Abstract
Guideline-based management of asthma focuses on disease severity and choosing the appropriate medical therapy to control symptoms and reduce the risk of exacerbations. However, irrespective of asthma severity and often despite optimal medical therapy, patients may experience acute exacerbations of symptoms and a loss of disease control. Asthma exacerbations are most commonly triggered by viral respiratory infections, particularly with human rhinovirus. Given the importance of these events to asthma morbidity and health care costs, we will review common inciting factors for asthma exacerbations and approaches to prevent and treat these events.
Key words: Asthma, Asthma exacerbation, Viral infection, Allergy, Prevention, Treatment, Inhaled corticosteroids, Long-acting β2-agonists, Leukotriene antagonist, Anticholinergics, Anti-IgE, Anti-IL5, Systemic corticosteroids
Abbreviations used: ED, Emergency department; FEV1, Forced expiratory volume in 1 second; ICS, Inhaled corticosteroids; LABA, Long-acting β-agonist; RV, Rhinovirus; SABA, Short-acting β2-agonist
Despite optimal guideline-directed treatment, and irrespective of underlying disease severity, patients with asthma experience exacerbations, which are caused by an accentuation of existing inflammatory processes and a loss of disease control.
Asthma exacerbations are a major cause of disease morbidity, increases in health care costs, and, in some patients, a greater progressive loss of lung function.1 The frequency of exacerbations can be reduced, but not always fully prevented, with adequate inhaled corticosteroid (ICS) treatment or combination ICS/long-acting β-agonists (LABA).2 Because asthma exacerbations can break through standard treatment regimens, identifying at-risk patients and having a plan of management can improve disease control and patient well-being.
Asthma exacerbations remain a major reason for health care utilization and a significant financial burden to patients and society. Patients with asthma exacerbations have significantly higher total health care costs, $9223 versus $5011 (2007 dollars) per person per year, and asthma-specific costs, $1740 versus $847 per person per year, compared with matched patients without exacerbations.3 In 2007, total expenditures for asthma were estimated to be $56 billion per year with productivity losses due to morbidity and mortality of $3.8 and $2.1 billion, respectively.4 Moreover, patients requiring an emergency department (ED) visit or hospitalization for asthma are at significantly increased risk for future exacerbations independent of demographic and clinical factors, asthma severity, and asthma control,5 collectively reflecting an ongoing need to develop better strategies to prevent and treat these events.
Pathogenesis
Viral respiratory infections
The most common triggers for an exacerbation are viral respiratory infections with human rhinovirus (RV), particularly subtypes A and C,6, 7 most frequent. In school-age children, hospital admission rates for asthma exacerbations correlate with the seasonal increase of RV infections in September through December and again in the spring.8 Similar asthma hospitalization peaks are observed in adults.9
Other respiratory viruses also may cause exacerbations. During the 2009 H1N1 influenza A pandemic, mortality and admissions to the intensive care unit with H1N1 infections were frequently associated with asthma.10, 11, 12 Respiratory syncytial virus, a frequent cause of wheezing in infants and young children, may also trigger acute asthma in adults, particularly, patients older than 65 years.13 Coronaviruses, human metapneumoviruses, parainfluenza viruses, adenoviruses, and bocaviruses have all been detected in asthma exacerbations, but in low frequencies.14
Patient risk factors
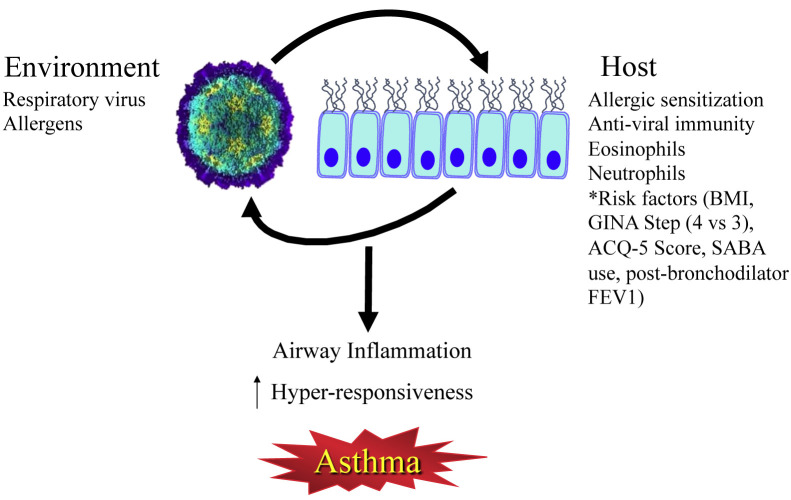
There are a number of susceptibility, or risk, factors that help to determine whether a viral respiratory infection causes an exacerbation (Figure 1 ).
Figure 1.
The interplay of the environment and host susceptibility factors in the pathogenesis of asthma exacerbations. Risk factors from Bateman et al.15ACQ, Asthma Control Questionnaire; BMI, body mass index; FEV1, forced expiratory volume in 1 second; GINA, Global Initiative for Asthma; SABA, short-acting β2-agonist.
Allergy and defective anti-viral immunity
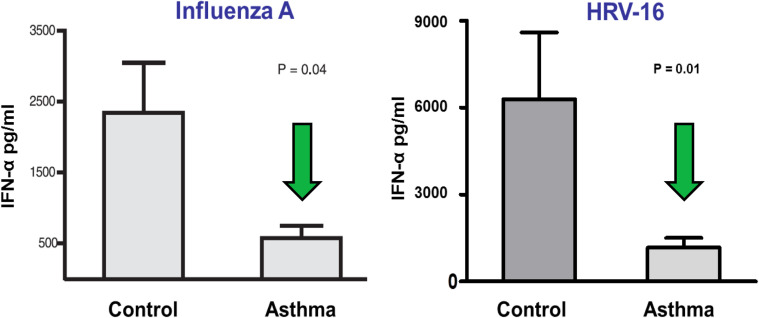
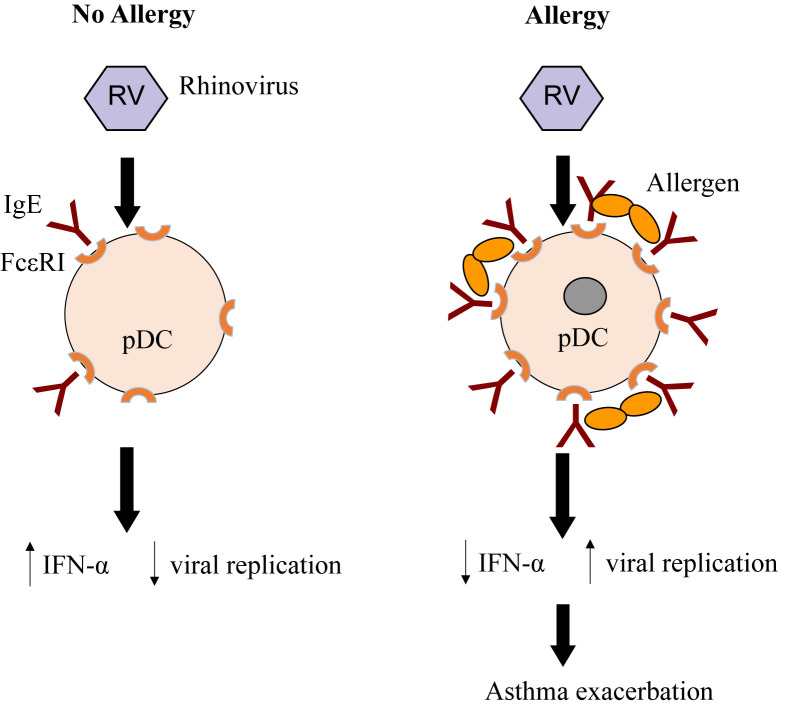
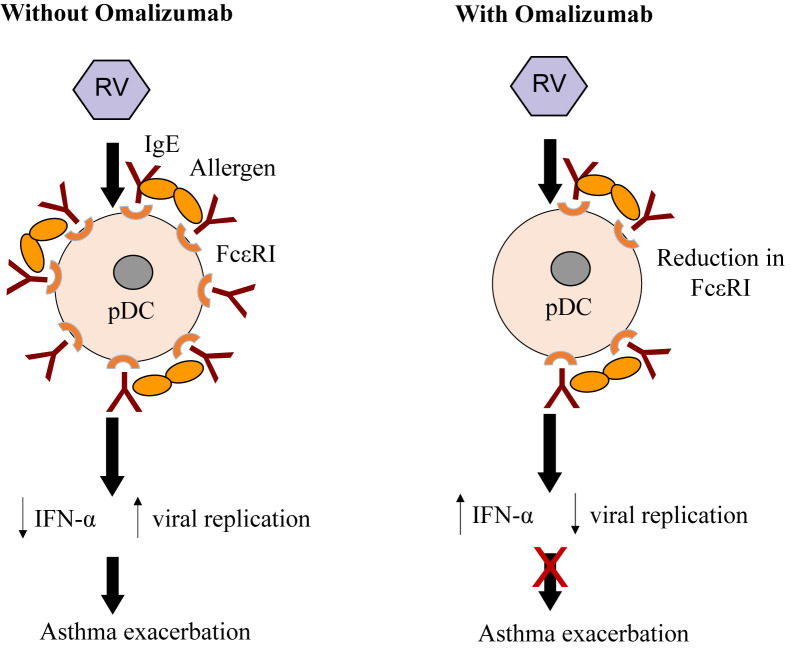
Allergic sensitization is a risk factor for wheezing with RV infection, particularly in children. Whether allergic inflammation often found with sensitization increases the susceptibility for viral infections or enhances their ability to provoke further inflammation is not entirely clear.16 Type I interferons are important innate antiviral responses to respiratory viruses.14, 17 There is evidence that virus-induced interferon generation from peripheral blood mononuclear cells,18, 19, 20 plasmacytoid dendritic cells,21 and bronchial epithelial cells22, 23 is reduced in some patients with allergic asthma (Figure 2 ). It has been show that IgE occupancy of their membrane receptors inhibits antiviral generation of IFN-α from plasmacytoid dendritic cells and may increase susceptibility to RV-induced wheezing and asthma exacerbations (Figure 3 ). Deficient immune responses to viral infections may be present in type 2 inflammatory conditions with interferon production being inversely correlated with increasing airway eosinophilia, IL-4 levels, and total serum IgE.23 Finally, the use of inhaled IFN-β at the time of an upper respiratory infection reduces the airway viral load and improves clinical symptoms in patients with asthma.24
Figure 2.
