Abstract
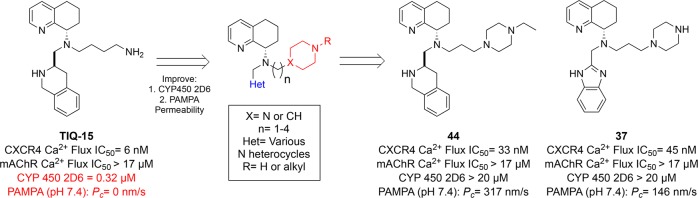
A novel series of CXCR4 antagonists with piperidinyl and piperazinyl alkylamine side chains designed as butyl amine replacements are described. Several of these compounds showed similar activity to the parent compound TIQ-15 (5) in a SDF-1 induced calcium flux assay. Preliminary structure–activity relationship investigations led us to identify a series containing N-propyl piperazine side chain analogs exemplified by 16 with improved off-target effects as measured in a muscarinic acetylcholine receptor (mAChR) calcium flux assay and in a limited drug safety panel screen. Further efforts to explore SAR and optimize drug properties led to the identification of the N′-ethyl-N-propyl-piperazine tetrahydroisoquinoline derivative 44 and the N-propyl-piperazine benzimidazole compound 37, which gave the best overall profiles with no mAChR or CYP450 inhibition, good permeability in PAMPA assays, and metabolic stability in human liver microsomes.
Keywords: CXCR4 receptor, CXCR4 antagonists, piperazine, tetrahydroisoquinoline, muscarinic receptor, calcium flux, liver microsomes, PAMPA, CYP450
The C–X–C chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4) is a seven transmembrane G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) and is classified as a family I or rhodopsin-like GPCR family.1,2 The endogenous ligand CXCL12, or stromal cell-derived factor-1 (SDF-1), plays a vital role in the homing of hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) to the bone marrow and HSC quiescence.3−5 When SDF-1 binds to CXCR4, it activates different signaling pathways, which lead to biological responses such as chemotaxis, cell survival and proliferation, intracellular calcium flux, and gene transcription.6 Levels of CXCR4 expression are low in healthy tissues, but this receptor is upregulated in ≥48 cancer types and has further been demonstrated as a prognostic marker in breast, lung, ovarian, prostate, and colorectal cancers, as well as in hematological cancers like leukemia.7 Organs and tissues that express high levels of SDF-1, such as the liver, lung, bone marrow, and lymph nodes, attract the migration of CXCR4-expressing cancer cells in cancer metastasis.7
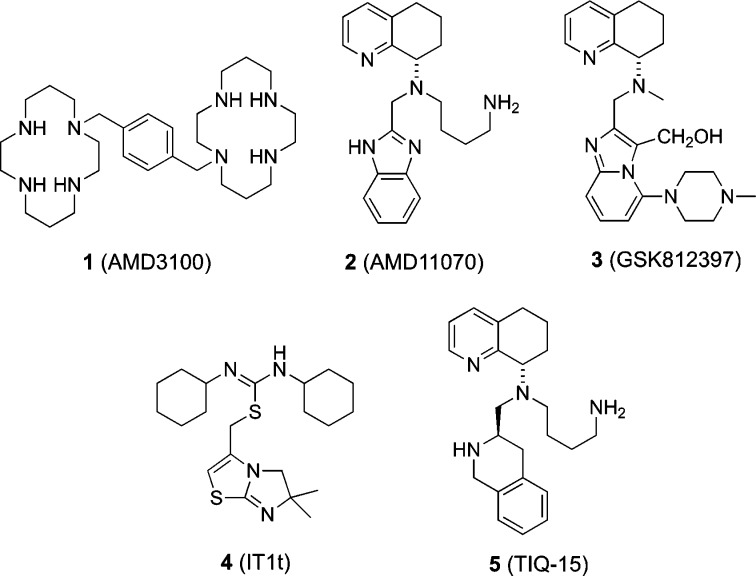
Previous research of CXCR4 antagonists has resulted in several types of small molecule inhibitors such as AMD3100 (1, Plerixafor), AMD11070 (2), GSK812397 (3), and IT1t (4) (Figure 1). Of these the first FDA approved CXCR4 antagonist drug was Plerixafor (1, AMD3100), which was first developed as an anti-HIV agent functioning as a potent antagonist, but drug toxicity prevented it from being administered daily.8,9 Aside from anti-HIV activity, 1 also showed the mobilization of hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs). Clinical investigations of Plerixafor led to its FDA-approval for hematopoietic stem cell mobilization in non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma and multiple myeloma patients with autologous transplants.10 The poor oral bioavailability displayed by 1 prompted the discovery of 2 as the first orally active CXCR4 antagonist, which is currently in clinical trials.6,11−13 Efforts to increase the potency by modifying structural features of 2 resulted in the novel piperazine-containing scaffold exemplified by 3 (GSK812397).
Figure 1.
Selected small molecule CXCR4 antagonists.
Alternatively, the isothiourea series typified by 4 (IT1t) was discovered through high throughput screening efforts.12−15 As the benzimidazole ring of 2 was considered to be the most likely source of reported off-target activity, much effort was exerted to replace this motif. Our lab discovered that a tetrahydroisoquinoline ring, exemplified by our parent compound TIQ-15 (5), was a suitable replacement of the benzimidazole core of 2. As previously reported, 5 is a potent and selective CXCR4 antagonist with good drug-like properties.16 Our efforts to improve the ADMET properties of compound 5, mainly the CYP450 2D6 inhibition and poor cell permeability, by structural changes to the n-butyl amine side chain have recently been reported.17,18 In this Letter, we describe synthetic efforts focused on replacement of the n-butylamine side chain with various alkyl-substituted heterocyclic side chains, such as alkyl piperidines and piperazines, and replacement of the tetrahydroisoquinoline ring with different heterocycles with the same goals of improving CYP 2D6 inhibition and low permeability.
