Abstract
Background
Tick-transmitted Borrelia species fall into two heterogeneous bacterial complexes comprised of multiple species, the relapsing fever (RF) group and the Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato group, which are the causative agents of Lyme borreliosis (LB), the most common tickborne disease in the northern hemisphere. Geographic expansion of human LB in the United States and discovery of emerging Borrelia pathogens underscores the importance of surveillance for disease causing Borrelia.
Methods
De-identified clinical specimens, submitted by providers throughout the United States, for patients suspected of LB, anaplasmosis, ehrlichiosis, or babesiosis, were screened using a Borrelia genus level TaqMan PCR. Borrelia species and sequence types (STs) were characterized by multi-locus sequence typing (MLST) utilizing next generation sequencing.
Results
Among the 7,292 tested specimens tested, five different Borrelia species were identified: two causing LB, B. burgdorferi (n=25) and B. mayonii (n=9), and three RF borreliae, B. hermsii (n=1), B. miyamotoi (n=8), and Candidatus B. johnsonii (n=1), a species previously detected only in the bat tick, Carios kelleyi. ST diversity was greatest for B. burgdorferi positive specimens, with new STs identified primarily among synovial fluids.
Conclusion
These results demonstrate broad PCR screening followed by MLST is a powerful surveillance tool for uncovering the spectrum of Borrelia species causing human disease, improving understanding of their geographic distribution, and investigating the correlation between B. burgdorferi STs and joint involvement. Detection of Candidatus B. johnsonii in a patient with suspected tickborne disease suggests this species may be a previously undetected cause of illness in humans with exposure to bat ticks.
Keywords: Borrelia, Lyme disease, Relapsing fever, Molecular surveillance, Amplicon sequencing
Introduction
The Borrelia genus encompasses at least 50 known species of spirochetes, only a subset of which are known to cause human illness [1, 2]. Species are generally divided into two major complexes, Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato (Bbsl) and relapsing fever (RF), comprised of 21 and 29 different species, respectively. The Bbsl complex includes the causative agents of Lyme borreliosis (LB), the most common tickborne illness in the northern hemisphere, which are transmitted through the bite of infected Ixodes spp. hard ticks [3, 4]. The second complex includes the etiologic agents of tickborne and louseborne RF [1, 5]. Tickborne RF is most often associated with transmission by infected soft (argasid) ticks; however, the emerging pathogen, Borrelia miyamotoi, is transmitted by Ixodes ticks.
In the United States, the geographic distribution of human cases of LB and RF is complex and linked to the range of key tick vectors and varied ecological factors [2, 6]. For example, in the Upper Midwest, three human disease causing Borrelia are transmitted by Ixodes scapularis. These include the LB causing spirochetes, B. burgdorferi sensu stricto (hereafter called B. burgdorferi) and Borrelia mayonii as well as the RF spirochete, B. miyamotoi [7, 8]. In the Northeast and mid-Atlantic, B. burgdorferi and B. miyamotoi, but not B. mayonii, also cause human illness [9]. In mountainous regions of western states, the RF spirochete, Borrelia hermsii, transmitted by the bite of the soft tick Ornithodoros hermsi, causes human disease [6]. Adding to this complexity, ticks can carry multiple Borrelia species that have not been associated with human illness [10].
Clinical presentations of LB and RF include a range of overlapping symptoms early in infection with more distinct symptoms at later stages of disease [3, 6, 8, 11]. Early LB is typically characterized by localized skin infection resulting in an erythema migrans (EM) rash, frequently accompanied by fatigue, fever, and headache. Without early treatment, spirochetes can disseminate to secondary sites causing neurologic effects, cardiac abnormalities or arthritis. Arthritis is more commonly associated with B. burgdorferi infection, whereas LB caused by B. mayonii has been associated with higher spirochetemia [8, 12]. Manifestations of RF consist of fever, fatigue, headache, chills, myalgia, arthralgia, nausea, with rash rarely reported. Recurring febrile episodes can occur as untreated illness advances, particularly for B. hermsii, but appears to be less frequent in B. miyamotoi infection [6, 11, 13].
In patients infected with B. burgdorferi, the most common cause of LB in the United States, the number of spirochetes/genomic copies in blood is low, estimated at only 0.1/102-103 per ml [14, 15], limiting sensitivity of direct detection methods. Laboratory diagnosis therefore relies primarily on serologic assays to detect the patient’s immune response to the infection [16], which is useful for diagnosis, but precludes surveillance for Bbsl genospecies and strain types causing human illness. In the case of the two emerging Borrelia species, B. mayonii and B. miyamotoi, higher numbers of spirochetes and/or genomic copies have been reported in infected patients, at 105-106 and 104-105 per ml of blood, respectively [8, 9]. Concentrations of B. hermsii spirochetes in patient blood are estimated at >106 per ml [6]. As spirochete levels for many Borrelia infections are directly detectable, a broad molecular approach (genus level PCR followed by multi-locus next generation sequencing typing) was utilized to screen clinical specimens from patients suspected of tickborne illness in order to expand knowledge of Borrelia species and strain types associated with human disease in the United States and the geographic regions where these infections occur.
