Abstract
Background
Two days after myocardial infarction (MI), the infarct consists mostly on necrotic tissue, and the myocardium is transformed through granulation tissue to scar in two weeks after the onset of ischemia in mice. In the current work, we determined and optimized cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR) methods for the detection of MI size during the scar formation without contrast agents in mice.
Methods
We characterized MI and remote areas with rotating frame relaxation time mapping including relaxation along fictitious field in nth rotating frame (RAFFn), T1ρ and T2 relaxation time mappings at 1, 3, 7, and 21 days after MI. These results were compared to late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) and Sirius Red-stained histology sections, which were obtained at day 21 after MI.
Results
All relaxation time maps showed significant differences in relaxation time between the MI and remote area. Areas of increased signal intensities after gadolinium injection and areas with increased TRAFF2 relaxation time were highly correlated with the MI area determined from Sirius Red-stained histology sections (LGE: R2 = 0.92, P < 0.01, TRAFF2: R2 = 0.95, P < 0.001). Infarct area determined based on T1ρ relaxation time correlated highly with Sirius Red histology sections (R2 = 0.97, P < 0.01). The smallest overestimation of the LGE-defined MI area was obtained for TRAFF2 (5.6 ± 4.2%) while for T1ρ overestimation percentage was > 9% depending on T1ρ pulse power.
Conclusion
T1ρ and TRAFF2 relaxation time maps can be used to determine accurately MI area at various time points in the mouse heart. Determination of MI size based on TRAFF2 relaxation time maps could be performed without contrast agents, unlike LGE, and with lower specific absorption rate compared to on-resonance T1ρ relaxation time mapping.
Keywords: Cardiovascular magnetic resonance, Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), Myocardial infarction (MI), Relaxation time, TRAFF2, TRAFF4, T1ρ, T2, LGE, Sirius red staining
Background
Cardiovascular diseases are the leading causes of death worldwide [1, 2]. Myocardial infarction (MI) is caused by a complete or partial blockage of the coronary artery, leading to inflammation, arrhythmia, and prolonged absence of perfusion [3–8]. The formation of fibrosis and collagen together with the loss of myocytes can lead to harmful remodeling of the myocardium and finally heart failure [3–7, 9]. Perfusion deficits cause cell death via necrosis and increases in extracellular space, which increases the tissue free water content and affects water-macromolecular interactions [10]. MI is a dynamic process since further loss of myocytes may occur, and collateral angiogenesis may decrease the infarct volume as a function of time [4, 6]. Scar tissue eventually replaces the damaged myocytes within 1–2 weeks after MI [4].
Several cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR) methods, for example T2 and T1ρ relaxation time mappings and CMR spectroscopy, have been implemented to detect both acute and chronic MI [11–13]. Currently, the golden standard to detect chronic or irreversible injury using CMR is late gadolinium (Gd) enhancement (LGE). LGE creates a high contrast between normal myocardium and irreversible infarcted areas [11, 14, 15]. Contraindications for the use of Gd-based contrast agents are known Gd allergy and acute or chronic renal dysfunction [11, 16], which limit its clinical use.
Conventional transverse, or spin-spin, relaxation time, T2, shows the difference between acute and chronic MI [15, 17]. Edema in the acute infarct phase increases free water content, significantly affecting heart function and T2 relaxation time [12, 18]. Regions of acute MI can involve a mixture of tissue edema, hemorrhage, and inflammation, which leads to the underestimation of water movement in extracellular space and the overestimation of the infarct area in the T2 relaxation time map [15, 19].
Rotating frame relaxation times are used to characterize the relaxation during radiofrequency (RF) pulses. This differs from conventional T1 and T2 relaxations where relaxation occurs during free precession. Longitudinal rotating frame relaxation time, T1ρ, refers to relaxation along the RF field, which takes place typically during on-resonance RF irradiation. When RF irradiation is on-resonance and spins are locked along the RF field, the spins experience the RF field, instead of the main magnetic field. This leads to sensitivity of T1ρ to slow molecular motions with frequencies close to RF pulse frequency, which are typically in the range of 0.1 to 10 kHz in vivo. Comparatively, conventional T1 is sensitive for Larmor frequency of the main magnetic field (B0) which is typically in the range 10–500 MHz resembling high frequencies, i.e., fast molecular motions including the motion of free water. Increased T1ρ relaxation in MI has been associated with increased extracellular volume and alterations in proton exchange between water and macromolecules [11, 16]. Furthermore, T1ρ relaxation times are affected by macromolecule concentrations, viscosity, molecular weight and pH, since these factors change water mobility in tissue. Collectively, these factors affect molecular correlation times and therefore can explain T1ρ relaxation time increases in MI and other pathologies [16, 20]. Area with elevated T1ρ relaxation time show high correspondence with the MI area detected by LGE in mice [21] and in humans [11].
Specific absorption rate (SAR) often limits rotating frame relaxation measurements, especially in clinical settings, since high SAR may lead to tissue heating. One method to reduce SAR in rotating frame relaxation measurements is relaxation along a fictitious field (RAFF) in nth rotating frame (RAFFn) [22–24]. RAFFn is produced by nested sine amplitude and cosine frequency modulated RF pulses operating in a sub-adiabatic regime and RF waveforms become more complicated when n increases [22, 23]. A fast, sub-adiabatic sweep of the effective RF field produces a fictitious field, which forms a part of the final effective RF field and magnetization precesses around this effective field [22]. When n increases in RAFFn, the tolerance for B0 and radiofrequency field (B1) inhomogeneities increases [23]. Due to lower flip angles with increasing n, the pulse bandwidth increases significantly [24]. Amplitude and frequency modulations, increase of bandwidth, decrease of flip angle together with remarkably lower (approximately 80%) SAR-values of RAFF4 and (approximately 30%) SAR-values of RAFF2 compared to continuous wave spin lock (T1ρ) are clear advantages of RAFFn [22–24] and make RAFFn more suitable for clinical use than T1ρ.
