Abstract
Patients harboring germline mutations in the succinate dehydrogenase complex subunit B (SDHB) gene present with pheochromocytomas and paragangliomas (PPGL) that are more likely malignant and clinically aggressive. The combination chemotherapy cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and dacarbazine (CVD) was retrospectively evaluated in patients with SDHB-associated metastatic PPGL.Query Twelve metastatic PPGL patients harboring SDHB mutations/polymorphisms with undetectable SDHB immunostaining were treated with CVD. CVD therapy consisted of 750 mg/m2 cyclophosphamide with 1.4 mg/m2 vincristine on day 1 and 600 mg/m2 dacarbazine on days 1 and 2, every 21–28 days. Treatment outcome was determined by RECIST criteria as well as determination of response duration and progression-free and overall survivals. A median of 20.5 cycles (range 4–41) was administered. All patients had tumor reduction (12–100% by RECIST). Complete response was seen in two patients, while partial response was observed in 8. The median number of cycles to response was 5.5. Median duration of response was 478 days, with progression-free and overall survivals of 930 and 1190 days, respectively. Serial [18F]-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography and computed tomography imaging demonstrated continued incremental reduction in maximal standardized uptake values (SUVmax) values in 26/30 lesions. During treatment administration, the median SUV decreased from > 25 to < 6, indicating the efficacy of chemotherapy over a prolonged period of time. Prolonged therapy results in continued incremental tumor reduction, and is consistent with persistent drug sensitivity. CVD chemotherapy is recommended to be considered part of the initial management in patients with metastatic SDHB-related PPGL.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (10.1007/s10571-018-0579-4) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keywords: Pheochromocytoma/paraganglioma, Succinate dehydrogenase, Cyclophosphamide, Vincristine, Dacarbazine
Introduction
Pheochromocytomas and paragangliomas (PPGLs) are rare catecholamine producing neoplasms that arise from chromaffin tissue of the adrenal medulla and the sympathetic or parasympathetic ganglia, respectively. PPGLs occur in 2–8 people per million with a peak incidence in the fourth and fifth decades of life (Andersen et al. 1988; Fernandez-Calvet and Garcia-Mayor 1994; Hartley and Perry-Keene 1985; Stenström and Svärdsudd 1986). Catecholamines (dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine) are a class of neurotransmitters (Eisenhofer et al. 2004). Hypertension, tachycardia, headache, pallor, sweating, and feelings of anxiety are the most common symptoms associated with catecholamine excess (Zelinka et al. 2007; Lenders et al. 2005), and sustained, uncontrolled catecholamine secretion can lead to severe cardiovascular complications. In 2013, Stolk et al. reported that compared to their essential hypertensive counterparts, PPGL patients were 14 times more likely to experience a cardiovascular event due to their prolonged exposure to catecholamines (Stolk et al. 2013). While surgical anesthesia and tumor manipulation are considered the most direct means of stimulating an eruption of catecholamines, excessive physical activity, traumatic psychological scenarios, certain foods, and medications used to treat nausea, depression, allergies, and infections may likewise elicit an unexpected significant release of catecholamines (Lenders et al. 2005; Pacak 2007). Even without a trigger, these tumors are capable of producing dangerous levels of catecholamines. Patients presenting with classic signs of catecholamine excess must be appropriately treated with an adrenoceptor blockade to achieve control of their blood pressure and heart rate and prevent other organ-specific damage (Agarwal et al. 2011). However, approximately 20% of patients do not display any symptoms related to an abundance of circulating catecholamines due to the downregulation of β-adrenergic receptors found in heart and adipose tissues after prolonged exposure to elevated circulating catecholamines (Tsujimoto et al. 1984). These patients are too at risk for suffering from cardiovascular catastrophes such as sudden death, myocardial infarction, heart failure, stroke, and shock, and should likewise be medically treated with an alpha adrenoceptor blockade.