Materials and Methods
Specimen Collection
Residual clinical specimens [whole blood (EDTA), synovial fluid, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), and tissue] submitted to Mayo Clinic from health care providers nationwide for patients suspected of having a tickborne illness [i.e. testing by either Tick Borne Pathogen PCR Panel (Babesia, Ehrlichia/Anaplasma) or Lyme (Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato) PCR] and the accompanying nucleic acid extract were stored at 4°C or −70°C, de-identified and shipped to the Minnesota Department of Health (MDH). Synovial fluid, CSF, and tissue specimens were originally submitted for Lyme PCR, whereas blood specimens were submitted for either Tick Borne Pathogen PCR Panel or Lyme PCR. Aliquots of each clinical specimen were prepared, frozen at −70°C, and shipped to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Fort Collins, CO. Associated patient information included specimen type, originating state of the ordering provider, patient age, and sex. As travel history of patients was not available, the state of the ordering provider does not necessarily correlate to the patient’s state of residence or exposure. Analysis of de-identified specimens was approved by the Institutional Review Board at Mayo Clinic (Protocol ID: 14-001148). Review at MDH and CDC determined the protocol to be non-human subjects research.
PCR
DNA was extracted at Mayo Clinic using the MagNA Pure 2.0 Instrument (Roche Diagnostics, Indianapolis, IN). Residual DNA (2.5 µl) was tested at MDH using a 16S rRNA pan-Borrelia TaqMan™ PCR assay. At CDC, 16S rRNA pan-Borrelia results were confirmed by testing DNA independently extracted from aliquots of the Borrelia positive specimens using the MagNA Pure 96 (Roche).
The pan-Borrelia TaqMan assay was modified from Parola et al. [17]. Degenerate nucleotides were incorporated into the forward primer and probe sequences, based on alignment of 19 Bbsl and RF Borrelia species. Primer and probe sequences are as follows. Forward: 5′-AGCYTTTAAAGCTTCGCTTGTAG-3′, Reverse: 5′-GCCTCCCGTAGGAGTCTG G-3′, Probe: 5′-FAM-CCGGCCTGAGAGGGTGAWCGG-BHQ-3. Optimized final PCR concentrations included 1X PerfeCTa™ FastMixII or qPCR ToughMix™ (Quanta Biosciences, Beverly, MA), 600 nM of each primer and 200 nM of probe. Real-time PCR [ViiA™ 7 (Thermo Fisher) or 7500 Fast (Applied Biosystems)] cycling conditions were 95°C for 5 minutes, followed by 40-45 cycles at 95°C for 15 seconds, and 60°C for 30 seconds. Sensitivity and specificity were analyzed as described (Supplemental Materials).
Amplicon Sequencing
Portions of the 16S rRNA, flaB, glpQ, uvrA, rplB, recG, pyrG, pepX, clpX, nifS, and clpA genes were amplified using previously described primers and cycling conditions [18-20] (http://pubmlst.org/borrelia) and Premix Ex Taq hot start master mix (Takara Bio USA, Inc, Mountain View, CA) (Supplemental Materials). DNA concentration of PCR products was measured using the Qubit fluorimeter (ThermoFisher, Grand Island, NY) and normalized to 0.2 ng/µl. Multiplexed libraries were prepared using the Nextera XT DNA library preparation kit (Illumina, Inc. San Diego, CA) per the manufacturer’s protocol with unique Nextera indexes (Illumina) added to all amplicons from the same specimen. Sequencing was performed on the MiSeq platform (Illumina) using the V2 300 cycle reagent kit (Illumina).
Sequence Analysis
Amplicon sequence reads were de-multiplexed and adapter sequences removed, followed by import into CLC Genomics Workbench 8.0 (Qiagen, Valencia, CA). Sequence reads were mapped to 8 reference housekeeping genes, clpA, clpX, nifS, pepX, pyrG, recG, rplB, and uvrA from B. burgdorferi B31, B. mayonii MN14-1420, and B. miyamotoi CT13-2396 using default parameters [21-23]. Sequence reads for 16S rDNA, flaB, and glpQ from sample 15-3581 were de-novo assembled.
Consensus sequences for the 8 housekeeping genes were trimmed to lengths present in the Borrelia PubMLST database (https://pubmlst.org/borrelia/), concatenated in frame in the order clpA, clpX, nifS, pepX, pyrG, recG, rplB, and uvrA using Lasergene 12 (DNASTAR, Inc, Madison, WI). Consensus sequences for glpQ, flaB, and 16S rDNA were concatenated. Concatenated sequences were imported into MEGA 6, aligned (ClustalW), and phylogenetic trees constructed by maximum likelihood analysis using the generalized time-reversible nucleotide substitution model with gamma distribution (four categories) followed by bootstrap analysis (1000 replicates). Pairwise genetic distances were calculated using the Kimura-2 model and Bbsl species identified using the threshold (98.3% similarity, genetic distance 0.017). Sequences for Borrelia species included in analyses were obtained from http://pubmlst.org/borrelia/ or NCBI. iTOL v3 was for circularization of phylogenetic trees. Alleles and sequence types (STs) were assigned using http://pubmlst.org/borrelia/.