Impaired plasmacytoid dendritic cell (pDC) IFN-α response in patients with allergic asthma. pDCs from patients with physician-diagnosed asthma and allergic sensitization secreted less IFN-α on exposure to viruses compared with patients without asthma.
Reproduced with permission from Gill et al.21
Figure 3.
Effect of high-affinity IgE receptors (FcεRI) on plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs) and antiviral immunity. In the absence of allergy, pDCs express low levels of cell surface FcεRI, some occupied by IgE. Rhinovirus (RV) infection induces secretion of interferon, thereby inhibiting viral replication. In the presence of allergen and allergic sensitization, FcεRI and IgE are increased, and cross-linking of IgE receptors by allergen can inhibit interferon secretion, resulting in increased viral replication, and an increased risk of asthma exacerbation.
Bacterial infections
Bacterial infections may impair mucociliary clearance and increase mucus production in the lung and may cause chronic lower airway inflammation. Evidence linking bacterial infections to acute asthma exacerbations has been limited.25, 26 However, respiratory viruses may impair the antibacterial defenses by human alveolar macrophages and thereby facilitate emergence of bacterial infections or change in the microbiome.27 How these interrelationships contribute to exacerbations is not established, but they may be of potential therapeutic importance28 to prevent acute asthma.
Allergen exposure
Environmental allergens can provoke asthma.29 Furthermore, more than 80% of children with asthma are sensitized to environmental allergens, with indoor allergens being especially important to underlying asthma.30, 31 Mast cell activation by allergens releases32, 33 histamine, prostaglandin D2, and cysteinyl leukotriene generation to cause airway smooth muscle constriction, increased microvascular permeability, mucus secretion, and enhanced inflammation. Allergic sensitization is also associated with diminished innate immune responses and may be a susceptibility factor to viral-induced wheezing. This allergen associated inflammation also increases airway responsiveness to RV34 to further enhance a loss of asthma control.
Mold sensitization and their seasonal increase parallel greater asthma severity and seasonal exacerbations. Patients sensitized to Alternaria alternata were approximately 5 times more likely to have asthma35 and increased airway responsiveness, wheeze, and bronchodilator use.36 Emergency visits for asthma exacerbations correlate with high airborne concentrations of mold.37 Finally, Alternaria sensitization was found to be associated with an approximate 200-fold increase in the risk of respiratory arrest in children and adults.28, 38
Other contributing causes
Pollutants such as tobacco smoke, ozone, and particulate matter, along with occupational exposures, provoke asthma exacerbations. Tobacco smoke has also been implicated in the development of persistent wheezing39 and greater asthma severity.40 Hospitalizations and ED visits for asthma occur more frequently among cigarette smokers.41
Particulate matter, ozone, nitrogen dioxide, sulfur dioxide, and diesel exhaust can increase airway inflammation and airway responsiveness.32, 33, 42 Airway pollutants, together with a viral infection, may act synergistically to cause asthma exacerbations. The severity of lower respiratory tract symptoms increased and peak expiratory flow measurements fell with rising exposure to nitrogen dioxide in the week before a respiratory infection.33
Prevention of exacerbations
Four essential components of asthma management include patient education, monitoring of symptoms and lung function, control of triggering factors and comorbid conditions, and pharmacologic therapy. Patient education on asthma decreases exacerbations and improves control.43, 44 However, because asthma severity varies and differs among individuals and age groups, it is essential to regularly monitor the effectiveness of asthma control to guide necessary treatment adjustments.
The Expert Panel Report 3 and Global Initiative for Asthma describe a stepwise treatment approach and strategy to reduce impairments and prevent future risks like asthma exacerbations.45, 46
Treatments
Inhaled corticosteroids
ICS improve disease control and reduce asthma exacerbations.47, 48, 49 In new onset, untreated persistent, asthma, low-dose inhaled budesonide reduces asthma exacerbations by almost 50%.50, 51 In asthmatic patients already taking moderate doses of ICS but under poor control,50 Pauwels et al showed that high-dose budesonide further reduced severe asthma exacerbations, that is, need for systemic corticosteroids, by nearly 50% compared with treatment with low-dose ICS in adults.50 However, as found by O'Byrne et al,51 a doubling of the budesonide dose in patients poorly controlled on low-dose ICS also reduced exacerbation rates by 30%, but the degree of protection was less than those patients who recently started ICS. These findings indicate that dose-response benefits with ICS are relatively flat.52 Overall, compared with placebo or a short-acting β2-agonist, ICS reduce clinically relevant exacerbations by nearly 55%.53 ICS also reduce exacerbations in children54 and are superior to a leukotriene antagonist, montelukast.55
For patients with diminishing asthma control, quadrupling the recommended dose of ICS decreases the likelihood of an asthma exacerbation.56 This protection does not occur with a doubling of the ICS maintenance.57, 58 However, the benefit of using an increase in ICS is time dependent to increased symptoms and need to be started early in the course of a cold. If higher doses of ICS are used pre-emptively at the onset of a respiratory tract infection and continued for 10 days, the need for oral corticosteroids is reduced.59
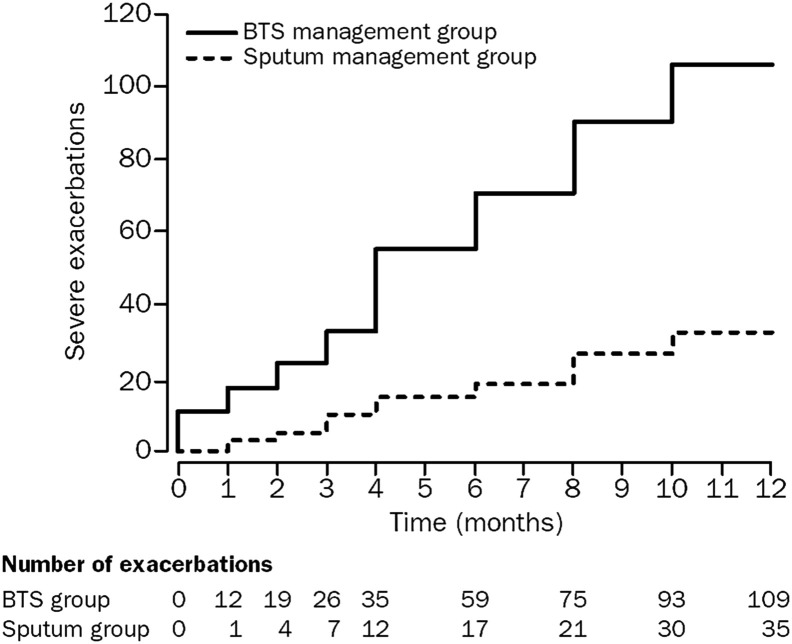
The mechanisms by which ICS prevent virus-induced exacerbations, beyond anti-inflammatory activity, are poorly understood. ICS can reduce the number of airway eosinophils that presumably reflect enhanced inflammation with a respiratory infection.60, 61 As approximately 50% of asthma exacerbations are associated with an increase in airway eosinophils, these cells are a reasonable target.62 This concept is substantiated by studies showing that a reduction in airway eosinophils significantly diminishes exacerbations (Figure 4 ),63, 64 but this approach does not eliminate all exacerbations, particularly for patients with more severe asthma.65, 66 Furthermore, as airway neutrophils increase early in asthma exacerbations,67 ICS treatment has no effect on these cells and alternative approaches will be needed.68
Figure 4.
