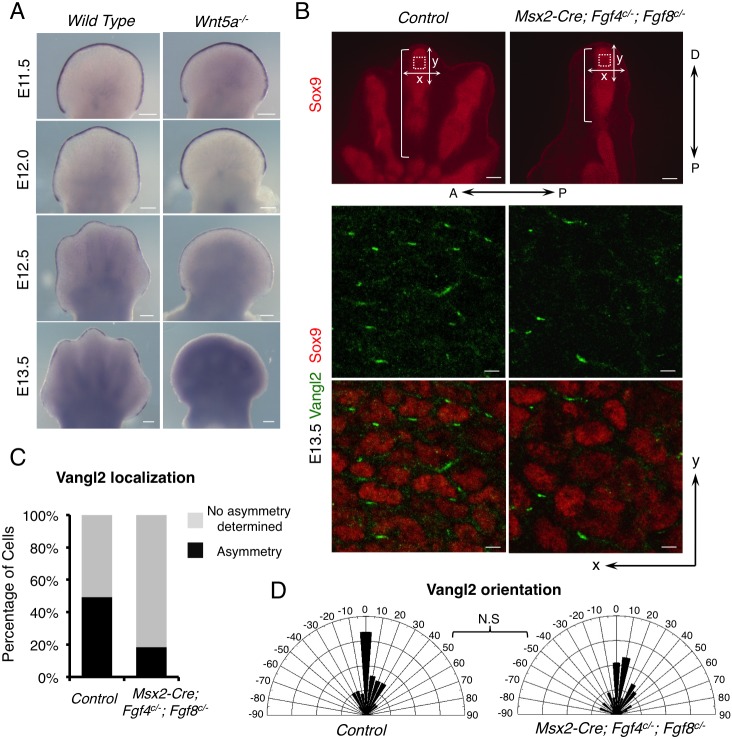
Fig. 1.
Fgfs from the AER are required for full PCP in limb development. (A) Whole-mount in situ hybridization of Fgf8 in wild-type and Wnt5a−/− embryonic forelimbs. (B) Compromised Vangl2 asymmetrical localization in distal digits of E13.5 Msx2-Cre; Fgf4c/−; Fgf8c/− forelimbs. The boxed regions were subjected to confocal scanning. Enlarged images of part of the scanned regions are shown in the middle and lower panels. Vangl2 (green) and Sox9 (red) protein are shown by fluorescence immunostaining. The brackets indicate the length of digits. Proximal-distal (P-D) and anterior-posterior (A-P) axes are indicated. x-and y-axes of the images are defined as shown in the upper panel. (C) The percentage of cells with discernible Vangl2 asymmetric localization in control and mutant limbs. (D) Schematics summarizing the quantification of orientation angles of Vangl2. x-axis, angle of orientation (−90° to 90°); y-axis, percentage of cells at angle x. Kolmogorov–Smirnov test, N.S, no significance. (C,D) Number of samples and number of cells analyzed for each genotype: control, N=3, n=325; Msx2-Cre; Fgf4c/−; Fgf8c/−, N=5, n=450. Scale bars: 200 μm (A, upper panel of B); 10 μm (middle and bottom panels of B).