Figure 1.
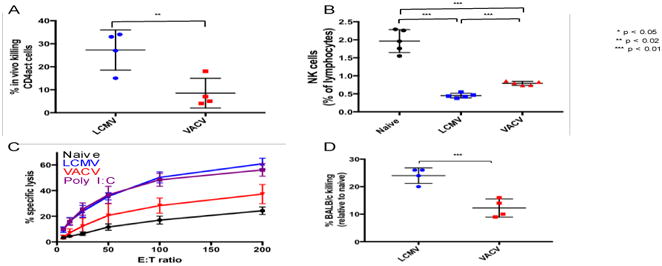
Comparison of cytolytic potential between LCMV-and VACV-induced NK cells. A. Percentage of labeled donor splenic CD4act cells from day 4 LCMV-infected mice killed in day 3 LCMV-infected and VACV-infected hosts after delivery of 6 × 107 labeled LCMV-infected (day 4) splenocytes, from NK cell-depleted donors, by tail vein injection and recovery in splenocyte preparation following 5 hour incubation. B. Splenic NK cell frequencies among naïve, LCMV- and VACV-infected mice at day 3 post-infection. C. Cytotoxicity of naïve, virally-induced, and poly I:C- activated splenic NK cells against 51Cr-labeled YAC-1 cells. D. Killing of BALB/c donor splenocytes in LCMV-and VACV-infected C57BL/6J hosts after delivery of 6 × 107 labeled naïve BALB/c splenocytes by tail vein injection and recovery in splenocyte preparations following 2-hour incubation. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.02, *** p < 0.01. NK cell gating scheme: Singlets (FSC)>Lymphocytes(SSC)>NK 1.1(+) CD3(-).