Results
PCR detection of Borrelia species in specimens from patients suspected of tickborne illness
Residual extracted DNA and originating specimens for 7,292 de-identified clinical specimens from patients suspected of LB, anaplasmosis, ehrlichiosis, or babesiosis were available for testing. Specimens were submitted by providers in 47 states and the District of Columbia (Figure 1; Supplemental Table 1) and were collected between 5/1/2014 - 11/15/2014 and 5/1/2015 – 12/11/2015. The majority (84%) of specimens were blood, followed by CSF (11.8%), synovial fluid (4.1%), and tissue (0.1%).
Figure 1. Origin of clinical specimens from patients suspected of tickborne illness.
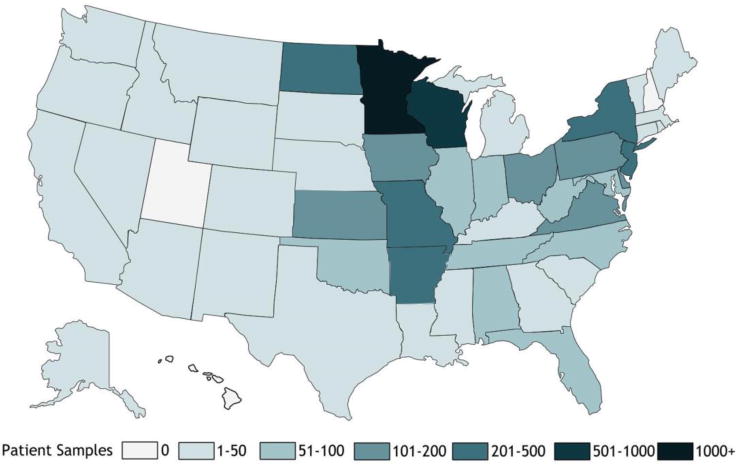
Origin of 7,292 clinical specimens tested in this study. Differential shading indicates the number of patient specimens originating from each state.
Of the 7,292 residual DNA specimens tested by Borrelia genus TaqMan PCR at the MDH, 44 were positive (31 bloods, 12 synovial fluids and 1 CSF). Independent DNA extraction and PCR testing at CDC confirmed all 44 specimens as Borrelia positive.
Multi-locus sequence typing (MLST) of Borrelia species in clinical specimens
Eight housekeeping genes (clpA, clpX, nifS, pepX, pyrG, recG, rplB, and uvrA) were amplified from 43 of the 44 Borrelia PCR positive specimens. For one specimen, amplicons were produced for 6 of the 8 housekeeping genes, likely due to a low level of spirochetal DNA. Sequence analysis of the 6 genes amplified confirmed the species as B. burgdorferi. Analysis of 8 concatenated housekeeping gene sequences (4,791 nucleotides) for the remaining 43 Borrelia positive specimens, identified five species falling into the two groups, LB or RF (Figure 2). These included two LB pathogens, B. burgdorferi (n=24; >99.2% identity to B. burgdorferi B31) and B. mayonii (n=9; >99.97% identity to B. mayonii MN14-1420) and three different RF Borrelia, B. miyamotoi (n=8; 100% identity to B. miyamotoi LB-2001), B. hermsii (n=1; 100% identity to B. hermsii YOR), and a Borrelia species (n=1) displaying highest sequence identity to B. parkeri (97.5%).
Figure 2. Phylogenetic relationships of identified Borrelia species.
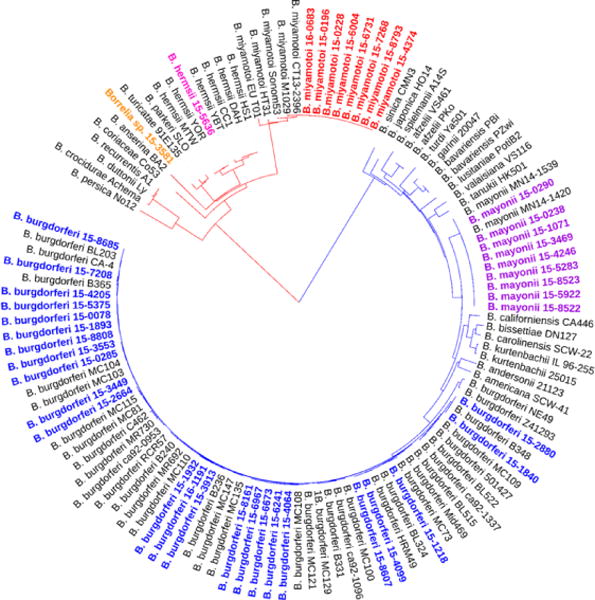
The phylogenetic tree is based on alignment of in frame concatenated DNA sequence fragments from 8 housekeeping genes (clpA, clpX, nifS, pepX, pyrG, recG, rplB, and uvrA) (n = 4,791 bp). Strains sequenced in this study are highlighted as follows: blue, B. burgdorferi; purple, B. mayonii; red, B. miyamotoi; pink, B. hermsii, and orange, Candidatus B. johnsonii. Publicly available sequences for 18 different Bbsl genospecies and 10 different RF borreliae (gray) were included for comparison. The scale bar corresponds to 0.1 substitutions per nucleotide position.
