Abstract
Squamous cell carcinoma of the anal canal (SCCA) is a rare gastrointestinal malignancy with an increasing annual incidence globally. The majority of cases are linked to prior infection with the human papillomavirus (HPV). For patients with metastatic SCCA, no consensus standard treatment exists. Identification of relevant targeted agents as novel therapeutic approaches for metastatic SCCA has been limited by a lack of comprehensive molecular profiling. For our study we performed whole-exome sequencing on tumor-normal pairs from 24 patients with metastatic SCCA. Tumor tissue from 17 additional patients was analyzed using a 263-gene panel as a validation cohort. Gene expression profiling was performed on available frozen tissue to assess for differential expression patterns. Based on these findings, patient-derived xenograft (PDX) models of SCCA were generated to test targeted therapies against PI3K and EGFR. Despite a low mutation burden, mutations in PIK3CA, MLL2, and MLL3 were among the most commonly mutated genes. An association between TP53 mutations and HPV-negative SCCA tumors was observed. Gene expression analysis suggested distinct tumor subpopulations harboring PIK3CA mutations and for which HPV had integrated into the host genome. In vivo studies demonstrated improvement with anti-EGFR treatment. Gene mutation frequencies, tumor mutation burden, and gene expression patterns for metastatic SCCA appear similar to other HPV-associated malignancies. Here we report the first comprehensive genomic characterization for patients with metastatic SCCA which provides further rationale for the integration of SCCA into the development of novel targeted therapies across HPV-related cancers.
Keywords: HPV, Anal Cancer, Genomic, Exome Sequencing, Gene Expression
Introduction
Squamous cell carcinoma of the anal canal (SCCA) represents approximately 2% of all gastrointestinal malignancies1, with a global incidence that continues to increase annually2. While the majority of patients afflicted with SCCA present with locoregional disease that can be definitively cured with chemoradiation3,4, approximately 25% of patients will develop distant metastases5,6. Median overall survival for metastatic SCCA is estimated between 15–20 months7, and patients are treated most commonly with standard cytotoxic doublet chemotherapy regimens8–10.
Human papilloma virus (HPV) has been linked to 80–95% of patients with SCCA and is regarded to be the seminal driver for oncogenesis11–14. To date, no targeted therapies have been prospectively proven to be effective for patients with metastatic SCCA based on a particular genomic abnormality. Off label, reports of targeted therapies against EGFR have been described in the management of metastatic SCCA15,16, an approach extrapolated from success in treating other HPV-associated metastatic malignancies (i.e., advanced squamous cell cancer of the head/neck)17.
Recently, targeted gene panels have provided insight into genomic features of patients with anal cancer across all stages of disease18,19. Comprehensive whole exome sequencing of SCCA has never been reported for patients with metastatic anal cancer. Here, we sought to describe the genomic landscape for SCCA by analyzing specimens from 41 patients with metastatic SCCA at our institution and to correlate these findings with clinical and pathologic features.
Methods
Collection of Patient Samples
The MD Anderson Cancer Center patient databases were searched for patients who were diagnosed with metastatic SCCA between August 2002 and August 2015 and who consented to an IRB–approved protocol for retrospective analysis of archival tissue. Patients with adenocarcinoma of the anal canal or of the rectum were excluded, as were patients with nonmetastatic squamous cell carcinoma the anal canal. The presence of HPV was tested by assessment of p16 expression by immunohistochemistry or detection of HPV DNA by in-situ hybridization.
DNA Sequencing
We performed whole exome sequencing using samples from 24 patients with paired tumor and normal tissue to identify somatic mutations present in metastatic SCCA. Targeted mutation profiling using a 263-gene panel (Supplementary Figure 1) was performed on a validation cohort of an additional 17 patients with only tumor tissue available. DNA was extracted from archived fixed-formalin, paraffin-embedded tumor tissue (see Supplemental Methods for further details on protocol for sequencing). To generate the lollipop diagrams with this data, the cBioPortal web tool, MutationMapper, was used (http://www.cbioportal.org/public-portal/mutation_mapper.jsp). To explore for any association between gene mutation or clinicopathologic feature and survival, we performed multivariate analyses by conducting log-rank tests for categorical variables and the Cox proportional hazards model for continuous variables to correlate each variable to survival outcome. The Benjamini-Hochberg correction was applied to adjust for multiple testing. Kaplan-Meier survival curves were generated for any significant genes or clinical variables with an adjusted p-value less than 0.05. To compare mutation frequencies among various squamous cell tumor types, the number of mutations detected per megabase of nucleotides examined during sequencing was calculated for each patient. A public database (www.cbioportal.org) was accessed to obtain these data for the non-SCCA tumor types not sequenced in our study. Mean values in mutation frequency for SCCA relative to other tumor types were compared using an independent t-test adjusted with a Bonferroni correction.
Gene Expression Profiling
RNA was isolated and sequenced from archived frozen specimens of patients at our institution (see Supplemental Methods for further details). We applied a Trimmed Mean of M-values method to normalize the count data. To examine relative similarities of the samples, we applied a principle component analysis (PCA) as well as a hierarchical clustering algorithm. The data analyses were performed using R, a publicly available statistical computing tool (http://www.r-project.org/) and Bioconductor packages (http://www.bioconductor.org/). Because no predetermined groups based on lack of historical information were available, the most variable genes, as measured by median absolute deviation based on gene expression, were selected for further analysis, from which we were able to classify samples into subtypes by evaluation of clustering, PCA plots, and correlation heatmaps. To determine patterns of HPV integration, a reference genome featuring a hybrid genome that combines selected virus genomes, including HPV6, HPV16, HPV18, HPV33, HPV35, HPV45, and HPV56, was used with the VirusSeq pipeline for the HPV integration analysis as previously described20.
