SUMMARY
Schwannomas are rare benign tumours that arise from Schwann cells. The most known and studied is the intracranial vestibular schwannoma, even if it is not the most frequent. More often schwannomas arise from peripheral sensitive nerves, and the vagous is most involved among the cranial nerves. Intraparotid schwannomas account for just 10% of all facial involvement, so they are an extremely rare localisation. At present, there are less than 100 cases described in the literature. We performed a retrospective analysis of parotidectomy in two Italian hospitals and present two cases of intraparotid schwannoma and a review of the literature. In the first case, we performed a parotidectomy with a stripping of tumour from the nerve. In the other case, a hypoglossal-facial neurorrhaphy was performed. Follow-up was 24 months in the first (House-Brackmann II degree in temporal-ocular and III in facial-cervical branches) and 30 months in the second case (House-Brackmann III degree in both temporal-ocular and facial-cervical branches). Preoperative diagnosis of facial nerve schwannoma is a challenge; however, it is extremely important since post-operative palsy is common and often higher grade. Unfortunately, schwannoma has similar radiologic finding as more common pleomorphic adenoma and often FNAC is not helpful. Due to its rarity and benign nature, there is debate in the literature on the need for surgical removal. Wait-and-see is a valid option, but may could give problems in secondary surgery. Stripping or near-total removal can be useful in cases of limited involvement of the nerve. Neurorrhaphy can provide good functional results when facial sacrifice is needed.
KEY WORDS: Schwannoma, Neurilemmoma, Parotid neoplasm, Facial nerve
RIASSUNTO
Gli schwannomi sono tumori benigni rari che prendono origine dalle cellule di Schwann. Tali cellule formano la guaina mielinica dei nervi periferici permettendo la trasmissione saltatoria, attraverso i nodi di Ranvier, del segnale neurale. Certamente quello più conosciuto e studiato è lo schwannoma vestibolare che ha origine generalmente dalla branca inferiore del nervo vestibolare. Più frequentemente, però, gli scwhannomi originano dai nervi sensitivi periferici e fra i nervi cranici il vago è quello più frequentemente interessato. Nel distretto testa-collo la localizzazione parafaringea è la più comune. Lo schwannoma del nervo facciale intraparotideo è un’evenienza molto rara che rende conto del 10% circa di tutti gli schwannomi che interessano il volto e fino a circa l’1,5% di tutti i tumori parotidei. Al momento in letteratura se ne contano meno di 100 casi. In questo studio abbiamo revisionato la casistica operatoria di due centri ospedalieri italiani riportando due casi di schwannoma del nervo facciale insieme ad una review della letteratura. Nel primo caso abbiamo eseguito una parotidectomia superficiale con dissezione smussa del tumore dalle fibre assonali realizzando una procedura molto simile alla demielinizzazione su base infiammatoria (es. sindromi demielinizzanti acute). Nel secondo caso invece, sempre dopo aver eseguito la parotidectomia, non è stato possibile salvare il nervo facciale per cui, dopo resezione, è stata praticata una neurorrafia con il nervo ipoglosso. Nell’immediato post-operatorio entrambi i pazienti hanno sviluppato una paresi facciale di grado V secondo House-Brackmann. Dopo terapia medica e riabilitativa il primo caso ha residuato un paresi di II-III grado (follow-up di 24 mesi) mentre il secondo una paresi di III (follow-up di 30 mesi). La diagnosi preoperatoria di questa neoplasia è alquanto difficoltosa, in particolare perché non esistono segni radiologici distintivi (di frequente anzi gli schwannomi sono confusi con i molto più comuni adenomi pleomorfi) e spesso anche la FNAC non consente una diagnosi. Fra le opzioni di trattamento, data la rarità e benignità, il wait-and-see può essere ritenuta una scelta valida, sebbene questa possa inficiare il risultato di un’eventuale chirurgia successiva. Al contrario la rimozione subtotale o la dissezione dalle fibre assonali possono essere utili anche se con precise limitazioni. Infine nei casi in cui la sezione del nervo è necessaria, la neurorrafia può consentire risultati soddisfacenti.
PAROLE CHIAVE: Schwannoma, Neurilemmoma, Neoplasia parotidea, Nervo facciale
Introduction
Schwannomas are very rare benign tumours that arise from the Schwann cells which form the sheath of peripheral nerves.
