Abstract
Atypical teratoid rhabdoid tumours (ATRTs) are the most common malignant central nervous system tumours in children ≤1 year of age and represent approximately 1–2% of all pediatric brain tumours. ATRT is a primarily monogenic disease characterized by the bi-allelic loss of the SMARCB1 gene, which encodes the hSNF5 subunit of the SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complex. Though conventional dose chemotherapy is not effective in most ATRT patients, high dose chemotherapy with autologous stem cell transplant, radiotherapy and/or intrathecal chemotherapy all show significant potential to improve patient survival. Recent epigenetic and transcriptional studies highlight three subgroups of ATRT, each with distinct clinical and molecular characteristics with corresponding therapeutic sensitivities, including epigenetic targeting, and inhibition of tyrosine kinases or growth/lineage specific pathways.
Keywords: Brain neoplasms; Rhabdoid tumour; SMARCB1 protein, Human; Antineoplastic agent; Epigenomics; Protein-tyrosine kinases
INTRODUCTION
Atypical teratoid rhabdoid tumours (ATRTs) are malignant embryonal tumours of the central nervous system (CNS) characterized by bi-allelic loss of function alterations of SMARCB1, which encodes the hSNF5/BAF47/INI1 subunit of the SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complex, and more rarely SMARCA4, which encodes the SWI/SNF subunit BRG1. ATRTs represent one of the most common and aggressive brain tumours of early childhood [22]. First identified as a distinct tumour type in 1996 [49], ATRTs were difficult to distinguish from other embryonal brain tumours (EBTs) due to similar neuroepithelial histology. Despite ATRT’s designation as a separate disease entity in the World Health Organization’s Classification of CNS tumours [23,42] since 2000, until recently, there has been limited progress in biological understanding and clinical management of this highly lethal tumor. Recent global transcriptional and methylation profiling of large tumor cohorts by two groups revealed ATRT comprises molecular subclasses with distinct clinicopathologic features, providing a much awaited breakthrough in clinical and biological understanding of ATRTs [32,58].
CLINICAL PRESENTATION
It is difficult to accurately estimate incidence of ATRT in part due to its rarity and misdiagnosis as other EBTs, however recent advances in awareness and availability of molecular or histological tests allow for more accurate identification of ATRT. These tumours represent anywhere from 1–2% of all pediatric CNS tumours [17], comprising up to 6.1% of malignant high grade tumours [68]. Overall, there is a slight male predominance of nearly 2 : 1 [28], though this does not carry to the subgroup level [58]. ATRT is primarily a disease of infants and toddlers, with a median age of diagnosis between 1.2 and 2.3 years [13,46,64,68] and roughly 2/3 of all patients are diagnosed at ≤3 years of age [57,68]. ATRTs have been identified throughout the CNS, with supratentorial presentations being most common and spinal presentations the most rare at 1–7% [2,57]. Classic ATRT morphology is diverse, with epithelial, mesenchymal and neuroepithelial features. “Rhabdoid cells” (hallmark of nearly all rhabdoid tumours), may account for only a very small percentage of the cells observed in ATRTs, with some tumors exhibiting mostly small round blue cell morphology similar to those seen in medulloblastoma (MB). As a result ATRTs were often diagnosed as what was then known as PNET or as MB prior to the establishment and introduction of SMARCB1 as a molecular marker [6].
Currently accepted diagnostic requirements of ATRT are genetic bi-allelic loss and/or negative immunohistochemistry staining of SMARCB1 or SMARCA4 and their respective gene products hSNF5/INI1/BAF47 and BRG1 [4,24]. Approximately 20–35% of ATRT patients are found to carry bi-allelic germline alterations of SMARCB1 or SMARCA4; children with consequent “rhabdoid tumour predisposition syndrome” have a propensity to develop additional intra- and extra-cranial rhabdoid tumours at a young age [5,8,14,27,37,51].
TREATMENT AND PROGNOSIS
There is presently no standardized treatment regimen for ATRTs. Retrospective data highlight the highly malignant nature of this disease with observed survival estimates at one year of ≤50% [13,64]. With increased use of hSNF5 immunohistochemistry as a diagnostic tool and recognition of the need for more aggressive therapy for ATRTs, survival of correctly diagnosed ATRT patients after multimodal therapies including surgery, chemotherapy and radiotherapy has improved (p=0.047) [68]. However much remains unknown about the prognostic role of specific patient features or treatments [10].
Currently available clinical literature on ATRTs is almost entirely retrospective, with frequently small and heterogeneously treated cohorts, from which only age, tumour location and metastatic status at diagnosis have been identified as key prognostic factors. Age >3 years at diagnosis correlates with better prognosis [3,28,29,57], possibly due to sparing of radiotherapy as well as reported increased incidence of metastasis in younger patients [10,13,28,57]. Furthermore, patients with rhabdoid tumour predisposition syndrome have been reported to carry a poorer prognosis. The extent to which age is a prognostic factor is still debated, with some groups reporting 50% disease free survival in younger patients [11,47], while another identified age <2 years as a prognostic factor only when combined with M-stage and Claudin 6 immunopositivity [13]. Favourable outcomes have also be linked with supratentorial tumour location [10,13,46,64], while poorer outcomes are reported in the 14–21% of patients presenting with metastases at diagnosis [2,9,28,57].