In the current study, we have optimized infarct sizing using TRAFF2 and TRAFF4 relaxation time mappings. The results were compared with T1ρ and T2 relaxation time mappings, LGE and histology staining with Sirius Red.
Methods
Animal model
The left anterior descending artery (LAD) was ligated permanently in 10 female C57BL mice (20-24 g) as previously described [25]. Mice were anesthetized by 4% of isoflurane (Piramal Healthcare, Northumberland, UK), and anesthesia was maintained with 2.0% during the operation. The left side of mouse chest from sternum to Linea axillaris posterior was shaved and disinfected with 75% ethanol. An approximately 1.5 cm long transversal incision was made at the level of the fourth rib to left intercostal space. Through the incision and with help of a self-retaining retractor, the heart was exposed. The LAD was ligated with a 6.0 silk suture approximately at midway between its origin and the apex of the heart. After the LAD ligation, the heart was placed back to its original location. The skin were sutured in layers with 5.0 nylon suture. After the surgery, 0.05–0.1 mg/kg buprenorphine (0.3 mg/ml Temgesic, RB Pharmaceuticals, Slough, UK) and 5 mg/kg carprofen (50 mg/ml, Rimadyl, Pfizer Oy Animal Health, Helsinki, Finland) for analgesia were injected subcutaneously and repeated at days 1 and 2 after the surgery. All surgical procedures were performed according to protocols approved by the Finnish Committee for the use and care of laboratory animals.
CMR
Mice underwent CMR at 1 (n = 10), 3 (n = 9), 7 (n = 5) and 21 (n = 5) days after LAD occlusion. All experiments were performed using a horizontal 9.4 T magnet (Varian Inc. Palo Alto, California, USA) with a gradient set with maximum gradient strength of 600 mT/m and controlled by a Bruker console (Bruker GmbH, Ettlingen, Germany). Quadrature volume transceiver with a coil diameter of 35 mm (Rapid Biomed GmbH, Ettlingen, Germany) was used for all CMR experiments. Mice were anesthetized for CMR with 4% isoflurane mixed in oxygen and nitrogen with ratio of 1:3. The level of isoflurane was decreased to 1% for the imaging. Mouse body temperature was kept close to 37 °C by circulating warm water tubes placed under the mouse. Electrocardiography (ECG) was measured from fore paws using needle electrodes and a pneumatic pillow placed under the mouse monitored respiration. Both signals were registered using Model 1025 monitoring and gating system (Small Animal Instruments Inc., Stony Brook, New York, USA) during the experiments. Both ECG and respiration signals were used to gate CMR experiments.
Multi-slice cine images covering the whole heart were taken using fast imaging with balanced steady state precession (FISP) readout sequence. The imaging parameters for cine images were FOV = 4 × 4 cm2, slice thickness = 1 mm, matrix size = 192 × 192, TE = 1.9 ms, TR = 8.0 ms, scan TR = 99.0 ms, flip angle = 10° and number of frames 10–11 depending on mouse heart rate. Depending on the size of the heart, 8–10 slices were imaged.
The rotating frame preparation modules used to measure TRAFFn consisted of RAFF2 or RAFF4 pulses (pulses RF power (γB1/(2π)) 1250 Hz and 648 Hz, respectively, duration 2.26 ms) which were applied in pulse trains of lengths 0, 9.1, 18.1 and 36.2 ms. Before the RAFFn pulse train, a delay with durations of 36.2, 27.15, 18.1 and 0 ms, respectively, was added to adjust imaging to occur at the same cardiac phase for weightings with different durations. An illustration of a rotating frame preparation module and readout sequence is shown in Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.
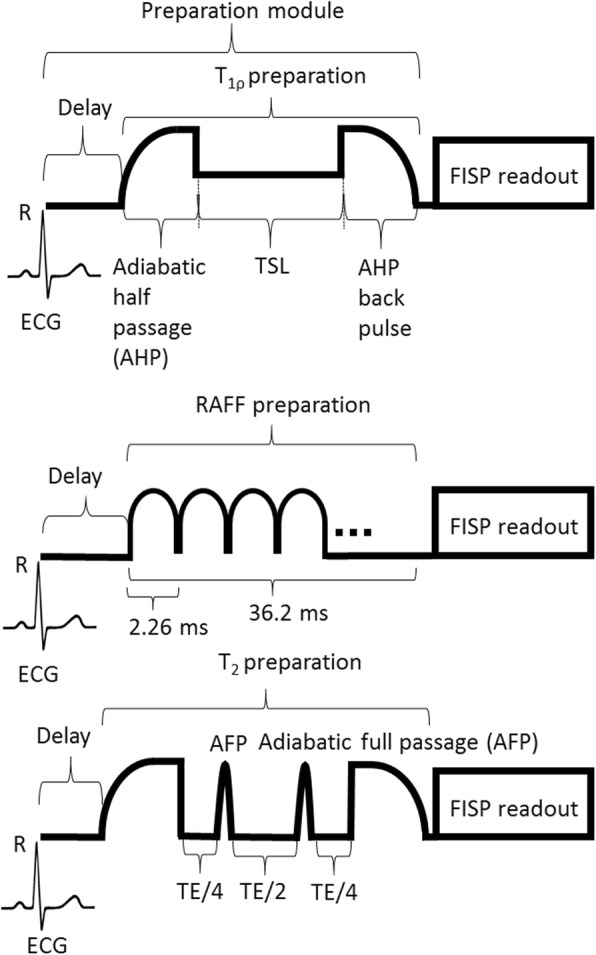
An illustration of CMR pulse sequences consisting of the preparation module for different weightings and FISP readout. ECG, electrocardiogram; TE, echo time
T1ρ preparation was performed using a rotating frame preparation module (Fig. 1) which contained adiabatic half passage (AHP) pulse (power 1250 Hz, duration 2.0 ms), continuous wave spin-lock-pulse with time-to-spin-lock (TSL) = 0.4, 9.4, 27.4 and 45.4 ms and AHP-back pulse (power 1250 Hz, duration 2.0 ms) [21]. Before T1ρ preparation a delay (45.4, 27.4, 9.4 and 0 ms, respectively to TSL) was added. T1ρ dispersion was measured by altering the spin lock power (γB1/(2π)) in a range of (400, 625 and 1250 Hz) and keeping AHP and AHP-back pulses the same.