Patient-Derived Xenograft Studies
A tumor collected under an IRB-approved protocol from a freshly resected liver metastasis from a patient with squamous cell cancer of the anal canal was implanted into the subcutaneous flank of a female, NOD-SCID-gamma mouse to create a patient-derived xenograft. This tumor was expanded into a second generation of mice in two separate experiments. In the first, 7 mice per arm were randomized into an untreated control group or into a group that received the oral p110α subunit-specific PI3K inhibitor BYL719 (Selleck Chemicals, Houston, TX) at a dose of 35 mg/kg body weight daily. In a second experiment, mice were randomized to receive twice weekly intraperitoneal injections of the chimeric anti-EGFR monoclonal antibody cetuximab (Bristol-Myers Squibb, New York, NY) at a dose of 30 mg/kg body weight or control solution. Tumor sizes were measured twice weekly for 21 days.
Results
Mutation frequency/patient characteristics
Table 1 details the demographic characteristics of these patients with unresectable/metastatic SCCA. The median age at diagnosis of metastatic disease was 57 years (interquartile range, 49–60 years). The majority of patients (63%) had been initially diagnosed with locoregional disease which later recurred/metastasized after definitive chemoradiation. The liver was the most common site for distant spread. HPV was detected in 16 of 18 tested tumors that underwent whole exome sequencing. Most tumors (66%) were poorly differentiated.
Table 1.
Patient Demographics
| Median Age at Diagnosis | 57 years (Interquartile Range, 49–60) |
|---|---|
| Stage at Diagnosis (%) | |
| II | 14 (34) |
| III | 12 (29) |
| IV | 15 (37) |
|
| |
| Gender (%) | |
| Female | 33 (80) |
| Male | 8 (20) |
| Ethnicity (%) | |
| Caucasian | 39 (95) |
| African-American | 2 (5) |
|
| |
| HIV-Positive (%) | 3 (7) |
|
| |
| Tumor Differentiation (%) | |
| Well differentiated | 1 (2) |
| Moderately differentiated | 13 (32) |
