Abstract
Somatic embryogenesis receptor-like kinases (SERKs) play an essential role in plant response to pathogen infection. Here we identified three SERK genes (HvSERK1/2/3) from barley, and aimed to determine their implication in defense responses to barley powdery mildew (Bgh). Although HvSERK1/2/3 share the characteristic domains of the SERK family, only HvSERK2 was significantly induced in barley leaves during Bgh infection. The expression of HvSERK2 was rapidly induced by hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) treatment, but not by treatment with salicylic acid (SA), methyl jasmonate (MeJA), ethephon (ETH), or abscisic acid (ABA). Bioinformatics analysis of the cloned HvSERK2 promoter revealed that it contains several elements responsible for defense responses against pathogens. Promoter functional analysis showed that the HvSERK2 promoter was induced by Bgh and H2O2. Subcellular localization analysis of HvSERK2 indicated that it is mainly located on the plasma membrane. Transient overexpression of HvSERK2 in epidermal cells of the susceptible barley cultivar Hua 30 reduced the Bgh haustorium index from 58.6% to 43.2%. This study suggests that the HvSERK2 gene plays a positive role in the improvement of barley resistance to powdery mildew, and provides new insight into the function of SERK genes in the biotic stress response of plants.
Keywords: barley, SERK, powdery mildew, transient overexpression
1. Introduction
Plant diseases are responsible for billions of dollars of crop losses worldwide every year. Powdery mildew, caused by Blumeria graminis f. sp. hordei (Bgh), is one of the most serious diseases affecting barley yield worldwide. Powdery mildew is an obligate biotroph, the fungus is entirely restricted to epidermal leaf cells for the establishment of a haustorium; an essential organ that provides nutrition to the fungi [1]. Plants exhibit a wide array of defense strategies to defend themselves against attacks from various micro-organisms [2]. The first defense strategy of the plant immune system is PAMP-triggered immunity (PTI), which involves basal defense responses that are triggered upon detection of pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) [3]. It is common for membrane proteins to format receptor complexes linking extracellular perception to intracellular signal transduction in the plant PTI response [3]. A typical response of PAMPs is the apoplastic accumulation of reactive oxygen species such as hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and the superoxide anion [4]. In order to suppress PTI, pathogens secrete small unique protein molecules known as effectors. Upon recognition of the effectors, the host plant triggers the second defense line, effector triggered immunity (ETI), which always leads to cell apoptosis [5].
Receptor-like kinases (RLKs), which comprise a large gene family responsible for various signal transduction processes, proved to play a significant role in plant–pathogen interactions [6]. Among various RLK genes, somatic embryogenesis receptor kinases (SERKs) belong to the leucine-rich repeat receptor-like protein kinase (LRR-RLK) superfamily [7]. This gene family shares a N-terminus signal peptide (SP), an extracellular leucine zipper (LZ), five leucine rich repeats (LRRs) in its extracellular domain, a distinct serine–proline–proline (SPP) domain, a single TM (transmembrane) domain, a serine/threonine kinase domain, and a C-terminus region. As well as playing a major role in embryogenesis, SERKs have been shown to participate in the pathogen cell death response [8]. Arabidopsis SERK3/BAK1 forms a complex with BRI1 to ensure full brassinosteroid signaling, SERK3 also exists in a preformed complex with FLS2 to act as a positive PTI regulator [9,10,11]. The rice SERK gene OsSERK1 was induced by defense signaling molecules such as salicylic acid (SA), jasmonic acid (JA), and abscisic acid (ABA), and was associated with host cell death, imparting resistance to the rice blast fungus [12]. OsSERK2 can positively regulate the immune response to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae, the function was mediated by XA21 and XA3 [13]. However, it is unknown whether SERK genes positively regulate defense to powdery mildew caused by Bgh. To the best of our knowledge, the role of SERKs in the barley–powdery mildew interaction has not been investigated previously.
The single-cell transient overexpression assay (TOA) is a highly reliable, quick, and powerful approach to study genes during Bgh infection, as the fungus only penetrates one cell layer. The technique was first applied with co-expression of the B-peru gene and defense-related genes in barley coleoptile cells [14]. Shirasu et al. [15] improved the system by co-expressing the green fluorescent protein (GFP) gene and Mlo or mlo alleles in barley leaves. Schweizer et al. [16] bombarded young wheat leaves with tungsten particles coated with a β-glucuronidase (GUS) reporter gene and a test gene. Currently TOA is widely used for elucidating the function of genes involved in the powdery mildew resistance of wheat and barley [17].
In this study, we reported that the gene HvSERK2 improved barley resistance to Bgh infection, which is verified by the results of the TOA. We identified three SERK genes (HvSERK1/2/3) from barley cultivar Hua 30, and characterized their expressions against Bgh induction. Given that the expression of HvSERK2 was significantly induced upon Bgh infection, its subcellular localization and response to defense signaling molecules were further investigated. Our research provides new insight into the roles of the SERK gene family in the plant biotic defense response.
2. Results
2.1. Cloning and Identification of Three SERK Genes from Barley
Three SERK genes were identified in the database (http://webblast.ipk-gatersleben.de/barley/) by a homology search for the SPP motif between the LRRs and the transmembrane domain (HvSERK1, GI: AK372118; HvSERK2, GI: AK252995; HvSERK3, GI: AK374641). We then homology cloned the three genes from the barley cultivar Hua 30. The amino acid sequences of three SERK genes were aligned with the three identified SERK proteins from Arabidopsis thaliana, indicating that the proteins shared the typical characteristic conserved domains of the SERK protein family, including five LRRs, a SPP motif, a TM domain, kinase domains, and a C-terminus domain (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
Comparison of three somatic embryogenesis receptor-like kinase (SERK) proteins from Hordeum vulgare L. and Arabidopsis thaliana SERK1, SERK2, and SERK3 proteins. Putative domains are indicated at the top of the sequences. The 11 subdomains of the protein kinase domain are marked with Roman numerals.
