Two new salts – 2,6-diamino-4-chloropyrimidin-1-ium 5-chlorosalicylate and bis(2,6-diamino-4-chloropyrimidin-1-ium) naphthalene-1,5-disulfonate – have been synthesized and characterized by single-crystal X-ray diffraction. The supramolecular interactions such as hydrogen bonding, halogen bonding, C—Cl⋯π and π–π interactions are investigated for these crystal structures.
Keywords: crystal structure, hydrogen bonding, supramolecular architecture, halogen–halogen interaction, quadruple array, homosynthon, heterosynthon
Abstract
The crystals of two new salts, 2,6-diamino-4-chloropyrimidin-1-ium 5-chlorosalicylate, C4H6ClN4 +·C7H4ClO3 −, (I), and bis(2,6-diamino-4-chloropyrimidin-1-ium) naphthalene-1,5-di-sulfonate, 2C4H6ClN4 +·C10H6O6S2 2−, (II), have been synthesized and characterized by single-crystal X-ray diffraction. In both compounds, the N atom of the pyrimidine group in between the amino substituents is protonated and the pyrimidinium cation forms a pair of N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds with the carboxylate/sulfonate ion, leading to a robust R 2 2(8) motif (supramolecular heterosynthon). In compound (I), a self-complementary base pairing involving the other pyrimidinium ring nitrogen atom and one of the amino groups via a pair of N—H⋯N hydrogen bonds [R 2 2(8) homosynthon] is also present. In compound (II), the crystallographic inversion centre coincides with the inversion centre of the naphthalene-1,5-disulfonate ion and all the sulfonate O atoms are hydrogen-bond acceptors, generating fused-ring motifs and a quadruple DDAA array. A halogen-bond (Cl⋯Cl) interaction is present in (I) with a distance and angle of 3.3505 (12) Å and 151.37 (10)°, respectively. In addition, a C—Cl⋯π interaction and a π–π interaction in (I) and a π–π interaction in (II) further stabilize these crystal structures.
Chemical context
The study of supramolecular interactions in the crystals of pyrimidinium salts continues to be an active field since the pyrimidine fragment is a component of nucleobases and many drug molecules. The pyrimidine group offers two protonation sites (the two ring nitrogens) and the site of protonation depends on the nature of the substituents. Tautomerism of the pyrimidinium cation has also been reported recently (Rajam et al., 2017 ▸). The pyrimidinium–carboxylate interaction is also of fundamental importance in biology since it is involved in protein–nucleic acid interactions and drug-receptor recognition (Hunt et al., 1980 ▸; Baker & Santi, 1965 ▸). The molecules are often self-assembled by hydrogen bonding, halogen bonding, cation⋯π, anion⋯π and π–π stacking interactions. Among these interactions, halogen bonding is of particular current interest (Cavallo et al., 2016 ▸). Various substituted pyrimidines and their interactions with different acids have been studied systematically in our laboratory. The variation in supramolecular architectures resulting from the different substituents in the base and the acid is being investigated, and crystal structures of 2,6-diamino-4-chloropyrimidinium salts with carboxylate/sulfonate have been reported recently from our laboratory (Mohana et al., 2017 ▸). The same pyrimidine derivative has been used to prepare the title compounds in order to further study the supramolecular architectures and the role of the halogen bond.
Structural commentary
The salt of compound (I) crystallizes with one CDAPY (2,6-diamino-4-chloropyrimidinium) cation and one CSA (5-chlorosalicylate) anion in the asymmetric unit (Fig. 1 ▸). The pyrimidinium cation is protonated at the N1 position (see Fig. 1 ▸ for atom numbering) and this is confirmed by an increase in the internal bond angle. The C2—N3—C4 angle at the unprotonated N3 atom is 115.1 (2)°, while for the protonated N1 atom, the C2—N1—C6 angle is 121.8 (2)°. The ion-pair (CDAPY and CSA) is almost planar [dihedral angle = 4.22 (11)°]. The carboxylate group of CSA is twisted slightly with respect to the remainder of the anion [dihedral angle= 3.9 (3)°]. The salt of compound (II) crystallizes with one CDAPY (2,6-diamino-4-chloropyrimidinium) cation and half a molecule of NSA (naphthalene-1,5-disulfonate) anion in the asymmetric unit (Fig. 2 ▸), the other half of NSA being generated by an inversion centre. A crystallographic inversion centre coinciding with the inversion centre of the NSA ion has also been reported earlier (Liu, 2012 ▸; Xu, 2012 ▸; Liu & Chen, 2012 ▸). The pyrimidinium cation is again protonated at the N1 position (see Fig. 2 ▸ for atom numbering) and this is confirmed by an increase in the internal bond angle. The C2—N3—C4 angle at the unprotonated N3 atom is 115.40 (16)°, while the angle at the protonated N1 atom (C2—N1—C6) is 121.84 (16)°. All of the sulfonate oxygen atoms of the NSA anion are involved in hydrogen bonding. The S1—O1, S1—O2 and S1—O3 distances are similar [1.4550 (15), 1.4584 (15) and 1.4431 (16) Å respectively].
Figure 1.
ORTEP view of compound (I) with the atom-numbering scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at 50% probability level. Dashed lines represent hydrogen bonds.
Figure 2.
ORTEP view of compound (II), with the atom-numbering scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at 50% probability level. Dashed lines represent hydrogen bonds.
