In the complex cation, the CoII atom, located on an inverse centre, is coordinated by two isonicotinamide and four water molecules in a distorted O4N2 octahedral geometry. The fumarate anion is located on another inverse centre and is linked to neighbouring complex cations via O—H⋯O and O—H⋯N hydrogen bonds and weak C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds. In the crystal, the complex cations are further linked by O—H⋯O, N—H⋯O an weak C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, forming a three-dimensional supramolecular architectecture.
Keywords: crystal structure, fumaric acid, isonicotinamide, cobalt(II), Hirshfeld surfaces
Abstract
The reaction of cobalt(II) with fumaric acid (H2fum) and isonicotinamide in a basic solution produces the title salt, [Co(C6H6N2O)2(H2O)4](C4H2O4). In the complex cation, the CoII atom, located on an inversion centre, is coordinated by two isonicotinamide and four water molecules in a distorted N2O4 octahedral geometry. The fumarate anion is located on another inversion centre and is linked to neighbouring complex cations via O—H⋯O and N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds and weak C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds. In the crystal, the complex cations are further linked by O—H⋯O, N—H⋯O and weak C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, forming a three-dimensional supramolecular architectecture. Hirshfeld surface analyses (d norm surfaces and two-dimensional fingerprint plots) for the title compound are presented and discussed.
Chemical context
Metal carboxylates have attracted intense attention because of their interesting framework topologies (Rao et al., 2004 ▸). Among metal carboxylates, fumarate dianions (fum) have good conformational freedom and they possess some desirable features such as being versatile ligands because of the four electron-donor oxygen atoms they carry, and their ability to link inorganic moieties (Zheng et al., 2003 ▸). Moreover, metal fumarates exhibit interesting structural varieties.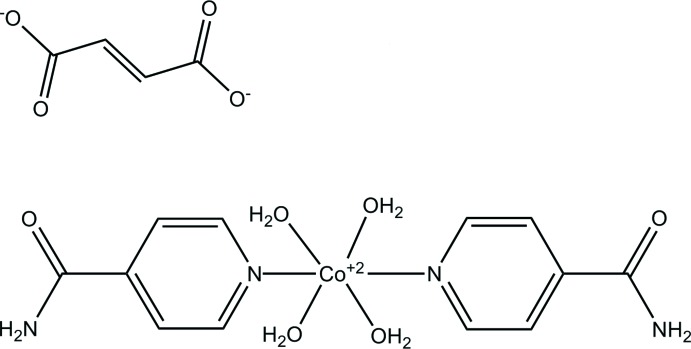
Dicarboxylic acids such as fumaric acid and amides have been particularly useful in creating many supramolecular structures involving isonicotinamide and a variety of carboxylic acid molecules (Vishweshwar et al., 2003 ▸; Aakeröy et al., 2002 ▸). Dicarboxylic acid ligands are utilized in the synthesis of a wide variety of metal carboxylates. For this reason they have been investigated extensively, both experimentally and computationally. We describe herein the synthesis, structural features and Hirshfeld surface analysis of the title salt.
Structural commentary
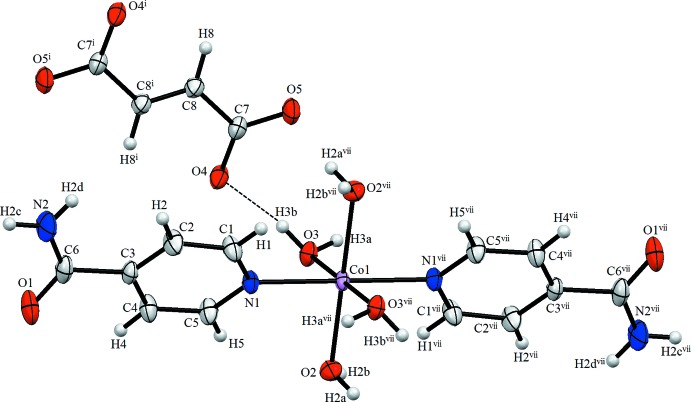
The molecular structure of the title compound is illustrated in Fig. 1 ▸. The CoII cation and midpoint of the C=C bond of the fumarate anion are each located on an inversion centre. In the complex cation, the CoII atom is coordinated to two isonicotinamide ligands and four water molecules in a distorted N2O4 octahedral geometry. The fumarate anion interacts with neighboring complex cations via O—H⋯O and N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds and weak C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds (Table 1 ▸).