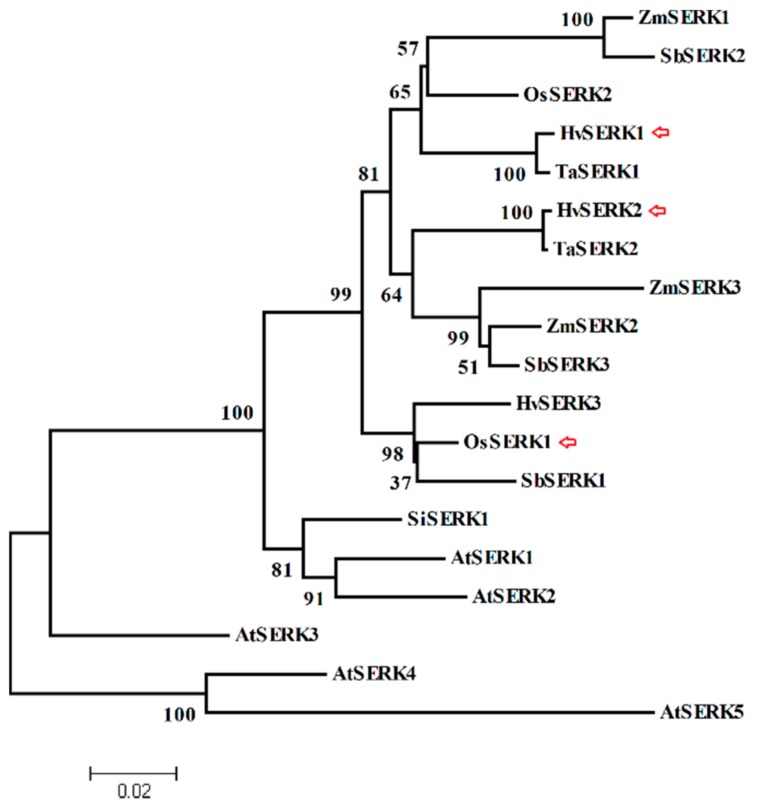
The phylogenetic relationships of the three barley SERK genes and other SERK homologs from different species were assessed by constructing a phylogenetic tree. As shown in Figure 2, the three barley SERK genes were located in different branches, which suggested that these genes have different functions during their evolution. Moreover, the HvSERK1/2/3 cluster was similar to the SERK proteins of monocot species, indicating that the function of the three SERK-like genes might remain conserved in monocot species.
Figure 2.
Phylogenetic analysis of the three barley SERK proteins and other plant SERK amino acid sequences. OsSERK1 (BAD05545.1), OsSERK2 (XP_015636497.1) from Oryza sativa; TaSERK1 (AEP14551.1) and TaSERK2 (AEP14552.1) from Triticum aestivum; ZmSERK1 (NP_001105132.1), ZmSERK2 (CAC37639.1), and ZmSERK3 (CAC37642.1) from Zea mays; SbSERK1 (EES13434.1), SbSERK2 (XP_002447957.1), and SbSERK3 (XP_002454054.1) from Sorghum bicolor; SlSERK1 (NP_001233866.1) from Solanum lycopersicum; AtSERK1 (NP_177328.1), AtSERK2 (AAK68073.1), AtSERK3 (AAK68074.1), At-SERK4 (NP_178999.2), and AtSERK5 (NP_179000.3)from Arabidopsis thaliana. The red arrows show SERK proteins from Hordeum vulgare L.
2.2. Characterization of the Response of Three SERK Genes to Bgh Infection
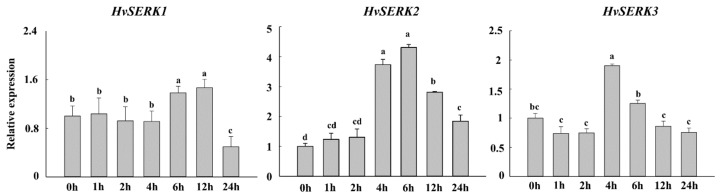
Three SERK gene expression profiles were investigated during Bgh infection in barley leaves. As shown in Figure 3, the expression profile of HvSERK2 upon Bgh inoculation showed that HvSERK2 was rapidly up-regulated (p < 0.05, ≥two-fold), peaked at 6 h post inoculation (hpi), remained stagnant for the next 6 h (12 hpi), thereafter the expression decreased to a normal level. However, there was no up- or down-regulation (p < 0.05, ≥two-fold) of the expression profile of the other two genes (HvSERK1/HvSERK3) after Bgh inoculation. This indicated that HvSERK2 may function in the barley-Bgh interaction, so we selected HvSERK2 for further investigation.
Figure 3.
Expression profiles of HvSERK1/2/3 in response to Bgh infection by qRT-PCR. The actin gene was used as an internal control to normalize qRT-PCR values. Different letters indicate statistically significant differences (p < 0.05, one-way ANOVA).