| Poorly differentiated | 27 (66) |
|
| |
| Metastatic Site (%) | |
| Liver | 21 (51) |
| Lung | 19 (46) |
| Lymph Node | 17 (41) |
| Local (Unresectable) Recurrence | 15 (37) |
Genomic sequencing
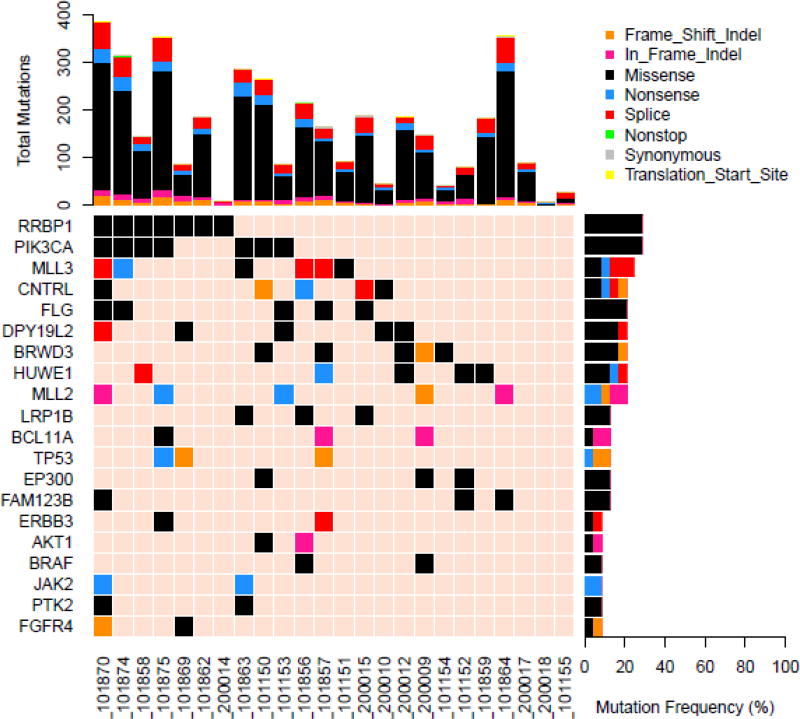
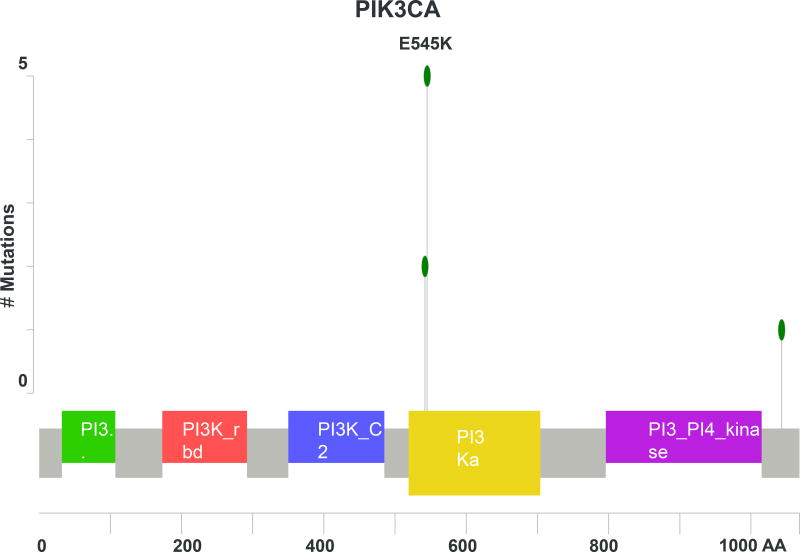
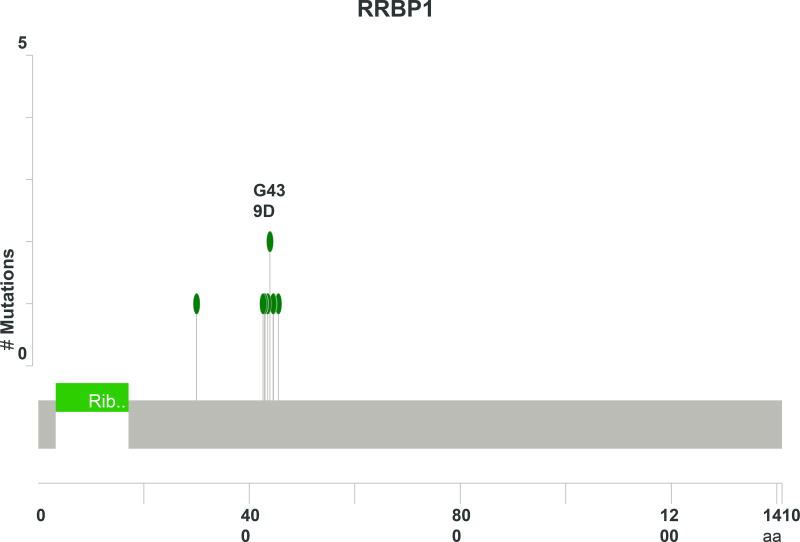
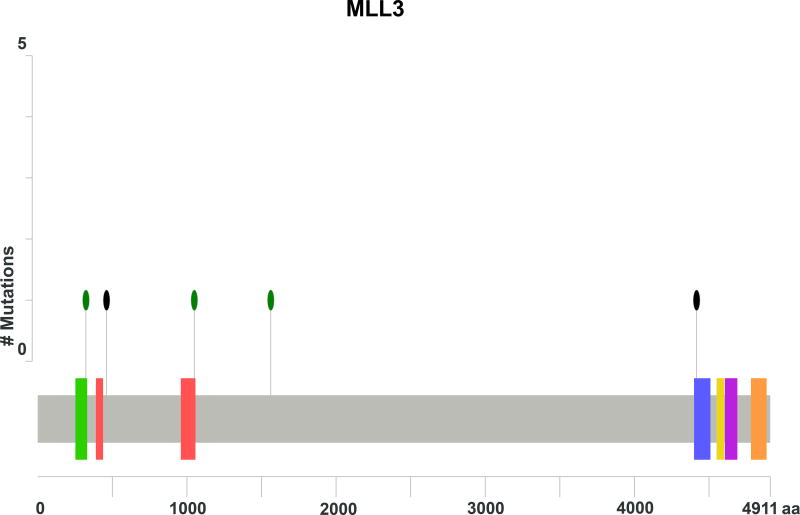
As seen in Figure 1, PIK3CA was the most commonly mutated gene in the cohort for which the entire exome was sequenced, present in 7 of 24 (29%) tumors. All of the mutations were located in the exon 2 and 4 hotspots (Figure 2A) known to generate oncogenic activity of PIK3CA/mTOR signaling21. Missense mutations of RRBP1 were likewise present in 7 patients with metastatic anal cancer. These mutations all localized to the same region of the RRBP1 gene (Figure 2B). Other genes mutated in 2 or greater of the 24 sequenced tumors are listed in Figure 1. MLL3 and MLL2 were mutated in 25% and 21% of tumors, respectively. In addition, genes important to cell cycle dysregulation (CNTRL), DNA damage repair (TP53, HUWE1), chromatin remodeling (EP300), cell differentiation (FLG, PTK2), and activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling (FAM123B) were all present in multiple tumors.
Figure 1.
Figure 2.
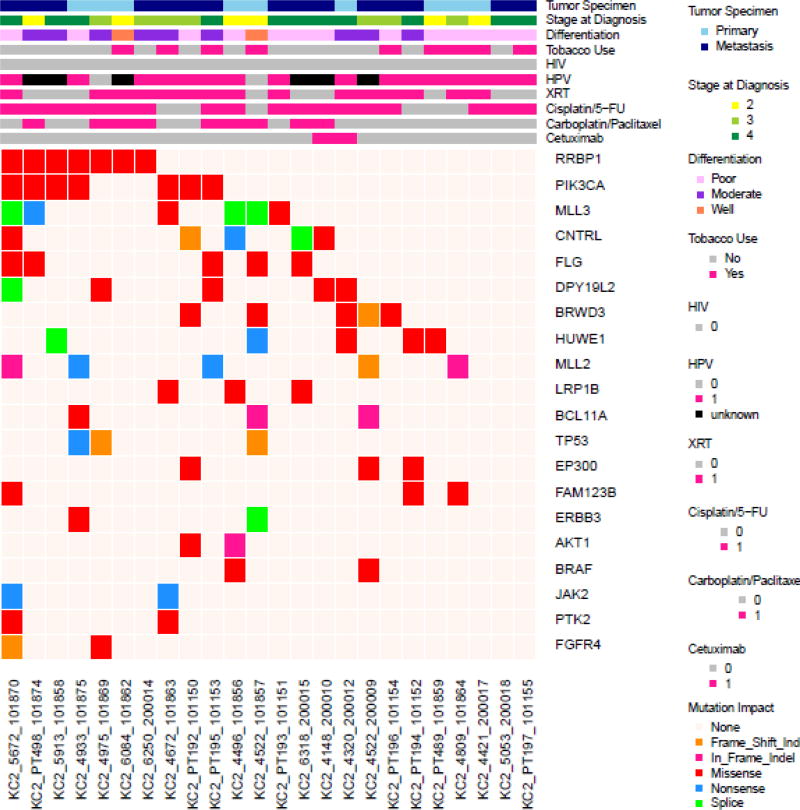
Of the 17 tumors tested with the 263-gene panel of the validation set, the most commonly mutated genes were MLL3 (39%), PIK3CA (28%), TP53 (28%), MLL2 (22%), and EP300 (22%). These genes were among the most frequently mutated among the independent set of tumors analyzed in the orthogonal whole exome cohort. Table 2 shows the pooled frequencies of the most common genes detected between the two sets. For the entire panel of 41 patients, MLL3 (32%) and PIK3CA (29%) were the most commonly mutated genes for these patients with unresectable squamous cell carcinoma of the anal canal. Notably, KRAS, NRAS, BRAF, and EGFR mutations were not common, detected in <5% of all patients.
Table 2.
