Abstract
The aim of this study was to Monitoring of physical and chemical characteristics of ground water including Ca2+, Mg2+, EC, pH, TDS, TH, , Na+, K+, Cl−, SAR, %Na and in Zanjan city, Iran. For assessing the physic-chemical parameters from 15 wells, water samples 4 times at different times were collected and examined. Data were analyzed using R and Arc GIS software. According to the calculated correlation coefficients, the highest correlation Coefficient belonged to TDS-EC while and Cl− showed low and weak correlations. However, Na+, Mg2+, K+, Ca2+ exhibited good positive correlations with EC and TDS. The results show that the water in the study area at the time of the study was based on the WHO standards and appropriate for drinking.
Keywords: Ground water, Zanjan, Iran
Specifications Table
| Subject area | Water chemistry |
| More specific subject area | Describe water subject area |
| Type of data | Table, Figure |
| How data was acquired | Analysis for Each sampling point was performed for 4 times at different times that included calcium, magnesium, chloride, temporary and permanent hardness, pH and electrical conductivity (EC). Sulfate analyzed by Hatch spectrophotometer (DR 5000). Total hardness was determined by EDTA method by titration method and TDS was measured gravimetrically. |
| Data format | Raw, Analyzed |
| Experimental features | The parameters mentioned in this paper have been analyzed according to Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater. |
| Data source location | Zanjan, Zanja province, Iran |
| Data accessibility | Data are included in this article and supplement file excel and ArcGIS |
Value of the data
-
•
Determination of the physical and chemical parameter including Ca2+, Mg2+, EC, pH, TDS, TH, , Na+, K+, Cl−, SAR, %Na and in ground water was conducted in Zanjan city, Iran.
-
•
Data of this study with Arc GIS can help to better understand the quality of groundwater in this area.
-
•
The results show that the water in the study area at the time of the study was based on the WHO standards and appropriate for drinking.
1. Data
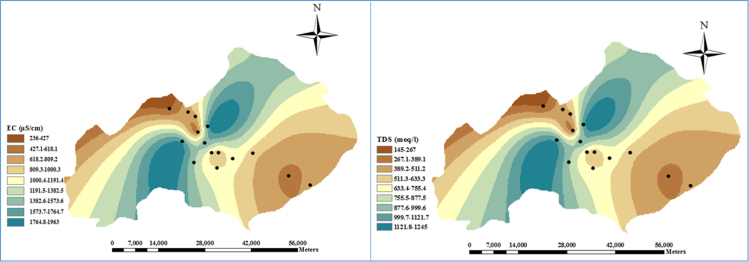
Monitoring of physical and chemical characteristics of ground water including Ca2+, Mg2+, EC, pH, TDS, TH, , Na+, K+, Cl−, SAR, %Na and was done in Zanjan city, Iran. In this regard data were analyzed using R and Arc GIS software. Table 1 summarizes analysis of the groundwater samples at the study area. Table 2 shows results of Pearson correlation matrix for 10 chemical constituents of the groundwater samples. The TDS and EC level in the study area depicted using the ArcGIS software, as shown in Fig. 1. In this figure, the brighter range represents fewer values, and the darker range is a large value.
Table 1.
Groundwater quality parameters analyzed in this study.
