SUMMARY
Stromal cells (SCs) establish the compartmentalization of lymphoid tissues critical to the immune response. However, the full diversity of lymph node (LN) SCs remains undefined. Using droplet-based single-cell RNA sequencing, we identified nine peripheral LN non-endothelial SC clusters. Included are the established subsets, Ccl19hi T-zone reticular cells (TRCs), marginal reticular cells, follicular dendritic cells (FDCs), and perivascular cells. We also identified Ccl19lo TRCs, likely including cholesterol-25-hydroxylase+ cells located at the T-zone perimeter, Cxcl9+ TRCs in the T-zone and interfollicular region, CD34+ SCs in the capsule and medullary vessel adventitia, indolethylamine N-methyltransferase+ SCs in the medullary cords, and Nr4a1+ SCs in several niches. These data help define how transcriptionally distinct LN SCs support niche-restricted immune functions and provide evidence that many SCs are in an activated state.
Graphical abstract
In Brief: Lymph node stromal cells support diverse processes, but bulk assessments obscure their niche-specific functions. Rodda et al. identify transcriptional profiles for nine lymph node stromal cell clusters using single-cell RNA sequencing, validate subset markers in situ, and suggest niche-restricted functions.
INTRODUCTION
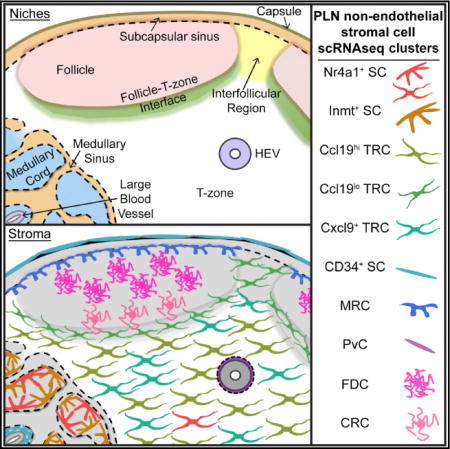
Lymph nodes (LNs) are organized into discrete niches to support the efficient antigen encounter and lymphocyte activation required for an effective adaptive immune response (Mueller and Germain, 2009). The stromal cells (SCs) that pattern these niches in reticular networks contribute to the structural and functional specificity of the niche by influencing lymphocyte migration, survival, antigen encounter, and tolerance (Chang and Turley, 2015; Schulz et al., 2016).
Follicular SCs, including CR2+ antigen-trapping follicular dendritic cells (FDCs) and TNFSF11+ marginal reticular cells (MRCs), express the chemokine CXCL13 and guide B cells to LN follicles. FDCs are positioned at the follicle center and the MRCs sit at the edge of the follicle adjacent to the subcapsular sinus (SCS) (Cyster et al., 2000; Katakai et al., 2008). During an immune response, light zone (LZ) FDCs and dark zone (DZ) CXCL12-expressing reticular cells (CRCs) emerge and support the respective germinal center (GC) niches (Bannard et al., 2013; Rodda et al., 2015). The transcriptional programs that control the specialized functions of follicular SCs are unknown.
CCL21- and CCL19-expressing SCs in the T-zone, termed T-zone reticular cells (TRCs), attract CCR7+ lymphocytes (Cyster, 2005). TRCs also produce trophic factors such as interleukin-7 (IL-7) and maintain the extracellular matrix (ECM)-rich conduit network that allows rapid diffusion of small molecules throughout the LN (Link et al., 2007; Mueller and Germain, 2009). During an immune response, activated B and T cells meet at the follicle-T-zone interface, but it is unclear whether SCs in this region differ from TRCs (Katakai et al., 2008).
Lymphocytes enter LNs through specialized blood vessels called high endothelial venules (HEVs). Many blood vessels in LNs are associated with ITGA7+ perivascular cells (PvCs) (Girard et al., 2012). CD34+ adventitial cells (ACs) may further support large vessels in the LN medulla (Díaz-Flores et al., 2014). Lymphocytes exit the LN through the medulla, where lymphatic sinuses weave around medullary cords. The cords are populated by medullary reticular cells (MedRCs), macrophages, and plasma cells. MedRCs highly express CXCL12 (Hargreaves et al., 2001), but little else is known about them.
The Immgen consortium has reported gene expression profiles for two SC and two endothelial cell subsets in LNs: PDPN+CD31− fibroblastic reticular cells (FRCs), PDPN− CD31− double-negative cells (DNCs), PDPN+CD31+ lymphatic endothelial cells (LECs), and PDPN− CD31+ blood endothelial cells (BECs) (Malhotra et al., 2012). While this work provides important insight into the possible contributions of SCs to LN function, niche-restricted stromal roles remain obscured because TRCs, MRCs, FDCs, and MedRCs all fall into the FRC subset.
To investigate the heterogeneity of LN SCs, we analyzed single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNAseq) of peripheral LN (pLN) non-endothelial SCs. We identified nine clusters of SCs previously partitioned into the FRC and DNC populations. We associated eight clusters with specific niches and validated markers identified in our dataset for MedRCs and FDCs.
RESULTS
Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Reveals Nine pLN Non-endothelial SC Clusters
We performed droplet-based scRNAseq on isolated mouse pLN CD45−CD31− cells from uninfected mice and mice at day 15 post-infection with LCMV-Armstrong (Figure 1A). After quality control, we retained 2,870 cells with 2,153 median genes per cell from the uninfected LNs and 12,669 cells with 1,938 median genes per cell from the post-infection LNs. After initial unsupervised clustering with Seurat (Satija et al., 2015) to select the >95.1% of non-endothelial SCs in Pdgfrb+ and/or Pdgfra+ clusters for further analysis, we combined the samples to investigate conserved heterogeneity.
Figure 1. Identification of Nine pLN Non-endothelial SC Clusters by scRNAseq.
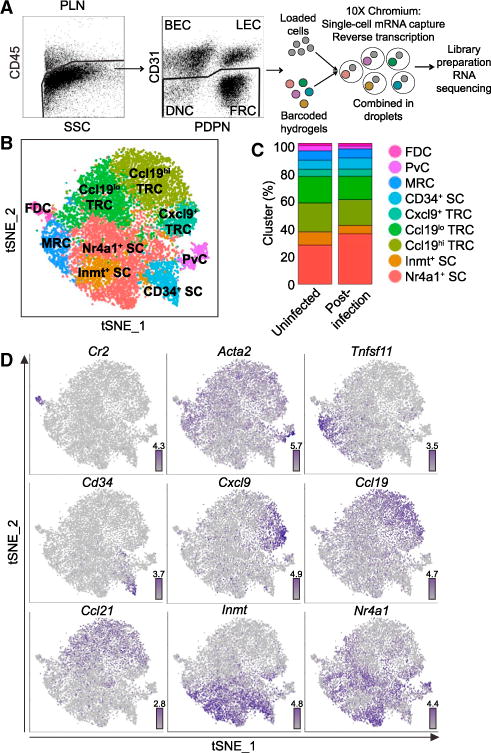
(A) Droplet-based scRNAseq workflow.
(B) Unsupervised clustering of pLN non-endothelial SCs visualized with tSNE. Each point is a single cell colored by cluster assignment.
(C) Percent of the nine clusters in two samples: Uninfected and day 15 post-LCMV infection (Post-infection).
(D) Gene expression distinguishing the nine clusters projected onto tSNE plots. Color scaled for each gene with highest log-normalized expression level noted.
See also Figure S1.
We chose to analyze pLN SCs on day 15 after infection with LCMV-Armstrong because the virus induces large GCs with LZ FDCs and DZ CRCs. Although SCs are diminished in the early days after LCMV infection, we decided it was appropriate to combine the samples because by day 15 the virus has been cleared, the percentage of CD45−VCAM1+PDPN+ SCs has almost recovered, the B and T zone organization is normal, and the expression of Cxcl13, Ccl19, and Ccl21 by the post-infection SCs is within 3-fold of the uninfected SCs (Figure S1A; Mueller et al., 2007; Rodda et al., 2015; Scandella et al., 2008). The mean expression of variable genes by cells in the two samples was also highly correlated (r = 0.99, p value < 2.2 × 10−16, Pearson) (Figure S1B).
Employing diagonal canonical correlation analysis (CCA) to combine the samples, we identified a shared gene correlation structure that explained more than 50% of the variance of 94.1% and 96.8% of cells from the uninfected and post-infection samples, respectively (Butler and Satija, 2017). The 14,243 cells adequately described by the structure were then aligned for clustering analysis. The removed cells came from both samples and 12.2% of the removed cells were enriched for cell cycle gene expression (cell cycle score > 0.1) compared to 0.39% of the remaining cells. Of the removed cycling cells, 98.5% were from the post-infection sample (Figure S1C).
Performing unsupervised clustering on the combined samples revealed nine conserved clusters, which we visualized with tSNE and a hierarchical cluster tree (Figures 1B and S1D). We chose this clustering resolution because higher resolutions did not reveal linearly increasing numbers of clusters. Cells from both samples contributed to each cluster, suggesting that the clustering was not due to sample batch effect (Figure S1E). In addition, the mean expression profile for each cluster was highly correlated between the two samples (r > 0.97, p value < 2.2 × 10−16, Pearson) and the cluster composition of each sample was similar (Figure 1C). We have included the mean gene expression profiles for each cluster for the 16,775 detected genes (Table S1).
We identified differentially expressed genes (DEGs) (log2-fold change > 0.5, FDR < 0.05, proportion of cluster expressing > 0.10) for each cluster calculated as the difference between the average expression by cells in the cluster and the average expression by cells not in the cluster (Tables S2, S3, S4, S5, S6, S7, and S8). While the clusters could represent distinct cell types or cell states, the DEGs suggested assignment of several of the clusters to the previously described niche-associated SC types Ccl21+ TRCs, Tnfsf11+ MRCs, Itga7+ Acta2+ PvCs, and Cr2+ FDCs (Figure 1D). The proportions of these cells corresponded to expectations based on sectioning and flow cytometric studies (Figure 1C; Jarjour et al., 2014; Link et al., 2007). The remaining clusters represented unappreciated heterogeneity and were distinguished as Inmt+Cd34−Tnfsf11− SCs (Inmt+ SCs), Cd34+ SCs (CD34+ SCs), Nr4a1+ SCs (Nr4a1+ SCs), and three subsets of TRCs: Ccl21+Ccl19hiIl7+ TRCs (Ccl19hi TRCs), Ccl21+Ccl19loIl7+ TRCs (Ccl19lo TRCs), and Ccl21+Ccl19loIl7+ Cxcl9+ TRCs (Cxcl9+ TRCs) (Figure 1D). Notably, historically used pLN non-endothelial SC markers, such as Pdpn, Pdgfra, and Pdgfrb, were insufficient to distinguish the clusters (Figure 2A). Since each cluster had at least 50 DEGs (Figure 2B), we have highlighted 10 marker candidates per subset using stricter thresholds (log2-fold change > 1, FDR < 0.05, proportion of cluster expressing > 0.20) (Figures 2C and S2). We proceeded to investigate the distinctive features of each pLN non-endothelial SC cluster.
Figure 2. Differential Gene Expression for Nine pLN Non-endothelial SC Clusters.
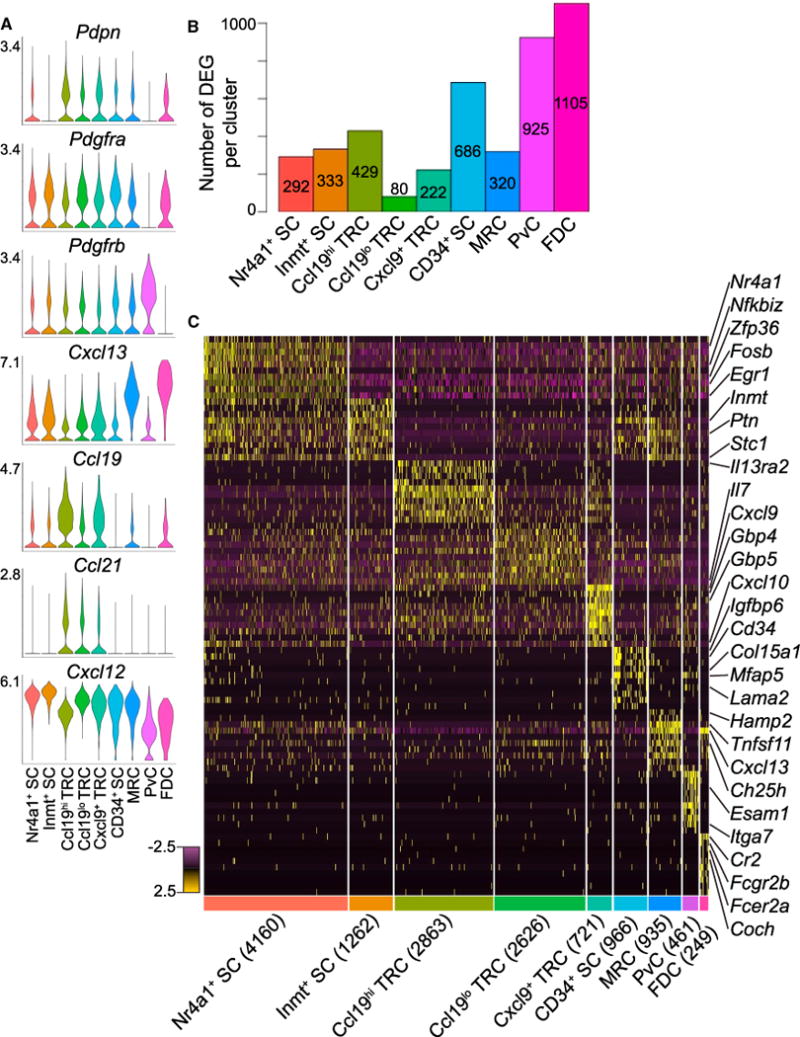
(A) Violin plots of canonical SC gene expression by cluster with highest log-normalized expression value labeled.
(B) Number of DEGs per cluster.
(C) Heatmap of each cell’s (columns) expression of the top ten DEGs per cluster (rows). Select genes are labeled. Log-normalized expression scaled for each gene. Cluster name and number of cells per cluster displayed below.
See also Figure S2.