Succinate dehydrogenase complex subunit B (SDHB)-related PPGLs are predominately norepinephrine and dopamine secreting tumors (Timmers et al. 2007a). In contrast to other hereditary PPGL syndromes, SDHB mutation carriers are more likely to present with clinical symptoms and biochemical evidence of elevated metanephrines and the novel biomarker plasma methoxytyramine, the O-methylated metabolite of dopamine (Zelinka et al. 2007; Eisenhofer et al. 2012). In addition, the rate of metastases is much higher in patients with germline SDHB mutations (Amar et al. 2005; Benn et al. 2006; Neumann et al. 2004; Timmers et al. 2007a; Srirangalingam et al. 2008; Bausch et al. 2014; Brouwers et al. 2006). Depending on the genetic background and location, 3–36% of PPGLs are metastatic at presentation (Edström Elder et al. 2003; Glodny et al. 2001; O’Riordain et al. 1996). Although some morphological or histological criteria to distinguish benign from malignant disease has been introduced, the diagnosis of malignancy is often made clinically (Bravo 1991; Eisenhofer and Tischler 2014; Goldstein et al. 1999; Plouin et al. 1997; Thompson 2002; Wu et al. 2009). Mutations in the SDHB gene have been found in families with abdominal, pelvic, and thoracic PPGLs. SDHB mutation carriers develop disease early in life and are more likely to develop malignant PPGLs as well as additional tumors (renal cell carcinoma, gastrointestinal stromal tumors, and rarely, pituitary tumors) (Benn et al. 2006; Neumann et al. 2004; Timmers et al. 2007a; Srirangalingam et al. 2008; Bausch et al. 2014). In contrast to sporadic cases where tumors are found outside the adrenal gland less than 40% of the time, SDHB-related malignant PPGLs usually present in an extra-adrenal location (Brouwers et al. 2006; Korpershoek et al. 2011). The most effective treatment for PPGL is surgical resection (Eisenhofer et al. 2004; Plouin et al. 2001; Shen et al. 2010). However, patients with metastatic PPGL have a 5-year survival < 50% than their age-matched controls (Niemeijer et al. 2014; Huang et al. 2008).
Several single agents and multi-drug regimens have been evaluated in a limited number of patients with variable results. The most active chemotherapy regimen—a combination of cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and dacarbazine (CVD)—produces remissions of moderate duration in symptomatic patients (Niemeijer et al. 2014; Huang et al. 2008; Averbuch et al. 1988; Hescot et al. 2013). An analysis of 18 patients with PPGL treated with CVD and followed for 22 years showed 2 (11%) complete and 8 (44%) partial responses (Niemeijer et al. 2014). All patients with tumors scored as responding reported symptom improvement. CVD was well tolerated with only grade I/II toxicities (Niemeijer et al. 2014). Since it is known that patients with PPGL harboring SDHB mutations have an earlier presentation of metastatic disease and a worse prognosis, we report the outcome of 12 patients with SDHB mutations/polymorphisms or lacking SDHB expression and metastatic PPGL treated with CVD at a single institution. We describe a high response rate to CVD and present evidence of prolonged treatment results in continued tumor reduction. The risk/benefits of continued long-term treatment are also discussed.
Methods (see also supplementary material)
Patients and Methods
In August 2005, 12 patients with metastatic PPGL consented to receive chemotherapy. These 12 patients included every patient with metastatic PPGL treated with chemotherapy during this period at our institution. The chemotherapy used, while now considered a “standard option,” had previously been administered on diagnostic and treatment protocols approved by the Institutional Review Board of the National Cancer Institute. All had adequate bone marrow function as well as normal renal and hepatic function with a Karnofsky PS > 30%.
Drug Therapy and Methods
Before starting CVD, drugs were administered to control symptoms of catecholamine excess and to maintain a normal blood pressure and heart rate. The initial treatment consisted of up to 240 mg/day oral of phenoxybenzamine, a α-adrenergic blocker, usually in combination with a β-adrenergic blocker such as propranolol or atenolol. If blood pressure remained elevated, a calcium channel blocker, or up to 2.0 g/day metyrosine, a catecholamine synthesis inhibitor, was administered. CVD consisted of intravenous cyclophosphamide (750 mg/m2) and vincristine (1.4 mg/m2) on day 1, and intravenous dacarbazine (600 mg/m2) on days 1 and 2, every 21–28 days.
Treatment Evaluation and Methods
Radiology and nuclear medicine studies were repeated every 6–16 weeks. If the original studies were abnormal, the interval varied for the various imaging modalities. Tumor response was based on RECIST (Hescot et al. 2013) and results observed on computed tomography (CT) and/or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) (Martucci and Pacak 2014). [18F]-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography and computed tomography ([18F]-FDG PET/CT) scans and [123/131I]-metaiodobenzylguanidine (MIBG) scintigraphy were not utilized to score responses.
