Abstract
Th17 cells contribute to the development of autoimmune diseases by secreting interleukin‐17 (IL‐17), which activates its receptor (IL‐17R) that is expressed on epithelial cells, macrophages, microglia, and resident neuroectodermal cells. However, the mechanisms through which IL‐17R‐mediated signaling contributes to the development of autoimmune disease have not been completely elucidated. Here, we demonstrate that Raf‐1 kinase inhibitor protein (RKIP) deficiency in mice ameliorates the symptoms of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE). Adoptive T‐cell‐transfer experiments demonstrate that RKIP plays a predominant role in Th17‐mediated, but not in Th1‐mediated immune responses. RKIP deficiency has no effect on Th17‐cell differentiation ex vivo, nor does it affect Th17‐cell differentiation in EAE mice. However, RKIP significantly promotes IL‐17R‐induced proinflammatory cytokine and chemokine production. Mechanistically, RKIP directly interacts with IL‐17RA and Act1 to promote the formation of an IL‐17R‐Act1 complex, resulting in enhanced MAPK‐ and P65‐mediated NF‐κB activation and downstream cytokine production. Together, these findings indicate that RKIP functions as an essential modulator of the IL‐17R‐Act1 axis in IL‐17R signaling, which promotes IL‐17‐induced inflammation and autoimmune neuroinflammation.
Keywords: Act1, EAE, IL‐17, RKIP
Subject Categories: Immunology, Molecular Biology of Disease, Neuroscience
Introduction
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a type of human demyelinating disease that causes central nervous system (CNS; i.e., the brain and spinal cord) inflammation, neuronal demyelination, and axonal damage, resulting in both physical and mental health impairment. MS is the most common autoimmune disorder affecting the central nervous system 1. Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) is a well‐established MS‐like animal disease model induced by immunizing mice with myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein peptide (MOG35‐55) and pertussis toxin (PTX) 2. It has been demonstrated that myelin‐specific T cells, particularly interleukin‐17 (IL‐17)‐producing Th17 cells, play a crucial pathogenic role in the mouse EAE model 3, 4. Specifically, Th17 cells participate in the development of EAE by secreting IL‐17, which comprises IL‐17A to IL‐17F 5, 6. IL‐17 levels have been shown to be increased in patients with MS and ulcerative colitis (UC) 7, 8. The binding of IL‐17 to a type I cell surface receptor known as the IL‐17 receptor (IL‐17R) activates IL‐17R signaling and ultimately triggers the production of proinflammatory cytokines (TNF‐α, IL‐1, IL‐6, IL‐8, G‐CSF, and GM‐CSF) and chemokines (CXCL1, CXCL2, CXCL5, CCL2, CCL7, and CCL20) 9. These cytokines subsequently contribute to the activation of resident CNS cells, including epithelial cells, macrophages, microglia, and astrocytes, resulting in the secretion of additional chemokines and the recruitment of additional leukocytes into the CNS, which leads to disseminated CNS inflammation, neuronal demyelination, and the development of EAE symptoms 3, 6, 10. Consistent with these findings, the findings of additional studies indicate that mice deficient in IL‐17 or IL‐17R display less severe EAE than wild‐type (WT) mice because they lack the cellular machinery responsible for facilitating IL‐17‐mediated IL‐17R signal transduction 11, 12.
IL‐17R signaling involves the recruitment of the key adaptor protein Act1 (also known as CIKS) and the E3 ubiquitin ligase TRAF6 to the cytoplasmic region of IL‐17R, where they bind with its SEFIR domain. Specifically, the SEFIR domain of IL‐17R interacts with the adaptor protein Act1 in response to IL‐17 stimulation 13, 14. Act1 subsequently recruits TRAF6 to IL‐17R, then triggers activation of the MAPK and NF‐κB pathways, and induces the production of proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines 15, 16. In addition to activating TRAF6, Act1 also recruits TRAF2 and TRAF5 to prolong the half‐life of the mRNA of some cytokines and chemokines, such as IL‐6 and CXCL1 17, 18. Previous studies have demonstrated the regulatory mechanisms through which multiple signaling molecules downstream of the IL‐17R‐Act1 complex exert their effects. For example, Xiao et al 10 reported that the serine/threonine kinase TPL2 functions as a pivotal mediator of TAK1 activation in the IL‐17R signaling pathway. However, the mechanism through which the IL‐17R‐Act1 signalosome is modulated remains poorly understood 14.
Raf‐1 kinase inhibitor protein (RKIP) is a member of the phosphatidylethanolamine‐binding protein (PEBP) family and is widely expressed in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms. RKIP modulates and controls crucial intracellular signaling networks, including the Raf/MEK/ERK, NF‐κB, glycogen synthase kinase‐3β (GSK3β), and G protein‐coupled receptor (GPCR) signaling cascades 19, 20, 21, 22. Therefore, RKIP is involved in regulating a variety of physiological processes, such as cell differentiation, cell cycle progression, and apoptosis 23. RKIP has been shown to inhibit cancer cell invasion and metastasis in several cancers and functions as an important tumor suppressor 24, 25. We recently determined that RKIP also plays a crucial role in mediating human and mouse colitis by promoting intestinal epithelial cell apoptosis 26. Furthermore, we determined that RKIP promotes anti‐viral innate immune responses by promoting TBK1 auto‐phosphorylation 27. Therefore, RKIP functions in more processes than tumor suppression. In the present study, we first obtained genetic evidence that RKIP deficiency in non‐hematopoietic cells renders affected mice refractory to EAE induction. Adoptive T‐cell‐transfer experiments demonstrated that RKIP promotes Th17‐mediated EAE development. We further demonstrated that RKIP deficiency in astrocytes significantly inhibits IL‐17‐induced proinflammatory cytokine and chemokine expression. More importantly, we found that RKIP serves as a pivotal mediator of the interactions between IL‐17R‐Act1 in the IL‐17R signaling pathway, resulting in enhanced IL‐17‐induced NF‐κB and the MAPK activation. RKIP deficiency in mice significantly impairs IL‐17‐induced pulmonary inflammation and peritonitis. IL‐17R signaling is involved in various inflammatory diseases, and these findings not only provided novel insights into the regulatory mechanisms through which IL‐17R signaling occurs, but also showed that targeting IL‐17R signaling may be useful for the treatment of IL‐17‐mediated autoimmune diseases.
Results
RKIP is a crucial mediator of the pathogenesis of EAE
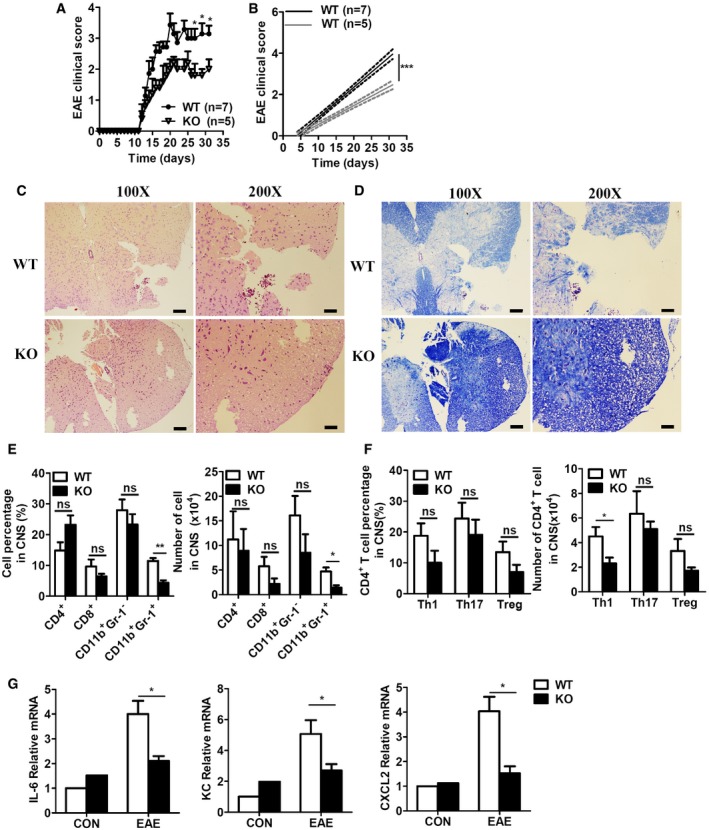
We previously determined that RKIP is involved in colitis and anti‐viral immune responses 26, 27. We thus attempted to determine whether RKIP can regulate autoimmune diseases. The well‐known mouse MS model, that is, the EAE model, was firstly established to determine the role of RKIP in the pathogenesis of EAE. We subcutaneously injected RKIP WT mice and their knockout (KO) littermates with MOG35‐55 and then intravenously injected them with pertussis toxin (PTX) to induce the EAE model. As shown in Fig 1A and B, RKIP‐KO mice suffered from relatively mild EAE disease symptoms compared to WT mice and had lower EAE clinical scores than their counterparts. Moreover, WT mice displayed diminished inflammatory cell infiltration (Fig 1C) and demyelination (Fig 1D), as demonstrated by hematoxylin–eosin (H&E) and luxol fast blue (LFB) staining, respectively, compared to their counterparts. Consistent with these results, flow cytometry analysis of mouse CNS tissues (brains and spinal cords) demonstrated that both the percentages and the absolute numbers of CNS‐infiltrating CD11b+Gr‐1+ neutrophils were significantly reduced in RKIP‐KO mice compared to WT mice (Fig 1E). Within the CNS‐infiltrating CD4+ T‐cell population, the percentages and absolute numbers of IL‐17+ Th17 cells and Foxp3+ Treg cells in RKIP‐KO mice were comparable to those in WT mice (Fig 1F), while the numbers of Th1 (IFNγ+ CD4+ T) cells in RKIP‐KO mice were slightly decreased compared to those in WT mice (Fig 1F). We also assessed the composition of the immune cell population in the spleen during EAE. The results of the assessment showed that RKIP deficiency inhibited CD11b+Gr‐1+ neutrophil infiltration into the spleen (Fig EV1A–C) without affecting the absolute numbers or percentages of other immune cells, namely CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells, and CD11b+Gr‐1− monocytes in the spleen. RKIP deficiency either did not alter T‐helper‐cell differentiation (namely Th1‐, Th17‐, and Treg‐cell differentiation; Fig EV1D and E). We subsequently examined the expression levels of several proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines in the CNS tissues of WT and RKIP‐KO EAE mice. As shown in Fig 1G, the gene expression levels of the proinflammatory cytokine IL‐6 and several chemokines known to mediate immune cell recruitment, such as CXCL1 (KC) and CXCL2, were significantly decreased in RKIP‐KO EAE mice versus WT EAE mice. These results suggest that RKIP deficiency restricts EAE development by reducing the gene expression levels of several proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines.
Figure 1. RKIP is a crucial mediator of the pathogenesis of EAE .
-
AThe mean clinical scores for RKIP‐KO (KO, n = 5) mice and their wild‐type littermates (WT, n = 7) induced by being immunized with MOG35‐55 were assessed from day 0 to day 31 after immunization.
-
BLinear regression curves of (A) dashed lines indicate the 95% confidence intervals of the regression lines.
-
C, DHistology of the spinal cord from WT and KO mice on day 31 after MOG35‐55 immunization was analyzed by hematoxylin–eosin (H&E) (C) and luxol fast blue (LFB) (D) staining. Scale bars (a whole spinal cord, 100X), 100 μm; scale bars (a portion of the spinal cord, 200X), 50 μm.
-
EIn a separated experiment, summary graph of the percentages of cells (left) and the absolute numbers of cells (right) in the CNS (brains and spinal cords). CNS‐infiltrating cells isolated from mice treated as in (A) on day 31 were stained with mouse anti‐CD4, anti‐CD8, anti‐CD11b, and anti‐Gr‐1 antibodies and analyzed by flow cytometry (FACS; WT n = 5, KO n = 5).
-
FT‐helper cells isolated from the CNS of mice treated as in (A) on day 31 were fixed and permeabilized, and the CD4+ T cells were analyzed by flow cytometry to measure intracellular IFN‐γ, IL‐17, and Foxp3 expression. The data are presented in summary graphs of percentages (left) and absolute cell numbers (right; WT n = 5, KO n = 5).
-
GThe expression levels of proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines in the CNS tissues of WT and KO EAE mice, as determined by real‐time PCR (WT n = 5, KO n = 5).
