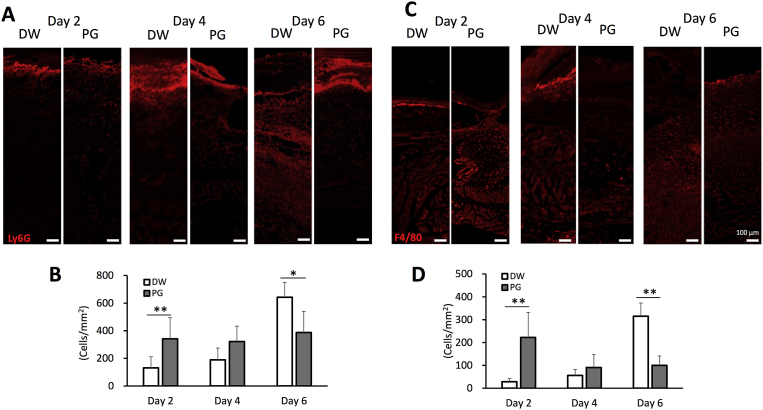
Fig. 3.
Effect of PG on recruitment of neutrophils and macrophages to S. aureus-inoculated wounds. Mice were inoculated with 20 μL of 2.5 × 109 CFU/mL of S. aureus at the sites of skin wound immediately after wounding, and then treated with 10 μL of 10 mg/mL PG daily. On days 2, 4 and 6 after infection, the skin tissues were collected and frozen sections were prepared. Immunofluorescent staining was performed using anti-Ly6G antibody for neutrophils (A) and anti-F4/80 antibody for macrophages (C). Ly6G+ cells (B) and F4/80+ cells (D) were randomly counted from eight histological sections. The data are representative of 2 independent experiments (4 mice per group per each experiment) (B, D). An asterisk (p < 0.05) and double asterisks (p < 0.01) indicate that the value is significantly different from the control group, respectively.