Ccl19hi TRC DEGs Suggest Additional Mechanisms for Lymphocyte Support and Conduit Maintenance
TRCs support the LN T-zone and have been among the most in-depth studied LN SCs (Mueller and Germain, 2009). The Ccl19hi TRC cluster differentially expressed genes previously associated with TRCs as well as unappreciated genes for surface and secreted molecules (Figure S3A, Table S2). While Ccl19hi TRCs expressed Pdpn shown to support DC motility and LN expansion (Acton et al., 2014; Astarita et al., 2015), they also distinctly expressed Cx3cl1, the chemokine ligand for CX3CR1+ activated CD8+ T cells, monocytes, and recently described T-zone macrophages (Figures 2A and S3A; Baratin et al., 2017). CX3CL1 has been detected in the LN T-zone, SCS, and interfollicular regions (IFR), but has not been attributed to TRCs (Johnson and Jackson, 2013; Kanazawa et al., 1999). Ccl19hi TRCs were also enriched for expression of Il13ra2, an IL-13 decoy receptor that could limit T-zone IL-13 (Fichtner-Feigl et al., 2006), and Il4i1, an L-amino acid oxidase that can inhibit the CD8+ T cell anti-tumor response in vivo (Figure S3A; Lasoudris et al., 2011).
TRCs make critical components of the reticular conduit network and themselves ensheath the conduits (Mueller and Germain, 2009). Highlighted previously as expressed by FRCs, Ccl19hi TRCs were enriched for collagen 14 (Col14a1) and fibromodulin (Fmod), components of the conduit core (Figure S3A; Malhotra et al., 2012). Ccl19hi TRCs expressed desmocolin-2 (Dsc2), a cadherin-type protein that links adjacent cells via desmosomes (Figure S3A; Jarjour et al., 2014). A portion of Ccl19hi TRCs expressed the latrophilin adhesion-type GPCR Adgrl3 and one of its ligands, Flrt3, which may support adhesion between Ccl19hi TRCs (Figure S3A, Table S2; O’Sullivan et al., 2012).
Ccl19hi TRC DEGs suggest mechanisms of Ccl19hi TRC development and maintenance. TNF family molecules have strong influences on TRCs (Cyster, 2005) and Ccl19hi TRCs expressed Nradd and shared Relt and Cd200 expression with FDCs (Figure S3A). Ccl19hi TRCs distinctly expressed Fabp7, a transport protein that may deliver lipids to nuclear hormone receptors and has been shown to be restricted to LN TRCs in situ (Figure S3A; Tokuda et al., 2010). Finally, Ccl19hi TRCs were enriched for expression of the transcription factors SpiC, Tead2, and Yeats4 among others (Figure S3A). The Ccl19hi TRC DEGs support this subset fulfilling the known TRC roles in chemotaxis to the T-zone, trophic support for T cells and DCs and building the conduit matrix while suggesting additional mechanisms to achieve these functions.
Ch25h-Expresssing Ccl19lo TRCs Populate the Follicle T-Zone Interface and IFRs
Ccl19lo TRCs expressed Ccl21, Il7, and Cxcl13, features of both the T cell zone and B cell follicle (Figures 2A and S3A). In addition, relative to Ccl19hi TRCs, they expressed high Tnfsf13b (Baff) (Figure 3A), a cytokine critical for B cell survival and non-redundantly produced by non-FDC FRCs (Wang et al., 2012; Cremasco et al., 2014), suggesting that Ccl19lo TRCs might occupy a niche that is engaged by migrating B cells such as the follicle T-zone interface.
Figure 3. Ch25h-Expressing Ccl19lo TRCs Populate the Follicle-T-Zone Interface and IFRs.
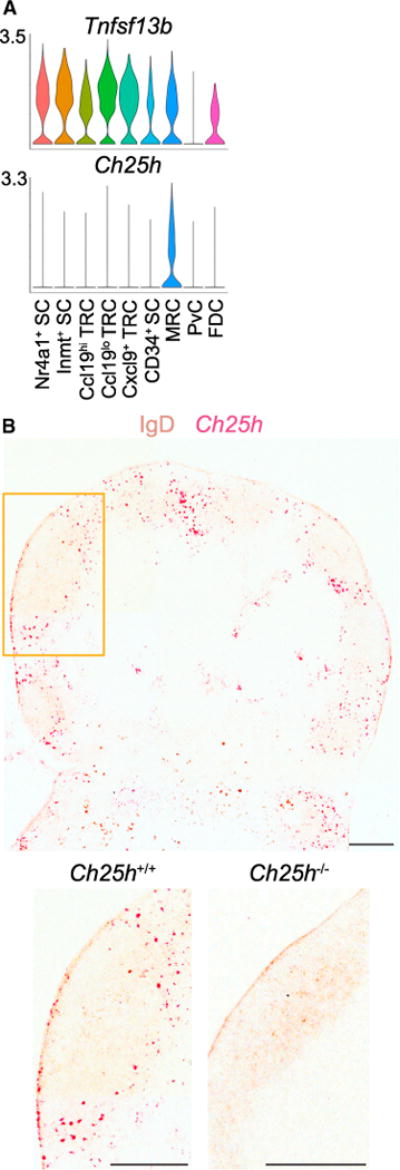
(A) Violin plots of cluster Tnfsf13b and Ch25h expression.
(B) RNAscope for Ch25h on Ch25h+/+ (box indicates enlarged area) and Ch25h−/− (enlarged only) pLNs counterstained for IgD. Representative of three mice per genotype. Scale bar is 200 μm.
See also Figure S3.
Cholesterol-25-hydroxylase (Ch25h) was expressed by a portion of Ccl19lo TRCs (log2-fold change = 0.68, FDR = 2.4 × 10−4, proportion of cluster expressing = 0.21) along with MRCs (log2-fold change = 2.83, FDR = 1.99 × 10−51, proportion of cluster expressing = 0.51) (Figure 3A, Table S2). Ccl19lo TRCs are not highlighted in the violin plot because the visualization has a higher cutoff for proportion of a cluster expressing a gene than our DEG cutoff. Stromal expression of this enzyme is important for generation of the EBI2 (GPR183) ligand 7α,25-HC to guide activated B cells, T cells, and DCs to the follicle T-zone interface and IFRs (Cyster et al., 2014; Li et al., 2016; Lu et al., 2017). Using RNAscope on pLNs and mesenteric LNs (mLNs), Ch25h was detected highly expressed by cells at the follicle-T-zone interface and in IFRs, as has been shown in spleen (Figures 3B and S3B; Lu et al., 2017). Ch25h expression was also found adjacent to the SCS in accordance with MRC expression and in ring-like structures in the T-zone in accordance with HEV expression (Figures 3B and S3B; Lee et al., 2014). Ch25h+Ccl19lo TRCs likely correspond to the Ch25h-expressing cells positioned at the follicle-T-zone interface and in IFRs, functioning to guide EBI2+ cells to these niches. While the low percentage of Ccl19lo TRCs with detectable Ch25h expression could reflect low expression of the enzyme, it likely indicates that Ccl19lo TRCs include Ch25h− cells that support other T-zone-adjacent niches. Determining whether this is the case will require additional marker assessment.
Cxcl9+ TRCs Are Likely Activated TRCs in the T-Zone and IFRs
While Cxcl9+ TRCs expressed Ccl21 and Il7 and differentially expressed Ccl19 suggestive of TRCs (Figures 2A and S3A), they were most distinguished by Cxcl9 and Cxcl10, the ligands for CXCR3, and MHCII-related gene expression (Figure 4A, Table S2). To validate pLN stromal Cxcl9 and Cxcl10 expression and localize Cxcl9+ TRCs in pLNs, we analyzed pLN stroma from REX3 mice, which express Cxcl9-driven RFP and Cxcl10-driven BFP (Groom et al., 2012). By flow cytometry (FC), portions of each classical subset (FRC, DNC, BEC, LEC) expressed the chemokines and 35.5% (SEM = 0.69%) of non-endothelial SCs (FRC and DNC) expressed both CXCL9 and CXCL10 (Figure 4B). While this is higher than the 10.6% of Cxcl9- and Cxcl10-expressing cells in our scRNAseq dataset (Table S2), the difference may reflect an underestimate due to the low mRNA capture per cell in scRNAseq.
Figure 4. Cxcl9+ TRCs Are Located in the T-Zone and IFRs.
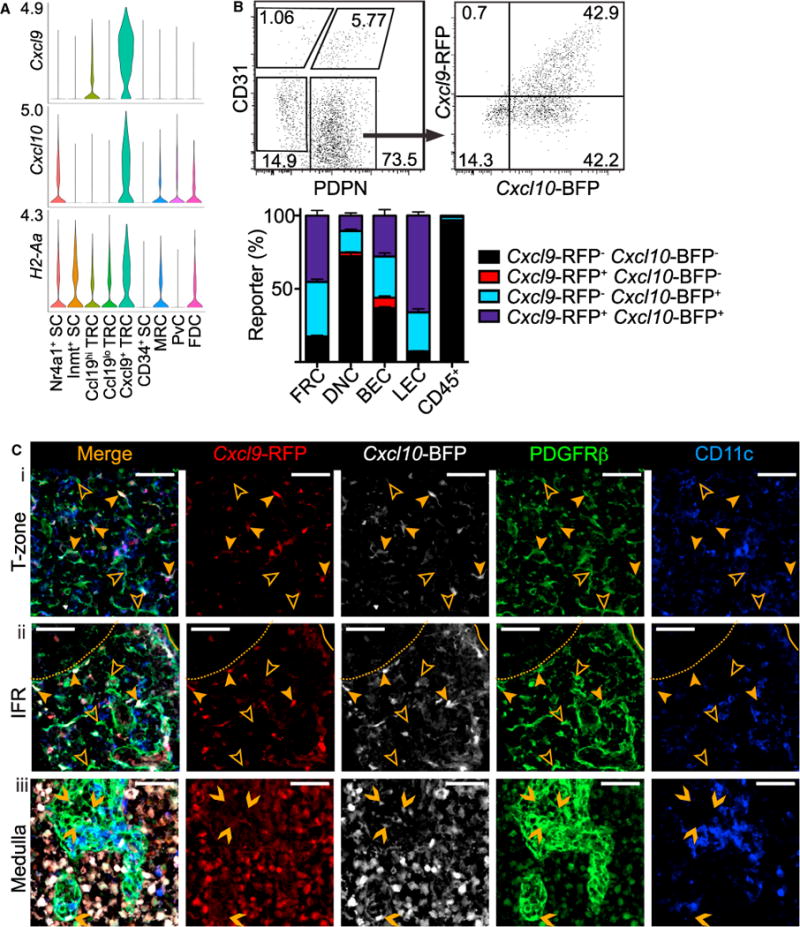
(A) Violin plots of cluster Cxcl9, Cxcl10, and H2-Aa expression.
(B) Representative gating and percent of REX3 pLN FRCs, DNCs, BECs, and LECs expressing Cxcl9-RFP and/or Cxcl10-BFP, both or neither by FC. Mean and SEM indicated (n = 3).
(C) IFM of REX3 pLN (i) T-zone, (ii) IFR, and (iii) medulla stained for PDGFRβ+CD11c− SCs (representative of 3 mice). Examples of Cxcl9-RFP+ Cxcl10-BFP+ SCs (filled arrowhead), Cxcl9-RFP− Cxcl10-BFP− SCs (empty arrowhead), and Cxcl9-RFP− Cxcl10-BFP+ SCs (chevron) indicated. Scale bar is 50 μm.
In REX3 pLN sections, immunofluorescence microscopy (IFM) revealed CXCL9+CXCL10+PDGFRβ+CD11c− stroma in the T-zone and IFRs interspersed with CXCL9−CXCL10−PDGFRβ+ CD11c− stroma (Figure 4C). CXCL9−CXCL10+PDGFRβ+CD11c− stroma was also detected in the medullary cords in accord with one-third of non-endothelial SCs expressing CXCL10 alone by FC and our scRNAseq analysis (Figures 4B and 4C). These are likely MedRCs that correspond to the Cxcl10-expressing Inmt+ SC subcluster of Nr4a1+Inmt+ SCs discussed in more detail in a following section (Figure 4A). Consistent with these findings, CXCL9 and CXCL10 expression by radio-resistant cells has been reported in REX3 reverse BM chimera popliteal LN T-zone, IFRs, and medulla (Groom et al., 2012).
The Cxcl9+ TRC DEGs were dominated by interferon (IFN)-inducible genes such as Gbp4 and Gbp5 (Figure 2C). The Cxcl9+ TRCs also expressed the type 1 IFN and IFN-γ receptors Ifnar2, Ifngr1, and Ifngr2, though not exclusively (Table S2). Prior work has shown that during an immune response, IFN-γ-induced CXCL9 and type 1 IFN-induced CXCL10 from myeloid cells and SCs can position CD4+ T cells, CD8+ memory T cells, and DCs in IFRs and support antigen encounter (Groom et al., 2012; Kastenmüller et al., 2013; Sung et al., 2012). Further study is required to determine whether the Cxcl9+ TRCs are an IFN-inducible state of Ccl19hi TRCs or a specialized, stable subset.
Cxcl9+ TRCs could also represent the FRCs reported to induce CD4+ T cell tolerance through presentation of peptide-MHC (Brown and Turley, 2015) since their DEGs included several MHCII genes (H2-Aa, H2-Eb1, and H2-Ab1), the invariant chain (Cd74), and peptide-loading chaperone (H2-DMa), but not co-stimulatory or inhibitory molecules (Cd80, Icosl, Cd274, Tnfsf9, Cd40, Tnfrsf14, Tnfsf18, Tnfsf14, Havcr1, Havcr2, Tnfsf15, Tnfsf8, Vsir, Csf1r, Cd86, Pdcd1lg2, Ctla4, Btla, Tnfrsf4, Cd70, Cd48, or Slamf1) (Tables S1 and S2). Cxcl9+ TRCs may be an activated subset of Ccl19hi TRCs that can tolerize T cells in a resting LN and help position CXCR3+ cells in IFRs during an immune response.