Results
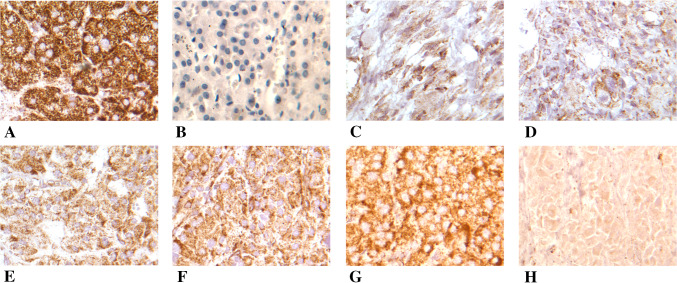
Patient demographics and laboratory data are summarized in Tables 1 and 2. All had a diagnosis of PPGL and evidence of a mutation/polymorphism in the SDHB gene (SDHB expression was not detectable in the patient with a polymorphism) (Fig. 1). Initial age of diagnosis was early in life (median 33, range 18–51), all previously underwent surgical resection of original tumors, and 7 of the 12 patients had had at least one metastasectomy. All patients were normotensive at the time of treatment, with nine requiring blood pressure control via antihypertensive medications.
Table 1.
Patient and tumor characteristics
| Sex | Age at diagnosis | Age CVD started | Initial site of disease | Sites of metastasis | Family history | Biochemical phenotype | BP treatment | Mutation status | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene | Nucleotide | Amino Acid | Exon | |||||||||
| 1 | F | 18 | 35 | Adrenal | Liver, bones | Pancreatic cancer | N | No | SDHB | 136 C → T | Arg46 → stop | 2 |
| 2 | M | 24 | 31 | Paraspinal (T3–4) | Lung, nodes, spine, bones | Cervical cancer | NEG | No | SDHB | 136 C → T | Arg46 → stop | 2 |
| 3 | M | 40 | 42 | Renal, paraspinal | Renal, bones, paraspinal, liver | Hodgkin’s lymphoma | N | Yes | SDHB | 136 C → T | Arg46 → stop | 2 |
| 4 | F | 51 | 52 | Retroperitoneum | Lung, spine, bones | No Cancer | N | Yes | SDHB | IVS3 + 1 G → A | Splice | 3 |
| 5 | M | 32 | 38 | Extra-adrenal | Liver, nodes | PHEO | N, D | Yes | SDHB | 72 + 1 G → T | (–) | Intron 1 |
| 6 | M | 27 | 29 | Pelvic | Lung | PHEO | A, N, D | Yes | SDHB | 196 C → T | Cys66 → Tyr66 | (-) |
| 7 | F | 38 | 41 | Adrenal, tail pancreas | Pelvic bones, spine, liver | No Cancer | NEG | Yes | SDHB | 136 C → T | Arg46 → stop | 2 |
| 8 | F | 21 | 25 | Adrenal | Liver | No Cancer | N, D | Yes | SDHB polymorphism | 487 T → C | Ser163 → Pro163 | 5 |
| 9 | M | 34 | 35 | Retroperitoneum | Nodes | Glomus tumor | N, D | Yes | SDHB | IVS3-1 G → C | Splice | 3 |
| 10 | M | 50 | 50 | Adrenal | Peri-aortic nodes, liver | PHEO/PGL | N, D | Yes | SDHB | Deletion | Deletion | 1 |
| 11 | M | 37 | 40 | Peri-aortic nodes | Liver | PGL | N, D | Yes | SDHB | 590 C → G | Pro197 → Arg197 | 6 |
| 12 | F | 32 | 41 | Adrenal | Chest wall, liver | PGL | N | No | SDHB | Deletion | Deletion | 1 |
PHEO pheochromocytoma, PGL paraganglioma, SDHB succinate dehydrogenase complex subunit B, IVS intervening sequence, A adrenergic, D dopaminergic, N noradrenergic, NEG biochemically negative
Table 2.