Extent of surgery is widely reported as a major prognostic indicator in ATRT [19,28,57,68,69], with gross-total resection (GTR) frequently correlated with improved outcomes compared to subtotal (STR), near total (NTR), or partial resections (PR) [10,48]. In one study, GTR and PR patients exhibited a median event free survival (EFS) of 14 months and 9.25 months respectively [28]. Some studies, however, do not report prognostic impact from extent of surgery [2,9,28], while Dufour et al. [13] noted surgical extent was only a prognostic marker in univariate but not multi-variate analysis. These discrepancies highlight the gap in collective prospective data to evaluate the importance of clinical and treatment variables to patient prognosis.
Conventional dose chemotherapy
Conventional dose chemotherapy has been largely non-curative for ATRT patients in first-generation studies including the North American CCG9921 and POG 9923 trials which only observed a 10% EFS [21]. A substantially better 1-year progression-free survival of 53% was reported with use of a sarcoma-based regimen by the Dana-Farber group which included doxorubicin and dactinomycin in a “modified IRS-III” protocol [10]. While some groups have reported benefits of methotrexate and anthracycline based protocols [10,65,69] others have noted no survival differences [16]. Similarly conf licting reports also exist regarding use of platinum and alkylating agent regimens in ATRT [39]. There is no consensus on the most promising and active agents for ATRTs, in part due to the heterogeneous, multiagent therapies frequently administered to ATRT patients, but mostly because large scale clinical trials to robustly examine the relative contribution of these multiple variables have not been possible in this rare disease.
High-dose chemotherapy (HDCT)
HDCT with autologous stem cell rescue (ASCR) was initially adopted to defer cranio-spinal irradiation in patients <3 years, and has become an increasingly popular mainstay of ATRT treatment [16,19,44,52]. High dose methotrexate has been included in some variations in the induction phase of treatment, including the Head Start (HS) II and HS II” studies, followed by consolidation therapy of 1–3 cycles of HDCT with carboplatin, etoposide and thiotepa [15]. Patients enrolled in the earlier HS I regimen (6/6 dead of disease) had worse outcomes than their HDCT HS II counterparts (3/7 alive, no evidence of disease [NED]), notably with long term radiation free survival. Two major registry studies have examined impact of HDCT, with the first noting 46% of patients survived with NED, amongst survivors 50% had GTR and 33% received radiation [28]. In the second, a Canadian registry study, HDCT conferred a survival benefit with 2-year overall survival improved from 27.3±9.5% to 47.9±12.1% compared to conventional chemotherapy treated patients (p=0.036) [38,48]. Although the benefit of HDCT may be difficult to separate from other favorable factors such as GTR and M0 status in 5/9 and 6/9 respectively, it is important to note that both studies demonstrate radiation free survival in a disease classically thought to be incurable. Based on these initial observations, the North American Children’s Oncology group conducted a HDCT prospective ATRT trial; preliminary reports from this ACNS0333 study is promising, with significantly improved survival observed in comparison to CCG9921 and POG9923 studies which used conventional chemotherapy approaches. Tekautz et al. [57] also reported improved survival in children >3 years treated at St. Jude’s Children’s Research Hospital with 4 tandem HDCT regiments and cranio-spinal radiation when compared to historical cohorts. Superior survival with high dose chemotherapy in ATRTs has also been recently reported by Sung et al. [55], who note that increased intensity of HDCT may allow for reduced craniospinal radiation in older children without compromising survival [40,47].
Radiation therapy (RT)
RT is typically deferred, avoided or dose and/or volume reduced in treatment of younger patients with ATRTs in order to avoid the associated neurocognitive toxicity; some protocols have also applied RT in a risk adapted manner [10]. The role of RT in ATRT therapy is hotly debated as mixed results have been reported in national and institutional series. In the Canadian cohort reported by Lafay-Cousin, 6/11 patients were long term survivors after HDCT treatment without any RT [38]. Similarly a German study showed no demonstrable survival benefit of RT on survival [64]. von Hoff et al. [64] also reported no significant difference in patients who received focal versus craniospinal irradiation (n=10, n=19, p=0.578), nor between those who received upfront versus salvage RT (p=0.314), thus suggesting that a group of ATRT patients may not need RT at all. However, Athale et al. [2] reported in a meta-analysis that there was a trend towards greater mean survival time (18.4 months vs. 9.5 months, p=0.097) with RT [2]. Buscariollo et al. [9] similarly reported survival benefit for ATRT patients given RT (p=0.02). Thus, the benefit, dose and volume of RT in ATRT, and the choice of patients in which RT is needed remain unresolved.
Intrathecal (IT) chemotherapy
IT chemotherapy has also been explored both for prophylaxis and treatment of metastatic disease as an alternative to radiation of the CNS axis [2]. Various combinations or single IT agents including methotrexate, cytarabine and/or hydrocortisone have been incorporated into several regimens, including the Dana-Farber ATRT protocol and intra-ventricular methotrexate in the German HIT SKK protocol. Contradictory findings are reported across studies, with a meta-analysis suggesting IT chemotherapy confers survival benefit [2] while other individual studies suggest no additional benefit [39,50,57]. However, as RT and/or HDCT are often applied together with IT chemotherapy in many of these regimens, the contribution of IT therapy alone to outcomes is difficult to discern. Interestingly, an institutional radiation-free treatment protocol at the Hospital for Sick Children in Canada, which uses monoagent IT during induction and in a prolonged maintenance – mirroring the practice in leukemia, has yielded surprising and encouraging survival in patients with M0 or M+ disease without use of RT (Fonseca, McKeown and Huang, 2018 in Prep). If proven to be efficacious in prospective studies, this strategy to spare craniospinal radiation would represent a significant step towards reducing toxicity for ATRT survivors.
