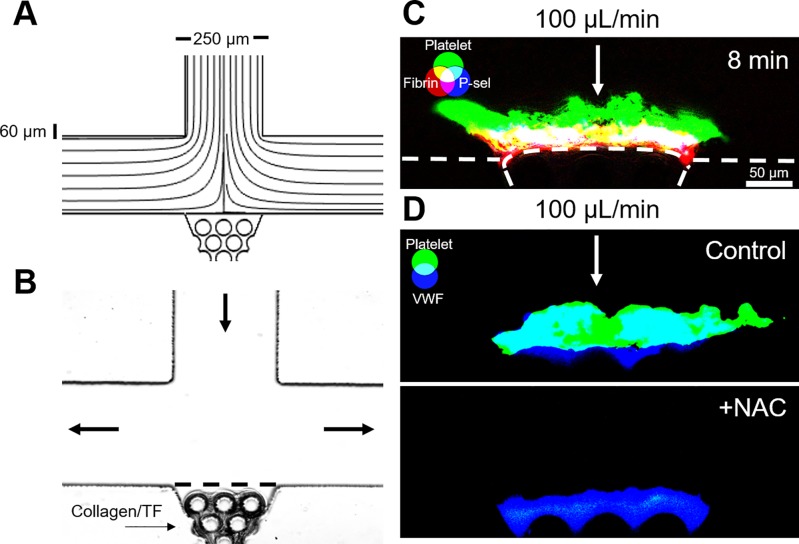
FIG. 3.
Stagnation point microfluidic device demonstrates the core-shell and VWF-dependent thrombus architecture. (a) COMSOL simulation streamline diagram confirms a stagnation point at the center of the collagen scaffold region. (b) Collagen/TF was loaded into the scaffold to create a thrombotic surface that could be observed from the side. (c) CTI-anticoagulated WB was perfused through the device at an inlet flow rate of 100 μl/min (wall shear rate, 1000 s−1). The resulting thrombi exhibited a core-shell architecture, with a fibrin-rich and P-selectin-positive core, and a P-selectin-negative platelet shell. (d) Thrombi formed with CTI-anticoagulated WB formed VWF-rich thrombi. Addition of 30 mM N-acetylcysteine (NAC) eliminated platelet deposition at high shear rates.