T2 measurements were conducted using Hahn double echo preparation containing an AHP excitation-pulse (power 1250 Hz, duration 3.0 ms), two Hyperbolic Secant (HS1)-pulses (power 1250 Hz, duration 4.5 ms) and a reversed AHP-pulse (power 1250 Hz, duration 3.0 ms) (Fig. 1). Between the pulses symmetric delays were used resulting in total TEs of 0.05, 2.3, 4.5, and 14.0 ms. Delays in front of T2 preparation were 14.0, 4.5, 2.3 and 0.05 ms, respectively.
B1 was measured by applying a block pulse with power of 625 Hz. The B1 block pulse was applied with pulse durations 0, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 1.0, 1.25, 1.5 and 1.75 ms [26].
All relaxation time maps and B1 measurements were acquired using a FISP-readout sequence in a single short-axis slice at the mid-ventricular level. The following parameters: FOV = 4 × 4 cm2, slice thickness = 1 mm, matrix size = 256 × 256 (for B1 measurements, the matrix size was 128 × 128), TE = 1.9 ms, TR = 14.9 ms, and flip angle = 90° were used for the FISP-readout. A delay between weighting pulses depended on respiratory rate being at least 1460 ms.
At the last time point before sacrificing the mice, LGE images were acquired in the same slice as all other measurements using an inversion prepared pulse sequence with an inversion time of 300 ms, FISP-readout, FOV = 4 × 4 cm2, slice thickness = 1 mm, matrix size = 256 × 192, TE = 2.0 ms, TR = 5.6 ms, scan TR = 3000.0 ms and flip angle = 90° [27]. The gadobutrol (Gadovist, Bayern Oy, Turku, Finland) intravenous injection volume was 5 ml/kg per mouse.
Only five mice survived to 21 days and were sacrificed for histology after imaging. For histology, the hearts were perfused through the left ventricle with phosphate buffered saline and then immersion fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde with sucrose in phosphate buffered solution for 4 h. After 4 h, the hearts were placed into 15% sucrose. Paraffin-embedded, 4 μm thick, cross-sections of the heart were stained with Sirius Red to determine the fibrotic areas of the infarcted myocardium. Histological sections were analyzed and photographed with microscopy (Nikon Eclipse, Ni-E, Tokyo, Japan).
Data analysis
All relaxation time maps were reconstructed from signal intensities with pixel-by-pixel analysis using Aedes software package (http://aedes.uef.fi/) in Matlab platform (Mathworks Inc. Natick, Massachusetts, USA). T1ρ and T2 relaxation time maps were fitted using linear function for linearized data. TRAFF2 and TRAFF4 were fitted by using single mono-exponential decay function without taking into account the steady state formation. Regions of interest (ROIs) were manually traced with visual delineations of MI and remote areas based on relaxation time maps, cine images and images of Sirius Red-stained sections. End systolic volume (ESV), end diastolic volume (EDV), ejection fraction (EF), and cardiac output (CO) were defined based on endocardial border in cine images.
Infarct percentage analysis was done with midline length-based method with a function of (L(infarct)/ L(circumference))•100%, where L denotes measured length from either TRAFF2, TRAFF4, T1ρ, T2, LGE or Sirius Red-stained section [28]. Relative relaxation time difference (RRTD) values were calculated with function of (T(infarct) –T(remote))/ T(remote), where T denotes either TRAFF2, TRAFF4, T1ρ or T2 relaxation time.
Amount of overestimation (AOE) of infarct area relative to the LGE-defined MI area, as the gold standard, was calculated based on midline length-based method with a function of ((L(infarct) –LGE(infarct))/ L(infarct)) •100%, where L denotes either TRAFF2, TRAFF4, T1ρ or T2 relaxation time [29].
Statistics: All numerical values are given as mean ± standard deviation (SD). Two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc testing was applied to compare the spatial and temporal changes between the infarct and remote areas of myocardium, and the analyses were performed using GraphPad Prism software (GraphPad Software, La Jolla, California, USA). Two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc testing was performed to compare changes between RRTD values of different relaxation times. One-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc testing for multiple comparisons were applied to compare time point differences between relaxation times and also the differences between time points of cardiac functions.
Results
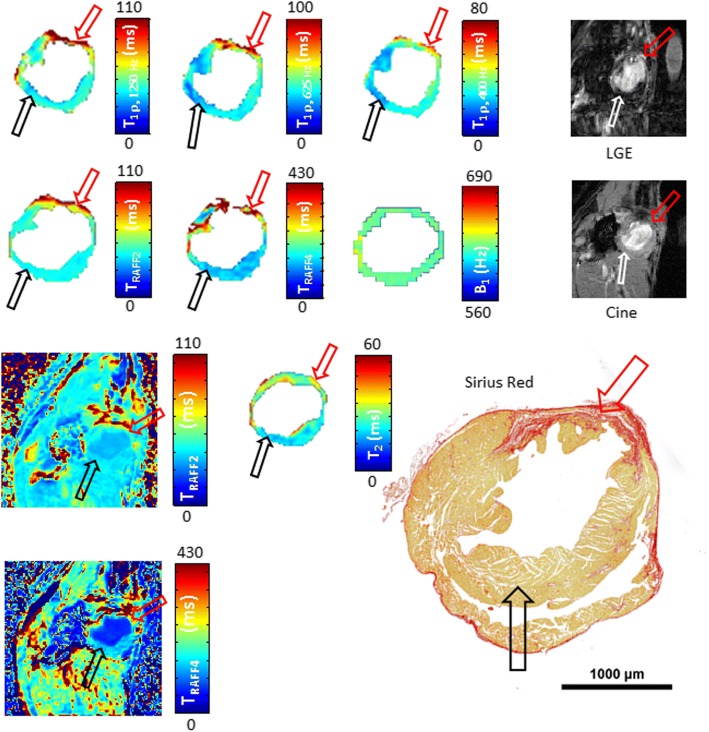
Increased relaxation time constants were found in the MI areas after LAD ligation. Infarct areas obtained with relaxation time mappings were compared with infarct areas derived based on LGE-images, cine-images and Sirius Red-stained histological sections (Fig. 2).
