not differ significantly in their conformations, as shown in (Dox)-1p20 in Fig. 4 ▸ below.
Figure 4.
Representative molecular overlays of doxorubicin from this study (purple) and the ones from the literature.
In another study, three molecules of (Dox) were found to bind the AcrB protein (PDB accession 4dx7; Eicher et al., 2012 ▸). Although the conformational differences are not as stark as they were in sorcin, the rotation now being about the bond between glycol-O carbon and the A ring [(Dox)-4dx7 in Fig. 5]. In the neurotoxin BoNT/B-(Dox) complex, O13 and O14 of the aglycone interact with the toxin and is stacked between Trp1261 and His1240 (Eswaramoorthy et al., 2001 ▸). All the O and H atoms of the structure are hydrogen-bonded with various amino acid residues of the neurotoxin. The conformational changes in this complex are minimal, similar to DNA-bound (Dox).
Synthesis and crystallization
By mixing an ethanolic solution of doxorubicin hydrochloride (3 mg, 0.005 mmol), abbreviated as (DoxH)Cl, Et3N and an MeCN solution of AgNO3 (1.7 mg, 0.01 mmol), an orange solution was obtained. This was allowed to evaporate to near dryness to afford an orange powder. The orange powder was then dissolved in EtOH. After filtration, the filtrate was layered with Et2O. Red sheet-like crystals of (DoxH)NO3 were obtained in two weeks.
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 4 ▸. All H atoms were positioned geometrically and refined using a riding model: O—H = 0.82, N—H = 0.89 and C—H = 0.93–0.98 Å with U
iso(H) = 1.2 or 1.5U
eq(parent atom). The structure was refined as a two-component twin (matrix to transform one domain into the other: (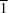 0 0 0
0 0 0 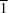 0 1 0 1); BASF = 0.3072). Atoms marked with a star correspond to the pyranose ring, following a numbering convention previously described for (Dox) (Eswaramoorthy et al., 2001 ▸).
0 1 0 1); BASF = 0.3072). Atoms marked with a star correspond to the pyranose ring, following a numbering convention previously described for (Dox) (Eswaramoorthy et al., 2001 ▸).
Table 4. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | C27H30NO11·NO3 |
| M r | 606.53 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, P21 |
| Temperature (K) | 298 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 8.3169 (12), 34.280 (5), 10.1010 (14) |
| β (°) | 114.293 (4) |
| V (Å3) | 2624.8 (6) |
| Z | 4 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.13 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.24 × 0.10 × 0.05 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Bruker D8 Quest CMOS |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2016 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.685, 0.745 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 33597, 10764, 7299 |
| R int | 0.049 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.626 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.050, 0.093, 1.01 |
| No. of reflections | 10764 |
| No. of parameters | 792 |
| No. of restraints | 1 |
| H-atom treatment | H-atom parameters constrained |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.24, −0.18 |
| Absolute structure | Flack x determined using 2632 quotients [(I +)−(I −)]/[(I +)+(I −)] (Parsons et al., 2013 ▸). |
| Absolute structure parameter | −0.3 (4) |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018002955/wm5435sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018002955/wm5435Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018002955/wm5435Isup3.cdx
CCDC reference: 1815074
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr Elumalai Pavadai for helpful technical inputs on molecular overlays.
supplementary crystallographic information
Crystal data
| C27H30NO11+·NO3− | F(000) = 1272 |
| Mr = 606.53 | Dx = 1.535 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 8.3169 (12) Å | Cell parameters from 9978 reflections |
| b = 34.280 (5) Å | θ = 2.9–26.4° |
| c = 10.1010 (14) Å | µ = 0.13 mm−1 |
| β = 114.293 (4)° | T = 298 K |
| V = 2624.8 (6) Å3 | Sheet, red |
| Z = 4 | 0.24 × 0.10 × 0.05 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker D8 Quest CMOS diffractometer | 7299 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Detector resolution: 10.42 pixels mm-1 | Rint = 0.049 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 26.4°, θmin = 2.8° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2016) | h = −10→10 |