2.3. Characterization of HvSERK2 Responses to Defense Signal Molecules
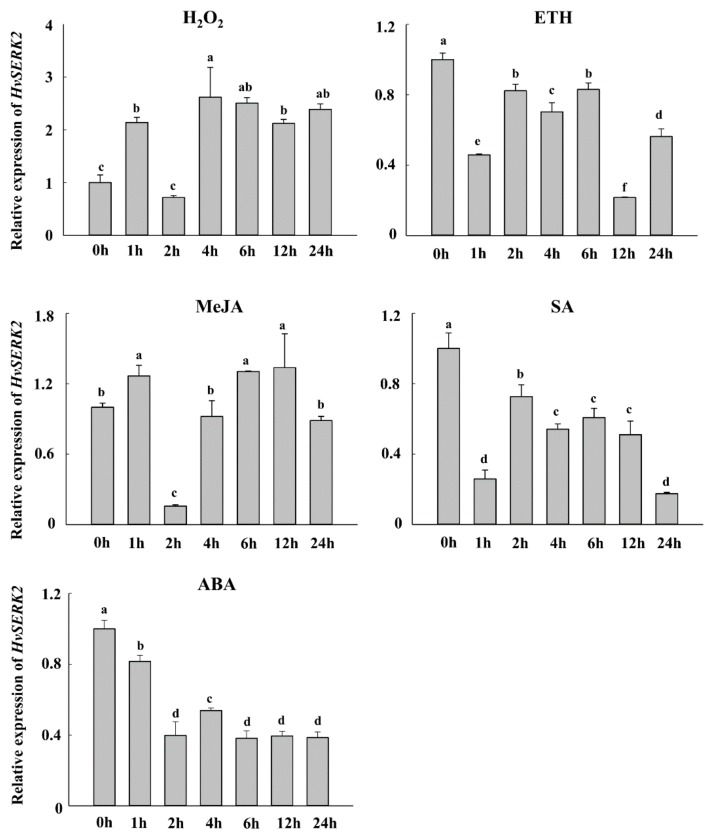
HvSERK2 expression profiles were further investigated under treatment with different signaling molecules, which closely correlated to the disease resistance of the plant. After H2O2 treatment, a HvSERK2 expression peak was first observed 1 h post-treatment (hpt), expression then decreased and peaked again 4 hpt, a high level of expression was maintained at the following detection time points (Figure 4). Upon both ethephon (ETH) and SA treatments, a slight decrease in the HvSERK2 expression occurred 1 hpt, whereas, a decrease in HvSERK2 expression was observed 2 hpt in response to methyl jasmonate (MeJA) and ABA application (Figure 4). These results indicated that HvSERK2 expression in barley was induced by H2O2, and that HvSERK2 might be involved in H2O2 signaling pathways in barley.
Figure 4.
Expression profiles of HvSERK2 in response to hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), ethephon (ETH), methyl jasmonate (MeJA), and salicylic (SA) treatments by quantitative RT-PCR. Expression profiles of HvSERK2 in leaves of barley upon treatment with H2O2 (7 mM), ETH (200 mΜ), MeJA (0.1 mM), SA (5 mM), an dabscisic acid (ABA) (0.2 mM), respectively. The actin gene was used as an internal control to normalize qRT-PCR values. Different letters indicate statistically significant differences (p < 0.05, one-way ANOVA).
2.4. Analysis of the Cis-Regulatory Motifs for Cloned HvSERK2 Promoter
As shown in the above results, HvSERK2 was induced by Bgh infection and H2O2 treatment (Figure 3 and Figure 4), therefore, we further cloned the HvSERK2 promoter to investigate whether it contained motifs related to biotic or abiotic stress. By searching the available databases and conducting a bioinformatics analysis, we designed primers and cloned 2 kb of sequence upstream from HvSERK2 (Supplementary Materials data 1). In silico analysis of the promoter of HvSERK2 in Plant CARE and PsLACE revealed several elements responsible for defense or stress responses to pathogens (Supplementary Materials Table S1). Among the cis-acting regulatory elements found in the HvSERK2 promoter, two fungal elicitor responsive elements, Box w1,were present on (−) strands at the positions of −325 bp and −961 bp, respectively. In addition, two motifs for MeJA responsiveness (TCT motif and CGTCA motif) and one TCA element for SA acid responsiveness were also annotated in the HvSERK2 promoter. The sequence analysis also detected a 14 TATA-box (Supplementary Materials Table S1).
Detailed analysis of the promoter also revealed the presence of some key regulating motifs for abiotic stresses (Supplementary Materials Table S1). For example, an ABRE motif that related to abscisic acid responsiveness was found at a distance of −1388 bp from the initiation codon, and a HSE motif that related to heat stress responsiveness was found at a distance of −446 bp from the initiation codon. TC-rich repeats, which are involved in defense and stress responsiveness, were found −392 bp from the initiation codon. A total of 8 regulatory motifs (ACE, AE-box, Box 4, G-Box, GA-motif, MNF1, Sp1, and TCCC) that are involved in the regulation of the light responses of plants were found in the HvSERK2 promoter. 21 CAAT box motifs were found on different strands (+ and −), and were found to enhance promoter activities (Supplementary Materials Table S1). These findings were partly consistent with HvSERK2 expression during powdery mildew infection.