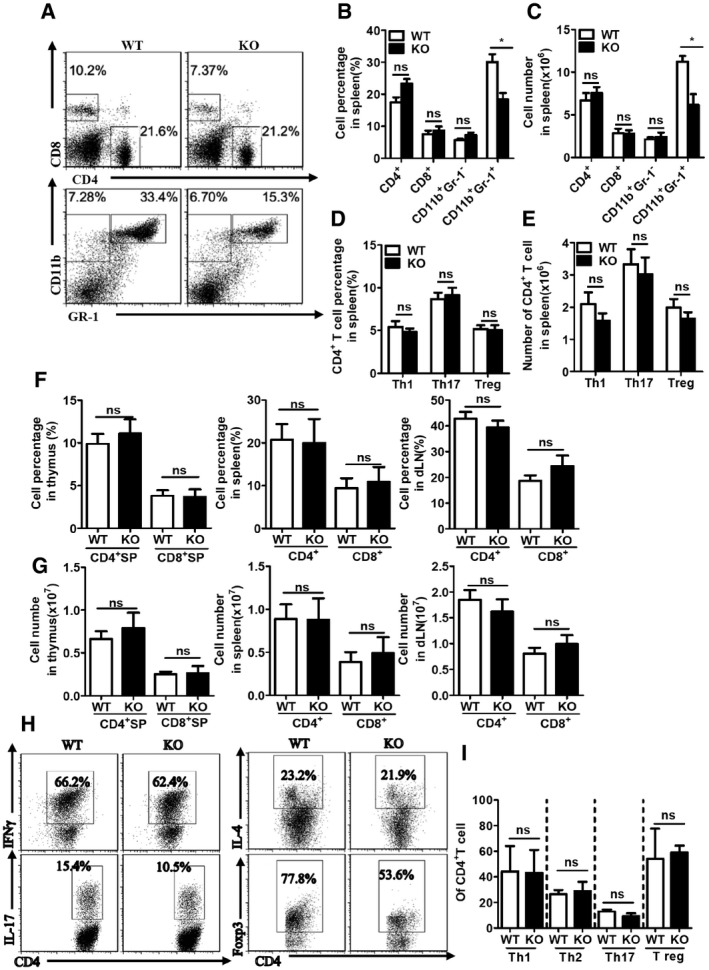
Figure EV1. RKIP deficiency has no effect on T cell development, polarization, and immune cell composition in the spleen from EAE mice.
-
A–CImmune cells isolated from spleen of day 31 MOG35‐55‐immunized WT and RKIP‐KO mice were stained with mouse anti‐CD4, anti‐CD8, anti‐CD11b, and anti‐Gr‐1 antibodies and analyzed by flow cytometry (FACS; WT n = 6, KO n = 5). Data are presented as the representative plot (A), summary graph of the percentages of cells (B), and the absolute numbers of cells (C).
-
D, ET‐helper cells isolated from spleen of day 31 MOG35‐55‐immunized WT and RKIP‐KO mice were fixed and permeabilized, and the CD4+ T cells were analyzed by flow cytometry to measure intracellular IFN‐γ, IL‐17, and Foxp3. Data are presented in summary graphs of percentages (D) and absolute cell numbers (E) (WT n = 6, KO n = 5).
-
F, GT cells from thymus, spleen, and dLNs of WT and RKIP‐KO mice (n = 5/per group) were analyzed with anti‐CD4 and anti‐CD8 staining.
-
H, IThe naïve CD4+ T cells were polarized under the Th1, Th2, Th17, or Treg condition, respectively, and 5 days later, the CD4+ T cells were fixed and permeabilized, followed by flow cytometry to measure intracellular IFN‐γ, IL‐4, IL‐17, and Foxp3. Data are presented as the representative plot (H) and summary graph of the percentages of cells (I), Th1 (n = 4), Th2 (n = 2), Th17 (n = 4), and Treg (n = 2).
RKIP deficiency in non‐hematopoietic cells impairs the pathogenesis of EAE
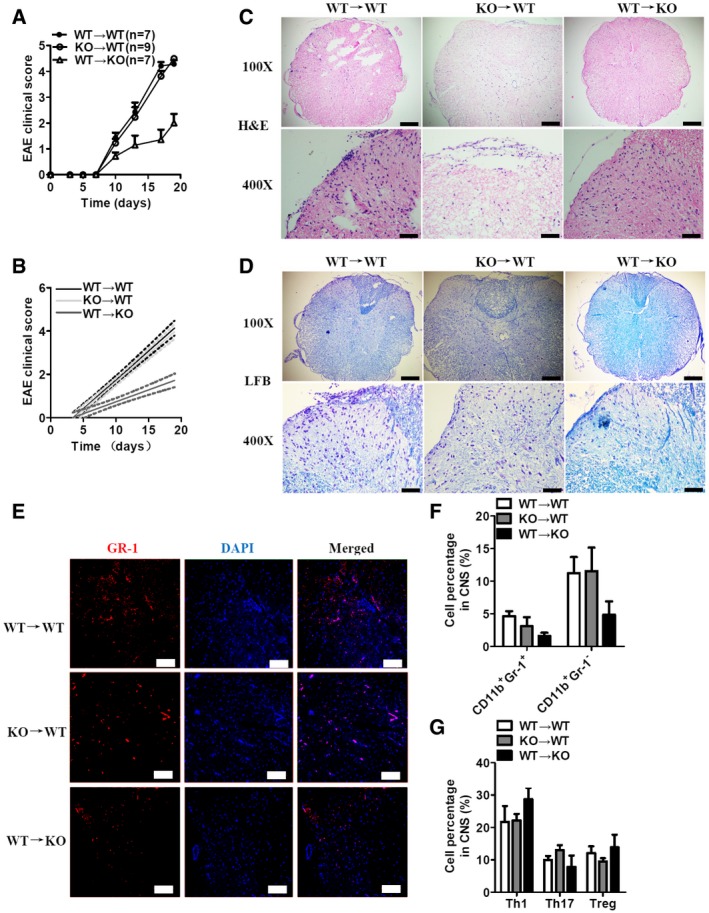
We subsequently attempted to identify the cellular compartment in which RKIP meditates the pathogenesis of EAE. We generated bone marrow chimeric mice by transferring WT or RKIP‐KO bone marrow cells to lethal dose‐irradiated (9.5 Glyc) WT or RKIP‐KO recipient mice. After 8 weeks of reconstitution, the chimeric mice were immunized with MOG35‐55 and injected with PTX to induce EAE. WT mice reconstituted with WT bone marrow cells (WT→WT group) or RKIP‐KO bone marrow cells (KO→WT group) displayed comparable EAE clinical scores, while RKIP‐KO mice reconstituted with WT bone marrow cells (WT→KO group) displayed lower EAE clinical scores than their counterparts (Fig 2A and B). H&E and LFB staining showed that inflammatory cell infiltration and neuronal demyelination were ameliorated in the WT→KO group compared to the KO→WT and WT→WT groups (Fig 2C and D). Consistently, the percentage of CNS‐infiltrating CD11b+Gr‐1+ neutrophils was significantly reduced in the WT→KO group compared to that in the KO→WT and WT→WT groups (Fig 2E and F). However, neuronal demyelination and infiltration of inflammatory cells were comparable between the spinal cords of KO→WT chimeras and that of WT→WT (Fig 2C and D). Moreover, the percentages and absolute numbers of IL‐17+ Th17 cells, IFN‐γ+ Th1 cells, and Foxp3+ Treg cells in the CNS‐infiltrating CD4+ T‐cell population were comparable among the three groups (Fig 2G). These results indicate that RKIP in non‐hematopoietic cells regulates the development of EAE.
Figure 2. RKIP deficiency in non‐hematopoietic cells mediates the pathogenesis of EAE .
-
AMice with reconstituted bone marrow cells (WT→WT n = 7, WT→KO n = 7, and KO→WT n = 9) were immunized with MOG‐35‐55 to induce EAE. The mean clinical scores were calculated every other day.
-
BLinear regression curves of (A) dashed lines indicate the 95% confidence intervals of the regression lines.
-
C, DHistology of spinal cord sections from MOG35‐55‐immunized mice was analyzed by H&E (C) and LFB (D) staining. Scale bars (a whole spinal cord, 100X), 200 μm; scale bars (a portion of the spinal cord, 400X), 50 μm.
-
EGr‐1 immunofluorescence staining of spinal cord sections from MOG35‐55‐immunized mice treated as in (A). The nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue). Scale bars, 100 μm.
-
FIn a separated experiment, CNS cells isolated from chimeric mice on day 18 after MOG35‐55‐immunization were analyzed as in Fig 1D (WT n = 5, KO n = 5).
-
GCNS T‐helper cells isolated from chimeric mice on day 18 after MOG35‐55 immunization were analyzed as in Fig 1E (WT n = 5, KO n = 5).
Homozygous RKIP‐KO mice were viable and did not display any abnormalities with respect to growth or survival, suggesting that RKIP is not essential for mouse growth and development. There are no underlying deficits in T‐cell, B‐cell, NK‐cell, or CD11b+ APC populations in homozygous RKIP‐KO mice 28. The compositions of the T‐cell populations in various organs (including the thymus, spleen, and lymph nodes) in 2‐ to 3‐month‐old RKIP‐KO mice were similar to those in their WT littermates (Fig EV1F and G), indicating that RKIP deficiency in mice does not affect the development of various types of immune cells. CD44loCD62Lhi naive CD4+ T cells were sorted by FACS, and in vitro polarization assays were performed under different T‐cell polarization conditions, including Th1, Th2, Th17, and Treg polarization conditions. As shown in Fig EV1H and I, knocking out RKIP had no significant effect on Th1‐, Th2‐, Th17‐, and Treg‐cell production. Taken together, these results indicate that RKIP deficiency does not affect T‐cell activation and differentiation in vivo and in vitro.
RKIP positively regulates the pathogenesis of EAE via IL‐17R‐mediated inflammation
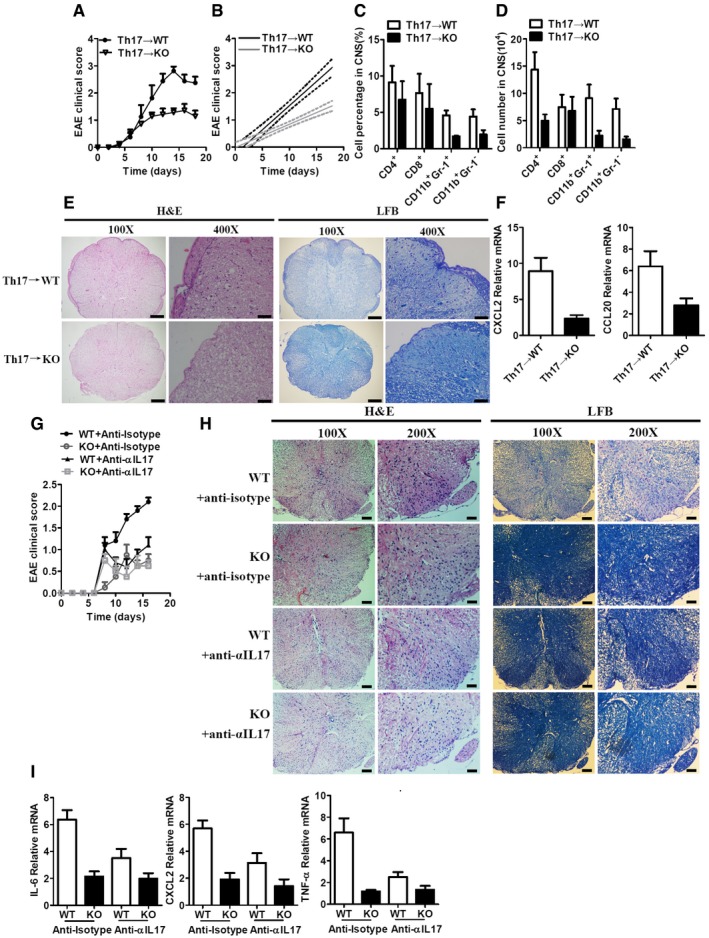
To elucidate the mechanisms through which RKIP contributes to EAE development, we transferred pre‐activated MOG35‐55‐specific Th17 cells or Th1 cells into γ‐irradiated (5Gylc) WT or RKIP‐KO recipient mice to induce EAE. After 6–8 days of MOG35‐55‐specific Th17‐cell transfer, both WT and RKIP‐KO recipient mice (Th17→WT and Th17→KO) exhibited severe EAE. However, RKIP‐KO recipient mice developed relatively mild EAE compared to WT recipient mice and exhibited lower clinical scores than their counterparts (Fig 3A and B). Moreover, CNS‐infiltrating immune cell recruitment, particularly CD11b+Gr‐1− monocytes, and CD11b+Gr‐1+ neutrophils recruitment, was significantly decreased in RKIP‐KO recipient mice compared to WT recipient mice (Fig 3C and D). Diminished inflammation and demyelination were also observed in RKIP‐KO recipient mice compared to WT recipient mice (Fig 3E). The gene expression levels of chemokines, such as CXCL2 and CCL20, in the CNS tissues of Th17→KO EAE mice were significantly lower than those in the CNS tissues of Th17→WT EAE mice (Fig 3F). We also transferred WT MOG35‐55‐specific Th1 cells into γ‐irradiated (5Gylc) WT or RKIP‐KO recipient mice and then assessed the EAE clinical scores of these mice. As shown in Fig EV2A and B, EAE clinical scores were comparable between the two groups (Th1→WT and Th1→KO). Recruitment of CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells, CD11b+Gr‐1− monocytes, and CD11b+Gr‐1+ neutrophils was also comparable between RKIP‐KO recipient mice and WT recipient mice (Fig EV2C and D). Moreover, inflammation, demyelination, and chemokine gene expression levels in the CNS tissues (Th1→WT and Th1→KO) were almost identical between the two groups (Fig EV2E and F). Taken together, these results indicate that RKIP plays a predominant role in the Th17‐mediated immune response but not in the Th1‐mediated immune response.