| Tmin = 0.685, Tmax = 0.745 | k = −42→42 |
| 33597 measured reflections | l = −12→12 |
| 10764 independent reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| Least-squares matrix: full | H-atom parameters constrained |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.050 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0405P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| wR(F2) = 0.093 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| S = 1.01 | Δρmax = 0.24 e Å−3 |
| 10764 reflections | Δρmin = −0.18 e Å−3 |
| 792 parameters | Absolute structure: Flack x determined using 2632 quotients [(I+)-(I-)]/[(I+)+(I-)] (Parsons et al., 2013). |
| 1 restraint | Absolute structure parameter: −0.3 (4) |
| Primary atom site location: dual |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refined as a 2-component twin. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O4 | −0.0502 (7) | 0.18514 (13) | 0.0931 (5) | 0.0585 (13) | |
| O4* | 0.6155 (6) | 0.48108 (13) | 0.5178 (5) | 0.0481 (11) | |
| H4* | 0.645686 | 0.465763 | 0.469977 | 0.072* | |
| O5 | 0.1037 (6) | 0.24134 (12) | 0.2718 (5) | 0.0513 (12) | |
| O5* | 0.5027 (5) | 0.42141 (11) | 0.6516 (4) | 0.0373 (10) | |
| O6 | 0.2581 (5) | 0.29480 (12) | 0.4514 (4) | 0.0385 (10) | |
| H6 | 0.249029 | 0.277163 | 0.393904 | 0.058* | |
| O7 | 0.2617 (5) | 0.38118 (10) | 0.5142 (4) | 0.0305 (9) | |
| O9 | 0.0248 (6) | 0.42485 (12) | 0.6025 (4) | 0.0404 (10) | |
| H9 | 0.008204 | 0.413375 | 0.526779 | 0.061* | |
| O11 | −0.3440 (5) | 0.31738 (12) | 0.5332 (5) | 0.0456 (12) | |
| H11 | −0.425673 | 0.303697 | 0.479458 | 0.068* | |
| O12 | −0.4933 (6) | 0.26575 (13) | 0.3438 (5) | 0.0518 (12) | |
| O13 | 0.1964 (6) | 0.41696 (14) | 0.9652 (5) | 0.0592 (13) | |
| O14 | −0.0341 (8) | 0.47530 (13) | 0.9372 (5) | 0.0622 (13) | |
| H14 | −0.003156 | 0.463169 | 1.013720 | 0.093* | |
| N3* | 0.3633 (7) | 0.46242 (16) | 0.2253 (6) | 0.0500 (14) | |
| H3*A | 0.297507 | 0.447837 | 0.149414 | 0.060* | |
| H3*B | 0.475149 | 0.461670 | 0.236527 | 0.060* | |
| H3*C | 0.324774 | 0.486934 | 0.210406 | 0.060* | |
| C1 | −0.5146 (9) | 0.21495 (18) | 0.1278 (7) | 0.0444 (17) | |
| H1 | −0.618929 | 0.221160 | 0.136119 | 0.053* | |
| C1* | 0.4370 (7) | 0.39312 (17) | 0.5417 (7) | 0.0370 (15) | |
| H1* | 0.513936 | 0.370188 | 0.572263 | 0.044* | |
| C2 | −0.5114 (10) | 0.18808 (19) | 0.0281 (7) | 0.0497 (18) | |
| H2 | −0.617255 | 0.176785 | −0.034084 | 0.060* | |
| C2* | 0.4371 (9) | 0.40795 (16) | 0.4007 (7) | 0.0420 (16) | |
| H2*A | 0.557785 | 0.409799 | 0.410350 | 0.050* | |
| H2*B | 0.375553 | 0.389406 | 0.323876 | 0.050* | |
| C3 | −0.3624 (10) | 0.17727 (19) | 0.0160 (7) | 0.0468 (18) | |
| H3 | −0.367212 | 0.158116 | −0.050736 | 0.056* | |
| C3* | 0.3507 (8) | 0.44697 (18) | 0.3592 (6) | 0.0374 (15) | |
| H3* | 0.225666 | 0.444100 | 0.339457 | 0.045* | |
| C4 | −0.2009 (9) | 0.19443 (17) | 0.1022 (7) | 0.0403 (16) | |
| C4* | 0.4339 (8) | 0.47586 (18) | 0.4843 (6) | 0.0384 (15) | |
| H4*A | 0.372292 | 0.500959 | 0.459076 | 0.046* | |
| C5 | −0.0353 (8) | 0.24605 (16) | 0.2879 (6) | 0.0321 (14) | |
| C5* | 0.4159 (8) | 0.45854 (16) | 0.6152 (6) | 0.0353 (14) | |
| H5* | 0.290226 | 0.454630 | 0.591093 | 0.042* | |
| C6 | 0.1027 (7) | 0.29952 (16) | 0.4623 (6) | 0.0286 (13) | |
| C6* | 0.4922 (10) | 0.48356 (18) | 0.7488 (7) | 0.0515 (18) | |
| H6*A | 0.464805 | 0.472349 | 0.824116 | 0.077* | |
| H6*B | 0.442708 | 0.509284 | 0.726627 | 0.077* | |
| H6*C | 0.617912 | 0.485033 | 0.780942 | 0.077* | |
| C7 | 0.2549 (7) | 0.35565 (15) | 0.6252 (6) | 0.0283 (13) | |
| H7 | 0.360579 | 0.339180 | 0.661049 | 0.034* | |
| C8 | 0.2488 (7) | 0.37850 (16) | 0.7521 (6) | 0.0291 (13) | |
| H8A | 0.278066 | 0.361105 | 0.834527 | 0.035* | |
| H8B | 0.337843 | 0.398804 | 0.779461 | 0.035* | |
| C9 | 0.0706 (7) | 0.39708 (16) | 0.7192 (6) | 0.0307 (14) | |
| C10 | −0.0675 (8) | 0.36543 (16) | 0.6807 (7) | 0.0358 (15) | |
| H10A | −0.056823 | 0.352417 | 0.769223 | 0.043* | |
| H10B | −0.183339 | 0.377406 | 0.637884 | 0.043* | |
| C11 | −0.2010 (8) | 0.31119 (17) | 0.5054 (6) | 0.0315 (14) | |
| C12 | −0.3558 (8) | 0.26088 (16) | 0.3247 (6) | 0.0343 (14) | |
| C13 | 0.0784 (8) | 0.42099 (16) | 0.8475 (7) | 0.0328 (14) | |
| C14 | −0.0640 (10) | 0.4493 (2) | 0.8234 (7) | 0.061 (2) | |
| H14A | −0.082796 | 0.464209 | 0.736602 | 0.074* | |
| H14B | −0.171787 | 0.435043 | 0.805093 | 0.074* | |
| C15 | −0.3541 (8) | 0.23265 (16) | 0.2165 (7) | 0.0335 (14) | |
| C16 | −0.1969 (8) | 0.22379 (16) | 0.2027 (6) | 0.0325 (14) | |