Prior therapies, treatment summary, and response parameters
| Prior therapies | Total number of chemotherapy cycles | Number of cycles to PR | Maximum response (percent tumor shrinkage) (%) | Duration of response (days) | PFS (days) | OS (days) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | XRT, MIBG | 22 | 20 | 48 | 142 | 623 | > 763 |
| 2 | XRT, RFA | 32 | 18 | 70 | 529 | 949 | 1461 + |
| 3 | XRT | 26 | Not achieved | 12 | (–) | 1369 | 2337 |
| 4 | Octreotide LAR | 8 | Not achieved | 19 | (–) | 1019 | 1349 |
| 5 | Bevacizumab | 24 | 6 | 100 | 1623 +a | 1734 +a | 1796 +a |
| 6 | None | 7 | 2 | 66 | > 127b | >175b | 870 |
| 7 | Carboplatin + Paclitaxel | 26 | 11 | 45 | 578 | 910 | 1032 + |
| 8 | XRT | 41 | 5 | 71 | 1561 | 1632c | 1632 |
| 9 | XRT | 4 | 2 | 36 | 176 | 337 | 513 |
| 10 | None | 11 | 2 | 53 | 245 | 327 | 532 + |
| 11 | RFA | 26 | 3 | 100 | 427 | 615 | 615 + |
| 12 | XRT | 19 | 14 | 51 | 796 | 1636 | > 1636d |
| Median | 20.5 | 5.5 | 52 | 478 | 930 | 1190 |
XRT radiation therapy, RFA radiofrequency ablation, PR partial response, PFS progression-free survival, OS overall survival
aContinues in complete remission
bAchieved partial response but did not return for follow up after 175 days. Still in PR at 175 days
cIn PR when last evaluated; died of acute myeloid leukemia
dDied in Mexico, date uncertain
Fig. 1.
SDHB immunostaining of pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma tumors. a Positive control; b negative control; c–g tumors staining less (granular) than normal control (clumps). h SNP negative for SDHB
Chemotherapy with CVD was initiated due to disease burden, location near critical structures (spinal cord), and refractory symptoms of catecholamine excess. In some, this occurred after a period of observation, while in others, CVD was started soon after referral to the National Institutes of Health. A median of 20.5 cycles was administered (range of 4–41). Reductions or delays in vincristine (after median 10 cycles) for peripheral neuropathy and dacarbazine (after median 6 cycles) for delayed/incomplete bone marrow recovery were made in 10/12 patients.
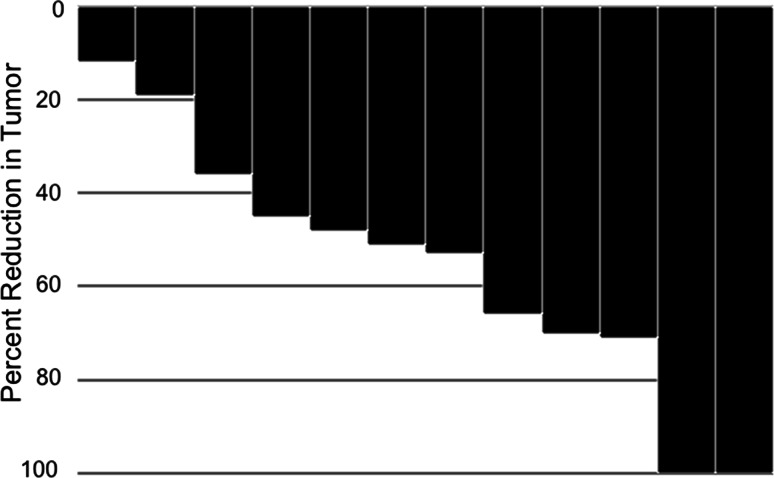
Tumor shrinkage was observed in all patients (12–100% by RECIST) with two complete responses (CR) and eight partial responses (PR) (Fig. 2 and Supplementary Fig. 1). All responses were confirmed a minimum of 4 weeks after initially documented. Responses were observed at all sites of disease including the liver, lungs, retroperitoneal nodes, and bones. The median number of cycles to response was 5.5. Median efficacy values included a median duration of response of 478 days (range 127–1623 days), median PFS of 930 days, and median OS of 1190 days.
Fig. 2.