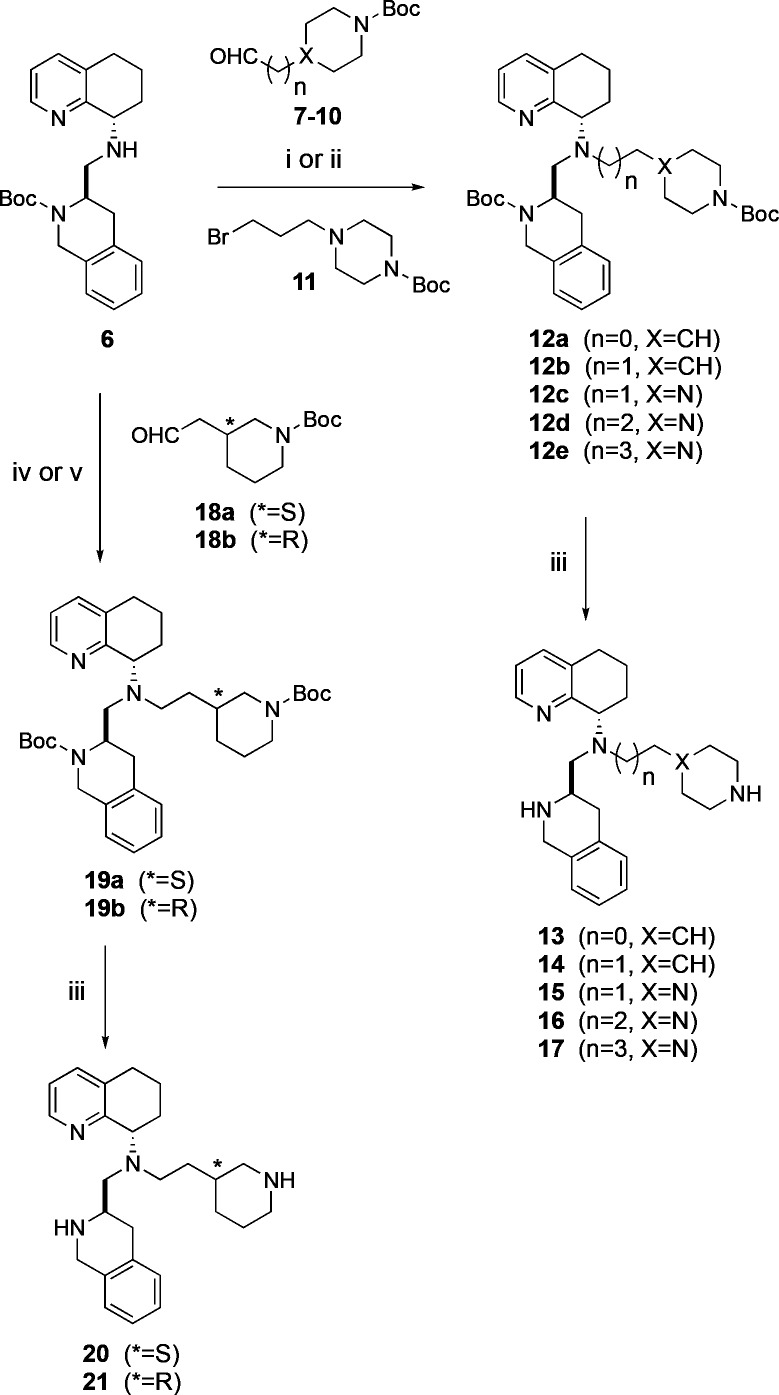
Synthetic modifications to the lead tetrahydroisoquinoline scaffold exemplified by 5 began with key intermediate 6.16 We first synthesized several piperidine and piperazine side chain analogs with varying carbon chain lengths, similar to the optimization efforts of the butylamine side chain of 2.11 Reductive amination reaction of 6 with Boc protected piperidinyl aldehydes (7, 8) and Boc protected piperazinyl aldehydes (9, 10) gave compounds 12a–c and 12e, respectively (Scheme 1). Subsequent removal of the Boc group with trifluoroacetic acid gave desired products 13–15 and 17. Alternatively, an alkylation reaction of 6 was necessary for the synthesis of propyl piperazine intermediate 12d. The secondary amine 6 was treated with alkyl bromide 11 to give 12d, followed by deprotection of the Boc groups to yield 16. A series of enantiomerically pure piperidines containing an ethyl linker (20 and 21) was also explored. These side chains closely resembled the parent butylamine side chain, but with limited free rotation. The protected ethylpiperidine intermediates 19a and 19b were prepared via a reductive amination of 6 with (S)-18a and (R)-18b, respectively. Protecting group removal from 19a and 19b yielded the ethylpiperidine analogs 20 and 21.
Scheme 1.
Reagents: (i) 7 (n = 0, X = CH), 8 (n = 1, X = CH), 9 (n = 1, X = N), 10 (n = 3, X = N), NaBH(OAc)3, DCE, 75–95% yield; (ii) tert-butyl-4-(3-bromopropyl)piperazine-1-carboxylate (11), DIPEA, MeCN, 65 °C, 73% yield; (iii) TFA, DCM, r.t. 35–48% yield; (iv) tert-butyl (S)-3-(2-oxoethyl)piperidine-1-carboxylate (18a), NaBH(OAc)3, DCE, 82% yield; (v) tert-butyl (R)-3-(2-oxoethyl)-piperidine-1-carboxylate (18b), NaBH(OAc)3, DCE, r.t.