| C17 | −0.1987 (7) | 0.28312 (16) | 0.4090 (6) | 0.0290 (13) | |
| C18 | −0.0431 (7) | 0.27627 (15) | 0.3858 (6) | 0.0277 (12) | |
| C19 | −0.0547 (7) | 0.33577 (15) | 0.5783 (6) | 0.0288 (13) | |
| C20 | 0.0949 (7) | 0.32995 (16) | 0.5542 (6) | 0.0264 (12) | |
| C21 | −0.0478 (11) | 0.1538 (2) | 0.0032 (9) | 0.076 (3) | |
| H21A | −0.133917 | 0.158353 | −0.093937 | 0.115* | |
| H21B | −0.075012 | 0.130013 | 0.039518 | 0.115* | |
| H21C | 0.067198 | 0.151890 | 0.002926 | 0.115* | |
| O34 | 0.9753 (7) | 0.82204 (16) | −0.0230 (6) | 0.0754 (16) | |
| O35 | 1.0122 (6) | 0.76876 (14) | 0.1649 (5) | 0.0599 (14) | |
| O36 | 1.0308 (5) | 0.71127 (12) | 0.3215 (5) | 0.0456 (12) | |
| H36 | 0.989301 | 0.689262 | 0.313851 | 0.068* | |
| O37 | 1.1071 (5) | 0.62664 (11) | 0.3901 (4) | 0.0343 (10) | |
| O39 | 1.4642 (7) | 0.58445 (12) | 0.5127 (5) | 0.0506 (12) | |
| H39 | 1.386575 | 0.591626 | 0.435418 | 0.076* | |
| O41 | 1.7277 (5) | 0.69683 (12) | 0.4310 (5) | 0.0428 (11) | |
| H41 | 1.755740 | 0.711119 | 0.378857 | 0.064* | |
| O42 | 1.6881 (6) | 0.75101 (12) | 0.2491 (5) | 0.0470 (12) | |
| O43 | 1.6156 (7) | 0.60300 (13) | 0.8710 (5) | 0.0591 (14) | |
| O44 | 1.8716 (6) | 0.55690 (13) | 0.8977 (4) | 0.0508 (12) | |
| H44 | 1.895492 | 0.533742 | 0.896090 | 0.076* | |
| O55 | 0.7047 (6) | 0.53757 (13) | 0.3706 (5) | 0.0498 (11) | |
| H55 | 0.698298 | 0.518809 | 0.418573 | 0.075* | |
| O56 | 0.9570 (5) | 0.59384 (11) | 0.5073 (4) | 0.0373 (10) | |
| N54 | 0.7120 (7) | 0.54394 (16) | 0.0945 (5) | 0.0469 (14) | |
| H54A | 0.721658 | 0.553201 | 0.015785 | 0.056* | |
| H54B | 0.607796 | 0.550745 | 0.092677 | 0.056* | |
| H54C | 0.720612 | 0.518053 | 0.095890 | 0.056* | |
| C31 | 1.4914 (9) | 0.80230 (17) | 0.0381 (7) | 0.0429 (16) | |
| H31 | 1.607255 | 0.797568 | 0.051785 | 0.052* | |
| C32 | 1.3907 (11) | 0.8297 (2) | −0.0621 (7) | 0.0523 (19) | |
| H32 | 1.440145 | 0.843813 | −0.114745 | 0.063* | |
| C33 | 1.2187 (11) | 0.83629 (19) | −0.0847 (7) | 0.0527 (19) | |
| H33 | 1.151700 | 0.854418 | −0.153945 | 0.063* | |
| C34 | 1.1447 (9) | 0.81639 (18) | −0.0061 (7) | 0.0453 (17) | |
| C35 | 1.1642 (9) | 0.76388 (18) | 0.1767 (7) | 0.0394 (15) | |
| C36 | 1.2008 (8) | 0.70888 (16) | 0.3421 (6) | 0.0324 (14) | |
| C37 | 1.2158 (8) | 0.65236 (16) | 0.5045 (6) | 0.0329 (14) | |
| H37 | 1.138142 | 0.667903 | 0.535057 | 0.040* | |
| C38 | 1.3426 (8) | 0.63079 (18) | 0.6346 (6) | 0.0361 (14) | |
| H38A | 1.281283 | 0.609083 | 0.654825 | 0.043* | |
| H38B | 1.381380 | 0.648111 | 0.717901 | 0.043* | |
| C39 | 1.5042 (8) | 0.61522 (16) | 0.6169 (6) | 0.0341 (14) | |
| C40 | 1.5997 (8) | 0.64825 (18) | 0.5799 (7) | 0.0387 (15) | |
| H40A | 1.668966 | 0.662410 | 0.668291 | 0.046* | |
| H40B | 1.680911 | 0.637217 | 0.543365 | 0.046* | |
| C41 | 1.5543 (8) | 0.70137 (16) | 0.3987 (6) | 0.0312 (14) | |
| C42 | 1.5295 (9) | 0.75381 (16) | 0.2251 (7) | 0.0344 (15) | |
| C43 | 1.6279 (8) | 0.59617 (17) | 0.7599 (7) | 0.0345 (14) | |
| C44 | 1.7663 (9) | 0.56963 (18) | 0.7555 (7) | 0.0424 (16) | |
| H44A | 1.712099 | 0.547390 | 0.693898 | 0.051* | |
| H44B | 1.838642 | 0.583201 | 0.715593 | 0.051* | |
| C45 | 1.4174 (8) | 0.78187 (17) | 0.1183 (6) | 0.0345 (14) | |
| C46 | 1.2408 (9) | 0.78777 (18) | 0.0958 (6) | 0.0381 (15) | |
| C47 | 1.4527 (8) | 0.72972 (16) | 0.3014 (6) | 0.0316 (14) | |
| C48 | 1.2731 (8) | 0.73373 (15) | 0.2749 (6) | 0.0291 (13) | |
| C49 | 1.4795 (8) | 0.67671 (15) | 0.4689 (6) | 0.0301 (14) | |
| C50 | 1.3049 (8) | 0.67947 (15) | 0.4398 (6) | 0.0308 (14) | |
| C51 | 0.8621 (12) | 0.8447 (3) | −0.1417 (9) | 0.085 (3) | |
| H51A | 0.862363 | 0.834571 | −0.230158 | 0.128* | |
| H51B | 0.902539 | 0.871270 | −0.128992 | 0.128* | |
| H51C | 0.744427 | 0.843774 | −0.146502 | 0.128* | |
| C52 | 0.9421 (8) | 0.61882 (18) | 0.3907 (7) | 0.0393 (15) | |
| H52 | 0.892273 | 0.643636 | 0.404134 | 0.047* | |
| C53 | 0.8221 (8) | 0.60273 (18) | 0.2455 (7) | 0.0451 (17) | |
| H53A | 0.700737 | 0.605672 | 0.233108 | 0.054* | |
| H53B | 0.836898 | 0.617729 | 0.169811 | 0.054* | |
| C54 | 0.8571 (8) | 0.56056 (18) | 0.2284 (6) | 0.0384 (15) | |
| H54 | 0.968632 | 0.558537 | 0.217536 | 0.046* | |
| C55 | 0.8725 (8) | 0.53706 (18) | 0.3605 (6) | 0.0367 (15) | |
| H55A | 0.905157 | 0.510103 | 0.350454 | 0.044* | |
| C56 | 1.0138 (8) | 0.55541 (16) | 0.4903 (6) | 0.0341 (14) | |
| H56 | 1.121379 | 0.557499 | 0.473420 | 0.041* | |
| C57 | 1.0544 (9) | 0.5327 (2) | 0.6275 (7) | 0.0515 (18) | |
