The title iron(II)–porphyrin complex possesses inversion symmetry with the metal atom located on a center of symmetry. The iron(II) atom is coordinated in a symmetric octahedral geometry by four pyrrole N atoms of the porphyrin ligand in the equatorial plane and two N atoms of 1-ethylimidazole ligands in the axial sites. The dihedral angle between the 1-ethylimidazole plane and the plane of the closest Fe—Np vector is 24.5(?)°.
Keywords: crystal structure, C—H⋯π interaction, 1-ethylimidazole, iron(II)
Abstract
The title complex, [Fe(C44H28N4)(C5H8N2)2]·C4H8O, possesses inversion symmetry with the iron(II) atom located on a center of symmetry. The metal atom is coordinated in a symmetric octahedral geometry by four pyrrole N atoms of the porphyrin ligand in the equatorial plane and two N atoms of 1-ethylimidazole ligands in the axial sites; the complex crystallizes with a tetrahydrofuran solvent molecule. The average Fe—Np (Np is a porphyrin N atom) bond length is 1.995 (3) Å and the axial Fe—NIm (NIm is an imidazole N atom) bond length is 1.994 (2) Å. The two 1-ethylimidazole ligands are mutually parallel. The dihedral angle between the 1-ethylimidazole plane and the plane of the closest Fe—Np vector is 24.5°. In the crystal, the only significant intermolecular interactions present are C—H⋯π interactions.
Chemical context
Bis-histidine coordinated hemes are present in various cytochrome b complexes, and are known to be involved in electron-transfer processes (Xia et al., 1997 ▸). As models of these six-coordinate heme complexes, a number of single-crystal structures of [Fe(II,III)(Porph)(L)2]0,+ (Porph is a porphyrinato ligand and L is a N-donor imidazole ligand) have been reported (Walker, 2004 ▸). The first ferrous porphyrin crystal structure with two 1-ethylimidazole ligands is [FeII(TpivPP)(1-EtIm)2]·0.5C7H8 [TpivPP = α,α,α,α-tetrakis(o-pivalamidophenyl)porphyrinato; 1-EtIm = 1-ethylimidazole], which was reported by Li and co-workers (Li et al., 2008 ▸). Later, another analogue of [FeII(TFPPBr8)(1-EtIm)2] [TFPPBr8 = 2,3,7,8,12,13,17,18-octabromo-5,10,15,20-tetrakis(pentafluorophenyl)πorphyrinato] was reported (Hu et al., 2016 ▸). Herein, we report the structural properties of the iron(II)–porphyrin complex [FeII(TPP)(1-EtIm)2]·THF where the metal center is likewise octahedrally coordinated.
Structural commentary
The asymmetric unit of the title compound (Fig. 1 ▸), contains half of an FeII porphyrin complex, with the iron(II) atom located on an inversion center, an 1-ethylimidazole ligand molecule, and half of a THF solvent molecule. The THF molecule is disordered over two positions; the site occupancy factors (SOFs) of the two disordered moieties being 0.35 and 0.15. The two 1-ethylimidazole ligands of [FeII(TPP)(1-EtIm)2] are mutually parallel, as required by the crystal symmetry. Additional quantitative information about the structure is