Figure 6. Neural representation of coarticulated kinematics.
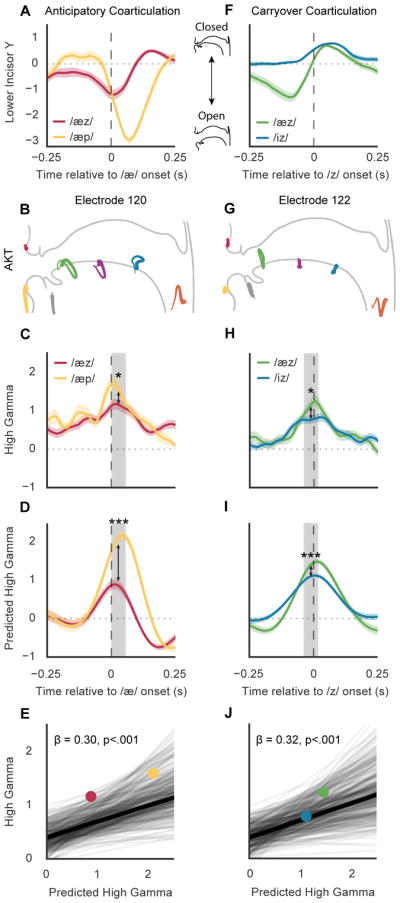
A, Example of different degrees of anticipatory coarticulation for the lower incisor. Average traces for the lower incisor (y-direction) are shown for /æz/ and /æp/ aligned to the acoustic onset of /æ/. B, Electrode 120 is crucially involved in the production of /æ/ with a vocalic AKT (jaw opening and laryngeal control), and has a high phonetic selectivity index for /æ/. C, Average high gamma activity for electrode 120 during the productions of /æz/ and /æp/. Median high gamma during 50 ms centered at the electrode’s point of peak phoneme discriminability (grey box) is significantly higher for /æp/ than /æz/ (p<.05, Wilcoxon signed ranks tests). D, Average predicted high gamma activity predicted by AKT in B. Median predicted high gamma is significantly higher for /æp/ than /æz/ (p<.001, Wilcoxon signed ranks tests). E, Mixed-effect model shows relationship of high gamma with kinematic variability due to anticipatory coarticulatory effects of following phonemes for all electrodes and phonemes (β = 0.30, SE = 0.04, χ2(1) = 38.96, p = 4e–10). Each line shows the relationship between high gamma and coarticulated kinematic variability for a given phoneme and electrode in all following phonetic contexts with at least 25 instances. Relationships from C and D for /æz/ (red) and /æp/ (yellow) are shown as points. Electrodes in all participants were used to construct the model. F, Example of different degrees of carryover coarticulation for the lower incisor. Average traces for the lower incisor (y-direction) are shown for /æz/ and /iz/ aligned to the acoustic onset of /z/. G, Electrode 122 is crucially involved in the production of /z/ with a coronal AKT, and has a high phonetic selectivity index for /z/. H, Average high gamma activity for electrode 122 during the productions of /æz/ and /iz/. Median high gamma is significantly higher for /æz/ than /iz/ (p<.05, Wilcoxon signed ranks tests). I, Average predicted high gamma activity predicted by AKT in G. Median predicted high gamma is significantly higher for /æz/ than /iz/ (p<.001, Wilcoxon signed ranks tests). J, Mixed-effect model shows relationship of high gamma with kinematic variability due to carryover coarticulatory effects of preceding phonemes for all electrodes (in all participants) and phonemes (β = 0.32, SE = 0.04, χ2(1) = 42.58, p = 6e–11). Relationships from H and I for /æz/ (green) and /iz/ (blue) are shown as points.