MOLECULAR CHARACTERIZATION
Initial genetic screens by Rorke et al. [49] identified monosomy 22 in rhabdoid tumours in 1996, leading to the discovery of SMARCB1 as a major tumour suppressor and etiologic gene in rhabdoid tumours including ATRT [63]. Previous studies suggested that loss of function of hSNF5 does not lead to genomic instability in cancer cell lines [43], which is consistent with recent next generation sequencing studies which show ATRT genomes are highly stable with a very low coding mutation rate [58]. The clinical heterogeneity seen in ATRTs despite its monogenic etiology emphasizes the extent to which epigenetic dysregulation resulting from loss of SWI/SNF components drives this devastating disease.
Recent high resolution molecular studies have begun to reconcile observed clinical heterogeneity with the relatively bland genome of ATRTs by noting substantial heterogeneity in transcriptional and epigenetic profiles. In 2011, Birks et al. [7] identified a subgroup of ATRT with high expression of bone morphological protein (BMP) pathway genes that correlated with shorter survival times. Torchia et al. [59] performed a much larger scale integrated analysis of clinical and transcriptional data from 259 patients and noted two major transcriptional groups of ATRT – one primarily supra-tentorial group characterized by neurogenic differentiation and high ASCL1 protein expression, and a second primarily infra-tentorial group with enriched BMP signatures, which they termed group 1 and group 2 ATRTs respectively. Johann et al. [32] and Torchia et al. [58] subsequently independently reported on genetic, epigenetic and transcriptional characterization of more than 300 patients which revealed ATRTs could be subdivided into three methylation subgroups, with distinct clinical characteristics and targetable pathways (Fig. 1). Patient age distribution within each subtype is similar in both studies, with the lowest median patient age in ATRTtyrosinase (TYR)/group 2A ATRTs while ATRT-MYC/group 2B ATRTs have the broadest patient age range and the most patients above 3 years of age. Neither group noted any subgroup predominance for metastasis or gender, as previously noted. Both the “ATRT-sonic hedgehog (SHH)” and “group 1” ATRTs have primarily neurogenic profiles, with increased Notch expression seen in both cohorts, which may indicate a potential therapeutic target for this subgroup. Though a comprehensive analysis comparing the two studies are pending, the ATRTSHH, ATRT-TYR and ATRT-MYC subgroups seem to correspond with the gene enrichment signatures seen in group 1, group 2A, and group 2B subgroups respectively [32,58]. These high resolution genetic analyses did not reveal any additional recurrent coding alterations, however differences in both global and SMARCB1 genotypes across ATRT subtypes were noted. ATRTSHH/group 1 ATRTs demonstrated a higher frequency of focal alterations on SMARCB1, whereas in contrast the ATRT-MYC/group 2B subgroup harbors broader deletions on chr22q encompassing large portions of SMARCB1 and surrounding genes.
Fig. 1.
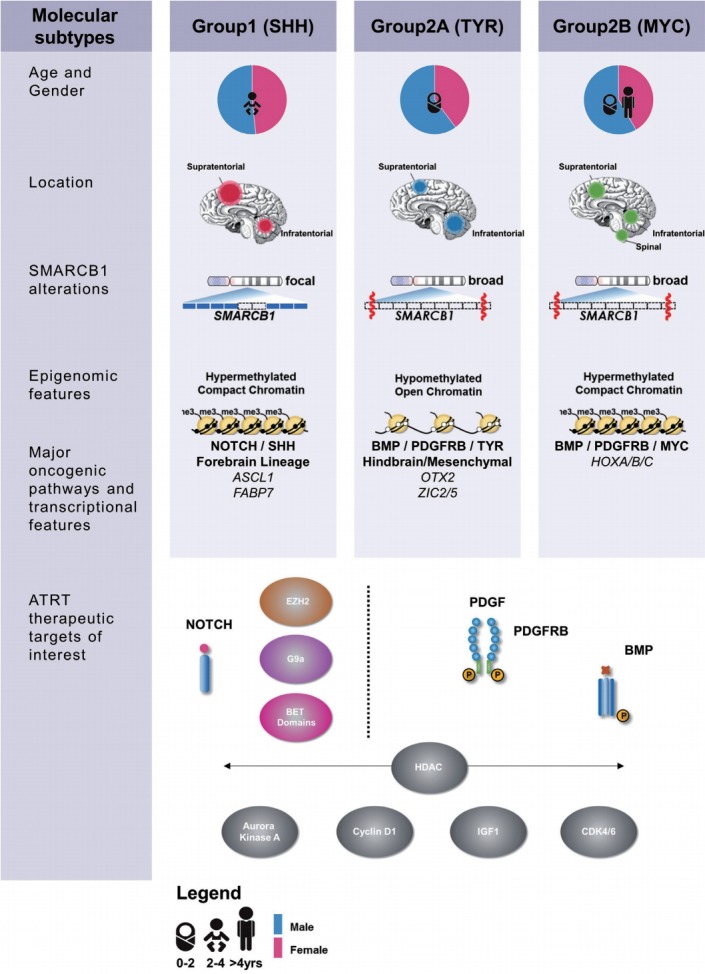
Summary of clinical, epigenetic and therapeutic sensitivity of ATRT subgroups. ATRT-SHH : sonic hedgehog subgroup, ATRT-TYR : tyrosinase subgroup, ATRT-MYC : MYC subgroup.