| H57A | 1.139700 | 0.546715 | 0.708267 | 0.077* | |
| H57B | 1.101245 | 0.507665 | 0.619801 | 0.077* | |
| H57C | 0.948384 | 0.529354 | 0.642242 | 0.077* | |
| O61 | 0.3752 (8) | 0.59449 (18) | 0.2043 (7) | 0.0812 (17) | |
| O62 | 0.3580 (7) | 0.5458 (2) | 0.0653 (6) | 0.092 (2) | |
| O63 | 0.2521 (7) | 0.54165 (16) | 0.2223 (6) | 0.0678 (14) | |
| N61 | 0.3272 (8) | 0.5614 (2) | 0.1620 (6) | 0.0525 (15) | |
| O64 | 0.6646 (9) | 0.4626 (2) | 0.1392 (8) | 0.102 (2) | |
| O65 | 0.9171 (9) | 0.4433 (3) | 0.1708 (8) | 0.138 (3) | |
| O66 | 0.7773 (11) | 0.4163 (2) | 0.2802 (8) | 0.119 (3) | |
| N62 | 0.7890 (10) | 0.4409 (2) | 0.1966 (7) | 0.0611 (17) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O4 | 0.058 (3) | 0.054 (3) | 0.070 (3) | −0.007 (2) | 0.032 (3) | −0.031 (3) |
| O4* | 0.046 (3) | 0.046 (3) | 0.049 (3) | −0.020 (2) | 0.016 (2) | −0.005 (2) |
| O5 | 0.046 (3) | 0.051 (3) | 0.068 (3) | −0.007 (2) | 0.034 (3) | −0.022 (2) |
| O5* | 0.038 (2) | 0.032 (2) | 0.035 (2) | −0.010 (2) | 0.0085 (19) | −0.005 (2) |
| O6 | 0.034 (3) | 0.039 (3) | 0.046 (3) | −0.003 (2) | 0.020 (2) | −0.013 (2) |
| O7 | 0.029 (2) | 0.0262 (19) | 0.037 (2) | −0.0035 (17) | 0.0146 (19) | 0.0007 (18) |
| O9 | 0.050 (3) | 0.036 (2) | 0.033 (2) | 0.004 (2) | 0.014 (2) | −0.001 (2) |
| O11 | 0.034 (3) | 0.044 (3) | 0.068 (3) | −0.010 (2) | 0.030 (3) | −0.019 (2) |
| O12 | 0.035 (3) | 0.053 (3) | 0.072 (3) | −0.012 (2) | 0.027 (2) | −0.021 (3) |
| O13 | 0.061 (3) | 0.070 (3) | 0.033 (3) | 0.010 (3) | 0.005 (3) | −0.014 (2) |
| O14 | 0.083 (4) | 0.049 (3) | 0.061 (3) | 0.000 (3) | 0.036 (3) | −0.022 (3) |
| N3* | 0.050 (3) | 0.054 (3) | 0.041 (3) | −0.010 (3) | 0.013 (3) | −0.001 (3) |
| C1 | 0.045 (4) | 0.038 (4) | 0.040 (4) | −0.013 (3) | 0.008 (3) | −0.001 (3) |
| C1* | 0.027 (3) | 0.032 (3) | 0.056 (4) | −0.003 (3) | 0.021 (3) | 0.002 (3) |
| C2 | 0.054 (5) | 0.040 (4) | 0.045 (4) | −0.013 (4) | 0.011 (4) | −0.007 (3) |
| C2* | 0.053 (4) | 0.030 (3) | 0.055 (4) | −0.009 (3) | 0.035 (4) | −0.008 (3) |
| C3 | 0.064 (5) | 0.042 (4) | 0.032 (4) | −0.010 (4) | 0.016 (4) | −0.009 (3) |
| C3* | 0.035 (4) | 0.046 (4) | 0.031 (3) | −0.008 (3) | 0.013 (3) | −0.004 (3) |
| C4 | 0.059 (5) | 0.026 (3) | 0.037 (4) | −0.001 (3) | 0.022 (4) | −0.002 (3) |
| C4* | 0.037 (4) | 0.036 (3) | 0.036 (4) | −0.001 (3) | 0.009 (3) | −0.005 (3) |
| C5 | 0.037 (4) | 0.029 (3) | 0.033 (3) | −0.002 (3) | 0.018 (3) | −0.001 (3) |
| C5* | 0.036 (4) | 0.028 (3) | 0.041 (4) | −0.011 (3) | 0.015 (3) | −0.007 (3) |
| C6 | 0.027 (3) | 0.031 (3) | 0.029 (3) | 0.000 (3) | 0.013 (3) | 0.004 (3) |
| C6* | 0.065 (5) | 0.039 (4) | 0.053 (4) | −0.015 (4) | 0.026 (4) | −0.013 (3) |
| C7 | 0.030 (3) | 0.021 (3) | 0.036 (3) | −0.001 (3) | 0.016 (3) | 0.001 (3) |
| C8 | 0.026 (3) | 0.029 (3) | 0.027 (3) | −0.002 (3) | 0.005 (3) | −0.001 (3) |
| C9 | 0.033 (4) | 0.030 (3) | 0.028 (3) | −0.001 (3) | 0.011 (3) | −0.002 (3) |
| C10 | 0.037 (4) | 0.030 (3) | 0.043 (4) | −0.007 (3) | 0.020 (3) | −0.014 (3) |
| C11 | 0.030 (4) | 0.029 (3) | 0.039 (3) | 0.002 (3) | 0.017 (3) | −0.001 (3) |
| C12 | 0.041 (4) | 0.024 (3) | 0.040 (4) | −0.007 (3) | 0.018 (3) | −0.001 (3) |
| C13 | 0.039 (4) | 0.023 (3) | 0.038 (4) | −0.001 (3) | 0.017 (3) | 0.000 (3) |
| C14 | 0.067 (5) | 0.066 (5) | 0.050 (4) | 0.006 (4) | 0.022 (4) | −0.024 (4) |
| C15 | 0.041 (4) | 0.023 (3) | 0.034 (3) | −0.003 (3) | 0.013 (3) | 0.002 (3) |
| C16 | 0.047 (4) | 0.020 (3) | 0.032 (3) | −0.002 (3) | 0.017 (3) | 0.000 (3) |
| C17 | 0.029 (3) | 0.022 (3) | 0.035 (3) | −0.006 (3) | 0.012 (3) | −0.002 (3) |
| C18 | 0.029 (3) | 0.022 (3) | 0.032 (3) | −0.004 (3) | 0.013 (3) | −0.002 (3) |
| C19 | 0.030 (3) | 0.017 (3) | 0.039 (3) | −0.007 (3) | 0.014 (3) | −0.005 (3) |
| C20 | 0.025 (3) | 0.022 (3) | 0.030 (3) | −0.006 (2) | 0.009 (3) | −0.001 (3) |
| C21 | 0.077 (6) | 0.079 (6) | 0.070 (5) | 0.009 (5) | 0.025 (5) | −0.035 (5) |
| O34 | 0.073 (4) | 0.090 (4) | 0.065 (3) | 0.034 (3) | 0.030 (3) | 0.042 (3) |
| O35 | 0.044 (3) | 0.065 (3) | 0.072 (3) | 0.020 (3) | 0.025 (3) | 0.034 (3) |
| O36 | 0.032 (3) | 0.041 (3) | 0.068 (3) | 0.002 (2) | 0.024 (2) | 0.012 (3) |
| O37 | 0.033 (2) | 0.029 (2) | 0.042 (2) | −0.0055 (19) | 0.017 (2) | 0.002 (2) |
| O39 | 0.067 (3) | 0.041 (2) | 0.035 (2) | 0.015 (2) | 0.012 (2) | −0.002 (2) |
| O41 | 0.033 (3) | 0.045 (3) | 0.055 (3) | 0.006 (2) | 0.023 (2) | 0.016 (2) |
| O42 | 0.040 (3) | 0.053 (3) | 0.051 (3) | −0.006 (2) | 0.021 (2) | 0.009 (2) |
| O43 | 0.081 (4) | 0.063 (3) | 0.037 (3) | 0.029 (3) | 0.028 (3) | 0.010 (2) |