Supramolecular features
In salt (I), the protonated N1 atom and the amino hydrogen (N6) atom of CDAPY are hydrogen bonded via two N—H⋯O bonds (Table 1 ▸) forming a robust  (8) ring motif (heterosynthon) involving the carboxylate group. The typical intramolecular hydrogen-bond S(6) motif (involving the carboxyl group and the phenolic –OH) observed in salicylates/salicylic acid is also present (Bernstein et al., 1995 ▸; Prabakaran et al., 2001 ▸; Panneerselvam et al., 2002 ▸) (Fig. 1 ▸). The 2-amino hydrogen atom of CDAPY interacts with the carboxylate oxygen O1 of CSA via an N—H⋯O hydrogen bond forming an
(8) ring motif (heterosynthon) involving the carboxylate group. The typical intramolecular hydrogen-bond S(6) motif (involving the carboxyl group and the phenolic –OH) observed in salicylates/salicylic acid is also present (Bernstein et al., 1995 ▸; Prabakaran et al., 2001 ▸; Panneerselvam et al., 2002 ▸) (Fig. 1 ▸). The 2-amino hydrogen atom of CDAPY interacts with the carboxylate oxygen O1 of CSA via an N—H⋯O hydrogen bond forming an  (6) ring motif. Thus, the O1 oxygen atom acts as a trifurcated acceptor. A similar set of three fused rings was observed in the crystal structure of 2,6-diamino-4-chloropyrimidinium 2-carboxy-3-nitrobenzoate (Mohana et al., 2017 ▸). However, in compound (I) the role of the 2-amino and 6-amino groups has been reversed. A self-complementary base pairing via a pair of N2—H⋯N3i (homosynthon) hydrogen bonds forming an
(6) ring motif. Thus, the O1 oxygen atom acts as a trifurcated acceptor. A similar set of three fused rings was observed in the crystal structure of 2,6-diamino-4-chloropyrimidinium 2-carboxy-3-nitrobenzoate (Mohana et al., 2017 ▸). However, in compound (I) the role of the 2-amino and 6-amino groups has been reversed. A self-complementary base pairing via a pair of N2—H⋯N3i (homosynthon) hydrogen bonds forming an  (8) ring motif is also been observed. This type of base pairing is also observed in the crystal structures of 2,6-diamino-4-chloropyridinium 4-carboxybutanoate (Edison et al., 2014 ▸), 2,6-diamino-4-chloropyrimidine-benzoic acid (Thanigaimani et al., 2012a
▸) and bis(2,6-diamino-4-chloropyrimidin-1-ium) fumarate (Thanigaimani et al., 2012b
▸). The 2,6-diamino-4-chloropyrimidinium 5-chlorosalicylate units are linked via a Cl⋯Cl interaction (a type I interaction; Cavallo et al., 2016 ▸) with a distance and angle of 3.3505 (12) Å and 151.37 (10)°, respectively (Durka et al., 2015 ▸) (Fig. 3 ▸). Furthermore, a weak C—H⋯Oiii hydrogen-bonding interaction is present in this crystal structure. In addition, a weak stacking interaction with Cg1⋯Cg2 [3.6624 (14) Å; symmetry code: x, −1 + y, z; Cg1 and Cg2 are the centroids of the N1/C2/N3/C4/C5/C6 and C8–C13 rings, respectively] and C—Cl⋯π interactions [3.4469 (13) Å with an angle of 152.24 (9)°; symmetry code: −
(8) ring motif is also been observed. This type of base pairing is also observed in the crystal structures of 2,6-diamino-4-chloropyridinium 4-carboxybutanoate (Edison et al., 2014 ▸), 2,6-diamino-4-chloropyrimidine-benzoic acid (Thanigaimani et al., 2012a
▸) and bis(2,6-diamino-4-chloropyrimidin-1-ium) fumarate (Thanigaimani et al., 2012b
▸). The 2,6-diamino-4-chloropyrimidinium 5-chlorosalicylate units are linked via a Cl⋯Cl interaction (a type I interaction; Cavallo et al., 2016 ▸) with a distance and angle of 3.3505 (12) Å and 151.37 (10)°, respectively (Durka et al., 2015 ▸) (Fig. 3 ▸). Furthermore, a weak C—H⋯Oiii hydrogen-bonding interaction is present in this crystal structure. In addition, a weak stacking interaction with Cg1⋯Cg2 [3.6624 (14) Å; symmetry code: x, −1 + y, z; Cg1 and Cg2 are the centroids of the N1/C2/N3/C4/C5/C6 and C8–C13 rings, respectively] and C—Cl⋯π interactions [3.4469 (13) Å with an angle of 152.24 (9)°; symmetry code: − + x,
+ x,  − y, −
− y, − + z] (Muthukumaran et al., 2011 ▸) further stabilize this crystal structure (Fig. 4 ▸).
+ z] (Muthukumaran et al., 2011 ▸) further stabilize this crystal structure (Fig. 4 ▸).
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °) for (I) .
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H1⋯O1 | 0.86 | 1.82 | 2.664 (3) | 168 |
| N2—H2A⋯O1 | 0.86 | 2.56 | 3.223 (3) | 135 |
| N2—H2B⋯N3i | 0.86 | 2.13 | 2.970 (3) | 165 |
| O3—H3⋯O1 | 0.82 | 1.83 | 2.557 (3) | 146 |
| N6—H6A⋯O2 | 0.86 | 1.97 | 2.824 (3) | 172 |
| N6—H6B⋯O2ii | 0.86 | 1.96 | 2.819 (3) | 172 |
| C10—H10⋯O3iii | 0.93 | 2.51 | 3.358 (4) | 151 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  .
.
Figure 3.
Supramolecular layered structure extended as a chain via Cl⋯Cl interactions in (I).
Figure 4.
A weak C—Cl⋯π interaction and π–π stacking interactions.
In salt (II), the sulfonate group mimics the role of the carboxylate oxygen atoms in generating an  (8) motif (heterosynthon) involving the aminopyrimidinium cation (CDAPY) (Bernstein et al., 1995 ▸; Balasubramani et al., 2007 ▸). All units of the CDAPY and NSA ions are hydrogen bonded (Table 2 ▸) to generate a quadruple DDAA array with fused ring motifs
(8) motif (heterosynthon) involving the aminopyrimidinium cation (CDAPY) (Bernstein et al., 1995 ▸; Balasubramani et al., 2007 ▸). All units of the CDAPY and NSA ions are hydrogen bonded (Table 2 ▸) to generate a quadruple DDAA array with fused ring motifs  (8),
(8), 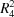 (8) and
(8) and  (8) (Fig. 5 ▸). This type of array has also been reported earlier (Robert et al., 2001 ▸; Umadevi et al., 2002 ▸; Raj et al., 2003 ▸; Subashini et al., 2007 ▸; Thanigaimani et al., 2007 ▸; Liu & Chen, 2012 ▸). In addition, the NSA anions also generate
(8) (Fig. 5 ▸). This type of array has also been reported earlier (Robert et al., 2001 ▸; Umadevi et al., 2002 ▸; Raj et al., 2003 ▸; Subashini et al., 2007 ▸; Thanigaimani et al., 2007 ▸; Liu & Chen, 2012 ▸). In addition, the NSA anions also generate  (10) and
(10) and  (21) ring motifs via N—H⋯O bonds. Weak π–π stacking interactions [Cg1⋯Cg4 = 3.4781 (11) Å; symmetry code:
(21) ring motifs via N—H⋯O bonds. Weak π–π stacking interactions [Cg1⋯Cg4 = 3.4781 (11) Å; symmetry code:  − x, −
− x, − + y,
+ y,  − z and Cg4⋯Cg2 =3.4781 (11) Å; symmetry code:
− z and Cg4⋯Cg2 =3.4781 (11) Å; symmetry code:  + x,
+ x,  − y,
− y,  + z; Cg1, Cg2 and Cg4 are the centroids of the C7/C8/C9/C9′/C10′/C11′, C9/C10/C11/C7′/C8′/C9′ and N1/C2/N3/C4/C5/C6 rings, respectively] is also present (Fig. 6 ▸).