Figure 3. RKIP deficiency inhibits Th17 cell passive transfer‐induced EAE .
-
AThe mean EAE clinical scores for γ‐irradiated (5Gylc) WT and RKIP‐KO mice (WT n = 8, KO n = 7) reconstituted with WT MOG‐35‐55‐pre‐sensitized Th17 cells were determined from day 0 to day 18 after Th17‐cell transfer.
-
BLinear regression curves of (A) dashed lines indicate the 95% confidence intervals of the regression lines.
-
C, DSummary graph of the percentages of cells (C) and absolute numbers of cells (D) in the CNS. CNS‐infiltrating cells isolated from mice treated as in (A) (WT n = 8, KO n = 7) were stained with the appropriate antibodies.
-
EHistology of the spinal cord from mice reconstituted with Th17 cells was analyzed by H&E (left) and LFB (right) staining. Scale bars (a whole spinal cord, 100X), 200 μm; scale bars (a portion of the spinal cord, 400X), 50 μm.
-
FReal‐time PCR analysis of CXCL2 and CCL20 mRNA expression in the CNS tissues of WT and RKIP‐KO mice treated as in (A) (WT n = 8, KO n = 7).
-
GThe mice (WT n = 5, KO n = 4) were treated with intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection of an anti‐IL‐17A antibody (100 μg per mouse each time) or appropriate isotype controls on days 7, 9, 11, and 13 after the second MOG‐35‐55 immunization. Mean clinical scores were calculated every other day according to the standards described in the Materials and Methods section.
-
HHistology of the spinal cord was analyzed by H&E (left) or LFB (right) staining on day 14 after the second MOG‐35‐55 immunization. Scale (a whole spinal cord, 100X), 100 μm; scale (a portion of the spinal cord, 200X), 50 μm.
-
IIL‐6, CXCL2, and TNF‐α mRNA in the CNS tissues (including brain and spinal cords) were measured by real‐time PCR on day 14 after the second MOG‐35‐55 immunization, (WT n = 5, KO n = 4).
Figure EV2. RKIP deficiency does not affect Th1 cells passive transferring‐induced EAE .
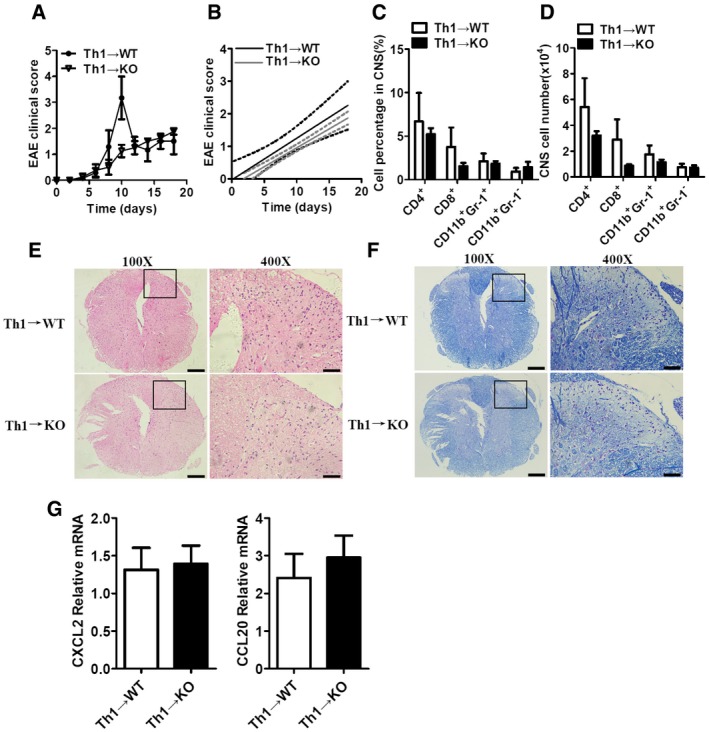
-
AThe mean EAE clinical scores of γ‐irradiated (5Gylc) WT and RKIP‐KO mice (WT n = 3, KO n = 4) reconstituted with WT MOG‐35‐55‐pre‐sensitized Th1 cells were determined from day 0 to day 18 after Th1‐cell transfer.
-
BLinear regression curves of (A) dashed lines indicate the 95% confidence intervals of the regression lines.
-
C, DSummary graph of the percentages of cells (C) and the absolute numbers of cells (D) in the CNS. CNS‐infiltrating cells isolated from mice treated as in (A) on day 18 after the Th1‐cell transfer was stained with the appropriate antibody.
-
E, FHistology of the spinal cord from mice reconstituted with Th1 cells was analyzed by H&E (E) and LFB (F) staining of spinal cord sections from mice reconstituted with Th1 cells. Scale bars (a whole spinal cord, 100X), 200 μm; scale bars (a portion of the spinal cord, 400X), 50 μm. Typical stainings in the black box region were magnified and shown in 400X panel.
-
GReal‐time PCR analysis of CXCL2 and CCL20 mRNA expression in the CNS tissues of WT and RKIP‐KO mice treated as in (A).
Th17 cells secret IL‐17A which initiates the IL‐17R signaling and plays an important role in the EAE pathogenesis 6. We next investigated whether the reduced EAE pathogenesis in RKIP deficiency mice was dependent on IL‐17R‐mediated signaling and its inflammation, an anti‐α‐IL‐17A‐specific blocking antibody was continually i.p. injected into RKIP WT and KO mice during the induction of EAE. As shown in Fig 3G and H, the injection of anti‐α‐IL‐17A antibody resulted in a significant inhibited EAE symptom, including clinical scores, inflammation, and demyelination, in RKIP WT and KO mice compared to the anti‐isotype control antibody‐injected RKIP WT group. The RKIP‐deficient mice exhibited much reduced EAE severity compared to WT mice, which was obliterated after the injection of IL‐17A‐blocking antibody. Consistently, the induction of IL‐17A‐induced genes, such as IL‐6, CXCL2, and TNF‐α, in CNS tissues was substantially attenuated in RKIP‐KO mice compared to WT mice. And the expression of these genes in WT mice decreased to comparable levels in KO mice after treatment with IL‐17A‐blocking antibody (Fig 3I). Collectively, these data suggest RKIP regulates EAE pathogenesis via IL‐17R‐mediated signaling‐associated inflammation.
RKIP positively regulates IL‐17‐induced gene expression and protein production
Myelin‐specific Th17 cells secrete IL‐17A, which bind IL‐17R‐expressing epithelial cells, macrophages, microglia, and resident neuroectodermal cells (neurons, astrocytes, and oligodendrocytes) and induce proinflammatory cytokine and chemokine gene expression in these resident CNS cells, particularly in astrocytes, a well‐known cell type that has been reported to be crucial for IL‐17‐induced EAE 10, 29. Given that RKIP regulates the pathogenesis of EAE via IL‐17R signaling, we assessed the involvement of RKIP in IL‐17‐induced inflammation in astrocytes by stimulating primary astrocytes isolated from WT and RKIP‐KO neonatal mouse brains with a recombinant murine IL‐17A protein. As shown in Fig 4A and B, both the gene (Fig 4A) and protein expression levels (Fig 4B) of IL‐6, CXCL2 and CCL20 were significantly induced by IL‐17A stimulation. However, the inductions were significantly lower in RKIP‐KO mice than those in WT mice (Fig 4A and B). Since the function of IL‐17F is similar to that of IL‐17A, we also investigated the gene expression levels of IL‐17F‐induced proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines in astrocytes. As shown in Fig 4C and D, RKIP deficiency significantly inhibited IL‐17F‐induced IL‐6, CXCL2, and CCL20 mRNA expression and protein production in astrocytes. U‐87MG 30, a kind of human glioblastoma‐like epithelial cells, were transfected with RKIP‐specific small interfering RNA (siRKIP) to investigate whether RKIP has effect on IL‐17‐triggered signaling in human cells. As shown in Fig 4E, RKIP knockdown in U‐87MG cells significantly inhibited the expression level of IL‐6 and CCL20 induced by IL‐17A. Taken together, these data suggest that RKIP promotes IL‐17‐induced proinflammatory gene expression in resident CNS cells.
Figure 4. RKIP deficiency inhibits IL‐17A/F‐induced proinflammatory cytokine and chemokine expression in primary astrocytes.
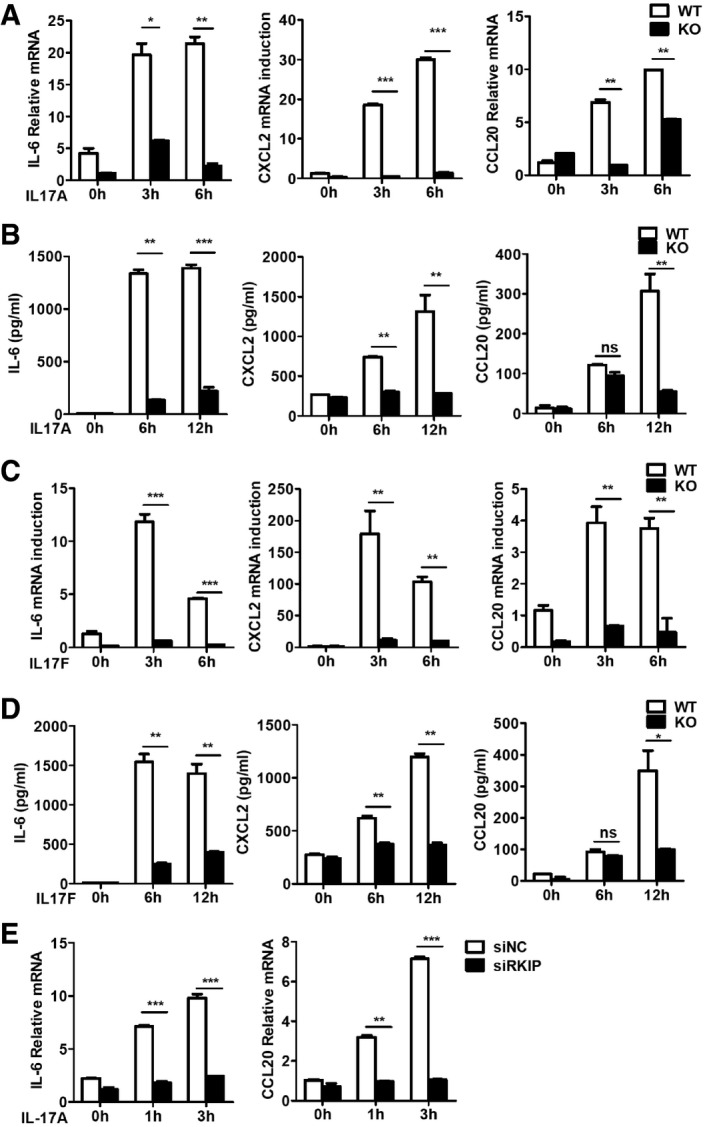
-
A, BReal‐time PCR analysis (A) and ELISA (B) of IL‐6, CXCL2, and CCL20 mRNA expression and protein production in WT and RKIP‐KO astrocytes stimulated with IL‐17A (100 ng ml−1) for the indicated time.
-
C, DReal‐time PCR analysis (C) and ELISA (D) of IL‐6, CXCL2, and CCL20 mRNA expression and protein production in WT and RKIP‐KO astrocytes stimulated with IL‐17F (100 ng ml−1) for the indicated time.
-
EReal‐time PCR analysis of IL‐6, and CCL20 mRNA expression in RKIP‐specific siRNA (siRKIP) or negative control siRNA (siNC) transfected human glioblastoma‐like epithelial cells, U‐87MG cells, stimulated with IL‐17A (100 ng ml−1) for the indicated time.