| O44 | 0.057 (3) | 0.051 (3) | 0.040 (3) | 0.012 (2) | 0.017 (2) | 0.012 (2) |
| O55 | 0.043 (3) | 0.057 (3) | 0.051 (3) | −0.011 (2) | 0.022 (2) | 0.019 (2) |
| O56 | 0.039 (3) | 0.034 (2) | 0.044 (2) | −0.001 (2) | 0.022 (2) | 0.005 (2) |
| N54 | 0.047 (3) | 0.053 (3) | 0.039 (3) | −0.006 (3) | 0.016 (3) | 0.005 (3) |
| C31 | 0.056 (4) | 0.030 (3) | 0.045 (4) | −0.008 (3) | 0.024 (4) | 0.003 (3) |
| C32 | 0.068 (5) | 0.046 (4) | 0.042 (4) | −0.014 (4) | 0.022 (4) | 0.007 (4) |
| C33 | 0.069 (5) | 0.037 (4) | 0.042 (4) | 0.002 (4) | 0.012 (4) | 0.012 (3) |
| C34 | 0.053 (5) | 0.035 (4) | 0.049 (4) | 0.010 (3) | 0.022 (4) | 0.005 (3) |
| C35 | 0.040 (4) | 0.034 (4) | 0.043 (4) | 0.003 (3) | 0.016 (3) | 0.002 (3) |
| C36 | 0.026 (3) | 0.029 (3) | 0.043 (4) | −0.001 (3) | 0.016 (3) | −0.006 (3) |
| C37 | 0.039 (4) | 0.028 (3) | 0.035 (3) | 0.004 (3) | 0.019 (3) | 0.002 (3) |
| C38 | 0.041 (4) | 0.041 (4) | 0.033 (3) | 0.001 (3) | 0.023 (3) | 0.006 (3) |
| C39 | 0.044 (4) | 0.028 (3) | 0.028 (3) | 0.005 (3) | 0.013 (3) | 0.003 (3) |
| C40 | 0.035 (4) | 0.047 (4) | 0.038 (3) | 0.010 (3) | 0.018 (3) | 0.009 (3) |
| C41 | 0.034 (4) | 0.024 (3) | 0.038 (3) | 0.000 (3) | 0.017 (3) | 0.000 (3) |
| C42 | 0.042 (4) | 0.028 (3) | 0.037 (4) | −0.008 (3) | 0.019 (3) | −0.009 (3) |
| C43 | 0.044 (4) | 0.028 (3) | 0.032 (3) | 0.002 (3) | 0.016 (3) | 0.002 (3) |
| C44 | 0.054 (4) | 0.036 (3) | 0.035 (4) | 0.007 (3) | 0.016 (3) | 0.001 (3) |
| C45 | 0.040 (4) | 0.032 (3) | 0.031 (3) | −0.003 (3) | 0.014 (3) | 0.002 (3) |
| C46 | 0.048 (4) | 0.035 (4) | 0.030 (3) | 0.002 (3) | 0.015 (3) | 0.001 (3) |
| C47 | 0.038 (4) | 0.024 (3) | 0.035 (3) | 0.000 (3) | 0.016 (3) | 0.001 (3) |
| C48 | 0.035 (4) | 0.018 (3) | 0.033 (3) | 0.001 (3) | 0.013 (3) | 0.002 (3) |
| C49 | 0.041 (4) | 0.019 (3) | 0.034 (3) | 0.004 (3) | 0.019 (3) | 0.002 (3) |
| C50 | 0.038 (4) | 0.019 (3) | 0.038 (3) | 0.003 (3) | 0.017 (3) | −0.002 (3) |
| C51 | 0.081 (6) | 0.109 (7) | 0.056 (5) | 0.041 (5) | 0.019 (5) | 0.014 (5) |
| C52 | 0.030 (4) | 0.036 (3) | 0.054 (4) | 0.005 (3) | 0.020 (3) | 0.015 (3) |
| C53 | 0.037 (4) | 0.042 (4) | 0.047 (4) | −0.003 (3) | 0.008 (3) | 0.019 (3) |
| C54 | 0.036 (4) | 0.044 (4) | 0.037 (3) | −0.001 (3) | 0.016 (3) | 0.008 (3) |
| C55 | 0.036 (4) | 0.034 (3) | 0.046 (4) | 0.002 (3) | 0.022 (3) | 0.004 (3) |
| C56 | 0.032 (3) | 0.035 (3) | 0.037 (4) | 0.002 (3) | 0.016 (3) | 0.013 (3) |
| C57 | 0.055 (4) | 0.051 (4) | 0.054 (4) | 0.011 (4) | 0.028 (4) | 0.009 (4) |
| O61 | 0.093 (5) | 0.055 (4) | 0.092 (4) | 0.003 (3) | 0.034 (4) | 0.016 (3) |
| O62 | 0.062 (4) | 0.158 (6) | 0.062 (3) | 0.001 (4) | 0.032 (3) | −0.026 (4) |
| O63 | 0.062 (3) | 0.072 (3) | 0.075 (3) | −0.001 (3) | 0.034 (3) | 0.009 (3) |
| N61 | 0.042 (4) | 0.065 (4) | 0.045 (4) | 0.007 (3) | 0.012 (3) | 0.012 (3) |
| O64 | 0.081 (4) | 0.079 (4) | 0.128 (6) | 0.012 (4) | 0.025 (4) | −0.004 (4) |
| O65 | 0.065 (4) | 0.254 (10) | 0.112 (6) | −0.004 (5) | 0.053 (4) | −0.001 (6) |
| O66 | 0.170 (8) | 0.114 (6) | 0.084 (5) | −0.013 (5) | 0.062 (5) | 0.005 (5) |
| N62 | 0.069 (5) | 0.064 (4) | 0.049 (4) | 0.001 (4) | 0.023 (4) | −0.008 (4) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O4—C4 | 1.332 (8) | O36—H36 | 0.8200 |
| O4—C21 | 1.411 (8) | O36—C36 | 1.344 (7) |
| O4*—H4* | 0.8200 | O37—C37 | 1.438 (7) |
| O4*—C4* | 1.417 (7) | O37—C52 | 1.400 (7) |
| O5—C5 | 1.243 (7) | O39—H39 | 0.8200 |
| O5*—C1* | 1.405 (7) | O39—C39 | 1.429 (7) |
| O5*—C5* | 1.435 (7) | O41—H41 | 0.8200 |
| O6—H6 | 0.8200 | O41—C41 | 1.351 (7) |
| O6—C6 | 1.351 (7) | O42—C42 | 1.243 (7) |
| O7—C1* | 1.427 (7) | O43—C43 | 1.190 (7) |
| O7—C7 | 1.441 (6) | O44—H44 | 0.8200 |
| O9—H9 | 0.8200 | O44—C44 | 1.409 (7) |
| O9—C9 | 1.439 (7) | O55—H55 | 0.8200 |
| O11—H11 | 0.8200 | O55—C55 | 1.440 (7) |
| O11—C11 | 1.347 (7) | O56—C52 | 1.420 (7) |
| O12—C12 | 1.247 (7) | O56—C56 | 1.434 (7) |
| O13—C13 | 1.198 (7) | N54—H54A | 0.8900 |
| O14—H14 | 0.8200 | N54—H54B | 0.8900 |
| O14—C14 | 1.394 (7) | N54—H54C | 0.8900 |
| N3*—H3*A | 0.8900 | N54—C54 | 1.506 (8) |
| N3*—H3*B | 0.8900 | C31—H31 | 0.9300 |
| N3*—H3*C | 0.8900 | C31—C32 | 1.382 (9) |
| N3*—C3* | 1.495 (7) | C31—C45 | 1.391 (8) |
| C1—H1 | 0.9300 | C32—H32 | 0.9300 |
| C1—C2 | 1.373 (9) | C32—C33 | 1.372 (10) |
| C1—C15 | 1.403 (8) | C33—H33 | 0.9300 |
| C1*—H1* | 0.9800 | C33—C34 | 1.370 (10) |
| C1*—C2* | 1.513 (9) | C34—C46 | 1.408 (8) |
| C2—H2 | 0.9300 | C35—C46 | 1.474 (8) |
| C2—C3 | 1.346 (10) | C35—C48 | 1.461 (8) |