Several in vitro pharmacological assays were used to screen these derivatives of 5, and the results revealed a range of potencies and divergent structure–activity relationships (SAR). All compounds were tested as both agonists and antagonists in CXCR4 calcium flux assays, and none showed any agonistic activity (Table 1). In addition, compounds were screened against the muscarinic receptor to measure potential off-target GPCR activity, and all compounds were found to be inactive in this assay. Replacing the butylamine side chain with 4-methylpiperidine (13), 4-ethylpiperidine (14), (S)-3-ethylpiperidine (20), or (R)-3-ethylpiperidine (21) resulted in robust CXCR4 inhibition, albeit with a slight loss in potency (2–3-fold) versus 5. We were encouraged to observe a decrease in CYP450 2D6 IC50 values for 13 and 14 relative to 5; however, 20 and 21 had slightly increased 2D6 activity. Also screened were the 2 through 4 carbon linked N-piperazines (15–17). Although all three had reduced CYP450 2D6 activity with IC50 values up to 10-fold higher than 5, propyl piperazine analog 16 proved to be the best in terms of CXCR4 potency. Overall, these efforts led to the discovery of compounds 21 and 16, which exhibited the most potent CXCR4 antagonist activity of all compounds screened in this initial series. In comparing piperidines to piperazines, an increase in 2D6 for piperidine 21 and the lower calcium flux value of piperidine 13 showed the limitations in trying to optimize the piperidine series further. In contrast, we found that the piperazine side chain analogs (15–17) had better liver microsomal stability than the parent compound 5, as well as piperidine analogs 13, 14, 20, and 21. In general, the piperidines were inferior compounds, having more problematic 2D6 potencies and liver microsomal stability across species. For example, ethyl piperazine 15 was less potent than the ethylpiperidine 14, but a slight improvement in metabolic stability and CYP450 2D6 inhibition was observed. The propyl and butyl piperazines (16, 17) had better on-target potency than ethyl piperazine 15 and also maintained good microsomal stability. Overall, propyl piperazine 16 was the best compound from these first generation results.
Table 1. Biological Data of Compounds from Scheme 1.
| compd. No. | CXCR4 Ca2+ flux IC50 (nM) | microsomal stability (H/R/M)a | CYP450 2D6 IC50 (μM)b | PAMPA pH 7.4 Pc (nm/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 6 | 77/37/17 | 0.32 | 0 |
| 13 | 65 | 86/65/13 | 1.87 | 0 |
| 14 | 150 | 66/17/32 | 1.04 | 19 |
| 15 | 553 | 96/62/79 | 4.21 | 10 |
| 16 | 17 | 100/100/92 | 2.14 | 0 |
| 17 | 66 | 82/15/96 | 1.43 | 14 |
| 20 | 161 | 75/28/23 | 0.03 | 0 |
| 21 | 16 | 93/55/56 | 0.11 | 55 |
Liver microsomal stability measured as percent remaining by LCMS after 10 min in human (H), rat (R), and mouse (M) microsomes.
All compounds have mAChR Ca2+ flux IC50 > 14 μM and CYP450 3A4 IC50 > 12 μM.
In order to further distinguish between the piperazine and piperidine side-chain series, we chose two compounds with the best profiles for each heterocycle type (16, 21) as well as TIQ-15 (5) for comparison to test for additional non-CXCR4 pharmacology beyond the CYP450 2D6 and Muscarinic receptor (mAChR) assays. A limited panel of four assays (Table 2) were selected based on proteins that are known to interact with many nitrogen-based chemotypes (such as phenethyl amines, pyridines, piperazines, and piperidines) similar to those found in our compounds. As there are a vast number of possibilities for cross-pharmacology and our goal was not New Chemical Entity (NCE) candidate selection at this stage, this panel was very limited to convey potential liabilities. First, no responses were observed lower than 3 μM for all compounds indicating a therapeutic index of at least 100-fold compared to the CXCR4 Ca2+ responses. In the two class A GPCRs (adrenergic, opioid) both 5 and 21 had similar responses in the single digit micromolar ranges but still with therapeutic indices at 100- to 1000-fold. Furthermore, compound 21 had similar responses in the nicotinic receptor and acetyl choline esterase with IC50 values in the 10 μM range, while both 5 and 16 were devoid of this activity up to 30 μM. In comparison, the propyl piperazine 16 had the least off-target effects with all four assays showing no responses up to 30 μM. Although piperidine 21 had slightly improved PAMPA permeability, all four off-target effects in the 6–11 μM range indicating a less favorable profile even compared to TIQ-15. Since the piperazine based side chain had the best profile, we selected compound 16 as a more selective agent for continued SAR exploration.