Schwannomas have no sex preference, in the literature there are studies with both female 1 and male prevalence 2.
Although the most studied and known schwannoma is intra-cranial vestibular, it is not the most frequently involved nerve. More often schwannomas arise from sensitive peripheral nerves, and the vagous is most involved among the cranial nerves. The parapharyngeal space is the most common head and neck site of occurrence 2-4.
A facial nerve schwannoma is very rare and normally grows from the intratemporal portion of the nerve. Intraparotid facial schwannoma account for just 10% of all cases of facial involvement, and so it is an extremely rare localisation. To our knowledge, less than 100 cases of intraparotid facial nerve schwannomas have been reported in the scientific literature.
Herein, we present two cases of intraparotid schwannoma, one in a 39-year-old woman and the other in a 45-year-old man, extracted from the clinical records of two otorhinolaryngology departments (San Giovanni Addolorata Hospital in Rome and Garibaldi Hospital in Palermo). We also review the literature on preoperative signs, surgical management and outcomes.
Case reports
1st case
A 39-year-old woman came to our ENT clinic with an asymptomatic parotid mass that appeared 2 years before and grew slowly. In the last 2 months, she started to feel a dull facial pain, but no signs of facial palsy. She had two FNAC (both undiagnosed), ultrasound and an MRI (mass rising from the deep portion of parotid, isointense in T1 image and hyperintense in T2-weighted without clear diagnostic indications) (Figs. 1, 2).
Fig. 1.
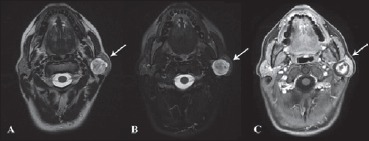
Axial MRI scan: A) T2 FrFSE (Fast Relaxation Fast Spin Echo), B) FrFSE FAT SAT (Fast Relaxation Fast Spin Echo Fat Saturation) and C) T1 with contrast medium. In all scans the arrows show a mass with more cellular central portion (with a good enhancement after contrast medium) opposite to a more mixoid peripheral component.
Fig. 2.
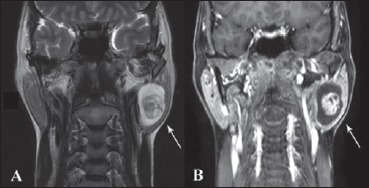
Coronal MRI scans: A) T2 FrFSE (Fast Relaxation Fast Spin Echo) and B) T1 with contrast medium. In both scans the arrows show, as in previous figure, a more cellular central portion opposite to a more mixoid peripheral portion mass. In this scan, we also observe the relatively proximity of the mass to the stylomastoid foramen even if there isn’t invasion of the Fallopian canal.
At parotidectomy, we found a tumour involving the facial nerve trunk near its division into the two main branches with an atypical aspect of multilobular soft and encapsulated mass, similar to a lipoma. We dissected the tumour from the facial nerve, helped by loupe magnification (3.5x), attempting to preserve as many fibres as possible and performed surgical excision as a neural unsheathing (Figs. 3, 4).
Fig. 3.
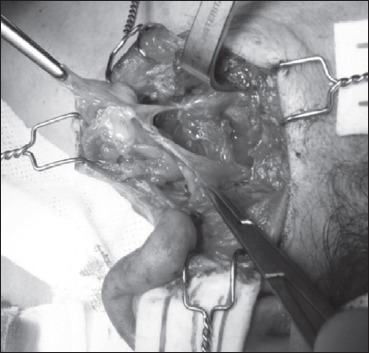
The facial nerve at its main trunk with yellowish and soft mass partially dissected from the nerve, but still adhering to it.
Fig. 4.
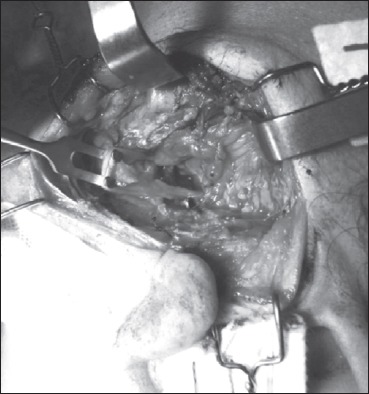
The facial nerve at its main trunk after radical dissection. The integrity of the nerve is achieved by unsheathed dissection.