+ z; Cg1, Cg2 and Cg4 are the centroids of the C7/C8/C9/C9′/C10′/C11′, C9/C10/C11/C7′/C8′/C9′ and N1/C2/N3/C4/C5/C6 rings, respectively] is also present (Fig. 6 ▸).
Table 2. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °) for (II) .
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H1⋯O1 | 0.86 | 1.92 | 2.708 (2) | 152 |
| N2—H2A⋯O2i | 0.86 | 2.08 | 2.868 (3) | 152 |
| N2—H2B⋯O2 | 0.86 | 2.10 | 2.953 (2) | 174 |
| N6—H6A⋯N3ii | 0.86 | 2.25 | 2.943 (2) | 138 |
| N6—H6B⋯O3iii | 0.86 | 2.01 | 2.808 (2) | 154 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  .
.
Figure 5.
Formation of a quadruple DDAA array in (II) via N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds.
Figure 6.
A view of the π–π stacking interactions between the pyrimidinium cation and the anion.
Database survey
Various salts of 5-chlorosalicylate have been reported: 2-methylquinolinium 5-chloro-2-hydroxybenzoate (Zhang et al., 2014 ▸), 4-amino-5-chloro-2,6-dimethylpyrimidinium 5-chloro-2-hydroxybenzoate (Rajam et al., 2017 ▸) and 2-amino-4,6-dimethylpyrimidinium 5-chlorosalicylate (Ebenezer & Muthiah, 2012 ▸). Similarly, various salts of half a molecule of naphthalene-1,5-disulfonate have been reported: bis(2-trifluoromethyl-1H-benzimidazole-3-ium) naphthalene-1,5-disulfonate (Liu, 2012 ▸), bis(3-methylanilinium) naphthalene-1,5-disulfonate (Liu & Chen, 2012 ▸) and bis(2-methylpiperidinium) naphthalene-1,5-disulfonate (Xu, 2012 ▸).
Synthesis and crystallization
Compounds (I) and (II) were synthesized by mixing hot ethanolic solutions (1:1) of 2,6-diamino-4-chloropyrimidine (36 mg) with 5-chlorosalicylic acid (43 mg) (I)/naphthalene-1,5-disulfonic acid (72 mg) (II). These mixtures were warmed to 333 K for 25 min. Colourless crystals separated out from the mother liquor at room temperature after a week.
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 3 ▸. All H atoms were initially located readily in difference-Fourier maps and were treated as riding atoms with C—H = 0.93 Å (aromatic), N—H = 0.86 Å and O—H = 0.82 Å with U iso(H) = kU eq(C,N,O), where k = 1.5 for hydroxy and 1.2 for all other H atoms.
Table 3. Experimental details.
| (I) | (II) | |
|---|---|---|
| Crystal data | ||
| Chemical formula | C4H6ClN4 +·C7H4ClO3 − | 2C4H6ClN4 +·C10H6O6S2 2− |
| M r | 317.13 | 577.42 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, P21/n | Monoclinic, P21/n |
| Temperature (K) | 293 | 293 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 13.9203 (14), 7.0285 (6), 15.4294 (14) | 9.1696 (4), 13.0848 (7), 9.9663 (5) |
| β (°) | 114.544 (12) | 90.526 (5) |
| V (Å3) | 1373.2 (3) | 1195.73 (10) |
| Z | 4 | 2 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.49 | 0.50 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.40 × 0.10 × 0.03 | 0.40 × 0.40 × 0.06 |
| Data collection | ||
| Diffractometer | Agilent SuperNova Dual Source diffractometer with an Atlas detector | Agilent SuperNova Dual Source diffractometer with an Atlas detector |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO); Agilent, 2013 ▸) | Multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Agilent, 2013 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.644, 1.000 | 0.527, 1.000 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 7906, 3144, 2137 | 10382, 2735, 2274 |
| R int | 0.027 | 0.028 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.649 | 0.649 |
| Refinement | ||
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.048, 0.128, 1.04 | 0.038, 0.102, 1.05 |
| No. of reflections | 3144 | 2735 |
| No. of parameters | 182 | 163 |
| H-atom treatment | H-atom parameters constrained | H-atom parameters constrained |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.29, −0.40 | 0.49, −0.59 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, II. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018001196/zl2723sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018001196/zl2723Isup2.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) II. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018001196/zl2723IIsup3.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018001196/zl2723Isup4.cml
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
The EN–FIST Centre of Excellence, Ljubljana, Slovenia, is thanked for the use of the SuperNova diffractometer.
