The authors wish to add the following corrections to their paper published in the International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health [1]. During the galley proof process, the production of the paper omitted the minus sign for the 95% CI of the results section on the project’s impact on child underweight, wasting, and stunting in the abstract (p. 1) and the manuscript (p. 15).
In the abstract, the sentence regarding the result should be:
“Propensity score matched/weighted models produced better results than the unmatched analyses, and hence we report findings from the radius matching. The intervention resulted in a 5.2 (adjusted difference-in-difference [ADID] = −5.16; 95% CI: −9.55, −0.77), 7.4 (ADID: −7.35; 95% CI: −11.62, −3.08) and 2.8 (ADID = −2.84; 95% CI: −5.58, −0.10) percentage point reduction in the prevalence of stunting, underweight, and wasting among children under the age of five, respectively. The intervention impact was greater in boys than girls for stunting and wasting; and greater in girls than boys for underweight. The intervention also resulted in a 6.7 (ADID = −6.66; 95% CI: −12.13, −1.18), 11.4 (ADID = −11.4; 95% CI: −16.66, −6.13), and 4.1 (ADID = −4.10; 95% CI: −6.43, −1.78) percentage point reduction in the prevalence of stunting, underweight, and wasting among older children (≥24 months). No impact was observed among younger children (<24 months).”
The last two paragraphs in page 15 should be:
Our results suggest that the three matching estimators produced different effects on outcomes. The radius matching algorithm produced more robust results than the nearest neighbor or kernel matching estimators, and hence we report findings from the radius matching. The intervention had a positive impact on height-for-age z-scores (adjusted difference-in-difference (ADID) = 0.18; 95% CI: 0.09, 0.27, p < 0.05), weight-for-age z-scores (ADID = 0.22, 95% CI: 0.15, 0.19, p < 0.01), and weight-for-height z-scores (ADID = 0.19; 95% CI: 0.09, 0.30, p < 0.05).
The intervention resulted in a 5.2 (ADID = −5.16; 95% CI: −9.55, −0.77), 7.4 (ADID: −7.35; 95% CI: −11.62, −3.08) and 2.8 (ADID = −2.84; 95% CI: −5.58, −0.10) percentage point reduction in the proportion of children under the age of five who were stunted, underweight and wasted respectively. Among boys, the intervention resulted in a 6.2 (ADID = −6.15; 95% CI: −11.76, −0.53) and 3.3 (ADID = −3.33; 95% CI: −6.16, −0.49) percentage point reduction in the prevalence of stunting and wasting respectively, but no impact was observed for underweight. Among girls, improvements were observed only for underweight, with a 9.0 (ADID = −9.02; 95% CI: −15.10, −2.94) percentage point reduction in the prevalence of underweight. No impact was observed for stunting or wasting. The analysis by children’s age groups revealed that the intervention resulted in a 6.7 (ADID = −6.66; 95% CI: −12.13, −1.18), 11.4 (ADID = −11.40; 95% CI: −16.66, −6.13), and 4.1 (ADID = −4.10; 95% CI: −6.43, −1.78) percentage point reduction in the prevalence of stunting, underweight, and wasting among older children (≥24 months). No impact was observed among children younger than two years (Table 4; radius matching).