Of the 25 B. burgdorferi positive specimens, one was CSF and the remainder comprised equally of blood and synovial fluid. The remaining non-B. burgdorferi positive specimens were all blood (Table 1). The B. burgdorferi positive specimens originated from 8 states in the Midwest, mid-Atlantic and Northeast (IA, MD, MN, MO, NJ, NY, PA, VA, and WI), whereas all 9 B. mayonii positives were submitted only from MN or WI. The B. burgdorferi positivity rate for synovial fluid samples differed between the Upper Midwest [MN (2/75; 2.7%] and four Northeastern and mid-Atlantic states [MD, VA, PA, and NY (9/99; 9%)]. The B. miyamotoi positives came from states in the Upper Midwest and the Northeast (MN, NJ, and WI). The single B. hermsii positive specimen originated from Montana.
Table 1.
| B. burgdorferi | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample ID | Originating state | Specimen type | clpA | clpX | nifS | pepX | pyrG | recG | rplB | uvrA | ST |
| 15-2664 | MN | Blood | 18 | 12 | 1 | 11 | 2 | 15 | 1 | 2 | 29 |
| 15-3449 | MN | Blood | 4 | 12 | 1 | 11 | 2 | 15 | 1 | 2 | 756* |
| 15-4099 | MN | Blood | 8 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 16 | 1 | 7 | 32 |
| 15-6241 | MN | Blood | 14 | 1 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 10 | 530 |
| 15-6673 | MN | Blood | 14 | 1 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 10 | 530 |
| 15-6967 | MN | Blood | 14 | 1 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 10 | 530 |
| 15-8161 | MN | Blood | 14 | 1 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 10 | 530 |
| 15-3553 | PA | Blood | 5 | 5 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 1 | 6 | 8 |
| 15-0285 | WI | Blood | 8 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 16 | 1 | 7 | 32 |
| 15-3913 | WI | Blood | 128 | 12 | 1 | 8 | 1 | 6 | 1 | 10 | 758* |
| 15-4064 | WI | Blood | 14 | 1 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 10 | 530 |
| 15-1932 | IA | CSF | 8 | 1 | 1 | 14 | 2 | 6 | 1 | 10 | 48 |
| 15-0078 | MD | Synovial Fluid | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 224* | 6 | 1 | 217* | 754* |
| 15-1218 | MN | Synovial Fluid | 24 | 14 | 4 | 18 | 11 | 19 | 1 | 12 | 56 |
| 16-1191 | MN | Synovial Fluid | 8 | 1 | 1 | 14 | 2 | 6 | 1 | 10 | 48 |
| 15-2880 | MO | Synovial Fluid | 4 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 19 |
| 15-5375 | NY | Synovial Fluid | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 225* | 6 | 1 | 7 | 759* |
| 15-7208 | NY | Synovial Fluid | 6 | 1 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 7 | 1 | 8 | 7 |
| 15-8685 | NY | Synovial Fluid | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 15-4205 | PA | Synovial Fluid | 14 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 6 | 200* | 7 | 758* |
| 15-8607 | PA | Synovial Fluid | 5 | 5 | 188* | 5 | 5 | 5 | 1 | 6 | 760* |
| 15-1840 | VA | Synovial Fluid | 4 | 4 | 3 | 217* | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 755* |
| 15-1893 | VA | Synovial Fluid | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 6 | 1 | 7 | 3 |
| 15-8808 | VA | Synovial Fluid | 4 | 1 | 189* | 1 | 1 | 6 | 1 | 7 | 761* |
| B. mayonii | |||||||||||
| clpA | clpX | nifS | pepX | pyrG | recG | rplB | uvrA | ST | |||
| 15-0238 | MN | Blood | 218 | 182 | 166 | 191 | 201 | 209 | 174 | 193 | 674 |
| 15-0290 | MN | Blood | 218 | 182 | 166 | 191 | 202 | 209 | 174 | 193 | 675 |
| 15-1071 | MN | Blood | 218 | 182 | 166 | 191 | 201 | 209 | 174 | 193 | 674 |
| 15-3469 | WI | Blood | 218 | 182 | 166 | 191 | 201 | 209 | 174 | 193 | 674 |
| 15-4246 | MN | Blood | 218 | 182 | 166 | 191 | 201 | 209 | 174 | 193 | 674 |
| 15-5283 | MN | Blood | 218 | 182 | 166 | 191 | 201 | 209 | 174 | 193 | 674 |