supplementary crystallographic information
2,6-Diamino-4-chloropyrimidin-1-ium 2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzoate (I). Crystal data
| C4H6ClN4+·C7H4ClO3− | F(000) = 648 |
| Mr = 317.13 | Dx = 1.534 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/n | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 13.9203 (14) Å | Cell parameters from 1734 reflections |
| b = 7.0285 (6) Å | θ = 3.9–27.5° |
| c = 15.4294 (14) Å | µ = 0.49 mm−1 |
| β = 114.544 (12)° | T = 293 K |
| V = 1373.2 (3) Å3 | Needle, colorless |
| Z = 4 | 0.40 × 0.10 × 0.03 mm |
2,6-Diamino-4-chloropyrimidin-1-ium 2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzoate (I). Data collection
| Agilent SuperNova Dual Source diffractometer with an Atlas detector | 3144 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: SuperNova (Mo) X-ray Source | 2137 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Mirror monochromator | Rint = 0.027 |
| Detector resolution: 10.4933 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 27.5°, θmin = 2.9° |
| ω scans | h = −18→17 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO); Agilent, 2013) | k = −7→9 |
| Tmin = 0.644, Tmax = 1.000 | l = −20→19 |
| 7906 measured reflections |
2,6-Diamino-4-chloropyrimidin-1-ium 2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzoate (I). Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | 0 restraints |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.048 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.128 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0482P)2 + 0.5033P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.04 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 3144 reflections | Δρmax = 0.29 e Å−3 |
| 182 parameters | Δρmin = −0.40 e Å−3 |
2,6-Diamino-4-chloropyrimidin-1-ium 2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzoate (I). Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
2,6-Diamino-4-chloropyrimidin-1-ium 2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzoate (I). Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Cl1 | 0.25461 (6) | −0.27636 (11) | −0.00641 (5) | 0.0674 (2) | |
| N1 | 0.38557 (14) | 0.2707 (3) | 0.12207 (13) | 0.0386 (4) | |
| H1 | 0.4128 | 0.3792 | 0.1450 | 0.046* | |
| N2 | 0.50448 (17) | 0.2485 (3) | 0.05504 (16) | 0.0566 (6) | |
| H2B | 0.5313 | 0.1895 | 0.0215 | 0.068* | |
| H2A | 0.5293 | 0.3573 | 0.0796 | 0.068* | |
| N3 | 0.38700 (15) | 0.0032 (3) | 0.03064 (13) | 0.0442 (5) | |
| N6 | 0.27205 (16) | 0.3072 (3) | 0.19347 (15) | 0.0503 (5) | |
| H6A | 0.3023 | 0.4141 | 0.2157 | 0.060* | |
| H6B | 0.2207 | 0.2687 | 0.2063 | 0.060* | |
| C2 | 0.42485 (18) | 0.1715 (3) | 0.06889 (16) | 0.0404 (5) | |
| C4 | 0.30522 (17) | −0.0606 (3) | 0.04713 (16) | 0.0414 (5) | |
| C5 | 0.26096 (16) | 0.0273 (3) | 0.09993 (15) | 0.0398 (5) | |
| H5 | 0.2048 | −0.0266 | 0.1089 | 0.048* | |
| C6 | 0.30401 (16) | 0.2033 (3) | 0.14025 (15) | 0.0368 (5) | |
| Cl2 | 0.50995 (6) | 1.29096 (12) | 0.45221 (5) | 0.0745 (3) | |
| O1 | 0.49261 (13) | 0.5917 (2) | 0.18881 (13) | 0.0534 (5) | |
| O2 | 0.38734 (12) | 0.6467 (2) | 0.26174 (12) | 0.0501 (4) | |
| O3 | 0.62982 (14) | 0.8382 (3) | 0.19368 (15) | 0.0617 (5) | |
| H3 | 0.5981 | 0.7365 | 0.1805 | 0.093* | |
| C7 | 0.46259 (17) | 0.6930 (3) | 0.24184 (16) | 0.0393 (5) | |
| C8 | 0.51962 (15) | 0.8751 (3) | 0.27862 (15) | 0.0362 (5) | |
| C9 | 0.60003 (17) | 0.9377 (4) | 0.25339 (17) | 0.0437 (6) | |
| C10 | 0.65092 (19) | 1.1105 (4) | 0.28915 (19) | 0.0563 (7) | |
| H10 | 0.7038 | 1.1527 | 0.2718 | 0.068* | |
| C11 | 0.6235 (2) | 1.2181 (4) | 0.34943 (19) | 0.0580 (7) | |
| H11 | 0.6576 | 1.3330 | 0.3729 | 0.070* | |
| C12 | 0.54500 (19) | 1.1548 (4) | 0.37507 (17) | 0.0488 (6) | |
| C13 | 0.49410 (17) | 0.9865 (3) | 0.34066 (16) | 0.0412 (5) | |
| H13 | 0.4417 | 0.9458 | 0.3590 | 0.049* |
2,6-Diamino-4-chloropyrimidin-1-ium 2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzoate (I). Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Cl1 | 0.0648 (4) | 0.0561 (5) | 0.0783 (5) | −0.0240 (3) | 0.0267 (4) | −0.0292 (4) |
| N1 | 0.0432 (10) | 0.0303 (10) | 0.0503 (10) | −0.0045 (8) | 0.0274 (9) | −0.0059 (9) |
| N2 | 0.0670 (13) | 0.0480 (13) | 0.0795 (15) | −0.0198 (11) | 0.0551 (12) | −0.0247 (12) |
| N3 | 0.0479 (11) | 0.0401 (11) | 0.0490 (11) | −0.0089 (9) | 0.0245 (9) | −0.0100 (10) |
| N6 | 0.0527 (11) | 0.0418 (12) | 0.0747 (14) | −0.0065 (10) | 0.0448 (11) | −0.0087 (11) |
| C2 | 0.0460 (12) | 0.0383 (13) | 0.0442 (12) | −0.0032 (11) | 0.0258 (10) | −0.0027 (11) |
| C4 | 0.0403 (12) | 0.0346 (13) | 0.0421 (11) | −0.0045 (10) | 0.0099 (10) | −0.0031 (11) |