2.5. Functional Analysis of HvSERK2 Promoter
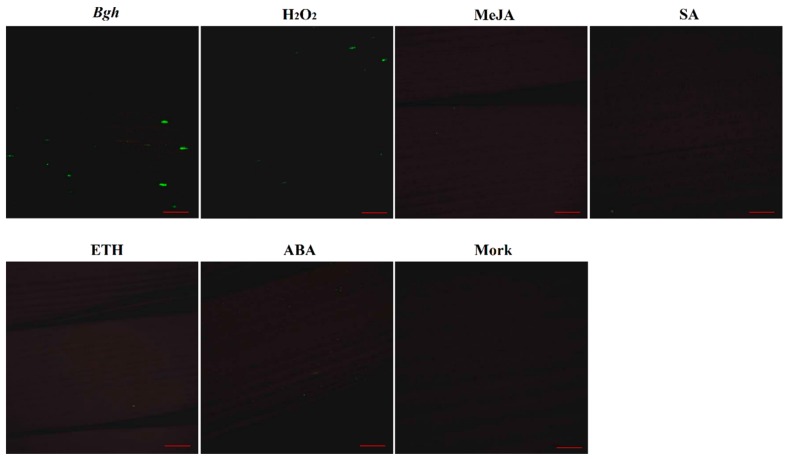
Based on in silico analysis of the HvSERK2 promoter, we constructed a pAN580:HvSERK2P:GFP plasmid by replacing the CaMV 35S promoter of the pAN580 vector with a HvSERK2 promoter. The plasmid was transiently expressed in barley leaves by use of a gene gun. Bombarded leaves were treated with Bgh, H2O2, MeJA, SA, ETH, and ABA, respectively. As shown in Figure 5, bombarded leaves were inoculated with Bgh and H2O2, and could detect GFP signal, whereas, GFP signal could not be detected in bombarded leaves treated with MeJA, SA, ETH, and ABA. These results were consistent with the expression profile of HvSERK2, and indicated that HvSERK2 is involved in the Bgh response and the H2O2 signaling pathway in barley.
Figure 5.
Activity of the HvSERK2 promoter in response to Bgh, H2O2, MeJA, SA, ETH, and ABA treatments. Mork is control. Bars = 1 mm.
2.6. Subcellular Localization of HvSERK2
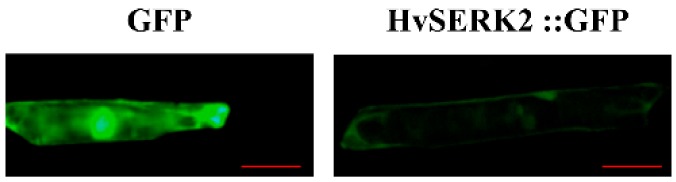
To determine HvSERK2 protein localization in plant cells, a construct containing the fusion product of the HvSERK2 coding sequence and coding region of the green fluorescent protein (HvSERK2::GFP), under the control of the cauliflower mosaic virus (CaMV) 35S promoter, was transiently expressed in living onion epidermal cells. As shown in Figure 6, cells transiently expressing GFP (control) exhibited a uniform distribution of green fluorescence throughout the cell. In contrast, signal generated in the onion epidermal cells that transiently expressed HvSERK2::GFP was confined to the plasma membrane (Figure 6), thus, suggesting that HvSERK2 was restricted to plasma membrane compartments.
Figure 6.
Subcellular localization of HvSERK2 protein in onion epidermal cells. Bars = 100 μm.
2.7. Functional Analysis of HvSERK2 in Bgh Infection by TOA
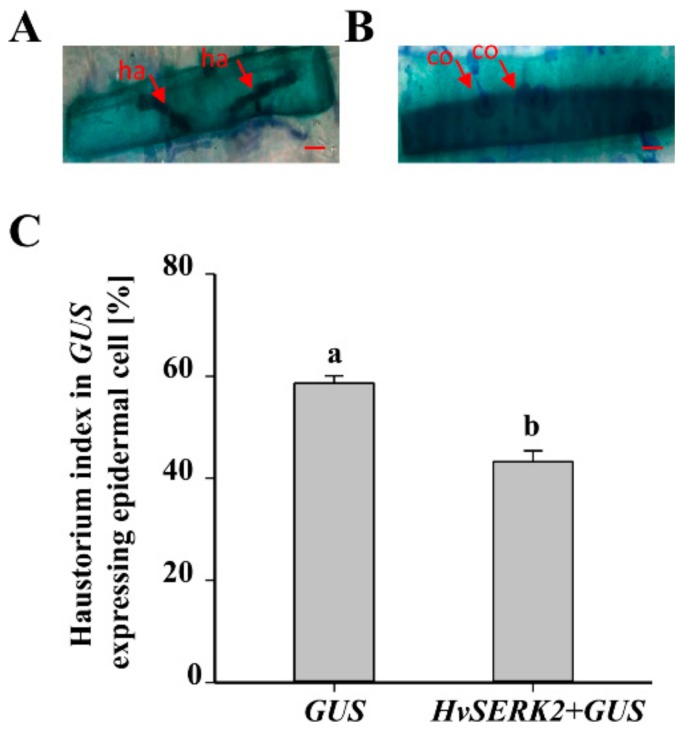
The haustorium index is usually used as a criterion to estimate the compatibility of interactions between the host and Bgh. To further characterize the role of HvSERK2 in the powdery mildew response, TOA was conducted using the susceptible barley cultivar Hua 30 as a receptor. Comparing GUS-staining cells with haustoria to all GUS-stained cells invaded by Bgh (Figure 7A,B), the haustorium index (HI) for Hua 30 was 58.6% when transformed with GUS alone, but decreased significantly to 43.2% when co-transformed with GUS and pBI220-HvSERK2 (Figure 7, Supplementary Materials Table S2). Whereas, when transformed with pBI220-HvSERK1/3, the HI for Hua 30 was 61.6% and 58%, respectively, compared to a HI for Hua 30 of 59.5% when transformed with GUS alone (Supplementary Materials Figure S1, Supplementary Materials Table S3). This indicated that the transient overexpression of HvSERK2 prevented haustorium formation, so that the barley transform cells gained resistance to Bgh. This result demonstrated the involvement of HvSERK2, but not HvSERK1/3, in response to Bgh infection.