Figure 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound, showing the atom labelling. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level. [Symmetry codes: (i) –x + 1, −y + 1, −z + 1; (vii) –x + 1, −y + 1, −z + 2.]
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O2—H2A⋯O5i | 0.86 | 1.96 | 2.814 (2) | 171 |
| O2—H2B⋯O4ii | 0.86 | 1.88 | 2.7165 (19) | 165 |
| O3—H3A⋯O1iii | 0.86 | 1.95 | 2.792 (2) | 168 |
| O3—H3B⋯O4 | 0.86 | 1.82 | 2.6652 (19) | 172 |
| N2—H2C⋯O5iv | 0.86 | 2.13 | 2.955 (2) | 160 |
| N2—H2D⋯O1v | 0.86 | 2.47 | 3.288 (3) | 159 |
| C1—H1⋯O4vi | 0.93 | 2.41 | 3.322 (2) | 168 |
| C2—H2⋯O1v | 0.93 | 2.30 | 3.225 (3) | 173 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 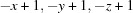 ; (ii)
; (ii) 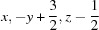 ; (iii)
; (iii) 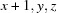 ; (iv)
; (iv) 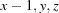 ; (v)
; (v) 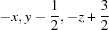 ; (vi)
; (vi) 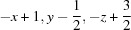 .
.
Supramolecular features
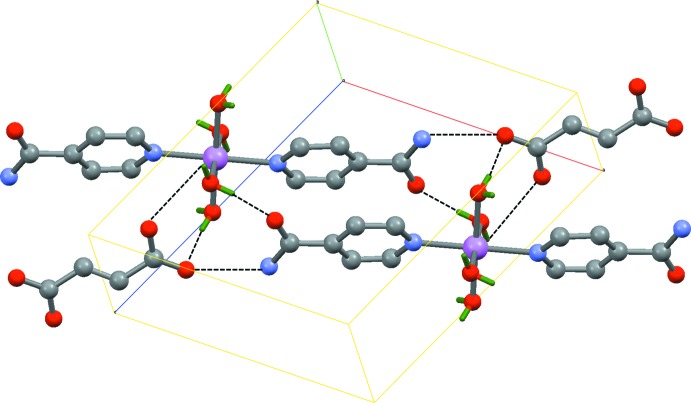
In the crystal, the fumarate anions and complex cations are linked by O—H⋯O, N—H⋯O and C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds; the complex cations also interact with each other through O—H⋯O, N—H⋯O and C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, forming a three-dimensional supramolecular architecture (Table 1 ▸, Fig. 2 ▸).
Figure 2.
Packing of the title compound in the unit cell. Dashed lines indicate hydrogen bonds.
Hirshfeld surface analysis
Crystal Explorer 17.5 (Turner et al., 2017 ▸) was used to analyse the interactions in the crystal and fingerprint plots mapped over d norm (Figs. 3 ▸ and 4 ▸) were generated. The contact distances to the closest atom inside (di) and outside (de) of the Hirshfeld surface are used to analyse the intermolecular interactions via the mapping of d norm. The molecular Hirshfeld surfaces were obtained using a standard (high) surface resolution with the three-dimensional d norm surfaces mapped over a fixed colour scale of −1.227 (red) to 1.279 (blue). Many studies on Hirshfeld surfaces can be found in the literature (see, for example, Şen et al., 2018 ▸; Yaman et al., 2018 ▸).