Cumulative asthma exacerbations in the British Thoracic Society (BTS) asthma guidelines management group versus the sputum management group. There were significantly less asthma exacerbations in the sputum management group (35 vs 109; P = .01), where inhaled corticosteroid dose was titrated to normalize induced sputum eosinophil counts and reduce symptoms.
Reproduced with permission from Green et al.63
Inhaled corticosteroids and long-acting β-agonists
In patients with poorly controlled asthma and a history of prior asthma exacerbations, the combination of budesonide and formoterol significantly reduces asthma exacerbations compared with ICS alone.50 ICS/LABA have consistently been shown to prevent exacerbations.69, 70, 71 The benefit of ICS/LABA to prevent exacerbations versus ICS alone is primarily seen in patients requiring higher doses of ICS, thus suggesting that combination therapy to prevent exacerbations should be reserved for patients with more severe disease.
Asthma control can vary even in the face of ongoing ICS/LABA treatment. Consequently, the use of ICS/LABA combinations both for maintenance and symptom relief has been investigated and shown to reduce exacerbations.72, 73, 74 These benefits are also seen in children with a prior history of severe asthma exacerbations and poorly controlled moderate-to-severe persistent asthma despite the use of moderate doses of ICS.75 The use of ICS/LABA as maintenance and reliever treatment should be restricted to formoterol because of its quick onset of action,76 safety profile,77 and dose-response effect.78
How the addition of LABA to ICS reduces asthma exacerbations remains unclear as LABA do not affect inflammation. ICS/LABA, however, attenuate allergen-induced airway eosinophilia and lung function changes to a greater extent than ICS alone.79 Edwards et al80 demonstrated that combination treatment synergistically suppressed induction of rhinovirus-generated chemokines in bronchial epithelial cells. Thus, the synergistic benefits of both ICS and LABA on airway eosinophilic inflammation might explain a greater reduction in exacerbations. Alternatively, an early use of ICS/LABA for relief of symptoms might simply deliver additional ICS to the airway early in the course of an emerging exacerbation.
Leukotriene antagonists
Antileukotrienes reduce asthma exacerbations in children72, 81 and adults.82, 83 Montelukast reduced asthma exacerbations to RV infections that occurred on return to school in September.81, 84 In a systematic review and meta-analysis, compared with placebo, leukotriene modifiers/receptor antagonists lowered exacerbation rates by 41% but were inferior to ICS.53
Adding montelukast to inhaled budesonide was as effective as doubling the dose of inhaled budesonide, with no difference in exacerbation rates and asthma free days.85
Tiotropium
The anticholinergic tiotropium reduces the frequency of asthma exacerbations and is FDA-approved for long-term, maintenance treatment for patients 6 years of age and older with persistent asthma, that is uncontrolled with ICS plus one or more controllers. In 2 replicate trials with a total of 912 adult patients with severe asthma and using ICS/LABA, adding tiotropium, 5 mcg, increased the time to first exacerbation by 56 days over placebo, and reduced exacerbations by 21% (Figure 5 ).86 In a systematic review of 13 randomized placebo-controlled trials,87 tiotropium decreased rates of exacerbations and improved asthma control in patients with moderate symptomatic asthma already receiving medium-to-high doses of ICS or ICS/LABA. Studies in children aged 6 to 11 years demonstrate improvements in forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) but not reductions in exacerbations, likely due to the short duration of the study.88 However, given that decreases in the FEV1/forced vital capacity ratio are associated with an increased risk of exacerbations,89 improvements in FEV1 with tiotropium may be associated with reduced exacerbations in children.
Figure 5.
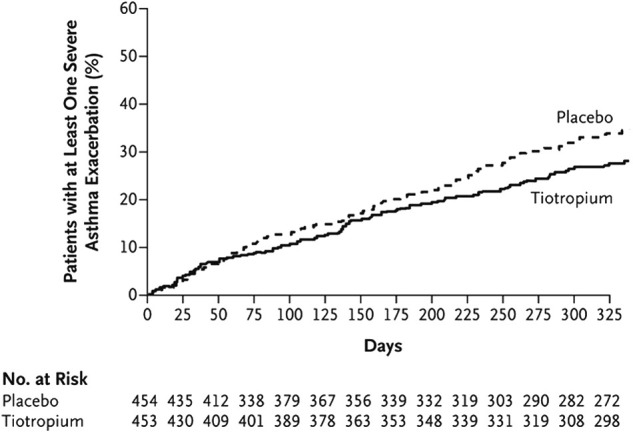
Cumulative number of severe exacerbations in patients with severe asthma on inhaled corticosteroid/long-acting β-agonist treated with the addition of tiotropium versus placebo. There was a 21% risk reduction in asthma exacerbations (hazard ratio, 0.79; P = .03 in pooled analysis) for the tiotropium group.
Reproduced with permission from Kerstjens et al.86
Environmental control
The benefit from environmental control measures to prevent exacerbations is limited. Perhaps, this is because environmental interventions usually focus on a single allergen, such as dust mites,90 or environmental tobacco smoke,91 and with this limited approach, no effect was seen on asthma morbidity. However, an Inner-City Asthma Study evaluated the effectiveness of a multifaceted, home-based, environmental intervention that used remediation of exposure to dust mites, passive smoking, cockroaches, pets, rodents, and mold92 and was tailored to each child's skin-test sensitization profile and environmental exposures. The intervention group reported significantly fewer symptoms of asthma during both the intervention year and, interestingly, the follow-up year as well (Figure 6 ), with significantly fewer unscheduled asthma-related visits to the ED or clinic for the intervention group (P = .04). The correlation between the reduction in levels of cockroach allergen on the bedroom floor and asthma-related morbidity was particularly strong during the active intervention. Although it is difficult to generalize these results to all children with asthma, a reduction in continuous exposure to environmental allergens and irritants, like those present in the homes of inner-city patients with asthma, may indicate the need for a more comprehensive intervention.
Figure 6.
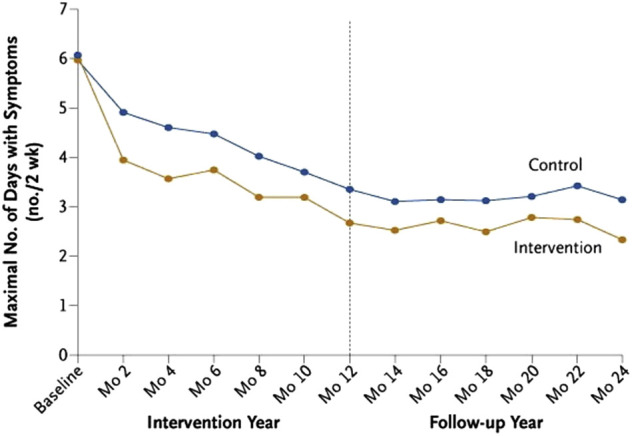
Mean maximal number of days with symptoms for every 2-week period before a follow-up assessment during the intervention year and follow-up year. The Inner-City Asthma Study evaluated the effectiveness of a multifaceted, home-based, environmental intervention for inner-city children with asthma. The difference between the 2 groups was significant in both the intervention year (P < .001) and the follow-up year (P < .001).
Reproduced with permission from Morgan et al.92
Targeted Biologic Therapy
Anti-IgE (omalizumab)
Omalizumab is approved for use in patients 6 years of age and older with allergies and uncontrolled, persistent asthma despite moderate-to-high dose ICS. Omalizumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody directed against IgE and reduces the risk for asthma exacerbations in allergic asthmatic patients.93, 94, 95, 96, 97 Omalizumab reduces asthma exacerbations when given with ICS97 and shortens the duration of exacerbations98 in adults and children.99, 100, 101
Some patients with asthma and allergy have a diminished interferon response to an in vitro challenge with respiratory viruses, and this reduction is related to IgE. In a study of inner-city children,99 omalizumab reduced seasonal exacerbations in the fall and spring, without altering the rates of infections with respiratory viruses, suggesting that omalizumab may not prevent viral infections, but rather modify the consequences of the infection. Teach et al20 showed that omalizumab improved antiviral defenses by increasing release of IFN-α from peripheral blood mononuclear cells to RV stimulation; in those subjects with a greater restoration of IFN responses, fewer exacerbations occurred (Figure 7 ). Thus, in addition to anti-inflammatory effects of omalizumab, a restoration of antiviral activity may prevent exacerbations.