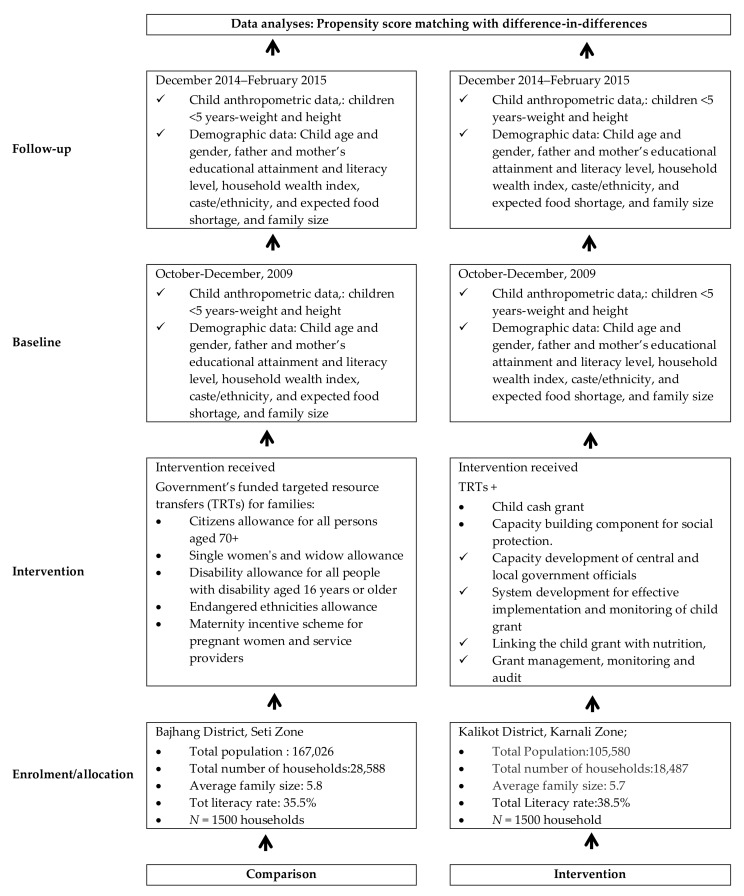
We deleted the word “baseline” in Figure 1:
Figure 1.
Flow diagram detailing the intervention implementation plan and data collection phases.
We also made some changes on Tables 2–4; therefore, the Tables should be as follows:
Table 2.
Summary statistics of the matching variables and estimates of logit regression models for stage 1 of propensity score matching.
| Matching Variables | All | Intervention | Control | Logit Model | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | Follow-Up | Baseline | Follow-Up | |||||||||||||||
| N | Mean | SD | N | Mean | SD | N | Mean | SD | N | Mean | SD | N | Mean | SD | Coefficient | SE | p-Value | |
| People per household | 3000 | 750 | 750 | 750 | 750 | |||||||||||||
| 4 people or less | 15.3% | 36.0% | 13.5% | 34.2% | 21.2% | 40.9% | 15.3% | 36.1% | 15.3% | 36.1% | 0.40 | 0.14 | 0.004 | |||||
| 5–8 people | 63.8% | 48.1% | 64.8% | 47.8% | 65.2% | 47.7% | 60.5% | 48.9% | 60.5% | 48.9% | 0.16 | 0.10 | 0.111 | |||||
| 9 people or above | 20.8% | 40.6% | 21.7% | 41.3% | 13.6% | 34.3% | 24.1% | 42.8% | 24.1% | 42.8% | Ref | |||||||
| Household wealth index | 2899 | 724 | 710 | 731 | 731 | |||||||||||||
| Poor | 60.0% | 49.0% | 89.1% | 31.2% | 54.2% | 49.9% | 10.1% | 30.2% | 10.1% | 30.2% | 2.17 | 0.13 | 0.000 | |||||
| Middle class | 20.0% | 40.0% | 9.7% | 29.6% | 35.9% | 48.0% | 23.9% | 42.7% | 23.9% | 42.7% | 2.08 | 0.15 | 0.000 | |||||
| Rich | 20.0% | 40.0% | 1.2% | 11.1% | 9.9% | 29.8% | 65.9% | 47.4% | 65.9% | 47.4% | Reference | |||||||
| Child’s age in months | 3000 | 27.98 | 15.53 | 750 | 28.66 | 15.36 | 750 | 28.4 | 15.71 | 750 | 28.08 | 15.4 | 750 | 28.08 | 15.4 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.045 |
| Child’s gender | 3000 | 750 | 750 | 750 | 750 | |||||||||||||
| Girl | 43.4% | 49.6% | 44.8% | 49.8% | 43.6% | 49.6% | 43.7% | 49.6% | 43.7% | 49.6% | Reference | |||||||
| Boy | 56.6% | 49.6% | 55.2% | 49.8% | 56.4% | 49.6% | 56.3% | 49.6% | 56.3% | 49.6% | −0.08 | 0.08 | 0.322 | |||||
| Ethnicity | 3000 | 750 | 750 | 750 | 750 | |||||||||||||