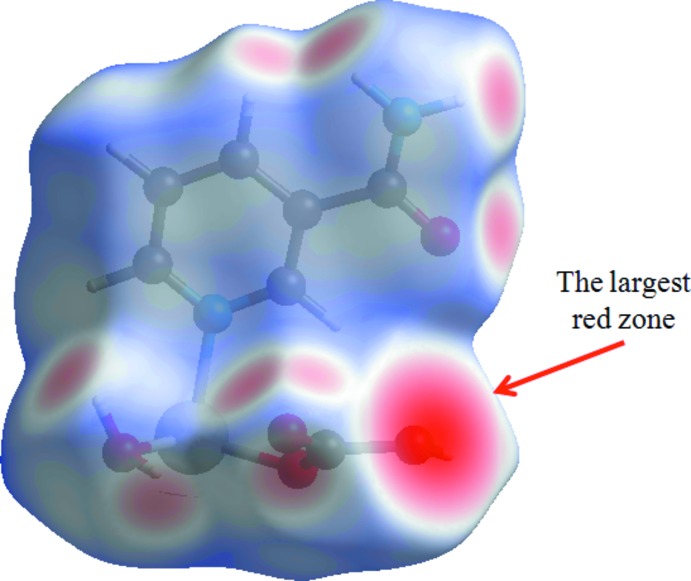
Figure 3.
The Hirshfeld surface of the title compound mapped with d norm. The red spots indicate the regions of the donor–acceptor interactions.
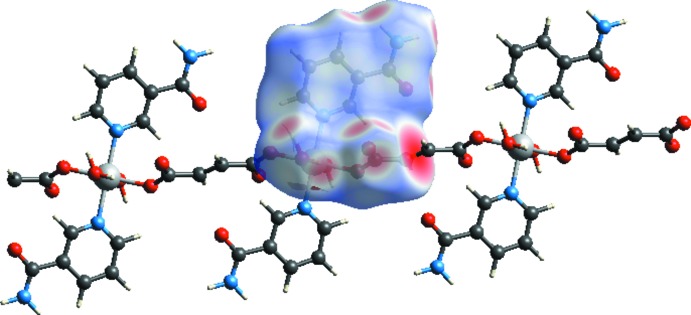
Figure 4.
d norm mapped on the Hirshfeld surfaces for the title structure.
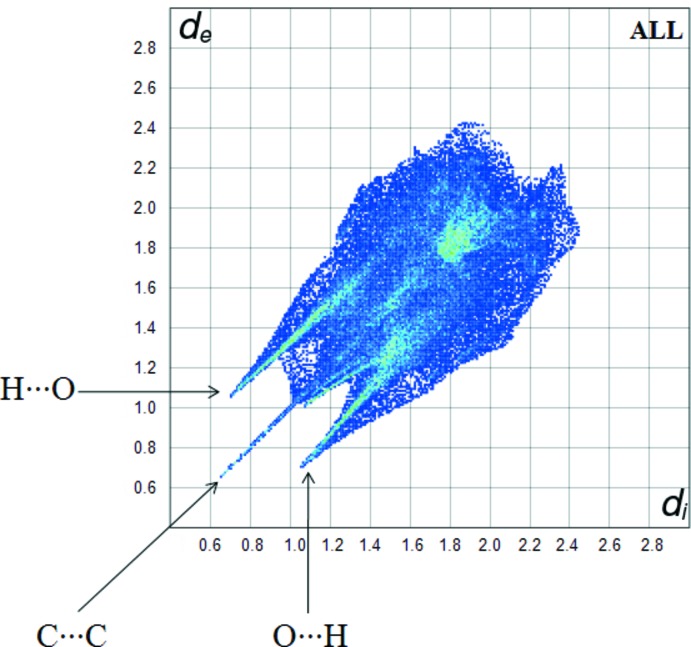
In a d norm surface, any intermolecular interactions will appear as red spots. The red spots indicate the regions of donor–acceptor interactions. There are many red spots in the d norm surface (Fig. 3 ▸), which are usually on the O-acceptor atoms involved in the interactions listed in Table 1 ▸. Strong hydrogen-bond interactions, such as O—H⋯O, are seen as a bright-red areas on the Hirshfeld surfaces (Şen et al., 2017 ▸).