| C5 | 0.0337 (11) | 0.0385 (13) | 0.0477 (12) | −0.0050 (10) | 0.0176 (10) | 0.0007 (11) |
| C6 | 0.0354 (11) | 0.0341 (12) | 0.0433 (11) | 0.0029 (9) | 0.0187 (10) | 0.0030 (10) |
| Cl2 | 0.0751 (5) | 0.0685 (5) | 0.0735 (5) | 0.0006 (4) | 0.0245 (4) | −0.0334 (4) |
| O1 | 0.0566 (10) | 0.0395 (10) | 0.0798 (12) | −0.0057 (8) | 0.0439 (9) | −0.0171 (9) |
| O2 | 0.0519 (10) | 0.0380 (9) | 0.0762 (11) | −0.0081 (8) | 0.0425 (9) | −0.0081 (9) |
| O3 | 0.0555 (11) | 0.0592 (13) | 0.0892 (13) | −0.0074 (9) | 0.0487 (10) | −0.0126 (11) |
| C7 | 0.0401 (12) | 0.0314 (12) | 0.0494 (12) | 0.0037 (10) | 0.0216 (10) | 0.0012 (10) |
| C8 | 0.0315 (10) | 0.0326 (12) | 0.0427 (11) | 0.0022 (9) | 0.0136 (9) | 0.0001 (10) |
| C9 | 0.0351 (11) | 0.0427 (14) | 0.0539 (13) | 0.0011 (10) | 0.0192 (10) | 0.0002 (12) |
| C10 | 0.0436 (13) | 0.0566 (17) | 0.0695 (16) | −0.0126 (13) | 0.0242 (13) | −0.0008 (15) |
| C11 | 0.0517 (15) | 0.0456 (15) | 0.0638 (16) | −0.0121 (13) | 0.0112 (13) | −0.0105 (14) |
| C12 | 0.0451 (13) | 0.0436 (14) | 0.0485 (13) | 0.0009 (11) | 0.0102 (11) | −0.0088 (12) |
| C13 | 0.0356 (11) | 0.0399 (13) | 0.0466 (12) | 0.0005 (10) | 0.0156 (10) | −0.0032 (11) |
2,6-Diamino-4-chloropyrimidin-1-ium 2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzoate (I). Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Cl1—C4 | 1.731 (2) | Cl2—C12 | 1.747 (3) |
| N1—C2 | 1.353 (3) | O1—C7 | 1.279 (3) |
| N1—C6 | 1.362 (3) | O2—C7 | 1.251 (3) |
| N1—H1 | 0.8600 | O3—C9 | 1.352 (3) |
| N2—C2 | 1.328 (3) | O3—H3 | 0.8200 |
| N2—H2B | 0.8600 | C7—C8 | 1.488 (3) |
| N2—H2A | 0.8600 | C8—C13 | 1.392 (3) |
| N3—C2 | 1.329 (3) | C8—C9 | 1.400 (3) |
| N3—C4 | 1.342 (3) | C9—C10 | 1.399 (4) |
| N6—C6 | 1.307 (3) | C10—C11 | 1.370 (4) |
| N6—H6A | 0.8600 | C10—H10 | 0.9300 |
| N6—H6B | 0.8600 | C11—C12 | 1.382 (4) |
| C4—C5 | 1.357 (3) | C11—H11 | 0.9300 |
| C5—C6 | 1.402 (3) | C12—C13 | 1.368 (3) |
| C5—H5 | 0.9300 | C13—H13 | 0.9300 |
| C2—N1—C6 | 121.80 (19) | C9—O3—H3 | 109.5 |
| C2—N1—H1 | 119.1 | O2—C7—O1 | 122.8 (2) |
| C6—N1—H1 | 119.1 | O2—C7—C8 | 119.9 (2) |
| C2—N2—H2B | 120.0 | O1—C7—C8 | 117.29 (19) |
| C2—N2—H2A | 120.0 | C13—C8—C9 | 118.4 (2) |
| H2B—N2—H2A | 120.0 | C13—C8—C7 | 119.85 (19) |
| C2—N3—C4 | 115.1 (2) | C9—C8—C7 | 121.7 (2) |
| C6—N6—H6A | 120.0 | O3—C9—C10 | 118.0 (2) |
| C6—N6—H6B | 120.0 | O3—C9—C8 | 122.3 (2) |
| H6A—N6—H6B | 120.0 | C10—C9—C8 | 119.7 (2) |
| N2—C2—N3 | 119.6 (2) | C11—C10—C9 | 120.6 (2) |
| N2—C2—N1 | 117.5 (2) | C11—C10—H10 | 119.7 |
| N3—C2—N1 | 122.8 (2) | C9—C10—H10 | 119.7 |
| N3—C4—C5 | 126.4 (2) | C10—C11—C12 | 119.5 (2) |
| N3—C4—Cl1 | 114.28 (18) | C10—C11—H11 | 120.2 |
| C5—C4—Cl1 | 119.28 (18) | C12—C11—H11 | 120.2 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 116.8 (2) | C13—C12—C11 | 120.7 (2) |
| C4—C5—H5 | 121.6 | C13—C12—Cl2 | 119.5 (2) |
| C6—C5—H5 | 121.6 | C11—C12—Cl2 | 119.8 (2) |
| N6—C6—N1 | 117.7 (2) | C12—C13—C8 | 121.0 (2) |
| N6—C6—C5 | 125.3 (2) | C12—C13—H13 | 119.5 |
| N1—C6—C5 | 117.0 (2) | C8—C13—H13 | 119.5 |
| C4—N3—C2—N2 | −178.7 (2) | O1—C7—C8—C9 | 2.6 (3) |
| C4—N3—C2—N1 | 1.2 (3) | C13—C8—C9—O3 | 179.9 (2) |
| C6—N1—C2—N2 | −180.0 (2) | C7—C8—C9—O3 | 0.7 (3) |
| C6—N1—C2—N3 | 0.2 (3) | C13—C8—C9—C10 | −1.2 (3) |
| C2—N3—C4—C5 | −1.7 (3) | C7—C8—C9—C10 | 179.5 (2) |
| C2—N3—C4—Cl1 | 178.08 (16) | O3—C9—C10—C11 | 179.5 (2) |
| N3—C4—C5—C6 | 0.9 (3) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | 0.7 (4) |
| Cl1—C4—C5—C6 | −178.93 (16) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | 0.1 (4) |
| C2—N1—C6—N6 | 179.0 (2) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | −0.2 (4) |
| C2—N1—C6—C5 | −1.1 (3) | C10—C11—C12—Cl2 | 179.8 (2) |
| C4—C5—C6—N6 | −179.5 (2) | C11—C12—C13—C8 | −0.3 (4) |
| C4—C5—C6—N1 | 0.6 (3) | Cl2—C12—C13—C8 | 179.61 (17) |
| O2—C7—C8—C13 | 4.7 (3) | C9—C8—C13—C12 | 1.1 (3) |
| O1—C7—C8—C13 | −176.68 (19) | C7—C8—C13—C12 | −179.7 (2) |
| O2—C7—C8—C9 | −176.1 (2) |
2,6-Diamino-4-chloropyrimidin-1-ium 2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzoate (I). Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H1···O1 | 0.86 | 1.82 | 2.664 (3) | 168 |
| N2—H2A···O1 | 0.86 | 2.56 | 3.223 (3) | 135 |
| N2—H2B···N3i | 0.86 | 2.13 | 2.970 (3) | 165 |
| O3—H3···O1 | 0.82 | 1.83 | 2.557 (3) | 146 |
| N6—H6A···O2 | 0.86 | 1.97 | 2.824 (3) | 172 |
| N6—H6B···O2ii | 0.86 | 1.96 | 2.819 (3) | 172 |
| C10—H10···O3iii | 0.93 | 2.51 | 3.358 (4) | 151 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, −y, −z; (ii) −x+1/2, y−1/2, −z+1/2; (iii) −x+3/2, y+1/2, −z+1/2.