Fig. 2.
Relaxation time maps, late gadolinium enhancement (LGE), cine and a corresponding histology image with Sirius Red-stained section from infarcted mouse heart at the last (21 day) time point after left anterior descending (LAD) myocardial infarction (MI). Red arrows indicate the infarct area and black/white arrows show the remote control area. B1 homogeneity was verified to be nominal ±10% Hz in the area of the whole myocardium
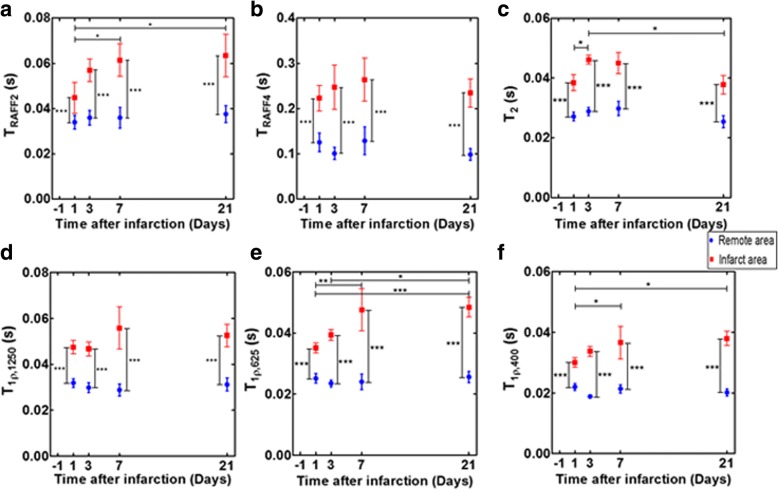
TRAFF2 relaxation times were significantly higher in the infarct areas compared to remote areas (P < 0.001) (Fig. 3a). TRAFF2 relaxation times in infarct area increased significantly up to 7 days and remained elevated until day 21 after the LAD ligation (P < 0.05, P < 0.05, respectively) (Fig. 3a). TRAFF4 relaxation time in the infarct area was significantly elevated at all time points compared to the remote area (P < 0.001, Fig. 3b). The remaining relaxation times (T1ρ1250, T1ρ625, T1ρ400 and T2) were significantly elevated in the infarct area compared to remote areas (P < 0.001, respectively), and there were significant differences, except in T1ρ1250, between time points (P < 0.05, respectively, Fig. 3c-f). Specifically, T1ρ625 relaxation times increased significantly in the infarct area at 7 days after the LAD ligation (P < 0.01) and remained elevated until day 21 (P < 0.001, Fig. 3e). There was a significant increase in T1ρ625 relaxation times in infarct area at days 7 and 21 compared to day 1 after the LAD occlusion (P < 0.05, P < 0.05 respectively), and it also increased significantly from day 3 to day 21 (P < 0.05, Fig. 3e). Additionally, the trend between infarct and remote areas in T1ρ625, T1ρ400 and T2 relaxation times differed significantly (P < 0.05, respectively) from each other (Fig. 3c, e, f). A decrease in T2 relaxation time was detected from day 3 to day 21 after the LAD ligation (P < 0.05, Fig. 3c).
Fig. 3.
Different relaxation times (mean ± SD). TRAFF2 (a), TRAFF4 (b), T2 (c), T1ρ1250 (d), T1ρ625 (e) and T1ρ400 (f) were calculated in infarct and remote areas at different time points after the LAD ligation. Blue circles indicate remote and red squares infarct area. (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001, Two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test)
There were no significant changes in the relaxation times in the remote areas between the imaging time points (P > 0.05, Fig. 3).
RRTD provided a measure of differences in relaxation time values between infarct and remote areas for the relaxation measurements (Table 1). RRTD values of TRAFF4 differed significantly from other relaxation time methods at several different time points (Table 1). There were significant differences in RRTD values of some of the T1ρ relaxation times when comparing RRTD values at day 1 (Table 1).
Table 1.
Relative relaxation time difference (RRTD) values formed by infarct and remote area relaxation times presented as mean ± SD
| Relaxation time constant | Day 1 | Day 3 | Day 7 | Day 21 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1ρ1250 | 0.49 ± 0.11□ | 0.60 ± 0.29□□□ | 0.91 ± 0.42* | 0.69 ± 0.16□□ |
| T1ρ625 | 0.41 ± 0.09□□ | 0.70 ± 0.27□□□ | 0.99 ± 0.44** | 0.90 ± 0.24* |
| T1ρ400 | 0.37 ± 0.09□□ | 0.79 ± 0.21**,□□ | 0.69 ± 0.33□ | 0.90 ± 0.27** |
| T2 | 0.41 ± 0.11□□ | 0.61 ± 0.19□□□ | 0.51 ± 0.11□□ | 0.50 ± 0.19□□□ |
| TRAFF2 | 0.41 ± 0.12□□ | 0.62 ± 0.43□□□ | 0.73 ± 0.22 | 0.66 ± 0.21□□ |
| TRAFF4 | 0.90 ± 0.45 | 1.36 ± 0.62 | 1.22 ± 0.59 | 1.39 ± 0.37 |
Significance of differences in RRTD values were calculated by Two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test (□=P<0.05, □□=P<0.01, □□□=P<0.001 for difference to TRAFF4 at that specific time point) and One-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test (*=P<0.05, **=P<0.01 for difference to day 1)
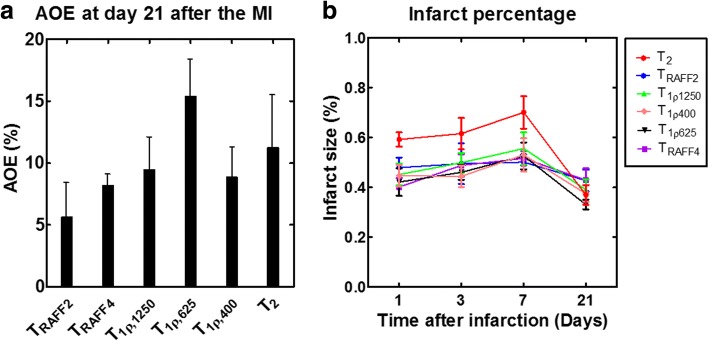
AOE values were determined for all relaxation times (Fig. 4a). AOE was lowest for TRAFF2 indicating that area of increased TRAFF2 is most similar to LGE-measured infarct area (Fig. 4a).
