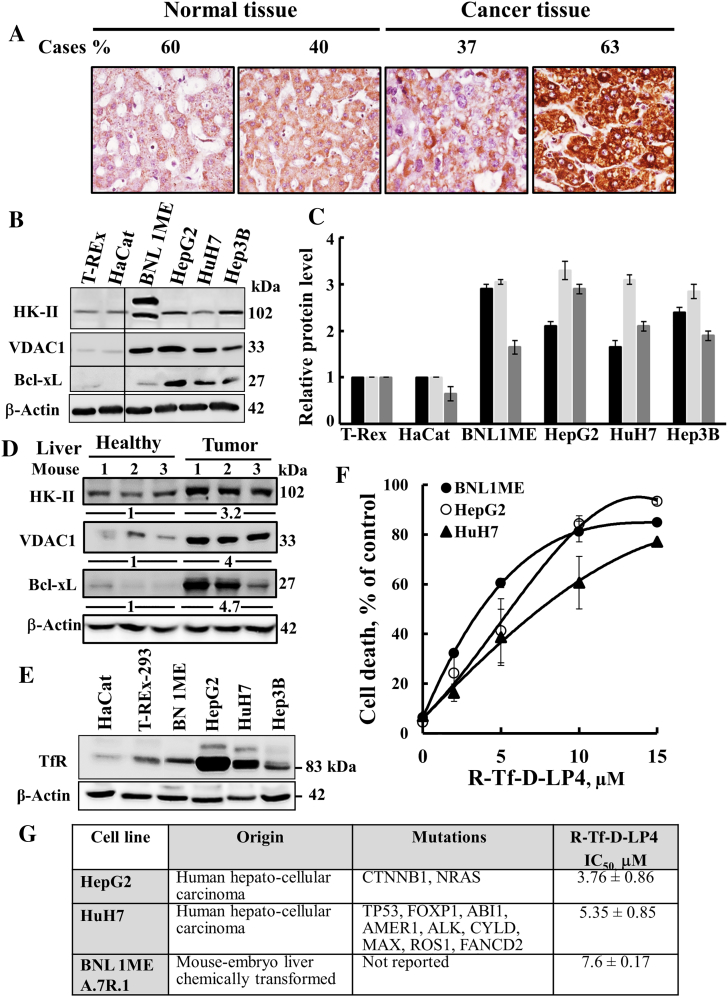
Figure 1.
VDAC1 is overexpressed in liver tumor and cancer cell lines, and cell death is inducted by the VDAC1-based peptide R-Tf-D-LP4.
(A) Tissue array (US Biomax) comprising human normal liver (n = 5) and liver cancer (n = 19) sections stained with anti-VDAC1 antibodies. Percentages of sections stained at the intensity indicated are shown. Immunoblot analysis of HK-II, VDAC1, and Bcl-xL (B) expression in noncancerous and liver cancer-derived cells. (C). The levels of HK-II (black bars), VDAC1 (light grey bars), and Bcl-xL (dark bars) in the indicated cell line are presented relative to their expression levels in the T-REx-293 cell line. (D) Immunoblot analysis of HK-II, VDAC1, and Bcl-xL expression in livers from healthy and DEN-treated mouse cancer-derived livers (n = 3). The fold increase in protein expression levels is also indicated. (E) Immunoblotting of TfR expression in noncancerous and liver cancer-derived cell lines. (F) R-Tf-D-LP4 effectively induced cell death of liver tumor cell lines. Human HepG2 (○), HuH7 (▲), and mouse BNL1MEA.7R.1 cells (●) were incubated for 6 hours with R-Tf-D-LP4, and cell death was analyzed as described in Materials and Methods. (G) IC50 values (μM) for peptide-induced apoptosis in liver tumor cell lines with the various indicated mutations [49]. Results show means ± SD (n = 3).