| Well no |
UTM |
EC (μmhos/cm | TDS (mg/l) | pH |
meq/l |
SAR | Na% | TH | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Utmy | Utmx | Cl− | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | Na+ | K+ | |||||||||
| P1 | 4074050 | 257400 | 236 | 145 | 7.77 | 1.64 | 0.25 | 0.415 | 1.4 | 0.44 | 0.42 | 0.01 | 0.44 | 18.60 | 92 |
| P 2 | 4064250 | 261300 | 1952 | 1245 | 7.47 | 4.28 | 4.08 | 10.44 | 5.95 | 6.18 | 6.80 | 0.06 | 2764 | 35.81 | 606.35 |
| P 3 | 4073050 | 263000 | 665 | 425 | 7.78 | 2.04 | 1.24 | 3.03 | 3.09 | 1.04 | 2.23 | 0.03 | 1553 | 34.88 | 206.95 |
| P 4 | 4057850 | 264850 | 1568 | 1005 | 7.45 | 3.72 | 1.93 | 9.33 | 4.27 | 3.75 | 7.09 | 0.06 | 3548.5 | 46.76 | 401.15 |
| P 5 | 4071800 | 265250 | 697.5 | 445 | 7.74 | 2.56 | 0.98 | 3.11 | 2.22 | 0.88 | 3.64 | 0.025 | 2923.5 | 53.80 | 154.95 |
| P 6 | 4067000 | 265900 | 518.5 | 325 | 7.84 | 2.56 | 0.78 | 1.61 | 2.87 | 0.9 | 1.23 | 0.02 | 0.8955 | 24.51 | 188.95 |
| P 7 | 4063750 | 268100 | 1747 | 1100 | 7.28 | 2.72 | 7.52 | 6.77 | 7.21 | 5.96 | 3.91 | 0.055 | 1059.7 | 19.68 | 658.5 |
| P 8 | 4068775 | 268950 | 1962 | 1245 | 7.3 | 5.36 | 4.73 | 8.8 | 9.28 | 4.02 | 5.73 | 0.07 | 2221 | 30 | 664.95 |
| P 9 | 4060825 | 270050 | 1039 | 665 | 7.73 | 2.96 | 1.32 | 5.61 | 4.77 | 1.14 | 4.07 | 0.03 | 2378.5 | 40.76 | 295.9 |
| P 10 | 4056200 | 271750 | 1040 | 665 | 7.79 | 3.52 | 1.67 | 4.74 | 3.47 | 1.21 | 5.35 | 0.025 | 3505.5 | 53.23 | 233.95 |
| P 11 | 4060850 | 272175 | 904 | 570 | 7.19 | 3.28 | 1.74 | 3.65 | 3.87 | 1.57 | 3.29 | 0.05 | 1996 | 37.5 | 272 |
| P 12 | 4059000 | 276500 | 1145 | 715 | 7.32 | 4.84 | 2.87 | 3.31 | 5.35 | 2.19 | 3.57 | 0.04 | 1834.5 | 31.91 | 377 |
| P 13 | 4060600 | 282475 | 889 | 560 | 7.49 | 4.28 | 1.75 | 2.52 | 4.29 | 1.56 | 2.75 | 0.03 | 1641 | 33.32 | 292.95 |
| P 14 | 4053850 | 293375 | 442.5 | 275 | 7.845 | 3.04 | 0.425 | 0.815 | 2.44 | 0.72 | 1.115 | 0.015 | 0.8895 | 26.045 | 157.95 |
| P 15 | 4051050.00 | 299800 | 538.33 | 336.67 | 7.72 | 2.93 | 0.90 | 1.33 | 2.40 | 0.95 | 1.87 | 0.02 | 1453.33 | 35.77 | 167.30 |
Table 2.
Pearson correlation matrix among the chemical constituents for the groundwater samples.
| Variables | K+ | Na+ | Mg2+ | Ca2+ | Cl− | TDS | EC | TH | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K | 1.00 | |||||||||
| Na+ | 0.81 | 1.00 | ||||||||
| Mg2+ | 0.90 | 0.70 | 1.00 | |||||||
| Ca2+ | 0.82 | 0.62 | 0.78 | 1.00 | ||||||
| 0.90 | 0.93 | 0.84 | 0.75 | 1.00 | ||||||
| Cl | 0.78 | 0.51 | 0.88 | 0.86 | 0.66 | 1.00 | ||||
| 0.60 | 0.61 | 0.46 | 0.71 | 0.54 | 0.42 | 1.00 | ||||
| TDS | 0.94 | 0.87 | 0.91 | 0.89 | 0.95 | 0.83 | 0.67 | 1.00 | ||
| EC | 0.94 | 0.87 | 0.91 | 0.89 | 0.94 | 0.83 | 0.67 | 0.99 | 1.00 | |
| TH | 0.91 | 0.70 | 0.93 | 0.94 | 0.84 | 0.92 | 0.63 | 0.95 | 0.96 | 1.00 |
Fig. 1.
The amount of EC and TDS in the samples studied.
2. Experimental design, materials and methods
2.1. Study area description
Zanjan is the capital of Zanjan province in Iran and located about 80 miles south from the Caspian Sea. That coordinates are 36°40′27.6204″N and 48°29′4.0812″E. 15 wells were selected as sampling points. Study area and the sampling points are shown and in Fig. 2.
Fig. 2.
The map and location of sampling points of Zanjan city,Zanjan,Iran.