Figure 7.
Functional analysis of HvSERK2 by single-cell transient overexpression assay. (A) Bgh conidia successfully penetrated epidermal cells co-expressing GUS and HvSERK2 with haustorium; (B) Bgh conidia failed to penetrate epidermal cells co-expressing GUS and HvSERK2. Bars in (A,B) = 20 μm; (C) in comparison with transforming GUS alone, the haustorium index of the cells co-transformed with GUS and HvSERK2 significantly decreased. ha: haustorium; co: conidium. Bars with different letters show significant differences at the level of p < 0.05.
3. Discussion
The present study identified three SERK-like genes from barley, and characterized the function of the HvSERK2 gene under Bgh infection. Typical SERK protein domain distribution is found in the three SERK proteins, phylogenetic analysis showed that the three barley SERK proteins were clustered closer to the SERK proteins from monocot species (Oryza sativa, Triticum aestivum, Zea mays, and Sorghum bicolor). This suggests that the SERKs of the grass family remained fairly conserved throughout their evolution. We also found that HvSERK2 was clustered closer to the wheat SERK protein (TaSERK2) in the phylogenetic tree, but further away from the two other SERK proteins (HvSERK1/3) of barley. According to our results, only HvSERK2 was induced by Bgh infection in barley leaves, which proved that HvSERK2 had a diverse function when compared to the other two barley SERK genes. At the subcellular level, GmSERK1, from soybean, was localized to the plasma membrane [18], this was consistent with HvSERK2. This evidence suggests that HvSERK2 functions as a LRR-RLK in the barley–powdery mildew interaction [19].
The typical model of LRR-RLK function states that extracellular domain binding of a signal molecule induces receptor dimerization, and then the intracellular kinase domain is activated by phosphorylation, which subsequently regulates the cellular response accordingly [20]. Depending on the system, the SERK gene family is not limited to somatic embryogenesis, and is involved in a diverse array of functions. Several elements, like abscisic acid responsiveness (ABRE), heat stress (HSE), TC-rich, and light responsive motifs (ACE, AE-box, Box 4, G-Box, GA-motif, MNF1, Sp1, and TCCC) were predicted in the in HvSERK2 promoter, showing its involvement in different developmental metabolic process. A number of reports have been published on the role of SERKs in disease resistance responses. The OsBISERK1 gene, isolated from rice, is reported to be involved in disease resistance responses and mediating defense signal transduction [21]. In Arabidopsis, the receptor kinase BAK1/SERK3 has been identified as a partner of brassinosteroid receptor BRI1 and immune receptor FLS2 [9]. The most important motif found that was related to pathogen defense in the HvSERK2 promoter was the W-Box, which is recognized by WRKY DNA binding proteins that trigger the promoter and activate downstream NPR1 genes for pathogen defense responses [22]. Functional analysis of the HvSERK2 promoter showed that it was induced upon Bgh inoculation. This is consistent with the result that the expression of HvSERK2 is induced by powdery mildew infection, suggesting that HvSERK2 is involved in fungal pathogen resistance. In the TOA experiment, transient overexpression of HvSERK2 in barley leaf epidermal cells decreased the HI of Bgh which provided direct evidence that HvSERK2 positively mediates barley resistance to Bgh.
Phytohormones have been shown to be closely correlated with disease resistance by regulating pathogenesis-related (PR) genes or acting as early signaling components [23]. During the early stages of incompatible barleyBgh interactions, H2O2 has been reported to act as a diffusible signal for the induction of cellular protectant genes [24]. H2O2 either induces the hypersensitive reaction [25,26] and subsequent PR gene expression, [27] or acts directly as the defense substance [28]. Our results show that the expression of HvSERK2 was quickly induced by exogenous H2O2 (2 hpt), this is consistent with the resulting functional analysis of the HvSERK2 promoter upon H2O2 treatment. These results were not in agreement with OsSERK1, which was activated by SA, JA, and ABA [13], and unexpectedly, were not consistent with the in silico analysis of the HvSERK2 promoter.
In conclusion, this study proposes that the HvSERK2 gene plays a positive role in powdery mildew resistance in barley, possibly though the H2O2 signaling pathway.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials, Growth Conditions and Treatment
Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) cv. Hua 30 is a popular variety cultivated in the Yangtze River Delta of China. The barley seedlings were grown at 22–25 °C with a photoperiod of 12 h. Mixed races of Bgh were maintained on seedlings susceptible to powdery mildew (Hua 30), in a spore-proof greenhouse, under a 14 h light/10 h darkness (22/18 °C, 70% humidity) regime. Two-leaf stage seedlings were inoculated with Bgh or treated with exogenous hormones, including 5 mM SA, 0.1 μM MeJA, 200 mΜ ETH, 7 mM H2O2, and 0.2 mΜ ABA. All chemicals were administered in a 0.05% Tween 20 solution, with a 0.05% Tween 20 solution used as a mock treatment, all of the treatments followed Zhu et al. [29]. For gene expression analysis, leaves were harvested at different time intervals after different treatments (0 h, 1 h, 2 h, 4 h, 6 h, 12 h and 24 h). Three biological replicates were used for each assay.