Table 2. Off-Target Panel of Compounds 5, 16, and 21.
| IC50 (μM) |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| off-target assay | 5 | 16 | 21 |
| α-adrenergic 2A | 3.7 | >30 | 5.9 |
| μ-opioid | 14.9 | >30 | 11.3 |
| nAChR α1 | >30 | >30 | 11.3 |
| acetylcholine esterase | >30 | >30 | 10.7 |
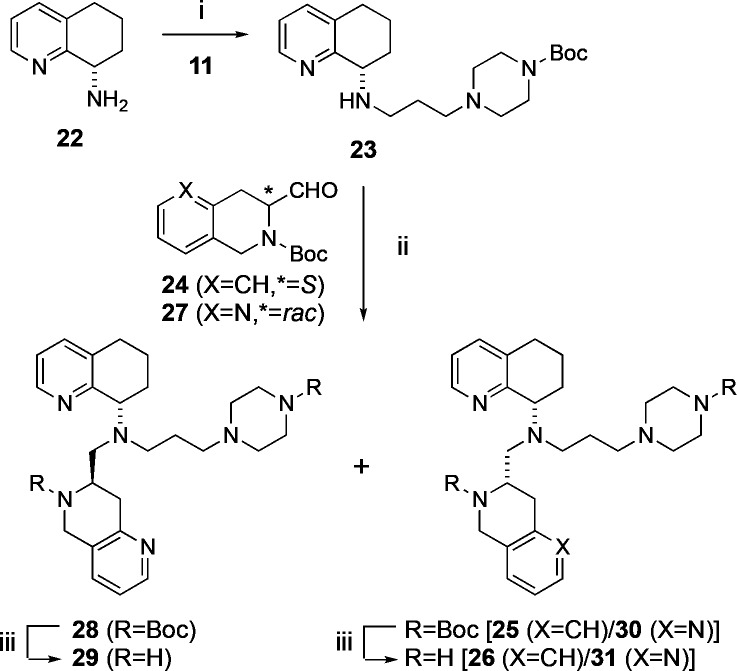
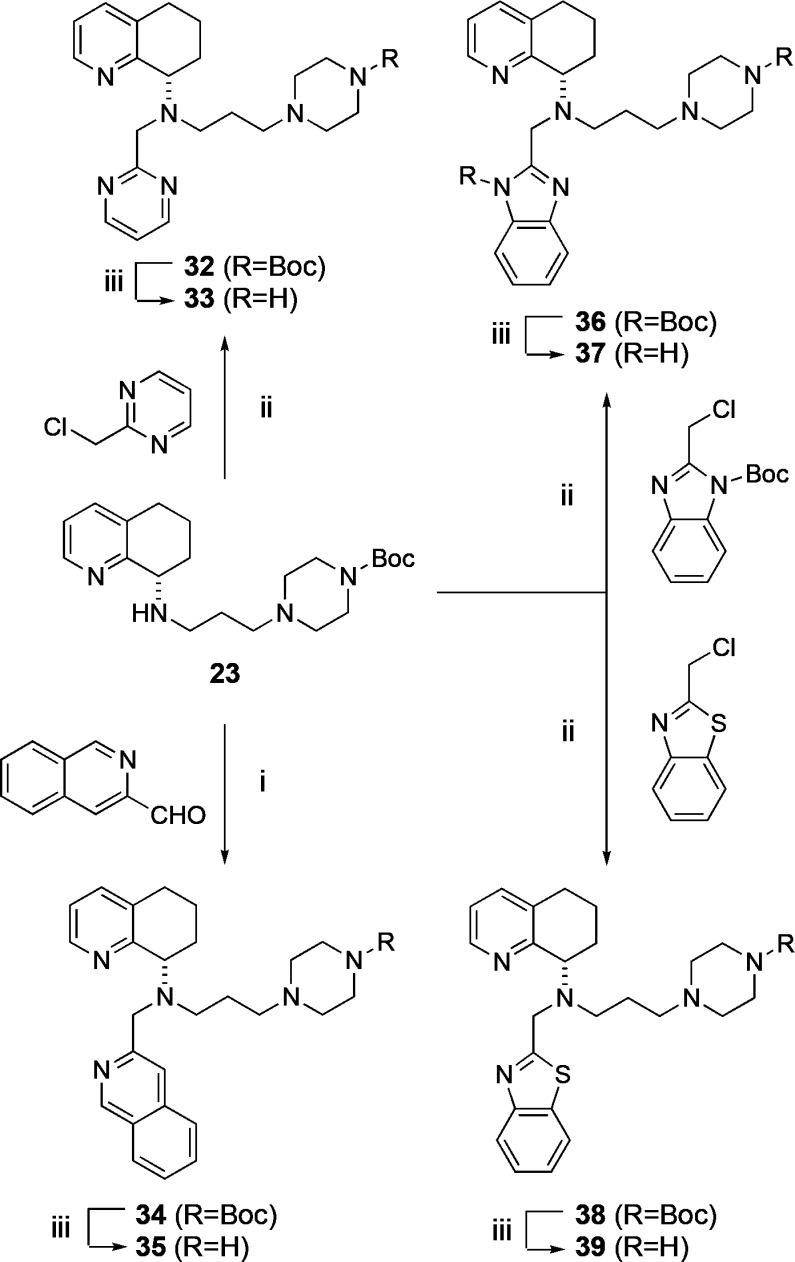
After finding that the propyl piperazine side chain delivered good CXCR4 activity, improved metabolic stability, and reduced off target activity, we focused our SAR on substituting different heterocycles for the bottom THIQ ring system. This effort was also designed to compare the different heterocycles used in CXCR4 medicinal chemistry with the novel propyl piperazine substitution versus the butyl amine. These included pyridine for phenyl swaps and various aromatic heterocyclic substitutions and the previously reported benzimidazole (as that found in 2) and isoquinoline rings.11,19 The synthesis of the THIQ and alternate heterocyclic scaffolds began with the alkylation of compound 22 with the side chain alkyl bromide 11 to yield the intermediate 23 (Scheme 2). Compound 23 was then either used in a reductive amination reaction with its corresponding aldehyde to give compounds 25, 28, 30, and 34 or alkylated with the corresponding chloride to give compounds 32, 36, or 38 (Schemes 2 and 3). Diastereomers 28 and 30 were readily separable by column chromatography. A final deprotection of the Boc group furnished the analogs 26, 29, 31, 33, 35, 37, and 39.