Waterfall plot. Waterfall plot depicting response to chemotherapy as assessed by RECIST
In our experience, [18F]-FDG PET imaging has been very sensitive in detecting metastases in patients with SDHB mutations, identifying both visceral as well as osseous sites of disease (Eisenhauer et al. 2009). Gradual and continued reduction in the standardized uptake values (SUVs) occurred with successive cycles of chemotherapy, the rate of fall varying over time, and amongst various lesions. Figure 3 shows evolution of [18F]-FDG PET images over time. The SUVmax values in 26/30 lesions evaluated in six patients who had serial [18F]-FDG PET scans fell from a median SUV > 25 to < 6 over a median time > 825 days, providing evidence of continued drug efficacy during prolonged administration. These reductions in SUVs were accompanied by reductions in tumor sizes on CT or MRI.
Fig. 3.
[18F]-FDG PET images and gradual reduction in SUVmax with chemotherapy in three patients treated with chemotherapy for 600–1300 days. Each line depicts the results in an individual lesion. The images on the left (Panel A) depict a patient who had widespread disease that responded to therapy, but an abdominal mass that measured nearly 15 cm did not demonstrate much of a change in SUVmax despite a 12% reduction in size by RECIST (This is shown as the least response on the Waterfall Plot). (Panel a = Patient #3; Panel b = Patient #8; Panel c = Patient #7)
Discussion
We report the results of 12 SDHB-related metastatic PPGL patients undergoing treatment with CVD chemotherapy. The previous studies have described the activity of CVD chemotherapy against PPGL and suggested that this treatment be used for cytoreduction and to relieve symptoms (Niemeijer et al. 2014; Martucci and Pacak 2014). In this report, we demonstrate two inter-related phenomena—the marked efficacy of CVD chemotherapy, and the slow emergence of drug resistance as evidenced by the ability to achieve continued, incremental reductions in viable tumor over multiple years. It is important to note that we cannot present a comparison to patients whose tumors do not harbor SDHB mutations, as the majority of patients treated during this period of time harbored SDHB mutations, which is a reflection of our referral pattern and natural, aggressive clinical course of SDHB-related PPGL.
Prior to the availability of [18F]-FDG PET/CT imaging and routine testing for SDHB mutation status, we observed a gradual reduction in tumor size as well as serum and urinary metanephrines and catecholamines in patients receiving chemotherapy over several years. These results suggested the effectiveness of continued therapy over time, which was later confirmed by demonstrating a continued decrease in [18F]-FDG PET activity (SUV values) over prolonged time periods—an outcome unlike what is normally observed in most solid tumors. Typically, an effective therapy will result in an initial response, only to be followed by progressive disease in a matter of months. However, the patients in the present report experienced continued reduction in tumor quantity with a median PFS of 930 days (30.6 months) and a median duration of response exceeding 478 days (15.7 months).
Several explanations for continued tumor response can be proposed, including (1) the existence of a large fraction of cells in G0 that were killed only when they emerged from this quiescent state and began to actively divide; and (2) the existence of cells with stem-like properties whose killing leads to a gradual decline in tumor volume as differentiated offspring die (Timmers et al. 2007b; Liu and Wicha 2010). More likely however, continued tumor reduction occurred, because resistance was slow to develop. Why resistance develops slowly may be explained if tumors harboring SDHB mutations are “genetically simpler” and less likely to harbor intrinsically resistant clone(s). The latter would also explain the high response rate.
All patients in this clinical series presented with advanced malignancy and had few existing therapeutic options. Each presented with multi-focal metastases often including anatomic sites such as vertebrae that required multidisciplinary management, including chemotherapy administration. However, prolonged CVD therapy is not without complications. While some patients tolerated nearly full doses over an extended period of time, gradual reductions in doses were required in the majority of patients as they experienced greater difficulty in recovering normal marrow function. Before receiving CVD, the patient previously required two rounds of radiation, and eventually developed acute myeloid leukemia, which highlights the possibility of this known complication, especially when both alkylating agents and radiation therapy are administered (Weisenthal and Lippman 1985; Hawkins et al. 1992). Although she had presumed additional uncharacterized genetic abnormalities (chronic hydrocephalus requiring stent placement in childhood and bilateral ureteral narrowing unrelated to her PPGL requiring bilateral stents), it was felt chemotherapy contributed to this complication. The standard therapeutic options often available for these patients—palliative radiation therapy and [131I]-MIBG—may also contribute to such long-term complications (Hawkins et al. 1992; Hijiya et al. 2009).
