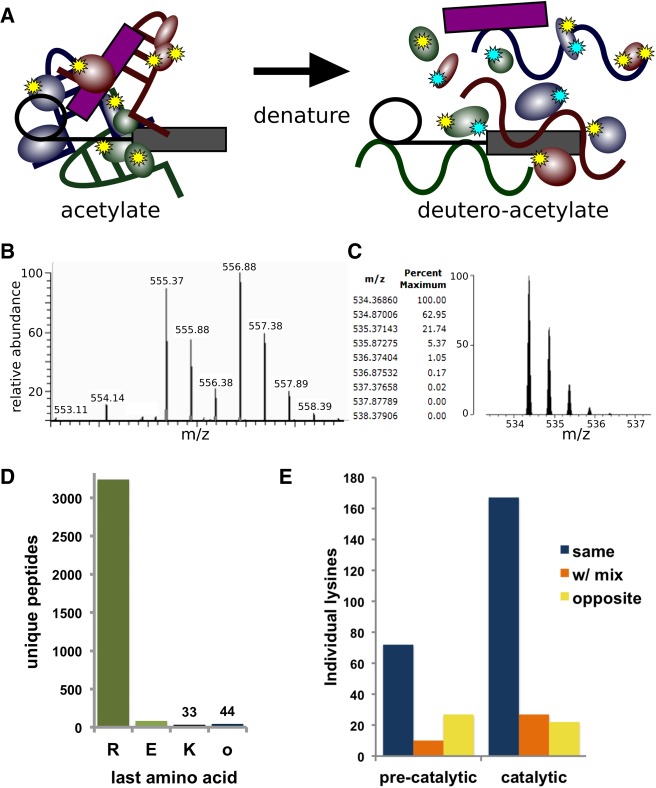
FIGURE 1.
Two-step lysine probing of spliceosomes. (A) Schematic of probing strategy: First lysines in native spliceosomes are modified by acetylation (yellow stars), and then following denaturation are modified with a deutero-acetylating reagent (cyan stars). (B) Sample MS spectra containing two doubly charged peptides of m/z 555.37 and m/z 556.88 corresponding to the peptide VLIGVGKLLR from splicing factor 3B subunit 3. In the m/z 555.37 version, the lysine is modified with an acetyl group, whereas in the m/z 556.88 version, the lysine is modified with a deuteron-acetyl group, leading to a 3 Dalton mass difference. (C) Theoretical modeling of the predicted isotope pattern for the lighter version using MS-Isotope (Chalkley et al. 2005) indicates a fourth isotope peak would contribute 5% peak intensity to the first isotope of the deuterated monoisotopic peak signal, and have an insignificant effect on overall quantification. (D) Frequency of C-terminal amino acid identity for all unique MS/MS measured peptides from precatalytic and catalytic spliceosomes. (E) Frequency of individual lysines identified with the same, mixed, or opposite modification state between replicate samples of preactivated and catalytic spliceosomes.