Bis(2,6-diamino-4-chloropyrimidin-1-ium) naphthalene-1,5-disulfonate (II). Crystal data
| 2C4H6ClN4+·C10H6O6S22− | F(000) = 592 |
| Mr = 577.42 | Dx = 1.604 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/n | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 9.1696 (4) Å | Cell parameters from 3749 reflections |
| b = 13.0848 (7) Å | θ = 3.7–30.1° |
| c = 9.9663 (5) Å | µ = 0.50 mm−1 |
| β = 90.526 (5)° | T = 293 K |
| V = 1195.73 (10) Å3 | Prism, colorless |
| Z = 2 | 0.40 × 0.40 × 0.06 mm |
Bis(2,6-diamino-4-chloropyrimidin-1-ium) naphthalene-1,5-disulfonate (II). Data collection
| Agilent SuperNova Dual Source diffractometer with an Atlas detector | 2735 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: SuperNova (Mo) X-ray Source | 2274 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Mirror monochromator | Rint = 0.028 |
| Detector resolution: 10.4933 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 27.5°, θmin = 3.0° |
| ω scans | h = −8→11 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Agilent, 2013) | k = −16→15 |
| Tmin = 0.527, Tmax = 1.000 | l = −12→12 |
| 10382 measured reflections |
Bis(2,6-diamino-4-chloropyrimidin-1-ium) naphthalene-1,5-disulfonate (II). Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | 0 restraints |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.038 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.102 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0444P)2 + 0.5881P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.05 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 2735 reflections | Δρmax = 0.49 e Å−3 |
| 163 parameters | Δρmin = −0.59 e Å−3 |
Bis(2,6-diamino-4-chloropyrimidin-1-ium) naphthalene-1,5-disulfonate (II). Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
Bis(2,6-diamino-4-chloropyrimidin-1-ium) naphthalene-1,5-disulfonate (II). Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Cl1 | 0.10474 (6) | 0.91005 (5) | 0.13497 (8) | 0.0693 (2) | |
| N1 | 0.47951 (17) | 0.72194 (12) | 0.24106 (15) | 0.0379 (4) | |
| H1 | 0.5541 | 0.6839 | 0.2572 | 0.045* | |
| N2 | 0.4259 (2) | 0.61789 (16) | 0.0635 (2) | 0.0675 (7) | |
| H2A | 0.3734 | 0.6006 | −0.0047 | 0.081* | |
| H2B | 0.5013 | 0.5823 | 0.0853 | 0.081* | |
| N3 | 0.27559 (18) | 0.75496 (14) | 0.10314 (17) | 0.0437 (4) | |
| N6 | 0.54208 (19) | 0.81915 (14) | 0.42350 (17) | 0.0444 (4) | |
| H6A | 0.6148 | 0.7789 | 0.4376 | 0.053* | |
| H6B | 0.5275 | 0.8701 | 0.4761 | 0.053* | |
| C2 | 0.3908 (2) | 0.69909 (16) | 0.1347 (2) | 0.0420 (5) | |
| C4 | 0.2528 (2) | 0.83590 (15) | 0.1817 (2) | 0.0393 (4) | |
| C5 | 0.3328 (2) | 0.86453 (15) | 0.2911 (2) | 0.0377 (4) | |
| H5 | 0.3089 | 0.9215 | 0.3422 | 0.045* | |
| C6 | 0.45350 (19) | 0.80277 (14) | 0.32183 (18) | 0.0333 (4) | |
| S1 | 0.80386 (5) | 0.55638 (4) | 0.21480 (4) | 0.03723 (15) | |
| O1 | 0.75993 (16) | 0.65802 (11) | 0.25770 (15) | 0.0491 (4) | |
| O2 | 0.68017 (17) | 0.49952 (12) | 0.15999 (15) | 0.0517 (4) | |
| O3 | 0.92854 (18) | 0.55687 (13) | 0.12748 (14) | 0.0541 (4) | |
| C7 | 0.7936 (2) | 0.40041 (15) | 0.39206 (19) | 0.0379 (4) | |
| H7 | 0.7184 | 0.3761 | 0.3375 | 0.045* | |
| C8 | 0.86088 (18) | 0.49007 (14) | 0.36151 (17) | 0.0307 (4) | |
| C9 | 0.97829 (18) | 0.52894 (13) | 0.44251 (17) | 0.0293 (4) | |
| C10 | 1.0523 (2) | 0.62150 (15) | 0.41375 (19) | 0.0385 (4) | |
| H10 | 1.0250 | 0.6595 | 0.3388 | 0.046* | |
| C11 | 1.1626 (2) | 0.65540 (16) | 0.4944 (2) | 0.0427 (5) | |
| H11 | 1.2097 | 0.7163 | 0.4739 | 0.051* |
Bis(2,6-diamino-4-chloropyrimidin-1-ium) naphthalene-1,5-disulfonate (II). Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Cl1 | 0.0446 (3) | 0.0740 (4) | 0.0888 (5) | 0.0223 (3) | −0.0221 (3) | −0.0052 (4) |
| N1 | 0.0362 (8) | 0.0366 (8) | 0.0405 (8) | 0.0056 (7) | −0.0128 (7) | −0.0061 (7) |
| N2 | 0.0709 (13) | 0.0633 (13) | 0.0676 (13) | 0.0230 (11) | −0.0364 (11) | −0.0346 (11) |
| N3 | 0.0371 (9) | 0.0485 (10) | 0.0454 (9) | 0.0019 (7) | −0.0144 (7) | −0.0041 (8) |