A recent study by Han et al. [25] created the first transgenic mouse model of ATRT by exploring the temporal deletion/inactivation of Smarcb1. They observed that Smarcb1 knockout at E6–10 resulted mainly in intra-cranial tumours resembling ATRTs, with occasional extracranial tumours reminiscent of malignant rhabdoid tumours (MRTs) [25]. This study reinforces that the epigenetic mechanism associated with hSNF5 loss drives ATRT formation and additionally suggests different targeted cell of origin may contribute to the heterogenous nature of ATRTs. Further studies in Drosophila melanogaster have identified increased expression of upstream regulators of the Hippo signalling pathway when the f ly homolog for SMARCB1 (snr1) was knocked down, denoting an additional potential therapeutic target [31]. Experimental studies have also shown that SMARCB1 loss leads to de-regulated expression of enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (EZH2), a histone methyl transferase which is a critical component of the PRC2 complex that antagonizes SWI/SNF activity during normal development [67]. Importantly, double knockouts of SMARCB1 and EZH2 induced senescence in vitro in MRT cell lines and prevented tumour formation in mice, indicating EZH2 as a promising therapeutic target.
ATRT-BIOLOGY TARGETED THERAPEUTICS
Improvement in ATRT outcomes has come with substantial toxicity associated with intense chemotherapy and/or radiation, therefore further therapy escalation may be difficult using conventional agents. Despite intensification of various modalities, up to 50% of ATRT patients have early disease progression and underscore the heterogeneous tumor biology inherent in this disease. Thus, further improvement in ATRT survival and functional outcome of survivors will need to come from incorporating and combining novel biologics with conventional treatments. To date, a spectrum of epigenetic and signalling inhibitors have been identified based on studies in ATRT or MRT cell lines - many of which are under evaluation in clinical trials.
Epigenetic inhibitors
Given that rhabdoid tumours are almost exclusively an epigenetically driven disease, targeting epigenetic regulatory mechanisms has been of great interest in ATRT and MRT treatment. Previous studies have shown that EZH2 expression is increased and required for tumour progression in hSNF5 deficient tumours [67], and further that EZH2 inhibitors such as EPZ-6438 and 3-deazaneplanocin A prevent proliferation either alone, or in combination with other chemotherapeutics respectively [35,61]. EZH2 inhibitor tazemetostat is currently under evaluation in phase 1 clinical trials for a spectrum of SWI/SNF defective tumors including MRTs and ATRTs. Bromo/BET domain inhibitors such as JQ1 has also been shown to attenuate rhabdoid tumour growth via the Hedgehog pathway [33,56], while other studies have noted success using histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACi) such as trichostatin A, SAHA and SNDX-275 [34]. Torchia et al. [58] investigated a panel of small molecule drug and drug-like epigenetic inhibitors in three group 1 and five group 2 cell lines and observed a distinct sensitivity of group 1 cell lines to UNC1999, UNC0638, and JQ1, while the HDACi LAQ824 reduced proliferation across all eight tested cell lines. Thus, it is likely that specific classes of epigenetic drugs may be more effective against one molecular class of ATRTs versus another.
Targeted and multi-kinase inhibitors
Observations that SMARCB1 loss leads to de-repression of Cyclin D1 [18], and lack of tumor formation in Ccnd1-/- Smarcb1+/- first demonstrated Cyclin D1 was essential for rhabdoid tumour growth presented Cyclin D1 as a promising therapeutic target [60]. These observations were further validated by observation of decreased Cyclin D1 expression and inhibition of rhabdoid tumor growth with combined treatment of the broad CDK inhibitors flavopiridol and tamoxifen [53,54]. These studies have led to evaluation of CDK4/6 inhibitor ribociclib in MRTs with some success in clinical studies [20] and plans for evaluation in an upcoming prospective North American Children's Oncology Group consortia clinical trial for ATRT. Pharmacologic inhibitors of the mitotic serine/threonine kinase Aurora A (also regulated by SWI/SNF, hSNF5) has also been of therapeutic interest [41]. In preclinical studies conducted by the NCI Pediatric Preclinical Testing Program, alisertib (MLN8237), an Aurora A kinase inhibitor exhibited IC50s <100 nM in BT12 and CHLA-266 ATRT cell lines and sensitized these cells to radiation [62]. Preliminary studies in patients with recurrent disease have been promising [66] which has led to an ongoing phase 2 trial evaluating alisertib in recurrent ATRT and MRT at St. Jude’s Children’s Research Hospital.
Due to the highly heterogeneous nature of ATRTs, multi-tyrosine kinase inhibitors (multi-TKIs) are attractive for potentially reducing escape mechanisms or resistance. Imatinib, a first generation multi-TKI, was reported to inhibit cell growth via c-abl in G401 and A204 rhabdoid lines [36]. Similarly in vitro studies of ATRT cell lines have identified dual vascular endothelial growth factor/dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1 (VEGF/MEK) inhibitors sorafenib and sunitinib as promising agents when tested alone or in combination with irinotecan, a topoisomerase I inhibitor [30]. Torchia et al. [58] recently reported that second generation multi-TKIs nilotinib and dasatinib reduced cellular proliferation at nanomolar concentrations specifically in group 2 ATRTs via inhibition of platelet derived growth factor receptor beta (PDGFRβ), which is differentially epigenetically regulated across subgroups. These observations suggest that tumor sub-group context will be important to consider in evaluation of targeted agents. The identification of TKIs with well characterized safety profiles, previous use in pediatric oncology, as well as demonstrated blood brain barrier permeability suggest they are attractive candidates for rapid translation into clinical management of ATRTs.