Scheme 2.
Reagents: (i) 11, DIPEA, MeCN, r.t., 75% yield; (ii) 24 or 27, NaBH(OAc)3, DCE, r.t., 16–26% yield; (iii) TFA, DCM, r.t., 85–98% yield.
Scheme 3.
Reagents: (i) isoquinoline-3-carbaldehyde, NaBH(OAc)3, DCE, r.t.; (ii) N-Boc-2-chloromethylbenzimidazole,11 2-(chlorometh-yl)benzo[d]thiazole, or 2-(chloromethyl)pyrimidine hydrochloride, DIPEA, MeCN, 65 °C; (iii) TFA, DCM, r.t., 22–52% yield over two steps.
First, the TIQ substitutions yielded further SAR. Pharmacological results of 26, the epimer of 16, demonstrated a nearly 100-fold reduction in CXCR4 activity, illustrating a preference for the R-isomer (Table 3), which was similarly observed during the discovery of TIQ-15.16 The pyridine for phenyl swap (29, 31) resulted in a compound (29) with 10-fold lower CXCR4 activity but a marked improvement in CYP 2D6. For the heteroaromatic substitution SAR, the pyrimidine (33), isoquinoline (35), benzimidazole (37), and benzothiazole (39) analogs were tested. The isoquinoline 35, synthesized as a replacement for the TIQ ring on 16, had similar CXCR4 and CYP450 2D6 potencies but with more potent muscarinic activity (3 μM versus >17 μM). The muscarinic activity, although not reported for the analogous n-butyl amine compound, are likely attributed solely to the isoquinoline ring.19 Benzimidazole (37) had 3-fold lower CXCR4 activity compared to 35, but showed no CYP450 2D6 or muscarinic activities. Benzothiazole (39) and pyrimidine (33) were much less active against CXCR4 with both compounds having single digit micromolar activities in the calcium flux assay. One advantage to the aromatic heterocycle compounds was an improvement in PAMPA permeability, especially 35 and 37 showing >100 nm/s Pc values. In this effort, the benzimidazole compound (37) had the best overall properties with slightly higher CXCR4 activity than 16 (2- to 3-fold) but no CYP450 2D6 inhibition and acceptable PAMPA permeability. Also, when comparing this n-propyl piperazine side chain compound (37) to AMD11070 (2), improvements in CYP450 2D6, liver microsomal stabilities, and PAMPA are observed with a 10-fold drop in CXCR4 activity. The majority of these trends were now consistent for both THIQ and benzimidazole substitutions (16 and 37).
Table 3. Biological Data of Compounds from Schemes 2 and 3.
| compd. No. | CXCR4 Ca2+ flux IC50 (nM) | microsomal stability (H/R/M)a | CYP450 2D6 IC50 (μM)b,c | PAMPA pH 7.4 Pc (nm/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 5 | 63/<1/<1 | 1.64 | 86 |
| 26 | 1154 | 99/88/88 | 1.40 | 16 |
| 29 | 171 | 79/79/78 | >20 | 9 |
| 31 | 2639 | 100/87/63 | >20 | 0 |
| 33 | 4316 | 100/68/78 | >20 | 31 |
| 35 | 17 | 66/59/74 | 2.96 | 243 |
| 37 | 45 | 63/29/68 | >20 | 146 |
| 39 | 1199 | 50/21/45 | >20 | ndd |
Liver microsomal stability measured as percent remaining by LCMS after 10 min in human (H), Rat (R), and mouse (M).
All compounds have mAChR Ca2+ flux IC50 > 17 μM except 35 (mAChR IC50 = 3.2 μM).
All CYP450 3A4 values IC50 > 20 μM, except 2 (>6.67 μM), 37 (12.7 μM), and 39 (9.4 μM).
nd = not determined.