Figure 7.
Effect of omalizumab on IgE-mediated functions in virus-provoked asthma exacerbations. FcεRI, High-affinity IgE receptor; pDC, plasmacytoid dendritic cell; RV, rhinovirus.
Selecting patients most likely to benefit from omalizumab has been difficult. In a post hoc analysis, patients with elevated levels of fractional exhaled nitric oxide, blood eosinophils, and serum periostin, likely reflecting greater T2 inflammation, had a greater likelihood of benefitting from omalizumab.102, 103
Anti-IL-5
Two anti-IL-5 monoclonal antibodies, mepolizumab and reslizumab, are approved as maintenance therapy for patients with uncontrolled, persistent eosinophilic asthma with an exacerbation phenotype despite high-dose ICS. IL-5 contributes to airway eosinophilic inflammation. Approximately 40% to 50% of patients with difficult-to-control asthma have persistent airway eosinophilia despite treatment with high-dose ICS. Although elevated sputum eosinophil counts predict the risk for asthma exacerbations, the use of sputum for routine measurements is impractical in clinical practice. Price et al104 found a relationship between the intensity of peripheral blood eosinophilia and asthma-related outcomes; patients with asthma with blood eosinophil counts greater than 400 cells/μL experience more frequent severe exacerbations, and serves as a convenient biomarker for anti-IL-5 therapy.
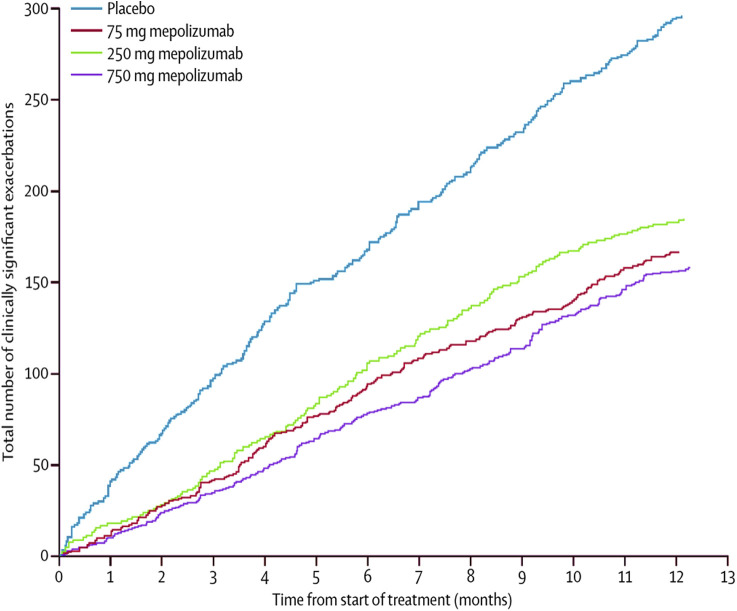
Mepolizumab, given subcutaneously, reduces exacerbations by approximately 50% in patients with severe asthma who have blood eosinophil counts 150 cells/μL or greater (Figure 8 ).65, 66, 105, 106 It has been FDA-approved for add-on maintenance treatment of severe asthma in patients 12 years of age or older. Although clinical trial data suggest that efficacy requires an absolute eosinophil count of at least 150 cells/μL,107 the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence recommends a threshold of 300 cells/μL. Reslizumab is also FDA-approved for add-on maintenance therapy of severe asthma in patients 18 years or older who have an eosinophil count of 400 cells/μL or higher. In clinical trials, intravenous reslizumab reduced asthma exacerbations by approximately 50%.108, 109
Figure 8.
Reduction in the cumulative number of asthma exacerbations with mepolizumab versus placebo.
Reproduced with permission from Pavord et al.105
RV infections lead to the generation of IL-5 and an increase in airway eosinophils, which correlate with exacerbation probability.110 These relationships provide a probable explanation for why anti-IL-5 mAb treatment reduces asthma exacerbations.
Other biologics to prevent asthma exacerbations are under study.
Treating Exacerbations
Despite optimal maintenance therapy and asthma control, exacerbations occur. Therefore, early recognition and intervention are important to successfully stabilize asthma. A limited number of treatments are currently available to alleviate asthma exacerbations, and the evidence supporting their use has limits.
Short-acting β2-agonists
Inhaled or nebulized short-acting β2-agonists (SABAs), such as albuterol or levalbuterol, resolve acute symptoms of asthma and can initially be used every 15 to 20 minutes for the first hour during acute asthma.107 Levalbuterol, the R-enantiomer of albuterol, and albuterol are equivalent.111, 112, 113 Data are conflicting whether continuous nebulization with a SABA is superior to intermittent nebulization.114, 115 In very severe asthma exacerbations, continuous nebulization should be considered based on evidence of reduced admissions and improved pulmonary function.114, 116, 117, 118 SABAs provide symptomatic relief but have no effect on airway inflammation or sustained benefit.
Ipratropium bromide
Adding ipratropium bromide to an inhaled SABA in severe exacerbations decreases rates of hospitalizations and shortens ED stays for patients with severe or moderate-to-severe asthma exacerbations.119, 120, 121 The benefit of ipratropium bromide to SABA therapy is seen primarily in more severe asthma exacerbations.120, 122
Corticosteroids
An underlying component of exacerbations is an increase in airway inflammation.103 Numerous studies evaluated ICS and oral corticosteroids (OCS) in asthma exacerbations, but the evidence for their efficacy remains limited. Moreover, because ICS often do not prevent exacerbations, it is unlikely that an increase in inflammation with an exacerbation will be fully responsive to corticosteroids. Nonetheless, their use is a reasonable and expected first step.
Inhaled corticosteroids
The administration of high-dose ICS for asthma exacerbations should be reserved for patients with mild or intermittent asthma and those unable to tolerate OCS because of side effects such as diabetes or psychiatric effects. A systematic review analyzed 8 studies comparing the efficacy of ICS with placebo in acute asthma exacerbations and found that ICS appeared superior to placebo, especially when given at high doses, that is, >1 mg of budesonide or fluticasone.123 However, patients in these studies were heterogeneous in severity, ICS dose and administration frequency, and outcomes measured. The role of ICS for asthma exacerbations remains to be established.
Comparisons between ICS and systemic corticosteroids have also been conflicting. OCS were superior to ICS in reducing hospital admission rates in some studies124, 125, 126 and others showed superiority of ICS.127 A systematic review of 12 trials concluded that there was no benefit to the addition of ICS to systemic corticosteroids in reducing the relapse rate of acute asthma.128 At present, insufficient evidence exists to support using ICS rather than OCS for exacerbations.
Systemic corticosteroids
Early administration of systemic corticosteroids for the treatment of acute exacerbations is standard guideline management with beneficial effects of systemic corticosteroids usually delayed for approximately 4 hours.129 Systemic glucocorticoids accelerate the rate of improvement when persistent airflow obstruction exists despite bronchodilator treatment.130 However, an evidence-based evaluation reported neither an improvement in airflow obstruction nor reduction in hospitalization rates with systemic corticosteroids.112 In contrast, a systematic review by Rowe et al113 concluded that the use of systemic corticosteroids in adults and children reduces the rate of hospital admission in ED treatment settings, especially in patients with severe asthma and those not currently receiving corticosteroids.
The optimal dose for systemic corticosteroids in asthma exacerbations also remains to be convincingly established. Doses above 2 mg/kg, or 60-80 mg/day, do not add benefit to improving pulmonary function, rates of hospital admission, or length of hospital stay.131, 132 Furthermore, no differences are found between oral and intravenous administration of comparable doses.133, 134
Prescribing a short course of oral corticosteroids after ED treatment of acute asthma exacerbations reduces the rate of relapse.113 Although the duration of therapy is not fully established, courses longer than 5 days did not provide additional benefit.135, 136 There is also no benefit from using a dose taper over a fixed-dose regimen and stopping.122 Difficulties, however, arise in assessing approaches to treating exacerbations in patients already taking systemic corticosteroids. Optimal exacerbation treatment strategies for this patient population remain undefined and reflect the need for more targeted therapy.