HeLa cells are epithelial cells and have been widely used to investigate IL‐17R signaling pathways 13, 30, 31. We have transfected RKIP‐specific small interfering RNA into HeLa cells to inhibit endogenous RKIP expression. RKIP knockdown significantly inhibited IL‐17A‐ or IL‐17F‐induced IL‐6, CXCL2, and CCL20 gene and protein expression (Fig EV3A–D), while RKIP overexpression increased IL‐17A‐induced IL‐6, CXCL2, and CCL20 mRNA and protein expression compared to mock control treatment (Fig EV3E and F). Simultaneously, we investigated the function of RKIP on TNF‐α‐, IL‐1β‐, and LPS‐induced inflammation in HeLa cells. As shown in Fig EV4A–C, RKIP silencing has no significant effect on the TNF‐α‐, IL‐1β‐, or LPS‐induced gene expression of proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines, such as IL‐6, CXCL2, and CCL20 in HeLa cells. The efficiency of RKIP knockout, knockdown, and overexpression was confirmed by Western blotting (Fig EV3G).
Figure EV3. RKIP positively regulates IL‐17A/F‐induced proinflammatory cytokine and chemokine expression in HeLa cells.
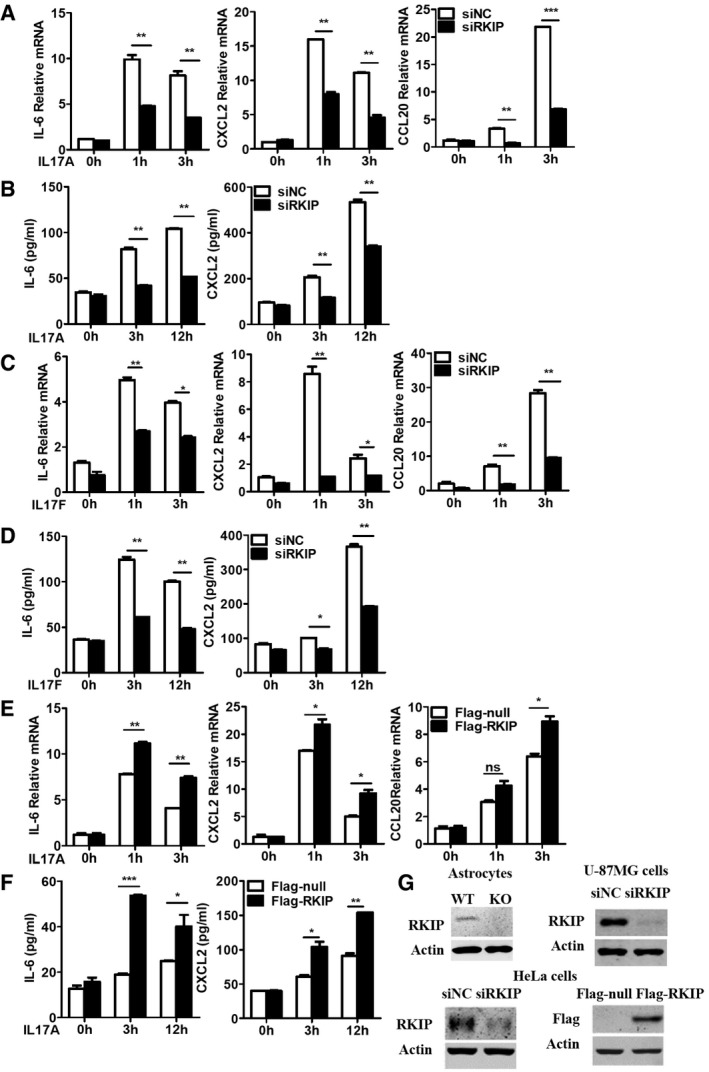
-
A, BHeLa cells were transfected with RKIP‐specific siRNA (siRKIP) or negative control siRNA (siNC), and then, the cells stimulated with IL‐17A (50 ng ml−1) for the indicated time. IL‐6, CXCL2, and CCL20 mRNA expression (A) and protein production (B) were analyzed by real‐time PCR and ELISA, respectively.
-
C, DHeLa cells were transfected with RKIP‐specific siRNA (siRKIP) or negative control siRNA (siNC), and then, the cells were stimulated with IL‐17F (50 ng ml−1) for the indicated time. IL‐6, CXCL2, and CCL20 mRNA expression (C) and protein production (D) were analyzed by real‐time PCR and ELISA, respectively.
-
E, FFlag‐tagged RKIP‐expressing or control mock (Flag‐tagged null) plasmid‐transfected HeLa cells were stimulated with IL‐17A (50 ng ml−1) for indicated time.
-
GImmunoblot analysis of RKIP protein expression in all of knockout, knockdown, and overexpression experiments.
Figure EV4. RKIP silencing has no effect on TNF‐α‐, IL‐1β‐, and LPS‐induced proinflammatory cytokine and chemokine expression in HeLa cells.
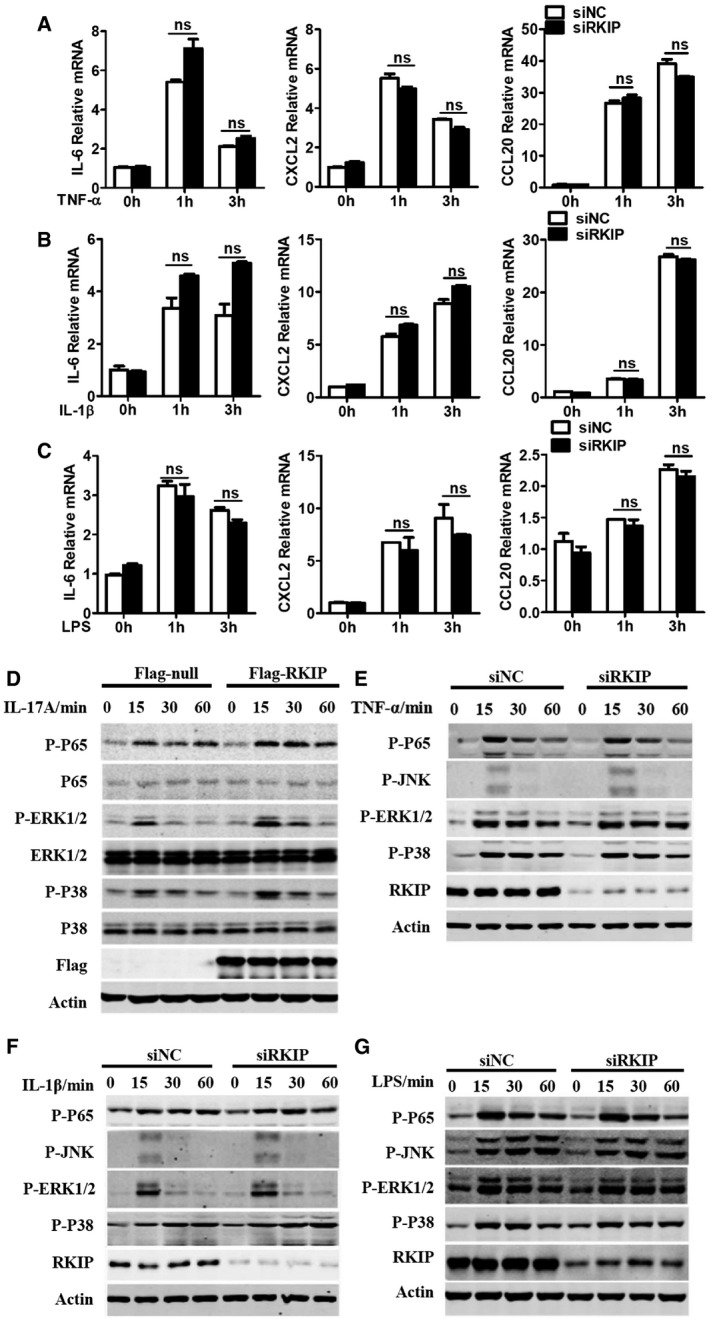
-
A–CHeLa cells were transfected with RKIP‐specific siRNA (siRKIP) or negative control siRNA (siNC), and then, the cells stimulated with TNF‐α (20 ng ml−1) (A), IL‐1β (20 ng ml−1) (B), and LPS (100 ng ml−1) (C) for the indicated time. IL‐6, CXCL2, and CCL20 mRNA expression was analyzed by real‐time PCR.
-
DHeLa cells were transfected with Flag‐tagged RKIP or Flag‐null control plasmids and then treated with 50 ng ml−1 IL‐17A for the indicated time. The WCLs were subsequently immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies.
-
E–GHeLa cells were transfected with RKIP‐specific siRNA (siRKIP) or negative control siRNA (siNC) and treated with TNF‐α (20 ng ml−1) (E), IL‐1β (20 ng ml−1) (F), and LPS (100 ng ml−1) (G) for the indicated time, and then, the WCLs were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies.
RKIP mediates IL‐17R signaling by interacting with Act1 and IL‐17RA
Upon the binding of IL‐17A or IL‐17F to the homodimer or heterodimer IL‐17R (IL‐17RA or IL‐17RA/F), IL‐17R recruits the key adaptor protein Act1 (also known as CIKS, an E3 ubiquitinase) to the cytoplasmic tail of IL‐17R and activates both MAPK and NF‐κB signaling to induce proinflammatory cytokine and chemokine production 10, 15. RKIP deficiency inhibited IL‐17A/F‐induced TAK1, NF‐κB P65 subunit, JNK1/2, ERK1/2, and P38 phosphorylation in astrocytes (Fig 5A and B). Reduced IL‐17A/F‐induced phosphorylation of these molecules was also observed in RKIP‐silenced HeLa cells and U‐87MG cells compared to negative control small interfering RNA (siNC)‐transfected cells (Fig 5C–E). Conversely, overexpressing RKIP in HeLa cells promoted IL‐17A‐induced NF‐κB P65 subunit, ERK1/2, and P38 phosphorylation (Fig EV4D). However, knockdown of RKIP in HeLa cells did not affect the TNF‐α‐, IL‐1β‐, or LPS‐induced signaling pathways activation (Fig EV4E–G).We next performed co‐immunoprecipitation assays in HEK293T cells to examine the interactions between RKIP and key molecules involved in IL‐17R signaling, such as Act1, TRAF2, TRAF3, TRAF5, and TRAF6. As shown in Fig 5F, Myc‐tagged RKIP specifically interacted with Flag‐tagged Act1 but not with TRAF2, TRAF3, and TRAF5 17, 18. Slighter interactions between RKIP and TRAF6, which have been reported in some cancer cell lines, were also observed (Fig 5F) 32. We also observed interactions between RKIP and IL‐17RA in HEK293T cells (Fig 5G).
Figure 5. RKIP positively regulates IL‐17R signaling.
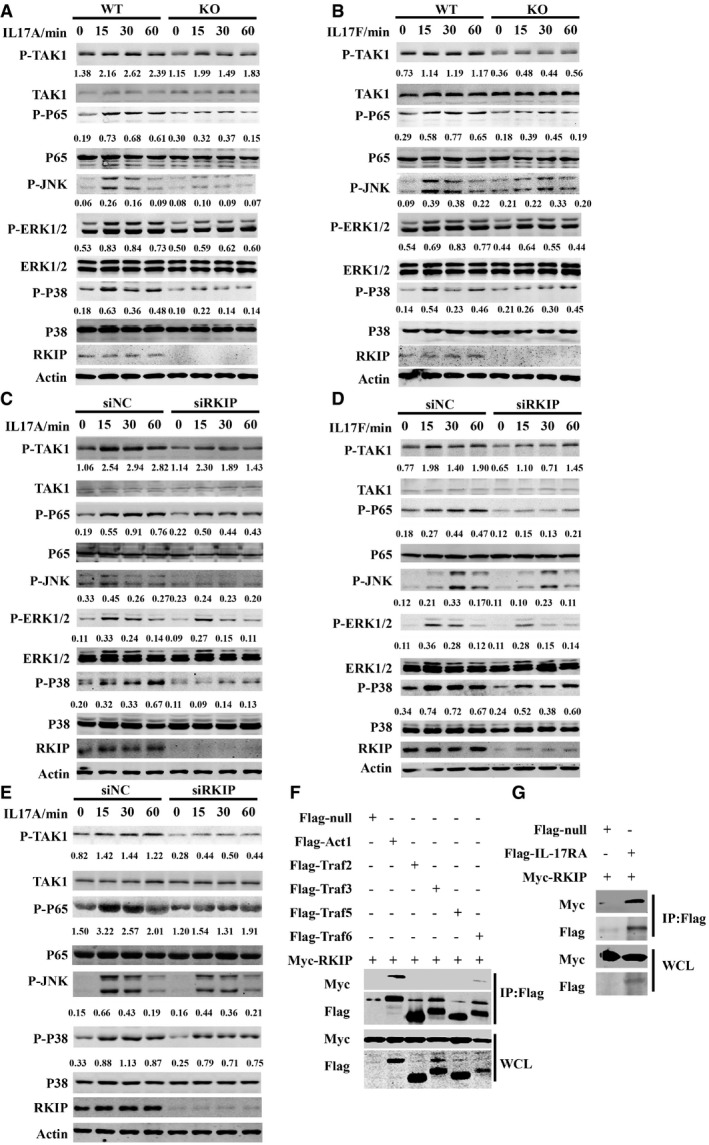
-
A, BWT or RKIP‐KO astrocytes were treated with 100 ng ml−1 IL‐17A (A) or IL‐17F (B) for the indicated time, and then, the whole‐cell lysates (WCLs) were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies.