Growth and lineage specific pathways
Interest in targeting growth and lineage signalling pathways has come from initial observations of an insulin-like growth factor (IGF) autocrine-paracrine loop in ATRTs between IGF-1R and IGF-2 [45], and more recent studies by Torchia et al. [58] which showed ATRT subtype specific cell lines were sensitive to inhibition of NOTCH and BMP signalling. Specifically a role for IGF-IR in ATRT therapies has been supported by knockdown or inhibition of IGF-IR by antisense oligonucleotide as well as treatment with IGF-IR inhibitor NVP-AEW541 which induced death and decreased proliferation in BT12 and BT16 ATRT cell lines [1,12].
Torchia et al. [58] tested the functional significance of subtype specific enrichment of NOTCH and BMP signaling in group 1 and 2 ATRTs and observed that γ-secretase inhibitor DAPT selectively inhibited growth of group 1 ATRT cell lines and reduced expression of NOTCH pathway markers NICD, HES1, and HES5 in a dose-dependent manner. Further, they observed that dorsomorphin, a selective BMP pathway inhibitor, reduced cellular proliferation and expression of BMP markers BAMBI, SOST, and pSMAD1/5 in group 2 cell lines only [58]. These experiments highlight future possibilities of exploiting lineage specific growth dependencies for ATRT therapies.
FUTURE DIRECTIONS
The last two decades have seen incredible advances in the understanding of ATRT biology and promising improvements in treatment of the disease. However, overall survival for ATRT is modest even with current approaches of maximal tolerated dose escalation. With greater understanding of subgroups of ATRTs and their molecular characteristics, more precise, biology-driven therapies can be developed to more effectively treat ATRT patients without unnecessary toxicity.
Identification of molecular classes of ATRTs with different therapeutic susceptibility represents a first step towards refinement in therapy through development and use of drugs matched to group specific biology. Classification of well-established ATRT cell lines into molecular subgroups [58] and progress in development of in vivo models of ATRT [25,26] will continue to critically inform and guide testing of potentially translatable therapies. Stratification in future trials will require not only matching potential therapeutics with sensitive ATRT subtypes but including prognostic impact of subtype with other clinical risk factors. Whether specific ATRT subgroups can be treated with less aggressive therapies and without radiation, and which subgroups require further development of biology-specific treatments remain important, outstanding questions that will require large scale clinical trials. Global collaborative efforts to conduct large prospective cohort trials with robust subtyping and evaluation of prognostic impact will be critical to fully realize the therapeutic potential of risk stratified, biology-tailored ATRT therapies.
Acknowledgments
This project was supported by a Canadian Cancer Society Research Institute Impact Grant (#705056) to AH.
Footnotes
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
INFORMED CONSENT
This type of study does not require informed consent.
References
- 1.Arcaro A, Doepfner KT, Boller D, Guerreiro AS, Shalaby T, Jackson SP, et al. Novel role for insulin as an autocrine growth factor for malignant brain tumour cells. Biochem J. 2007;406:57–66. doi: 10.1042/BJ20070309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Athale UH, Duckworth J, Odame I, Barr R. Childhood atypical teratoid rhabdoid tumor of the central nervous system: a meta-analysis of observational studies. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2009;31:651–663. doi: 10.1097/MPH.0b013e3181b258a9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Bartelheim K, Nemes K, Seeringer A, Kerl K, Buechner J, Boos J, et al. Improved 6-year overall survival in AT/RT-results of the registry study rhabdoid 2007. Cancer Med. 2016;5:1765–1775. doi: 10.1002/cam4.741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Biegel JA. Molecular genetics of atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumors. Neurosurg Focus. 2006;20:1–7. doi: 10.3171/foc.2006.20.1.12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Biegel JA, Zhou JY, Rorke LB, Stenstrom C, Wainwright LM, Fogelgren B. Germ-line and acquired mutations of INI1 in atypical teratoid and rhabdoid tumors. Cancer Res. 1999;59:74–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Bikowska B, Grajkowska W, Józ’wiak J. Atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumor: short clinical description and insight into possible mechanism of the disease. Eur J Neurol. 2011;18:813–818. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-1331.2010.03277.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Birks DK, Donson AM, Patel PR, Dunham C, Muscat A, Algar EM, et al. High expression of BMP pathway genes distinguishes a subset of atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumors associated with shorter survival. Neuro Oncol. 2011;13:1296–1307. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/nor140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Bourdeaut F, Lequin D, Brugières L, Reynaud S, Dufour C, Doz F, et al. Frequent hSNF5/INI1 germline mutations in patients with rhabdoid tumor. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17:31–38. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-1795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Buscariollo DL, Park HS, Roberts KB, Yu JB. Survival outcomes in atypical teratoid rhabdoid tumor for patients undergoing radiotherapy in a surveillance, epidemiology, and end results analysis. Cancer. 2012;118:4212–4219. doi: 10.1002/cncr.27373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Chi SN, Zimmerman MA, Yao X, Cohen KJ, Burger P, Biegel JA, et al. Intensive multimodality treatment for children with newly diagnosed CNS atypical teratoid rhabdoid tumor. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:385–389. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2008.18.7724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Cohen BH, Geyer JR, Miller DC, Curran JG, Zhou T, Holmes E, et al. Pilot study of intensive chemotherapy with peripheral hematopoietic cell support for children less than 3 years of age with malignant brain tumors, the CCG-99703 phase I/II study. a report from the Children’s Oncology Group. Pediatr Neurol. 2015;53:31–46. doi: 10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2015.03.019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.D’cunja J, Shalaby T, Rivera P, von Büren A, Patti R, Heppner FL, et al. Antisense treatment of IGF-IR induces apoptosis and enhances chemosensitivity in central nervous system atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumours cells. Eur J Cancer. 2007;43:1581–1589. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2007.03.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Dufour C, Beaugrand A, Le Deley MC, Bourdeaut F, André N, Leblond P, et al. Clinicopathologic prognostic factors in childhood atypical teratoid and rhabdoid tumor of the central nervous system: a multicenter study. Cancer. 2012;118:3812–3821. doi: 10.1002/cncr.26684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Eaton KW, Tooke LS, Wainwright LM, Judkins AR, Biegel JA. Spectrum of SMARCB1/INI1 mutations in familial and sporadic rhabdoid tumors. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2011;56:7–15. doi: 10.1002/pbc.22831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Fangusaro J, Finlay J, Sposto R, Ji L, Saly M, Zacharoulis S, et al. Intensive chemotherapy followed by consolidative myeloablative chemotherapy with autologous hematopoietic cell rescue (AuHCR) in young children with newly diagnosed supratentorial primitive neuroectodermal tumors (sPNETs): report of the head start I and I. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2008;50:312–318. doi: 10.1002/pbc.21307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Finkelstein-Shechter T, Gassas A, Mabbott D, Huang A, Bartels U, Tabori U, et al. Atypical teratoid or rhabdoid tumors: improved outcome with high-dose chemotherapy. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2010;32:e182–e186. doi: 10.1097/MPH.0b013e3181dce1a2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Frühwald MC, Biegel JA, Bourdeaut F, Roberts CW, Chi SN. Atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumors-current concepts, advances in biology, and potential future therapies. Neuro Oncol. 2016;18:764–778. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/nov264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Fujisawa H, Misaki K, Takabatake Y, Hasegawa M, Yamashita J. Cyclin D1 is overexpressed in atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumor with hSNF5/INI1 gene inactivation. J Neurooncol. 2005;73:117–124. doi: 10.1007/s11060-004-4276-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Gardner SL, Asgharzadeh S, Green A, Horn B, McCowage G, Finlay J. Intensive induction chemotherapy followed by high dose chemotherapy with autologous hematopoietic progenitor cell rescue in young children newly diagnosed with central nervous system atypical teratoid rhabdoid tumors. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2008;51:235–240. doi: 10.1002/pbc.21578. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Geoerger B, Bourdeaut F, DuBois SG, Fischer M, Geller JI, Gottardo NG, et al. A phase I study of the CDK4/6 inhibitor ribociclib (LEE011) in pediatric patients with malignant rhabdoid tumors, neuroblastoma, and other solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 2017;23:2433–2441. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-2898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Geyer JR, Sposto R, Jennings M, Boyett JM, Axtell RA, Breiger D, et al. Multiagent chemotherapy and deferred radiotherapy in infants with malignant brain tumors: a report from the Children’s Cancer Group. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:7621–7631. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2005.09.095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Ginn KF, Gajjar A. Atypical teratoid rhabdoid tumor: current therapy and future directions. Front Oncol. 2012;2:114. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2012.00114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Gonzales M. The 2000 World Health Organization classification of tumours of the nervous system. J Clin Neurosci. 2001;8:1–3. doi: 10.1054/jocn.2000.0829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Haberler C, Laggner U, Slavc I, Czech T, Ambros IM, Ambros PF, et al. Immunohistochemical analysis of INI1 protein in malignant pediatric CNS tumors: lack of INI1 in atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumors and in a fraction of primitive neuroectodermal tumors without rhabdoid phenotype. Am J Surg Pathol. 2006;30:1462–1468. doi: 10.1097/01.pas.0000213329.71745.ef. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Han ZY, Richer W, Fréneaux P, Chauvin C, Lucchesi C, Guillemot D, et al. The occurrence of intracranial rhabdoid tumours in mice depends on temporal control of Smarcb1 inactivation. Nat Commun. 2016;7:10421. doi: 10.1038/ncomms10421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Hashizume R, Gupta N, Berger MS, Banerjee A, Prados MD, Ayers-Ringler J, et al. Morphologic and molecular characterization of ATRT xenografts adapted for orthotopic therapeutic testing. Neuro Oncol. 2010;12:366–376. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/nop033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Hasselblatt M, Gesk S, Oyen F, Rossi S, Viscardi E, Giangaspero F, et al. Nonsense mutation and inactivation of SMARCA4 (BRG1) in an atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumor showing retained SMARCB1 (INI1) expression. Am J Surg Pathol. 2011;35:933–935. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0b013e3182196a39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Hilden JM, Meerbaum S, Burger P, Finlay J, Janss A, Scheithauer BW, et al. Central nervous system atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumor: results of therapy in children enrolled in a registry. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22:2877–2884. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2004.07.073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Ho DMT, Hsu CY, Wong TT, Ting LT, Chiang H. Atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumor of the central nervous system: a comparative study with primitive neuroectodermal tumor/medulloblastoma. Acta Neuropathol. 