| 15-5922 | MN | Blood | 218 | 182 | 166 | 218* | 201 | 209 | 174 | 193 | 762* |
| 15-8522 | MN | Blood | 218 | 182 | 166 | 191 | 201 | 209 | 174 | 193 | 674 |
| 15-8523 | MN | Blood | 218 | 182 | 166 | 191 | 201 | 209 | 174 | 193 | 674 |
| B. miyamotoi | |||||||||||
| clpA | clpX | nifS | pepX | pyrG | recG | rplB | uvrA | ST | |||
| 15-0196 | WI | Blood | 200 | 117 | 151 | 173 | 184 | 191 | 160 | 70 | 634 |
| 15-0228 | MN | Blood | 200 | 117 | 151 | 173 | 184 | 191 | 160 | 70 | 634 |
| 15-4374 | NJ | Blood | 200 | 117 | 151 | 173 | 184 | 191 | 160 | 70 | 634 |
| 15-6004 | MN | Blood | 200 | 117 | 151 | 173 | 184 | 191 | 160 | 70 | 634 |
| 15-6731 | NJ | Blood | 200 | 117 | 151 | 173 | 184 | 191 | 160 | 70 | 634 |
| 15-7268 | NJ | Blood | 200 | 117 | 151 | 173 | 184 | 191 | 160 | 70 | 634 |
| 15-8793 | MN | Blood | 200 | 117 | 151 | 173 | 184 | 191 | 160 | 70 | 634 |
| 16-0683 | NJ | Blood | 200 | 117 | 151 | 173 | 184 | 191 | 160 | 70 | 634 |
| B. hermsii | |||||||||||
| clpA | clpX | nifS | pepX | pyrG | recG | rplB | uvrA | ST | |||
| 15-5636 | MT | Blood | 246* | 206* | 190* | 219* | 226* | 236* | 201* | 218* | 763* |
| Candidatus B. johnsonii | |||||||||||
| clpA | clpX | nifS | pepX | pyrG | recG | rplB | uvrA | ST | |||
| 15-3581 | WI | Blood | 247* | 207* | 191* | 220* | 227* | 237* | 202* | 219* | 764* |
Denotes allele or sequence type identified in this study
ST diversity was greatest among the B. burgdorferi positive specimens (Figure 2). Eighteen different MLST sequence types (STs) were identified, including 10 known STs (ST1, ST3, ST7, ST8, ST19, ST29, ST32, ST48, ST56, ST530) and 8 new STs (ST754, ST755, ST756, ST757, ST758, ST759, ST760, ST761) comprised of either known loci in previously unobserved combinations or newly observed loci (Table 1). New B. burgdorferi STs were predominately associated with synovial fluid specimens (6/8; 75%). The 6 synovial fluid specimens assigned new STs were submitted by providers in Northeast and mid-Atlantic states (Table 1).
In contrast to the B. burgdorferi positive specimens, limited or no sequence diversity across the 8 housekeeping genes was observed among the B. mayonii or B. miyamotoi positive specimens, respectively (Table 1). For the 9 B. mayonii positive specimens, three different MLST STs were identified, which included the known STs, ST674, ST675, and a new ST (ST762), which has a single nucleotide variant in pepX as compared to ST674 (Supplemental Table 3).
Identification of Candidatus Borrelia johnsonii in a patient specimen
To further characterize the RF Borrelia spp. (15-3581) most closely related to B. parkeri, sequencing and phylogenetic analysis of the 16S rRNA, flaB and glpQ genes was performed. As these genes have historically been utilized for characterization of RF Borrelia, more sequences are publicly available as compared to the housekeeping genes more commonly used for Bbsl species. Analysis of the concatenated glpQ, flaB and 16S rDNA sequence (3,048 nucleotides) demonstrated 100% identity between 15-3581 and Candidatus Borrelia johnsonii strain IA-1, a Borrelia species previously identified only in bat ticks (Carios kelleyi) (Figure 3) [24]. The Candidatus Borrelia johnsonii positive blood specimen was submitted from a provider in Wisconsin.
Figure 3. Identification of Candidatus Borrelia johnsonii in patient blood.
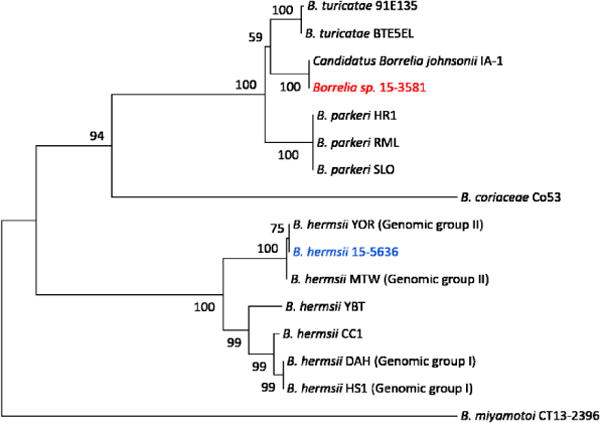
Phylogenetic relationship of Borrelia spp. 15-3581 (red) based on analysis of concatenated glpQ, flaB, and 16S rDNA sequences (n = 3048 bp). Publicly available sequences for 6 different RF borreliae (gray) and B. hermsii 15-5636 from this study were included for comparison. Bootstrap support values greater than 50% are shown. The scale bar corresponds to 0.01 substitutions per nucleotide position.