| C2*—H2*A | 0.9700 | C36—C48 | 1.373 (8) |
| C2*—H2*B | 0.9700 | C36—C50 | 1.427 (8) |
| C2*—C3* | 1.494 (8) | C37—H37 | 0.9800 |
| C3—H3 | 0.9300 | C37—C38 | 1.499 (8) |
| C3—C4 | 1.395 (9) | C37—C50 | 1.496 (8) |
| C3*—H3* | 0.9800 | C38—H38A | 0.9700 |
| C3*—C4* | 1.529 (8) | C38—H38B | 0.9700 |
| C4—C16 | 1.420 (8) | C38—C39 | 1.524 (8) |
| C4*—H4*A | 0.9800 | C39—C40 | 1.515 (8) |
| C4*—C5* | 1.512 (8) | C39—C43 | 1.533 (8) |
| C5—C16 | 1.476 (8) | C40—H40A | 0.9700 |
| C5—C18 | 1.452 (8) | C40—H40B | 0.9700 |
| C5*—H5* | 0.9800 | C40—C49 | 1.512 (8) |
| C5*—C6* | 1.501 (8) | C41—C47 | 1.393 (8) |
| C6—C18 | 1.390 (8) | C41—C49 | 1.403 (8) |
| C6—C20 | 1.416 (8) | C42—C45 | 1.460 (8) |
| C6*—H6*A | 0.9600 | C42—C47 | 1.445 (8) |
| C6*—H6*B | 0.9600 | C43—C44 | 1.482 (8) |
| C6*—H6*C | 0.9600 | C44—H44A | 0.9700 |
| C7—H7 | 0.9800 | C44—H44B | 0.9700 |
| C7—C8 | 1.521 (7) | C45—C46 | 1.405 (9) |
| C7—C20 | 1.508 (7) | C47—C48 | 1.412 (8) |
| C8—H8A | 0.9700 | C49—C50 | 1.361 (8) |
| C8—H8B | 0.9700 | C51—H51A | 0.9600 |
| C8—C9 | 1.519 (8) | C51—H51B | 0.9600 |
| C9—C10 | 1.510 (8) | C51—H51C | 0.9600 |
| C9—C13 | 1.512 (8) | C52—H52 | 0.9800 |
| C10—H10A | 0.9700 | C52—C53 | 1.499 (9) |
| C10—H10B | 0.9700 | C53—H53A | 0.9700 |
| C10—C19 | 1.485 (8) | C53—H53B | 0.9700 |
| C11—C17 | 1.375 (8) | C53—C54 | 1.499 (9) |
| C11—C19 | 1.412 (8) | C54—H54 | 0.9800 |
| C12—C15 | 1.464 (8) | C54—C55 | 1.518 (8) |
| C12—C17 | 1.448 (8) | C55—H55A | 0.9800 |
| C13—C14 | 1.472 (9) | C55—C56 | 1.493 (8) |
| C14—H14A | 0.9700 | C56—H56 | 0.9800 |
| C14—H14B | 0.9700 | C56—C57 | 1.501 (8) |
| C15—C16 | 1.404 (8) | C57—H57A | 0.9600 |
| C17—C18 | 1.426 (8) | C57—H57B | 0.9600 |
| C19—C20 | 1.377 (8) | C57—H57C | 0.9600 |
| C21—H21A | 0.9600 | O61—N61 | 1.221 (7) |
| C21—H21B | 0.9600 | O62—N61 | 1.228 (7) |
| C21—H21C | 0.9600 | O63—N61 | 1.237 (7) |
| O34—C34 | 1.361 (8) | O64—N62 | 1.212 (8) |
| O34—C51 | 1.414 (9) | O65—N62 | 1.200 (9) |
| O35—C35 | 1.231 (7) | O66—N62 | 1.223 (8) |
| C4—O4—C21 | 119.3 (5) | C39—O39—H39 | 109.5 |
| C4*—O4*—H4* | 109.5 | C41—O41—H41 | 109.5 |
| C1*—O5*—C5* | 114.8 (4) | C44—O44—H44 | 109.5 |
| C6—O6—H6 | 109.5 | C55—O55—H55 | 109.5 |
| C1*—O7—C7 | 112.8 (4) | C52—O56—C56 | 112.0 (4) |
| C9—O9—H9 | 109.5 | H54A—N54—H54B | 109.5 |
| C11—O11—H11 | 109.5 | H54A—N54—H54C | 109.5 |
| C14—O14—H14 | 109.5 | H54B—N54—H54C | 109.5 |
| H3*A—N3*—H3*B | 109.5 | C54—N54—H54A | 109.5 |
| H3*A—N3*—H3*C | 109.5 | C54—N54—H54B | 109.5 |
| H3*B—N3*—H3*C | 109.5 | C54—N54—H54C | 109.5 |
| C3*—N3*—H3*A | 109.5 | C32—C31—H31 | 120.4 |
| C3*—N3*—H3*B | 109.5 | C32—C31—C45 | 119.3 (7) |
| C3*—N3*—H3*C | 109.5 | C45—C31—H31 | 120.4 |
| C2—C1—H1 | 121.4 | C31—C32—H32 | 119.7 |
| C2—C1—C15 | 117.2 (7) | C33—C32—C31 | 120.6 (6) |
| C15—C1—H1 | 121.4 | C33—C32—H32 | 119.7 |
| O5*—C1*—O7 | 112.7 (4) | C32—C33—H33 | 119.7 |
| O5*—C1*—H1* | 108.3 | C34—C33—C32 | 120.5 (7) |
| O5*—C1*—C2* | 111.2 (5) | C34—C33—H33 | 119.7 |
| O7—C1*—H1* | 108.3 | O34—C34—C33 | 123.0 (6) |
| O7—C1*—C2* | 108.0 (5) | O34—C34—C46 | 116.0 (6) |
| C2*—C1*—H1* | 108.3 | C33—C34—C46 | 121.0 (7) |
| C1—C2—H2 | 118.4 | O35—C35—C46 | 122.1 (6) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 123.2 (7) | O35—C35—C48 | 119.1 (6) |
| C3—C2—H2 | 118.4 | C48—C35—C46 | 118.7 (5) |
| C1*—C2*—H2*A | 109.2 | O36—C36—C48 | 122.1 (5) |
| C1*—C2*—H2*B | 109.2 | O36—C36—C50 | 116.8 (5) |
| H2*A—C2*—H2*B | 107.9 | C48—C36—C50 | 121.1 (5) |
| C3*—C2*—C1* | 112.2 (5) | O37—C37—H37 | 108.0 |
| C3*—C2*—H2*A | 109.2 | O37—C37—C38 | 112.6 (4) |
| C3*—C2*—H2*B | 109.2 | O37—C37—C50 | 106.9 (4) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 119.6 | C38—C37—H37 | 108.0 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 120.9 (6) | C50—C37—H37 | 108.0 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 119.6 | C50—C37—C38 | 113.2 (5) |
| N3*—C3*—H3* | 108.3 | C37—C38—H38A | 108.8 |
| N3*—C3*—C4* | 110.0 (5) | C37—C38—H38B | 108.8 |
| C2*—C3*—N3* | 111.5 (5) | C37—C38—C39 | 114.0 (5) |
| C2*—C3*—H3* | 108.3 | H38A—C38—H38B | 107.7 |
| C2*—C3*—C4* | 110.3 (5) | C39—C38—H38A | 108.8 |
| C4*—C3*—H3* | 108.3 | C39—C38—H38B | 108.8 |
| O4—C4—C3 | 123.2 (6) | O39—C39—C38 | 113.3 (5) |
| O4—C4—C16 | 118.2 (6) | O39—C39—C40 | 110.9 (5) |
| C3—C4—C16 | 118.6 (6) | O39—C39—C43 | 104.0 (4) |
| O4*—C4*—C3* | 110.8 (5) | C38—C39—C43 | 108.7 (5) |
| O4*—C4*—H4*A | 110.1 | C40—C39—C38 | 110.2 (5) |
| O4*—C4*—C5* | 108.7 (5) | C40—C39—C43 | 109.5 (5) |