2000;99:482–488. doi: 10.1007/s004010051149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Jayanthan A, Bernoux D, Bose P, Riabowol K, Narendran A. Multi-tyrosine kinase inhibitors in preclinical studies for pediatric CNS AT/RT: evidence for synergy with topoisomerase-I inhibition. Cancer Cell Int. 2011;11:44. doi: 10.1186/1475-2867-11-44. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Jeibmann A, Eikmeier K, Linge A, Kool M, Koos B, Schulz J, et al. Identification of genes involved in the biology of atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumours using drosophila melanogaster. Nat Commun. 2014;5:4005. doi: 10.1038/ncomms5005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Johann PD, Erkek S, Zapatka M, Kerl K, Buchhalter I, Hovestadt V, et al. Atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumors are comprised of three epigenetic subgroups with distinct enhancer landscapes. Cancer Cell. 2016;29:379–393. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2016.02.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Kerl K, Holsten T, Frühwald MC. Rhabdoid tumors: clinical approaches and molecular targets for innovative therapy. Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2013;30:587–604. doi: 10.3109/08880018.2013.791737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Knipstein JA, Birks DK, Donson AM, Alimova I, Foreman NK, Vibhakar R. Histone deacetylase inhibition decreases proliferation and potentiates the effect of ionizing radiation in atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumor cells. Neuro Oncol. 2012;14:175–183. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/nor208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Knutson SK, Warholic NM, Wigle TJ, Klaus CR, Allain CJ, Raimondi A, et al. Durable tumor regression in genetically altered malignant rhabdoid tumors by inhibition of methyltransferase EZH2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110:7922–7927. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1303800110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Koos B, Jeibmann A, Lünenbürger H, Mertsch S, Nupponen NN, Roselli A, et al. The tyrosine kinase c-Abl promotes proliferation and is expressed in atypical teratoid and malignant rhabdoid tumors. Cancer. 2010;116:5075–5081. doi: 10.1002/cncr.25420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Kordes U, Gesk S, Frühwald MC, Graf N, Leuschner I, Hasselblatt M, et al. Clinical and molecular features in patients with atypical teratoid rhabdoid tumor or malignant rhabdoid tumor. Genes Chromosom Cancer. 2010;49:176–181. doi: 10.1002/gcc.20729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Lafay-Cousin L, Hawkins C, Carret AS, Johnston D, Zelcer S, Wilson B, et al. Central nervous system atypical teratoid rhabdoid tumours: the Canadian Paediatric Brain Tumour Consortium experience. Eur J Cancer. 2012;48:353–359. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2011.09.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Lafay-Cousin L, Strother D. Current treatment approaches for infants with malignant central nervous system tumors. Oncologist. 2009;14:433–444. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2008-0193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Lee J, Kim DS, Han JW, Suh CO. Atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumors in children treated with multimodal therapies: the necessity of upfront radiotherapy after surgery. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2017;64:e26663. doi: 10.1002/pbc.26663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Lee S, Cimica V, Ramachandra N, Zagzag D, Kalpana GV. Aurora A is a repressed effector target of the chromatin remodeling protein INI1/hSNF5 required for rhabdoid tumor cell survival. Cancer Res. 2011;71:3225–3235. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-2167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Louis DN, Perry A, Reifenberger G, von Deimling A, Figarella-Branger D, Cavenee WK, et al. The 2016 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: a summary. Acta Neuropathol. 2016;131:803–820. doi: 10.1007/s00401-016-1545-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.McKenna ES, Sansam CG, Cho YJ, Greulich H, Evans JA, Thom CS, et al. Loss of the epigenetic tumor suppressor SNF5 leads to cancer without genomic instability. Mol Cell Biol. 2008;28:6223–6233. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00658-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Nicolaides T, Tihan T, Horn B, Biegel J, Prados M, Banerjee A. High-dose chemotherapy and autologous stem cell rescue for atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumor of the central nervous system. J Neurooncol. 2010;98:117–123. doi: 10.1007/s11060-009-0071-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Ogino S, Kubo S, Abdul-Karim FW, Cohen ML. Comparative immunohistochemical study of insulin-like growth factor II and insulin-like growth factor receptor type 1 in pediatric brain tumors. Pediatr Dev Pathol. 2001;4:23–31. doi: 10.1007/s100240010112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Pai Panandiker AS, Merchant TE, Beltran C, Wu S, Sharma S, Boop FA, et al. Sequencing of local therapy affects the pattern of treatment failure and survival in children with atypical teratoid rhabdoid tumors of the central nervous system. Int J Radiat Oncol. 2012;82:1756–1763. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2011.02.059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Park ES, Sung KW, Baek HJ, Park KD, Park HJ, Won SC, et al. Tandem high-dose chemotherapy and autologous stem cell transplantation in young children with atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumor of the central nervous system. J Korean Med Sci. 2012;27:135–140. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2012.27.2.135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Picard D, Miller S, Hawkins CE, Bouffet E, Rogers HA, Chan TS, et al. Markers of survival and metastatic potential in childhood CNS primitive neuro-ectodermal brain tumours: an integrative genomic analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2012;13:838–848. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(12)70257-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Rorke LB, Packer RJ, Biegel JA. Central nervous system atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumors of infancy and childhood: definition of an entity. J Neurosurg. 