Frequency of most commonly occurring mutations in a separate sequencing methodology for 17 SCCA tumors
| Gene | Patients with Gene Mutation in whole exome analysis (N=24) |
Patients with Gene Mutation in 263-gene panel (N=17) |
Frequency (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| MLL3 | 6 | 7 | 32 |
| PIK3CA | 7 | 5 | 29 |
| MLL2 | 5 | 4 | 22 |
| EP300 | 3 | 4 | 22 |
| TP53 | 3 | 5 | 20 |
| AKT1 | 2 | 1 | 7 |
| ERBB3 | 2 | 1 | 7 |
| PTK2 | 2 | 1 | 7 |
| EGFR | 1 | 1 | 5 |
| BRAF | 2 | 0 | 5 |
| FGFR2 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| KRAS | 1 | 0 | 2 |
| NRAS | 1 | 0 | 2 |
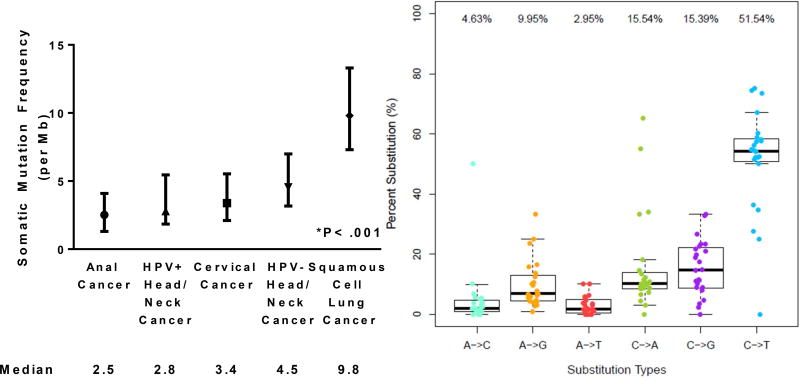
Figure 3A shows a median 2.5 somatic mutations/Mb detected across the entire exome (range, 0.1–6 mutations/Mb). The median number of mutations/Mb is similar to what has been seen from publicly available data for cervical cancer and HPV-positive head/neck cancer, and lower than squamous cell cancer of the lung (P<.001)22–24. In addition, when analyzed according to the prevalence of specific nucleotide substitution, C>T substitutions were the most common, accounting for over half of all mutations detected (Figure 3B).
Figure 3.
Median frequency of somatic mutations per megabase of nucleotides analyzed (with interquartle range) for anal cancer and other squamous cell cancer types (A) and of the nucleotide substitutions detected for SCCA (B).
Next, various clinicopathologic characteristics were analyzed for a correlation with various gene aberrations. HPV status was tested in 18 of 24 tumors that underwent whole exome sequencing (16 were HPV+; 2 were HPV−). TP53 mutations were present in both of the HPV-negative tumors and were more likely to be associated with the absence of HPV relative to HPV-positive tumors (odds ratio [OR] 52, P = .03). The median survival from the time of diagnosis of metastatic disease was 4.3 years for the pooled population of 42 patients. Using a multivariate analysis, being HIV-negative (P < .001) and of female gender (P=.01), were associated with prolonged survival. However, no mutations for any gene were noted to associate with survival.
RNA Profiling
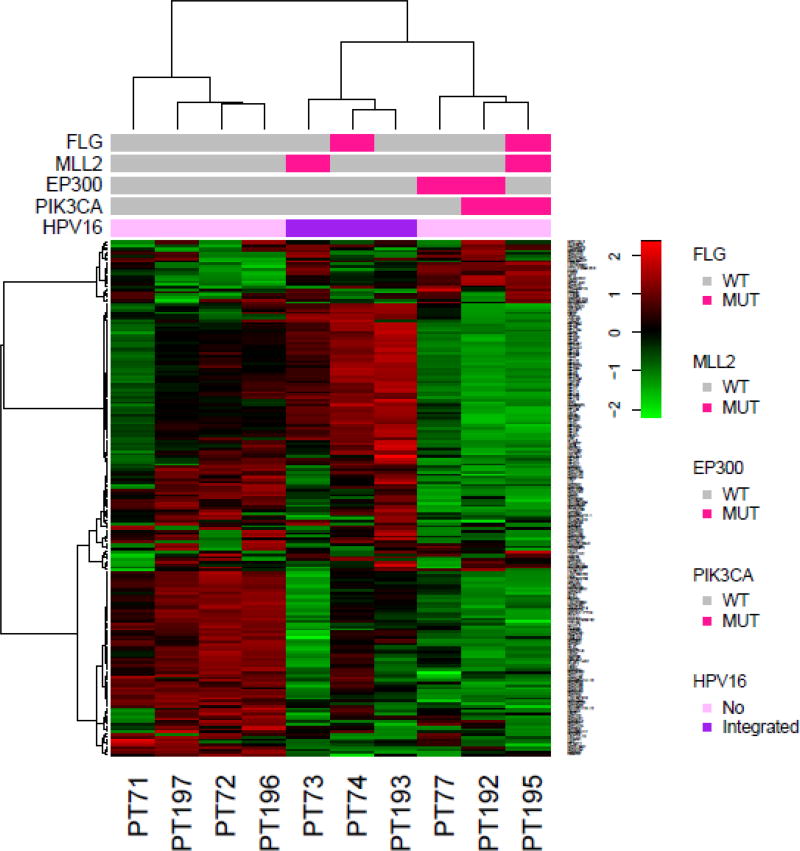
Ten patients had fresh frozen tumor available for gene expression profiling. The top 200 most variably expressed genes for expression were clustered to generate the heatmap shown in Figure 5. Three distinct subgroups of 4, 3, and 3 patients are noted in this analysis. To provide additional insight into possible distinguishing features we examined select frequently mutated genes and HPV-16 integration status. HPV-16 integration into the host genome DNA was unique/specific to the second subgroup and present in all three of these tumors (OR 105, P=.03). Similarly, a trend towards a mutation in PIK3CA (OR 25, P=.07) and subgroup 3 was also observed.
Figure 5.