Conclusions
In summary, we report a high level of activity of CVD chemotherapy in patients with metastatic PPGL and mutations/polymorphisms in the SDHB gene. Chronic therapy over prolonged periods of time resulted in continued tumor reduction consistent with ongoing drug sensitivity. In patients with difficult clinical presentations who demonstrate tumor reduction when CVD chemotherapy is instituted, consideration can be given to extend their current treatment regimen, while balancing the benefit gained with possible long-term complications.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Author Contributions
IJ, KP, and TF designed the study. MV, RD, KIW, KA, AMV, SB, MSP, and JCR were involved in data collection, analysis, and interpretation. All authors have read and approve the final version of this manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Intramural Research Program of the National Institutes of Health; the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development; and the German Research Foundation (DFG) (Grant Number DA 1630/1-1 to RD).
Compliance with Ethical Standards
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the Institutional Review Board of the National Cancer Institute of the National Institutes of Health and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
References
- Agarwal G, Sadacharan D, Kappor A et al (2011) Cardiovascular dysfunction and catecholamine cardiomyopathy in pheochromocytoma patients and their reversal following surgical cure: results of a prospective case-control study. Surgery 150:1202–1211 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amar L, Bertherat J, Baudin E et al (2005) Genetic testing in pheochromocytoma or functional paraganglioma. J Clin Oncol 23:8812–8818 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen GS, Toftdahl DB, Lund JO et al (1988) The incidence rate of phaeochromocytoma and Conn’s syndrome in Denmark, 1977–1981. J Hum Hypertens 2:187–189 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Averbuch SD, Steakley CS, Young RC et al (1988) Malignant pheochromocytoma: effective treatment with a combination of cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and dacarbazine. Ann Intern Med 109:267–273 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bausch B, Wellner U, Bausch D et al (2014) Long-term prognosis of patients with pediatric pheochromocytoma. Endocr Relat Cancer 21:17–25 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benn DE, Gimenez-Roqueplo AP, Reilly JR et al (2006) Clinical presentation and penetrance of pheochromocytoma/paraganglioma syndromes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 91:827–836 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bravo EL (1991) Pheochromocytoma: new concepts and future trends. Kidney Int 40:544–556 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brouwers FM, Eisenhofer G, Tao JJ et al (2006) High frequency of SDHB germline mutations in patients with malignant catecholamine-producing paragangliomas: implications for genetic testing. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 91:4505–4509 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edström Elder E, Hjelm Skog AL, Höög A et al (2003) The management of benign and malignant pheochromocytoma and abdominal paraganglioma. Eur J Surg Oncol 29:278–283 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J et al (2009) New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer 45:228–247 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenhofer G, Tischler AS (2014) Neuroendocrine cancer: closing the GAPP on predicting metastases. Nat Rev Endocrinol 10:315–316 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenhofer G, Bornstein SR, Brouwers FM et al (2004) Malignant pheochromocytoma: current status and initiatives for future progress. Endocr Relat Cancer 11:423–436 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenhofer G, Lenders JW, Siegert G et al (2012) Plasma methoxytyramine: a novel biomarker of metastatic pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma in relation to established risk factors of tumour size, location and SDHB mutation status. Eur J Cancer 48:1739–1749 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Calvet L, Garcia-Mayor RV (1994) Incidence of pheochromocytoma in South Galicia, Spain. J Intern Med 236:675–677 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glodny B, Winde G, Herwig R et al (2001) Clinical differences between benign and malignant pheochromocytomas. Endocr J 48:151–159 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein RE, O’Neill JA Jr, Holcomb GW III et al (1999) Clinical experience over 48 years with pheochromocytoma. Ann Surg 229:755–764 discussion 764–766 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley L, Perry-Keene D (1985) Phaeochromocytoma in Queensland—1970–83. Aust N Z J Surg 55:471–475 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins MM, Wilson LM, Stovall MA et al (1992) Epipodophyllotoxins, alkylating agents, and radiation and risk of secondary leukaemia after childhood cancer. BMJ 304:951–958 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hescot S, Leboulleux S, Amar L et al (2013) One-year progression-free survival of therapy-naive patients with malignant pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 98:4006–4012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hijiya N, Ness KK, Ribeiro RC et al (2009) Acute leukemia as a secondary malignancy in children and adolescents: current findings and issues. Cancer 115:23–25 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang H, Abraham J, Hung E et al (2008) Treatment of malignant pheochromocytoma/paraganglioma with cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and dacarbazine: recommendation from a 22-year follow-up of 18 patients. Cancer 113:2020–2028 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korpershoek E, Favier J, Gaal J et al (2011) SDHA immunohistochemistry detects germline SDHA gene mutations in apparently sporadic paragangliomas and pheochromocytomas. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 96:E1472–E1476 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenders JW, Eisenhofer G, Mannelli M et al (2005) Phaeochromocytoma. Lancet 35(366):665–675 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu S, Wicha MS (2010) Targeting breast cancer stem cells. J Clin Oncol 28:4006–4012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martucci VL, Pacak K (2014) Pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma: diagnosis, genetics, management, and treatment. Curr Probl Cancer 38:7–41 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neumann HP, Pawlu C, Peczkowska M et al (2004) Distinct clinical features of paraganglioma syndromes associated with SDHB and SDHD gene mutations. JAMA 292:943–951 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niemeijer ND, Alblas G, van Hulsteijn LT et al (2014) Chemotherapy with cyclophosphamide, vincristine and dacarbazine for malignant paraganglioma and pheochromocytoma: systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 81:642–651 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O’Riordain DS, Young WF Jr, Grant CS et al (1996) Clinical spectrum and outcome of functional extraadrenal paraganglioma. World J Surg 20:916–921 discussion 922 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacak K (2007) Preoperative management of the pheohromocytoma patient. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 92:4069–4079 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plouin PF, Chatellier G, Fofol I et al (1997) Tumor recurrence and hypertension persistence after successful pheochromocytoma operation. Hypertension 29:11331139 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plouin PF, Duclos JM, Soppelsa F et al (2001) Factors associated with perioperative morbidity and mortality in patients with pheochromocytoma: analysis of 165 operations at a single center. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86:1480–1486 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen WT, Grogan R, Vriens M et al (2010) One hundred two patients with pheochromocytoma treated at a single institution since the introduction of laparoscopic adrenalectomy. Arch Surg 145:893–897 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srirangalingam U, Walker L, Khoo B et al (2008) Clinical manifestations of familial paraganglioma and phaeochromocytomas in succinate dehydrogenase B (SDH-B) gene mutation carriers. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 69:587–596 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenström G, Svärdsudd K (1986) Pheochromocytoma in Sweden 1958–1981. An analysis of the national cancer registry data. Acta Med Scand 220:225–232 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stolk RF, Bakx C, Mulder J et al (2013) Is the excess cardiovascular morbidity in pheochromocytoma related to blood pressure or to catecholamines? J Clin Endocrinol Metab 98:1100–1106 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson LD (2002) Pheochromocytoma of the adrenal gland scaled score (PASS) to separate benign from malignant neoplasms: a clinicopathologic and immunophenotypic study of 100 cases. Am J Surg Pathol 26:551–566 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timmers HJ, Kozupa A, Eisenhofer G et al (2007a) Clinical presentations, biochemical phenotypes, and genotype-phenotype correlations in patients with succinate dehydrogenase subunit B-associated pheochromocytomas and paragangliomas. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 92:779–786 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timmers HJ, Kozupa A, Chen CC et al (2007b) Superiority of fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography to other functional imaging techniques in the evaluation of metastatic SDHB-associated pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma. J Clin Oncol 25:2262–2269 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujimoto G, Manger WM, Hoffman BB (1984) Desensitization of beta-adrenergic receptors by pheochromocytoma. Endocrinology 114:1272–1278 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisenthal LM, Lippman ME (1985) Clonogenic and nonclonogenic in vitro chemosensitivity assays. Cancer Treat Rep 69:615–632 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu D, Tischler AS, Lloyd RV et al (2009) Observer variation in the application of the pheochromocytoma of the adrenal gland scaled score. Am J Surg Pathol 33:599–608 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zelinka T, Eisenhofer G, Pacak K (2007) Pheochromocytoma as a catecholamine producing tumor: implications for clinical practice. Stress 10:195–203 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.