MRC Gene Expression Suggests Involvement in Barrier Defense
MRCs are situated at the base of the SCS, where lymph drains antigen from peripheral tissues, and have been described as PDPN+TNFSF11+MADCAM1+VCAM1+ICAM1+BST1+RELB+CXCL13+ LN stroma (Katakai et al., 2008). One cluster expressed almost all of these markers and was enriched for Tnfsf11 and Cxcl13 expression, suggesting that the constituent cells are MRCs (Figure 5A, Tables S1 and S3). However, this subset was not enriched for Madcam1 expression. The basis for this discrepancy is unclear, but MRCs may more efficiently translate Madcam1 mRNA or maintain the stability of the protein better than the TRCs which had detectable expression in our dataset. Alternatively, Madcam1 may be expressed by cells closely associated with MRCs, such as LECs (Cordeiro et al., 2016) (Immgen.com). In this regard it is notable that Madcam1 expression is LTβR signaling dependent while Tnfsf11 expression is not (van de Pavert and Mebius, 2010).
Figure 5. Tnfsf11+ MRCs Express Enpp2 in the SCS.
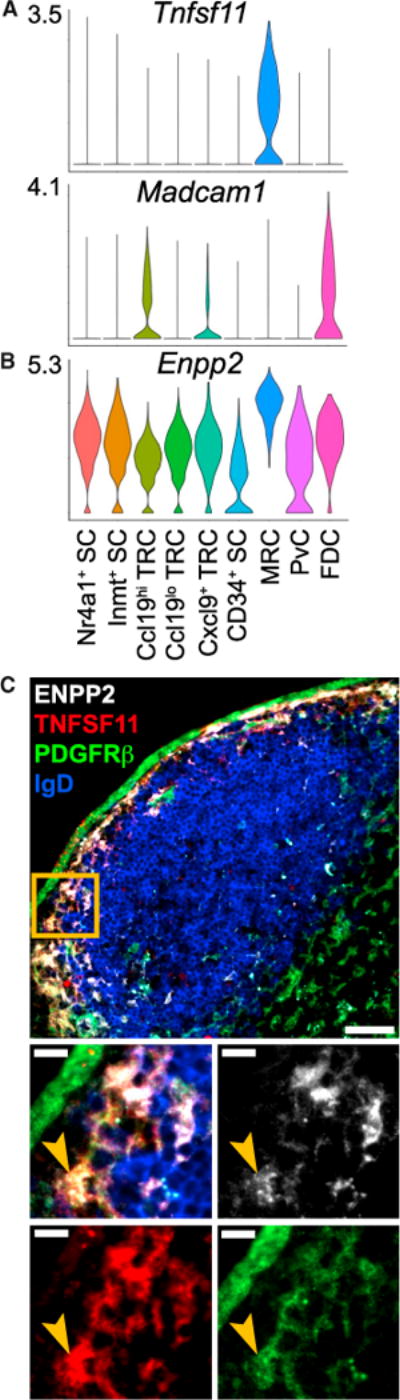
(A and B) Violin plots of cluster Tnfsf11 (A), Madcam1 (A), and (B) Enpp2 expression.
(C) IFM of pLN SCS stained for ENPP2 and TNFSF11+PDGFRβ+IgD− MRCs (representative of 3 mice). Scale bar is 50 μm. Box indicates area shown in merged and single channel images beneath. Arrowhead indicates example ENPP2+ MRC. Scale bar is 10 μm.
Little is understood about the role of MRCs in the SCS, a niche critical for antigen capture. The MRC subset had enriched expression of Enpp2 (autotaxin) (Figure 5B), a secreted enzyme required for the production of lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) that has been linked to T cell high-speed motility (Katakai et al., 2014). This may allow MRCs to influence lymphocyte-antigen interaction in the SCS. In pLN sections, IFM revealed that ENPP2 colocalized with TNFSF11 on the follicle edge of the SCS, consistent with MRC expression. ENPP2 was also detected to a lesser extent in the T-zone and HEVs (Figure 5C) in accord with expression by several other stromal subsets (Figure 5B) and with previous work (Kanda et al., 2008; Katakai et al., 2014).
MRCs may also interact with cells in the SCS to influence the initiation of the immune response and possibly prevent pathogen spread. Sensory nerves containing the neurotransmitter calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) are abundant in lymphoid organs and nerve fibers have been reported in the LN SCS (Iannacone et al., 2010). The MRC subset was enriched for Ramp1 expression, which directs CALCRL (also expressed) to form the receptor for CGRP (Table S3; McLatchie et al., 1998). The MRCs also expressed embigin (Emb), which has roles in nerve terminal sprouting (Table S3; Lain et al., 2009). MRCs may also influence cKit+ DCs, BECs, lymphoid tissue inducer cells, and neuronal precursors through expression of the cytokine Kitl, which we found differentially expressed (Table S3; Chappaz et al., 2010; Goldstein et al., 2015). Finally, the most differentially expressed gene for the MRC subset is hepcidin antimicrobial peptide 2 (Hamp2), which could suggest a direct role in barrier defense (Figure 2C).
Itga7+ PvC DEGs Suggest Roles in Endothelial Support and Leukocyte pLN Entry
Non-adventitial PvCs support multiple functions of blood vessels and have been found around some vessels in the pLN cortex and medulla (Chang and Turley, 2015). Non-adventitial PvCs include pericytes and vascular smooth muscle cells, which can be distinguished in situ only by their location surrounding capillaries and large vessels, respectively (Armulik et al., 2011). One particularly transcriptionally distinct stromal cluster in our dataset expresses the hallmarks of non-adventitial PvCs including Pdgfrb, Acta2, Itgb1, Esam1, Myl9, Mcam, and Notch3 (Figure S4, Table S4; Armulik et al., 2011; Malhotra et al., 2012). This subset is similar to the Itga7+ PvCs described as making up more than 50% of isolated LN DNCs (Malhotra et al., 2012). Our analysis did not, however, detect a transcriptionally distinct Cnn1+Itga7−Pdpn−PvC subset as proposed and the canonical PvC gene Cspg4 was detected in only a few cells, likely reflecting low expression and the transcript capture limitations of scRNAseq (Table S1; Malhotra et al., 2012).
The PvC subset was enriched for expression of thrombospondin (Thbs1), Il34, and endothelin-A receptor (Ednra), a gene involved in crosstalk between tissue cells and PvCs in kidneys (Figure S4; Kitazawa et al., 2011). PvCs also distinctly expressed ECM-adhesion factors Bcam and Nexn and several transcription factors including Mef2c and Fhl2 (Figure S4). The PvCs expressed a constellation of genes that may aid interactions at the vascular portals to the pLN parenchyma.
CD34+ SCs Express Features of ACs and Are Positioned in the Capsule and Medulla
CD34+ SCs were distinguished by expression of the sialomucin CD34, which on CD31+ LN BECs can bind L-selectin on passing lymphocytes (Figure 6A; Baumheter et al., 1993). Recent work characterized PDPN+BST1−ACTA2−CD31−CD34+ SCs surrounding large vessels in the LN medullary cords as ACs based on shared gene expression with ACs in other tissues (Corselli et al., 2012; Sitnik et al., 2016). In accord with CD34+ SCs being ACs, the subset expressed Pdpn but had no detectable expression of Bst1, Acta2, or Cd31 (Table S1). In addition, LN ACs have been described to secrete vasculogenic and angiogenic factors and CD34+ SCs expressed Igf1, Igfbp3, Igfbp4, and exclusively Igfbp6 along with growth factors and ECM factors (Figure 2C, Tables S1 and S5; Sitnik et al., 2016).
Figure 6. Characterization of CD34+ SCs, Inmt+ SCs, and Nr4a1+ SCs.
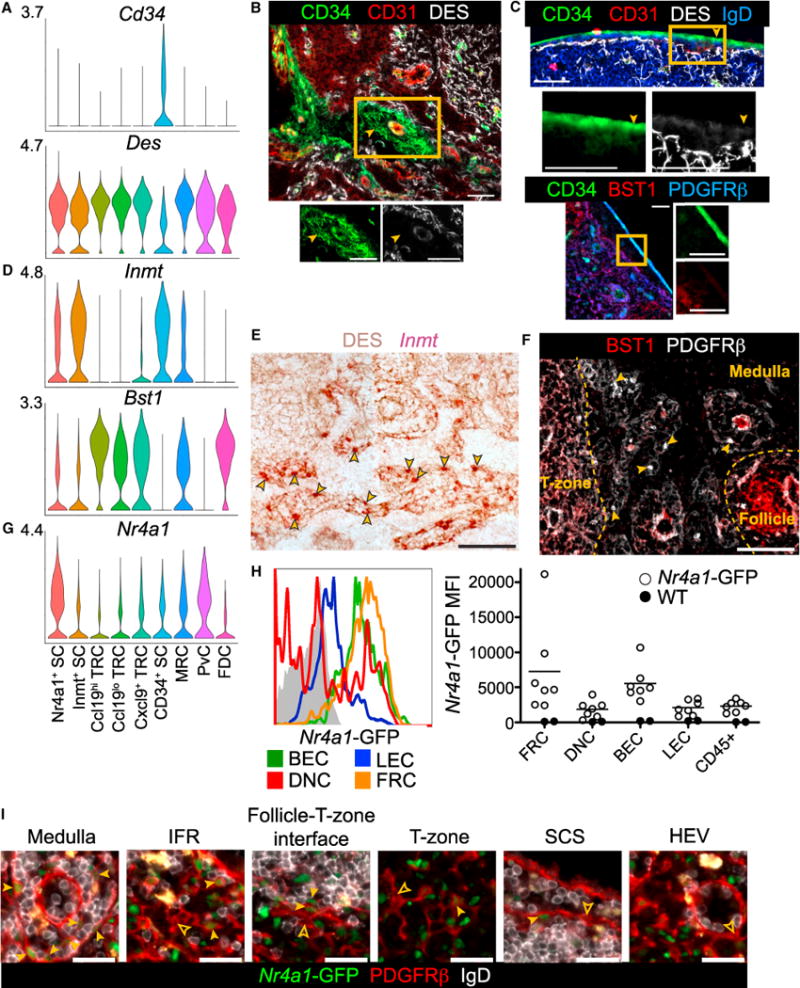
(A) Violin plots of cluster Cd34 and Des expression.
(B and C) IFM of pLN medulla (B) and capsule (C) for CD34+ cells with co-stains indicated. Filled arrowheads indicate examples of CD34+DES− staining. Box indicates area shown with individual channels (representative of 3 mice).
(D) Violin plots of cluster Inmt and Bst1 expression.
(E) RNAscope for Inmt with DES counterstain on pLN medullary cords (representative of 3 mice). Arrowheads indicate examples of Inmt+ cells.
(F) IFM of BST1 and PDGFRβ on pLN medullary cords (representative of 3 mice). Arrowheads indicate examples of BST1− PDGFRβ+ SCs and yellow dotted lines mark the niche boundaries.
(G) Violin plot of cluster Nr4a1 expression.
(H) GFP MFI of Nr4a1-GFP pLN FRCs, DNCs, BECs, LECs, and CD45+ cells detected by FC (n = 7, 3 experiments).
(I) IFM of Nr4a1-GFP pLN niches for PDGFRβ+GFP+IgD− SCs (filled arrowheads) and PDGFRβ+GFP−IgD− SCs (empty arrowheads) (representative of 2 mice).
Scale bar is 50 μm in (B), (C), (E), and (F) and 25 μm in (I). See also Figure S5.
IFM on pLNs revealed CD34+CD31− cells surrounding blood vessels in the medulla near the efferent lymphatics, in keeping with these being ACs (Figure 6B). However, CD34+CD31− cells that were PDGFRβ+BST1− were most prominently detected in the capsule (Figure 6C). CD34+ SCs were the only stromal subset with low desmin (Des) expression and DES was not detected on the CD34+ cells in either niche (Figures 6A–6C).
CD34+ SCs positioning in the pLN capsule is in accord with a study of human LNs showing CD34+ cells in the capsule as well as around large vessels (Díaz-Flores et al., 2014). CD34+ SCs were also enriched for endosialin (Cd248) expression, which is reported in the resting LN capsule and required for LN expansion after immunization (Table S5; Lax et al., 2010). These capsular cells were likely not LECs lining the SCS as LECs do not express Cd34 (Immgen.org) and expression of the LEC markers Lyve1, Prox1, and Ackr4 (Ulvmar et al., 2014) was not detected in CD34+ SCs (Table S1). CD34+ cells may, however, communicate with LECs as LECs highly express the secreted ligand for CD248, MMRN2 (Immgen.org) (Khan et al., 2017). CD34+ SCs could play a role in capsule integrity as the subset was enriched for expression of the ECM component and assembly associated genes Col5a3, Col15a1, Lama2, Vit, Loxl1, Mfap5, and Fbln1. This subset was distinctly enriched for the expression of the transcription factors Peg3 and Ar (Table S5). These data suggest that CD34+ SCs include ACs and capsular fibroblasts.
Inmt+ SCs Populate Medullary Cords and Likely Include MedRCs
The Inmt+ SC cluster expressed intermediate Cxcl13 and low Ccl19 and did not distinctly express any known niche- or subset-associated markers (Figure 2A). Instead, these cells differentially expressed indolethylamine N-methyltransferase (Inmt), an enzyme that can catalyze the N-methylation of tryptamine and could play a role in cell-cell communication (Mavlyutov et al., 2012), and stanniocalcin-1 (Stc1), a LIM-domain protein that may have a role in heterchromatin stability (Figures 2C and 6D, Table S6; He et al., 2013).
To determine whether Inmt+ SCs are associated with a specific LN niche, we used RNAscope and detected Inmt expression in pLN and mLN medullary cords, identified by DES+ ECM patterning and F4/80+ macrophages (Figures 6E and S5A). The Inmt signal location, density, and pattern is suggestive of MedRCs. An additional distinguishing feature of the Inmt+ SCs was low expression of Bst1 relative to the FDC, MRC, and TRC subsets (Figure 6D). In IFM on pLN sections, BST1 was detected throughout the cortical stroma (FDCs, MRCs, TRCs) but was absent from the MedRCs in accord with previous work (Figure 6F; Link et al., 2007). While Inmt was also expressed in other stromal clusters (CD34+ SCs and MRCs) and other cell types do populate the medullary cords (B cells, memory T cells, and plasma cells), these cell types are either not found in the medulla with this frequency or do not express Inmt (Figure 6D; Gray and Cyster, 2012; Immgen.org). A portion of the Nr4a1+ SCs also expressed Inmt and are discussed in the next section. Further analysis will be needed to determine whether medullary Inmt expression also involves medullary macrophages, which have no available expression data. This differential expression profile will enable investigation of the Inmt+ SC function in the medullary cords.