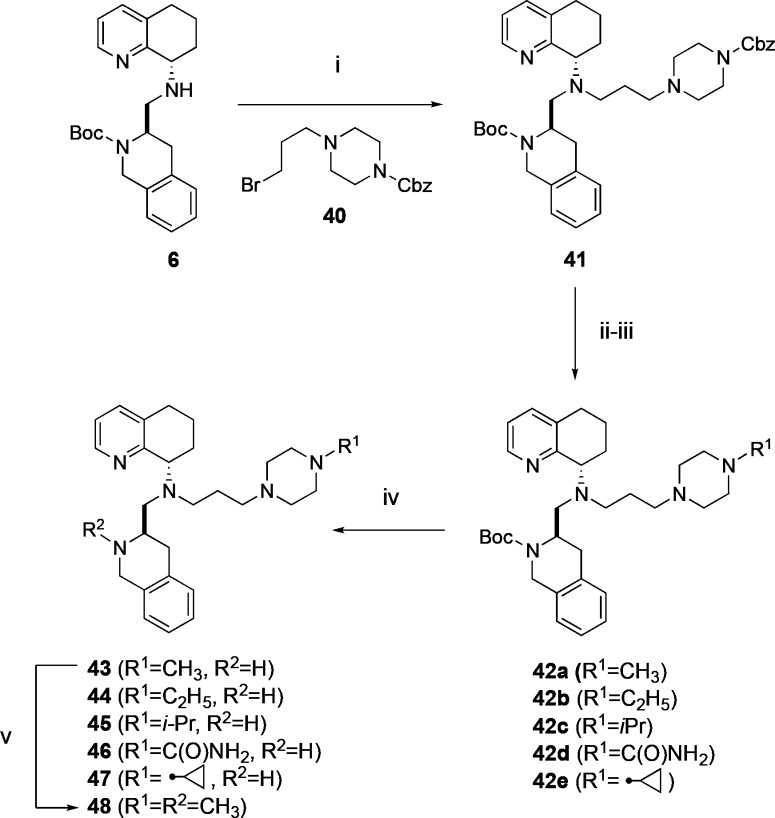
Since compound 16 had low permeability observed in the PAMPA assay, we decided to continue to alter the structure of the propyl piperazine side chain of this compound by focusing on the terminal piperazine nitrogen. Altering the basicity of the piperazine nitrogen and reducing H-bond donor count have been shown to improve permeability in other efforts.20 A series of N-substituted propyl piperazines 43–48 were synthesized to probe how substitution at the terminal piperazine might alter CXCR4 activity, metabolic stability, and permeability. The side chain benzyl 4-(3-bromopropyl)piperazine-1-carboxylate 40 was synthesized using Cbz protected piperazine and 1,3-dibromopiperazine (see Supporting Information). Alkylation of 6 with 40 gave intermediate 41 (Scheme 4), and deprotection of the Cbz group with Pd/C followed by reductive amination with either formaldehyde, acetaldehyde, acetone, or (1-ethoxycyclopropoxy)trimethylsilane furnished compounds 42a–c and 42e, respectively, whereas reaction with (trimethylsilyl)isocyanate resulted in compound 42d. Boc deprotection of compounds 42a–e provided compounds 43–47. Reductive methylation of 43 gave compound 48.
Scheme 4.
Reagents (i) benzyl-4-(3-bromopropyl)piperazine-1-carboxylate) (40), DIPEA, MeCN, 65 °C, 78% yield; (ii) Pd(OH)2, HCOONH4, EtOH, reflux; (iii) HCHO (for 42a), CH3–CHO (for 42b), acetone (for 42c), NaBH(OAc)3, DCE, r.t. or TMSNCO, DIPEA, THF (for 42d) or (1-ethoxycyclopropoxy)trimethylsilane, AcOH, NaBH3CN, MeOH (for 42e), r.t.; (iv) TFA, DCM, 40–61% yield over three steps (v) H–CHO, NaBH(OAc)3, DCE, r.t.
Compounds (43–48) were subsequently assessed for CXCR4 and mAChR inhibition, microsomal stability, CYP450 2D6 inhibition, and PAMPA permeability. A methyl substitution on piperazine 43 resulted in an almost 10-fold loss in CXCR4 potency, increased muscarinic activity, and a reduction in microsomal stability. In contrast, the CYP450 2D6 liability saw a slight improvement. The biggest change was the large enhancement in PAMPA permeability, which increased 100-fold versus 16. The compound with both the piperazine nitrogen and THIQ nitrogen methylated (48) was less active in the CXCR4 calcium flux assay by 20-fold but again saw an improvement in PAMPA permeability as compared to 16. The effect on PAMPA permeability in reduction of H-bond donor count, from two on 16 to one on 43 and then none on 48, showed the biggest improvement came from capping the piperazine N–H. The Pc values for 43 and 48 were not substantially different (Table 4, 360 versus 513 nm/s) but over 100-fold better than 16. Showing great improvement in the PAMPA permeability, we continued our focus on the terminal piperazine nitrogen. The ethyl-substituted piperazine 44 had better CXCR4 potency than 43, but a decrease in microsomal stability across all three species was observed. However, this compound was devoid of CYP450 2D6 inhibition and additionally retained the improvement in PAMPA permeability (Table 4). Further alkyl group substitutions, including isopropyl (45) and cyclopropyl (47) motifs, had similar results to 43, exhibiting less potent CXCR4 inhibition and no improvement in CYP450 2D6 or liver microsomal stability. Urea substituted piperazine 46 demonstrated a 50-fold potency loss and also introduced moderate muscarinic activity. Surprisingly, this compound (46) also showed lower permeability by 10-fold versus the alkylated analogs (43–45, 47, 48) despite the nonbasic terminal piperazine nitrogen. Overall, the ethyl analog 44 was the best compound in this series, having similar potency to 16 and greatly improved CYP450 2D6 and PAMPA properties.
Table 4. Biological Data of Compounds from Scheme 4.
| compd No. | CXCR4 Ca2+ flux IC50 (nM) | microsomal stability (H/R/M)a | CYP450 2D6 IC50 (μM)b | PAMPA pH 7.4 Pc (nm/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 43 | 125 | 72/10/53 | 5.60 | 360 |
| 44 | 33 | 59/1/19 | >20 | 317 |
| 45 | 62 | 46/4/58 | 6.65 | 344 |
| 46 | 959 | 79/4/42 | 4.14 | 67 |
| 47 | 50 | 21/2/3 | 6.04 | 505 |
| 48 | 536 | 60/2/43 | 5.14 | 513 |
Liver microsomal stability measured as percent remaining by LCMS after 10 min in human (H), rat (R), and mouse (M).
All compounds have mAChR Ca2+ flux IC50 > 17 μM, except 43 (6.56 μM) and 46 (4.98 μM). All compounds have CYP450 3A4 IC50 > 20 μM.