Fig. 4.
Amount of overestimation (AOE) with regard to the LGE-defined MI area based on the relaxation time maps at 21 days after infarct (a) and infarct percentages at every time point based on the relaxation time maps (b)
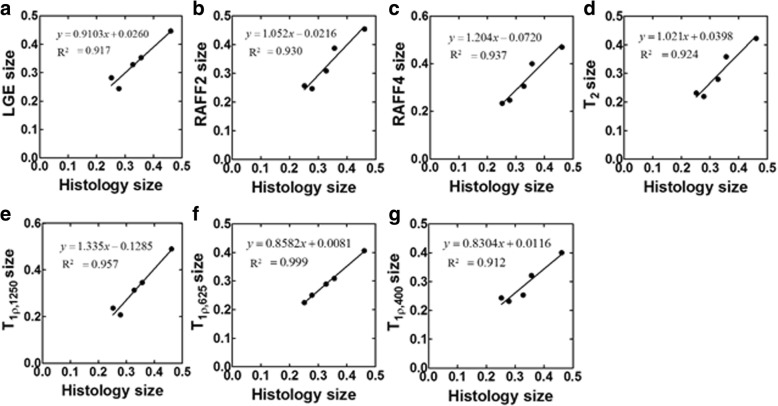
Infarct sizes were calculated also as a ratio between the arc of infarct and the circumference of the whole myocardium from relaxation time maps and LGE-images (Figs. 4b and 5). These infarct sizes were correlated with the ones measured based on Sirius Red-stained histology-images (Fig. 5). The highest Spearman correlations were obtained with T1ρ (R2 = 0.97, P < 0.01). Infarct sizes from TRAFF2 (R2 = 0.93, P < 0.001) and TRAFF4 (R2 = 0.94, P < 0.001) showed a high correlation as well as LGE (R2 = 0.92, P < 0.01) with infarct size from Sirius Red-stained sections (Fig. 5). The infarct fraction given as a percentage at early time points obtained from T2 relaxation time map was largest but decreased to similar percentages as obtained from the other relaxation time maps at day 21 (Fig. 4b).
Fig. 5.
Linear correlation from the ratios between the arc of infarct and the circumferences of the whole myocardium determined from LGE-image (a), TRAFF2 (b), TRAFF4 (c), T2 (d), T1ρ1250 (e), T1ρ625 (f), T1ρ400 (g) and Sirius Red-stained histology sections. Formulas of linear relationships are shown next to correlation line
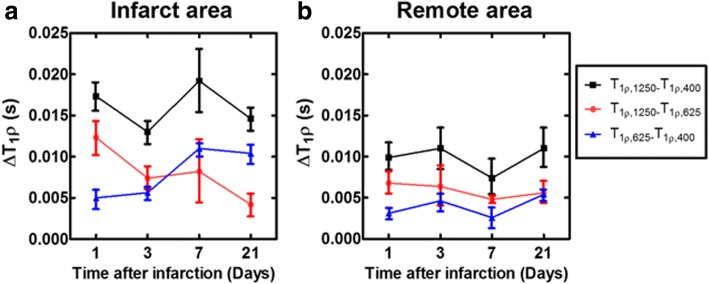
Dispersion of T1ρ relaxation times (ΔT1ρ) was calculated by subtracting T1ρ relaxation times measured with different spin lock powers (Fig. 6). Significant differences between different T1ρ relaxation times in infarct and remote areas were not found, and the difference in both areas remained almost constant between the time points (Fig. 6).
Fig. 6.
Dispersion of T1ρ relaxation time in infarct area (a) and in remote area (b). Red color shows subtraction between T1ρ1250 - T1ρ625, black color shows subtraction between T1ρ1250 - T1ρ400 and blue color shows subtraction between T1ρ625 - T1ρ400
Parameters of cardiac function indicate that MI has developed as a function of time (Table 2). Specifically EF decreased as a function of time and, three weeks after MI, EF had decreased to 0.35 (Table 2). Increased cardiac output between days 1 and 7 was found, although it was assumed to decrease (Table 2).
Table 2.
Values of cardiac function parameters which are presented as mean ± SD
| Cardiac function parameters | Day 1 | Day 3 | Day 7 | Day 21 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| End diastolic volume (mm3) | 48.4 ± 20.7 | 47.1 ± 24.6 | 72.9 ± 26.7 | 90.3 ± 30.2*,□ |
| End systolic volume (mm3) | 22.7 ± 13.0 | 21.9 ± 13.8 | 39.9 ± 17.6 | 58.0 ± 18.5**,□□ |
| Ejection Fraction (%) | 0.55 ± 0.12 | 0.56 ± 0.09 | 0.46 ± 0.09 | 0.35 ± 0.04**,□□ |
| Cardiac output (mm3) | 14,570 ± 3680 | 15,140 ± 5770 | 20,280 ± 8130* | 19,800 ± 8680 |
| Heart rate (bpm) | 580.2 ± 82.5 | 599.0 ± 64.9 | 615.5 ± 48.0 | 632.0 ± 52.3 |
Differences between time points of different cardiac measures were analyzed by One-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test (*=P<0.05 for difference to day 1) (□=P<0.05, □□=P<0.01 for difference to day 3)
Discussion
In this murine study, relaxation times were measured in infarct and remote areas at several time points after MI. Infarct size was measured based on different relaxation times, the results were compared to infarct sizes derived from CMR LGE-image and Sirius Red-stained histology sections. MI size from T1ρ, TRAFF2 and TRAFF4 relaxation time maps showed a high correlation with MI size determined based on Sirius Red-stained histology sections.
TRAFF2 relaxation times in infarct areas increased significantly from day 1 to day 21 after the LAD ligation and the RRTD values increased as a function of time. Differences between infarct and remote areas in TRAFF2 relaxation times were statistically significant. Low AOE-value obtained with TRAFF2 relaxation time demonstrate that elevated TRAFF2 denotes permanently damaged area. These findings together with a high correlation between TRAFF2 and histology derived infarct size, demonstrate that TRAFF2 relaxation time detects MI area with high accuracy. Previously, TRAFF2 relaxation time has been measured in a rat malignant glioma model where TRAFF2 showed a high correlation with decreased cell density in tumors [30]. Furthermore, cell density decreases in the infarct area as the tissue is replaced by fibrotic tissue, which leads to an increase of extracellular space [10]. Most likely, increase of TRAFF2 in both of these cases is caused by increases in extracellular space and, therefore, an increase in free water content. This suggest that fibrotic tissue can be differentiated healthy tissue using the TRAFF2 map. This is important since fibrosis detection also plays a central role in MI detection. Our results demonstrate the potential of TRAFF2 mapping to determine and accurately assess the MI area in both acute and chronic phase of the disease. Another explanation for elevated TRAFF2 is altered 1H chemical exchange between water and macromolecules due to changes induced by infarct in exchange of populations, exchange rates, or chemical shifts between exchanging sites [30]. The extracellular pH may also change in MI, which may induce alterations to exchange rates [30].
Our results showed that TRAFF4 relaxation times were elevated at all time points in the MI area and the difference between infarct and remote areas in TRAFF4 was significant. Our findings suggest that TRAFF4 relaxation time mapping can be applied to detect chronic MI since infarct size derived from TRAFF4 map correlated highly (R2 = 0.94, P < 0.001) with histology derived infarct area together with small AOE-value.
T1ρ1250 relaxation time determined at infarct area was significantly higher when compared to remote areas of the myocardium. In addition, infarct size derived from T1ρ1250 map correlated with infarct size from Sirius Red sections (R2 = 0.96, P < 0.01) and its AOE-value was close to zero. The largest RRTD between infarct and remote area was found with T1ρ625. Infarct size based on T1ρ625 and T1ρ400 relaxation time maps showed high correlations (R2 = 0.99, P < 0.001, R2 = 0.96, P < 0.05, respectively) with Sirius Red staining but T1ρ625 showed the largest AOE-value (15.4 ± 6.1%). T1ρ relaxation times have previously been known to be two times longer in scar tissue than in normal myocardium in porcine heart [16]. However, the origin of T1ρ increase at MI is still unclear. Most likely it is due to increased fibrosis content, cellularity, or 1H chemical exchange [11, 31]. In addition, there is a suggestion that leaking protein material from sarcolemma into extracellular space minimizes effects of proteins on water molecules or macromolecules in acute MI in patients and swine [10, 17]. Selective sensitivity to correlation times near to 1/(γB1) is an advantage of T1ρ relaxation time [21].
In a previous study, the T1ρ relaxation time with different spin-lock powers increased significantly 7 days after MI compared to the remote area [21] and T1ρ relaxation times elevated almost monotonically during 2 weeks after MI [21]. These findings were explained by granulation and scar tissue formation [11, 21]. Similar increase was detected in this study with T1ρs, TRAFF2, and TRAFF4.
T2 relaxation times increased significantly from day 1 to day 3 in infarct area and T2 relaxation times in infarct area were significantly higher than T2 relaxation times in remote area. These results are in line with previous findings showing that damaged area in myocardium is reversible in acute phase of MI [12, 18, 32]. It has previously been shown that T2 relaxation time overestimates the size of acute MI compared to chronic MI, since the inflammation and edema have resolved from the chronic MI [18]. Similar findings were observed in this study since infarct percentages based on T2 maps were higher as compared to percentages based on the other relaxation times at early time points. Therefore, increased T2 relaxation time shows the area of edema rather than the actual size of MI [18]. T2 relaxation times did not differ between day 1 and day 21, which suggests that part of the damage in myocardium was reversible without the scar formation. In a previous study, T2 relaxation times were significantly higher in acute MI area compared to chronic MI area [12].
The MI areas defined based on CMR images were in good agreement with the areas determined with Sirius Red-stained histology. To our knowledge, elevated relaxation times, at least T1ρ relaxation times, at 21 days after MI are due to fibrosis and scar tissue formation. The locations of fibrotic areas in Sirius Red-stained sections and the elevated relaxation times on relaxation time maps agreed well. Notable, our results are based on quantitative relaxation times instead of weighted images. These results also suggest that especially TRAFF2, TRAFF4 and T1ρ relaxation time mappings may be useful for broad range of clinical applications where myocardial tissue characterization is needed, for example in myocarditis, various size and locations of scars, sarcoidosis and hypertrophy. Operating at lower main magnetic field strengths will have some impact on rotating frame relaxation times; however, the main influence is the strength of the spin-lock power [33]. Water molecules with correlation times close to 1/(γB1) contribute to rotating frame contrasts [33]. Adaption of rotating frame measurements to MI characterization at clinics needs further study since we demonstrated advantages of relaxation times only in MI mouse model where one artery (LAD) was occluded.
MI area was detectable in all relaxation time maps and it was the most visible at day 21. At the first time points, the MI area was larger than at the later time points most likely due to inflammation surrounding the infarction area. In a mouse model, MI area consists of over 90% of necrotic tissue only two days after LAD ligation and the necrotic tissue is transformed into granulation tissue one week after MI and into scar two weeks after the LAD ligation [5].