-
C, DHeLa cells were transfected with RKIP‐specific siRNA (siRKIP) or negative control siRNA (siNC) and treated with 50 ng ml−1 IL‐17 A (C) or IL‐17F (D) for the indicated time, and then, the WCLs were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies.
-
EU‐87MG cells were transfected with RKIP‐specific siRNA (siRKIP) or negative control siRNA (siNC) and then treated with 100 ng ml−1 IL‐17A for the indicated time. The WCLs were subsequently immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies.
-
FFlag‐null, Flag‐tagged Act1, or Flag‐tagged TRAF2/3/5/6 were co‐expressed with Myc‐tagged RKIP in HEK293T cells and then immunoprecipitated with anti‐Flag beads (M2 beads). The WCLs were subsequently immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies.
-
GFlag‐null or the Flag‐tagged IL‐17RA was co‐expressed with Myc‐tagged RKIP in HEK293T cells and then immunoprecipitated with anti‐Flag beads (M2 beads). The WCLs were subsequently immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. Numbers between two blots indicate densitometry of phosphorylated proteins relative to that of total proteins, respectively. Densitometry of phosphorylated JNK was relative to actin.
RKIP promotes interactions between Act1 and IL‐17RA to promote IL‐17R signaling
We subsequently examined the endogenous interactions between RKIP and IL‐17R and Act1 in HeLa cells. We stimulated HeLa cells or Flag‐tagged RKIP‐expressing HeLa cells with IL‐17A for the indicated time and then incubated the whole‐cell lysate (WCL) with anti‐RKIP, anti‐Flag, or anti‐Act1 antibodies to immunoprecipitate endogenous RKIP or Flag‐tagged RKIP or endogens Act1, respectively. As shown in Fig 6A and B, endogenous Act1 and IL‐17R were co‐immunoprecipitated by endogenous RKIP and Flag‐tagged RKIP, and the interactions between the two molecules peaked at 10 min after IL‐17A stimulation. Endogenous Act1 also dynamically bound with Flag‐tagged RKIP or IL‐17R, and this interaction also peaked at 10 min after IL‐17A stimulation (Fig 6B and C). Since the commercially available anti‐IL‐17R antibody could not efficiently immunoprecipitate the endogenous IL‐17R, we stimulated HA‐tagged IL‐17RA‐overexpressing HeLa cells with IL‐17A for the indicated time and then immunoprecipitated the HA‐tagged IL‐17RA with the anti‐HA antibody. Endogenous RKIP and Act1 bound with HA‐IL‐17RA, and RKIP dynamically interacted with the Act1‐IL‐17RA complex, an interaction that also peaked at 10 min after IL‐17A treatment (Fig 6D). We next investigated which domain of Act1 or IL‐17RA binds with RKIP. It has been reported that the SEFIR domain of Act1 is critical for the binding of Act1 to the SEFIR domain of IL‐17RA and TRAF6 15, 33. Therefore, we mutated WT Flag‐tagged Act1 to Flag‐tagged Act1‐SEFIR or Flag‐tagged Act1‐∆SEFIR, as shown in Fig EV5A. We found that Myc‐tagged RKIP bound with both WT Flag‐tagged Act1 and Flag‐tagged Act1‐SEFIR but not with the Flag‐tagged Act1‐∆SEFIR, indicating that RKIP bound with Act1 in a SEFIR domain‐dependent manner. WT HA‐tagged IL‐17RA and its truncated counterparts were screened via co‐immunoprecipitation assay in HEK293T cells to identify the IL‐17RA domain that interacts with RKIP. As shown in Fig EV5B, Myc‐tagged RKIP bound with all the HA‐tagged IL‐17RA mutants but not with HA‐tagged IL‐17RA ∆SEFIR. We then examined whether RKIP can directly bind with Act1 or IL‐17RA. For this experiment, GST‐tagged RKIP proteins were purified from Escherichia coli strain Bl21, and Flag‐tagged EGFP, Flag‐tagged Act1 protein, or Flag‐tagged Act1‐ΔSEFIR were purified from Flag‐tagged EGFP, Flag‐tagged Act1, or Flag‐tagged Act1‐ΔSEFIR‐transfected HEK293T cells. Flag‐tagged Act1 but not Flag‐tagged EGFP control protein or Flag‐tagged Act1‐ΔSEFIR pulled down GST‐RKIP (Fig 6E). HA‐tagged IL‐17RA, which was purified from HA‐tagged IL‐17RA‐transfected HEK293T cells, could pull down GST‐tagged RKIP protein, but not HA‐tagged EGFP or HA‐tagged IL‐17RA‐ΔSEFIR protein (Fig 6F). Taken together, these data suggest that RKIP directly interacts with both Act1 and IL‐17RA in a SEFIR domain‐dependent manner.
Figure 6. RKIP directly binds to Act1 and IL‐17RA and promotes formation of the IL‐17RA‐Act1 complex.
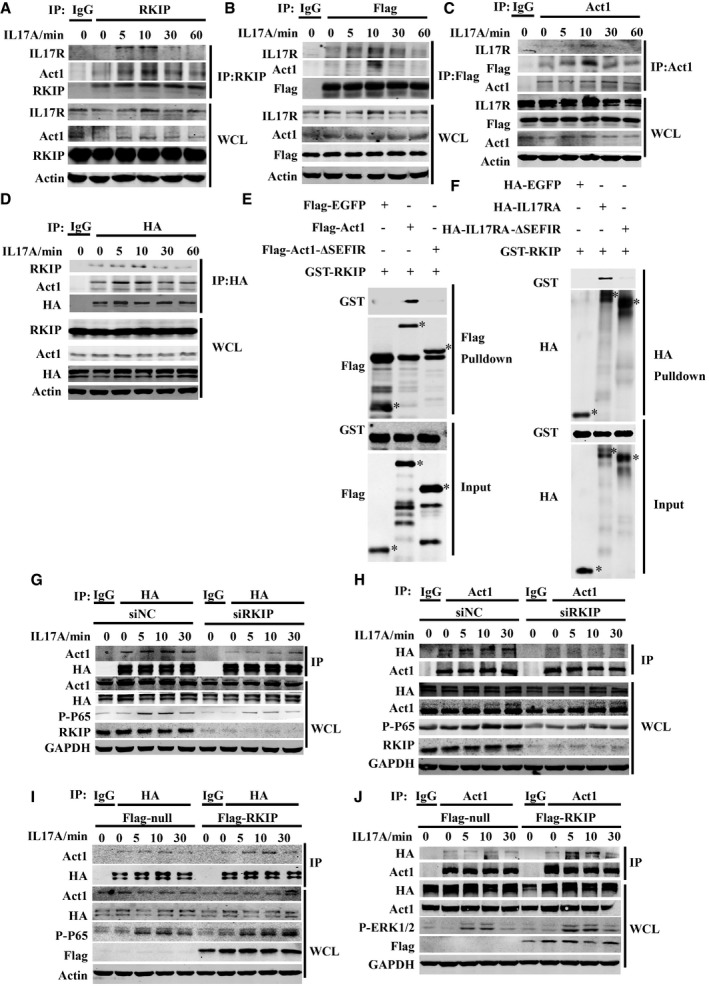
-
AThe lysates form HeLa cells stimulated with IL‐17A (50 ng ml−1) were immunoprecipitated with anti‐RKIP antibody and then subjected to immunoblot analysis with the indicated antibodies.
-
B, CThe lysates from Flag‐RKIP‐stable expressing HeLa cells stimulated with IL‐17A (50 ng ml−1) were immunoprecipitated with anti‐Flag beads (B) or anti‐Act1 antibody (C) and then subjected to immunoblot analysis with the indicated antibodies.
-
DThe lysates form HA‐IL‐17RA‐stable expressing HeLa cells stimulated with IL‐17A (50 ng ml−1) were immunoprecipitated with anti‐HA beads and then subjected to immunoblot analysis with the indicated antibodies.
-
EPurified Flag‐tagged EGFP, Flag‐tagged Act1, or Flag‐tagged Act1‐ΔSEFIR proteins were mixed with recombinant GST‐tagged RKIP proteins, and then, the proteins were pulled down with anti‐Flag beads. Asterisk (*) indicates the target band.
-
FPurified HA‐tagged EGFP, HA‐tagged IL‐17RA, or HA‐tagged IL‐17RA‐ΔSEFIR proteins were mixed with recombinant GST‐tagged RKIP proteins, and then, the proteins were pulled down with anti‐HA beads. Asterisk (*) indicates the target band.
-
G, HHA‐IL‐17RA‐overexpressing HeLa cells were transfected with siRKIP or siNC and then stimulated with IL‐17A (50 ng ml−1), followed by immunoprecipitation (IP) with antibodies to HA (G) or Act1 (H) and subjected to immunoblot analysis with the indicated antibodies.
-
I, JHA‐IL‐17RA‐overexpressing HeLa cells were transfected with Flag‐tagged RKIP or control (Flag‐tagged null) plasmids and then stimulated with IL‐17A (50 ng ml−1), followed by immunoprecipitation (IP) with antibodies to HA (I) or Act1 (J) and subjected to immunoblot analysis with the indicated antibodies.
Figure EV5. RKIP interacts with Act1 and IL‐17RA and promotes the formation of IL‐17RA‐Act1 complex.
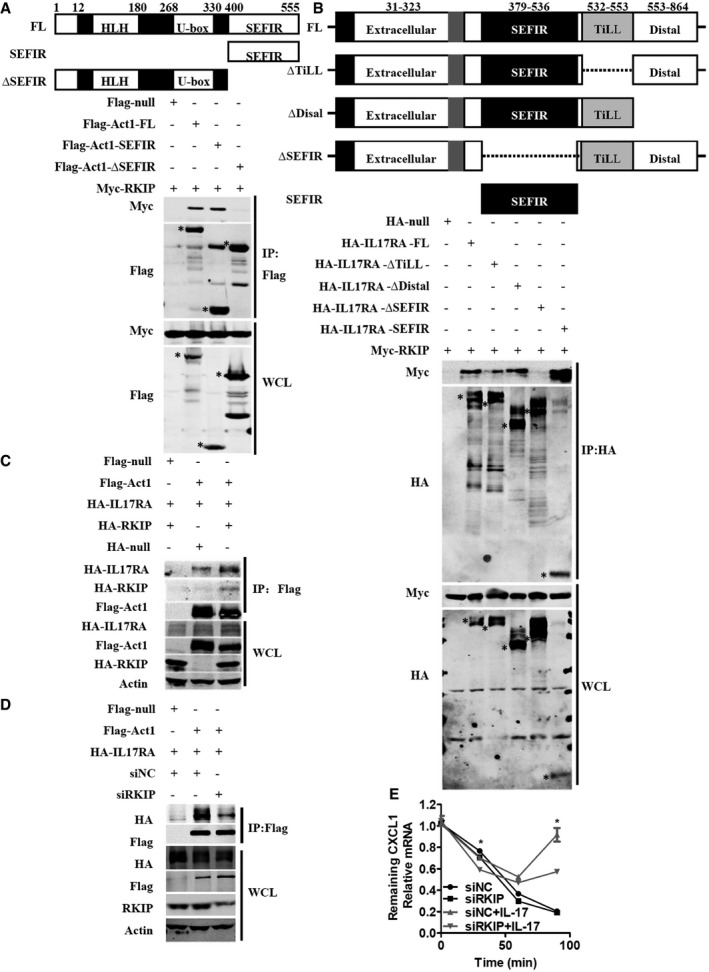
-
ASchematic diagram of Act1 deletion mutants. Flag‐tagged null, Flag‐tagged full‐length Act1, Flag‐tagged Act1‐SEFIR (400–555), or Flag‐tagged Act1‐∆SEFIR (1–400) mutants were co‐expressed with Myc‐tagged RKIP in HEK293T cells, and the lysates from the transfected cells were immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti‐Flag beads and then subjected to immunoblot analysis with the indicated antibodies. Asterisk (*) indicates the target band.
-
BSchematic diagram of IL‐17RA deletion mutants. HA‐tagged null, HA‐tagged full‐length IL‐17RA, HA‐tagged IL‐17RA‐∆TiLL (∆532–553), HA‐tagged IL‐17RA‐∆Distal (1–553), HA‐tagged IL‐17RA‐∆SEFIR (∆379–536), or HA‐tagged IL‐17RA‐SEFIR (379–536) mutants were co‐expressed with Myc‐tagged RKIP in HEK293T cells, and the lysates from the transfected cells were immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti‐HA beads and then subjected to immunoblot analysis with the indicated antibodies. Asterisk (*) indicates the target band.