In conclusion, a novel series of highly potent and selective CXCR4 antagonists featuring N-alkyl-substituted heterocycles as replacements of the butylamine side chain of lead compound TIQ-15 (5) was presented. The SAR around these side chain replacements led to the N-propyl piperazine compound 16, which not only retained CXCR4 activity and improved metabolic stability in human, rat, and mouse liver microsomes, but also reduced CYP450 2D6 activity, as compared to 5. In addition, compound 16 had fewer off-target liabilities than the best piperidine compound 21 or 5 (TIQ-15; Table 2). We were also able to replace the THIQ bottom ring with various heterocycles using the newly discovered n-propyl piperazine side chain with mixed results showing both the THIQ and benzimidazole rings having the best overall properties. In fact, the benzimidazole compound 37 had eliminated CYP450 2D6 activity with only a 3-fold drop in CXCR4 potency but did increase CYP450 23A4 activity. Also, compound 37 had slightly improved PAMPA permeability compared to 16, likely due to the lower basicity of the benzimidazole versus THIQ rings. The N-alkylations of the piperazine nitrogen on 37 were not carried out as it already had optimal properties and the CXCR4 activity was already significantly higher than TIQ-15 and 2 (∼10-fold). In contrast, substituting the distal piperazine nitrogen of 16 in order to improve permeability was merited, providing a greater than 100-fold increase in Pc values in the PAMPA assay. This led to identification of the N′-ethyl-substituted N-propyl piperazine compound 44, which provided the best overall combination of properties. In comparison to the starting butyl amine compound 5 (TIQ-15), compound 44 was equivalent or superior in all respects with the exception of CXCR4 activity being 5-fold less potent. However, with good CXCR4 potency, reduced off-target effects, good human liver microsomal stability, PAMPA permeability, and greatly reduced CYP450 2D6 activity, compounds 37 and 44 offer improved selections to progress into lead optimization.
When comparing the newly discovered n-propyl-piperazine side chain to our other n-butyl amine structural changes, we can directly determine that this current effort provides the best overall compound identified in 44. Previously, one effort found a cyclo-hexyl amine compound with similar CXCR4 potency but lower 2D6 activity and PAMPA permeability than 44.17 Our other work found that substituting the butyl chain with methyl groups and unsaturation coupled with nitrogen substitutions provided compounds similar in CXCR4 activity and PAMPA permeability to 44 but lower 2D6 activity.18 In the latter case, it was the nitrogen substitutions not structural changes on the butyl amine chain that led to the improvements over TIQ-15. Many of these previously described structural variations (gem-dimethyls, unsaturation, nitrogen pyranyl groups) were not attempted in the current series due to the quick identification of compounds 37 and 44; however, our interest in these modifications may lead to further improvements. Future efforts, including pharmacokinetic studies and evaluation in models of immuno-oncology, will be reported in due course.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge Dr. Shaoxiang Wu of Emory NMR facility, and Dr. Fred Strobel for mass spectrometry.
Glossary
ABBREVIATIONS
- CXCR4
CXC chemokine receptor type 4
- GPCR
G protein-coupled receptor
- CXCL12
CXC chemokine ligand type 12
- THQ
5,6,7,8-tetrahydroquinoline
- THIQ
1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline
- HLM
human liver microsomes
- RLM
rat liver microsomes
- MLM
mouse liver microsomes
- TFA
trifluoroacetic acid
- DCE
1,2-dichloroethane
- mAChR
muscarinic acetylcholine receptor
- STAB-H
sodium triacetoxyborohydride
- PAMPA
parallel artificial membrane permeability assay
Supporting Information Available
The Supporting Information is available free of charge on the ACS Publications website at DOI: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.8b00030.
Experimental and characterization data for all new compounds and all biological data (PDF)
Author Contributions
The manuscript was written by Y.A.T. and through contributions of all authors. All authors have given approval to the final version of the manuscript.
The authors acknowledge the use of shared instrumentation provided by grants from NSF (CHE1531620).
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): D.C.L. is the principle investigator on a research grant from Bristol-Myers Squibb Research and Development to Emory University. D.C.L., L.J.W., Y.A.T., E.J.M., E.J., H.H.N., R.J.W., V.T.T., and M.B.K. are coinventors on Emory-owned Intellectual Property that includes CXCR4 antagonists.