displayed in Fig. 2 ▸, which includes the displacement of each porphyrin core atom (in units of 0.01 Å) from the 24-atom mean plane. The orientation of the 1-ethylimidazole ligand including the value of the dihedral angles is also given. As can be seen in Fig. 2 ▸, the porphyrin core of [FeII(TPP)(1-EtIm)2] is near-planar and the iron(II) atom is in the 24-atom plane. The displacements of every porphyrin core atom is less than 0.06 Å.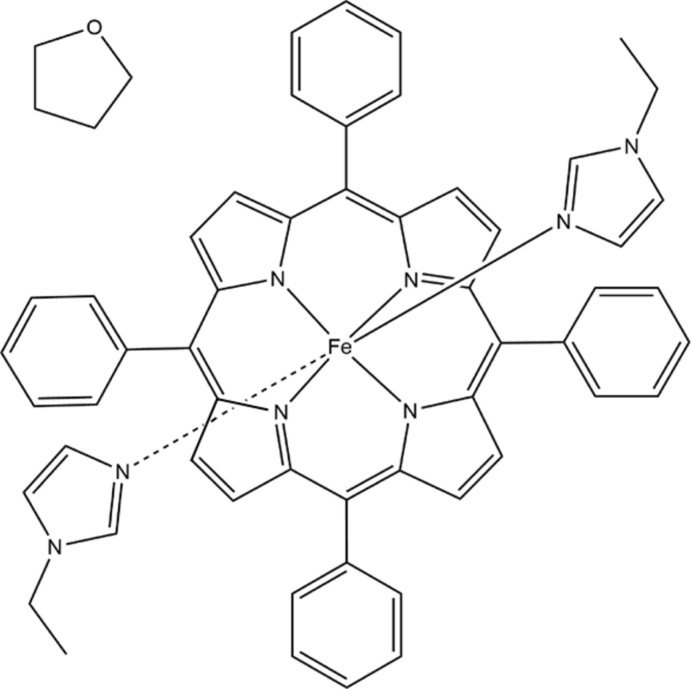
Figure 1.
The molecular structure of the title complex, with displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 50% probability level. The disordered THF molecule has been omitted for clarity, and unlabelled atoms are related to labelled atoms by the inversion symmetry code: (i) −x, −y + 1, −z + 1.
Figure 2.
Formal diagram of the porphyrinate core of [FeII(TPP)(1-EtIm)2]. Averaged values of the chemically unique bond distances (in Å) and angles (in °) are shown. The numbers in parentheses are the e.s.d.’s calculated on the assumption that the averaged values were all drawn from the same population. The perpendicular displacements (in units of 0.01 Å) of the porphyrin core atoms from the 24-atom mean plane are also displayed. Positive values of the displacement are towards the hindered porphyrin side, the solid line and dashed line indicate the plane of imidazole on the unhindered porphyrin side.
The average Fe—Np bond length of 1.995 (3) Å is similar to 1.993 (6) Å in [FeII(TpivPP)(1-EtIm)2] (Li et al., 2008 ▸) and 1.994 (10) Å in [FeII(TFPPBr8)(1-EtIm)2] (Hu et al., 2016 ▸), which are typical values for six-coordinated low-spin (porphinato)iron(II) derivatives (Scheidt et al., 1981 ▸). The axial Fe—NIm bond length is 1.994 (2) Å. The average Np—Fe—Np angle is ideal at 90.00 (6)°. The dihedral angle between the 1-ethylimidazole plane and the plane of the closest Fe—Np vector is 24.5°.
Supramolecular features
In the title compound, as shown in Fig. 3 ▸, the distance between the hydrogen atom H14B (C14) of the ethyl group of 1-EtIm and the pyrrole plane of the neighboring porphyrin is 2.66 Å, smaller than 2.9 Å, which is a limit suggested for the existence of a C—H⋯π interaction (Takahashi et al., 2001 ▸). Details of this interaction are given in Table 1 ▸. The molecular packing is shown in Fig. 4 ▸.
Figure 3.
The C—H⋯π interactions in the title compound. Dashed lines show the distances between H atoms of 1-ethylimidazole and the pyrrole core planes. Solvent (THF) molecules and other H atoms have been omitted for clarity.
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
Cg is the centroid of the N2/C7–C10 ring.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C14—H14B⋯Cg i | 0.99 (4) | 2.69 (4) | 3.437 (3) | 133 (2) |
Symmetry code: (i)  .
.
Figure 4.
A view along the a axis of the molecular packing of the title compound. H atoms have been omitted for clarity.