-
C, DHEK293T cells were transfected with HA‐tagged IL‐17RA and Flag‐tagged Act1 with or without HA‐tagged RKIP (C) or with or without RKIP‐specific siRNA (D). The lysates from the transfected cells were immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti‐Flag beads and then subjected to immunoblot analysis with the indicated antibodies.
-
EsiRKIP‐ or siNC‐transfected Hela cells were pretreated with TNF‐α (20 ng ml−1) for 1 h, followed by treatment (horizontal axes) with actinomycin D (5 μg ml−1) alone or actinomycin D plus IL‐17 (25 ng ml−1) for the indicated time and then were subjected to real‐time PCR analysis of CXCL1 mRNA expression. *P < 0.05 (unpaired, two‐tailed Student's t‐test). Data are representative of three independent experiments with similar results. Data are means ± SEM values.
Source data are available online for this figure.
Since RKIP binds with the structurally homologous SEFIR domains of Act1 and IL‐17RA, we next assessed whether RKIP can promote interactions between Act1 and IL‐17RA under IL‐17A stimulation to positively regulate the IL‐17R signaling pathway. HA‐IL‐17RA‐overexpressing HeLa cells were transfected with RKIP siRNA or RKIP‐expressing plasmids and then incubated with anti‐HA or anti‐Act1 antibodies to immunoprecipitate HA‐IL‐17RA or Act1, respectively. As shown in Fig 6G and H, RKIP knockdown prevented interactions between Act1 and HA‐IL‐17RA, while RKIP overexpression promoted interactions between Act1 and HA‐IL‐17RA (Fig 6I and J). HA‐tagged IL‐17RA and Flag‐tagged Act1 were co‐expressed in HEK 293T cells in which RKIP was overexpressed or silenced. Flag‐tagged Act1 was immunoprecipitated using anti‐Flag (M2) beads. As shown in Fig EV5C, overexpressing RKIP in HEK293T cells promoted interactions between Flag‐tagged Act1 and HA‐tagged IL‐17RA, while knocking down RKIP inhibited this interaction (Fig EV5D). These data indicate that RKIP promotes interactions between IL‐17RA and Act1. We subsequently investigated whether RKIP modulates IL‐17A‐mediated stabilization of CXCL1 mRNA. We stimulated RKIP‐silenced HeLa cells with TNF‐α and then treated them with actinomycin D (ActD) with or without IL‐17A. As shown in Fig EV5E, the half‐life of CXCL1 was similar in siNC‐ and siRKIP‐transfected HeLa cells treated with actinomycin D alone; however, treatment with IL‐17A plus actinomycin D promoted greater degradation of CXCL1 mRNA in RKIP‐silenced HeLa cells than in siNC‐transfected HeLa cells. Collectively, these data indicate that RKIP functions upstream of IL‐17R signaling and serves as a crucial adaptor to promote the formation of the IL‐17RA‐Act1 complex, which controls multiple downstream signal transduction pathways and the expression of downstream cytokines or chemokines.
RKIP deficiency inhibits IL‐17A‐induced inflammation in vivo
To confirm the role of RKIP in IL‐17A‐induced inflammation responses in vivo, we intraperitoneally injected WT and RKIP‐KO mice with PBS or IL‐17A and examined IL‐17A‐induced IL‐6, CXCL1, CXCL2, and CCL20 mRNA expression in peritoneal mesothelial cells. As shown in Fig 7A, RKIP deficiency significantly inhibited IL‐17A‐induced IL‐6, TNF‐α, CXCL1 (KC), CXCL2, and CCL20 mRNA expression in peritoneal mesothelial cells. IL‐17A‐induced chemokines amplify inflammatory responses by recruiting neutrophils to local tissues, as observed in an inflammation model in which administration of aerosolized IL‐17A caused considerable pulmonary inflammation 31. To determine whether RKIP can affect IL‐17A‐induced pulmonary inflammation by recruiting neutrophils to lung tissues, we treated WT and RKIP‐KO mice with intratracheal injections of PBS or IL‐17A and quantified the total numbers of cells and neutrophils (CD11b+Gr1+) in mouse bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) by FACS analysis. As shown in Fig 7B, RKIP‐KO mice displayed significantly reduced IL‐17A‐induced total cell and neutrophil recruitment in BALF compared to WT mice. Moreover, RKIP‐KO mice showed less inflammation and tissue damage in lung tissues than WT mice (Fig 7C). Consistently, the mRNA level of IL‐6, TNF‐α, and KC in lung tissues and IL‐6 and TNF‐α production in BALF were much lower in RKIP‐KO mice than that in WT mice (Fig 7D and E). Taken together, these data demonstrate that RKIP positively regulates IL‐17A‐induced inflammation in vivo.
Figure 7. RKIP promotes IL‐17A‐induced inflammation in vivo .
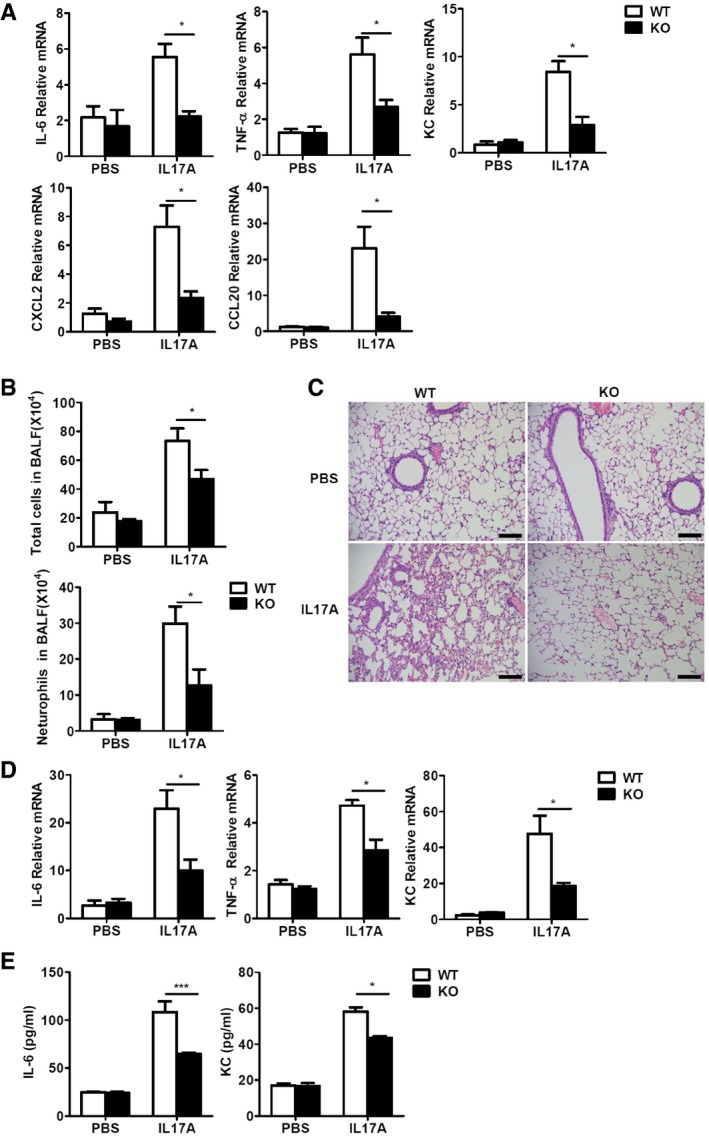
- Real‐time PCR analysis of IL‐6, TNF‐α, KC(CXCL1), CXCL2, and CCL20 mRNA expression in peritoneal mesothelial cells isolated from WT and RKIP‐KO mice treated with intraperitoneal injection of PBS (n = 3) or IL‐17A (n = 7; 0.5 μg in 200 μl PBS).
- Total cells and Gr‐1+ neutrophil infiltration in BALF from mice treated with intranasal injections of PBS (25 μl, n = 3) or IL‐17 (2 μg in 25 μl of PBS, n = 5) was assessed 24 h after injection.
- Histology of lung tissues from mice treated as in (B) was analyzed by H&E staining of. Scale bars, 50 μm.
- Real‐time PCR analysis of IL‐6, TNF‐α, and KC mRNA expression in the lung tissues of WT and RKIP‐KO mice treated as in (B).
- ELISA of IL‐6 and TNF‐α production in the BALF of mice treated as in (B).
Discussion
Th17 cells and IL‐17/IL‐17R signaling have been extensively studied, as they play important roles in various autoimmune diseases and inflammatory processes 4, 14, 16. In the current study, we determined that the Raf‐1 kinase inhibitor protein (RKIP) participates in the pathogenesis of IL‐17‐mediated autoimmune diseases and inflammation. Specifically, we found that RKIP deficiency in mice ameliorated MOG35‐55‐induced EAE disease symptoms without affecting CD4+ T‐cell development and polarization in vivo and in vitro. CD4+ T‐cell‐transfer experiments demonstrated that RKIP was involved in the pathogenesis of Th17 cell‐mediated EAE but not Th1 cell‐mediated EAE. Further mechanism studies revealed that RKIP regulated IL‐17‐induced signal transduction and inflammation by directly binding with IL‐17RA and Act1 and promoting interactions between IL‐17RA and Act1.
Raf‐1 kinase inhibitor protein belongs to the phosphatidylethanolamine‐binding protein (PEBP) family and is widely involved in functionally regulating many types of cancer cells 34, 35. However, RKIP is much more than a well‐defined cancer inhibitory protein. We recently demonstrated that RKIP contributed to the development of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and anti‐viral immune responses 26, 27; however, its functional role in autoimmune diseases remains unclear. Using genetic approaches, we found that RKIP contributes to the development of MOG35‐55‐induced EAE disease symptoms and is responsible for increases in EAE clinical scores and increases in inflammatory cell infiltration and neuronal demyelination. Bone marrow cell‐transfer experiments demonstrated that RKIP positively regulates the pathogenesis of EAE in non‐hematopoietic cells, findings supported by the observation that the EAE phonotype was significantly attenuated in the WT→KO group compared to KO→WT and WT→WT groups. The myelin‐specific Th17 cell or Th1 cell passive transfer‐induced EAE experiments confirmed the hypothesis that RKIP mediated the pathogenesis of Th17‐mediated EAE but not Th1‐mediated EAE. We also found that RKIP deficiency does not affect Th17‐cell differentiation in vitro and in vivo. Taken together, these data confirmed that RKIP plays a crucial role in positively regulating the pathogenesis of Th17 cell‐mediated EAE.
It has been reported that IL‐17‐mediated activation of IL‐17R signal transduction and cytokine production in astrocytes is involved in the pathogenesis of EAE 10, 36. By investigating IL‐17R signaling‐mediated inflammation in RKIP WT and RKIP‐KO astrocytes, we found that RKIP promoted IL‐17‐induced proinflammatory cytokine and chemokine expression. Moreover, our signaling pathway studies demonstrated that RKIP serves as an indispensable regulatory protein that mediates IL‐17‐induced MAPK (including P38, JNK and ERK) and NF‐κB (including TAK1 and NF‐κB) signaling. All of these data suggest that RKIP mediates the pathogenesis of EAE by positively regulating IL‐17‐induced signaling and pathological cytokine and chemokine production in astrocytes in the CNS. Consistently, RKIP knockdown inhibits IL‐17‐induced signaling and downstream cytokine production, while overexpressing RKIP promotes IL‐17‐induced signaling in HeLa cells.
IL‐17 receptors are structurally analogous to the toll‐like receptors (TLRs), the IL‐1β receptor and the TNF receptors 37. The IL‐17R signaling pathway shares some of the downstream regulatory molecules with the other three signaling pathways but has different upstream mediators. Upon IL‐17 stimulation, IL‐17R first recruits the adaptor protein and E3 ubiquitinase Act1, which utilizes the E3 ubiquitinase TRAF6 to activate the TAK1/IKK complex to activate multiple downstream signaling pathways, including the NF‐κB, MAPK, JNK, and P38 signaling pathways 17, 38. Researchers have made a concerted effort to construct a detailed map of IL‐17R‐mediated signaling events 13, 33, 39, 40; however, the upstream mediators of IL‐17R‐mediated signaling remain unclear. Using biochemical approaches, we determined that RKIP positively regulates IL‐17R‐mediated signaling by promoting interactions between Act1 and IL‐17RA. RKIP physically associates with Act1 and IL‐17RA in HeLa cells, and IL‐17A stimulation enhances this association. In vitro pull‐down assays demonstrated that RKIP directly binds with both Act1 and IL‐17RA, and domain mapping studies of Act1 and IL‐17RA showed that RKIP interacts with Act1 and IL‐17RA through their SEFIR domains. Moreover, RKIP knockdown significantly inhibited Act1‐IL‐17RA interaction, while RKIP overexpression strongly promoted this interaction. Collectively, our data indicate that RKIP serves as a crucial upstream adaptor protein by directly promoting interaction between Act1 and IL‐17RA in the IL‐17R signaling pathway. We further demonstrated that RKIP is indispensable for IL‐17A‐mediated inflammation in vivo, including IL‐17A‐induced pulmonary inflammation and peritonitis. RKIP deficiency in mice significantly impaired IL‐17A‐induced cytokine and chemokine expression in peritoneal mesothelial cells. In addition, fewer neutrophils were recruited to the lung tissues of RKIP‐KO mice than to the lung tissues of WT mice after administration of aerosolized IL‐17A.