At the end of the surgical procedure, we verified neural functions by a needle neurostimulator using 1.2 μV of electrical tension with complete but weaker facial contraction (demonstrating an integrity of the facial nerve even if its structure was not completely preserved).
Post-operative histology found an “ancient schwannoma” with cystic and haemorrhagic areas and perivascular hyalinisation; immunophenotype: vimentin+, S100+, CD34- and actin-.
At post-operative Day 1, the patient had a House-Brackmann grade IV palsy and after rehabilitation and medical therapy at 24 months follow-up she had grade II-III HB.
2nd case
A 45-years-old man in good health came to our clinic with a left parotid mass that had appeared 3 years prior and slowly increased in volume. The mass was soft and elastic at palpation, not fixed on the skin or deep plane and not painful. No facial deficit was found.
The patient had a FNAC positive for fibromixoid tissue and a contrast medium CT (bulky mass arising from the deep portion of left parotid without enhancement after contrast medium) (Figs. 5, 6).
Fig. 5.
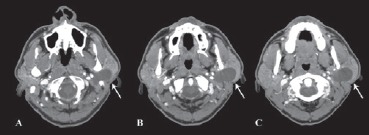
Axial CT scan with contrast medium. The arrows show the schwannoma growth in deep gland portion that goes upward under the mastoid tip (A scan).
Fig. 6.
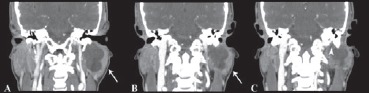
Coronal CT scan with contrast medium. The arrows in the A and B scan show the mass growth toward the stylo-mastoid foramen, which is more evident in last scan (arrow head in C scan).
At parotidectomy, we found a multilobular and encapsulated mass involving the facial nerve at its exit from the stylo-mastoid foramen until the division into the main branches. Unfortunately, we could not dissect the tumour without the sacrifice of the facial nerve so we performed hypoglossal-facial neurorrhaphy.
Post-operative histology founded a neuroma (immunophenotype: vimentin+, S100+, CD34- and actin-).
On post-operative Day 1, the patient had House-Brackmann grade V palsy, whereas at 30-month-follow-up, after rehabilitation and medical therapy, this was HB grade III.
Discussion
An intraparotid facial schwannoma is extremely rare tumour. In a retrospective study (2004), Caughey et al 5 reviewed 3722 patients in a tertiary referral centre (Shadyside Facial Paralysis Center in Pittsburgh) finding only 29 (18 women and 11 men; 0.78%) patients with facial schwannomas. Among these only 8 cases (27.5% of facial schwannomas and 0.21% of the entire cohort) had an intraparotid localisation.
In another study focused on extracranial schwannomas, Kang et al. 3 found only 4 cases of intraparotid localisation in 22 patients with cranial nerve schwannomas over a 10 year personal review.
Similarly, in a series of 113 nerve sheath tumours of the head and neck, Tabriz et al. found only 7 (6%) cases of intraparotid schwannoma 6.
Normally, the intraparotid facial nerve schwannoma is characterised by an intraglandular longstanding mass without specific symptoms and a low growth rate 5,7. At physical examination, it appears as a painless mass with increased but soft consistency and well-defined margins. A functional deficit of the facial nerve is rarely observed. In cases in which it is, it would be more often over a longtime and with a large mass 5,8,9. Facial pain is observed on occasion.
Preoperative diagnosis of facial nerve schwannoma is a major challenge. However, it is extremely important since post-operative palsy is common and often of higher grade (IV or higher in House-Brackmann scale).
Unfortunately, schwannomas have similar radiologic signs to more common parotid tumours, among which pleomorphic adenoma is the most common. At MRI, they usually show an isointensity to muscle in T1-weighted and hyperintensity in T2-weighted image with well defined margins. In contrast enhanced scans they show heterogeneous enhancement due to more cellular Antoni A parts mixed with the more mixoid Antoni B. Moreover, in “ancient schwannoma” type (as in our case), the tumour can present with degenerative changes typified by perivascular hyalinisation, calcification, cystic necrosis, relative loss of Antoni type A tissue and degenerative nuclei that may be misinterpreted as sarcomatous pleomorphisms 10-13.