Synthesis and crystallization
4.1 General information. All reactions were done using standard Schlenk techniques unless otherwise specified. All solvents were freeze/pump/thaw/degassed prior to use. Benzene and tetrahydrofuran (THF) were refluxed in the presence of sodium and benzophenone under argon until the solution was blue. Hexanes was distilled from sodium/potassium alloy under argon. Ethanethiol and 1-ethylimidazole were distilled under an argon atmosphere. (H2TPP), [Fe(TPP)Cl] and [Fe(TPP)]2O were prepared according to the literature method (Adler et al., 1967 ▸, 1970 ▸; Fleischer & Srivastava, 1969 ▸).
4.2 Synthesis of bis(1-ethyl-1 H -imidazole-κ N 3)(5,10,15,20-tetraphenylporphyrinato-κ4 N )iron(II) tetrahydrofuran monosolvate
The purple powder [Fe(TPP)]2O (15.9 mg, 0.018 mmol) was dried in vacuum for 1 h in a Schlenk tube. Benzene (∼5 ml) was transferred into the Schlenk tube by cannula and ethanethiol (2 ml, 0.028 mol) was added via syringe. The mixture was stirred under argon at ambient temperature. After 36 h, the reduction was complete and the solvent was evaporated by pump. THF (∼5 ml) was transferred into the Schlenk tube via a cannula, and 1-ethylimidazole (0.5 ml, 5.19 mmol) was added using a syringe. Hexanes were then allowed to diffuse slowly into the reaction solution. After several weeks purple block-shaped crystals of the title compound were obtained.
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 2 ▸. The hydrogen atoms (H14A, H14B) attached to atom C14 of the 1-ethylimidazole ligand were located in a difference-Fourier map and refined freely. All other hydrogen atoms were placed in calculated positions (C—H = 0.95, 0.98 and 0.99 Å for aryl, methyl and methlyene H atoms, respectively) and refined using a riding model with U iso(H) = 1.5U eq(C) for methyl H atoms or U iso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C) otherwise. The C—O, C—C, C⋯C distances in the disordered THF molecule were constrained to 1.42 (1), 1.50 (1) and 1.55 (1) Å, respectively. Six atoms (C30A, C28B, C29B, C30B, C31B, O1B) of the THF solvent molecule exhibited unusual thermal motion and were restrained by a SIMU command. Five outlier reflections were omitted in the final cycles of refinement.
Table 2. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | [Fe(C44H28N4)(C5H8N2)2]·C4H8O |
| M r | 932.92 |
| Crystal system, space group | Triclinic, P

|
| Temperature (K) | 100 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 9.2962 (3), 10.7051 (4), 13.4920 (5) |
| α, β, γ (°) | 79.809 (1), 76.034 (1), 75.933 (1) |
| V (Å3) | 1253.90 (8) |
| Z | 1 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.35 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.26 × 0.17 × 0.08 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Bruker D8 QUEST System |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2014 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.931, 0.972 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 19292, 5147, 4542 |
| R int | 0.044 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.626 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.058, 0.167, 1.11 |
| No. of reflections | 5147 |
| No. of parameters | 386 |
| No. of restraints | 113 |
| H-atom treatment | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 1.53, −0.47 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018006308/qm2123sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018006308/qm2123Isup2.hkl
CCDC reference: 1839313
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the CAS Hundred Talent Program and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant No.21371167, to JL).