2.2. Materials and methods
For assessing the physicochemical parameters, from 15 wells, water samples 4 times at different times during the year were collected from Zajan city in 2016. Analysis included calcium, magnesium, chloride, temporary and permanent hardness, pH and electrical conductivity (EC) [1], [2], [3], [4], [5]. Sulfate analyzed by Hatch spectrophotometer (DR 5000) [6], [7], [8], [9], [10]. Total hardness was determined by EDTA method by titration method and TDS was measured gravimetrically. All of parameters in this paper have been analyzed according to handbook of Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater [1], [2], [3], [4], [5], [6], [7], [8], [9], [10], [11], [12]. Since a simple a method for evaluating the changes of high sodium is the Sodium Adsorption Ratio (SAR) and the sodium percentage (Na %).The excess concentration of sodium in groundwater creates adverse effects as it reacts with the soil and decreases soil permeability and influences plant growth. Sodium percentage is also widely used to evaluate the suitability of water quality for irrigation. The percentage of sodium solution is calculated from the following formula [2] (Table 3).
Table 3.
sodium percentage (Na%) in present study.
| Parameter | Range | Water class |
|---|---|---|
| Na% | < 20 | Excellent |
| 20–40 | Good | |
| 40–60 | Permissible | |
| 60–80 | Doubtful | |
| > 80 | Unsuitable |
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Iran for their support.
Footnotes
Supplementary data associated with this article can be found in the online version at doi:10.1016/j.dib.2018.03.059.
Transparency document. Supplementary material
Supplementary material
.
References
- 1.Soleimani H., Abbasnia A., Yousefi M., Mohammadi A.A., Changani Khorasgani F. Data on assessment of groundwater quality for drinking and irrigation in rural area Sarpol-e Zahab city, Kermanshah province, Iran. Data Breif. 2018;17:528–531. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2017.12.061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Yousefi M., Najafi Saleh H., Mohammad A.A., Mahvi A.H., Ghadrpoori M., Suleimani H. Data on water quality index for the groundwater in rural area Neyshabur County, Razavi province, Iran. Data Brief. 2017;15:901–907. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2017.10.052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Yousefi M., Dehghani M.H., Nasab S.M., Taghavimanesh V., Nazmara S., Mohammadi A.A. Data on trend changes of drinking groundwater resources quality: a case study in Abhar. Data Brief. 2018 doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2018.01.032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Mohammadi A.A., Yousefi M., Mahvi A.H. Fluoride concentration level in rural area in Poldasht city and daily fluoride intake based on drinking water consumption with temperature. Data Brief. 2017;13:312–315. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2017.05.045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Abbasnia A., Alimohammadi M., Mahvi A.H., Nabizadeh R., Yousefi M., Mohammadi A.A., Pasalari H., Mirzabeigi M. Assessment of groundwater quality and evaluation of scaling and corrosiveness potential of drinking water samples in villages of Chabahr city, Sistan and Baluchistan province in Iran. Data Brief. 2018;16:182–192. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2017.11.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Asghari F.B., Mohammadi A.A., Aboosaedi Z., Yaseri M., Yousefi M. Data on fluoride concentration levels in cold and warm season in rural area of Shout (West Azerbaijan, Iran) Data Brief. 2017;15:528–531. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2017.10.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Yousefi M., Mohammadi A.A., Yaseri M., Mahvi A.H. Epidemiology of fluoride and its contribution to fertility, infertility, and abortion: an ecological study in West Azerbaijan Province, Poldasht County, Iran. Fluoride. 2017;50:343–353. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Yousefi M., Ghoochani M., Mahvi A.H. Health risk assessment to fluoride in drinking water of rural residents living in the Poldasht city, Northwest of Iran. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018;148:426–430. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.10.057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Yousefi M., Saleh H.N., Yaseri M., Mahvi A.H., Soleimani H., Saeedi Z. Data on microbiological quality assessment of rural drinking water supplies in Poldasht county. Data Brief. 2018 doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2018.02.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Asghari F.B., Jaafari J., Yousefi M., Mohammadi A.A., Dehghanzadeh R. Evaluation of water corrosion, scaling extent and heterotrophic plate count bacteria in asbestos and polyethylene pipes in drinking water distribution system. Human. Ecol. Risk Assess.: Int. J. 2018:1–12. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Yousefi M., Saleh H.N., Mahvi A.H., Alimohammadi M., Nabizadeh R., Mohammadi A.A. Data on corrosion and scaling potential of drinking water resources using stability indices in Jolfa, East Azerbaijan, Iran. Data Brief. 2018;16:724–731. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2017.11.099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Mohammadi A.A., Yaghmaeian K., Faraji H., Nabizadeh R., Dehghani M.H., Khaili J.K., Mahvi A.H. Temporal and spatial variation of chemical parameter concentration in drinking water resources of Bandar-e Gaz City using geographic information system. Desalination Water Treat. 2017;68:170–176. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary material