The fifth author is listed incorrectly in the citation. The correct citation is: Xu Y, Shoamanesh A, Schulman S, Dowlatshahi D, Al-Shahi Salman R, Moldovan ID, et al. (2018) Oral anticoagulant re-initiation following intracerebral hemorrhage in non-valvular atrial fibrillation: Global survey of the practices of neurologists, neurosurgeons and thrombosis experts. PLoS ONE 13(1): e0191137. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0191137.
An incorrect file was used for Fig 1. Please see the complete, correct Fig 1 here.
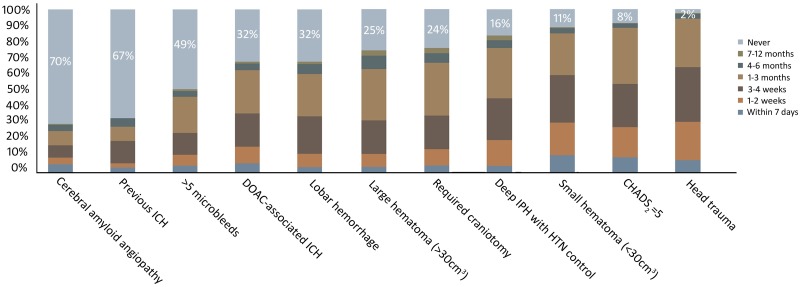
Fig 1. Overall response from survey participants on timing of OAC re-initiation across 11 clinical scenarios.
ICH, intracerebral haemorrhage; DOAC, direct oral anticoagulants; IPH, intraparenchymal haemorrhage; HTN, hypertension; CHADS2, Congestive heart failure, hypertension, age (≥75), diabetes, stroke/TIA score.
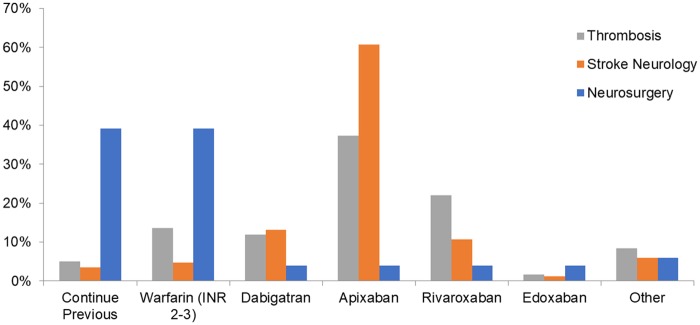
The images for Figs 2 and 3 are incorrectly switched. The image that appears as Fig 2 should be Fig 3, and the image that appears as Fig 3 should be Fig 2. The figure captions appear in the correct order.
Fig 2. Choice of anticoagulant for re-initiation across thrombosis experts, stroke neurologists and neurosurgeons.
Fig 3. Rates of neuro-imaging utilization for risk stratification among patients with anticoagulant-associated ICH across specialties.
Intracranial vessel imaging includes CT angiography, MR angiography or Digital Subtraction Angiography.
Reference
- 1.Xu Y, Shoamanesh A, Schulman S, Dowlatshahi D, Salman RA-S, Moldovan ID, et al. (2018) Oral anticoagulant re-initiation following intracerebral hemorrhage in non-valvular atrial fibrillation: Global survey of the practices of neurologists, neurosurgeons and thrombosis experts. PLoS ONE 13(1): e0191137 https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0191137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]