supplementary crystallographic information
Crystal data
| [Fe(C44H28N4)(C5H8N2)2]·C4H8O | Z = 1 |
| Mr = 932.92 | F(000) = 490 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.235 Mg m−3 |
| a = 9.2962 (3) Å | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| b = 10.7051 (4) Å | Cell parameters from 9016 reflections |
| c = 13.4920 (5) Å | θ = 2.4–26.4° |
| α = 79.809 (1)° | µ = 0.35 mm−1 |
| β = 76.034 (1)° | T = 100 K |
| γ = 75.933 (1)° | Block, purple |
| V = 1253.90 (8) Å3 | 0.26 × 0.17 × 0.08 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker D8 QUEST System diffractometer | 4542 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | Rint = 0.044 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 26.4°, θmin = 2.5° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2014) | h = −11→11 |
| Tmin = 0.931, Tmax = 0.972 | k = −13→13 |
| 19292 measured reflections | l = −16→16 |
| 5147 independent reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | 113 restraints |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: mixed |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.058 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| wR(F2) = 0.167 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0784P)2 + 2.6414P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.11 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 5147 reflections | Δρmax = 1.53 e Å−3 |
| 386 parameters | Δρmin = −0.46 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > 2sigma(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | Occ. (<1) | |
| Fe1 | 0.0000 | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | 0.00924 (16) | |
| N3 | 0.1978 (2) | 0.5561 (2) | 0.45844 (17) | 0.0121 (4) | |
| N4 | 0.3804 (2) | 0.6544 (2) | 0.45874 (17) | 0.0138 (5) | |
| N1 | 0.0234 (2) | 0.4581 (2) | 0.35771 (16) | 0.0118 (4) | |
| N2 | 0.1056 (2) | 0.3198 (2) | 0.54207 (16) | 0.0108 (4) | |
| C1 | −0.1057 (3) | 0.6676 (3) | 0.2771 (2) | 0.0130 (5) | |
| C2 | −0.0246 (3) | 0.5395 (3) | 0.2750 (2) | 0.0141 (5) | |
| C3 | 0.0205 (3) | 0.4727 (3) | 0.1849 (2) | 0.0205 (6) | |
| H3 | 0.0037 | 0.5084 | 0.1180 | 0.025* | |
| C4 | 0.0910 (3) | 0.3506 (3) | 0.2132 (2) | 0.0196 (6) | |
| H4 | 0.1318 | 0.2835 | 0.1704 | 0.024* | |
| C5 | 0.0927 (3) | 0.3410 (3) | 0.3208 (2) | 0.0137 (5) | |
| C6 | 0.1548 (3) | 0.2286 (2) | 0.3780 (2) | 0.0127 (5) | |
| C7 | 0.1616 (3) | 0.2208 (2) | 0.4811 (2) | 0.0120 (5) | |
| C8 | 0.2351 (3) | 0.1062 (3) | 0.5377 (2) | 0.0147 (5) | |
| H8 | 0.2822 | 0.0254 | 0.5126 | 0.018* | |
| C9 | 0.2248 (3) | 0.1346 (3) | 0.6327 (2) | 0.0144 (5) | |
| H9 | 0.2643 | 0.0783 | 0.6871 | 0.017* | |
| C10 | 0.1421 (3) | 0.2673 (2) | 0.6363 (2) | 0.0114 (5) | |
| C11 | 0.2390 (3) | 0.6380 (3) | 0.5032 (2) | 0.0152 (5) | |
| H11 | 0.1767 | 0.6800 | 0.5598 | 0.018* | |
| C12 | 0.3189 (3) | 0.5190 (3) | 0.3805 (2) | 0.0168 (5) | |
| H12 | 0.3230 | 0.4604 | 0.3340 | 0.020* | |
| C13 | 0.4321 (3) | 0.5794 (3) | 0.3804 (2) | 0.0183 (6) | |
| H13 | 0.5283 | 0.5710 | 0.3346 | 0.022* | |
| C14 | 0.4615 (3) | 0.7433 (3) | 0.4831 (2) | 0.0193 (6) | |
| H14A | 0.454 (4) | 0.818 (3) | 0.431 (3) | 0.021 (8)* | |
| H14B | 0.570 (4) | 0.701 (3) | 0.468 (3) | 0.024 (9)* | |
| C15 | 0.4039 (3) | 0.7774 (3) | 0.5914 (2) | 0.0204 (6) | |
| H15A | 0.2967 | 0.8210 | 0.6004 | 0.031* | |
| H15B | 0.4627 | 0.8354 | 0.6041 | 0.031* | |
| H15C | 0.4148 | 0.6980 | 0.6403 | 0.031* | |
| C16 | −0.1574 (3) | 0.7373 (3) | 0.1816 (2) | 0.0153 (5) | |
| C17 | −0.1145 (4) | 0.8526 (3) | 0.1325 (2) | 0.0235 (6) | |
| H17 | −0.0500 | 0.8880 | 0.1596 | 0.028* | |
| C18 | −0.1651 (4) | 0.9162 (3) | 0.0440 (2) | 0.0304 (7) | |
| H18 | −0.1365 | 0.9956 | 0.0122 | 0.037* | |
| C19 | −0.2562 (4) | 0.8655 (3) | 0.0023 (2) | 0.0307 (8) | |
| H19 | −0.2888 | 0.9087 | −0.0588 | 0.037* | |
| C20 | −0.2998 (4) | 0.7512 (3) | 0.0498 (2) | 0.0265 (7) | |
| H20 | −0.3630 | 0.7159 | 0.0214 | 0.032* | |
| C21 | −0.2516 (3) | 0.6879 (3) | 0.1388 (2) | 0.0194 (6) | |
| H21 | −0.2830 | 0.6098 | 0.1711 | 0.023* | |
| C22 | 0.2182 (3) | 0.1072 (3) | 0.3273 (2) | 0.0138 (5) | |
| C23 | 0.3640 (3) | 0.0857 (3) | 0.2667 (2) | 0.0156 (5) | |
| H23 | 0.4234 | 0.1495 | 0.2557 | 0.019* | |
| C24 | 0.4230 (3) | −0.0285 (3) | 0.2222 (2) | 0.0195 (6) | |
| H24 | 0.5230 | −0.0426 | 0.1815 | 0.023* | |
| C25 | 0.3368 (3) | −0.1223 (3) | 0.2370 (2) | 0.0210 (6) | |
| H25 | 0.3771 | −0.1998 | 0.2059 | 0.025* | |
| C26 | 0.1915 (4) | −0.1018 (3) | 0.2975 (2) | 0.0230 (6) | |
| H26 | 0.1324 | −0.1659 | 0.3084 | 0.028* | |
| C27 | 0.1325 (3) | 0.0123 (3) | 0.3422 (2) | 0.0201 (6) | |
| H27 | 0.0329 | 0.0259 | 0.3834 | 0.024* | |
| O1A | 0.6922 (6) | 0.1716 (5) | 0.1646 (4) | 0.0128 (6) | 0.35 |
| C29A | 0.8416 (9) | 0.3157 (7) | 0.0625 (5) | 0.0124 (7) | 0.35 |
| H29A | 0.9472 | 0.3111 | 0.0233 | 0.015* | 0.35 |