4.2. Identification of Three SERK Genes in Barley
To identify SERK genes in barley, the amino acid sequences of reported SERK proteins in model plants including Arabidopsis (NP_177328.1, AAK68073.1, AAK68074.1, NP_178999.2, and NP_179000.3) and rice (BAD05545.1 and XP_015636497.1) were used to search in the International Barley Sequencing Consortium (http://webblast.ipk-gatersleben.de/barley/), and the National Centre for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) database (http://www.ncbi.nim.nih.gov/BLAST/nr/EST) using the TBLASTN program with a cut off E-value of 1 × 10−10. Three SERK genes (AK372118, AK252995 and AK374641) were found from the high-throughput sequencing of barley cv. Morex. The homology cloning of the ORF of SERK candidates from barley cultivar Hua 30 (cDNA) was carried out using specific primers (Supplementary Materials Table S4). For gene cloning, cDNA was used as template. PCR was performed in 25 μL using a 1× Taq DNA polymerase buffer, 0.8 mM/L MgCl2, 0.8 mM/L dNTPs, 100 mM/L primers, 1 unit of KOD-Taq (TOYOBO, Osaka, Japan) polymerase, and 50 ng Hua 30 cDNA as a template. The PCR was programmed for 95 °C 5 min for denaturation, followed by 29 cycles of 94 °C for 30 s, 59 °C for 45 s, and 68 °C for 2 min 30 s, and a final extension of 10 min at 68 °C. The PCR product was cloned using a p-easy cloning kit (TransGen Biotech, Beijing, China) and sequenced by the Thermo Fisher Scientific Corporation (Suzhou, China). The phylogenetic associations were inferred using the neighbor-joining method in MEGA 4.0 software (Tempe, AZ, USA) with SERK proteins from different species at 2000 bootstrap.
4.3. Cloning and In Silico Analysis of HvSERK2 Promoter
To search the putative promoter region of HvSERK2 in barley, the complete ORF of HvSERK2 was used for a homology search in the International Barley Sequencing Consortium (http://webblast.ipk-gatersleben.de/barley/). A 2 kb sequence upstream from Morex was found and used to design forward primers, while the only reverse primer was located in the ORF of HvSERK2. The list of all primers used in the study is given in the Supplementary Materials Table S4. For promoter analysis, the sequence was searched for cis regulatory elements in two plant promoter data bases viz. Plant CARE (http://bioinformatics.psb.ugent.be/webtools/plantcare/html/) and PLACE (http://www.dna.affrc.go.jp/htdocs/PLACE/).
4.4. DNA, RNA Extraction and Transcription Analysis
DNA was extracted from 5 g of leaves of Hua 30 seedlings using the Cetyltrimethyl Ammonium Bromide (CTAB) method. For promoter amplification, genomic DNA was used as the template. PCR conditions included initial denaturation at 94 °C for 5 min then 29 cycles (94 °C for 30 s, 57 °C for 45 s, and 68 °C for 2 min 30 s) followed by final elongation at 68 °C for 10 min. The PCR product was cloned using a p-easy cloning kit and sequenced by the Thermo Fisher Scientific Corporation.
Total RNA of each sample was extracted using TRIZOL reagent, according to the manufacturer’s protocol (Thermo Fisher Scientific Corporation). Two microgram aliquots of total RNA of each sample were used to synthesize the first-strand cDNA using a Prime Script™ II first strand cDNA synthesis kit (TAKARA, Dalian, China). For expression pattern analysis, specific pairs of primers were used, and the actin gene GI: AK356840.1 was used as the internal control for normalization. qRT-PCR was performed with a SYBR Green ABI 7500 fast detection system (Thermo Fisher Scientific Corporation): 95 °C for 1 min, 41 cycles of 95 °C for 10 s, and 60 °C for 31 s. For each sample, the Ct value of each target gene was normalized to the Ct value of the actin gene (Supplementary Materials Table S4). The relative value of gene expression was derived from 2−∆∆CT [30]. Three independent biological replications were performed for each treatment. The significant differences in each treatment were analyzed by paired sample one-way ANOVA using SPSS software (International Business Machines Corporation, New York, NY, USA).
4.5. Subcellular Localization of HvSERK2
XbaI and SmaI sites were added to the 5′ and 3′ ends of the full length open reading frame of HvSERK2, respectively (Supplementary Materials Table S4), with the stop codon deleted, as per appropriate design of the HvSERK2-SmaI-R primer. The PCR product and the pAN580 vector were digested by XbaI and SmaI, and the fragments were ligated to produce the fusion gene expression vector p35S::HvSERK2-GFP::Nos3. For transient expression in onion, the constructs were delivered to epidermal cells on the adaxial surfaces of tissue peeled from an onion by particle bombardment, as described by Faheem et al. [31]. GFP signals were assessed by OLYMPUS SZX16 (OLYMPUS, Tokyo, Japan) imaging 16–20 h after bombardment.