| Disadvantage ethnic groups | 0.4% | 6.6% | 1.5% | 12.0% | 0.1% | 3.7% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 2.04 | 1.04 | 0.050 | |||||
| Dalit Hill/Terai | 21.1% | 40.8% | 21.3% | 41.0% | 25.5% | 43.6% | 16.8% | 37.4% | 16.8% | 37.4% | 0.01 | 0.10 | 0.911 | |||||
| Upper caste Group | 78.5% | 41.1% | 77.2% | 42.0% | 74.4% | 43.7% | 83.2% | 37.4% | 83.2% | 37.4% | Reference | |||||||
| Father’s education | 3000 | 750 | 750 | 750 | 750 | |||||||||||||
| Intermediate or higher | 12.6% | 33.2% | 2.1% | 14.5% | 16.8% | 37.4% | 5.6% | 23.1% | 25.9% | 43.8% | Reference | |||||||
| Secondary level | 30.0% | 45.8% | 33.1% | 47.1% | 22.3% | 41.6% | 38.3% | 48.6% | 26.4% | 44.1% | −0.05 | 0.14 | 0.744 | |||||
| Primary or less | 57.4% | 49.5% | 64.8% | 47.8% | 60.9% | 48.8% | 56.1% | 49.7% | 47.7% | 50.0% | 0.27 | 0.14 | 0.052 | |||||
Table 3.
Evaluation of standardized differences in matched sample.
| Intervention | Comparison | % Bias | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unmatched | Matched | Unmatched | Matched | ||
| No. of people per household | |||||
| 4 people or less | 0.159 | 0.082 | 0.128 | 0.118 | −10.30 |
| 5–8 people | 0.657 | 0.664 | 0.629 | 0.659 | 1.20 |
| 9 people or more | 0.184 | 0.254 | 0.243 | 0.223 | 7.40 |
| Household wealth index | |||||
| Poor | 0.717 | 0.648 | 0.484 | 0.683 | −7.40 |
| Middle class | 0.227 | 0.275 | 0.174 | 0.240 | 8.80 |
| Rich | 0.056 | 0.077 | 0.342 | 0.077 | 0.00 |
| Child’s age in months | 28.341 | 25.429 | 27.476 | 27.602 | −14.00 |
| Child’s gender | |||||
| Girl | 0.438 | 0.395 | 0.429 | 0.421 | 5.30 |
| Boy | 0.562 | 0.605 | 0.571 | 0.579 | −5.30 |
| Ethnicity | |||||
| Disadvantage ethnic groups | 0.008 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.00 |
| Dalit Hill/Terai | 0.224 | 0.208 | 0.179 | 0.212 | −1.00 |
| Upper caste Group | 0.768 | 0.791 | 0.820 | 0.787 | 1.00 |
| Father’s education | |||||
| Primary or less | 0.630 | 0.496 | 0.519 | 0.540 | −8.90 |
| Secondary level | 0.277 | 0.378 | 0.323 | 0.338 | 8.70 |
| Intermediate or higher | 0.093 | 0.127 | 0.158 | 0.122 | −1.20 |
Table 4.
Program impact on child undernutrition.