In summary, this study provided us with additional information regarding the functional role of RKIP in IL‐17R signaling and IL‐17‐induced gene expression and showed that RKIP regulates IL‐17R‐related autoimmune diseases (Fig EV6). Thus, RKIP serves as a multi‐functional protein in inflammation and autoimmunity and, based on our findings, may be a target for the treatment of IL‐17R‐related inflammation and autoimmune disorders.
Figure EV6. Mechanism schematic diagram of RKIP regulating IL‐17R signaling.
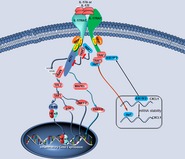
Upon binding with IL‐17A or IL‐17F, IL‐17R cytoplasm domain recruits the adaptor protein Act1. RKIP functions as an important adaptor protein to promote Act1 to IL‐17R in a SEFIR domain‐dependent manner. Activated Act1 mediates the downstream signaling in a TRAF6‐dependent or TRAF6‐independent manner to regulate signaling transduction and gene expression of cytokines or chemokines.
Materials and Methods
Mice
RKIP knockout (RKIP−/−, RKIP‐KO) mice were provided by Professor John Sedivy of Brown University, and 5~6‐week‐old RKIP‐KO mice and their littermates with a C57BL/6 background were used for the EAE induction, and 6~8‐week‐old mice were used for the induction of pulmonary inflammation and peritonitis. Mice were genotyped by PCR analysis of isolated tail DNA using the following primers: RKIP‐KO sense (5′‐GAGCCCTGGCCGGTCTCCCTTGTCCCAAACTTT‐3′), RKIP WT antisense (5′‐CACAAAACCAATCTTAAAGAGCCA‐3′), RKIP‐KO antisense (5′‐CCAAAAGGGTCTTTGAGCACCAGAGGACATCCG‐3′). The mice were maintained and bred in specific pathogen free (SPF) conditions. Animal care and experiments were undertaken in accordance with the National Institute of Health Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals with approval from the Scientific Investigation Board of Zhejiang University, Hangzhou.
Induction and assessment of EAE
Acute EAE was induced and assessed as previously described 29, 30. Briefly, acute EAE was induced by a subcutaneous immunization with 200 μg of the MOG‐35‐55 peptide (Met‐Glu‐Val‐Gly‐Trp‐Tyr‐Arg‐Ser‐Pro‐Phe‐Ser‐Arg‐Val‐Val‐His‐Leu‐Tyr‐Arg‐Asn‐Gly‐Lys, Sangon Biotech Co.) in CFA containing 5 mg ml−1 heat‐killed H37Ra strain of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Chondrex, Inc) in the back region and both sides of the vertebrae. And the immunized mice were i.v. injected with pertussis toxin (List Biological Laboratories, Inc.) at a dose of 200 ng per mouse in PBS on the day of immunization and once more 48 h after first injection. Passive EAE was also induced as previously described 10. Briefly, to prepare MOG35‐55‐specific polarized T cells, WT donor mice were subcutaneously immunized with MOG35‐55 plus twice injection i.v. of PTX. Draining lymph node cells were prepared from donor mice 10 days after immunization. Cells were cultured with MOG35‐55 at a concentration of 25 μg ml−1 under Th17‐polarizing conditions (20 ng ml−1 rmIL‐23, R&D) or Th1‐polarizing conditions (20 ng ml−1 rmIL‐12, R&D, and 2 μg ml−1anti‐mIL23p19) for 5 days. And then, the 5~6‐week‐old RKIP wild‐type or RKIP‐KO recipient mice were injected with 3.0 × 107 polarized MOG35‐55‐specific Th17 cells or Th1 cells 4 h after 5Glyc γ‐irradiation. The clinical score was performed in double‐blinded manner. Mice were examined every 2–3 days for disease symptoms and were double‐blinded scored for disease severity using the EAE scoring rulers: 0, no clinical signs; 1, limp tail; 2, paraparesis (weakness, incomplete paralysis of one or two hind limbs); 3, paraplegia (complete paralysis of two hind limbs); 4, paraplegia with fore limb weakness or paralysis; and 5, moribund state or death.
Isolation and analysis of CNS inflammatory cells
Central nervous system tissues, including spinal cords and brains, were homogenized in ice‐cold tissue grinders, filtered through a 70‐μm cell strainer (Falcon), and the cells were collected by centrifugation at 160 g for 5 min at 4°C. Cells were re‐suspended in 10 ml of 35% Percoll (GE) and centrifuged onto a 5 ml 70% Percoll cushion in 15‐ml tubes at 280 g for 25 min with a low accelerating or breaking speed. Cells at the 35–70% interface were collected and subjected to flow cytometry. Fluorescence‐conjugated monoclonal antibodies to APC‐Cy7‐CD4, Pacific Blue‐CD8, FITC‐CD11b, APC‐F4/80, and PE‐Gr‐1 were stained together for the cell face marker analysis. Antibodies to PE‐IL‐17A, APC‐IFN‐γ, and Pacific Blue‐Foxp3 were stained together for the intracellular analysis.
Reagents and plasmids
MOG‐35‐55 peptide was purchased from Shengong Biomedicals (purity > 99.0%); CFI, and M2 (anti‐Flag) beads were purchased from Sigma‐Aldrich. CFA with 10 mg/ml heat‐killed H37Ra strain of Mycobacterium tuberculosis was purchased from Chondrex, Inc. Human recombinant IL‐17A/F, murine IL‐17A, and human CXCL2 ELISA kit were purchased from PeproTech. Mouse IL‐6 and human IL‐6 ELISA kit was purchased from eBioscience. Mouse CXCL2 and CCL20 ELISA kit were purchased from R&D. Antibodies for P‐P65 (3033s), P‐P38(4511S), P‐ERK1/2(4370S), P‐JNK1/2(4668S), P65(8242), P38(8690), and ERK1/2(4695) were purchased from Cell Signaling Technology. Antibodies P‐TAK1 (S439) (ab109404) and TAK1 (ab109526) were purchased from Abcam. Antibodies for RKIP (sc‐28837), Act1 (sc‐11444), IL‐17R (sc‐376600), and protein A/G agarose (sc‐2003) were purchased from Santa Cruz. Antibodies for β‐actin (M20011), GAPDH (M130718), Flag (M20008), Myc (M20002), HA (M20003), and HA beads (M20013S) were purchased from Abmart. Antibodies for Flag (M1403‐2), Myc (R1208‐1), HA (0906‐1), and GST (ET1611‐47) were purchased from HuaBio. DAPI was purchased from Life Technology. GST beads were purchased from Thermo Scientific. Fluorescence‐conjugated monoclonal antibodies to APC‐Cy7‐CD4 (100413), Pacific Blue‐CD8 (100728), FITC‐CD11b (101211), Alexa Fluor®594‐Gr‐1(108448), and Pacific Blue‐Foxp3 (126409) were purchased from BioLegend. Recombinant mouse IL‐6 (575702), TGF‐β (763102), IL‐4(715004), anti‐CD3 (B202621), anti‐CD28 (B209363), anti‐IL‐4 (B213843), anti‐IFN‐γ (B193599), and anti‐IL‐12/IL‐23P40 (B174522) were purchased from BioLegend. Antibodies for PE‐IL‐17A (12‐7177‐81) and APC‐IFN‐γ (17‐7319‐82) were obtained from eBioscience. Anti‐α‐IL‐17A neutralization antibody (16‐7173‐95) and relative isotype IgG were purchased from eBioscience. Mouse naïve CD4+ T Cell Isolation Kit (15L66873) was purchased from STEMCELL Technologies. PEI was purchased from Polyscience, and INTERFERin@ was purchased from Polyplus Transfection. Scramble siRNA, and RKIP‐targeted siRNA were purchased from Genepharma (Shanghai, China). Myc‐RKIP plasmid was cloned from the HeLa cell line cDNA and constructed in the pcDNA3.1‐Myc‐His vector, and GST‐His‐RKIP were subcloned into pGEX‐4T1‐10His vector, respectively. Flag‐Act1 plasmid and HA‐IL‐17RA‐expressed stable HeLa cells were kind gifts from Qian's Laboratory (Institute of Health Sciences, Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences). Flag‐TRAF2 and TRAF5 were kind gifts from Xia's Laboratory (Life Sciences Institute of ZJU, LSI). Flag‐Act1 deletion mutants were subcloned into the pcDNA3.1‐Flag‐His vector. HA‐IL‐17RA plasmid was purchased from Addgene, and its deletion mutants were subcloned into pCMV4‐HA‐Neo vector.
Histological analysis
Paraffin‐embedded sections (4 mm thick) were subjected to either hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) or luxol fast blue (LFB) to evaluate inflammation and demyelination, respectively. H&E and LFB were performed by the Histomorphology Platform, Zhejiang University, with the standard protocol performed according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Culture of primary astrocytes
Astrocytes were prepared from 1‐day‐old neonatal mice as previously described 10, 41. Briefly, brains freed of meninges were dissociated with 1‐ml pipettes. Debris was removed by filtration with a 70‐μm cell strainer (Falcon). Cells were cultured in DMEM plus 10% fetal bovine serum (vol/vol) supplemented with 50 μg ml−1 penicillin and 50 μg ml−1 streptomycin. After 7 day, astrocytes were stained with antibody to GFAP (Sigma, G3893, 1:500) and purity was > 95%.
Bone marrow chimeras
Bone marrow chimeras were performed as reported before 26, 30. Briefly, recipient mice underwent sublethal dose of γ‐ray irradiation (9.5Gly, which was divided into two times of irradiation at a dose of 5Gly or 4.5Gly, respectively) to kill the bone marrow cells, and 4 h post‐irradiation WT or RKIP‐KO recipients were received 100 μl fresh WT or RKIP‐KO bone marrow cells at the concentration of 1 × 108 ml−1, respectively, which are WT→WT, WT→KO, and KO→WT groups. Eight weeks after bone marrow transplantation, mice's blood was collected and determined with a RKIP genotyping analysis to exclude failure mice and then immunized with MOG35‐55 for indicated time to induce EAE.
In vitro CD4+ T‐cell differentiation
In vitro CD4+ T‐cell differentiation was performed as previously described with little modification 10. Purified naive CD4+ T cells (CD44loCD62Lhi) were activated with 1 μg ml−1 of plate‐bound anti‐CD3 and 3 μg ml−1 anti‐CD28 under Th0 (10 μg ml−1 anti‐IL‐4 and 10 μg ml−1 anti‐IFN‐γ), Th1 (10 μg ml−1 anti‐IL‐4 and 10 ng ml−1 IL‐12), Th2 (50 ng ml−1 IL‐4 and 10 μg ml−1 anti‐IFN‐γ), Th17 (10 μg ml−1 anti‐IL‐4, 10 μg ml−1 anti‐IFN‐γ, 20 ng ml−1 IL‐6, and 5 ng ml−1 TGF‐β), or Treg cells (10 μg ml−1 anti‐IL‐4, 10 μg ml−1 anti‐IFN‐γ, and 5 ng ml−1 TGF‐β) conditions. After 4 day of activation, the differentiated T cells were stained with Foxp3 to quantify the frequency of Treg cells or re‐stimulated for 4 h with PMA and ionomycin in the presence of the protein transport inhibitor monensin (BFA), followed by intracellular staining of IFN‐γ, IL‐4, and IL‐17 to quantify the frequency of Th1, Th2, and Th17 cells.
Cell culture, plasmid transfection, and siRNA silencing
HeLa and HEK293T cells were obtained from American Type Culture Collection (ATCC), and primary astrocytes were isolated from RKIP+/−mice and grown in Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium (DMEM) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS; Bioindustry). The HeLa and HEK293T cells were transfected with PEI according to the manufacturer's protocol. RKIP‐specific siRNA (siRKIP) or negative control siRNA (siNC) were transfected in HeLa cells using INTERFERin@ according to the manufacturer's protocol. The following siRNA oligonucleotide sequences were used: RKIP siRNA (5‐TGGTCAACATGAAGGGTAA‐3).
