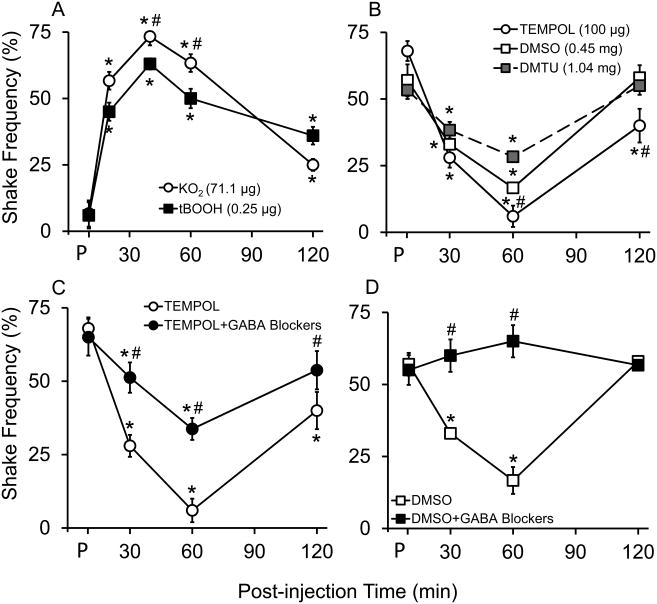
Figure 2.
Specific reactive oxygen species (ROS) subtype donors and scavengers affect pain behaviors of naïve and neuropathic mice in different magnitudes. Behavioral responses of 10 weeks old C57BL/6 mice to VFF (# 3.00 = 0.1 g force) stimulations at pre-drug (P) and post-intrathecal drug injections (5 μL). (A) Superoxide radical donor (KO2; 71.1 μg, N=6) induced greater hyperalgesia than hydroxyl radical donor (tBOOH; 0.25 μg, N=6) in naïve mice. (B) Superoxide radical scavenger (TEMPOL; 100 μg, N=8) induced greater anti-hyperalgesia than hydroxyl radical scavengers (DMSO; 0.45 mg and DMTU; 1.04 mg, N=8) in neuropathic mice. (C) Combination of GABAA (Bicuculline, 1 μg) and GABAB (CGP46381, 0.5 μg) receptor antagonists partially blocked TEMPOL's anti-hyperalgesic effect in neuropathic mice (N=8). (D) The GABA receptor antagonists completely blocked DMSO's anti-hyperalgesic effect in neuropathic mice (N=8). Data were analyzed by 2-way repeated measures ANOVA followed by Holm-Sidak multiple comparison test; values at multiple time points within a group were compared with the group's pre-drug value (P). Effects of ROS scavengers on pain behaviors were compared between treatments at each time point. Data were presented as mean ± SEM (*, different from pre-drug within a treatment; #, different between treatments, P<0.05).