| Original Dataset | Matched Dataset: Matching Algorithms | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Comparison | Intervention | Comparison | Intervention | Kernel ! | Nearest Neighbor ! | Radius !# | ||||||||||
| N = 748 | N = 743 | N = 749 | N = 750 | ADID | 95% CI | ADID | 95% CI | ADID | 95% CI | ADID | 95% CI | |||||
| Girls a | ||||||||||||||||
| Height | 77.2 (10.3) | 77.8 (10.9) | 78.7 (11.1) | 78.8 (11.7) | 0.17 | −0.05 | 0.40 | 0.65 | −0.87 | 2.18 | 0.01 | −1.43 | 1.45 | 0.69 | −0.99 | 2.36 |
| Weight | 9.3 (2.4) | 9.3 (2.5) | 9.7 (2.6) | 9.8 (2.9) | 0.31 *** | 0.22 | 0.40 | 0.32 | −0.06 | 0.71 | 0.13 | −0.25 | 0.51 | 0.33 * | 0.06 | 0.6 |
| HAZ | −2.3 (1.3) | −2.6 (1.4) | −2.1 (1.3) | −2.2 (1.3) | 0.21 | −0.01 | 0.44 | 0.11 | −0.06 | 0.27 | 0.07 | −0.18 | 0.32 | 0.15 | −0.06 | 0.36 |
| WAZ | −1.7 (1.0) | −2.1 (1.1) | −1.5 (1.1) | −1.6 (1.1) | 0.33 *** | 0.23 | 0.44 | 0.17 * | 0.06 | 0.28 | 0.13 | −0.1 | 0.37 | 0.19 * | 0.09 | 0.29 |
| WHZ | −0.5 (0.9) | −0.8 (1.1) | −0.5 (1.0) | −0.4 (1.0) | 0.31 *** | 0.15 | 0.46 | 0.17 * | 0.05 | 0.3 | 0.13 | −0.06 | 0.33 | 0.18 | −0.01 | 0.36 |
| Stunting | 61.9 | 68 | 55.5 | 61 | −3.98 | −15.44 | 7.48 | −2.65 | −9.15 | 3.85 | −5.07 | −11.78 | 1.63 | −4.24 | −10.4 | 1.93 |
| Underweight | 37.1 | 53.1 | 30.8 | 34.9 | −16.25 *** | −24.12 | −8.38 | −7.83 *** | −14.39 | −1.26 | −8.89 | −18.96 | 1.17 | −9.02 *** | −15.1 | −2.94 |
| Wasting | 4.5 | 9.3 | 7 | 4.9 | −9.29 *** | −15.86 | −2.72 | −2.62 | −6.33 | 1.09 | −3.31 | −8.2 | 1.58 | −2.47 | −5.9 | 0.95 |
| Boys a | ||||||||||||||||
| Height | 80.2 (11.2) | 80.6 (11.2) | 82.4 (11.2) | 81.6 (11.8) | −0.05 | −1.17 | 1.06 | 0.21 | −1.31 | 1.74 | 0.13 | −1.13 | 1.39 | 0.22 | −0.9 | 1.35 |
| Weight | 10.2 (2.6) | 10.2 (2.7) | 10.9 (2.8) | 10.7 (3.0) | 0.17 | −0.17 | 0.52 | 0.23 | −0.11 | 0.57 | 0.21 | −0.23 | 0.66 | 0.25 | −0.09 | 0.6 |
| HAZ | −2.4 (1.3) | −2.6 (1.5) | −2.0 (1.3) | −2.2 (1.4) | 0.14 | −0.14 | 0.43 | 0.16 * | 0 | 0.31 | 0.08 | −0.17 | 0.33 | 0.22 * | 0.08 | 0.35 |
| WAZ | −1.7 (1.0) | −2.1 (1.1) | −1.4 (1.1) | −1.6 (1.1) | 0.26 | 0.01 | 0.51 | 0.19 ** | 0.1 | 0.29 | 0.17 * | 0.01 | 0.32 | 0.25 * | 0.08 | 0.42 |
| WHZ | −0.6 (0.9) | −0.9 (1.2) | −0.3 (1.1) | −0.4 (1.0) | 0.27 *** | 0.08 | 0.47 | 0.21 * | 0.06 | 0.36 | 0.20 * | 0.02 | 0.38 | 0.21 * | 0.07 | 0.36 |
| Stunting | 63.7 | 65.7 | 50.8 | 58.8 | 0.69 | −14.00 | 15.37 | −4.14 | −10.48 | 2.19 | −1.27 | −10.49 | 7.95 | −6.15 * | −11.76 | −0.53 |
| Underweight | 37.4 | 48.8 | 27.5 | 34.8 | −9.74 | −23.38 | 3.90 | −5.03 | −11.19 | 1.13 | −3.39 | −13.45 | 6.67 | −6.49 | −13.15 | 0.16 |