In a retrospective analysis of 5 cases of extratemporal facial nerve schwannomas, Shimizu et al. reported, as radiological signs of suspicion, tumour growth toward the facial canal and the presence of a “target sign” (peripheral hyperintensity with central hypointensity), corresponding to more cellular Antoni A type in central regions and more myxoid Antoni B peripherally 10.
In another study, Banks analysed the target sign, reporting its validity to identify the PNSTs (peripheral nerve sheath tumours), but were not able to distinguish a benign from malignant one 14.
In the same way, FNAC is of little help. In most cases, cytology is non-specific and non-diagnostic; or worse it can give a misleading diagnosis of more common pleomorphic adenoma or suspected a malignant tumour 3,12,14-18.
All these make treatment of this tumour very challenging because diagnosis is often intra-operative. Moreover, there is still debate on the relevance of surgical removal since radical surgery leads to facial nerve deficit.
The same group of authors suggest a decision-making algorithm 19 based on a previous proposed classification 9 of facial nerve schwannomas. They recognise four kinds of schwannoma presentations: type A and B (the tumour grows on the neural edge or involves a peripheral nerve branch), type C (the tumour grows around the nerve involving it completely at the main branch or trunk) and D (the tumour grows around the nerve involving both main branch and trunk). If the patient has a type A or B tumour or pre-operative House-Brackmann grade IV or worst, the authors propose radical resection with nerve reconstruction. Otherwise, with a type C or D tumour or preserved nerve function (HB III or less grade), they avoid resection and suggest only biopsy to rule out malignancy 19.
Other authors have also proposed intra-operative biopsy to obtain diagnosis and then manage it conservatively 20.
This could be a good algorithm, but one point needs deeper discussion: frozen sections of a malignant peripheral sheath nerve tumour may not be diagnosed due to inexperience of the pathologist or to inappropriateness of the intra-operative biopsy. Moreover, frozen section can lead to misinterpreting a schwannoma as a sarcoma, leading to a unnecessary radical surgery 8.
Thus, the assumption on what the surgical choice should based on can be, in same cases, unreliable.
Moreover, it is more difficult to perform a conservative approach to the facial nerve after first surgery with a mass biopsy, due to post-surgical fibrosis as in relapses of a pleomorphic adenoma.
Other authors suggest a “stripping microscopic surgery” or a “subtotal surgery” to remove the mass of schwannoma from the facial nerve while preserving the neural continuity without functional deficit (Lee et al. in their series had preservation of facial nerve function in all their 6 cases) 21,22.
In a more recent paper Rigante et al. 23, propose intracapsular enucleation under microscopic vision. They made a longitudinal epineurium incision on the schwannoma body and gently blunt dissected the neural fascicles from the tumour under microscopic magnification. They report a post-operative facial nerve deficit of IV on the HB scale, which improved after three months of medical and physical rehabilitation (reaching II-III).
We agree with these authors. In fact, as schwannomas arise from Schwan cells (the peripheral sheath of the nerve), theoretically radical dissection can be obtained by removing the nerve sheath along with the mass, in a process similar to “acute demyelination”. Probably this can explain our observation of more weak contraction of facial muscles at stimulation after tumour removal and the need for higher electrical tension to stimulate the nerve (1.2 μV isn’t normally used on nude nerves).
This could achieve a radical resection with nerve function recovery by new myelination of axons. This procedure would require, however, careful dissection of the mass from the nerve without lesion to the axons; moreover, the re-myelination may not be complete a remaining a partial facial deficit.
Thus, we would suggest such a procedure only in limited involvement of nerve branches or the main trunk (as in our case), so the rate of a axonal lesion is very low and the portion of unsheathed nerve is small.
In this way, radical dissection of the mass can be performed, even in type C schwannoma (by Marchioni classification) in cases with a limited extension of nerve involvement (we suggest 1 cm or less).
In all other cases, we would suggest subtotal surgery (considering the exceptionality of malignant transformation of solitary schwannomas) 3 or MRI annual follow-up avoiding surgery in agreement with Alicandri-Ciufelli et al. 19.
Conclusions
Intraparotid schwannomas are a rare entity. Pre-operative diagnosis is difficult despite FNAC and radiological investigation, and most often diagnosis is intra-operative.