| N6 | 0.0459 (10) | 0.0451 (9) | 0.0420 (9) | 0.0073 (8) | −0.0150 (8) | −0.0107 (7) |
| C2 | 0.0415 (11) | 0.0420 (11) | 0.0424 (10) | 0.0010 (8) | −0.0122 (9) | −0.0066 (8) |
| C4 | 0.0275 (9) | 0.0429 (11) | 0.0474 (11) | 0.0012 (8) | −0.0047 (8) | 0.0052 (9) |
| C5 | 0.0347 (9) | 0.0367 (10) | 0.0416 (10) | 0.0032 (8) | −0.0022 (8) | −0.0028 (8) |
| C6 | 0.0327 (9) | 0.0338 (9) | 0.0333 (9) | −0.0023 (7) | −0.0023 (7) | 0.0000 (7) |
| S1 | 0.0411 (3) | 0.0401 (3) | 0.0303 (2) | 0.0063 (2) | −0.00909 (19) | 0.00095 (18) |
| O1 | 0.0499 (8) | 0.0425 (8) | 0.0545 (9) | 0.0128 (7) | −0.0185 (7) | −0.0033 (7) |
| O2 | 0.0563 (9) | 0.0532 (9) | 0.0451 (8) | 0.0030 (7) | −0.0252 (7) | −0.0052 (7) |
| O3 | 0.0625 (10) | 0.0643 (10) | 0.0356 (8) | 0.0090 (8) | 0.0075 (7) | 0.0121 (7) |
| C7 | 0.0326 (9) | 0.0426 (11) | 0.0382 (10) | −0.0054 (8) | −0.0048 (8) | −0.0017 (8) |
| C8 | 0.0295 (8) | 0.0349 (9) | 0.0276 (8) | 0.0026 (7) | −0.0017 (7) | 0.0004 (7) |
| C9 | 0.0279 (8) | 0.0325 (9) | 0.0276 (8) | 0.0019 (7) | −0.0002 (6) | 0.0012 (7) |
| C10 | 0.0415 (10) | 0.0380 (10) | 0.0361 (9) | −0.0029 (8) | −0.0033 (8) | 0.0086 (8) |
| C11 | 0.0437 (11) | 0.0387 (10) | 0.0456 (11) | −0.0133 (8) | −0.0023 (9) | 0.0073 (8) |
Bis(2,6-diamino-4-chloropyrimidin-1-ium) naphthalene-1,5-disulfonate (II). Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Cl1—C4 | 1.7290 (19) | S1—O3 | 1.4431 (16) |
| N1—C6 | 1.352 (2) | S1—O1 | 1.4550 (15) |
| N1—C2 | 1.363 (2) | S1—O2 | 1.4584 (15) |
| N1—H1 | 0.8600 | S1—C8 | 1.7749 (17) |
| N2—C2 | 1.319 (3) | C7—C8 | 1.361 (3) |
| N2—H2A | 0.8600 | C7—C11i | 1.403 (3) |
| N2—H2B | 0.8600 | C7—H7 | 0.9300 |
| N3—C2 | 1.321 (3) | C8—C9 | 1.433 (2) |
| N3—C4 | 1.335 (3) | C9—C10 | 1.419 (3) |
| N6—C6 | 1.311 (2) | C9—C9i | 1.427 (3) |
| N6—H6A | 0.8600 | C10—C11 | 1.361 (3) |
| N6—H6B | 0.8600 | C10—H10 | 0.9300 |
| C4—C5 | 1.361 (3) | C11—C7i | 1.403 (3) |
| C5—C6 | 1.402 (3) | C11—H11 | 0.9300 |
| C5—H5 | 0.9300 | ||
| C6—N1—C2 | 121.84 (16) | O3—S1—O1 | 113.34 (10) |
| C6—N1—H1 | 119.1 | O3—S1—O2 | 113.21 (10) |
| C2—N1—H1 | 119.1 | O1—S1—O2 | 111.10 (9) |
| C2—N2—H2A | 120.0 | O3—S1—C8 | 105.66 (8) |
| C2—N2—H2B | 120.0 | O1—S1—C8 | 106.56 (8) |
| H2A—N2—H2B | 120.0 | O2—S1—C8 | 106.34 (9) |
| C2—N3—C4 | 115.40 (16) | C8—C7—C11i | 120.15 (17) |
| C6—N6—H6A | 120.0 | C8—C7—H7 | 119.9 |
| C6—N6—H6B | 120.0 | C11i—C7—H7 | 119.9 |
| H6A—N6—H6B | 120.0 | C7—C8—C9 | 121.31 (16) |
| N2—C2—N3 | 121.08 (18) | C7—C8—S1 | 118.35 (13) |
| N2—C2—N1 | 116.65 (18) | C9—C8—S1 | 120.31 (13) |
| N3—C2—N1 | 122.27 (18) | C10—C9—C9i | 119.00 (19) |
| N3—C4—C5 | 127.02 (18) | C10—C9—C8 | 123.19 (15) |
| N3—C4—Cl1 | 114.47 (14) | C9i—C9—C8 | 117.8 (2) |
| C5—C4—Cl1 | 118.51 (16) | C11—C10—C9 | 120.90 (17) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 115.80 (18) | C11—C10—H10 | 119.6 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 122.1 | C9—C10—H10 | 119.6 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 122.1 | C10—C11—C7i | 120.83 (18) |
| N6—C6—N1 | 118.48 (17) | C10—C11—H11 | 119.6 |
| N6—C6—C5 | 123.87 (18) | C7i—C11—H11 | 119.6 |
| N1—C6—C5 | 117.64 (16) | ||
| C4—N3—C2—N2 | −179.1 (2) | O3—S1—C8—C7 | −116.17 (16) |
| C4—N3—C2—N1 | 0.7 (3) | O1—S1—C8—C7 | 122.99 (16) |
| C6—N1—C2—N2 | −179.4 (2) | O2—S1—C8—C7 | 4.41 (18) |
| C6—N1—C2—N3 | 0.8 (3) | O3—S1—C8—C9 | 61.75 (17) |
| C2—N3—C4—C5 | −1.8 (3) | O1—S1—C8—C9 | −59.08 (16) |
| C2—N3—C4—Cl1 | 178.00 (16) | O2—S1—C8—C9 | −177.67 (14) |
| N3—C4—C5—C6 | 1.3 (3) | C7—C8—C9—C10 | 179.44 (18) |
| Cl1—C4—C5—C6 | −178.48 (14) | S1—C8—C9—C10 | 1.6 (2) |
| C2—N1—C6—N6 | 178.92 (19) | C7—C8—C9—C9i | −0.6 (3) |
| C2—N1—C6—C5 | −1.3 (3) | S1—C8—C9—C9i | −178.50 (17) |
| C4—C5—C6—N6 | −179.95 (19) | C9i—C9—C10—C11 | −0.3 (3) |
| C4—C5—C6—N1 | 0.3 (3) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | 179.62 (19) |
| C11i—C7—C8—C9 | 0.8 (3) | C9—C10—C11—C7i | 0.1 (3) |
| C11i—C7—C8—S1 | 178.73 (16) |
Symmetry code: (i) −x+2, −y+1, −z+1.