1996;85:56–65. doi: 10.3171/jns.1996.85.1.0056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Schrey D, Carceller Lechón F, Malietzis G, Moreno L, Dufour C, Chi S, et al. Multimodal therapy in children and adolescents with newly diagnosed atypical teratoid rhabdoid tumor: individual pooled data analysis and review of the literature. J Neurooncol. 2016;126:81–90. doi: 10.1007/s11060-015-1904-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Sévenet N, Sheridan E, Amram D, Schneider P, Handgretinger R, Delattre O. Constitutional mutations of the hSNF5/INI1 gene predispose to a variety of cancers. Am J Hum Genet. 1999;65:1342–1348. doi: 10.1086/302639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Shih CS, Hale GA, Gronewold L, Tong X, Laningham FH, Gilger EA, et al. High-dose chemotherapy with autologous stem cell rescue for children with recurrent malignant brain tumors. Cancer. 2008;112:1345–1353. doi: 10.1002/cncr.23305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Smith ME, Cimica V, Chinni S, Challagulla K, Mani S, Kalpana GV. Rhabdoid tumor growth is inhibited by flavopiridol. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14:523–532. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-1347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Smith ME, Cimica V, Chinni S, Jana S, Koba W, Yang Z, et al. Therapeutically targeting cyclin D1 in primary tumors arising from loss of Ini1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108:319–324. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0913297108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Sung KW, Lim DH, Yi ES, Choi YB, Lee JW, Yoo KH, et al. Tandem highdose chemotherapy and autologous stem cell transplantation for atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumor. Cancer Res Treat. 2016;48:1408–1419. doi: 10.4143/crt.2015.347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Tang Y, Gholamin S, Schubert S, Willardson MI, Lee A, Bandopadhayay P, et al. Epigenetic targeting of hedgehog pathway transcriptional output through BET bromodomain inhibition. Nat Med. 2014;20:732–740. doi: 10.1038/nm.3613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Tekautz TM, Fuller CE, Blaney S, Fouladi M, Broniscer A, Merchant TE, et al. Atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumors (ATRT): improved survival in children 3 years of age and older with radiation therapy and high-dose alkylator-based chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:1491–1499. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2005.05.187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Torchia J, Golbourn B, Feng S, Ho KC, Sin-Chan P, Vasiljevic A, et al. Integrated (epi)-genomic analyses identify subgroup-specific therapeutic targets in CNS rhabdoid tumors. Cancer Cell. 2016;30:891–908. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2016.11.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Torchia J, Picard D, Lafay-Cousin L, Hawkins CE, Kim SK, Letourneau L, et al. Molecular subgroups of atypical teratoid rhabdoid tumours in children: an integrated genomic and clinicopathological analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16:569–582. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(15)70114-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Tsikitis M, Zhang Z, Edelman W, Zagzag D, Kalpana GV. Genetic ablation of cyclin D1 abrogates genesis of rhabdoid tumors resulting from Ini1 loss. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102:12129–12134. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0505300102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Unland R, Borchardt C, Clemens D, Kool M, Dirksen U, Frühwald MC. Analysis of the antiproliferative effects of 3-deazaneoplanocin A in combination with standard anticancer agents in rhabdoid tumor cell lines. Anticancer Drugs. 2015;26:301–311. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0000000000000181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Venkataraman S, Alimova I, Tello T, Harris PS, Knipstein JA, Donson AM, et al. Targeting aurora kinase A enhances radiation sensitivity of atypical teratoid rhabdoid tumor cells. J Neurooncol. 2012;107:517–526. doi: 10.1007/s11060-011-0795-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Versteege I, Sévenet N, Lange J, Rousseau-Merck MF, Ambros P, Handgretinger R, et al. Truncating mutations of hSNF5/INI1 in aggressive paediatric cancer. Nature. 1998;394:203–206. doi: 10.1038/28212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.von Hoff K, Hinkes B, Dannenmann-Stern E, von Bueren AO, Warmuth-Metz M, Soerensen N, et al. Frequency, risk-factors and survival of children with atypical teratoid rhabdoid tumors (AT/RT) of the CNS diagnosed between 1988 and 2004, and registered to the German HIT database. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2011;57:978–985. doi: 10.1002/pbc.23236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Weinblatt M, Kochen J. Rhabdoid tumor of the central. Med Pediatr Oncol. 1992;20:258. doi: 10.1002/mpo.2950200317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Wetmore C, Boyett J, Li S, Lin T, Bendel A, Gajjar A, et al. Alisertib is active as single agent in recurrent atypical teratoid rhabdoid tumors in 4 children. Neuro Oncol. 2015;17:882–888. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/nov017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Wilson BG, Wang X, Shen X, McKenna ES, Lemieux ME, Cho Y, et al. Epigenetic antagonism between polycomb and SWI/SNF complexes during oncogenic transformation. Cancer Cell. 2010;18:316–328. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2010.09.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Woehrer A, Slavc I, Waldhoer T, Heinzl H, Zielonke N, Czech T, et al. Incidence of atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumors in children: a populationbased study by the Austrian Brain Tumor Registry, 1996-2006. Cancer. 2010;116:5725–5732. doi: 10.1002/cncr.25540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Zimmerman MA, Goumnerova LC, Proctor M, Scott RM, Marcus K, Pomeroy SL, et al. Continuous remission of newly diagnosed and relapsed central nervous system atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumor. J Neurooncol. 2005;72:77–84. doi: 10.1007/s11060-004-3115-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