The gold standard management is radical surgery with preservation of acceptable neural function, which can be obtained in almost 50% of cases. In other cases, a reasonable approach is wait-and-see, with strict clinical and radiological follow-up. However, an alternative approach has also a place in management, i.e. microscopic or loupes magnification surgery (for limited involvement of nerve) or subtotal surgery (due to the extremely rare malignant transformation) which can achieve good functional results.
References
- 1. Torossian JM, Beziat JL, Abou Chebel N, et al. Extracranial cephalic schwannomas: a series of 15 patients. J Craniofac Surg 1990;10:389-94. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Leu YS, Chang KC. Extracranial head and neck schwannomas: a review of 8 years experience. Acta Otolaryngol 2002;122:435-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Kang GCW, Khee-Chee S, Lim DTH. Extracranial non-vestibular head and neck schwannomas: a ten year experience. Ann Acad Med Singapore 2007;36:233-40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Malone JP, Lee WJ, Levin RJ. Clinical characteristics and treatment outcome for nonvestibular schwannomas of the head and neck. Am J Otolaryngol 2005;26:108-12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Caughey RJ, May M, Schaitkin BM. Intraparotid facial nerve schwannoma: diagnosis and management. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2004;130:586-92. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Tabriz HM, Razmpa E, Abdollahi A. Head and neck nerve sheath tumors: a 10-year evaluation in Iran. Iranian Journal of Pathology 2009;4,118-22. [Google Scholar]
- 7. Fyrmpas G, Konstantinidis I, Hatzibougias D, et al. Intraparotid facial nerve schwannoma: management options. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 2008;265:699-703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Shah HK, Kantharia C, Shenoy AS. Intraparotid facial nerve schwannoma. J Postgrad Med 1997;43:14-5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Marchioni D, Alicandri Ciufelli M, Presutti L. Intraparotid facial nerve schwannoma: literature review and classification proposal. J Laryngol Otol 2007;121:707-12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Shimizu K, Hiroshi I, Koshi I, et al. Intraparotid facial nerve schwannomas: a report of five cases and an analysis of MR imaging results. Am J Neuroradiol 2005;26:1328-30. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Tsushima Y, Matsumoto M, Endo K, et al. Characteristic bright signal of parotid pleomorphic adenomas on T2-weighted MR images with pathological correlation. Clin Radiol 1994;49:485-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Ikeda K, Katoh T, Ha-Kawa SK, et al. The usefulness of MR in establishing the diagnosis of parotid pleomorphic adenoma. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1996;17:555-9. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Isobe K, Shimizu T, Akahane T, et al. Imaging of ancient schwannoma. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2004;183:331-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Banks KP. The target sign: extremity. Radiology 2005;234:899-900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Tanna N, Zapanta PE, Lavasani L, et al. Intraparotid facial nerve schwannoma: clinician beware. Ear Nose Throat J 2009;88:E18-20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Jayaraj SM, Levine T, Frosh AC, et al. Ancient schwannoma masquerading as parotid pleomorphic adenoma. J Laryngol Otol 1997;111:1088-90. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Kapila K, Mathur S, Verma K. Schwannomas: a pitfall in the diagnosis of pleomorphic adenomas on fine-needle aspiration cytology. Diagn Cytopathol 2002;27:53-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Chong KW, Chung YF, Khoo ML, et al. Management of intraparotid facial nerve schwannomas. Aust N Z J Surg 2000;70:732-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Alicandri-Ciufelli M, Marchioni D, Mattioli F, et al. Critical literature review on the management of intraparotid facial nerve schwannoma and proposed decision-making algorithm. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 2009;266:475-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Mehta RP, Deschler DG. Intraoperative diagnosis of facial nerve schwannoma at parotidectomy. Am J Otolaryngol 2008;29:126-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Lee JD, Kim SH, Song MH, et al. Management of facial nerve schwannoma in patients with favorable facial function. Laryngoscope 2007;117:1063-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Malone JP, Lee WJ, Levin RJ. Clinical characteristics and treatment outcome for nonvestibular schwannomas of the head and neck. Am J Otolaryngol 2005;26:108-12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Rigante M, Petrelli L, De Corso E, et al. Intracapsular microenucleation technique in a case of intraparotid facial nerve schwannoma. Technical notes for a conservative approach. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital 2015;35:49-52. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