Nr4a1+ SCs Likely Consist of Activated Cells from Other Subsets
The Nr4a1+ SC cluster could not be readily assigned to a known stromal subset or specific niche. Instead, this cluster was distinguished by expression of early-response genes including Nr4a1 (Nur77), Fosb, Fos, Junb, Egr1, Nfkbia (Ikba), Nfkbiz, and Zfp36 (Figures 2C and 6G, Table S7; Ullman et al., 1990). To validate that these SCs are present in uninfected pLNs, we isolated pLN stroma from Nr4a1-GFP transcriptional reporter mice (Zikherman et al., 2012). Indeed, a portion of FRCs, DNCs, BECs, and LECs expressed Nr4a1-GFP greater than the GFP− control, with FRCs and BECs having the highest Nr4a1-GFP expression (Figure 6H).
Early-response genes can be activated by TLR, cytokine, mitogen, or growth factor signaling as well as physical stimuli (Ullman et al., 1990). To investigate whether Nr4a1+ SCs were activated cells from other subsets, we subclustered the Nr4a1+ SCs and compared the subcluster DEGs to those from the other original clusters (Table S7). We distinguished three subclusters with more than 300 DEGs each (log2-fold change > 0.5, FDR < 0.05, proportion of cluster expressing > 0.10) that significantly correlated with Inmt+ SCs (r = 0.49, FDR = 8.9 × 10−31, Pearson; 84.4% of Nr4a1+ SCs), Ccl19hi TRCs (r = 0.78, FDR = 1.5 × 10−90, Pearson; 13.1% of Nr4a1+ SCs), and CD34+ SCs (r = 0.44, FDR = 7.7 × 10−17, Pearson; 2.6% of Nr4a1+ SCs) (Figures S5B and S5C, Table S7). Cells from both samples contributed to each subcluster (Figure S5D).
To test whether Nr4a1+ SCs populate a specific niche or, as our subclustering would suggest, are found in multiple niches, we stained PDGFRβ+ stroma in Nr4a1-GFP+ pLN sections. PDGFRβ+Nr4a1-GFP+ cells were found frequently in the medullary cords and occasionally in IFRs, the follicle-T-zone interface, the T-zone, and the SCS in accord with expression by Inmt+ SCs, TRCs, and MRCs (Figure 6I). Medullary CD34+ SCs and PDGFRβ−FDCs could not be distinguished with this stain. The medulla is a site of high lymph flow and macrophage-mediated clearance of antigens. Further study is required to determine whether Nr4a1+ Inmt+ SCs in the medullary cords are activated by lymph-borne material.
FDCs Distinctly Express Pthlh and Tmem119 and Share Sox9 Expression with CRCs
LN FDCs have been difficult to isolate in sufficient numbers for transcriptional profiling because they are rare and FDC markers are lost during tissue digestion. However, with scRNAseq we identified a small cluster highly enriched for well-defined FDC-expressed genes including complement receptor 2 (Cr2), Fc receptors (Fcgr2b and Fcer2a), Coch (Py et al., 2013), Prnp, Madcam1, Vcam1, Cxcl13, and Mfge8 (Figures 2A and 2C, Table S8; Allen and Cyster, 2008). Matching published estimates for FDCs, this cluster made up 1.7% of the recovered pLN non-endothelial SCs (Figure 1C; Jarjour et al., 2014). The FDCs were the most transcriptionally distinct subset, possibly reflecting their unique dendritic morphology and specialized function in antigen presentation (Figure 2B; Heesters et al., 2014).
The FDC cluster distinctly expressed parathyroid hormone like hormone (Pthlh or Pthrp), a secreted protein that could be involved in development or maintenance of the follicle or GC (Figure 7A). Initially described as an inducer of hypercalcemia of malignancy, Pthlh has since been established to regulate the differentiation of a number of cell types (McCauley and Martin, 2012). RNAscope analysis revealed Pthlh expression in the center of pLN primary follicles and in the LZs of mLN GCs in accord with expression by the CR2+ FDCs detected in a sequential stain (Figure 7B). FDCs depend on LT and TNF signaling for their maintenance (Allen and Cyster, 2008). Four-day in vivo blockade of these cytokines with LTβR-Fc and TNFR1-Fc led to a loss of Pthlh signal, consistent with expression by FDCs (Figure 7C). Pthlh is thought to largely act through Pth1r, though some receptor-independent actions have been proposed (McCauley and Martin, 2012). Of all the SC clusters, only Ccl19hi TRCs expressed Pth1r consistent with previous detection in bulk FRCs (Immgen.org) (Figure 7A). It will be of interest to determine whether this factor functions in cross-talk between FDCs and Ccl19hi TRCs.
Figure 7. FDCs Express Pthlh and Tmem119 while FDCs and CRCs Express Sox9.
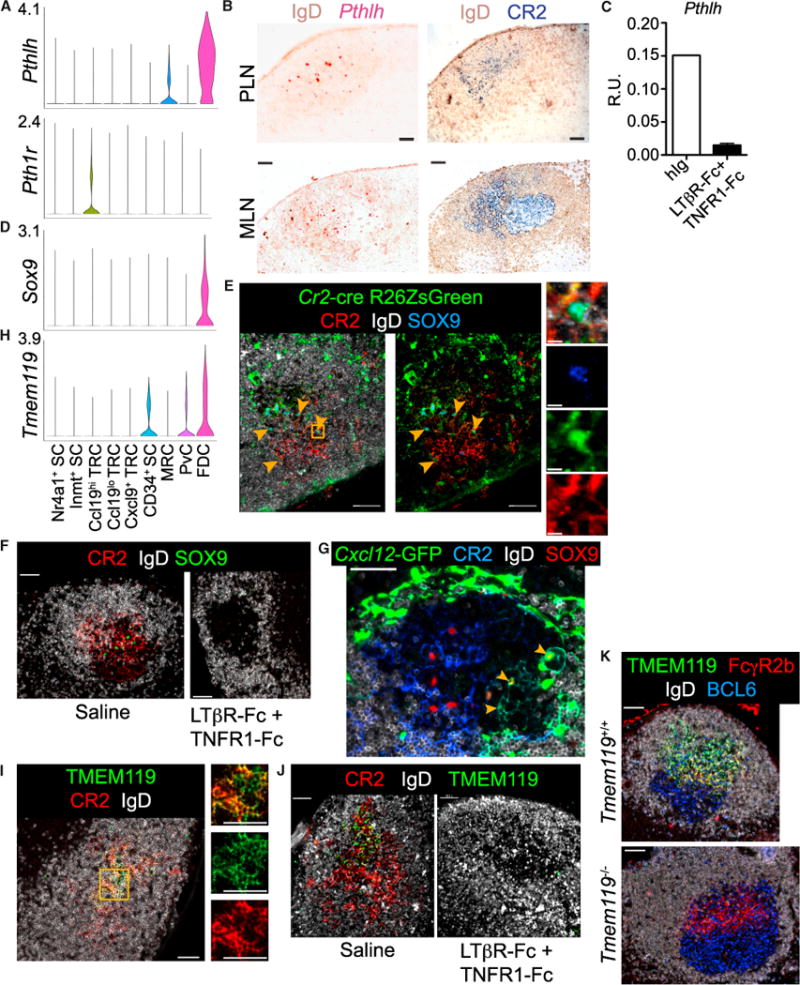
(A) Violin plot of cluster Pthlh and Pth1r expression.
(B) RNAscope for Pthlh with IgD counterstain on pLN primary follicle and mLN GC. Sequential stains for CR2hi FDCs and IgD (representative of 2 mice).
(C) QPCR of pLN Pthlh expression from mice treated 1 or 2 times with LTβR-Fc and TNFR1-Fc (n = 2) or once with human IgG (hIg) (n = 1) (R.U. = relative units).
(D) Violin plot of cluster Sox9 expression.
(E) IFM of Cr2-cre R26ZsGreen reverse BM chimera pLN follicle (representative of 2 mice). Arrowheads indicate examples of CR2hiZsGreen+SOX9+ FDCs. Box indicates area shown with merged and individual channels. Scale bar is 10 μm.
(F) IFM of SOX9+ cells among CR2hi FDC networks in pLN GC from mice immunized with SRBC and on day 10 treated with LTβR-Fc and TNFR1-Fc or saline for analysis on day 14 (representative of 6 pLNs from 1 mouse per treatment).
(G) Thick-section IFM of Cxcl12-GFP pLN GCs day 10 post-SRBC immunization (representative of 6 pLNs from 1 mouse per treatment). Arrowheads indicate Cxcl12-GFP+SOX9+CR2lo CRCs.
(H) Violin plot of cluster Tmem119 expression.
(I) IFM of pLN primary follicle TMEM119+CR2hi FDCs (representative of 2 mice). Box indicates area shown with individual channels.
(J) IFM of TMEM119 on CR2hi FDCs in pLN GCs post-immunization and treatment as in (F) (representative of 6 pLN from 1 mouse per treatment).
(K) IFM of TMEM119 on FcγR2b+ FDCs in BCL6+ pLN GCs from Tmem119+/+ and Tmem119−/− mice on day 11 post-NP-CGG immunization (representative of 2 mice per genotype).
Scale bars are 50 μm unless otherwise noted. See also Figure S6.
The FDC cluster was also enriched for Sox9 expression, a transcription factor that could play a role in FDC differentiation (Figure 7D). SOX9 has roles in the differentiation of multiple cell types including chondrocytes and neural crest cells (Huang et al., 2015). In pLN follicles from irradiated Cr2-cre R26-ZsGreen reporter mice (reconstituted with reporter negative hematopoietic cells), SOX9 co-stained ZsGreen+ CR2+ FDC cell bodies (Figure 7E). SOX9 also stained within GC LZ CR2+ FDC networks (Figure 7F). Consistent with FDC SOX9 expression, the SOX9 detection was lost along with CR2+ FDCs after short-term LT and TNF blockade (Figure 7F).
GCs also contain CXCL12+CR2lo DZ CRCs, SCs with a frequency and morphology similar to FDCs, but which guide CXCR4+ GC B cells to the DZ (Bannard et al., 2013; Rodda et al., 2015). To probe whether SOX9 expression is unique to FDCs or a shared feature of GC stroma, we stained SOX9 in pLNs from immunized Cxcl12-GFP reporter mice and detected expression in both CR2hi Cxcl12-GFP− LZ FDCs and CR2lo Cxcl12-GFP+ DZ CRCs (Figure 7G).
While we expect LZ FDCs and DZ CRCs to have distinct transcriptional programs, their similar morphology and shared role in GCs suggests that they may be at least more similar to each other than to other SCs. Thus we attempted to identify distinguishing expression by subclustering the FDCs from the post-infection sample predicted to contain GC stroma (Rodda et al., 2015). However, the subclusters did not pass our significance threshold (more than 50 DEGs relative to the other subclusters and original clusters). Still, among post-infection FDCs, Cxcl12 expression was negatively correlated with canonical FDC gene (Fcgr2b and Fcer2a) and Sox8 expression (Figure S6A). Sox8 is a transcription factor in the same SoxE family as Sox9 (Huang et al., 2015). Notably, Sox9 was less negatively correlated with Cxcl12 (Figure S6A). More cells or increased depth of mRNA capture are required to determine whether the heterogeneity in the post-infection FDCs reflects the inclusion of DZ CRCs or mRNA sampling variability and whether Sox8-directed expression contributes to the distinct phenotypes of LZ FDCs and DZ CRCs.
The FDC cluster also differentially expressed Tmem119, a surface protein that could facilitate FDC-lymphocyte interactions in the follicle and GC. Tmem119 encodes an O-glycosylated surface protein found on microglia and involved in osteoblast development (Figure 7H; Bennett et al., 2016; Kanamoto et al., 2009). Using IFM on pLN primary follicles, TMEM119 selectively labeled CR2+ FDC networks (Figure 7I). In addition, short-term blockade of LT and TNF led to a loss of CR2 and TMEM119 staining in accord with FDC expression (Figure 7J). To test for a role of FDC TMEM119 in support of the GC, Tmem119+/+ and Tmem119−/− mice (Bennett et al., 2016) were immunized with NP-CGG in Sigma Adjuvant and analyzed on day 11. While Tmem119−/− pLN LZ FcγR2b+ FDC networks had undetectable TMEM119, there was no change in FDC morphology, GC polarization, or frequencies of GC B cell, NP-specific GC B cell, follicular B cell, plasma cell, and memory-phenotype B cell (Figures 7K and S6B). TMEM119 was therefore not essential for mounting this type of GC response, but could be important in responses to more complex antigens or in shaping specialized features of the GC.
DISCUSSION
Here we used scRNAseq to identify nine pLN non-endothelial SC clusters. We mapped eight clusters to specific anatomical niches and established differential expression profiles for Ccl19hi TRCs (T-zone), Ccl19lo TRCs (Ch25h+ cells in follicle-T-zone interface and IFR), Cxcl9+ TRCs (T-zone and IFR), MRCs (SCS), PvCs (perivascular), CD34+ SCs (capsule and medullary adventitia), Inmt+ SCs (medullary cords), and FDCs (follicle center). While the Cxcl9+ TRCs and Nr4a1+ SCs, found in several niches, are likely distinguished by transient activation programs instead of niche-establishing programs, the niche association of the majority of transcriptional clustering suggests that this resolution of non-endothelial SC heterogeneity will be useful for studying their niche-specific functions.
The differential gene expression profiles of the nine clusters provide a unique opportunity to identify positive markers, develop additional tools, and study functions of rare and poorly studied SC types. Previously published FDC expression profiles have suffered from B cell, myeloid cell, or FRC contamination or required additional manipulation, such as irradiation of the mice or in vitro culture (Heesters et al., 2014; Suzuki et al., 2010; Wilke et al., 2010). Our analysis of freshly harvested pLN FDCs revealed Pthlh, Sox9, and Tmem119 as markers of FDCs that could be used to develop more specific genetic tools. Staining for SOX9 and TMEM119 on human tonsil and LN GCs supports conserved expression of these genes by human FDCs (Uhlén et al., 2015) (proteinatlas.org). DZ CRC expression of SOX9 in combination with Cxcl12 also suggests an isolation strategy for these rare and poorly understood cells. In addition, MedRCs previously had no distinctive positive markers, but in situ validation of top DEGs Inmt, Cxcl9, and Cxcl10 suggests that MedRCs are Inmt+Cxcl10+Cxcl9−.