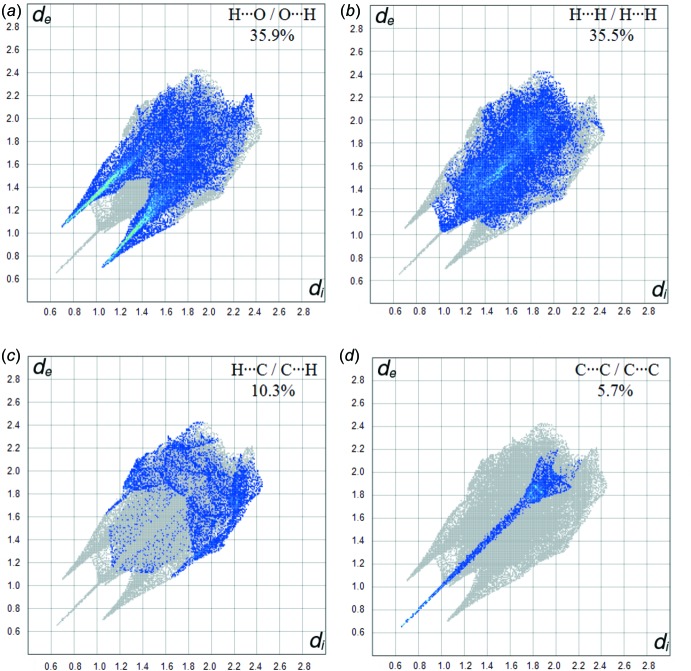
The fingerprint plot for the title complex is presented in Fig. 5 ▸. The H⋯H interactions appear in the middle of the scattered points in the two-dimensional fingerprint plots with an overall contribution to the Hirshfeld surface of 35.5% (Fig. 6 ▸ b). The contribution from the O⋯H/H⋯O contacts, corresponding to C—H⋯O, N—H⋯O and O—H⋯O interactions, is represented by a pair of sharp spikes characteristic of a strong hydrogen-bond interaction (35.9%) (Fig. 6 ▸ a). The C⋯C/C⋯C contacts have a sharp spike between the O⋯H and H⋯O spikes (5.7%) (Fig. 6 ▸ d). The contribution of the other intermolecular contacts to the Hirshfeld surfaces is C⋯H/H⋯C (10.3%) (Fig. 6 ▸ c).
Figure 5.
A fingerprint plot of the title complex.
Figure 6.
(a) O⋯H/H⋯O, (b) H⋯H/H⋯H, (c) C⋯H/H⋯C and (d) C⋯C/C⋯C contacts in the title complex, showing the percentages of contacts contributing to the total Hirshfeld surface area.
Database survey
A search of the Cambridge Structural Database for fumaric acid and isonicotinamide revealed the presence of seven structures: isonicotinohyrazide nicotinamide fumaric acid (Aitipamula et al., 2013 ▸), catena-poly[[aquabis[N-(pyridin-3-yl)isonicotinamide-κN 1)copper(II)]-(μ2-fumarato-κO,O′)-(Qiblawi & LaDuca, 2012 ▸), bis(isonicotinamide) fumaric acid (Aakeröy et al., 2002 ▸), catena-[bis(μ2-fumarato)bis(μ2-3-pyridylisonicotinamide)dizinctrihydrate] (Uebler et al., 2013 ▸) and catena-[bis(μ-but-2-enedioato)bis(μ-pyridine-4-carbohydrazide)dizinc(II)] (Naskar et al., 2017 ▸). In these compounds, the C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds have H⋯O distances ranging from 2.56 to 3.59 Å and C⋯O distances ranging from 3.27 to 3.96 Å. The N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds have H⋯O distances ranging from 1.86 to 2.33 Å and N⋯O distances ranging from 2.82 to 3.15 Å.
Synthesis and crystallization
An aqueous solution of fumaric acid (26 mmol, 3 g) in water was added to a solution of NaOH (52 mmol, 2.07 g) while stirring. A solution of CoCl2·6H2O (25 mmol, 6.19 g) in water was added. The reaction mixture was stirred for an hour at room temperature. The pink mixture was filtered and left to dry. The pink crystals (0.88 mmol, 0.20 g) were dissolved in water and added to an aqueous solution of isonicotinamide (1.75 mmol, 0.21 g). The resulting suspension was filtered and allowed to crystallize for five weeks at room temperature yielding orange block-shaped crystals suitable for X-ray diffraction analysis.