| C3*—C4*—H4*A | 110.1 | C39—C40—H40A | 108.7 |
| C5*—C4*—C3* | 107.1 (5) | C39—C40—H40B | 108.7 |
| C5*—C4*—H4*A | 110.1 | H40A—C40—H40B | 107.6 |
| O5—C5—C16 | 122.0 (5) | C49—C40—C39 | 114.3 (5) |
| O5—C5—C18 | 119.1 (5) | C49—C40—H40A | 108.7 |
| C18—C5—C16 | 118.8 (5) | C49—C40—H40B | 108.7 |
| O5*—C5*—C4* | 110.6 (5) | O41—C41—C47 | 121.9 (5) |
| O5*—C5*—H5* | 108.4 | O41—C41—C49 | 117.4 (5) |
| O5*—C5*—C6* | 107.1 (5) | C47—C41—C49 | 120.7 (5) |
| C4*—C5*—H5* | 108.4 | O42—C42—C45 | 119.9 (5) |
| C6*—C5*—C4* | 113.8 (5) | O42—C42—C47 | 121.2 (6) |
| C6*—C5*—H5* | 108.4 | C47—C42—C45 | 118.8 (5) |
| O6—C6—C18 | 122.1 (5) | O43—C43—C39 | 121.3 (5) |
| O6—C6—C20 | 116.4 (5) | O43—C43—C44 | 121.2 (6) |
| C18—C6—C20 | 121.5 (5) | C44—C43—C39 | 117.5 (5) |
| C5*—C6*—H6*A | 109.5 | O44—C44—C43 | 108.9 (5) |
| C5*—C6*—H6*B | 109.5 | O44—C44—H44A | 109.9 |
| C5*—C6*—H6*C | 109.5 | O44—C44—H44B | 109.9 |
| H6*A—C6*—H6*B | 109.5 | C43—C44—H44A | 109.9 |
| H6*A—C6*—H6*C | 109.5 | C43—C44—H44B | 109.9 |
| H6*B—C6*—H6*C | 109.5 | H44A—C44—H44B | 108.3 |
| O7—C7—H7 | 108.7 | C31—C45—C42 | 117.5 (6) |
| O7—C7—C8 | 111.6 (4) | C31—C45—C46 | 121.1 (6) |
| O7—C7—C20 | 107.1 (4) | C46—C45—C42 | 121.5 (5) |
| C8—C7—H7 | 108.7 | C34—C46—C35 | 123.2 (6) |
| C20—C7—H7 | 108.7 | C45—C46—C34 | 117.4 (6) |
| C20—C7—C8 | 111.9 (5) | C45—C46—C35 | 119.4 (6) |
| C7—C8—H8A | 108.9 | C41—C47—C42 | 120.1 (5) |
| C7—C8—H8B | 108.9 | C41—C47—C48 | 119.3 (5) |
| H8A—C8—H8B | 107.7 | C48—C47—C42 | 120.6 (5) |
| C9—C8—C7 | 113.5 (5) | C36—C48—C35 | 120.0 (5) |
| C9—C8—H8A | 108.9 | C36—C48—C47 | 119.4 (5) |
| C9—C8—H8B | 108.9 | C47—C48—C35 | 120.7 (5) |
| O9—C9—C8 | 111.2 (5) | C41—C49—C40 | 117.9 (5) |
| O9—C9—C10 | 110.3 (5) | C50—C49—C40 | 121.8 (5) |
| O9—C9—C13 | 104.3 (4) | C50—C49—C41 | 120.3 (5) |
| C10—C9—C8 | 109.0 (4) | C36—C50—C37 | 118.2 (5) |
| C10—C9—C13 | 111.7 (5) | C49—C50—C36 | 119.2 (5) |
| C13—C9—C8 | 110.2 (5) | C49—C50—C37 | 122.6 (5) |
| C9—C10—H10A | 108.8 | O34—C51—H51A | 109.5 |
| C9—C10—H10B | 108.8 | O34—C51—H51B | 109.5 |
| H10A—C10—H10B | 107.7 | O34—C51—H51C | 109.5 |
| C19—C10—C9 | 114.0 (5) | H51A—C51—H51B | 109.5 |
| C19—C10—H10A | 108.8 | H51A—C51—H51C | 109.5 |
| C19—C10—H10B | 108.8 | H51B—C51—H51C | 109.5 |
| O11—C11—C17 | 121.9 (5) | O37—C52—O56 | 111.6 (5) |
| O11—C11—C19 | 116.3 (5) | O37—C52—H52 | 107.8 |
| C17—C11—C19 | 121.8 (5) | O37—C52—C53 | 109.0 (5) |
| O12—C12—C15 | 119.7 (5) | O56—C52—H52 | 107.8 |
| O12—C12—C17 | 120.1 (5) | O56—C52—C53 | 112.7 (5) |
| C17—C12—C15 | 120.2 (5) | C53—C52—H52 | 107.8 |
| O13—C13—C9 | 121.1 (5) | C52—C53—H53A | 109.1 |
| O13—C13—C14 | 121.0 (6) | C52—C53—H53B | 109.1 |
| C14—C13—C9 | 117.9 (5) | H53A—C53—H53B | 107.8 |
| O14—C14—C13 | 115.3 (6) | C54—C53—C52 | 112.6 (5) |
| O14—C14—H14A | 108.5 | C54—C53—H53A | 109.1 |
| O14—C14—H14B | 108.5 | C54—C53—H53B | 109.1 |
| C13—C14—H14A | 108.5 | N54—C54—H54 | 108.6 |
| C13—C14—H14B | 108.5 | N54—C54—C55 | 109.6 (5) |
| H14A—C14—H14B | 107.5 | C53—C54—N54 | 110.3 (5) |
| C1—C15—C12 | 117.6 (6) | C53—C54—H54 | 108.6 |
| C1—C15—C16 | 121.5 (6) | C53—C54—C55 | 111.1 (5) |
| C16—C15—C12 | 120.8 (5) | C55—C54—H54 | 108.6 |
| C4—C16—C5 | 122.1 (6) | O55—C55—C54 | 108.8 (5) |
| C15—C16—C4 | 118.4 (6) | O55—C55—H55A | 109.7 |
| C15—C16—C5 | 119.5 (5) | O55—C55—C56 | 111.6 (5) |
| C11—C17—C12 | 120.8 (5) | C54—C55—H55A | 109.7 |
| C11—C17—C18 | 120.6 (5) | C56—C55—C54 | 107.4 (5) |
| C18—C17—C12 | 118.5 (5) | C56—C55—H55A | 109.7 |
| C6—C18—C5 | 121.0 (5) | O56—C56—C55 | 108.3 (5) |
| C6—C18—C17 | 117.2 (5) | O56—C56—H56 | 108.9 |
| C17—C18—C5 | 121.8 (5) | O56—C56—C57 | 109.0 (5) |
| C11—C19—C10 | 118.6 (5) | C55—C56—H56 | 108.9 |
| C20—C19—C10 | 123.4 (5) | C55—C56—C57 | 112.9 (5) |
| C20—C19—C11 | 117.9 (5) | C57—C56—H56 | 108.9 |
| C6—C20—C7 | 118.2 (5) | C56—C57—H57A | 109.5 |
| C19—C20—C6 | 120.7 (5) | C56—C57—H57B | 109.5 |
| C19—C20—C7 | 121.1 (5) | C56—C57—H57C | 109.5 |
| O4—C21—H21A | 109.5 | H57A—C57—H57B | 109.5 |
| O4—C21—H21B | 109.5 | H57A—C57—H57C | 109.5 |
| O4—C21—H21C | 109.5 | H57B—C57—H57C | 109.5 |
| H21A—C21—H21B | 109.5 | O61—N61—O62 | 122.5 (7) |
| H21A—C21—H21C | 109.5 | O61—N61—O63 | 119.6 (7) |
| H21B—C21—H21C | 109.5 | O62—N61—O63 | 117.8 (7) |
| C34—O34—C51 | 118.6 (6) | O64—N62—O66 | 117.4 (8) |
| C36—O36—H36 | 109.5 | O65—N62—O64 | 120.8 (9) |
| C52—O37—C37 | 114.0 (5) | O65—N62—O66 | 121.8 (9) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
Cg2 is the centroid of the C1–C4/C15/C16 ring.