How distinct, niche-associated stromal subsets develop and their degree of plasticity in the adult is incompletely understood. Previous work with Ccl19- and Pdpn-directed lineage reporters have demonstrated the shared lineage of LN SCs across niches (Chai et al., 2013; Onder et al., 2011). While the SC clustering suggests that most pLN non-endothelial SC subsets are transcriptionally similar, the cluster DEGs can guide selection of specific markers and unique transcription factors for additional fate-mapping efforts to address the developmental relationships between niche-associated subsets. Since SCs cultured in vitro tend to lose their specific features, studying the cluster-specific transcription factors defined here could help explore non-endothelial SC plasticity and improve in vitro models.
While the nine pLN non-endothelial SC clusters are conserved in two biological samples, we expect proportional composition will vary with digestion protocols and more heterogeneity will be found with improved scRNA capture technology. The large proportion of Ccl19lo TRCs suggests that this cluster includes not only the Ch25h+ cells at the follicle-T-zone interface, but also stroma in another T-zone-adjacent niche such as the T-zone-medulla interface or deep cortex periphery (Sainte Marie, 2010). In addition, our dataset did not resolve versatile SCs, non-FDC Cr2-lineage marked cells in the follicle and T-zone (Mionnet et al., 2013), and these may also be included in the Ccl19lo TRC or in another cluster. We anticipate that as more is learned about subset heterogeneity and niche localization, it will be appropriate to revise the draft nomenclature used here. Nevertheless, our transcriptomic analysis of nine niche-associated pLN non-endothelial SC clusters can aid study of their roles in the compartmentalized steps of the immune response as well as facilitate comparisons to SCs at sites of chronic inflammation to identify methods for clinical targeting.
STAR★METHODS
Detailed methods are provided in the online version of this paper and include the following:
KEY RESOURCES TABLE
| REAGENT or RESOURCE | SOURCE | IDENTIFIER |
|---|---|---|
| Antibodies | ||
| Rat monoclonal anti-Thy1.2 (clone 30-H12) - Biotin | Biolegend | CAT#105304; RRID:AB_313175 |
| Rat anti-CD45 (clone 30-F11) - MACS microbeads | Miltenyi | CAT#130-052-301 |
| Rat anti-CD45 (clone 30-F11) - PerCpCy5.5 | Biolegend | CAT#103132; RRID:AB_893340 |
| Rat anti-CD31 (clone MEC 13.3) - PE | BD Biosciences | CAT#553373; RRID:AB_394819 |
| Syrian hamster anti-gp38 (clone 8.1.1) - APC | Biolegend | CAT#127410; RRID:AB_10613649 |
| Mouse anti-CD45.2 (clone 104) - Pacific Blue | Biolegend | CAT#109820; RRID:AB_492872 |
| Streptavidin - PECy7 | Biolegend | CAT#405206 |
| Syrian hamster anti-gp38 (clone 8.1.1) - Alexa488 | Biolegend | CAT#127405; RRID:AB_1133992 |
| anti-CD31 PECy7 (clone 390) | Biolegend | CAT#102417; RRID:AB_830756 |
| anti-CD45 BUV395 (clone 30-F11) | BD Biosciences | CAT#565967 |
| Rat anti-CD16/32 (clone 93) | Biolegend | CAT#101320; RRID:AB_1574975 |
| Fixable Viability Dye eFluor780 | eBioscience | CAT#65-0865-14 |
| Rat anti-B220 (clone RA3-6B2) - BV785 | Biolegend | CAT#103246; RRID:AB_2563256 |
| Rat anti-IgD (clone 11-26c.2a) - BV650 | Biolegend | CAT#405721; RRID:AB_2562731 |
| Rat anti-IgD (clone 11-26c.2a) - Alexa647 | Biolegend | CAT#405708; RRID:AB_893528 |
| Rat anti-IgD (clone 11-26c.2a) - Pacific Blue | Biolegend | CAT#405712; RRID:AB_1937244 |
| Armenian hamster anti-Fas (clone Jo2) - PE-Cy7 | BD Biosciences | CAT#557653; RRID:AB_396768 |
| Rat anti-T- and B Cell Activation Antigen (clone GL7) – Alexa647 | Biolegend | CAT#144606; RRID:AB_2562185 |
| Rat anti-T- and B Cell Activation Antigen (clone GL7) – Pacific Blue | Biolegend | CAT#144614; RRID:AB_2563292 |
| NP - PE | Biosearch Technologies | CAT#N-5070-1 |
| Rat anti-CD138 (clone 281-2) - BV421 | Biolegend | CAT#142508; RRID:AB_11203544 |
| Rat anti-CD73 (clone TY/11.8) - PerCpCy5.5 | Biolegend | CAT#127214; RRID:AB_11219403 |
| Rat anti-CD38 (clone 90) - Alexa647 | Biolegend | CAT#102716; RRID:AB_2073334 |
| Rabbit anti-Tmem119 | B. Barres | Bennett et al., 2016 |
| Goat anti-ENPP2 | R&D Systems | CAT#AF5255; RRID:AB_2277989 |
| Goat anti-TNFSF11 | R&D Systems | CAT#AF462; RRID:AB_2206198 |
| Rat anti-CD34 FITC (clone RAM34) | BD PharMingen | CAT#553733; RRID:AB_395017 |
| Rat anti-CD31 (clone MEC13.3) - biotin | Biolegend | CAT#102504; RRID:AB_312911 |
| Goat anti-IgD | Cedarlane Labs | Code: GAM/IGD(FC) |
| Goat anti-desmin | R&D Systems | CAT#AF3844; RRID:AB_2092419 |
| Mouse anti-BST-1 (clone BP-3) | BD Biosciences | CAT#552545; RRID:AB_394419 |
| Rabbit anti-PDGFRβ (clone 28E1) | Cell Signaling Technology | CAT#3169T; RRID:AB_2162497 |
| Armenian hamster anti-CD11c (clone N418) - Alexa647 | Biolegend | CAT#117312; RRID:AB_389328 |
| Rabbit anti-Sox9 | Millipore | CAT#AB5535; RRID:AB_2239761 |
| Rat anti-CD35 (clone 8C12) - biotin | BD Biosciences | CAT#553816; RRID:AB_395068 |
| anti-CD16/32 (clone 2.4G2) - biotin | UCSF Monoclonal Antibody Core | Lot MC080081 |
| Mouse anti-Bcl6 (clone K112-91) - Alexa647 | BD PharMingen | CAT#561525; RRID:AB_10898007 |
| Rabbit anti-GFP - Alexa488 | Life Technologies | CAT#A21311; RRID:AB_221477 |
| Rat anti-F4/80 (clone C1:A3-1) - biotin | Cedarlane Laboratories | CAT#CL8940B; RRID:AB_10059797 |
| Mouse anti-FITC - Alexa488 | Jackson Immunoresearch | CAT#200-542-037; RRID:AB_2339038 |
| Streptavidin - Cy3 | Jackson Immunoresearch | CAT#016-160-084; RRID:AB_2337244 |
| Donkey anti-goat IgG - AMCA | Jackson Immunoresearch | CAT#705-156-147; RRID:AB_2340410 |
| Donkey anti-rabbit IgG - Alexa488 | Life Technologies | CAT#A21206; RRID:AB_2535792 |
| Donkey anti-rabbit IgG - Alexa647 | Jackson Immunoresearch | CAT#711-606-152; RRID:AB_2340625 |
| Streptavidin - Alexa555 | Life Technologies | CAT#S-21381; RRID:AB_2307336 |
| Donkey anti-goat IgG - Horseradish Peroxidase | Jackson Immunoresearch | CAT#705-035-147; RRID:AB_2313587 |
| Streptavidin - Alkaline Phosphatase | Jackson Immunoresearch | CAT# 016-050-084; RRID:AB_2337239 |
| Bacterial and Virus Strains | ||
| Lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV)-Armstrong | M. Matloubian | Clingan and Matloubian, 2013 |
| Biological Samples | ||
| pLN frozen blocks REX3-Tg, Cxcl9-RFP Cxcl10-BFP (REX3) | A. Luster | Groom et al., 2012 |
| Chemicals, Peptides, and Recombinant Proteins | ||
| Collagenase IV | Worthington Biochemical | CAT#LS004188 |
| DNase I, bovine pancreas (single cell stromal cell analysis) | Sigma-Aldrich | CAT#DN25 |
| DNase I grade II, bovine pancreas (REX3 stromal cell analysis) | Roche | CAT#10104159001 |
| Collagenase P | Sigma-Aldrich | CAT#11213857001 |
| Dispase II | Sigma-Aldrich | CAT#D4693 |
| NP(25)-CGG | Biosearch Technologies | CAT#N-5055C-5 |
| Sigma Adjuvant System | Sigma-Aldrich | CAT#S6322 |
| Sheep red blood cells (SRBCs) (Sheep #0469) | Colorado Serum Company | CAT#38112 |
| mLTβR-huIgG1 (LTβR-Fc) | J. Browning | N/A |
| TNFR55-huIgG1 (TNFR1-Fc) | J. Browning | N/A |
| human IgG1 (hIg) | J. Browning | N/A |
| Critical Commercial Assays | ||
| Chromium Single Cell 3′ Reagent Kit (v2 Chemistry) | 10X Genomics | CAT#120267 |
| RNAscope RED 2.5HD manual assay kit | Advanced Cell Diagnostics | CAT#322350 |
| Deposited Data | ||
| Raw and analyzed data | This paper | GEO: GSE112903 |
| Violin plot web tool | This paper | http://scorpio.ucsf.edu/shiny/LNSC/ |
| Experimental Models: Organisms/Strains | ||
| Mouse: C57BL/6 | National Cancer Institute, Charles River | CAT#027 |
| Mouse: B6-CD45.1 | National Cancer Institute, Charles River | CAT#564 |
| Mouse: B6.Cg-Cxcl12tm2Tng (Cxcl12-GFP) | T. Nagasawa | Ara et al., 2003; RRID:IMSR_RBRC04200 |
| Mouse: B6.Tg(Cr2-Cre)3Cgn (Cr2-Cre) | K. Rajewsky | Kraus et al., 2004; RRID:IMSR_JAX:006368 |
| Mouse: B6.Cg-Gt(ROSA) 26Sortm6(CAG-Zsgreen1)Hze/J (R26-ZsGreen) | The Jackson Laboratory | CAT#007906; RRID:007906 |
| Mouse: 129S5-Tmem119<tm1Lex > /Mmcd (Tmem119 KO) | B. Barres | Bennett et al., 2016; RRID:MMRRC_041484-UCD |
| Mouse: Nr4a1-EGFP BAC-transgenic (Nr4a1 -GFP) | A. Weiss | Zikherman et al., 2012; RRID:MMRRC_036737-UCD |
| Mouse: B6.129S6-Ch25htm1Rus/J (Ch25h KO) | D. Russell | Bauman et al., 2009; RRID:IMSR_JAX:016263 |
| Mouse: Tg(UBC-GFP)30Scha/J (UBI-GFP) | The Jackson Laboratory | CAT#004353; RRID:IMSR_JAX:004353 |
| Oligonucleotides | ||
| Primers: Inmt-F CCTTCTCTACAGGAGGTGTAGG; Inmt-R GTTCTGCGGGGTGTAGTCAG | This paper | NA |
| Primers: Siglec1-F GGTCAGCCAACAGTTCACTC; Siglec1 -R GAGACTCCTGTGGGCACC | This paper | NA |
| Primers: Pdgfrβ-F GCAGAAGAAGCCACGCTATG; Pdgfrβ-R CAGGTGGAGTCGTAAGGCAA | This paper | NA |
| Primers: Pthlh-F GGAGTGTCCTGGTATTCCTGC; Pthlh-R CCCTTGTCATGCAGTAGCTGA | This paper | NA |
| Software and Algorithms | ||
| Flowjo (version 9.9.6) | Treestar | https://www.flowjo.com/ |
| Prism (version 5.0a) | GraphPad | https://www.graphpad.com/scientific-software/prism/ |
| 10X Cell Ranger package | 10X Genomics | https://support.10xgenomics.com |
| Seurat (version 2.2) | R. Satija | Butler and Satija, 2017; http://satijalab.org/seurat/ |
| R (version 3.4.2) and dependencies | The Comprehensive R Archive Network | https://cran.r-project.org/ |
| RStudio (version 1.0.153) | RStudio, Inc. | https://www.rstudio.com/ |
| DESeq2 (version 1.16.1) | Love et al., 2014 | https://bioconductor.org/packages/release/bioc/html/DESeq2.html |
| Other | ||
| RNAscope probe: Ch25h (NM_009890.1, targeting bp 115-1240) | Advanced Cell Diagnostics | CAT#424561 |
| RNAscope probe: Inmt (NM_009349.3, targeting bp 3-1017) | Advanced Cell Diagnostics | CAT#486371 |
| RNAscope probe: Pthlh (NM_008970.4, targeting bp 173-1231) | Advanced Cell Diagnostics | CAT#456521 |
CONTACT FOR REAGENT AND RESOURCE SHARING
Further information and requests for resources and reagents should be directed to and will be fulfilled by the Lead Contact, Jason Cyster (Jason.Cyster@ucsf.edu).
