Figure 4.
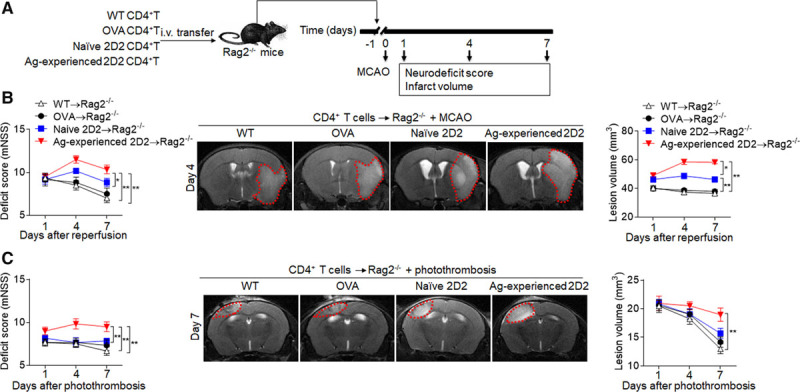
Diversified T-cell responses exacerbate neurodeficits and brain infarction. CD4+ T cells (CD4+CD44lowCD62Lhigh) were obtained from spleens of wild-type mice (WT→Rag2−/−) and OVA mice (OVA→Rag2−/−) at day 7 after sham surgery, naive 2D2 mice (naive 2D2→Rag2−/−) at day 7 after sham surgery, or 2D2 mice at day 7 after middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) or photothrombosis (antigen [Ag]-experienced 2D2→Rag2−/−). These T cells were injected intravenous (i.v.) into Rag2−/− recipients and followed by 60 min of MCAO or photothrombotic stroke procedures at 24 hours after injection. A, Schematic graph showing the experimental design. B, The neurological deficit scores (mNSS) were assessed in different groups at the indicated days after MCAO (B) or photothrombosis (C). 7T magnetic resonance imaging shows brain lesions in different groups at day 4 after MCAO (B) or photothrombosis (C). Cumulative results show quantifications of lesion volume. n=12 mice per group. *P<0.05, **P<0.01.