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O6—H6···O5 | 0.82 | 1.81 | 2.526 (6) | 146 |
| O11—H11···O12 | 0.82 | 1.80 | 2.526 (6) | 146 |
| O14—H14···O65i | 0.82 | 2.07 | 2.779 (9) | 145 |
| N3*—H3*A···O13ii | 0.89 | 2.00 | 2.874 (7) | 167 |
| N3*—H3*C···O63 | 0.89 | 1.99 | 2.865 (8) | 168 |
| O41—H41···O42 | 0.82 | 1.82 | 2.537 (6) | 146 |
| O44—H44···O14iii | 0.82 | 2.08 | 2.888 (6) | 168 |
| O55—H55···O4* | 0.82 | 1.93 | 2.724 (6) | 163 |
| N54—H54A···O43iv | 0.89 | 2.18 | 2.890 (7) | 136 |
| N54—H54A···O44iv | 0.89 | 2.05 | 2.843 (7) | 147 |
| N54—H54B···O62 | 0.89 | 1.99 | 2.836 (8) | 159 |
| N54—H54C···O64 | 0.89 | 2.05 | 2.876 (9) | 155 |
| C38—H38B···Cg2v | 0.97 | 2.64 | 3.556 (7) | 157 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x−1, y, z+1; (ii) x, y, z−1; (iii) x+2, y, z; (iv) x−1, y, z−1; (v) −x+1, y+1/2, −z+1.
Funding Statement
This work was funded by China Scholarship Council grant 201707045007 to G. Yang.
References
- Agrawal, P., Barthwal, S. K. & Barthwal, R. (2009). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 44, 1437–1451. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Arcamone, F. (1981). Doxorubicin: Anticancer Antibiotics. Academic Press.
- Arcamone, F., Cassinelli, G., Fantini, G., Grein, A., Orezzi, P., Pol, C. & Spalla, C. (1969). Biotechnol. Bioeng. 11, 1101–1110. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Barthwal, R., Agrawal, P., Tripathi, A. N., Sharma, U., Jagannathan, N. R. & Govil, G. (2008). Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 474, 48–64. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Berman, H. M., Westbrook, J., Feng, Z., Gilliland, G., Bhat, T. N., Weissig, H., Shindyalov, I. N. & Bourne, P. E. (2000). Nucleic Acids Res. 28, 235–242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Bruker (2016). APEX3, SAINT and SADABS. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Cagel, M., Grotz, E., Bernabeu, E., Moretton, M. A. & Chiappetta, D. A. (2017). Drug Discov. Today, 22, 270–281. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Cappetta, D., Rossi, F., Piegari, E., Quaini, F., Berrino, L., Urbanek, K. & De Angelis, A. (2018). Pharmacol. Res. 127, 4–14. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Chaires, J. B. (1998). Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 8, 314–320. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Courseille, C., Busetta, B., Geoffre, S. & Hospital, M. (1979). Acta Cryst. B35, 764–767.
- Dassault Systèmes BIOVIA (2017). Discovery Studio Visualizer. San Diego, CA, USA.
- Denel-Bobrowska, M. & Marczak, A. (2017). Life Sci. 178, 1–8. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K. & Puschmann, H. (2009). J. Appl. Cryst. 42, 339–341.
- Duggan, S. T. & Keating, G. M. (2011). Drugs, 71, 2531–2558. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Eckle, E. & Stezowski, J. J. (1980). European Crystallographic Meeting, 6, 296.
- Eckle, E. & Stezowski, J. J. (1983). Z. Kristallogr. 162, 63.
- Eicher, T., Cha, H., Seeger, M. A., Brandstätter, L., El-Delik, J., Bohnert, J. A., Kern, W. V., Verrey, F., Grütter, M. G., Diederichs, K. & Pos, K. M. (2012). Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. 109, 5687–5692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Eswaramoorthy, S., Kumaran, D. & Swaminathan, S. (2001). Acta Cryst. D57, 1743–1746. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Frederick, C. A., Williams, L. D., Ughetto, G., Van der Marel, G. A., Van Boom, J. H., Rich, A. & Wang, A. H. J. (1990). Biochemistry, 29, 2538–2549. [PubMed]
- Genovese, I., Fiorillo, A., Ilari, A., Masciarelli, S., Fazi, F. & Colotti, G. (2017). Cell Death Dis. 8, e2950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Groom, C. R., Bruno, I. J., Lightfoot, M. P. & Ward, S. C. (2016). Acta Cryst. B72, 171–179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Howerton, S. B., Nagpal, A. & Dean Williams, L. (2003). Biopolymers, 69, 87–99. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Jung, K. & Reszka, R. (2001). Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 49, 87–105. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Leonard, G. A., Hambley, T. W., McAuley-Hecht, K., Brown, T. & Hunter, W. N. (1993). Acta Cryst. D49, 458–467. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Leung, K. K. K. & Shilton, B. H. (2015). Biochemistry, 54, 7438–7448. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Lipscomb, L. A., Peek, M. E., Zhou, F. X., Bertrand, J. A., VanDerveer, D. & Williams, L. D. (1994). Biochemistry, 33, 3649–3659. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Liu, L. F. (1989). Annu. Rev. Biochem. 58, 351–375. [DOI] [PubMed]
- López-González, A., Diz, P., Gutierrez, L., Almagro, E., Palomo, A. G. & Provencio, M. (2013). Ann. Transl. Med. 1, 5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Ming, L.-J. (2003). Med. Res. Rev. 23, 697–762. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Murakami, S., Nakashima, R., Yamashita, E., Matsumoto, T. & Yamaguchi, A. (2006). Nature, 443, 173–179. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Neidle, S. & Taylor, G. (1977). Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 479, 450–459. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Palmer, D. (2017). CrystalMaker. Begbroke, Oxfordshire, England: CrystalMaker Software Ltd.
- Parsons, S., Flack, H. D. & Wagner, T. (2013). Acta Cryst. B69, 249–259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Post, G. C., Barthel, B. L., Burkhart, D. J., Hagadorn, J. R. & Koch, T. H. (2005). J. Med. Chem. 48, 7648–7657. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Shafei, A., El-Bakly, W., Sobhy, A., Wagdy, O., Reda, A., Aboelenin, O., Marzouk, A., El Habak, K., Mostafa, R., Ali, M. A. & Ellithy, M. (2017). Biomed. Pharmacother. 95, 1209–1218. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015a). Acta Cryst. A71, 3–8.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015b). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Weiss, R. B. (1992). Semin. Oncol. 19, 670–686. [PubMed]
- Yang, X.-L. & Wang, A. H.-J. (1999). Pharmacol. Ther. 83, 181–215. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Yu, M. K., Jeong, Y. Y., Park, J., Park, S., Kim, J. W., Min, J. J., Kim, K. & Jon, S. (2008). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 47, 5362–5365. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S., Yan, L., Ji, X. & Lu, W. (2010). J. Mol. Struct. Theochem, 951, 60–68.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018002955/wm5435sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018002955/wm5435Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018002955/wm5435Isup3.cdx
CCDC reference: 1815074
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report