EXPERIMENTAL MODEL DETAILS
Adult C57BL/6 (B6) and B6-CD45.1 mice were purchased from the National Cancer Institute at Charles River. B6.Cg-Cxcl12tm2Tng (Cxcl12-GFP) gene-targeted mice were provided by T. Nagasawa and were backcrossed to the B6 background more than seven generations. B6.Tg(Cr2-Cre)3Cgn (Cr2-Cre) BAC-transgenic mice were fully backcrossed to B6 and provided by K. Rajewsky (Immune Disease Institute, Boston, MA). B6.Cg-Gt(ROSA) 26Sortm6(CAG-Zsgreen1)Hze/J (R26ZsGreen) mice have a floxed stop ZsGreen1 reporter genetically targeted to the Gt(ROSA)26Sor locus and were purchased from The Jackson Laboratory. 129S5-Tmem119<tm1Lex > /Mmcd (Tmem119−/−) mice were fully backcrossed to B6 and provided by B. Barres (Bennett et al., 2016). Nr4a1-EGFP BAC-transgenic (Nr4a1-GFP) mice (Zikherman et al., 2012) were backcrossed to B6 at least 6 generations from A. Weiss and provided by J. Roose. B6.129S6-Ch25htm1Rus/J (Ch25h−/−) mice were fully backcrossed to C57BL/6. Cxcl9-RFP Cxcl10-BFP transgenic mice (REX3) were made on a B6 background (Groom et al., 2012) and pLNs provided in frozen blocks by A. Luster. Tg(UBC-GFP)30Scha/J (UBI-GFP) transgenic mice were backcrossed to C57BL/6 for more than 8 generations and were from The Jackson Laboratory.
Bone marrow (BM) chimeras were made as described previously and analyzed after at least 8 weeks (Bannard et al., 2013). UBI-GFP mice were treated intraperitoneally (ip) with 500 μg anti-Thy1.2 (clone 30H12) to ablate radio-resistant T cells before being irradiated and reconstituted with wild-type CD45.1 BM. Cr2-Cre R26ZsGreen mice were irradiated and reconstituted with WT CD45.1 BM.
Animals were housed in a specific pathogen–free environment in the Laboratory Animal Research Center at the University of Cal-ifornia, San Francisco, and all experiments conformed to ethical principles and guidelines approved by the University of California, San Francisco, Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee.
METHOD DETAILS
Stromal Cell Preparation and Flow Cytometry
PLN stromal cells (SCs) were prepared for scRNAseq from the inguinal, brachial and axillary LNs of 12 uninfected, adult, female C57BL/6 mice and 9 post-LCMV infected adult, female C57BL/6 mice. PLNs were harvested into DMEM (Fisher Scientific) with 2% FCS (HyClone), 10mM HEPES (Fisher Scientific) and Pen/Strep (P/S)(Fisher Scientific) on ice and minced with 25G needles (Fisher Scientific). Tissue was transferred to room temperature digestion buffer (DMEM + 2%FCS + HEPES + P/S + 3mg/ml Collagenase IV (Worthington Biochemical) and 40 μg/ml DNase I (Sigma-Aldrich) and incubated at 37°C in a beaker with water and a stir bar gently spinning for 15 min. Tissue was pipetted 50× with a Pasteur pipet and incubated another 15min before being pipetted 100× and filtered through a 100 μm filter into MACS Buffer (PBS with 2% FCS and 2mM EDTA) on ice. The cell suspension was spun down and resuspended to 1×107 cells/ml in MACS buffer with 10 μl/4×107cells anti-CD45 MACS microbeads (Miltenyi) to rotate for 40min at 4°C. After MACS depletion of CD45+ cells, the remaining suspension was stained with anti-CD45 PerCpCy5.5 (30-F11, Biolegend), anti-CD31 PE (MEC 13.3, BD Biosciences), anti-gp38 APC (8.1.1, Biolegend) and DAPI (Invitrogen) for flow cytometry assisted cell sorting for viable CD45− CD31− cells on a FACSAria Fusion into PBS + 0.04% BSA. Cells with the lowest DAPI staining were excluded as SSC-Alo CD45− CD31− PDPN− insufficiently stained CD45+ cells. Data was analyzed using FlowJo (Treestar). PLN SCs from individual Nr4a1-GFP mice were processed using the same protocol and additionally stained with anti-CD45 Pacific Blue (104, Biolegend), anti-BST-1 (BP-3, BD Biosciences) conjugated to biotin and streptavidin PECy7 (Biolegend).
For the analysis of REX3 pLN stroma, whole LNs were placed on 70 μm sterile filters and mechanically disrupted and subjected to digestion in DNase I (100 μg/ml), Collagenase P (200 μg/ml), Dispase II (800 μg/ml), 1% FCS in RPMI. LNs were placed in the pre-warmed enzyme mixture and incubated at 37°C. At 8 minute intervals, any supernatant was removed, added to RPMI/2mM EDTA/1% FCS, and replaced with fresh enzyme media. This was repeated at 8min intervals until no large tissue fragments remained. For flow cytometry (FC) on Rex3 pLN stroma, single-cell suspensions of 2×106 cells underwent staining in PBS/0.5% FCS with anti-gp38 Alexa488 (Biolegend), anti-CD31 PECy7 (Biolegend), anti-CD45 BUV395 (BD Biosciences), anti-CD16/32 (Biolegend), and Fixable Viability Dye eFluor780 (eBioscience). Samples were run on BD Fortessa X20 and data was analyzed using FlowJo (TreeStar) and Prism (GraphPad).
Single-cell suspensions of B cells were generated and stained as previously described (Allen et al., 2007). The following antibodies were used for cell staining: anti-B220 BV785 (RA3-6B2, Biolegend), anti-IgD BV650 and Pacific Blue (11-26c.2a, Biolegend), anti-Fas PE-Cy7 (Jo2, BD Biosciences/Fisher), anti-T- and B Cell Activation Antigen Pacific Blue and Alexa647 (GL7, Biolegend), NP-PE (Biosearch Technologies), Fixable Viability Dye ef780 (eBioscience), anti-CD138 BV421 (281-2, Biolegend), anti-CD73 PerCpCy5.5 (TY/11.8, Biolegend) and anti-CD38 Alexa647 (90, Biolegend). Samples were acquired and analyzed with a BD LSRII, Flowjo (Treestar) and Prism (GraphPad).
Droplet-based single-cell RNA sequencing
Immediately post-sorting, DAPI− CD45− CD31− pLN SCs were run on the 10X Chromium (10X Genomics)(Zheng et al., 2017) and then through library preparation by the Institute for Human Genetics at UCSF following the recommended protocol for the Chromium Single Cell 3′ Reagent Kit (v2 Chemistry). Libraries were run on the HiSeq4000 for Illumina sequencing. Post-processing and quality control were performed by the Genomics Core Facility at the Institute for Human Genetics at UCSF using the 10X Cell Ranger package (v1.2.0, 10X Genomics). Reads were aligned to mm10 reference assembly (v1.2.0, 10X Genomics). Primary assessment with this software for the uninfected sample reported 2,912 cell-barcodes with 5,542 median unique molecular identifiers (UMIs, transcripts) per cell and 2,148 median genes per cell sequenced to 87.8% sequencing saturation with 116,135 mean reads per cell. Primary assessment with this software for the post-LCMV infection sample reported 12,686 cell-barcodes with 4,477 median unique transcripts per cell and 1,937 median genes per cell sequenced to 59.9% sequencing saturation with 26,050 mean reads per cell.
Infections, Immunizations and Treatments
Mice were infected with LCMV-Armstrong intravenously (iv) at 2.5×105 pfu and analyzed on day 15 for scRNAseq and immunocytochemistry.
Mice were immunized with 0.5mg/ml NP(25)-CGG (Biosearch Technologies) in Sigma Adjuvant System (Sigma-Aldrich) in a total of 185 μl/mouse subcutaneously (sc) at the shoulders, flanks and above the tail and analyzed on day 10.
For LTβR and TNFR1 signaling blockade, Cxcl12-GFP (for SOX9 assessment) or UBI-GFP reverse chimeric mice (for TMEM119 assessment) were immunized sc at the shoulders, flanks and above the tail with SRBCs (Colorado Serum Company) on day 0 and day 5 and on day 10 treated iv with 100 μL each of 1mg/ml mLTβR-huIgG1 (LTβR-Fc, provided by J. Browning) and 1mg/ml TNFR55-huIgG1 (TNFR1-Fc, provided by J. Browning) or saline. Draining pLNs (axillary, brachial and inguinal) were analyzed 4 days later. C57BL/6 mice were treated on day 0 with LTβR-Fc and TNFR1-Fc and analyzed on day 3 (n = 1) or treated on day 0 and day 4 with LTβR-Fc and TNFR1-Fc (n = 1) or human IgG (hIg)(n = 1) and analyzed day 7. The n number listed in the figure legend and here indicates the number of mice examined in each experiment.
Immunofluorescence Microscopy
Tissues expressing GFP or ZsGreen were fixed in 4% PFA for 2 hours at 4°C, washed and sunk in 30% sucrose before freezing in OCT. REX3 tissues were fixed in PLP and processed as previously described (Groom et al., 2012). All other tissues were directly frozen in OCT and slides were fixed in acetone. 7μm cryosections and 30μm sections were stained as described (Rodda et al., 2015) with primary antibodies: Rabbit anti-Tmem119 (produced and gifted by B. Barres)(Bennett et al., 2016), anti-ENPP2 (polyclonal, R&D Systems), anti-TNFSF11 (polyclonal, R&D Systems), anti-CD34 FITC (RAM34, BD PharMingen), anti-CD31 biotin (MEC13.3, Biolegend), goat anti-IgD (polyclonal GAM/IGD(FC)/7S, Cedarlane Labs), goat anti-desmin (polyclonal, R&D Systems), anti-IgD Alexa647 (11-26c.2a, Biolegend), anti-BST-1 (BP-3, BD Biosciences) conjugated to Alexa647, rabbit anti-PDGFRβ (28E1, Cell Signaling), anti-CD11c Alexa647 (Biolegend), Rabbit anti-Sox9 (Millipore), anti-CD35 biotin (8C12, BD PharMingen), anti-CD16/32 biotin (93, Biolegend), Alexa647-conjugated anti-Bcl6 (K112-91, BD PharMingen), anti-GFP Alexa488 (Life Technologies) and anti-F4/80 biotin (Cedarlane Laboratories).
Sections were stained with the following secondary antibodies as previously described (Lu et al., 2017; Rodda et al., 2015): anti-FITC Alexa488, streptavidin Cy3, anti-goat AMCA, anti-Rabbit Alexa488 (Life Technologies), anti-Rabbit Alexa647, streptavidin Alexa555 (Life Technologies), anti-goat horseradish peroxidase, and streptavidin alkaline phosphatase. All secondary antibodies are from Jackson Immunoresearch unless otherwise noted.
Confocal microscopy on thick sections (30μm) was performed as described previously (Bannard et al., 2013). All other images were captured with a Zeiss AxioObserver Z1 microscope.
RNAscope
Performed as previously described (Lu et al., 2017) on 14μm sections using the RNAscope RED 2.5HD manual assay kit (Advanced Cell Diagnostics)(Wang et al., 2012). The RNAscope probes used targeted: Ch25h (NM_009890.1, targeting bp 115-1240), Inmt (NM_009349.3, targeting bp 3-1017) and Pthlh (NM_008970.4, targeting bp 173-1231).
Quantitative RT-PCR
Total RNA from pLNs was extracted using an RNeasy kit (QIAGEN) and reverse-transcribed. Quantitative PCR was performed as described (Lu et al., 2017) with the following primers: Inmt-F CCTTCTCTACAGGAGGTGTAGG; Inmt-R GTTCTGCGGGGTGTAGT CAG; Siglec1-F GGTCAGCCAACAGTTCACTC; Siglec1-R GAGACTCCTGTGGGCACC; Pdgfrb-F GCAGAAGAAGCCACGCTATG; Pdgfrb-R CAGGTGGAGTCGTAAGGCAA; Pthlh-F GGAGTGTCCTGGTATTCCTGC; Pthlh-R CCCTTGTCATGCAGTAGCTGA; Hprt-F AGGTTGCAAGCTTGCTGGT; Hprt-R TGAAGTACTCATTATAGTCAAGGGCA. Data were analyzed using the comparative CT (2-ΔΔCt) method with Hprt as the reference. Data plotted and unpaired t test p value calculated with Prism (GraphPad).
QUANTIFICATION AND STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
Unsupervised clustering of scRNAseq data
We used the Seurat R package (version 2.2)(Butler and Satija, 2017) for graph-based clustering and visualizations, all functions mentioned are from this package or the standard R version 3.4.2 package unless otherwise noted and were used with the default parameters unless otherwise noted. We analyzed only cells (unique barcodes) that passed quality control processing (above) and expressed at least 200 genes and only genes that were expressed in at least 3 cells, leaving us with 2,870 cells (5,573 median unique transcripts detected per cell and 2,153 median genes per cell) and 15,633 genes from the uninfected sample and 12,669 cells (4,482 median unique transcripts detected per cell and 1,938 median genes per cell) and 17,257 genes from the post-infection sample for further analysis. We also removed cells with greater than 5% mitochondrial genes and greater than 30% ribosomal protein genes.
Initially analyzing each sample separately, we applied library-size normalization to each cell with NormalizeData. Normalized expression for gene i in cell j was calculated by taking the natural log of the UMI counts for gene i in cell j divided by the total UMI counts in cell j multiplied by 10,000 and added to 1. To reduce the influence of variability in the number of UMIs, mitochondrial gene expression and ribosomal gene expression between cells on the clustering, we used the ScaleData function to linearly regress out these sources of variation before scaling and centering the data for dimensionality reduction. Principle component analysis was run using RunPCA on the variable genes calculated with FindVariableGenes (uninfected sample: 872 genes using x = (0.1,6), y = (0.5, 15); post-infection sample: 1193 genes using x = (0.0125,6), y = (0.5, 15) and then extended to the full dataset with ProjectPCA. Based on the PCElbowPlot result we decided to use 24 and 39 principle components (PCs) for the clustering of the uninfected sample cells and post-infection sample cells, respectively.
We ran FindClusters to apply shared nearest neighbor (SNN) graph-based clustering to each sample (0.5 for the uninfected sample and 0.4 for the post-infection sample) and used FindAllMarkers (Wilcoxon rank sum test, min.pct = 0.25, only.pos = True, thresh.use = 0.25) to identify the small clusters of endothelial (Cd31+) and non-SCs (Pdgfra− Pdgfrb− and/or CD45+) to be removed. These included neutrophils (Lyz2+), mast cells (Mcpt8+) and BECs (Clnd5+). Rare keratinocytes (Krt18+ Krt19+), LECs (Lyve1+ Prox1+) and Schwann cells (Mbp+ Plp1+) were also removed. The non-stromal and endothelial cells may have been collected due to low CD45 expression, low CD31 expression or sorting impurity. The remaining cells in each sample were then normalized and scaled as above. Mean expression and dispersion for each gene were calculated again for each sample as above.