| H29B | 0.8013 | 0.4026 | 0.0856 | 0.015* | 0.35 |
| C28A | 0.8331 (9) | 0.2105 (7) | 0.1517 (5) | 0.0127 (7) | 0.35 |
| H28A | 0.9189 | 0.1358 | 0.1379 | 0.015* | 0.35 |
| H28B | 0.8380 | 0.2429 | 0.2148 | 0.015* | 0.35 |
| C30A | 0.7387 (8) | 0.2857 (7) | −0.0043 (5) | 0.0122 (7) | 0.35 |
| H30A | 0.6901 | 0.3657 | −0.0431 | 0.015* | 0.35 |
| H30B | 0.7972 | 0.2230 | −0.0528 | 0.015* | 0.35 |
| C31A | 0.6257 (9) | 0.2286 (7) | 0.0775 (5) | 0.0128 (7) | 0.35 |
| H31A | 0.5353 | 0.2970 | 0.0981 | 0.015* | 0.35 |
| H31B | 0.5932 | 0.1616 | 0.0511 | 0.015* | 0.35 |
| O1B | 0.5583 (12) | 0.4284 (11) | −0.0007 (7) | 0.0124 (7) | 0.15 |
| C28B | 0.5266 (16) | 0.4209 (16) | 0.1079 (8) | 0.0118 (8) | 0.15 |
| H28C | 0.4395 | 0.3790 | 0.1392 | 0.014* | 0.15 |
| H28D | 0.5040 | 0.5083 | 0.1299 | 0.014* | 0.15 |
| C29B | 0.6701 (15) | 0.3396 (16) | 0.1373 (10) | 0.0126 (6) | 0.15 |
| H29C | 0.6608 | 0.2484 | 0.1609 | 0.015* | 0.15 |
| H29D | 0.6966 | 0.3747 | 0.1921 | 0.015* | 0.15 |
| C30B | 0.7903 (17) | 0.3508 (18) | 0.0340 (10) | 0.0125 (7) | 0.15 |
| H30C | 0.8286 | 0.4317 | 0.0238 | 0.015* | 0.15 |
| H30D | 0.8767 | 0.2754 | 0.0320 | 0.015* | 0.15 |
| C31B | 0.6999 (14) | 0.3523 (16) | −0.0446 (11) | 0.0125 (7) | 0.15 |
| H31C | 0.7441 | 0.3940 | −0.1130 | 0.015* | 0.15 |
| H31D | 0.6909 | 0.2638 | −0.0506 | 0.015* | 0.15 |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Fe1 | 0.0091 (3) | 0.0097 (3) | 0.0089 (3) | −0.00137 (18) | −0.00237 (19) | −0.00117 (18) |
| N3 | 0.0125 (11) | 0.0108 (10) | 0.0129 (10) | −0.0014 (8) | −0.0040 (8) | −0.0004 (8) |
| N4 | 0.0117 (10) | 0.0141 (11) | 0.0160 (11) | −0.0036 (8) | −0.0033 (9) | −0.0013 (9) |
| N1 | 0.0110 (10) | 0.0118 (10) | 0.0120 (10) | −0.0012 (8) | −0.0024 (8) | −0.0013 (8) |
| N2 | 0.0109 (10) | 0.0112 (10) | 0.0107 (10) | −0.0032 (8) | −0.0024 (8) | −0.0011 (8) |
| C1 | 0.0125 (12) | 0.0152 (12) | 0.0113 (12) | −0.0038 (10) | −0.0036 (10) | 0.0006 (10) |
| C2 | 0.0138 (12) | 0.0172 (13) | 0.0111 (12) | −0.0024 (10) | −0.0029 (10) | −0.0021 (10) |
| C3 | 0.0249 (15) | 0.0221 (14) | 0.0118 (13) | 0.0036 (11) | −0.0059 (11) | −0.0041 (11) |
| C4 | 0.0225 (14) | 0.0213 (14) | 0.0126 (13) | 0.0034 (11) | −0.0040 (11) | −0.0061 (11) |
| C5 | 0.0117 (12) | 0.0162 (13) | 0.0130 (12) | −0.0015 (10) | −0.0020 (10) | −0.0043 (10) |
| C6 | 0.0111 (12) | 0.0122 (12) | 0.0152 (12) | −0.0017 (9) | −0.0020 (10) | −0.0041 (10) |