A single dose of benralizumab, an anti-IL-5 receptor monoclonal antibody, reduces the rate and severity of subsequent exacerbations when given at the time of an initial exacerbation.137 Thus, biologic therapy may also be beneficial in the acute treatment of asthma exacerbations to prevent subsequent events.
Conclusions
Asthma exacerbations can be prevented with ICS, ICS/LABA, and biologics in some patients. Exacerbations are more frequent in patients with severe disease and preventative strategies with biologics, such as anti-IgE and anti-IL-5, are seen. When exacerbations occur, systemic corticosteroids remain the primary intervention when bronchodilator therapy is not effective, but the evidence for their benefit has limitations. Prevention of exacerbations remains a major unmet need in asthma management. An improved understanding of the pathogenesis of asthma exacerbations will likely lead to new strategies to prevent and treat asthma exacerbations.
Footnotes
No funding was received for this work.
Conflicts of interest: J. R. Castillo declares no relevant conflicts of interest. W. W. Busse has received consultancy fees from Novartis, GlaxoSmithKline, Genentech, Roche, Boston Scientific, ICON, Boehringer Ingelheim, Regeneron, Sanofi, 3M, AstraZeneca, Circassia, and PrEPBiopharm; has received research support from the National Institutes of Health - National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases and National Institutes of Health - National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; receives royalties from Elsevier; and has received payment for developing educational presentations from Medscape. S. P. Peters has received payment for preparing the manuscript from Medical Learning Institute, Inc.; has received consultancy fees from AstraZeneca, Teva, Novartis, National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, Elsevier, PRIME, Gilead, Sanofi-Regeneron, Quintiles, Haymarket Media, American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology, American College of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology, InVivo Brands, and Johns Hopkins; receives royalties from UpToDate.
References
- 1.Bai T.R., Vonk J.M., Postma D.S., Boezen H.M. Severe exacerbations predict excess lung function decline in asthma. Eur Respir J. 2007;30:452–456. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00165106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.O'Byrne P.M., Pedersen S., Lamm C.J., Tan W.C., Busse W.W. Severe exacerbations and decline in lung function in asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2009;179:19–24. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200807-1126OC. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Ivanova J.I., Bergman R., Birnbaum H.G., Colice G.L., Silverman R.A., McLaurin K. Effect of asthma exacerbations on health care costs among asthmatic patients with moderate and severe persistent asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012;129:1229–1235. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2012.01.039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Barnett S.B., Nurmagambetov T.A. Costs of asthma in the United States: 2002-2007. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011;127:145–152. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2010.10.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Miller M.K., Lee J.H., Miller D.P., Wenzel S.E., Group T.S. Recent asthma exacerbations: a key predictor of future exacerbations. Respir Med. 2007;101:481–489. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2006.07.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Johnston S.L., Pattemore P.K., Sanderson G., Smith S., Lampe F., Josephs L. Community study of role of viral infections in exacerbations of asthma in 9-11 year old children. BMJ. 1995;310:1225–1229. doi: 10.1136/bmj.310.6989.1225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Nicholson K.G., Kent J., Ireland D.C. Respiratory viruses and exacerbations of asthma in adults. BMJ. 1993;307:982–986. doi: 10.1136/bmj.307.6910.982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Johnston S.L., Pattemore P.K., Sanderson G., Smith S., Campbell M.J., Josephs L.K. The relationship between upper respiratory infections and hospital admissions for asthma: a time-trend analysis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1996;154:654–660. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.154.3.8810601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Johnston N.W., Johnston S.L., Norman G.R., Dai J., Sears M.R. The September epidemic of asthma hospitalization: school children as disease vectors. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006;117:557–562. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2005.11.034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.O'Riordan S., Barton M., Yau Y., Read S.E., Allen U., Tran D. Risk factors and outcomes among children admitted to hospital with pandemic H1N1 influenza. CMAJ. 2010;182:39–44. doi: 10.1503/cmaj.091724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Plessa E., Diakakis P., Gardelis J., Thirios A., Koletsi P., Falagas M.E. Clinical features, risk factors, and complications among pediatric patients with pandemic influenza A (H1N1) Clin Pediatr (Phila) 2010;49:777–781. doi: 10.1177/0009922810368558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Libster R., Bugna J., Coviello S., Hijano D.R., Dunaiewsky M., Reynoso N. Pediatric hospitalizations associated with 2009 pandemic influenza A (H1N1) in Argentina. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:45–55. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0907673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Falsey A.R., Hennessey P.A., Formica M.A., Cox C., Walsh E.E. Respiratory syncytial virus infection in elderly and high-risk adults. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:1749–1759. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa043951. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Yoo J.K., Kim T.S., Hufford M.M., Braciale T.J. Viral infection of the lung: host response and sequelae. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013;132:1263–1276. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2013.06.006. quiz 77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Bateman E.D., Buhl R., O'Byrne P.M., Humbert M., Reddel H.K., Sears M.R. Development and validation of a novel risk score for asthma exacerbations: The risk score for exacerbations. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015;135:1457–1464.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2014.08.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Soto-Quiros M., Avila L., Platts-Mills T.A., Hunt J.F., Erdman D.D., Carper H. High titers of IgE antibody to dust mite allergen and risk for wheezing among asthmatic children infected with rhinovirus. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012;129:1499–1505.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2012.03.040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.MacMicking J.D. Interferon-inducible effector mechanisms in cell-autonomous immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2012;12:367–382. doi: 10.1038/nri3210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Papadopoulos N.G., Stanciu L.A., Papi A., Holgate S.T., Johnston S.L. Rhinovirus-induced alterations on peripheral blood mononuclear cell phenotype and costimulatory molecule expression in normal and atopic asthmatic subjects. Clin Exp Allergy. 2002;32:537–542. doi: 10.1046/j.0954-7894.2002.01313.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Gehlhar K., Bilitewski C., Reinitz-Rademacher K., Rohde G., Bufe A. Impaired virus-induced interferon-alpha2 release in adult asthmatic patients. Clin Exp Allergy. 2006;36:331–337. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2006.02450.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Teach S.J., Gill M.A., Togias A., Sorkness C.A., Arbes S.J., Jr., Calatroni A. Preseasonal treatment with either omalizumab or an inhaled corticosteroid boost to prevent fall asthma exacerbations. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015;136:1476–1485. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2015.09.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Gill M.A., Bajwa G., George T.A., Dong C.C., Dougherty I.I., Jiang N. Counterregulation between the FcepsilonRI pathway and antiviral responses in human plasmacytoid dendritic cells. J Immunol. 2010;184:5999–6006. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0901194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Wark P.A., Johnston S.L., Bucchieri F., Powell R., Puddicombe S., Laza-Stanca V. Asthmatic bronchial epithelial cells have a deficient innate immune response to infection with rhinovirus. J Exp Med. 2005;201:937–947. doi: 10.1084/jem.20041901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Baraldo S., Contoli M., Bazzan E., Turato G., Padovani A., Marku B. Deficient antiviral immune responses in childhood: distinct roles of atopy and asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012;130:1307–1314. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2012.08.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Djukanovic R., Harrison T., Johnston S.L., Gabbay F., Wark P., Thomson N.C. The effect of inhaled IFN-beta on worsening of asthma symptoms caused by viral infections. A randomized trial. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2014;190:145–154. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201312-2235OC. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Von H.L. Role of persistent infection in the control and severity of asthma: focus on Chlamydia pneumoniae. Eur Respir J. 2002;19:546–556. doi: 10.1183/09031936.02.00254402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Martin R.J., Kraft M., Chu H.W., Berns E.A., Cassell G.H. A link between chronic asthma and chronic infection. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001;107:595–601. doi: 10.1067/mai.2001.113563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Oliver B.G., Lim S., Wark P., Laza-Stanca V., King N., Black J.L. Rhinovirus exposure impairs immune responses to bacterial products in human alveolar macrophages. Thorax. 2008;63:519–525. doi: 10.1136/thx.2007.081752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Zureik M., Neukirch C., Leynaert B., Liard R., Bousquet J., Neukirch F. Sensitisation to airborne moulds and severity of asthma: cross sectional study from European Community respiratory health survey. BMJ. 2002;325:411–414. doi: 10.1136/bmj.325.7361.411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Sporik R., Holgate S.T., Platts-Mills T.A., Cogswell J.J. Exposure to house-dust mite allergen (Der p I) and the development of asthma in childhood. A prospective study. N Engl J Med. 1990;323:502–507. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199008233230802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Permaul P., Hoffman E., Fu C., Sheehan W., Baxi S., Gaffin J. Allergens in urban schools and homes of children with asthma. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2012;23:543–549. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3038.2012.01327.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Olivieri M., Zock J.P., Accordini S., Heinrich J., Jarvis D., Kunzli N. Risk factors for new-onset cat sensitization among adults: a population-based international cohort study. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012;129:420–425. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2011.10.044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Samoli E., Nastos P.T., Paliatsos A.G., Katsouyanni K., Priftis K.N. Acute effects of air pollution on pediatric asthma exacerbation: evidence of association and effect modification. Environ Res. 2011;111:418–424. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2011.01.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Trasande L., Thurston G.D. The role of air pollution in asthma and other pediatric morbidities. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005;115:689–699. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2005.01.056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Message S.D., Laza-Stanca V., Mallia P., Parker H.L., Zhu J., Kebadze T. Rhinovirus-induced lower respiratory illness is increased in asthma and related to virus load and Th1/2 cytokine and IL-10 production. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105:13562–13567. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0804181105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Gergen P.J., Turkeltaub P.C. The association of individual allergen reactivity with respiratory disease in a national sample: data from the second National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1976-80 (NHANES II) J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1992;90:579–588. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(92)90130-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Downs S.H., Mitakakis T.Z., Marks G.B., Car N.G., Belousova E.G., Leuppi J.D. Clinical importance of Alternaria exposure in children. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001;164:455–459. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.164.3.2008042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Rosas I., McCartney H.A., Payne R.W., Calderon C., Lacey J., Chapela R. Analysis of the relationships between environmental factors (aeroallergens, air pollution, and weather) and asthma emergency admissions to a hospital in Mexico City. Allergy. 1998;53:394–401. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.1998.tb03911.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.O'Hollaren M.T., Yunginger J.W., Offord K.P., Somers M.J., O'Connell E.J., Ballard D.J. Exposure to an aeroallergen as a possible precipitating factor in respiratory arrest in young patients with asthma. N Engl J Med. 1991;324:359–363. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199102073240602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Copenhaver C.C., Gern J.E., Li Z., Shult P.A., Rosenthal L.A., Mikus L.D. Cytokine response patterns, exposure to viruses, and respiratory infections in the first year of life. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2004;170:175–180. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200312-1647OC. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Eisner M.D., Klein J., Hammond S.K., Koren G., Lactao G., Iribarren C. Directly measured second hand smoke exposure and asthma health outcomes. Thorax. 2005;60:814–821. doi: 10.1136/thx.2004.037283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Thomson N.C., Chaudhuri R., Livingston E. Asthma and cigarette smoking. Eur Respir J. 2004;24:822–833. doi: 10.1183/09031936.04.00039004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Hansel N.N., Breysse P.N., McCormack M.C., Matsui E.C., Curtin-Brosnan J., Williams D.L. A longitudinal study of indoor nitrogen dioxide levels and respiratory symptoms in inner-city children with asthma. Environ Health Perspect. 2008;116:1428–1432. doi: 10.1289/ehp.11349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Castro M., Zimmermann N.A., Crocker S., Bradley J., Leven C., Schechtman K.B. Asthma intervention program prevents readmissions in high healthcare users. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2003;168:1095–1099. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200208-877OC. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Janson S.L., McGrath K.W., Covington J.K., Cheng S.C., Boushey H.A. Individualized asthma self-management improves medication adherence and markers of asthma control. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009;123:840–846. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2009.01.053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Clark J.M., Abraham W.M., Fishman C.E., Forteza R., Ahmed A., Cortes A. Tryptase inhibitors block allergen-induced airway and inflammatory responses in allergic sheep. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1995;152:2076–2083. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.152.6.8520778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Cockcroft D.W., Killian D.N., Mellon J.J., Hargreave F.E. Bronchial reactivity to inhaled histamine: a method and clinical survey. Clin Allergy. 1977;7:235–243. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1977.tb01448.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Juniper E.F., Kline P.A., Vanzieleghem M.A., Ramsdale E.H., O'Byrne P.M., Hargreave F.E. Effect of long-term treatment with an inhaled corticosteroid (budesonide) on airway hyperresponsiveness and clinical asthma in nonsteroid-dependent asthmatics. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990;142:832–836. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/142.4.832. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Juniper E.F., Kline P.A., Vanzieleghem M.A., Ramsdale E.H., O'Byrne P.M., Hargreave F.E. Long-term effects of budesonide on airway responsiveness and clinical asthma severity in inhaled steroid-dependent asthmatics. Eur Respir J. 1990;3:1122–1127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Dahl R., Lundback B., Malo J.L., Mazza J.A., Nieminen M.M., Saarelainen P. A dose-ranging study of fluticasone propionate in adult patients with moderate asthma. International Study Group. Chest. 1993;104:1352–1358. doi: 10.1378/chest.104.5.1352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Pauwels R.A., Lofdahl C.G., Postma D.S., Tattersfield A.E., O'Byrne P., Barnes P.J. Effect of inhaled formoterol and budesonide on exacerbations of asthma. Formoterol and Corticosteroids Establishing Therapy (FACET) International Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1997;337:1405–1411. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199711133372001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.O'Byrne P.M., Barnes P.J., Rodriguez-Roisin R., Runnerstrom E., Sandstrom T., Svensson K. Low dose inhaled budesonide and formoterol in mild persistent asthma: the OPTIMA randomized trial. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001;164:1392–1397. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.164.8.2104102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Busse W.W., Chervinsky P., Condemi J., Lumry W.R., Petty T.L., Rennard S. Budesonide delivered by Turbuhaler is effective in a dose-dependent fashion when used in the treatment of adult patients with chronic asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1998;101:457–463. doi: 10.1016/S0091-6749(98)70353-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Sin D.D., Man J., Sharpe H., Gan W.Q., Man S.F. Pharmacological management to reduce exacerbations in adults with asthma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA. 2004;292:367–376. doi: 10.1001/jama.292.3.367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Bisgaard H. Use of inhaled corticosteroids in pediatric asthma. Pediatr Pulmonol Suppl. 1997;15:27–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Covar R.A., Szefler S.J., Zeiger R.S., Sorkness C.A., Moss M., Mauger D.T. Factors associated with asthma exacerbations during a long-term clinical trial of controller medications in children. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008;122:741–747. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2008.08.021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Oborne J., Mortimer K., Hubbard R.B., Tattersfield A.E., Harrison T.W. Quadrupling the dose of inhaled corticosteroid to prevent asthma exacerbations: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group clinical trial. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2009;180:598–602. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200904-0616OC. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.FitzGerald J.M., Becker A., Sears M.R., Mink S., Chung K., Lee J. Doubling the dose of budesonide versus maintenance treatment in asthma exacerbations. Thorax. 2004;59:550–556. doi: 10.1136/thx.2003.014936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Harrison T.W., Oborne J., Newton S., Tattersfield A.E. Doubling the dose of inhaled corticosteroid to prevent asthma exacerbations: randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2004;363:271–275. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(03)15384-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Ducharme F.M., Lemire C., Noya F.J., Davis G.M., Alos N., Leblond H. Preemptive use of high-dose fluticasone for virus-induced wheezing in young children. N Engl J Med. 2009;360:339–353. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0808907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Gibson P.G., Saltos N., Borgas T. Airway mast cells and eosinophils correlate with clinical severity and airway hyperresponsiveness in corticosteroid-treated asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2000;105:752–759. doi: 10.1067/mai.2000.105319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Brightling C.E., Green R.H., Pavord I.D. Biomarkers predicting response to corticosteroid therapy in asthma. Treat Respir Med. 2005;4:309–316. doi: 10.2165/00151829-200504050-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Turner M.O., Hussack P., Sears M.R., Dolovich J., Hargreave F.E. Exacerbations of asthma without sputum eosinophilia. Thorax. 1995;50:1057–1061. doi: 10.1136/thx.50.10.1057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Green R.H., Brightling C.E., McKenna S., Hargadon B., Parker D., Bradding P. Asthma exacerbations and sputum eosinophil counts: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2002;360:1715–1721. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(02)11679-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Jayaram L., Pizzichini M.M., Cook R.J., Boulet L.P., Lemiere C., Pizzichini E. Determining asthma treatment by monitoring sputum cell counts: effect on exacerbations. Eur Respir J. 2006;27:483–494. doi: 10.1183/09031936.06.00137704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Haldar P., Brightling C.E., Hargadon B., Gupta S., Monteiro W., Sousa A. Mepolizumab and exacerbations of refractory eosinophilic asthma. N Engl J Med. 2009;360:973–984. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0808991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Nair P., Pizzichini M.M., Kjarsgaard M., Inman M.D., Efthimiadis A., Pizzichini E. Mepolizumab for prednisone-dependent asthma with sputum eosinophilia. N Engl J Med. 2009;360:985–993. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0805435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Fahy J.V., Kim K.W., Liu J., Boushey H.A. Prominent neutrophilic inflammation in sputum from subjects with asthma exacerbation. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1995;95:843–852. doi: 10.1016/s0091-6749(95)70128-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Cox G. Glucocorticoid treatment inhibits apoptosis in human neutrophils. Separation of survival and activation outcomes. J Immunol. 1995;154:4719–4725. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Bateman E.D., Boushey H.A., Bousquet J., Busse W.W., Clark T.J., Pauwels R.A. Can guideline-defined asthma control be achieved? The Gaining Optimal Asthma Control study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2004;170:836–844. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200401-033OC. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Stanford R.H., Fuhlbrigge A., Riedel A., Rey G.G., Stempel D.A. An observational study of fixed dose combination fluticasone propionate/salmeterol or fluticasone propionate alone on asthma-related outcomes. Curr Med Res Opin. 2008;24:3141–3148. doi: 10.1185/03007990802462990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Papi A., Paggiaro P.L., Nicolini G., Vignola A.M., Fabbri L.M. Beclomethasone/formoterol versus budesonide/formoterol combination therapy in asthma. Eur Respir J. 2007;29:682–689. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00095906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.O'Byrne P.M., Bisgaard H., Godard P.P., Pistolesi M., Palmqvist M., Zhu Y. Budesonide/formoterol combination therapy as both maintenance and reliever medication in asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2005;171:129–136. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200407-884OC. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Rabe K.F., Atienza T., Magyar P., Larsson P., Jorup C., Lalloo U.G. Effect of budesonide in combination with formoterol for reliever therapy in asthma exacerbations: a randomised controlled, double-blind study. Lancet. 2006;368:744–753. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(06)69284-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Bousquet J., Boulet L.P., Peters M.J., Magnussen H., Quiralte J., Martinez-Aguilar N.E. Budesonide/formoterol for maintenance and relief in uncontrolled asthma vs. high-dose salmeterol/fluticasone. Respir Med. 2007;101:2437–2446. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2007.07.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Bisgaard H., Le Roux P., Bjamer D., Dymek A., Vermeulen J.H., Hultquist C. Budesonide/formoterol maintenance plus reliever therapy: a new strategy in pediatric asthma. Chest. 2006;130:1733–1743. doi: 10.1378/chest.130.6.1733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Palmqvist M., Persson G., Lazer L., Rosenborg J., Larsson P., Lotvall J. Inhaled dry-powder formoterol and salmeterol in asthmatic patients: onset of action, duration of effect and potency. Eur Respir J. 1997;10:2484–2489. doi: 10.1183/09031936.97.10112489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Balanag V.M., Yunus F., Yang P.C., Jorup C. Efficacy and safety of budesonide/formoterol compared with salbutamol in the treatment of acute asthma. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2006;19:139–147. doi: 10.1016/j.pupt.2005.04.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Palmqvist M., Ibsen T., Mellen A., Lotvall J. Comparison of the relative efficacy of formoterol and salmeterol in asthmatic patients. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1999;160:244–249. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.160.1.9901063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Kelly M.M., O'Connor T.M., Leigh R., Otis J., Gwozd C., Gauvreau G.M. Effects of budesonide and formoterol on allergen-induced airway responses, inflammation, and airway remodeling in asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010;125:349–356.e13. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2009.09.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Edwards M.R., Johnson M.W., Johnston S.L. Combination therapy: synergistic suppression of virus-induced chemokines in airway epithelial cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2006;34:616–624. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2005-0385OC. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Johnston N.W., Mandhane P.J., Dai J., Duncan J.M., Greene J.M., Lambert K. Attenuation of the September epidemic of asthma exacerbations in children: a randomized, controlled trial of montelukast added to usual therapy. Pediatrics. 2007;120:e702–e712. doi: 10.1542/peds.2006-3317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Reiss T.F., Chervinsky P., Dockhorn R.J., Shingo S., Seidenberg B., Edwards T.B. Montelukast, a once-daily leukotriene receptor antagonist, in the treatment of chronic asthma: a multicenter, randomized, double-blind trial. Montelukast Clinical Research Study Group. Arch Intern Med. 1998;158:1213–1220. doi: 10.1001/archinte.158.11.1213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Bjermer L., Bisgaard H., Bousquet J., Fabbri L.M., Greening A.P., Haahtela T. Montelukast and fluticasone compared with salmeterol and fluticasone in protecting against asthma exacerbation in adults: one year, double blind, randomised, comparative trial. BMJ. 2003;327:891. doi: 10.1136/bmj.327.7420.891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Weiss K.B., Gern J.E., Johnston N.W., Sears M.R., Jones C.A., Jia G. The Back to School asthma study: the effect of montelukast on asthma burden when initiated prophylactically at the start of the school year. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2010;105:174–181. doi: 10.1016/j.anai.2010.04.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Price D.B., Hernandez D., Magyar P., Fiterman J., Beeh K.M., James I.G. Randomised controlled trial of montelukast plus inhaled budesonide versus double dose inhaled budesonide in adult patients with asthma. Thorax. 2003;58:211–216. doi: 10.1136/thorax.58.3.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Kerstjens H.A., Engel M., Dahl R., Paggiaro P., Beck E., Vandewalker M. Tiotropium in asthma poorly controlled with standard combination therapy. N Engl J Med. 2012;367:1198–1207. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1208606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Rodrigo G.J., Castro-Rodriguez J.A. What is the role of tiotropium in asthma?: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Chest. 2015;147:388–396. doi: 10.1378/chest.14-1698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Szefler S.J., Murphy K., Harper T., III, Boner A., Laki I., Engel M. A phase III randomized controlled trial of tiotropium add-on therapy in children with severe symptomatic asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017 doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2017.01.014. [e-pub ahead of print] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Quezada W., Kwak E.S., Reibman J., Rogers L., Mastronarde J., Teague W.G. Predictors of asthma exacerbation among patients with poorly controlled asthma despite inhaled corticosteroid treatment. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2016;116:112–117. doi: 10.1016/j.anai.2015.11.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Carter M.C., Perzanowski M.S., Raymond A., Platts-Mills T.A. Home intervention in the treatment of asthma among inner-city children. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001;108:732–737. doi: 10.1067/mai.2001.119155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Irvine L., Crombie I.K., Clark R.A., Slane P.W., Feyerabend C., Goodman K.E. Advising parents of asthmatic children on passive smoking: randomised controlled trial. BMJ. 1999;318:1456–1459. doi: 10.1136/bmj.318.7196.1456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Morgan W.J., Crain E.F., Gruchalla R.S., O'Connor G.T., Kattan M., Evans R., III Results of a home-based environmental intervention among urban children with asthma. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:1068–1080. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa032097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Busse W., Corren J., Lanier B.Q., McAlary M., Fowler-Taylor A., Cioppa G.D. Omalizumab, anti-IgE recombinant humanized monoclonal antibody, for the treatment of severe allergic asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001;108:184–190. doi: 10.1067/mai.2001.117880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Busse W.W., Massanari M., Kianifard F., Geba G.P. Effect of omalizumab on the need for rescue systemic corticosteroid treatment in patients with moderate-to-severe persistent IgE-mediated allergic asthma: a pooled analysis. Curr Med Res Opin. 2007;23:2379–2386. doi: 10.1185/030079907X226258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Ohta K., Miyamoto T., Amagasaki T., Yamamoto M. Efficacy and safety of omalizumab in an Asian population with moderate-to-severe persistent asthma. Respirology. 2009;14:1156–1165. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1843.2009.01633.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Hanania N.A., Alpan O., Hamilos D.L., Condemi J.J., Reyes-Rivera I., Zhu J. Omalizumab in severe allergic asthma inadequately controlled with standard therapy: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med. 2011;154:573–582. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-154-9-201105030-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Walker S., Monteil M., Phelan K., Lasserson T.J., Walters E.H. Anti-IgE for chronic asthma in adults and children. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006;19:Cd003559. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003559.pub3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Rees P.J. Review: omalizumab reduces exacerbation and steroid use in chronic asthma. Arch Dis Child Educ Pract Ed. 2007;92:ep127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Busse W.W., Morgan W.J., Gergen P.J., Mitchell H.E., Gern J.E., Liu A.H. Randomized trial of omalizumab (anti-IgE) for asthma in inner-city children. N Engl J Med. 2011;364:1005–1015. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1009705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Lanier B., Bridges T., Kulus M., Taylor A.F., Berhane I., Vidaurre C.F. Omalizumab for the treatment of exacerbations in children with inadequately controlled allergic (IgE-mediated) asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009;124:1210–1216. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2009.09.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Massanari M., Milgrom H., Pollard S., Maykut R.J., Kianifard F., Fowler-Taylor A. Adding omalizumab to the therapy of adolescents with persistent uncontrolled moderate—severe allergic asthma. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 2009;48:859–865. doi: 10.1177/0009922809339054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Hanania N.A., Wenzel S., Rosen K., Hsieh H.J., Mosesova S., Choy D.F. Exploring the effects of omalizumab in allergic asthma: an analysis of biomarkers in the EXTRA study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013;187:804–811. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201208-1414OC. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.CONTROLLED trial of effects of cortisone acetate in status asthmaticus; report to the Medical Research Council by the subcommittee on clinical trials in asthma. Lancet. 1956;271:803–806. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Price D.B., Rigazio A., Campbell J.D., Bleecker E.R., Corrigan C.J., Thomas M. Blood eosinophil count and prospective annual asthma disease burden: a UK cohort study. Lancet Respir Med. 2015;3:849–858. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(15)00367-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Pavord I.D., Korn S., Howarth P., Bleecker E.R., Buhl R., Keene O.N. Mepolizumab for severe eosinophilic asthma (DREAM): a multicentre, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2012;380:651–659. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)60988-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Bel E.H., Wenzel S.E., Thompson P.J., Prazma C.M., Keene O.N., Yancey S.W. Oral glucocorticoid-sparing effect of mepolizumab in eosinophilic asthma. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:1189–1197. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1403291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Ortega H.G., Yancey S.W., Mayer B., Gunsoy N.B., Keene O.N., Bleecker E.R. Severe eosinophilic asthma treated with mepolizumab stratified by baseline eosinophil thresholds: a secondary analysis of the DREAM and MENSA studies. Lancet Respir Med. 2016;4:549–556. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(16)30031-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Castro M., Mathur S., Hargreave F., Boulet L.P., Xie F., Young J. Reslizumab for poorly controlled, eosinophilic asthma: a randomized, placebo-controlled study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2011;184:1125–1132. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201103-0396OC. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Castro M., Zangrilli J., Wechsler M.E., Bateman E.D., Brusselle G.G., Bardin P. Reslizumab for inadequately controlled asthma with elevated blood eosinophil counts: results from two multicentre, parallel, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trials. Lancet Respir Med. 2015;3:355–366. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(15)00042-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Jackson D.J., Makrinioti H., Rana B.M., Shamji B.W., Trujillo-Torralbo M.B., Footitt J. IL-33-dependent type 2 inflammation during rhinovirus-induced asthma exacerbations in vivo. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2014;190:1373–1382. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201406-1039OC. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Kelly H.W. Levalbuterol for asthma: a better treatment? Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2007;7:310–314. doi: 10.1007/s11882-007-0046-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Rodrigo G., Rodrigo C. Corticosteroids in the emergency department therapy of acute adult asthma: an evidence-based evaluation. Chest. 1999;116:285–295. doi: 10.1378/chest.116.2.285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Rowe B.H., Spooner C., Ducharme F.M., Bretzlaff J.A., Bota G.W. Early emergency department treatment of acute asthma with systemic corticosteroids. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001;(1):CD002178. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Camargo C.A., Jr., Spooner C.H., Rowe B.H. Continuous versus intermittent beta-agonists in the treatment of acute asthma. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003;(4):CD001115. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Rodrigo G.J., Rodrigo C. Continuous vs intermittent beta-agonists in the treatment of acute adult asthma: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Chest. 2002;122:160–165. doi: 10.1378/chest.122.1.160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Camargo C.A., Jr., Rachelefsky G., Schatz M. Managing asthma exacerbations in the emergency department: summary of the National Asthma Education and Prevention Program Expert Panel Report 3 guidelines for the management of asthma exacerbations. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2009;6:357–366. doi: 10.1513/pats.P09ST2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Cates C.J., Welsh E.J., Rowe B.H. Holding chambers (spacers) versus nebulisers for beta-agonist treatment of acute asthma. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013;(9):CD000052. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000052.pub3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Hasegawa K., Sullivan A.F., Tovar Hirashima E., Gaeta T.J., Fee C., Turner S.J. A multicenter observational study of US adults with acute asthma: who are the frequent users of the emergency department? J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2014;2:733–740. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2014.06.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Qureshi F., Pestian J., Davis P., Zaritsky A. Effect of nebulized ipratropium on the hospitalization rates of children with asthma. N Engl J Med. 1998;339:1030–1035. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199810083391503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Rodrigo G.J., Castro-Rodriguez J.A. Anticholinergics in the treatment of children and adults with acute asthma: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Thorax. 2005;60:740–746. doi: 10.1136/thx.2005.040444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Zorc J.J., Pusic M.V., Ogborn C.J., Lebet R., Duggan A.K. Ipratropium bromide added to asthma treatment in the pediatric emergency department. Pediatrics. 1999;103:748–752. doi: 10.1542/peds.103.4.748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Krishnan J.A., Davis S.Q., Naureckas E.T., Gibson P., Rowe B.H. An umbrella review: corticosteroid therapy for adults with acute asthma. Am J Med. 2009;122:977–991. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2009.02.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Rodrigo G.J. Rapid effects of inhaled corticosteroids in acute asthma: an evidence-based evaluation. Chest. 2006;130:1301–1311. doi: 10.1378/chest.130.5.1301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Schuh S., Reisman J., Alshehri M., Dupuis A., Corey M., Arseneault R. A comparison of inhaled fluticasone and oral prednisone for children with severe acute asthma. N Engl J Med. 2000;343:689–694. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200009073431003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Lee-Wong M., Dayrit F.M., Kohli A.R., Acquah S., Mayo P.H. Comparison of high-dose inhaled flunisolide to systemic corticosteroids in severe adult asthma. Chest. 2002;122:1208–1213. doi: 10.1378/chest.122.4.1208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Levy M.L., Stevenson C., Maslen T. Comparison of short courses of oral prednisolone and fluticasone propionate in the treatment of adults with acute exacerbations of asthma in primary care. Thorax. 1996;51:1087–1092. doi: 10.1136/thx.51.11.1087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Rodrigo G.J. Comparison of inhaled fluticasone with intravenous hydrocortisone in the treatment of adult acute asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2005;171:1231–1236. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200410-1415OC. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Edmonds M.L., Milan S.J., Brenner B.E., Camargo C.A., Jr., Rowe B.H. Inhaled steroids for acute asthma following emergency department discharge. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012;12:Cd002316. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002316.pub2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Rowe B.H., Edmonds M.L., Spooner C.H., Diner B., Camargo C.A., Jr. Corticosteroid therapy for acute asthma. Respir Med. 2004;98:275–284. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2003.11.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Fanta C.H., Rossing T.H., McFadden E.R., Jr. Glucocorticoids in acute asthma. A critical controlled trial. Am J Med. 1983;74:845–851. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(83)91076-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Manser R., Reid D., Abramson M. Corticosteroids for acute severe asthma in hospitalised patients. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001;(1):CD001740. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Marquette C.H., Stach B., Cardot E., Bervar J.F., Saulnier F., Lafitte J.J. High-dose and low-dose systemic corticosteroids are equally efficient in acute severe asthma. Eur Respir J. 1995;8:22–27. doi: 10.1183/09031936.95.08010022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Becker J.M., Arora A., Scarfone R.J., Spector N.D., Fontana-Penn M.E., Gracely E. Oral versus intravenous corticosteroids in children hospitalized with asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1999;103:586–590. doi: 10.1016/s0091-6749(99)70228-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Ratto D., Alfaro C., Sipsey J., Glovsky M.M., Sharma O.P. Are intravenous corticosteroids required in status asthmaticus? JAMA. 1988;260:527–529. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Jones A.M., Munavvar M., Vail A., Aldridge R.E., Hopkinson L., Rayner C. Prospective, placebo-controlled trial of 5 vs 10 days of oral prednisolone in acute adult asthma. Respir Med. 2002;96:950–954. doi: 10.1053/rmed.2002.1369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Altamimi S., Robertson G., Jastaniah W., Davey A., Dehghani N., Chen R. Single-dose oral dexamethasone in the emergency management of children with exacerbations of mild to moderate asthma. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2006;22:786–793. doi: 10.1097/01.pec.0000248683.09895.08. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Nowak R.M., Parker J.M., Silverman R.A., Rowe B.H., Smithline H., Khan F. A randomized trial of benralizumab, an antiinterleukin 5 receptor alpha monoclonal antibody, after acute asthma. Am J Emerg Med. 2015;33:14–20. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2014.09.036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]