Canonical Correlation Analysis
To combine both samples and identify a conserved gene correlation structure, we applied diagonal Canonical Correlation Analysis with RunCCA. We used the top 2000 variable genes from each sample (2,817 genes, 59.2% overlap) to calculate the correlation components (CCs) and determined 10 CCs captured the variability in the dataset by inspecting the results of DimHeatmap. Using CalcVarExpRatio to calculate the percentage of variance explained by the CCs for each cell, we retained cells with 50% or more variance explained. Discarded cells were analyzed for sample bias and enrichment for cell cycle signature. The Cell Cycle Score (CC Score) was calculated with CellCycleScoring using 96 canonical cell cycle genes (Tirosh et al., 2016) and cells with a score greater than 0.1 were considered cycling.
The retained cells from both samples were then aligned with AlignSubspace using 10 CC dimensions. Alignment quality was assessed by Pearson correlation of averaged log-normalized variable gene expression from each sample with cor.test. We then used FindClusters to apply SNN clustering to the combined cells using the 10 aligned CCs and resolution 0.5. After calculating differentially expressed genes (DEGs), we made sure this choice of resolution meant each cluster had at least 50 DEGs. The clustering was visualized with t-distributed stochastic neighbor embedding (tSNE) dimensionality reduction using RunTSNE (10 aligned CCs) and TSNEPlot. We also used BuildClusterTree to report the hierarchical distance matrix relating an ‘average’ cell from each cluster.
Differential gene expression
Since single-cell technologies currently capture only a portion of the transcripts in any cell, cells of the same type will not all report expression of exactly the same genes. This creates zero-inflated data making it challenging to determine differential expression of lowly expressed genes. To address this issue, we summed the raw UMI counts for each gene in each cluster over groups of twenty cells from the same sample and then treated these ‘pseudobulks’ (Lun et al., 2016) as technical replicates for DESeq differential gene analysis between each cluster’s pseudobulk samples and all other pseudobulk samples (DESeq2 package, version 1.16.1)(Love et al., 2014). We included the sample origin of each pseudobulk in the design formula of DESeqDataSetFromMatrix to account for batch effects in the p values. The Benjamini-Hochberg method was applied to adjust the p values for multiple testing (reported as FDR). Normalization was performed by the estimateSizeFactors and estimateDispersions functions as part of the DESeq function. We also calculated the proportion of cells in the cluster of interest expressing each gene to focus on differential expression of only well detected genes (pct_in).
Since there is a 4.5-fold difference in the number of cells between our two samples, we considered that batch effects from the larger sample could unduly influence the differential expression analysis. Therefore, we also used FindConservedMarkers to calculate the DEGs. This method calculates the cluster DEGs for the samples separately and then identifies the DEGs for each cluster conserved between the two sample analyses using the Fisher’s combined probability to calculate the p values and the Benjamini-Hochberg method to adjust for multiple testing. We found this method to be more conservative as it reports the minimum log2 fold change and maximum FDR for each gene, but all clusters still had at least 50 DEGs. All gene expression enriched for in a cluster and highlighted in the paper was found by both methods.
Subclustering analysis
The Nr4a1+ SCs were further subclustered by reapplying the CCA component analysis and alignment as above to cells in this cluster alone and used 10 aligned CCs for SNN clustering (resolution 0.3). DEGs between the three Nr4a1+ SC subclusters (greater than 50 DEGs each) were calculated with DESeq2 on pseudobulks as above with batch included in the design. Pearson correlation of the subclusters with the other subsets was calculated by comparing the differential expression (log2 fold change) of the DEGs for each subcluster with the differential expression (log2 fold change) of the genes for each other original subset.
The post-infection FDCs were analyzed for further subclustering by normalizing and performing unbiased clustering as above without CCA (14 PCs, resolution = 0.3), but the subclusters did not have 50 DEGs when compared to the other subcluster and all other clusters using DESeq2 as above.
Visualization
Log-normalized gene expression data was used for visualizations with violin plots (VlnPlot), tSNE plots (FeaturePlot) and expression comparison plots (GenePlot). Pearson correlations were calculated with cor and cor.test and visualized with plot. Scaled log-normalized gene expression data was used for visualizations with dot plots (DotPlot), heatmaps (DoHeatmap) and bar plots made with Prism (GraphPad). We plotted proportions with barplot. We reported DEG lists with write.table. Additional packages used: readxl (1.0), dplyr (0.7.4), Matrix (1.2-12), ggplot2 (2.2.1), cowplot (0.9.2), pheatmap (1.0.8), SummarizedExperiment (1.6.5), DelayedArray (0.2.7), matrixStats (0.52.2), GenomicRanges (1.28.6), GenomeInfoDb (1.12.3), IRanges (2.10.5), S4Vectors (0.14.7), Biobase (2.36.2) and BiocGenerics (0.22.1).
DATA AND SOFTWARE AVAILABILITY
The two scRNAseq datasets have been deposited in GEO under ID code GSE112903. Violin plot visualization of the datasets is available as a web tool at http://scorpio.ucsf.edu/shiny/LNSC.
Supplementary Material
Highlights.
Single-cell RNA sequencing of lymph node stromal cells reveals nine clusters
Known subsets TRCs, MRCs, FDCs, and perivascular cells identified
Five additional stromal cell clusters identified and anatomical locations determined
Two clusters, Cxcl9+ TRCs and Nr4a1+ SCs, are defined by activation signatures
Acknowledgments
We thank Y. Xu and J. An for technical assistance, H.-Y. Huang for the SC isolation protocol, E. Wan, S. Wong, and the Genomics Core Facility for mRNA library processing, sequencing, and alignment, R. Camire for preparation of REX3 LNs, M. Spitzer and M. Subramaniam for coding advice, T. Nagasawa for the Cxcl12-GFP mice, K. Rajewsky for the Cr2-Cre mice, D. Myers and J. Roose for the Nr4a1-GFP mice, and J. Browning for LTβR-Fc and TNFR1-Fc. This work and L.B.R. were supported by National Institutes of Health grants AI040098 and AI45073, E.L. was supported by NSF grant 1144247, C.L.S. was supported by NIH grant K08AI121421, A.D.L. was supported by NIH grant R01CA204028, and S.A.L. was supported by Swiss National Science Foundation grant 31003-146944/1. J.G.C. is an investigator of the Howard Hughes Medical Institute.
Footnotes
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
Conceptualization, L.B.R. and J.G.C.; Investigation, L.B.R., E.L., C.L.S., and X.W.; Software, L.B.R.; Formal Analysis, L.B.R.; Resources and protocols, M.L.B., B.A.B., A.D.L., S.A.L., and J.G.C.; Writing, L.B.R. and J.G.C.; Supervision, C.J.Y. and J.G.C.; Funding Acquisition, J.G.C.
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
Supplemental Information includes six figures and eight tables and can be found with this article online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2018.04.006.
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS
The authors declare no competing interests.
References
- Acton SE, Farrugia AJ, Astarita JL, Mourão-Sá D, Jenkins RP, Nye E, Hooper S, van Blijswijk J, Rogers NC, Snelgrove KJ, et al. Dendritic cells control fibroblastic reticular network tension and lymph node expansion. Nature. 2014;514:498–502. doi: 10.1038/nature13814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen CDC, Cyster JG. Follicular dendritic cell networks of primary follicles and germinal centers: phenotype and function. Semin Immunol. 2008;20:14–25. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2007.12.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen CDC, Okada T, Tang HL, Cyster JG. Imaging of germinal center selection events during affinity maturation. Science. 2007;315:528–531. doi: 10.1126/science.1136736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ara T, Tokoyoda K, Sugiyama T, Egawa T, Kawabata K, Nagasawa T. Long-term hematopoietic stem cells require stromal cell-derived factor-1 for colonizing bone marrow during ontogeny. Immunity. 2003;19:257–267. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(03)00201-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armulik A, Genové G, Betsholtz C. Pericytes: developmental, physiological, and pathological perspectives, problems, and promises. Dev Cell. 2011;21:193–215. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2011.07.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Astarita JL, Cremasco V, Fu J, Darnell MC, Peck JR, Nieves-Bonilla JM, Song K, Kondo Y, Woodruff MC, Gogineni A, et al. The CLEC-2-podoplanin axis controls the contractility of fibroblastic reticular cells and lymph node microarchitecture. Nat Immunol. 2015;16:75–84. doi: 10.1038/ni.3035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bannard O, Horton RM, Allen CDC, An J, Nagasawa T, Cyster JG. Germinal center centroblasts transition to a centrocyte phenotype according to a timed program and depend on the dark zone for effective selection. Immunity. 2013;39:912–924. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2013.08.038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baratin M, Simon L, Jorquera A, Ghigo C, Dembele D, Nowak J, Gentek R, Wienert S, Klauschen F, Malissen B, et al. T cell zone resident macrophages silently dispose of apoptotic cells in the lymph node. Immunity. 2017;47:349–362.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2017.07.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauman DR, Bitmansour AD, McDonald JG, Thompson BM, Liang G, Russell DW. 25-Hydroxycholesterol secreted by macrophages in response to Toll-like receptor activation suppresses immunoglobulin A production. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106:16764–16769. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0909142106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumheter S, Singer MS, Henzel W, Hemmerich S, Renz M, Rosen SD, Lasky LA. Binding of L-selectin to the vascular sialomucin CD34. Science. 1993;262:436–438. doi: 10.1126/science.7692600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett ML, Bennett FC, Liddelow SA, Ajami B, Zamanian JL, Fernhoff NB, Mulinyawe SB, Bohlen CJ, Adil A, Tucker A, et al. New tools for studying microglia in the mouse and human CNS. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2016;113:E1738–E1746. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1525528113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown FD, Turley SJ. Fibroblastic reticular cells: organization and regulation of the T lymphocyte life cycle. J Immunol. 2015;194:1389–1394. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1402520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler A, Satija R. Integrated analysis of single cell transcriptomic data across conditions, technologies, and species. bioRxiv. 2017:164889. doi: 10.1038/nbt.4096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chai Q, Onder L, Scandella E, Gil-Cruz C, Perez-Shibayama C, Cupovic J, Danuser R, Sparwasser T, Luther SA, Thiel V, et al. Maturation of lymph node fibroblastic reticular cells from myofibroblastic precursors is critical for antiviral immunity. Immunity. 2013;38:1013–1024. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2013.03.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang JE, Turley SJ. Stromal infrastructure of the lymph node and coordination of immunity. Trends Immunol. 2015;36:30–39. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2014.11.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chappaz S, Gärtner C, Rodewald HR, Finke D. Kit ligand and Il7 differentially regulate Peyer’s patch and lymph node development. J Immunol. 2010;185:3514–3519. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1000665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clingan JM, Matloubian M. B Cell-intrinsic TLR7 signaling is required for optimal B cell responses during chronic viral infection. J Immunol. 2013;191:810–818. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1300244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordeiro OG, Chypre M, Brouard N, Rauber S, Alloush F, Romera-Hernandez M, Bénézech C, Li Z, Eckly A, Coles MC, et al. Integrin-alpha IIb identifies murine lymph node lymphatic endothelial cells responsive to RANKL. PLoS ONE. 2016;11:e0151848. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0151848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corselli M, Chen CW, Sun B, Yap S, Rubin JP, Péault B. The tunica adventitia of human arteries and veins as a source of mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2012;21:1299–1308. doi: 10.1089/scd.2011.0200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cremasco V, Woodruff MC, Onder L, Cupovic J, Nieves-Bonilla JM, Schildberg FA, Chang J, Cremasco F, Harvey CJ, Wucherpfennig K, et al. B cell homeostasis and follicle confines are governed by fibroblastic reticular cells. Nat Immunol. 2014;15:973–981. doi: 10.1038/ni.2965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cyster JG. Chemokines, sphingosine-1-phosphate, and cell migration in secondary lymphoid organs. Annu Rev Immunol. 2005;23:127–159. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.23.021704.115628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cyster JG, Ansel KM, Reif K, Ekland EH, Hyman PL, Tang HL, Luther SA, Ngo VN. Follicular stromal cells and lymphocyte homing to follicles. Immunol Rev. 2000;176:181–193. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-065x.2000.00618.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cyster JG, Dang EV, Reboldi A, Yi T. 25-Hydroxycholesterols in innate and adaptive immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2014;14:731–743. doi: 10.1038/nri3755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Díaz-Flores L, Gutiérrez R, García MP, Sáez FJ, Díaz-Flores L, Jr, Valladares F, Madrid JF. CD34+ stromal cells/fibroblasts/fibrocytes/telocytes as a tissue reserve and a principal source of mesenchymal cells. Location, morphology, function and role in pathology Histol Histopathol. 2014;29:831–870. doi: 10.14670/HH-29.831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fichtner-Feigl S, Strober W, Kawakami K, Puri RK, Kitani A. IL-13 signaling through the IL-13alpha2 receptor is involved in induction of TGF-beta1 production and fibrosis. Nat Med. 2006;12:99–106. doi: 10.1038/nm1332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girard JP, Moussion C, Förster R. HEVs, lymphatics and homeostatic immune cell trafficking in lymph nodes. Nat Rev Immunol. 2012;12:762–773. doi: 10.1038/nri3298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein BJ, Goss GM, Hatzistergos KE, Rangel EB, Seidler B, Saur D, Hare JM. Adult c-Kit(+) progenitor cells are necessary for maintenance and regeneration of olfactory neurons. J Comp Neurol. 2015;523:15–31. doi: 10.1002/cne.23653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray EE, Cyster JG. Lymph node macrophages. J Innate Immun. 2012;4:424–436. doi: 10.1159/000337007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groom JR, Richmond J, Murooka TT, Sorensen EW, Sung JH, Bankert K, von Andrian UH, Moon JJ, Mempel TR, Luster AD. CXCR3 chemokine receptor-ligand interactions in the lymph node optimize CD4+ T helper 1 cell differentiation. Immunity. 2012;37:1091–1103. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2012.08.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hargreaves DC, Hyman PL, Lu TT, Ngo VN, Bidgol A, Suzuki G, Zou YR, Littman DR, Cyster JG. A coordinated change in chemokine responsiveness guides plasma cell movements. J Exp Med. 2001;194:45–56. doi: 10.1084/jem.194.1.45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He C, Pillai SS, Taglini F, Li F, Ruan K, Zhang J, Wu J, Shi Y, Bayne EH. Structural analysis of Stc1 provides insights into the coupling of RNAi and chromatin modification. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013;110:E1879–E1888. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1212155110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heesters BA, Myers RC, Carroll MC. Follicular dendritic cells: dynamic antigen libraries. Nat Rev Immunol. 2014;14:495–504. doi: 10.1038/nri3689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang YH, Jankowski A, Cheah KSE, Prabhakar S, Jauch R. SOXE transcription factors form selective dimers on non-compact DNA motifs through multifaceted interactions between dimerization and high-mobility group domains. Sci Rep. 2015;5:10398. doi: 10.1038/srep10398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iannacone M, Moseman EA, Tonti E, Bosurgi L, Junt T, Henrickson SE, Whelan SP, Guidotti LG, von Andrian UH. Subcapsular sinus macrophages prevent CNS invasion on peripheral infection with a neurotropic virus. Nature. 2010;465:1079–1083. doi: 10.1038/nature09118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarjour M, Jorquera A, Mondor I, Wienert S, Narang P, Coles MC, Klauschen F, Bajénoff M. Fate mapping reveals origin and dynamics of lymph node follicular dendritic cells. J Exp Med. 2014;211:1109–1122. doi: 10.1084/jem.20132409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson LA, Jackson DG. The chemokine CX3CL1 promotes trafficking of dendritic cells through inflamed lymphatics. J Cell Sci. 2013;126:5259–5270. doi: 10.1242/jcs.135343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanamoto T, Mizuhashi K, Terada K, Minami T, Yoshikawa H, Furukawa T. Isolation and characterization of a novel plasma membrane protein, osteoblast induction factor (obif), associated with osteoblast differentiation. BMC Dev Biol. 2009;9:70. doi: 10.1186/1471-213X-9-70. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanazawa N, Nakamura T, Tashiro K, Muramatsu M, Morita K, Yoneda K, Inaba K, Imamura S, Honjo T. Fractalkine and macrophage-derived chemokine: T cell-attracting chemokines expressed in T cell area dendritic cells. Eur J Immunol. 1999;29:1925–1932. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1521-4141(199906)29:06<1925::AID-IMMU1925>3.0.CO;2-U. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanda H, Newton R, Klein R, Morita Y, Gunn MD, Rosen SD. Autotaxin, an ectoenzyme that produces lysophosphatidic acid, promotes the entry of lymphocytes into secondary lymphoid organs. Nat Immunol. 2008;9:415–423. doi: 10.1038/ni1573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastenmüller W, Brandes M, Wang Z, Herz J, Egen JG, Germain RN. Peripheral prepositioning and local CXCL9 chemokine-mediated guidance orchestrate rapid memory CD8+ T cell responses in the lymph node. Immunity. 2013;38:502–513. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2012.11.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katakai T, Suto H, Sugai M, Gonda H, Togawa A, Suematsu S, Ebisuno Y, Katagiri K, Kinashi T, Shimizu A. Organizer-like reticular stromal cell layer common to adult secondary lymphoid organs. J Immunol. 2008;181:6189–6200. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.9.6189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katakai T, Kondo N, Ueda Y, Kinashi T. Autotaxin produced by stromal cells promotes LFA-1-independent and Rho-dependent interstitial T cell motility in the lymph node paracortex. J Immunol. 2014;193:617–626. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1400565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan KA, Naylor AJ, Khan A, Noy PJ, Mambretti M, Lodhia P, Athwal J, Korzystka A, Buckley CD, Willcox BE, et al. Multimerin-2 is a ligand for group 14 family C-type lectins CLEC14A, CD93 and CD248 spanning the endothelial pericyte interface. Oncogene. 2017;36:6097–6108. doi: 10.1038/onc.2017.214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitazawa T, Sato T, Nishiyama K, Asai R, Arima Y, Uchijima Y, Kurihara Y, Kurihara H. Identification and developmental analysis of endothelin receptor type-A expressing cells in the mouse kidney. Gene Expr Patterns. 2011;11:371–377. doi: 10.1016/j.gep.2011.04.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraus M, Alimzhanov MB, Rajewsky N, Rajewsky K. Survival of resting mature B lymphocytes depends on BCR signaling via the Igalpha/beta heterodimer. Cell. 2004;117:787–800. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2004.05.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lain E, Carnejac S, Escher P, Wilson MC, Lømo T, Gajendran N, Brenner HR. A novel role for embigin to promote sprouting of motor nerve terminals at the neuromuscular junction. J Biol Chem. 2009;284:8930–8939. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M809491200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasoudris F, Cousin C, Prevost-Blondel A, Martin-Garcia N, Abd-Alsamad I, Ortonne N, Farcet JP, Castellano F, Molinier-Frenkel V. IL4I1: an inhibitor of the CD8+ antitumor T-cell response in vivo. Eur J Immunol. 2011;41:1629–1638. doi: 10.1002/eji.201041119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lax S, Hardie DL, Wilson A, Douglas MR, Anderson G, Huso D, Isacke CM, Buckley CD. The pericyte and stromal cell marker CD248 (endosialin) is required for efficient lymph node expansion. Eur J Immunol. 2010;40:1884–1889. doi: 10.1002/eji.200939877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M, Kiefel H, LaJevic MD, Macauley MS, Kawashima H, O’Hara E, Pan J, Paulson JC, Butcher EC. Transcriptional programs of lymphoid tissue capillary and high endothelium reveal control mechanisms for lymphocyte homing. Nat Immunol. 2014;15:982–995. doi: 10.1038/ni.2983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J, Lu E, Yi T, Cyster JG. EBI2 augments Tfh cell fate by promoting interaction with IL-2-quenching dendritic cells. Nature. 2016;533:110–114. doi: 10.1038/nature17947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Link A, Vogt TK, Favre S, Britschgi MR, Acha-Orbea H, Hinz B, Cyster JG, Luther SA. Fibroblastic reticular cells in lymph nodes regulate the homeostasis of naive T cells. Nat Immunol. 2007;8:1255–1265. doi: 10.1038/ni1513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Love MI, Huber W, Anders S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014;15:550. doi: 10.1186/s13059-014-0550-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu E, Dang EV, McDonald JG, Cyster JG. Distinct oxysterol requirements for positioning naïve and activated dendritic cells in the spleen. Sci Immunol. 2017;2:2. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.aal5237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lun ATL, Bach K, Marioni JC. Pooling across cells to normalize single-cell RNA sequencing data with many zero counts. Genome Biol. 2016;17:75. doi: 10.1186/s13059-016-0947-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malhotra D, Fletcher AL, Astarita J, Lukacs-Kornek V, Tayalia P, Gonzalez SF, Elpek KG, Chang SK, Knoblich K, Hemler ME, et al. Immunological Genome Project Consortium Transcriptional profiling of stroma from inflamed and resting lymph nodes defines immunological hallmarks. Nat Immunol. 2012;13:499–510. doi: 10.1038/ni.2262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mavlyutov TA, Epstein ML, Liu P, Verbny YI, Ziskind-Conhaim L, Ruoho AE. Development of the sigma-1 receptor in C-terminals of motoneurons and colocalization with the N,N′-dimethyltryptamine forming enzyme, indole-N-methyl transferase. Neuroscience. 2012;206:60–68. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.12.040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCauley LK, Martin TJ. Twenty-five years of PTHrP progress: from cancer hormone to multifunctional cytokine. J Bone Miner Res. 2012;27:1231–1239. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.1617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLatchie LM, Fraser NJ, Main MJ, Wise A, Brown J, Thompson N, Solari R, Lee MG, Foord SM. RAMPs regulate the transport and ligand specificity of the calcitonin-receptor-like receptor. Nature. 1998;393:333–339. doi: 10.1038/30666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mionnet C, Mondor I, Jorquera A, Loosveld M, Maurizio J, Arcangeli ML, Ruddle NH, Nowak J, Aurrand-Lions M, Luche H, Bajénoff M. Identification of a new stromal cell type involved in the regulation of inflamed B cell follicles. PLoS Biol. 2013;11:e1001672. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller SN, Germain RN. Stromal cell contributions to the homeostasis and functionality of the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol. 2009;9:618–629. doi: 10.1038/nri2588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller SN, Hosiawa-Meagher KA, Konieczny BT, Sullivan BM, Bachmann MF, Locksley RM, Ahmed R, Matloubian M. Regulation of homeostatic chemokine expression and cell trafficking during immune responses. Science. 2007;317:670–674. doi: 10.1126/science.1144830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O’Sullivan ML, de Wit J, Savas JN, Comoletti D, Otto-Hitt S, Yates JR, 3rd, Ghosh A. FLRT proteins are endogenous latrophilin ligands and regulate excitatory synapse development. Neuron. 2012;73:903–910. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2012.01.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onder L, Scandella E, Chai Q, Firner S, Mayer CT, Sparwasser T, Thiel V, Rülicke T, Ludewig B. A novel bacterial artificial chromosome-transgenic podoplanin-cre mouse targets lymphoid organ stromal cells in vivo. Front Immunol. 2011;2:50. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2011.00050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Py BF, Gonzalez SF, Long K, Kim MS, Kim YA, Zhu H, Yao J, Degauque N, Villet R, Ymele-Leki P, et al. Cochlin produced by follicular dendritic cells promotes antibacterial innate immunity. Immunity. 2013;38:1063–1072. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2013.01.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodda LB, Bannard O, Ludewig B, Nagasawa T, Cyster JG. Phenotypic and morphological properties of germinal center dark zone Cxcl12-expressing reticular cells. J Immunol. 2015;195:4781–4791. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1501191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sainte-Marie G. The lymph node revisited: development, morphology, functioning, and role in triggering primary immune responses. Anat Rec (Hoboken) 2010;293:320–337. doi: 10.1002/ar.21051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satija R, Farrell JA, Gennert D, Schier AF, Regev A. Spatial reconstruction of single-cell gene expression data. Nat Biotechnol. 2015;33:495–502. doi: 10.1038/nbt.3192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scandella E, Bolinger B, Lattmann E, Miller S, Favre S, Littman DR, Finke D, Luther SA, Junt T, Ludewig B. Restoration of lymphoid organ integrity through the interaction of lymphoid tissue-inducer cells with stroma of the T cell zone. Nat Immunol. 2008;9:667–675. doi: 10.1038/ni.1605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulz O, Hammerschmidt SI, Moschovakis GL, Förster R. Chemokines and chemokine receptors in lymphoid tissue dynamics. Annu Rev Immunol. 2016;34:203–242. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-041015-055649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sitnik KM, Wendland K, Weishaupt H, Uronen-Hansson H, White AJ, Anderson G, Kotarsky K, Agace WW. Context-dependent development of lymphoid stroma from adult CD34(+) adventitial progenitors. Cell Rep. 2016;14:2375–2388. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.02.033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sung JH, Zhang H, Moseman EA, Alvarez D, Iannacone M, Henrickson SE, de la Torre JC, Groom JR, Luster AD, von Andrian UH. Chemokine guidance of central memory T cells is critical for antiviral recall responses in lymph nodes. Cell. 2012;150:1249–1263. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.08.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki K, Maruya M, Kawamoto S, Sitnik K, Kitamura H, Agace WW, Fagarasan S. The sensing of environmental stimuli by follicular dendritic cells promotes immunoglobulin A generation in the gut. Immunity. 2010;33:71–83. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2010.07.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tirosh I, Izar B, Prakadan SM, Wadsworth MH, 2nd, Treacy D, Trombetta JJ, Rotem A, Rodman C, Lian C, Murphy G, et al. Dissecting the multicellular ecosystem of metastatic melanoma by single-cell RNA-seq. Science. 2016;352:189–196. doi: 10.1126/science.aad0501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokuda N, Adachi T, Adachi Y, Higashi M, Sharifi K, Tuerxun T, Sawada T, Kondo H, Owada Y. Identification of FABP7 in fibroblastic reticular cells of mouse lymph nodes. Histochem Cell Biol. 2010;134:445–452. doi: 10.1007/s00418-010-0754-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhlén M, Fagerberg L, Hallström BM, Lindskog C, Oksvold P, Mardinoglu A, Sivertsson Å, Kampf C, Sjöstedt E, Asplund A, et al. Proteomics. Tissue-based map of the human proteome. Science. 2015;347:1260419. doi: 10.1126/science.1260419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullman KS, Northrop JP, Verweij CL, Crabtree GR. Transmission of signals from the T lymphocyte antigen receptor to the genes responsible for cell proliferation and immune function: the missing link. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:421–452. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.002225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulvmar MH, Werth K, Braun A, Kelay P, Hub E, Eller K, Chan L, Lucas B, Novitzky-Basso I, Nakamura K, et al. The atypical chemokine receptor CCRL1 shapes functional CCL21 gradients in lymph nodes. Nat Immunol. 2014;15:623–630. doi: 10.1038/ni.2889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Pavert SA, Mebius RE. New insights into the development of lymphoid tissues. Nat Rev Immunol. 2010;10:664–674. doi: 10.1038/nri2832. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang F, Flanagan J, Su N, Wang LC, Bui S, Nielson A, Wu X, Vo HT, Ma XJ, Luo Y. RNAscope: a novel in situ RNA analysis platform for formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues. J Mol Diagn. 2012;14:22–29. doi: 10.1016/j.jmoldx.2011.08.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilke G, Steinhauser G, Grün J, Berek C. In silico subtraction approach reveals a close lineage relationship between follicular dendritic cells and BP3(hi) stromal cells isolated from SCID mice. Eur J Immunol. 2010;40:2165–2173. doi: 10.1002/eji.200940202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng GXY, Terry JM, Belgrader P, Ryvkin P, Bent ZW, Wilson R, Ziraldo SB, Wheeler TD, McDermott GP, Zhu J, et al. Massively parallel digital transcriptional profiling of single cells. Nat Commun. 2017;8:14049. doi: 10.1038/ncomms14049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zikherman J, Parameswaran R, Weiss A. Endogenous antigen tunes the responsiveness of naive B cells but not T cells. Nature. 2012;489:160–164. doi: 10.1038/nature11311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