4.6. Single-Cell Transient Overexpression Assay
The TOA of HvSERK1/2/3 was performed using a Bio-Rad He/1000 particle delivery system (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA) with barley leaves, according to Schweizer et al. [15]. In brief, HvSERK1/2/3 was cloned into the plant expression vector pBI220 [29] to produce a pBI220:HvSERK1/2/3 plasmid, while under the regulation of the CaMV 35S promoter (Supplementary Materials Table S3). The reporter plasmid pWMB002, containing the β-glucuronidase (GUS) gene and the expression plasmid pBI220: HvSERK1/2/3, was mixed before coating of the particles (molar ratio of 1:1; 1 µg of total DNA). The second leaves of one-week-old barley seedlings were firmly placed on the 1% agar plates, which were supplemented with 85 µM of benzimidazoles for the delivery of mixed plasmids into host cells by gene gun. Delivery of pWMB002 alone was used as control. Bombarded leaves were incubated at 22 °C for 4 to 6 h in darkness, then infected with fresh Bgh conidia spores and placed in a growth chamber with a 14 h light/10 h darkness photoperiod for 48 h. Leaves were stained to determine the GUS activity, then bleached with 95% ethanol, and observed under a microscope to record the haustorial index (HI, percentage of GUS-staining cells with haustoria among all GUS-stained cells invaded by Bgh). The assay was repeated thrice and significant differences between treatments were analyzed by paired sample t-tests using SPSS software.
4.7. Function Analysis of HvSERK2 Promoter
The HvSERK2 promoter was cloned into plant expression vector pAN580 [31] by replacing the CaMV 35S promoter to produce a pAN580:HvSERK2P:GFP plasmid (Supplementary Materials Table S3). Second leaves of one-week-old barley seedlings were firmly placed on the 1% agar plates and were supplemented with 85 µM of benzimidazoles for the delivery of the pAN580:HvSERK2P:GFP plasmid into host cells by gene gun. Bombarded leaves were incubated at 22 °C for 4 to 6 h in darkness, then were inoculated with Bgh or treated with exogenous hormones, including 5 mM SA, 0.1 mΜ MeJA, 200 mΜ ETH, 7 mM H2O2, and 0.2 mΜ ABA. All chemicals were administered in a 0.05% Tween 20 solution, and a 0.05% Tween 20 solution was used as a mock treatment. All treatments followed the instructions outlined by Zhu et al. [29]; solutions were placed in a darkness growth chamber after treatment. GFP signals were assessed by OLYMPUS SZX16 imaging 16–20 h after bombardment.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Shanghai Agriculture Applied Technology Development Program, China (Grant No. G2016060102), China Agriculture Research System (CARS-05-01A-02), and Funding of State Key Laboratory of Crop Genetics and Germplasm Enhancement, Nanjing Agricultural University (ZW2015003).
Abbreviations
| SERK | Somatic embryogenesis receptor-like kinase |
| Bgh | Blumeria graminis f. Sp. hordei |
| PAMP | Pathogen-associated molecular patterns |
| PTI | PAMP-triggered immunity |
| ETI | Effector-triggered immunity |
| RLKs | Receptor-like kinases |
| LZ | Leucine zipper |
| LRRs | Leucine rich repeats |
| SPP | Serine proline proline |
| BR | Brassinosteroid |
| Xoo | Xanthomonas oryzae pv. Oryzae |
| TOA | Transient overexpression assay |
| MeJA | Methyl jasmonate |
| SA | Salicylic acid |
| H2O2 | Hydrogen peroxide |
| ETH | Ethephon |
| ABA | Abscisic acid |
| hpt | Hours post-treatment |
| hpi | Hours post-inoculation |
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary materials can be found at http://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/19/4/1226/s1.
Author Contributions
Yingbo Li was responsible for article writing, participated in manuscript writing and the subcellular localization experiment. Qingwei Li participated in the TOA experiment. Guimei Guo participated in parts of the experiment and sequence analysis. Ting He participated in plant cultivation. Runhong Gao participated in the expression experiment. Muhammad Faheem participated in manuscript writing. Jianhua Huang participated in manuscript writing. Ruiju Lu and Chenghong Liu were responsible for the experiment design and funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- 1.Zhang Z., Henderson C., Perfect E., Carver T.L.W., Thomas B.J., Skamnioti P., Gurr S.J. Of genes and genomes, needles and haystacks: Blumeria graminis and functionality. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2005;6:561–575. doi: 10.1111/j.1364-3703.2005.00303.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Dangl J.L., Dietrich R.A., Richberg M.H. Death don’t have no mercy: Cell death programs in plant-microbe interactions. Plant Cell. 1996;18:1793–1807. doi: 10.1105/tpc.8.10.1793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Zipfel C. Early molecular events in PAMP-triggered immunity. Curr. Opin. Plant Boil. 2009;12:414–420. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2009.06.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Chisholm S.T., Coaker G., Day B., Staskawicz B.J. Host-microbe interactions: Shaping the evolution of the plant immune response. Cell. 2006;124:803–814. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.02.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Nicaise V., Roux M., Zipfel C. Recent advances in PAMP-triggered immunity against bacteria: Pattern recognition receptors watch over and raise the alarm. Plant Physiol. 2009;150:1638–1647. doi: 10.1104/pp.109.139709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Zipfel C. Plant pattern-recognition receptors. Trends Immunol. 2014;35:345–351. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2014.05.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Li J. Multi-tasking of somatic embryogenesis receptor-like protein kinases. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2010;13:509–514. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2010.09.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Santos M.O., Aragão F.J. Role of SERK genes in plant environmental response. Plant Signal. Behav. 2009;4:1111–1113. doi: 10.4161/psb.4.12.9900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Heese A., Hann D.R., Gimenez-Ibanez S., Jones A.M.E., He K., Li J., Schroeder I.J., Peck S.C., Rathjen J.P. The receptor-like kinase SERK3/BAK1 is a central regulator of innate immunity in plants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2007;104:12217–12222. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0705306104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Clouse S.D. Brassinosteroid signal transduction: From receptor kinase activation to transcriptional networks regulating plant development. Plant Cell. 2011;23:1219–1230. doi: 10.1105/tpc.111.084475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.He K., Gou X., Yuan T., Lin H., Asami T., Yoshida S., Russell1 S.D., Li J. BAK1 and BKK1 regulate brassinosteroid-dependent growth and brassinosteroid-independent cell-death pathways. Curr. Biol. 2007;17:1109–1115. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2007.05.036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Hu H., Xiong L., Yang Y. Rice SERK1 gene positively regulates somatic embryogenesis of cultured cell and host defense response against fungal infection. Planta. 2005;222:107–117. doi: 10.1007/s00425-005-1534-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Chen X., Zuo S., Schwessinger B., Chern M., Canlas P.E., Ruan D., Zhou X., Wang J., Daudi A., Petzold C.J., et al. An XA21-associated kinase (OsSERK2) regulates immunity mediated by the XA21 and XA3 immune receptors. Mol. Plant. 2014;7:874–892. doi: 10.1093/mp/ssu003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Nelson A.J., Bushnell W.R. Transient expression of an thocyanin genes in barley epidermal cells: Potential for use in evaluation of disease response genes. Transgenic Res. 1997;6:233–244. doi: 10.1023/A:1018498309562. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Shirasu K., Nielsen K., Piffanelli P., Oliver R., Schulze-Lefert P. Cell-autonomous complementation of mlo resistance using a biolistic transient expression system. Plant J. 1999;17:293–299. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313X.1999.00376.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Schweizer P., Pokorny J., Abderhalden O., Dudler R. A transient assay system for the functional assessment of defense-related genes in wheat. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 1999;12:647–654. doi: 10.1094/MPMI.1999.12.8.647. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Rajaraman J., Douchkov D., Hensel G., Stefanato F.L., Gordon A., Ereful N., Caldararu O.F., Petrescu A.J., Kumlehn J., Boyd L.A., et al. An LRR/malectin receptor-like kinase mediates resistance to non-adapted and adapted powdery mildew fungi in barley and wheat. Front. Plant Sci. 2016;7 doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.01836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Yang C., Zhao T., Yu D., Gai J. Isolation and functional characterization of a SERK gene from soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merr.) Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 2011;29:334–344. doi: 10.1007/s11105-010-0235-8. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Walker J.C. Structure and function of the receptor-like protein kinases of higher plants. Plant Mol. Biol. 1994;26:1599–1609. doi: 10.1007/BF00016492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Becraft P.W. Receptor kinase signaling in plant development. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2002;18:163–192. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cellbio.18.012502.083431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Song D., Li G., Song F., Zheng Z. Molecular characterization and expression analysis of OsBISERK1, a gene encoding a leucine rich repeat receptor-like kinase, during disease resistance responses in rice. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2008;35:275–283. doi: 10.1007/s11033-007-9080-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Yu D., Chen C., Chen Z. Evidence for an important role of WRKY DNA binding proteins in the regulation of NPR1 gene expression. Plant Cell. 2001;13:1527–1540. doi: 10.1105/tpc.13.7.1527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Bari R., Jones J.D. Role of plant hormones in plant defence responses. Plant Mol. Biol. 2009;69:473–488. doi: 10.1007/s11103-008-9435-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Vanacker H., Carver T.L., Foyer C.H. Early H2O2 accumulation in mesophyll cells leads to induction of glutathione during the hypersensitive response in the barley powdery mildew interaction. Plant Physiol. 2000;123:1289–1300. doi: 10.1104/pp.123.4.1289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Tenhaken R., Levine A., Brisson L.F., Dixon R.A., Lamb C. Function of the oxidative burst in hypersensitive disease resistance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1995;92:4158–4163. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.10.4158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Torres M.A., Jones J.D.G., Dangl J.L. Pathogen-induced, NADPH oxidase-derived reactive oxygen intermediates suppress spread of cell death in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nat. Genet. 2005;37:1130–1134. doi: 10.1038/ng1639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Alvarez M.E., Pennell R.I., Meijer P.J., Ishikawa A., Dixon R.A., Lamb C. Reactive oxygen intermediates mediate a systemic signal network in the establishment of plant immunity. Cell. 1998;92:773–784. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81405-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Baker C.J., Orlandi E.W. Active oxygen in plant pathogenesis. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 1995;33:299–321. doi: 10.1146/annurev.py.33.090195.001503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Zhu Y., Li Y., Fei F., Wang Z., Wang W., Cao A., Liu Y., Han S., Xing L., Wang H., et al. An E3 ubiquitin ligase gene CMPG1-V from Haynaldia villosa L. contributes to the powdery mildew resistance in common wheat. Plant J. 2015;84:154–168. doi: 10.1111/tpj.12966. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Livak K.J., Schmittgen T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods. 2001;25:402–408. doi: 10.1006/meth.2001.1262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Faheem M., Li Y., Arshad M., Cheng J., Zhao J., Wang Z., Xiao J., Wang H., Cao A., Xing L., et al. A disulphide isomerase gene (PDI-V) from Haynaldia villosa contributes to powdery mildew resistance in common wheat. Sci. Rep. 2016;6:24227. doi: 10.1038/srep24227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.