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 2 ▸. The N-bound and C-bound hydrogen atoms were positioned geometrically and treated as riding: N—H = 0.86 Å and C—H = 0.93 Å with U iso(H) = 1.2U eq(C,N). Water H atoms were found in a difference-Fourier map, restrained with O—H = 0.85 Å and refined with U iso(H) = 1.5U eq(O).
Table 2. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | [Co(C6H6N2O)2(H2O)4](C4H2O4) |
| M r | 489.30 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, P21/c |
| Temperature (K) | 296 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 9.6914 (10), 10.0106 (11), 11.3811 (12) |
| β (°) | 113.416 (3) |
| V (Å3) | 1013.22 (19) |
| Z | 2 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.91 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.25 × 0.19 × 0.16 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Bruker APEXII CCD |
| Absorption correction | Analytical (X-RED32; Stoe & Cie, 2002 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.394, 0.746 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 19963, 1962, 1830 |
| R int | 0.032 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.617 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.032, 0.077, 1.14 |
| No. of reflections | 1962 |
| No. of parameters | 144 |
| H-atom treatment | H-atom parameters constrained |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.35, −0.35 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901800107X/xu5915sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901800107X/xu5915Isup2.hkl
CCDC reference: 1561543
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
supplementary crystallographic information
Crystal data
| [Co(C6H6N2O)2(H2O)4](C4H2O4) | F(000) = 506 |
| Mr = 489.30 | Dx = 1.604 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 9.6914 (10) Å | Cell parameters from 9553 reflections |
| b = 10.0106 (11) Å | θ = 3.1–28.3° |
| c = 11.3811 (12) Å | µ = 0.91 mm−1 |
| β = 113.416 (3)° | T = 296 K |
| V = 1013.22 (19) Å3 | Block, orange |
| Z = 2 | 0.25 × 0.19 × 0.16 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker APEXII CCD diffractometer | 1830 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| φ and ω scans | Rint = 0.032 |
| Absorption correction: analytical (X-RED32; Stoe & Cie, 2002) | θmax = 26.0°, θmin = 3.1° |
| Tmin = 0.394, Tmax = 0.746 | h = −11→11 |
| 19963 measured reflections | k = −12→12 |
| 1962 independent reflections | l = −14→13 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | 0 restraints |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: mixed |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.032 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.077 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0211P)2 + 1.1735P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.14 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 1962 reflections | Δρmax = 0.35 e Å−3 |