Xenograft studies
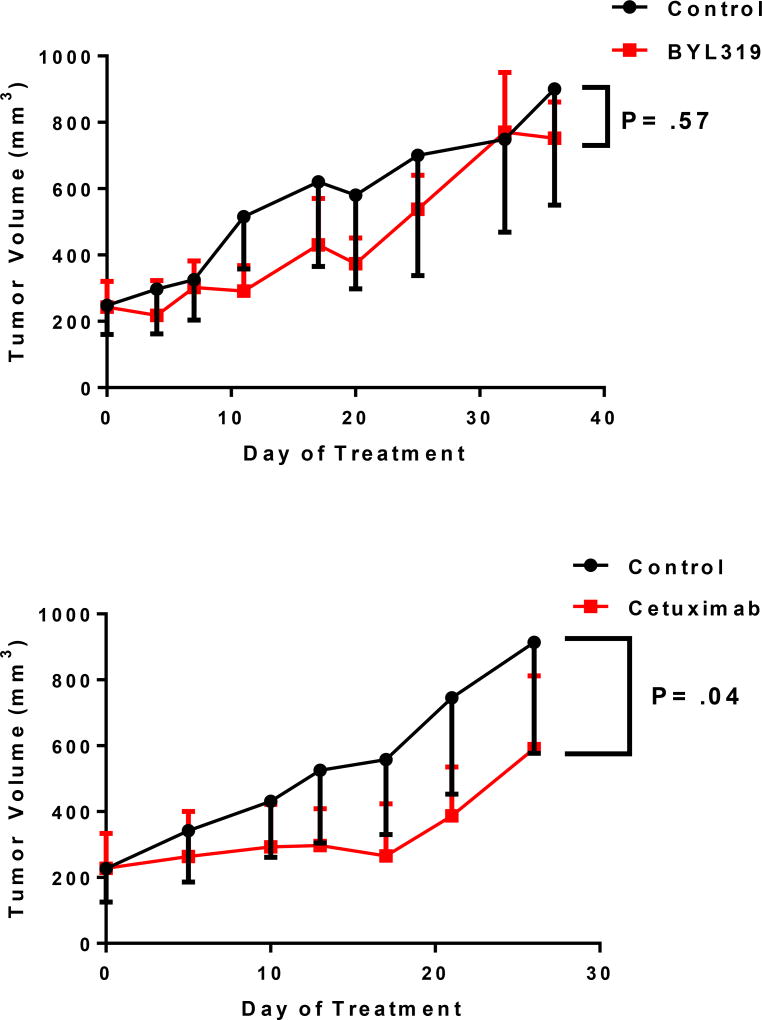
Mice were treated with the PI3K inhibitor BYL719 alone, and no difference in mean tumor volume after 35 days was noted between the untreated control group and the experimental group (899 mm3 vs 752 mm3, respectively; P=.57). However, cetuximab was also tested on the same PDX model, and a significantly lower mean tumor volume was noted for the experimental group relative to the untreated controls after 28 days (914 mm3 vs 591 mm3, respectively; P=.04).
Discussion
Here we report for the first time comprehensive genomic profiling with whole exome sequencing and gene expression profiling specifically for patients with metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the anal canal. With only cytotoxic chemotherapy agents approved for the treatment of metastatic disease at present, these results provide an important step in the rational design of novel therapies for this understudied malignancy.
PIK3CA was commonly mutated noted across the entire population associated with both methods of sequencing, present in 29% of patients. The E545K substitution was the most commonly detected mutation of PIK3CA. This specific mutation in the helical domain of the PI3K kinase results in constitutive activation of Akt signaling associated with downstream oncogenic activity20,21,25,26. In previous studies of patients with anal cancer sequenced with more limited gene panels, PIK3CA was mutated in approximately one-third of all cases18,19, consistent with our findings here. Similarly, for squamous cell carcinomas of the head/neck, PIK3CA is more frequently mutated in HPV-positive tumors relative to the HPV-negative counterparts27,28 and at similar prevalence to our observations here for anal cancer, a disease in which the majority of tumors are HPV-positive. Use of a PI3K inhibitor generated no antitumor response in a PIK3CA wild-type PDX model of SCCA. Based on the relatively high prevalence of PIK3CA mutations in this disease, further analysis of PI3K inhibitors in PIK3CA mutant models, once available, are warranted to assess the potential application of these agents. Nonetheless, these findings lend further support to the notion that aberrant PIK3CA activity is present across the spectrum of HPV-associated malignancies.
Genes important in histone modification were also frequently mutated in our series. For examples, mutations in MLL2 and MLL3 were present in 21% and 31% of cases, with the latter being the most commonly mutated gene among all that were assessed across the entire 41 patient cohort. EP300, a histone acetyltransferase that modulates transcription of genes critical to physiologic cell proliferation and differentiation including TP5329–31, was mutated in 17% of anal cancers. MLL2 and MLL3 belong to the family of histone H3-lysine-4 (H3K4) methyltransferases32, and trimethylation of H3K4 promotes physiologic gene expression33,34. Mutations in MLL2 and MLL3 generate aberrant methylation of H3K4 and have been associated with oncogenic transformation in preclinical models35,36. For example, MLL3 is important in activation of TP53 gene expression, and in TP53 +/− models, loss of MLL3 activity gas been associated with increased cell stress via loss of intact DNA damage repair37. Similarly, high frequencies of double-stranded DNA breaks have been identified in tumor cells with MLL2 mutations, and are attributed to decreased expression of the RNAPOLII gene encoding for the DNA-proofreading RNA polymerase II38. Given that HPV oncoprotein E6 suppresses p53 and its downstream DNA repair mechanisms in the predominance of anal cancers39,40, these additional mutations responsible for histone/chromatin modulation provide additional insight into defective DNA repair mechanisms as drivers for this malignancy. This notion may be critical for all anal squamous cancers regardless of HPV status, as HPV-negative tumors were also associated in our study with TP53 mutations, consistent with prior genomic characterizations of other HPV-associated squamous cancers19,27.