| C7 | 0.0101 (12) | 0.0105 (12) | 0.0156 (12) | −0.0031 (9) | −0.0022 (10) | −0.0018 (10) |
| C8 | 0.0168 (13) | 0.0104 (12) | 0.0176 (13) | −0.0032 (10) | −0.0052 (10) | −0.0014 (10) |
| C9 | 0.0167 (13) | 0.0115 (12) | 0.0158 (13) | −0.0037 (10) | −0.0061 (10) | 0.0009 (10) |
| C10 | 0.0106 (12) | 0.0115 (12) | 0.0129 (12) | −0.0039 (9) | −0.0040 (9) | 0.0003 (9) |
| C11 | 0.0138 (12) | 0.0177 (13) | 0.0150 (12) | −0.0043 (10) | −0.0031 (10) | −0.0031 (10) |
| C12 | 0.0148 (13) | 0.0157 (13) | 0.0183 (13) | −0.0028 (10) | 0.0000 (11) | −0.0038 (10) |
| C13 | 0.0141 (13) | 0.0183 (13) | 0.0207 (14) | −0.0034 (10) | 0.0011 (11) | −0.0043 (11) |
| C14 | 0.0171 (14) | 0.0199 (14) | 0.0242 (15) | −0.0095 (11) | −0.0066 (11) | −0.0003 (12) |
| C15 | 0.0233 (15) | 0.0176 (13) | 0.0236 (15) | −0.0058 (11) | −0.0102 (12) | −0.0018 (11) |
| C16 | 0.0144 (13) | 0.0176 (13) | 0.0110 (12) | 0.0020 (10) | −0.0027 (10) | −0.0012 (10) |
| C17 | 0.0253 (15) | 0.0252 (15) | 0.0183 (14) | −0.0060 (12) | −0.0050 (12) | 0.0027 (12) |
| C18 | 0.0369 (18) | 0.0284 (17) | 0.0189 (15) | −0.0022 (14) | −0.0047 (13) | 0.0075 (12) |
| C19 | 0.0352 (18) | 0.0357 (18) | 0.0130 (14) | 0.0101 (14) | −0.0093 (13) | 0.0001 (12) |
| C20 | 0.0250 (16) | 0.0354 (18) | 0.0175 (14) | 0.0070 (13) | −0.0088 (12) | −0.0117 (13) |
| C21 | 0.0199 (14) | 0.0203 (14) | 0.0162 (13) | 0.0026 (11) | −0.0042 (11) | −0.0066 (11) |
| C22 | 0.0162 (13) | 0.0135 (12) | 0.0126 (12) | −0.0002 (10) | −0.0070 (10) | −0.0022 (10) |
| C23 | 0.0158 (13) | 0.0179 (13) | 0.0144 (13) | −0.0022 (10) | −0.0049 (10) | −0.0046 (10) |
| C24 | 0.0199 (14) | 0.0220 (14) | 0.0145 (13) | 0.0048 (11) | −0.0053 (11) | −0.0073 (11) |
| C25 | 0.0300 (16) | 0.0152 (13) | 0.0182 (14) | 0.0046 (11) | −0.0121 (12) | −0.0064 (11) |
| C26 | 0.0298 (16) | 0.0153 (14) | 0.0279 (16) | −0.0061 (12) | −0.0111 (13) | −0.0038 (12) |
| C27 | 0.0175 (14) | 0.0193 (14) | 0.0242 (14) | −0.0042 (11) | −0.0048 (11) | −0.0038 (11) |
| O1A | 0.0166 (15) | 0.0189 (15) | 0.0051 (13) | −0.0094 (12) | −0.0044 (12) | 0.0030 (11) |
| C29A | 0.0171 (15) | 0.0180 (15) | 0.0047 (13) | −0.0091 (12) | −0.0046 (12) | 0.0024 (12) |
| C28A | 0.0169 (15) | 0.0187 (15) | 0.0049 (14) | −0.0093 (12) | −0.0043 (12) | 0.0028 (12) |
| C30A | 0.0174 (15) | 0.0176 (15) | 0.0042 (13) | −0.0090 (12) | −0.0048 (12) | 0.0025 (12) |