| Wasting | 6.6 | 15.3 *** | 5.9 | 6.4 | −9.55 *** | −14.46 | −4.64 | −3.11 | −6.4 | 0.19 | −3.54 | −8.31 | 1.23 | −3.33 * | −6.16 | −0.49 |
| <2 years b | ||||||||||||||||
| Height | 70.0 (6.5) | 69.6 (6.7) | 70.8 (7.4) | 69.2 (7.4) | −0.28 | −1.16 | 0.60 | −0.85 * | −1.67 | −0.02 | −0.91 | −2.45 | 0.63 | −0.81 * | −1.6 | −0.02 |
| Weight | 7.8 (1.5) | 7.5 (1.6) | 8.1 (1.8) | 7.6 (1.8) | 0.03 | −0.30 | 0.37 | −0.15 | −0.38 | 0.08 | −0.17 | −0.45 | 0.11 | −0.14 | −0.36 | 0.08 |
| HAZ | −2.0 (1.4) | −2.2 (1.5) | −1.6 (1.4) | −1.9 (1.5) | 0.03 | −0.21 | 0.28 | 0.12 | −0.09 | 0.33 | −0.1 | −0.37 | 0.18 | 0.13 | −0.08 | 0.33 |
| WAZ | −1.5 (1.1) | −2.0 (1.2) | −1.2 (1.2) | −1.6 (1.2) | 0.18 | −0.04 | 0.41 | 0.08 | −0.06 | 0.22 | −0.01 | −0.24 | 0.23 | 0.09 | −0.08 | 0.27 |
| WHZ | −0.6 (0.9) | −1.1 (1.3) | −0.5 (1.1) | −0.7 (1.1) | 0.18 | −0.04 | 0.41 | 0.05 | −0.09 | 0.2 | 0.1 | −0.15 | 0.34 | 0.07 | −0.08 | 0.21 |
| Stunting | 52 | 58.2 | 39.8 | 50.8 | 2.76 | −5.16 | 10.68 | −2.48 | −8.1 | 3.14 | 1.61 | −6.44 | 9.66 | −3.57 | −10.37 | 3.23 |
| Underweight | 32.6 | 47.1 | 23.8 | 37.1 | −5.39 | −18.43 | 7.66 | −0.46 | −7.8 | 6.89 | 1.86 | −8.42 | 12.15 | −1.24 | −8.08 | 5.6 |
| Wasting | 6.7 | 18.8 | 6.8 | 10.3 | −9.19 *** | −15.81 | −2.57 | −1.2 | −5.16 | 2.76 | −1.91 | −6.88 | 3.05 | −1.03 | −4.2 | 2.13 |
| ≥2 years b | ||||||||||||||||
| Height | 87.1 (7.1) | 86.4 (7.9) | 88.3 (7.1) | 87.9 (7.6) | 0.53 | −0.12 | 1.18 | 0.41 | −0.18 | 1.01 | 0.59 | −0.45 | 1.63 | 0.74 | −0.16 | 1.64 |
| Weight | 11.7 (1.9) | 11.4 (2.0) | 12.1 (2.0) | 12.1 (2.1) | 0.39 *** | 0.12 | 0.66 | 0.36 *** | 0.12 | 0.6 | 0.44 ** | 0.18 | 0.69 | 0.44 *** | 0.25 | 0.63 |
| HAZ | −2.6 (1.1) | −2.8 (1.2) | −2.4 (1.1) | −2.4 (1.3) | 0.15 | −0.02 | 0.31 | 0.17 * | 0.06 | 0.28 | 0.12 | −0.03 | 0.28 | 0.21 * | 0.06 | 0.35 |
| WAZ | −1.9 (1.0) | −2.1 (1.1) | −1.6 (1.0) | −1.6 (1.0) | 0.28 *** | 0.12 | 0.44 | 0.28 *** | 0.18 | 0.37 | 0.27 ** | 0.13 | 0.41 | 0.30 *** | 0.19 | 0.41 |
| WHZ | −0.5 (0.9) | −0.6 (1.0) | −0.3 (1.0) | −0.2 (0.9) | 0.29 *** | 0.11 | 0.47 | 0.26 *** | 0.17 | 0.35 | 0.29 ** | 0.12 | 0.46 | 0.27 *** | 0.14 | 0.4 |
| Stunting | 73 | 73.1 | 62.8 | 65.8 | 0.05 | −6.01 | 6.11 | −4.82 | −10.23 | 0.6 | −4.05 | −12.54 | 4.44 | −6.66 ** | −12.13 | −1.18 |
| Underweight | 41.5 | 53.3 | 32.8 | 33.3 | −14.87 *** | −23.27 | −6.46 | −10.45 *** | −16.02 | −4.88 | −9.2 | −18.52 | 0.11 | −11.40 *** | −16.66 | −6.13 |
| Wasting | 4.9 | 8.2 | 6.1 | 2.7 | −8.51 *** | −13.91 | −3.11 | −3.86 ** | −5.98 | −1.74 | −6.22 ** | −9.22 | −3.22 | −4.10 ** | −6.43 | −1.78 |
| All c | ||||||||||||||||