Mutated RRBP1 was a novel finding present in 29% of anal cancers analyzed across the entire exome, and all mutations localized to the same hotspot. This protein functions in post-translational processing of proteins secreted from the endoplasmic reticulum41 and has been implicated in cell autophagy42,43. While these mutations have not been previously described for RRBP1, overexpression of this gene has been reported in other solid tumors, including breast and colorectal adenocarcinomas44,45. In non-metastatic colorectal cancer, high expression of RRBP1 has been described as a poor prognostic biomarker44. While no effect on metastatic survival was noted in this population of patients with metastatic SCCA based on RRBP1 mutation status, our findings of this gene warrants further evaluation in future studies for anal cancer.
Mutations in oncogenes critical to MAPK signaling were not routinely detected in the tumors analyzed here. Lack of such mutations has been previously described in anal cancer and is also consistent with other HPV-positive squamous tumors18,19. Based on our findings, we do not believe routine testing for mutations in KRAS, NRAS, or BRAF is required, as the results are unlikely to influence clinical decision making in the management of metastatic anal cancer7. Given that cetuximab, a monoclonal antibody against EGFR and its downstream signaling targets, is approved for surgically unresectable and advanced head/neck cancers, we tested cetuximab in a PDX model wild-type for PIK3CA and for EGFR, KRAS, NRAS, and BRAF. While reduction in tumor size was not noted following treatment with BYL719, a significant reduction in tumor volume was seen in tumors treated with cetuximab relative to untreated controls. Our findings provide rationale for future combination studies involving anti-EGFR therapies in metastatic anal cancers lacking activating mutations of MAPK and PI3K/mTOR signaling.
Notably, unlike other solid tumors such as melanoma, renal cell carcinoma, and microsatellite-high colorectal cancer46,47, which have demonstrated response to immune checkpoint inhibitors associated with a high underlying mutation burden, our analysis of metastatic anal cancer by whole exome sequencing did not feature a high mutational load. Indeed, the overall mutation frequency was similar to what has been detected in other HPV-associated squamous cancers. The anti-PD-1 antibody nivolumab has been reported as an effective therapy for patients with metastatic SCCA from a recent phase II study48. For a proportion of patients treated with nivolumab, response appeared to be associated with an inflammatory tumor microenvironment characterized by the presence of cytotoxic T cells and a PD-1:PD-L1 axis amenable to blockade by nivolumab. Applying our findings here, we surmise that the immunogenicity of these tumors is not driven by hypermutated tumors given that our results are consistent with low mutation rates.
In an effort to characterize better these metastatic anal canal cancers, we performed gene expression profiling of ten available frozen tumors. Despite the small number of available specimens, three separate subgroups were identified based on RNA levels of variable genes. PIK3CA-mutant tumors appeared to cluster into one distinct group, whereas a second subgroup featured only tumors characterized by integration of HPV-16 DNA into the tumor cell genome. Our findings here are consistent with reported data from head/neck cancers, whereby HPV-negative tumors and PIK3CA-mutated tumors clustered into distinct subtypes49. Detection of HPV DNA into the host genome using this approach has been previously described for HPV-positive cervical and head/neck tumors50. The differential gene expression patterns, in the background of low mutation burdens, highlight the role of non-mutation aberrations which affect gene expression in a manner relevant to defining subclassifications potentially of this disease. Given the aforementioned genes vital to chromatin remodeling, it is feasible that epigenetic aberrations may contribute to defining gene expression signatures within this population.
No survival differences or other clinical features were found to be correlated with mutation status in our series. We recognize that our analyses are limited by a relatively small number of tumor samples, a testimony to the sparse number of patients with metastatic anal cancer. In addition, as all patients included in our work had distant metastases, it is possible that their tumors uniformly featured aberrations driving a more aggressive underlying phenotype such that genomic drivers responsible for differential clinical features could not be distinguished among a cohort of only metastatic patients. Future studies comparing genome profiling for patients with early-stage anal cancer, for which the majority of patients will be cured with chemoradiation, are clearly warranted to identify relevant drivers of disease progression or chemoradiation resistance that potentially can be targeted with matched novel therapies.
This series represents the first cohort of patients with metastatic squamous cell cancer of the anal canal to undergo complete exome sequencing. Our findings are strengthened by similar results in an independent cohort of patients whose tumors were sequenced with an alternate methodology. In addition, mutation profiles for our series are consistent with prior data for other HPV-positive malignancies and provide further rationale for the study of these solid tumors not only by disease site but also by the responsible underlying biological drivers. Given the emerging role of immunotherapeutic agents in the treatment of metastatic anal cancer, these results provide an important step forward into understanding the relevant drivers for this disease upon which subsequent future clinical trials may be designed.
Supplementary Material
Figure 4.
Figure 6.
Acknowledgments
Financial Support: This work was supported by the generous philanthropic contributions to The University of Texas MD Anderson Moon Shots Program, The Zayed Institute for Personalized Cancer Therapy, the Robert J. Kleberg, Jr., and Helen C. Kleberg Foundation, and an anonymous philanthropic donor.