| 144 parameters | Δρmin = −0.35 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Co1 | 0.500000 | 0.500000 | 0.500000 | 0.01658 (12) | |
| O3 | 0.60307 (15) | 0.65750 (13) | 0.62150 (13) | 0.0237 (3) | |
| H3A | 0.696404 | 0.660264 | 0.635017 | 0.035* | |
| H3B | 0.594575 | 0.646860 | 0.692916 | 0.035* | |
| O2 | 0.39661 (15) | 0.64187 (13) | 0.35319 (13) | 0.0240 (3) | |
| H2A | 0.368923 | 0.604165 | 0.279836 | 0.036* | |
| H2B | 0.458953 | 0.704445 | 0.358200 | 0.036* | |
| O4 | 0.55105 (17) | 0.63859 (14) | 0.83392 (14) | 0.0283 (3) | |
| O1 | −0.09235 (17) | 0.70328 (16) | 0.68073 (17) | 0.0365 (4) | |
| O5 | 0.72605 (18) | 0.48025 (16) | 0.88934 (16) | 0.0356 (4) | |
| N1 | 0.31337 (18) | 0.52596 (16) | 0.55744 (16) | 0.0208 (3) | |
| C7 | 0.6189 (2) | 0.54056 (19) | 0.90123 (18) | 0.0221 (4) | |
| C3 | 0.1007 (2) | 0.5713 (2) | 0.66124 (18) | 0.0216 (4) | |
| C8 | 0.5656 (2) | 0.48648 (19) | 0.99864 (19) | 0.0239 (4) | |
| H8 | 0.629871 | 0.429951 | 1.061428 | 0.029* | |
| N2 | −0.0347 (3) | 0.5112 (2) | 0.7922 (2) | 0.0491 (6) | |
| H2C | −0.102155 | 0.523521 | 0.822413 | 0.059* | |
| H2D | 0.020826 | 0.440936 | 0.812861 | 0.059* | |
| C4 | 0.1453 (2) | 0.6727 (2) | 0.6015 (2) | 0.0268 (4) | |
| H4 | 0.103978 | 0.757665 | 0.594549 | 0.032* | |
| C2 | 0.1627 (2) | 0.4464 (2) | 0.6655 (2) | 0.0297 (5) | |
| H2 | 0.134441 | 0.375248 | 0.703564 | 0.036* | |
| C6 | −0.0163 (2) | 0.6003 (2) | 0.7141 (2) | 0.0279 (4) | |
| C5 | 0.2516 (2) | 0.64642 (19) | 0.5523 (2) | 0.0263 (4) | |
| H5 | 0.281757 | 0.715892 | 0.513627 | 0.032* | |
| C1 | 0.2671 (2) | 0.4283 (2) | 0.6126 (2) | 0.0275 (4) | |
| H1 | 0.307396 | 0.343382 | 0.615691 | 0.033* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Co1 | 0.01724 (19) | 0.01624 (19) | 0.0214 (2) | −0.00028 (12) | 0.01310 (14) | 0.00056 (13) |
| O3 | 0.0239 (7) | 0.0251 (7) | 0.0276 (7) | −0.0036 (6) | 0.0162 (6) | −0.0033 (6) |
| O2 | 0.0259 (7) | 0.0220 (7) | 0.0258 (7) | −0.0015 (5) | 0.0121 (6) | 0.0031 (5) |
| O4 | 0.0421 (8) | 0.0219 (7) | 0.0319 (7) | 0.0059 (6) | 0.0264 (7) | 0.0046 (6) |
| O1 | 0.0332 (8) | 0.0303 (8) | 0.0602 (11) | −0.0001 (7) | 0.0334 (8) | −0.0075 (7) |
| O5 | 0.0354 (8) | 0.0430 (9) | 0.0409 (9) | 0.0129 (7) | 0.0284 (7) | 0.0091 (7) |
| N1 | 0.0207 (8) | 0.0199 (8) | 0.0274 (8) | −0.0003 (6) | 0.0154 (7) | −0.0003 (6) |
| C7 | 0.0262 (9) | 0.0217 (9) | 0.0234 (9) | −0.0018 (8) | 0.0151 (8) | −0.0023 (8) |
| C3 | 0.0178 (9) | 0.0268 (10) | 0.0247 (9) | −0.0017 (7) | 0.0134 (7) | −0.0023 (8) |
| C8 | 0.0282 (10) | 0.0240 (10) | 0.0243 (10) | 0.0033 (8) | 0.0155 (8) | 0.0037 (7) |
| N2 | 0.0411 (12) | 0.0675 (15) | 0.0591 (14) | 0.0163 (11) | 0.0416 (11) | 0.0225 (11) |
| C4 | 0.0285 (10) | 0.0182 (9) | 0.0425 (12) | 0.0012 (8) | 0.0234 (9) | −0.0016 (8) |