Discussion
A better understanding of the scope and geographic distribution of Borrelia species infecting humans is essential for improving clinical recognition, laboratory diagnosis, and prevention. Here, we demonstrated a broad molecular surveillance approach successfully detected both known pathogens and a novel Borrelia species in specimens from US patients suspected of tickborne illness. The five Borrelia species identified included the 2 Bbsl genospecies known to cause LB, B. burgdorferi and B. mayonii, the 2 known RF pathogens, B. hermsii and B. miyamotoi, and a third RF species, Candidatus B. johnsonii, not previously associated with human illness.
Prior description of Candidatus B. johnsonii is limited to molecular and microscopic detection in bat ticks, Carios kelleyi, collected from an Iowa farmhouse [24, 25]. C. kelleyi ticks are widely distributed in the Americas and can be found in houses and buildings infested with bats. Although this tick prefers to feed on bats, it will also feed on humans and persons presumably bitten by C. kelleyi ticks have reported expanding, erythematous skin lesions, lymphadenopathy, fever, weight loss, malaise, and fatigue [26]. Whether these symptoms were due to infection with Candidatus B. johnsonii is unknown. The clinical presentation for the Candidatus B. johnsonii infected patient identified here is also unknown. Nonetheless, we can infer that the physician suspected a tickborne illness, given that the blood specimen was originally submitted for either Lyme or Tickborne Pathogen PCR Panel.
Notably, ten infections due to three RF Borrelia species, B. miyamotoi (n=8), B. hermsii (n=1) and Candidatus B. johnsonii (n=1), associated with three different tick species, I. scapularis, O. hermsi and C. kelleyi, respectively, were detected in patient samples submitted for tickborne diseases other than RF. As B. miyamotoi is transmitted by I. scapularis, the same tick which transmits B. burgdorferi, B. mayonii, Anaplasma phagocytophilum, Ehrlichia muris ssp. eauclairensis and Babesia microti, its detection in this sample set is not unexpected and has been reported previously [9, 27, 28]. All 8 B. miyamotoi positive samples originated from patients in the Northeast and Upper Midwest where human cases or B. miyamotoi infected I. scapularis have been previously described [7, 9, 27]. Detection of B. hermsii in these samples was unexpected. The specimen originated from Montana where cases of RF are reported due to the bite of infected O. hermsi and locally acquired cases of LB, anaplasmosis, ehrlichiosis and babesiosis are not known to occur.
Of the 11 Bbsl genospecies identified in ticks or animals in the United States [2, 5, 29], only B. burgdorferi and B. mayonii were detected in samples from over 7000 US patients. Consistent with the initial description of B. mayonii as a cause of LB in the Upper Midwest [8], all 9 B. mayonii positive specimens described here were submitted by providers in either Minnesota or Wisconsin. Given that 3 of the identified B. mayonii positives were from 2014, the same time period in which the initial 6 B. mayonii infected patients were detected by Lyme PCR [9], it appears likely the providers suspected these patients of having a tickborne illness other than LB. All 9 B. mayonii positive specimens were blood, as compared to B. burgdorferi positive specimens, which were an equal distribution of synovial fluid and blood. The B. burgdorferi positive specimens originated from Lyme endemic regions in the Northeast, mid-Atlantic and Upper Midwest, with the exception of a synovial fluid specimen from Missouri. Due to lack of patient travel information, exposure to ticks in a Lyme endemic region for this patient cannot be excluded and appears likely, given the ST of the infecting strain, ST19, has only been observed previously in the Northeast. No Bbsl positives were identified among specimens originating from 10 southeast or southcentral states (FL, GA, SC, AL, TN, NC, LA, AR, OK, and TX), where I. scapularis is also present, and which accounted for 10% (739/7292) of the samples tested.
ST diversity among B. burgdorferi positive specimens contrasted with what was observed for B. mayonii and B. miyamotoi positive specimens. Only a single MLST ST, ST634, was observed among B. miyamotoi positive specimens from the upper midwestern and northeastern United States, in agreement with previous studies demonstrating low genetic variability [30]. ST diversity among B. mayonii positive specimens was also limited, with 7 of the 9 identified as ST674. The three identified B. mayonii ST’s differ by only 1 or 2 loci, and thus appear to belong to the same clonal complex. In contrast, among the B. burgdorferi positive samples, 18 STs were identified. The most common B. burgdorferi ST in this study, ST530, appears to have a localized geographic distribution in the Upper Midwest (MN, WI). Consistent with this, the only previous reported detection of this ST is from I. scapularis collected from Manitoba, Canada (http://pubmlst.org/borrelia/).
Newly observed B. burgdorferi MLST STs were most abundant in synovial fluids (71%), a specimen type for which 8 housekeeping MLST data is publicly lacking [18, 19, 31-33]. Four of the STs identified in synovial fluid specimens submitted by providers in the Northeast and mid-Atlantic regions, grouped with MLST ST3 (node support 0.89), a ST previously associated with disseminated LB [32]. Whether MLST STs may be predictive of arthritic outcome requires further study.