The LAD ligations were successfully performed since our results show a clear visibility of infarct in Sirius Red-stained sections and decreased EF values as a function of time. Additionally, EDV and ESV tend to increase post MI due to changes in physiology of the myocardium. Changes in physiology with decreased perfusion inside the myocardium lead also to a decrease of EF as a function of time. Our EF values agreed with EF values reported in the literature [34, 35]. Increased EDV and ESV at day 21 compared to day 1 after MI resulted in an increased stroke volume (23%) which together with increased heart rate (8%) lead to increased cardiac output. The ventricular dilation after MI is typical [34, 35] and was also observed in our cine images. However, increased stroke volume after MI is rare [34, 35]. Differences in anesthesia level or mice increased tolerance to anesthetic during subsequent CMR exams might be the reasons for the increased heart rates.
Conclusions
All relaxation time maps showed high contrast between infarct and remote areas. T1ρ, TRAFF2 and TRAFF4 relaxation time maps correlated significantly with the infarct size determined by histology. As a conclusion, TRAFF2 and TRAFF4 relaxation time maps can be used to accurately determine infarct size in mouse myocardial infarct without the use of contrast agent with clinically tolerable specific absorption rates.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Maarit Pulkkinen for technical assistance. The authors thank Nicholas Downes for checking the language of the manuscript.
Funding
Sigrid Juselius foundation and University of Eastern Finland Doctoral Programme of Molecular Medicine.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- AHP
Adiabatic half passage
- AOE
Amount of overestimation
- CMR
Cardiovascular magnetic resonance
- CO
Cardiac output
- ECG
Electrocardiogram
- EDV
End-diastolic volume
- EF
Ejection fraction
- ESV
End-systolic volume
- Gd
Gadolinium
- LAD
Left anterior descending coronary artery
- LGE
Late gadolinium enhancement
- MI
Myocardial infarction
- RAFF
Relaxation along a fictitious field
- RF
Radiofrequency
- ROI
Region of interest
- RRTD
Relative relaxation time difference
- SAR
Specific absorption rate
- TSL
Time to spin lock
Authors’ contributions
Each author contributed significantly to the submitted work: EYH was involved in the design of the study, performed CMR measurements, performed data analysis, interpreted the data and drafted the manuscript. SL did LAD surgeries, histology and revised the manuscript. HL helped to design CMR measurements, helped in CMR measurements and revised the manuscript. TL designed the study and revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All surgical procedures were performed according to protocols approved by the Finnish Committee for the use and care of laboratory animals.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Elias Yla-Herttuala, Email: elias.yla-herttuala@uef.fi.
Svetlana Laidinen, Email: svetlana.laidinen@uef.fi.
Hanne Laakso, Email: hanne.laakso@uef.fi.
Timo Liimatainen, Phone: +358 44 550 5777, Email: timo.liimatainen@oulu.fi.
References
- 1.Ylä-Herttuala S, Bridges C, Katz MG, Korpisalo P. Angiogennic gene therapy in cardiovascular diseases: dream or vision? Eur Heart J. 2017;38:1365–1371. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehw547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Ylä-Herttuala S, Baker AH. Cardiovascular gene therapy: past, present, and future. Mol Ther. 2017;25:1095–1106. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2017.03.027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Blankesteijn WM, Creemers E, Lutgens E, Cleutjens JP, Daemen MJ, Smits JF. Dynamics of cardiac wound healing following myocardial infarction: observations in genetically altered mice. Acta Physiol Scand. 2001;173:75–82. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-201X.2001.00887.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Ertl G, Frantz S. Healing after myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc Res. 2005;66:22–32. doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2005.01.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Virag JI, Murry CE. Myofibroblast and endothelial cell proliferation during murine myocardial infarct repair. Am J Pathol. 2003;163:2433–2440. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63598-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Holmes JW, Yamashita H, Waldman LK, Covell JW. Scar remodeling and transmural deformation after infarction in the pig. Circulation. 1994;90:411–420. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.90.1.411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.McKay RG, Pfeffer MA, Pasternak RC, Markis JE, Come PC, Nakao S, Alderman JD, Ferguson JJ, Safian RD, Grossman W. Left ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction: a corollary to infarct expansion. Circulation. 1986;74:693–702. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.74.4.693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Frangogiannis NG, Smith CW, Entman ML. The inflammatory response in myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc Res. 2002;53:31–47. doi: 10.1016/S0008-6363(01)00434-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Gaudron P, Kugler I, Hu K, Bauer W, Eilles C, Ertl G. Time course of cardiac structural, functional and electrical changes in asymptomatic patients after myocardial infarction: their inter-relation and prognostic impact. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2001;38:33–40. doi: 10.1016/S0735-1097(01)01319-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Muthupillai R, Flamm SD, Wilson JM, Pettigrew RI, Dixon WT. Acute myocardial infarction: tissue characterization with T1ρ-weighted MR imaging - initial experience. Radiology. 2004;232:606–610. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2322030334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.van Oorschot JWM, El Aidi H, Jansen of Lorkeers SJ, Gho JM, Froeling M, Visser F, Chamuleau SA, Doevendans PA, Luijten PR, Lainer T, Zwanenburg JJ. Endogenous assessment of chronic myocardial infarction with T1ρ-mapping in patients. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2014;16:104–112. doi: 10.1186/s12968-014-0104-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Verhaert D, Thavendiranathan P, Giri S, Mihai G, Rajagopalan S, Simonetti OP, Raman SV. Direct T2 quantification of myocardial edema in acute ischemic injury. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2011;4:269–278. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2010.09.023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.de Roos A, van der Wall EE. Evaluation of ischemic heart disease by magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy. Radiol Clin N Am. 1994;32:581–592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Huber S, Muthupillai R, Lambert B, Pereyra M, Napoli A, Flamm SD. Tissue characterization of myocardial infarction using T1ρ: influence of contrast dose and time of imaging after contrast administration. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2006;24:1040–1046. doi: 10.1002/jmri.20720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Abdel-Aty H, Zagrosek A, Schultz-Menger J, Taylor AJ, Messroghli D, Kumar A, Gross M, Dietz T, Friedrich MG. Delayed enhancement and T2-weighted cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging differentiate acute from chronic myocardial infarction. Circulation. 2004;109:2411–2416. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000127428.10985.C6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Witschey WR, Zsido GA, Koomalsingh K, Kondo N, Minakawa M, Shuto T, McGarvey JR, Levack MM, Contijoch F, Pilla JJ, Gorman JH, 3rd, Gorman RC. In vivo chronic myocardial infarction characterization by spin locked cardiovascular magnetic resonance. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2012;14:37. doi: 10.1186/1532-429X-14-37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Witschey WR, Pilla JJ, Ferrari G, Koomalsingh K, Haris M, Himmon R, Zsido G, Gorman JH, 3rd, Gorman RC, Reddy R. Rotating frame spin lattice relaxation in a swine model of chronic, left ventricular myocardial infarction. Magn Reson Med. 2010;64:1453–1460. doi: 10.1002/mrm.22543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Abdel-Aty H, Simonetti O, Friedrich MG. T2-weighted cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2017;26:452–459. doi: 10.1002/jmri.21028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Reimer KA, Jennings RB. The changing anatomic reference base of evolving myocardial infarction. Underestimation of myocardial collateral blood flow and overestimation of experimental anatomic infarct size due to tissue edema, hemorrhage and acute inflammation. Circulation. 1979;60:866–876. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.60.4.866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Hakumäki JM, Gröhn OH, Tyynelä K, Valonen P, Ylä-Herttuala S, Kauppinen RA. Early gene therapy-induced apoptotic response in BT4C gliomas by magnetic resonance relaxation contrast T1 in the rotating frame. Cancer Gene Ther. 2002;9:338–345. doi: 10.1038/sj.cgt.7700450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Mustafa HSN, Dragneva G, Lottonen L, Merentie M, Petrov L, Heikura T, Ylä-Herttuala E, Ylä-Herttuala S, Gröhn O, Liimatainen T. Longitudinal rotating frame relaxation time measurements in infarcted mouse myocardium in vivo. Magn Reson Med. 2013;69:1389–1395. doi: 10.1002/mrm.24382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Liimatainen T, Sorce DJ, O’Donnell R, Michaeli S. MRI contrasts from relaxation along a fictitious field (RAFF) Magn Reson Med. 2010;64:983–994. doi: 10.1002/mrm.22372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Liimatainen T, Hakkarainen H, Mangia S, Huttunen JM, Storino C, Idiyatullin D, Sorce D, Garwood M, Michaeli S. MRI contrasts in high rank rotating frames. Magn Reson Med. 2015;73:254–262. doi: 10.1002/mrm.25129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Hakkarainen H, Sierra A, Mangia S, Garwood M, Michaeli S, Gröhn O, Liimatainen T. MRI relaxation in the presence of fictitious fields correlates with myelin content in normal rat brain. Magn Reson Med. 2016;75:161–168. doi: 10.1002/mrm.25590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Gao E, Lei YH, Shang X, Huang ZM, Zuo L, Boucher M, Fan Q, Chuprun JK, Ma XL, Koch WJ. A novel and efficient model of coronary artery ligation and myocardial infarction in the mouse. Circ Res. 2010;107:1445–1453. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.223925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Vaughan JT, Garwood M, Collins CM, Liu W, DelaBarre L, Adriany G, Andersen P, Merkle H, Goebel R, Smith MB, Urgurbil K. 7 T vs. 4 T: RF power, homogeneity, and signal-to-noise comparison in head images. Magn Reson Med. 2001;46:24–30. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Amano Y, Tachi M, Kumita S. Three-dimensional look-locker MRI for evaluation of postcontrast myocardial and blood T1 values: comparison with two-dimensional look-locker and late gadolinium enhancement MRI. Acta Radiol. 2013;54:8–13. doi: 10.1258/ar.2012.120378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Park C, Park EH, Chang K, Hong KS. Sector-based assessment of infarct size on late-gadolinium-enhancement MRI in a mouse model of acute myocardial infarction. Int Heart J. 2016;57:736–741. doi: 10.1536/ihj.16-052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Ugander M, Bagi PS, Oki AJ, Chen B, Hsu LY, Aletras AH, Shah S, Greiser A, Kellman P, Arai AE. Myocardial edema as detected by pre-contrast T1 andT2 CMR delineates area at risk associated with acute myocardial infarction. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2012;5:595–603. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2012.01.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Liimatainen T, Sierra A, Hanson T, Sorce DJ, Ylä-Herttuala S, Garwood M, Michaeli S, Gröhn O. Glioma cell density in a rat gene therapy model gauged by water relaxation rate along a fictitious magnetic field. Magn Reson Med. 2012;67:269–277. doi: 10.1002/mrm.22997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Kettunen MI, Sierra A, Närväinen MJ, Valonen PK, Ylä-Herttuala S, Kauppinen RA, Gröhn OH. Low spin-lock field T1 relaxation in the rotating frame as a sensitive MR imaging marker for gene therapy treatment response in rat glioma. Radiology. 2007;243:796–803. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2433052077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Bönner F, Jacoby C, Temme S, Borg N, Ding Z, Schrader J, Flögel U. Multifunctional MR monitoring of the healing process after myocardial infarction. Basic Res Cardiol. 2014;109:430. doi: 10.1007/s00395-014-0430-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Mäkelä HI, De Vita E, Gröhn OH, Kettunen MI, Kayec M, Lythgoe M, Garwood M, Ordidge R, Kauppinen RA. B0 dependence of the on-resonance longitudinal relaxation time in the rotating frame (T1rho) in protein phantoms and rat brain in vivo. Magn Reson Med. 2004;51:4–8. doi: 10.1002/mrm.10669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Haberkorn SM, Jacoby C, Ding Z, Keul P, Bönner F, Polzin A, Levkau B, Schrader J, Kelm M, Flögel U. Cardiocascular magnetic resonance relaxometry predicts regional functional outcome after experimental myocardial infarction. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2017;10:e006025. doi: 10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.116.006025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Nahrendorf M, Hiller KH, Hu K, Ertl G, Haase A, Bauer WR. Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging in small animal models of human heart failure. Med Image Anal. 2003;7:369–375. doi: 10.1016/S1361-8415(03)00011-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.