Supplementary Material
References
- Lefrançois M.; Lefebvre M.-R.; Saint-Onge G.; Boulais P. E.; Lamothe S.; Leduc R.; Lavigne P.; Heveker N.; Escher E. Agonists for the Chemokine Receptor CXCR4. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 2 (8), 597–602. 10.1021/ml200084n. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhan W.; Liang Z.; Zhu A.; Kurtkaya S.; Shim H.; Snyder J. P.; Liotta D. C. Discovery of Small Molecule CXCR4 Antagonists. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50 (23), 5655–5664. 10.1021/jm070679i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapidot T.; Petit I. Current Understanding of Stem Cell Mobilization. Exp. Hematol. 2002, 30 (9), 973–981. 10.1016/S0301-472X(02)00883-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama T.; Kohara H.; Noda M.; Nagasawa T. Maintenance of the Hematopoietic Stem Cell Pool by CXCL12-CXCR4 Chemokine Signaling in Bone Marrow Stromal Cell Niches. Immunity 2006, 25 (6), 977–988. 10.1016/j.immuni.2006.10.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzeng Y. S.; Li H.; Kang Y. L.; Chen W. C.; Cheng W. C.; Lai D. M. Loss of CXCL12/SDF-1 in Adult Mice Decreases the Quiescent State of Hematopoietic Stem/Progenitor Cells and Alters the Pattern of Hematopoietic Regeneration after Myelosuppression. Blood 2011, 117 (2), 429–39. 10.1182/blood-2010-01-266833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi W.-T.; Duggineni S.; Xu Y.; Huang Z.; An J. Drug Discovery Research Targeting the CXC Chemokine Receptor 4 (CXCR4). J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55 (3), 977–994. 10.1021/jm200568c. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furusato B.; Mohamed A.; Uhlen M.; Rhim J. S. CXCR4 and Cancer. Pathol. Int. 2010, 60 (7), 497–505. 10.1111/j.1440-1827.2010.02548.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Clercq E. The Bicyclam AMD3100 Story. Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery 2003, 2 (7), 581–587. 10.1038/nrd1134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda S.; Oishi S.; Wang Z.-x.; Araki T.; Tamamura H.; Cluzeau J.; Ohno H.; Kusano S.; Nakashima H.; Trent J. O.; Peiper S. C.; Fujii N. Structure–Activity Relationships of Cyclic Peptide-Based Chemokine Receptor CXCR4 Antagonists: Disclosing the Importance of Side-Chain and Backbone Functionalities. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50 (2), 192–198. 10.1021/jm0607350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiPersio J. F.; Uy G. L.; Yasothan U.; Kirkpatrick P. Plerixafor. Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery 2009, 8 (2), 105–107. 10.1038/nrd2819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skerlj R. T.; Bridger G. J.; Kaller A.; McEachern E. J.; Crawford J. B.; Zhou Y.; Atsma B.; Langille J.; Nan S.; Veale D.; Wilson T.; Harwig C.; Hatse S.; Princen K.; De Clercq E.; Schols D. Discovery of Novel Small Molecule Orally Bioavailable C–X–C Chemokine Receptor 4 Antagonists That Are Potent Inhibitors of T-Tropic (X4) Hiv-1 Replication. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53 (8), 3376–3388. 10.1021/jm100073m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone N. D.; Dunaway S. B.; Flexner C.; Tierney C.; Calandra G. B.; Becker S.; Cao Y. J.; Wiggins I. P.; Conley J.; MacFarland R. T.; Park J. G.; Lalama C.; Snyder S.; Kallungal B.; Klingman K. L.; Hendrix C. W. Multiple-Dose Escalation Study of the Safety, Pharmacokinetics, and Biologic Activity of Oral AMD070, a Selective CXCR4 Receptor Inhibitor, in Human Subjects. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51 (7), 2351–8. 10.1128/AAC.00013-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson L. J.; Liotta D. C. Emergence of Small-Molecule CXCR4 Antagonists as Novel Immune and Hematopoietic System Regulatory Agents. Drug Dev. Res. 2011, 72 (7), 598–602. 10.1002/ddr.20469. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkinson S.; Thomson M.; McCoy D.; Edelstein M.; Danehower S.; Lawrence W.; Wheelan P.; Spaltenstein A.; Gudmundsson K. Blockade of X4-Tropic HIV-1 Cellular Entry by GSK812397, a Potent Noncompetitive CXCR4 Receptor Antagonist. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54 (2), 817–824. 10.1128/AAC.01293-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoma G.; Streiff M. B.; Kovarik J.; Glickman F.; Wagner T.; Beerli C.; Zerwes H.-G. Orally Bioavailable Isothioureas Block Function of the Chemokine Receptor CXCR4 in Vitro and in Vivo. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51 (24), 7915–7920. 10.1021/jm801065q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truax V. M.; Zhao H.; Katzman B. M.; Prosser A. R.; Alcaraz A. A.; Saindane M. T.; Howard R. B.; Culver D.; Arrendale R. F.; Gruddanti P. R.; Evers T. J.; Natchus M. G.; Snyder J. P.; Liotta D. C.; Wilson L. J. Discovery of Tetrahydroisoquinoline-Based CXCR4 Antagonists. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 4 (11), 1025–1030. 10.1021/ml400183q. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jecs E.; Miller E. J.; Wilson R. J.; Nguyen H. H.; Tahirovic Y. A.; Katzman B. M.; Truax V. M.; Kim M. B.; Kuo K. M.; Wang T.; Sum C. S.; Cvijic M. E.; Schroeder G. M.; Wilson L. J.; Liotta D. C. Synthesis of Novel Tetrahydroisoquinoline CXCR4 Antagonists with Rigified Side-Chains. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 9 (2), 89–93. 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.7b00406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller E. J.; Jecs E.; Truax V. M.; Katzman B. M.; Tahirovic Y. A.; Wilson R. J.; Kuo K. M.; Kim M. B.; Nguyen H. H.; Saindane M. T.; Zhao H.; Wang T.; Sum C. S.; Cvijic M. E.; Schroeder G. M.; Wilson L. J.; Liotta D. C. Discovery of Tetrahydroisoquinoline-Containing CXCR4 Antagonists with Improved in Vitro ADMET Properties. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61 (3), 946–979. 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.7b01420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. F.; Gudmundsson K. S.; Richardson L. D. A.; Jenkinson S.; Spaltenstein A.; Thomson M.; Wheelan P. Synthesis and Sar of Novel Isoquinoline CXCR4 Antagonists with Potent Anti-HIV Activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20 (10), 3026–3030. 10.1016/j.bmcl.2010.03.118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock S. A. Structural Modifications That Alter the P-Glycoprotein Efflux Properties of Compounds. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55 (11), 4877–4895. 10.1021/jm201136z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.