Bis(2,6-diamino-4-chloropyrimidin-1-ium) naphthalene-1,5-disulfonate (II). Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H1···O1 | 0.86 | 1.92 | 2.708 (2) | 152 |
| N2—H2A···O2ii | 0.86 | 2.08 | 2.868 (3) | 152 |
| N2—H2B···O2 | 0.86 | 2.10 | 2.953 (2) | 174 |
| N6—H6A···N3iii | 0.86 | 2.25 | 2.943 (2) | 138 |
| N6—H6B···O3iv | 0.86 | 2.01 | 2.808 (2) | 154 |
Symmetry codes: (ii) −x+1, −y+1, −z; (iii) x+1/2, −y+3/2, z+1/2; (iv) x−1/2, −y+3/2, z+1/2.
Funding Statement
This work was funded by University Grants Commission grants and . Javna Agencija za Raziskovalno Dejavnost RS grant PI-0230–0175.
References
- Agilent. (2013). CrysAlis PRO. Agilent Technologies UK Ltd, Yarnton, England.
- Baker, B. R. & Santi, D. V. (1965). J. Pharm. Sci. 54, 1252–1257. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Balasubramani, K., Thomas Muthiah, P. & Lynch, D. E. (2007). Chem. Cent. J. 1, 28. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Bernstein, J., Davis, R. E., Shimoni, L. & Chang, N. L. (1995). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 34, 1555–1573.
- Cavallo, G., Metrangolo, P., Milani, R., Pilati, T., Priimagi, A., Resnati, G. & Terraneo, G. (2016). Chem. Rev. 116, 2478–2601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Durka, K., Kliś, T. & Serwatowski, J. (2015). Acta Cryst. E71, 1471–1474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Ebenezer, S. & Muthiah, P. T. (2012). Cryst. Growth Des. 12, 3766–3785.
- Edison, B., Balasubramani, K., Thanigaimani, K., Khalib, N. C., Arshad, S. & Razak, I. A. (2014). Acta Cryst. E70, o857–o858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Hunt, W. E., Schwalbe, C. H., Bird, K. & Mallinson, P. D. (1980). Biochem. J. 187, 533–536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.-L. (2012). Acta Cryst. E68, o342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.-L. & Chen, Z.-Q. (2012). Acta Cryst. E68, o1745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Macrae, C. F., Bruno, I. J., Chisholm, J. A., Edgington, P. R., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Rodriguez-Monge, L., Taylor, R., van de Streek, J. & Wood, P. A. (2008). J. Appl. Cryst. 41, 466–470.
- Mohana, M., Thomas Muthiah, P. & Butcher, R. J. (2017). Acta Cryst. C73, 536–540. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Muthukumaran, J., Parthiban, A., Kannan, M., Rao, H. S. P. & Krishna, R. (2011). Acta Cryst. E67, o898–o899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Panneerselvam, P., Stanley, N. & Muthiah, P. T. (2002). Acta Cryst. E58, o180–o182.
- Prabakaran, P., Murugesan, S., Muthiah, P. T., Bocelli, G. & Righi, L. (2001). Acta Cryst. E57, o933–o936. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Raj, S. B., Muthiah, P. T., Rychlewska, U. & Warzajtis, B. (2003). CrystEngComm, 5, 48–53.
- Rajam, A., Muthiah, P. T., Butcher, R. J., Jasinski, J. P. & Glidewell, C. (2017). Acta Cryst. C73, 862–868. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Robert, J. J., Raj, S. B. & Muthiah, P. T. (2001). Acta Cryst. E57, o1206–o1208.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015a). Acta Cryst. A71, 3–8.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015b). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Subashini, A., Muthiah, P. T., Bocelli, G. & Cantoni, A. (2007). Acta Cryst. E63, o3775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Thanigaimani, K., Khalib, N. C., Arshad, S. & Razak, I. A. (2012a). Acta Cryst. E68, o3442–o3443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Thanigaimani, K., Khalib, N. C., Farhadikoutenaei, A., Arshad, S. & Razak, I. A. (2012b). Acta Cryst. E68, o3321–o3322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Thanigaimani, K., Muthiah, P. T. & Lynch, D. E. (2007). Acta Cryst. E63, o4555–o4556. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Umadevi, B., Prabakaran, P. & Muthiah, P. T. (2002). Acta Cryst. C58, o510–o512. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q. (2012). Acta Cryst. E68, o1733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J., Jin, S., Tao, L., Liu, B. & Wang, D. (2014). J. Mol. Struct. 1072, 208–220.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, II. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018001196/zl2723sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018001196/zl2723Isup2.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) II. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018001196/zl2723IIsup3.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018001196/zl2723Isup4.cml
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report