It is important to clarify the 0.6% (44/7,292) Borrelia positivity rate in this sample set does not reflect disease incidence or PCR positivity rates for a given Borrelia species. To enhance the likelihood of uncovering the spectrum of Borrelia species causing human disease in US patients, specimens from persons suspected of a number of tickborne diseases (LB, anaplasmosis, ehrlichiosis or babesiosis) were tested. The percentage of samples submitted specifically for Lyme as opposed to Tickborne Pathogen PCR Panel (Babesia, Ehrlichia/Anaplasma) was unknown. Second, the ability to detect Borrelia DNA by PCR is dependent on a number of factors, including when the specimen is collected in relation to illness onset, whether the sample is taken pre-treatment, and the level of spirochetemia resulting from the infecting Borrelia species. These factors could lead to over and under-representation of specific Borrelia species or even MLST STs. This is particularly relevant to B. burgdorferi, where the number of spirochetes/genomic copies in blood is low, often below the limit of PCR detection [14, 15].
Our results demonstrate that broad PCR followed by MLST utilizing next generation sequencing is a powerful surveillance tool for uncovering Borrelia species causing human disease, understanding the geographic distribution of disease-causing Borrelia and improving understanding of the pathogenic properties of B. burgdorferi STs. Ongoing surveillance for Borrelia pathogens in US patients suspected of tickborne illness is in progress. In ill patients with potential exposure to bat ticks,, Candidatus B. johnsonii may be considered.
Supplementary Material
Summary.
Broad molecular surveillance for Borrelia species in patients suspected of tickborne illness followed by next-generation sequence typing provides insight into the different Borrelia species causing human illness and geographical distribution of Borrelia infections and sequence types throughout the United States.
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our thanks to Katherine Caflisch and the Mayo Clinic Microbiology Initial Processing Laboratory for their work collecting, aliquoting, recording, and shipping of specimens and John Young for sample receiving and processing. Special thanks to Alison Hinckley and Sarah Hook for study coordination and to Kirk Smith for critical review of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Office of Advanced Molecular Detection, Project ID AMD90.
Footnotes
Publisher's Disclaimer: Disclaimer
The views and opinions expressed herein are those of the authors alone and do not represent the official position of the CDC.
Potential conflicts of interest
All authors: No reported conflicts. All authors have submitted the ICMJE Form for Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest.
References
- 1.Cutler SJ. Relapsing Fever Borreliae: A Global Review. Clin Lab Med. 2015;35(4):847–65. doi: 10.1016/j.cll.2015.07.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Schotthoefer AM, Frost HM. Ecology and Epidemiology of Lyme Borreliosis. Clin Lab Med. 2015;35(4):723–43. doi: 10.1016/j.cll.2015.08.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Steere AC, Strle F, Wormser GP, et al. Lyme borreliosis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2:16090. doi: 10.1038/nrdp.2016.90. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Stanek G, Wormser GP, Gray J, Strle F. Lyme borreliosis. Lancet. 2012;379(9814):461–73. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60103-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Cutler SJ, Ruzic-Sabljic E, Potkonjak A. Emerging borreliae - Expanding beyond Lyme borreliosis. Mol Cell Probes. 2017;31:22–7. doi: 10.1016/j.mcp.2016.08.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Dworkin MS, Schwan TG, Anderson DE, Jr, Borchardt SM. Tick-borne relapsing fever. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2008;22(3):449–68. viii. doi: 10.1016/j.idc.2008.03.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Jobe DA, Lovrich SD, Oldenburg DG, Kowalski TJ, Callister SM. Borrelia miyamotoi Infection in Patients from Upper Midwestern United States, 2014–2015. Emerg Infect Dis. 2016;22(8):1471–3. doi: 10.3201/eid2208.151878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Pritt BS, Mead PS, Johnson DK, et al. Identification of a novel pathogenic Borrelia species causing Lyme borreliosis with unusually high spirochaetaemia: a descriptive study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2016;16(5):556–64. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(15)00464-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Molloy PJ, Telford SR, 3rd, Chowdri HR, et al. Borrelia miyamotoi Disease in the Northeastern United States: A Case Series. Ann Intern Med. 2015;163(2):91–8. doi: 10.7326/M15-0333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Rudenko N, Golovchenko M, Grubhoffer L, Oliver JH., Jr Updates on Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato complex with respect to public health. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2011;2(3):123–8. doi: 10.1016/j.ttbdis.2011.04.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Telford SR, 3rd, Goethert HK, Molloy PJ, et al. Borrelia miyamotoi Disease: Neither Lyme Disease Nor Relapsing Fever. Clin Lab Med. 2015;35(4):867–82. doi: 10.1016/j.cll.2015.08.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Arvikar SL, Steere AC. Diagnosis and treatment of Lyme arthritis. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2015;29(2):269–80. doi: 10.1016/j.idc.2015.02.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Platonov AE, Karan LS, Kolyasnikova NM, et al. Humans infected with relapsing fever spirochete Borrelia miyamotoi, Russia. Emerg Infect Dis. 2011;17(10):1816–23. doi: 10.3201/eid1710.101474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Aguero-Rosenfeld ME, Wang G, Schwartz I, Wormser GP. Diagnosis of lyme borreliosis. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2005;18(3):484–509. doi: 10.1128/CMR.18.3.484-509.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Liveris D, Schwartz I, McKenna D, et al. Comparison of five diagnostic modalities for direct detection of Borrelia burgdorferi in patients with early Lyme disease. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2012;73(3):243–5. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2012.03.026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Marques AR. Laboratory diagnosis of Lyme disease: advances and challenges. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2015;29(2):295–307. doi: 10.1016/j.idc.2015.02.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Parola P, Diatta G, Socolovschi C, et al. Tick-borne relapsing fever borreliosis, rural senegal. Emerg Infect Dis. 2011;17(5):883–5. doi: 10.3201/eid1705.100573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Margos G, Gatewood AG, Aanensen DM, et al. MLST of housekeeping genes captures geographic population structure and suggests a European origin of Borrelia burgdorferi. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105(25):8730–5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0800323105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Margos G, Vollmer SA, Cornet M, et al. A new Borrelia species defined by multilocus sequence analysis of housekeeping genes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2009;75(16):5410–6. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00116-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Schwan TG, Raffel SJ, Schrumpf ME, et al. Phylogenetic analysis of the spirochetes Borrelia parkeri and Borrelia turicatae and the potential for tick-borne relapsing fever in Florida. J Clin Microbiol. 2005;43(8):3851–9. doi: 10.1128/JCM.43.8.3851-3859.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Fraser CM, Casjens S, Huang WM, et al. Genomic sequence of a Lyme disease spirochaete, Borrelia burgdorferi. Nature. 1997;390(6660):580–6. doi: 10.1038/37551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Kingry LC, Batra D, Replogle A, Rowe LA, Pritt BS, Petersen JM. Whole Genome Sequence and Comparative Genomics of the Novel Lyme Borreliosis Causing Pathogen, Borrelia mayonii. PLoS One. 2016;11(12):e0168994. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0168994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Kingry LC, Replogle A, Batra D, et al. Toward a Complete North American Borrelia miyamotoi Genome. Genome Announc. 2017;5(5) doi: 10.1128/genomeA.01557-16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Gill JS, Ullmann AJ, Loftis AD, et al. Novel relapsing fever spirochete in bat tick. Emerg Infect Dis. 2008;14(3):522–3. doi: 10.3201/eid1403.070766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Schwan TG, Raffel SJ, Schrumpf ME, Gill JS, Piesman J. Characterization of a novel relapsing fever spirochete in the midgut, coxal fluid, and salivary glands of the bat tick Carios kelleyi. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2009;9(6):643–7. doi: 10.1089/vbz.2008.0177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Gill JS, Rowley WA, Bush PJ, Viner JP, Gilchrist MJ. Detection of human blood in the bat tick Carios (Ornithodoros) kelleyi (Acari: Argasidae) in Iowa. J Med Entomol. 2004;41(6):1179–81. doi: 10.1603/0022-2585-41.6.1179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Gugliotta JL, Goethert HK, Berardi VP, Telford SR., 3rd Meningoencephalitis from Borrelia miyamotoi in an immunocompromised patient. N Engl J Med. 2013;368(3):240–5. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1209039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Pritt BS, Allerdice MEJ, Sloan LM, et al. Proposal to reclassify Ehrlichia muris as Ehrlichia muris subsp. muris subsp. nov. and description of Ehrlichia muris subsp. eauclairensis subsp. nov., a newly recognized tick-borne pathogen of humans. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2017 doi: 10.1099/ijsem.0.001896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Postic D, Garnier M, Baranton G. Multilocus sequence analysis of atypical Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato isolates–description of Borrelia californiensis sp. nov., and genomospecies 1 and 2. Int J Med Microbiol. 2007;297(4):263–71. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2007.01.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Mukhacheva TA, Salikhova II, Kovalev SY. Multilocus spacer analysis revealed highly homogeneous genetic background of Asian type of Borrelia miyamotoi. Infect Genet Evol. 2015;31:257–62. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2015.02.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Coipan EC, Jahfari S, Fonville M, et al. Imbalanced presence of Borrelia burgdorferi s.l. multilocus sequence types in clinical manifestations of Lyme borreliosis. Infect Genet Evol. 2016;42:66–76. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2016.04.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Hanincova K, Mukherjee P, Ogden NH, et al. Multilocus sequence typing of Borrelia burgdorferi suggests existence of lineages with differential pathogenic properties in humans. PLoS One. 2013;8(9):e73066. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0073066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Jungnick S, Margos G, Rieger M, et al. Borrelia burgdorferi sensu stricto and Borrelia afzelii: Population structure and differential pathogenicity. Int J Med Microbiol. 2015;305(7):673–81. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2015.08.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