Footnotes
Conflict of Interest: The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
References
- 1.Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2016. CA: a cancer journal for clinicians. 2016;66(1):7–30. doi: 10.3322/caac.21332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Johnson LG, Madeleine MM, Newcomer LM, Schwartz SM, Daling JR. Anal cancer incidence and survival: the surveillance, epidemiology, and end results experience, 1973–2000. Cancer. 2004;101(2):281–288. doi: 10.1002/cncr.20364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Bartelink H, Roelofsen F, Eschwege F, et al. Concomitant radiotherapy and chemotherapy is superior to radiotherapy alone in the treatment of locally advanced anal cancer: results of a phase III randomized trial of the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Radiotherapy and Gastrointestinal Cooperative Groups. Journal of clinical oncology : official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. 1997;15(5):2040–2049. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1997.15.5.2040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Flam M, John M, Pajak TF, et al. Role of mitomycin in combination with fluorouracil and radiotherapy, and of salvage chemoradiation in the definitive nonsurgical treatment of epidermoid carcinoma of the anal canal: results of a phase III randomized intergroup study. Journal of clinical oncology : official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. 1996;14(9):2527–2539. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1996.14.9.2527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Das P, Bhatia S, Eng C, et al. Predictors and patterns of recurrence after definitive chemoradiation for anal cancer. International journal of radiation oncology, biology, physics. 2007;68(3):794–800. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2006.12.052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Eng C. Anal cancer: current and future methodology. Cancer investigation. 2006;24(5):535–544. doi: 10.1080/07357900600815208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Eng C, Chang GJ, You YN, et al. The role of systemic chemotherapy and multidisciplinary management in improving the overall survival of patients with metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the anal canal. Oncotarget. 2014;5(22):11133–11142. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Ajani JA, Carrasco CH, Jackson DE, Wallace S. Combination of cisplatin plus fluoropyrimidine chemotherapy effective against liver metastases from carcinoma of the anal canal. The American journal of medicine. 1989;87(2):221–224. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(89)80702-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Faivre C, Rougier P, Ducreux M, et al. 5-fluorouracile and cisplatinum combination chemotherapy for metastatic squamous-cell anal cancer. Bulletin du cancer. 1999;86(10):861–865. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kim R, Byer J, Fulp WJ, Mahipal A, Dinwoodie W, Shibata D. Carboplatin and paclitaxel treatment is effective in advanced anal cancer. Oncology. 2014;87(2):125–132. doi: 10.1159/000361051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Frisch M, Glimelius B, van den Brule AJ, et al. Sexually transmitted infection as a cause of anal cancer. The New England journal of medicine. 1997;337(19):1350–1358. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199711063371904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Baricevic I, He X, Chakrabarty B, et al. High-sensitivity human papilloma virus genotyping reveals near universal positivity in anal squamous cell carcinoma: different implications for vaccine prevention and prognosis. European journal of cancer. 2015;51(6):776–785. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2015.01.058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.De Vuyst H, Clifford GM, Nascimento MC, Madeleine MM, Franceschi S. Prevalence and type distribution of human papillomavirus in carcinoma and intraepithelial neoplasia of the vulva, vagina and anus: a meta-analysis. International journal of cancer Journal international du cancer. 2009;124(7):1626–1636. doi: 10.1002/ijc.24116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Hoots BE, Palefsky JM, Pimenta JM, Smith JS. Human papillomavirus type distribution in anal cancer and anal intraepithelial lesions. International journal of cancer Journal international du cancer. 2009;124(10):2375–2383. doi: 10.1002/ijc.24215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Lukan N, Strobel P, Willer A, et al. Cetuximab-based treatment of metastatic anal cancer: correlation of response with KRAS mutational status. Oncology. 2009;77(5):293–299. doi: 10.1159/000259615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Rogers JE, Ohinata A, Silva NN, Mehdizadeh A, Eng C. Epidermal growth factor receptor inhibition in metastatic anal cancer. Anti-cancer drugs. 2016 doi: 10.1097/CAD.0000000000000383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Vermorken JB, Psyrri A, Mesia R, et al. Impact of tumor HPV status on outcome in patients with recurrent and/or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck receiving chemotherapy with or without cetuximab: retrospective analysis of the phase III EXTREME trial. Annals of oncology : official journal of the European Society for Medical Oncology/ESMO. 2014;25(4):801–807. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdt574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Smaglo BG, Tesfaye A, Halfdanarson TR, et al. Comprehensive multiplatform biomarker analysis of 199 anal squamous cell carcinomas. Oncotarget. 2015;6(41):43594–43604. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Chung JH, Sanford E, Johnson A, et al. Comprehensive genomic profiling of anal squamous cell carcinoma reveals distinct genomically defined classes. Annals of oncology : official journal of the European Society for Medical Oncology/ESMO. 2016;27(7):1336–1341. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdw152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Chen Y, Yao H, Thompson EJ, Tannir NM, Weinstein JN, Su X. VirusSeq: software to identify viruses and their integration sites using next-generation sequencing of human cancer tissue. Bioinformatics. 2013;29(2):266–267. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Bader AG, Kang S, Vogt PK. Cancer-specific mutations in PIK3CA are oncogenic in vivo. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2006;103(5):1475–1479. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0510857103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Center BITGDA. Aggregate Analysis Features (CESC) 2016 [Google Scholar]
- 23.Center BITGDA. Aggregate Analysis Features (HNSC) 2016 [Google Scholar]
- 24.Center BITGDA. Aggregate Analysis Features (LUSC-TP) 2016 [Google Scholar]