Immunoprecipitation and Western blot analysis
Western blots were performed as described previously 26, 27. Stably expressed HeLa cell or HEK293T cell lysates were immunoprecipitated using anti‐Flag, anti‐HA, or anti‐Act1 antibodies plus protein A/G agarose. The proteins were then separated using SDS–PAGE and subjected to Western blot analysis with anti‐Act1, anti‐HA, anti‐Flag, anti‐IL‐17R, or anti‐RKIP antibodies.
In vitro Flag‐tagged pull‐down and HA‐tagged pull‐down assay
The fusion proteins of GST‐His‐RKIP protein were expressed in E. coli B21 strain and purified according to standard protocols. For Flag‐tagged pull‐down assay, Flag‐tagged Act1, Flag‐tagged Act1‐ΔSEFIR, or Flag‐tagged EGFP proteins were purified from Flag‐Act1, Flag‐Act1‐ΔSEFIR, or Flag‐EGFP‐transfected HEK293T cells, ~3 μg GST fusion proteins were mixed with Flag‐tagged proteins, respectively, and incubated with M2 beads at 4°C for 4 h with gentle rotation. The beads were washed three times with cell lysis buffer, and the bound proteins were eluted with SDS sample buffer and analyzed with Western blotting. For HA‐tagged pull‐down assay, HA‐tagged IL‐17RA, HA‐tagged IL‐17RA‐ΔSEFIR, or HA‐tagged EGFP proteins were purified from HA‐IL‐17RA, HA‐IL‐17RA‐ΔSEFIR, or HA‐EGFP‐transfected HEK293T cells and preformed pull‐down assay similarly as that in in vitro Flag pull‐down assay.
Quantitative real‐time PCR
Quantitative real‐time PCR was performed using SYBR Green fluorescence as previously described 26. The primer sequences are listed in Table EV1.
Statistical analysis
All data are expressed as the mean ± SEM. Results presented as fold induction were relative to those of the unstimulated cells or control group, and the baseline values were set as “1” in each panel. Statistical significance between two experimental groups was assessed using unpaired two‐tailed Student's t‐test.
Author contributions
WL, NW, KZ, FS, and CM performed the experiments. JS and HL assisted in the conduction of experiments. YJ, HL, KW, and YQ contributed the reagents; XW and WL designed experiments and assisted in analyzing the data and edited the manuscripts.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Supporting information
Expanded View Figures PDF
Table EV1
Source Data for Expanded View
Review Process File
Source Data for Figure 5
Source Data for Figure 6
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by grants from the National Key Basic Research Program of China (2014CB542101), National Natural Science Foundation of China (31570864, 31400740, and 31700765), Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (LY15H160006), and National Postdoctoral Science Foundation of China (2017M612006, 2017T100433).
EMBO Reports (2018) 19: e44951
References
- 1. Compston A, Coles A (2008) Multiple sclerosis. Lancet 372: 1502–1517 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Simmons SB, Pierson ER, Lee SY, Goverman JM (2013) Modeling the heterogeneity of multiple sclerosis in animals. Trends Immunol 34: 410–422 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Goverman J (2009) Autoimmune T cell responses in the central nervous system. Nat Rev Immunol 9: 393–407 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Iwakura Y, Nakae S, Saijo S, Ishigame H (2008) The roles of IL‐17A in inflammatory immune responses and host defense against pathogens. Immunol Rev 226: 57–79 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Kebir H, Kreymborg K, Ifergan I, Dodelet‐Devillers A, Cayrol R, Bernard M, Giuliani F, Arbour N, Becher B, Prat A (2007) Human TH17 lymphocytes promote blood‐brain barrier disruption and central nervous system inflammation. Nat Med 13: 1173–1175 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Iwakura Y, Ishigame H, Saijo S, Nakae S (2011) Functional specialization of interleukin‐17 family members. Immunity 34: 149–162 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Kolls JK, Linden A (2004) Interleukin‐17 family members and inflammation. Immunity 21: 467–476 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Yang J, Sundrud MS, Skepner J, Yamagata T (2014) Targeting Th17 cells in autoimmune diseases. Trends Pharmacol Sci 35: 493–500 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Isailovic N, Daigo K, Mantovani A, Selmi C (2015) Interleukin‐17 and innate immunity in infections and chronic inflammation. J Autoimmun 60: 1–11 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Xiao Y, Jin J, Chang M, Nakaya M, Hu H, Zou Q, Zhou X, Brittain GC, Cheng X, Sun SC (2014) TPL2 mediates autoimmune inflammation through activation of the TAK1 axis of IL‐17 signaling. J Exp Med 211: 1689–1702 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Gonzalez‐Garcia I, Zhao Y, Ju S, Gu Q, Liu L, Kolls JK, Lu B (2009) IL‐17 signaling‐independent central nervous system autoimmunity is negatively regulated by TGF‐beta. J Immunol 182: 2665–2671 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Komiyama Y, Nakae S, Matsuki T, Nambu A, Ishigame H, Kakuta S, Sudo K, Iwakura Y (2006) IL‐17 plays an important role in the development of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Immunol 177: 566–573 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Qian Y, Liu C, Hartupee J, Altuntas CZ, Gulen MF, Jane‐Wit D, Xiao J, Lu Y, Giltiay N, Liu J et al (2007) The adaptor Act1 is required for interleukin 17‐dependent signaling associated with autoimmune and inflammatory disease. Nat Immunol 8: 247–256 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Song X, Qian Y (2013) The activation and regulation of IL‐17 receptor mediated signaling. Cytokine 62: 175–182 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Liu C, Qian W, Qian Y, Giltiay NV, Lu Y, Swaidani S, Misra S, Deng L, Chen ZJ, Li X (2009) Act1, a U‐box E3 ubiquitin ligase for IL‐17 signaling. Sci Signal 2: ra63 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Zhu S, Qian Y (2012) IL‐17/IL‐17 receptor system in autoimmune disease: mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Clin Sci 122: 487–511 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Bulek K, Liu C, Swaidani S, Wang L, Page RC, Gulen MF, Herjan T, Abbadi A, Qian W, Sun D et al (2011) The inducible kinase IKKi is required for IL‐17‐dependent signaling associated with neutrophilia and pulmonary inflammation. Nat Immunol 12: 844–852 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Sun D, Novotny M, Bulek K, Liu C, Li X, Hamilton T (2011) Treatment with IL‐17 prolongs the half‐life of chemokine CXCL1 mRNA via the adaptor TRAF5 and the splicing‐regulatory factor SF2 (ASF). Nat Immunol 12: 853–860 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Yeung K, Seitz T, Li S, Janosch P, McFerran B, Kaiser C, Fee F, Katsanakis KD, Rose DW, Mischak H et al (1999) Suppression of Raf‐1 kinase activity and MAP kinase signalling by RKIP. Nature 401: 173–177 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Al‐Mulla F, Bitar MS, Al‐Maghrebi M, Behbehani AI, Al‐Ali W, Rath O, Doyle B, Tan KY, Pitt A, Kolch W (2011) Raf kinase inhibitor protein RKIP enhances signaling by glycogen synthase kinase‐3beta. Can Res 71: 1334–1343 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Yeung KC, Rose DW, Dhillon AS, Yaros D, Gustafsson M, Chatterjee D, McFerran B, Wyche J, Kolch W, Sedivy JM (2001) Raf kinase inhibitor protein interacts with NF‐kappaB‐inducing kinase and TAK1 and inhibits NF‐kappaB activation. Mol Cell Biol 21: 7207–7217 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Van Tongel A, Karelse A, Berghs B, Van Isacker T, De Wilde L (2014) Diagnostic value of active protraction and retraction for sternoclavicular joint pain. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 15: 421 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Lorenz K, Schmid E, Deiss K (2014) RKIP: a governor of intracellular signaling. Crit Rev Oncog 19: 489–496 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Frankenberger C, Rabe D, Bainer R, Sankarasharma D, Chada K, Krausz T, Gilad Y, Becker L, Rosner MR (2015) Metastasis suppressors regulate the tumor microenvironment by blocking recruitment of prometastatic tumor‐associated macrophages. Cancer Res 75: 4063–4073 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Yesilkanal AE, Rosner MR (2014) Raf kinase inhibitory protein (RKIP) as a metastasis suppressor: regulation of signaling networks in cancer. Crit Rev Oncog 19: 447–454 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Lin W, Ma C, Su F, Jiang Y, Lai R, Zhang T, Sun K, Fan L, Cai Z, Li Z et al (2016) Raf kinase inhibitor protein mediates intestinal epithelial cell apoptosis and promotes IBDs in humans and mice. Gut 66: 597–610 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Gu M, Liu Z, Lai R, Liu S, Lin W, Ouyang C, Ye S, Huang H, Wang X (2016) RKIP and TBK1 form a positive feedback loop to promote type I interferon production in innate immunity. EMBO J 35: 2553–2565 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Wright KT, Vella AT (2013) RKIP contributes to IFN‐gamma synthesis by CD8+ T cells after serial TCR triggering in systemic inflammatory response syndrome. J Immunol 191: 708–716 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Kang Z, Altuntas CZ, Gulen MF, Liu C, Giltiay N, Qin H, Liu L, Qian W, Ransohoff RM, Bergmann C et al (2010) Astrocyte‐restricted ablation of interleukin‐17‐induced Act1‐mediated signaling ameliorates autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Immunity 32: 414–425 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Zhu S, Pan W, Shi P, Gao H, Zhao F, Song X, Liu Y, Zhao L, Li X, Shi Y et al (2010) Modulation of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis through TRAF3‐mediated suppression of interleukin 17 receptor signaling. J Exp Med 207: 2647–2662 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Zhong B, Liu X, Wang X, Chang SH, Liu X, Wang A, Reynolds JM, Dong C (2012) Negative regulation of IL‐17‐mediated signaling and inflammation by the ubiquitin‐specific protease USP25. Nat Immunol 13: 1110–1117 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Tang H, Park S, Sun SC, Trumbly R, Ren G, Tsung E, Yeung KC (2010) RKIP inhibits NF‐kappaB in cancer cells by regulating upstream signaling components of the IkappaB kinase complex. FEBS Lett 584: 662–668 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Onishi RM, Park SJ, Hanel W, Ho AW, Maitra A, Gaffen SL (2010) SEF/IL‐17R (SEFIR) is not enough: an extended SEFIR domain is required for il‐17RA‐mediated signal transduction. J Biol Chem 285: 32751–32759 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Das SK, Bhutia SK, Sokhi UK, Azab B, Su ZZ, Boukerche H, Anwar T, Moen EL, Chatterjee D, Pellecchia M et al (2012) Raf kinase inhibitor RKIP inhibits MDA‐9/syntenin‐mediated metastasis in melanoma. Can Res 72: 6217–6226 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Park S, Yeung ML, Beach S, Shields JM, Yeung KC (2005) RKIP downregulates B‐Raf kinase activity in melanoma cancer cells. Oncogene 24: 3535–3540 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Ma C, Lin W, Liu Z, Tang W, Gautam R, Li H, Qian Y, Huang H, Wang X (2017) NDR1 protein kinase promotes IL‐17‐ and TNF‐alpha‐mediated inflammation by competitively binding TRAF3. EMBO Rep 18: 586–602 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Maitra A, Shen F, Hanel W, Mossman K, Tocker J, Swart D, Gaffen SL (2007) Distinct functional motifs within the IL‐17 receptor regulate signal transduction and target gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104: 7506–7511 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Qu F, Gao H, Zhu S, Shi P, Zhang Y, Liu Y, Jallal B, Yao Y, Shi Y, Qian Y (2012) TRAF6‐dependent Act1 phosphorylation by the IkappaB kinase‐related kinases suppresses interleukin‐17‐induced NF‐kappaB activation. Mol Cell Biol 32: 3925–3937 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Garg AV, Amatya N, Chen K, Cruz JA, Grover P, Whibley N, Conti HR, Hernandez Mir G, Sirakova T, Childs EC et al (2015) MCPIP1 endoribonuclease activity negatively regulates interleukin‐17‐mediated signaling and inflammation. Immunity 43: 475–487 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Garg AV, Ahmed M, Vallejo AN, Ma A, Gaffen SL (2013) The deubiquitinase A20 mediates feedback inhibition of interleukin‐17 receptor signaling. Sci Signal 6: ra44 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Kang Z, Wang C, Zepp J, Wu L, Sun K, Zhao J, Chandrasekharan U, DiCorleto PE, Trapp BD, Ransohoff RM et al (2013) Act1 mediates IL‐17‐induced EAE pathogenesis selectively in NG2+ glial cells. Nat Neurosci 16: 1401–1408 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Expanded View Figures PDF
Table EV1
Source Data for Expanded View
Review Process File
Source Data for Figure 5
Source Data for Figure 6