| C2 | 0.0303 (10) | 0.0270 (10) | 0.0428 (12) | 0.0024 (9) | 0.0261 (10) | 0.0110 (9) |
| C6 | 0.0208 (9) | 0.0359 (12) | 0.0330 (11) | −0.0056 (9) | 0.0170 (8) | −0.0089 (9) |
| C5 | 0.0300 (10) | 0.0191 (9) | 0.0397 (11) | −0.0005 (8) | 0.0245 (9) | 0.0032 (8) |
| C1 | 0.0274 (10) | 0.0204 (10) | 0.0432 (12) | 0.0039 (8) | 0.0229 (9) | 0.0058 (8) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Co1—O3i | 2.0731 (13) | C7—C8 | 1.498 (3) |
| Co1—O3 | 2.0731 (13) | C3—C2 | 1.380 (3) |
| Co1—O2i | 2.1171 (13) | C3—C4 | 1.383 (3) |
| Co1—O2 | 2.1171 (13) | C3—C6 | 1.509 (3) |
| Co1—N1 | 2.1694 (16) | C8—C8ii | 1.313 (4) |
| Co1—N1i | 2.1694 (16) | C8—H8 | 0.9300 |
| O3—H3A | 0.8556 | N2—C6 | 1.320 (3) |
| O3—H3B | 0.8555 | N2—H2C | 0.8600 |
| O2—H2A | 0.8564 | N2—H2D | 0.8600 |
| O2—H2B | 0.8564 | C4—C5 | 1.380 (3) |
| O4—C7 | 1.258 (2) | C4—H4 | 0.9300 |
| O1—C6 | 1.236 (3) | C2—C1 | 1.379 (3) |
| O5—C7 | 1.254 (2) | C2—H2 | 0.9300 |
| N1—C1 | 1.332 (3) | C5—H5 | 0.9300 |
| N1—C5 | 1.337 (2) | C1—H1 | 0.9300 |
| O3i—Co1—O3 | 180.0 | O4—C7—C8 | 118.86 (17) |
| O3i—Co1—O2i | 88.15 (6) | C2—C3—C4 | 117.75 (17) |
| O3—Co1—O2i | 91.85 (6) | C2—C3—C6 | 123.14 (18) |
| O3i—Co1—O2 | 91.85 (6) | C4—C3—C6 | 119.07 (18) |
| O3—Co1—O2 | 88.15 (6) | C8ii—C8—C7 | 124.4 (2) |
| O2i—Co1—O2 | 180.0 | C8ii—C8—H8 | 117.8 |
| O3i—Co1—N1 | 93.08 (6) | C7—C8—H8 | 117.8 |
| O3—Co1—N1 | 86.92 (6) | C6—N2—H2C | 120.0 |
| O2i—Co1—N1 | 91.85 (6) | C6—N2—H2D | 120.0 |
| O2—Co1—N1 | 88.15 (6) | H2C—N2—H2D | 120.0 |
| O3i—Co1—N1i | 86.92 (6) | C5—C4—C3 | 119.29 (18) |
| O3—Co1—N1i | 93.08 (6) | C5—C4—H4 | 120.4 |
| O2i—Co1—N1i | 88.14 (6) | C3—C4—H4 | 120.4 |
| O2—Co1—N1i | 91.85 (6) | C1—C2—C3 | 119.26 (18) |
| N1—Co1—N1i | 180.0 | C1—C2—H2 | 120.4 |
| Co1—O3—H3A | 109.8 | C3—C2—H2 | 120.4 |
| Co1—O3—H3B | 109.6 | O1—C6—N2 | 123.2 (2) |
| H3A—O3—H3B | 109.1 | O1—C6—C3 | 119.28 (19) |
| Co1—O2—H2A | 109.9 | N2—C6—C3 | 117.5 (2) |
| Co1—O2—H2B | 109.8 | N1—C5—C4 | 123.21 (18) |
| H2A—O2—H2B | 109.1 | N1—C5—H5 | 118.4 |
| C1—N1—C5 | 117.00 (16) | C4—C5—H5 | 118.4 |
| C1—N1—Co1 | 122.07 (13) | N1—C1—C2 | 123.47 (19) |
| C5—N1—Co1 | 120.48 (13) | N1—C1—H1 | 118.3 |
| O5—C7—O4 | 124.37 (18) | C2—C1—H1 | 118.3 |
| O5—C7—C8 | 116.71 (18) | ||
| O5—C7—C8—C8ii | −161.6 (3) | C2—C3—C6—N2 | 15.6 (3) |
| O4—C7—C8—C8ii | 15.7 (4) | C4—C3—C6—N2 | −166.7 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −1.8 (3) | C1—N1—C5—C4 | 0.4 (3) |
| C6—C3—C4—C5 | −179.59 (19) | Co1—N1—C5—C4 | −172.01 (17) |
| C4—C3—C2—C1 | 1.1 (3) | C3—C4—C5—N1 | 1.1 (3) |
| C6—C3—C2—C1 | 178.8 (2) | C5—N1—C1—C2 | −1.2 (3) |
| C2—C3—C6—O1 | −162.7 (2) | Co1—N1—C1—C2 | 171.10 (17) |
| C4—C3—C6—O1 | 14.9 (3) | C3—C2—C1—N1 | 0.5 (4) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, −y+1, −z+1; (ii) −x+1, −y+1, −z+2.