| Height | 78.9 (10.9) | 79.3 (11.1) | 80.8 (11.3) | 80.3 (11.9) | 0.11 | −0.51 | 0.72 | 0.42 | −0.68 | 1.52 | −0.11 | −1.08 | 0.86 | 0.48 | −0.33 | 1.28 |
| Weight | 9.8 (2.6) | 9.8 (2.7) | 10.4 (2.8) | 10.3 (3.0) | 0.26 ** | 0.05 | 0.47 | 0.27 * | 0 | 0.55 | 0.17 | −0.12 | 0.47 | 0.29 | −0.01 | 0.6 |
| HAZ | −2.3 (1.3) | −2.6 (1.4) | −2.1 (1.3) | −2.2 (1.4) | 0.17 * | 0.03 | 0.31 | 0.14 * | 0.03 | 0.25 | 0.05 | −0.12 | 0.23 | 0.18 * | 0.09 | 0.27 |
| WAZ | −1.7 (1.0) | −2.1 (1.1) | −1.4 (1.1) | −1.6 (1.1) | 0.29 *** | 0.15 | 0.44 | 0.19 ** | 0.11 | 0.28 | 0.18 * | 0.07 | 0.29 | 0.22 ** | 0.15 | 0.29 |
| WHZ | −0.5 (0.9) | −0.8 (1.1) | −0.4 (1.1) | −0.4 (1.0) | 0.29 *** | 0.15 | 0.42 | 0.18 * | 0.09 | 0.28 | 0.24 * | 0.08 | 0.4 | 0.19 * | 0.09 | 0.3 |
| Stunting | 63 | 66.7 | 52.9 | 59.8 | −1.34 | −7.12 | 4.44 | −3.51 | −7.83 | 0.82 | −2.18 | −10.22 | 5.87 | −5.16 * | −9.55 | −0.77 |
| Underweight | 37.3 | 50.7 | 28.9 | 34.8 | −12.54 *** | −19.82 | −5.25 | −6.29 *** | −10.96 | −1.62 | −5.19 | −10.75 | 0.37 | −7.35 *** | −11.62 | −3.08 |
| Wasting | 5.8 | 12.7 | 6.4 | 5.7 | −9.32 *** | −14.86 | −3.79 | −2.86 * | −4.91 | −0.8 | −4.84 *** | −8.62 | −1.06 | −2.84 ** | −5.58 | −0.1 |
* p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001. ADID = Adjusted difference-in-differences. a Adjusted for father’s educational attainment, household wealth index, child age, caste/ethnicity, and family size; weighted with bootstrapping; b Adjusted for father’s educational attainment, household wealth index, caste/ethnicity, gender, and family size, weighted with bootstrapping; c Adjusted for father’s educational attainment, household wealth index, caste/ethnicity, gender, child age in month, and family size, weighted with bootstrapping. # Radius = 0.02; ! Weighted with bootstrapping. Z scores for height-for-age (HAZ), weight-for-age (WAZ) and weight-height (WHZ).
We apologize for any inconvenience caused to the readers by this error.
Author Contributions
This study was designed and implemented by UNICEF Nepal. A.M.N.R. carried out the analyses and drafted the manuscript. All authors critically revised the manuscript for intellectual contents, and read and approved the final manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Reference
- 1.Renzaho A.M.N., Chitekwe S., Chen W., Rijal S., Dhakal T., Dahal P. The Synergetic Effect of Cash Transfers for Families, Child Sensitive Social Protection Programs, and Capacity Building for Effective Social Protection on Children’s Nutritional Status in Nepal. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2017;14:1502. doi: 10.3390/ijerph14121502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]