- 25.Ikenoue T, Kanai F, Hikiba Y, et al. Functional analysis of PIK3CA gene mutations in human colorectal cancer. Cancer research. 2005;65(11):4562–4567. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-4114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Wang Y, Helland A, Holm R, Kristensen GB, Borresen-Dale AL. PIK3CA mutations in advanced ovarian carcinomas. Hum Mutat. 2005;25(3):322. doi: 10.1002/humu.9316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Cancer Genome Atlas N. Comprehensive genomic characterization of head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Nature. 2015;517(7536):576–582. doi: 10.1038/nature14129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Lui VW, Hedberg ML, Li H, et al. Frequent mutation of the PI3K pathway in head and neck cancer defines predictive biomarkers. Cancer discovery. 2013;3(7):761–769. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-13-0103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Gayther SA, Batley SJ, Linger L, et al. Mutations truncating the EP300 acetylase in human cancers. Nat Genet. 2000;24(3):300–303. doi: 10.1038/73536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Lill NL, Grossman SR, Ginsberg D, DeCaprio J, Livingston DM. Binding and modulation of p53 by p300/CBP coactivators. Nature. 1997;387(6635):823–827. doi: 10.1038/42981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Avantaggiati ML, Ogryzko V, Gardner K, Giordano A, Levine AS, Kelly K. Recruitment of p300/CBP in p53-dependent signal pathways. Cell. 1997;89(7):1175–1184. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80304-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Ruthenburg AJ, Allis CD, Wysocka J. Methylation of lysine 4 on histone H3: intricacy of writing and reading a single epigenetic mark. Mol Cell. 2007;25(1):15–30. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2006.12.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Schneider R, Bannister AJ, Myers FA, Thorne AW, Crane-Robinson C, Kouzarides T. Histone H3 lysine 4 methylation patterns in higher eukaryotic genes. Nat Cell Biol. 2004;6(1):73–77. doi: 10.1038/ncb1076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Santos-Rosa H, Schneider R, Bannister AJ, et al. Active genes are tri-methylated at K4 of histone H3. Nature. 2002;419(6905):407–411. doi: 10.1038/nature01080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Hu D, Gao X, Morgan MA, Herz HM, Smith ER, Shilatifard A. The MLL3/MLL4 branches of the COMPASS family function as major histone H3K4 monomethylases at enhancers. Molecular and cellular biology. 2013;33(23):4745–4754. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01181-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Herz HM, Mohan M, Garruss AS, et al. Enhancer-associated H3K4 monomethylation by Trithorax-related, the Drosophila homolog of mammalian Mll3/Mll4. Genes Dev. 2012;26(23):2604–2620. doi: 10.1101/gad.201327.112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Lee J, Kim DH, Lee S, et al. A tumor suppressive coactivator complex of p53 containing ASC-2 and histone H3-lysine-4 methyltransferase MLL3 or its paralogue MLL4. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2009;106(21):8513–8518. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0902873106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Kantidakis T, Saponaro M, Mitter R, et al. Mutation of cancer driver MLL2 results in transcription stress and genome instability. Genes Dev. 2016;30(4):408–420. doi: 10.1101/gad.275453.115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Werness BA, Levine AJ, Howley PM. Association of human papillomavirus types 16 and 18 E6 proteins with p53. Science. 1990;248(4951):76–79. doi: 10.1126/science.2157286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Li X, Coffino P. High-risk human papillomavirus E6 protein has two distinct binding sites within p53, of which only one determines degradation. Journal of virology. 1996;70(7):4509–4516. doi: 10.1128/jvi.70.7.4509-4516.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Savitz AJ, Meyer DI. 180-kD ribosome receptor is essential for both ribosome binding and protein translocation. J Cell Biol. 1993;120(4):853–863. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.4.853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Cardoso CM, Groth-Pedersen L, Hoyer-Hansen M, et al. Depletion of kinesin 5B affects lysosomal distribution and stability and induces peri-nuclear accumulation of autophagosomes in cancer cells. PloS one. 2009;4(2):e4424. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0004424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Diefenbach RJ, Diefenbach E, Douglas MW, Cunningham AL. The ribosome receptor, p180, interacts with kinesin heavy chain, KIF5B. Biochemical and biophysical research communications. 2004;319(3):987–992. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.05.069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Pan Y, Cao F, Guo A, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum ribosome-binding protein 1, RRBP1, promotes progression of colorectal cancer and predicts an unfavourable prognosis. Br J Cancer. 2015;113(5):763–772. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2015.260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Telikicherla D, Marimuthu A, Kashyap MK, et al. Overexpression of ribosome binding protein 1 (RRBP1) in breast cancer. Clin Proteomics. 2012;9(1):7. doi: 10.1186/1559-0275-9-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Topalian SL, Hodi FS, Brahmer JR, et al. Safety, activity, and immune correlates of anti-PD-1 antibody in cancer. The New England journal of medicine. 2012;366(26):2443–2454. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1200690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Le DT, Uram JN, Wang H, et al. PD-1 Blockade in Tumors with Mismatch-Repair Deficiency. The New England journal of medicine. 2015;372(26):2509–2520. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1500596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Van Karlyle Morris KKC, Salem Mohamed E, Nimeiri Halla Sayed, Iqbal Syma, Singh Paul Preet, Polite Blase N, Deming Dustin A, Chan Emily, Wade James Lloyd, Bekaii-Saab Tanios S, Uronis Hope Elizabeth, Pasia Manolo G, Bland Gail, Wolff Robert A, Ohinata Aki, Ohaji Chimela, Rogers Jane, Sharma Padmanee, En Cathy. NCI9673: A multi-institutional eETCTN phase II study of nivolumab in refractory metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the anal canal (SCCA) Journal of clinical oncology : official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. 2016;34(suppl) abstr 3503. [Google Scholar]
- 49.Zhang YX, Koneva LA, Virani S, et al. Subtypes of HPV-Positive Head and Neck Cancers Are Associated with HPV Characteristics, Copy Number Alterations, PIK3CA Mutation, and Pathway Signatures. Clinical Cancer Research. 2016;22(18):4735–4745. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-0323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Chandrani P, Kulkarni V, Iyer P, et al. NGS-based approach to determine the presence of HPV and their sites of integration in human cancer genome. British journal of cancer. 2015;112(12):1958–1965. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2015.121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Li H, Durbin R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics. 2009;25(14):1754–1760. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.DePristo MA, Banks E, Poplin R, et al. A framework for variation discovery and genotyping using next-generation DNA sequencing data. Nat Genet. 2011;43(5):491-+. doi: 10.1038/ng.806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Zhou W, Chen T, Zhao H, et al. Bias from removing read duplication in ultra-deep sequencing experiments. Bioinformatics. 2014 doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btt771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Lonigro RJ, Grasso CS, Robinson DR, et al. Detection of somatic copy number alterations in cancer using targeted exome capture sequencing. Neoplasia. 2011;13(11):1019–1025. doi: 10.1593/neo.111252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Bamford S, Dawson E, Forbes S, et al. The COSMIC (Catalogue of Somatic Mutations in Cancer) database and website. British journal of cancer. 2004;91(2):355–358. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6601894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.McLaren W, Pritchard B, Rios D, Chen Y, Flicek P, Cunningham F. Deriving the consequences of genomic variants with the Ensembl API and SNP Effect Predictor. Bioinformatics. 2010;26(16):2069–2070. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btq330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Wang K, Li M, Hakonarson H. ANNOVAR: functional annotation of genetic variants from high-throughput sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010;38(16):e164. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Mao Y, Chen H, Liang H, Meric-Bernstam F, Mills GB, Chen K. CanDrA: Cancer-Specific Driver Missense Mutation Annotation with Optimized Features. PLoS One. 2013;8(10):e77945. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0077945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.