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O2—H2A···O5i | 0.86 | 1.96 | 2.814 (2) | 171 |
| O2—H2B···O4iii | 0.86 | 1.88 | 2.7165 (19) | 165 |
| O3—H3A···O1iv | 0.86 | 1.95 | 2.792 (2) | 168 |
| O3—H3B···O4 | 0.86 | 1.82 | 2.6652 (19) | 172 |
| N2—H2C···O5v | 0.86 | 2.13 | 2.955 (2) | 160 |
| N2—H2D···O1vi | 0.86 | 2.47 | 3.288 (3) | 159 |
| C1—H1···O4vii | 0.93 | 2.41 | 3.322 (2) | 168 |
| C2—H2···O1vi | 0.93 | 2.30 | 3.225 (3) | 173 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, −y+1, −z+1; (iii) x, −y+3/2, z−1/2; (iv) x+1, y, z; (v) x−1, y, z; (vi) −x, y−1/2, −z+3/2; (vii) −x+1, y−1/2, −z+3/2.
Funding Statement
This work was funded by Female Center for Scientific and Medical Colleges, King Saud University grant .
References
- Aakeröy, C. B., Beatty, A. M. & Helfrich, B. A. (2002). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 124, 14425–14432. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Aitipamula, S., Wong, A. B. H., Chow, P. S. & Tan, R. B. H. (2013). CrystEngComm, 15, 5877–5887.
- Bruker (2007). APEX2 and SAINT. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Farrugia, L. J. (2012). J. Appl. Cryst. 45, 849–854.
- Naskar, K., Dey, A., Dutta, B., Ahmed, F., Sen, C., Mir, M. H., Roy, P. P. & Sinha, C. (2017). Cryst. Growth Des. 17, 3267–3276.
- Qiblawi, S. H. & LaDuca, R. L. (2012). Acta Cryst. E68, m1514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Rao, C. N. R., Natarajan, S. & Vaidhyanathan, R. (2004). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 43, 1466–1496. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Şen, F., Çapan, İ., Dincer, M. & Cukurovali, A. (2018). J. Mol. Struct. 1155, 278–287.
- Şen, F., Kansiz, S. & Uçar, İ. (2017). Acta Cryst. C73, 517–524. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015a). Acta Cryst. A71, 3–8.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015b). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Stoe & Cie (2002). X-RED32. Stoe & Cie, Darmstadt, Germany.
- Turner, M. J., MacKinnon, J. J., Wolff, S. K., Grimwood, D. J., Spackman, P. R., Jayatilaka, D. & Spackman, M. A. (2017). Crystal Explorer. University of Western Australia.
- Uebler, J. W., Wilson, J. A. & LaDuca, R. L. (2013). CrystEngComm, 15, 1586–1596.
- Vishweshwar, P., Nangia, A. & Lynch, V. M. (2003). CrystEngComm, 5, 164–168.
- Yaman, M., Almarhoon, Z. M., Çakmak, Ş., Kütük, H., Meral, G. & Dege, N. (2018). Acta Cryst. E74, 41–44. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.-Q., Sun, J. & Lin, J.-L. (2003). J. Mol. Struct. 650, 49–56.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901800107X/xu5915sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901800107X/xu5915Isup2.hkl
CCDC reference: 1561543
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report