| C31A | 0.0170 (15) | 0.0185 (15) | 0.0050 (13) | −0.0088 (12) | −0.0045 (12) | 0.0030 (12) |
| O1B | 0.0180 (16) | 0.0178 (16) | 0.0042 (14) | −0.0089 (13) | −0.0050 (13) | 0.0023 (13) |
| C28B | 0.0168 (16) | 0.0179 (16) | 0.0039 (15) | −0.0093 (14) | −0.0051 (13) | 0.0024 (13) |
| C29B | 0.0170 (15) | 0.0185 (15) | 0.0048 (13) | −0.0092 (12) | −0.0047 (12) | 0.0030 (11) |
| C30B | 0.0174 (15) | 0.0181 (15) | 0.0045 (14) | −0.0090 (13) | −0.0046 (12) | 0.0025 (12) |
| C31B | 0.0177 (16) | 0.0182 (16) | 0.0044 (15) | −0.0090 (13) | −0.0048 (13) | 0.0022 (13) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Fe1—N2 | 1.992 (2) | C18—C19 | 1.375 (5) |
| Fe1—N2i | 1.992 (2) | C18—H18 | 0.9500 |
| Fe1—N3 | 1.994 (2) | C19—C20 | 1.382 (5) |
| Fe1—N3i | 1.994 (2) | C19—H19 | 0.9500 |
| Fe1—N1i | 1.998 (2) | C20—C21 | 1.388 (4) |
| Fe1—N1 | 1.998 (2) | C20—H20 | 0.9500 |
| N3—C11 | 1.320 (3) | C21—H21 | 0.9500 |
| N3—C12 | 1.375 (3) | C22—C23 | 1.392 (4) |
| N4—C11 | 1.346 (3) | C22—C27 | 1.396 (4) |
| N4—C13 | 1.364 (4) | C23—C24 | 1.389 (4) |
| N4—C14 | 1.471 (3) | C23—H23 | 0.9500 |
| N1—C5 | 1.381 (3) | C24—C25 | 1.390 (4) |
| N1—C2 | 1.383 (3) | C24—H24 | 0.9500 |
| N2—C7 | 1.379 (3) | C25—C26 | 1.388 (4) |
| N2—C10 | 1.382 (3) | C25—H25 | 0.9500 |
| C1—C10i | 1.396 (4) | C26—C27 | 1.390 (4) |
| C1—C2 | 1.397 (4) | C26—H26 | 0.9500 |
| C1—C16 | 1.494 (3) | C27—H27 | 0.9500 |
| C2—C3 | 1.442 (4) | O1A—C28A | 1.431 (9) |
| C3—C4 | 1.346 (4) | O1A—C31A | 1.432 (8) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9500 | C29A—C28A | 1.497 (10) |
| C4—C5 | 1.440 (4) | C29A—C30A | 1.580 (10) |
| C4—H4 | 0.9500 | C29A—H29A | 0.9900 |
| C5—C6 | 1.388 (4) | C29A—H29B | 0.9900 |
| C6—C7 | 1.395 (4) | C28A—H28A | 0.9900 |
| C6—C22 | 1.502 (3) | C28A—H28B | 0.9900 |
| C7—C8 | 1.438 (4) | C30A—C31A | 1.486 (10) |
| C8—C9 | 1.346 (4) | C30A—H30A | 0.9900 |
| C8—H8 | 0.9500 | C30A—H30B | 0.9900 |
| C9—C10 | 1.444 (4) | C31A—H31A | 0.9900 |
| C9—H9 | 0.9500 | C31A—H31B | 0.9900 |
| C10—C1i | 1.396 (4) | O1B—C28B | 1.415 (9) |
| C11—H11 | 0.9500 | O1B—C31B | 1.421 (9) |
| C12—C13 | 1.363 (4) | O1B—O1Bii | 1.65 (2) |
| C12—H12 | 0.9500 | C28B—C29B | 1.505 (10) |
| C13—H13 | 0.9500 | C28B—H28C | 0.9900 |
| C14—C15 | 1.507 (4) | C28B—H28D | 0.9900 |
| C14—H14A | 0.97 (4) | C29B—C30B | 1.568 (9) |
| C14—H14B | 0.99 (4) | C29B—H29C | 0.9900 |
| C15—H15A | 0.9800 | C29B—H29D | 0.9900 |
| C15—H15B | 0.9800 | C30B—C31B | 1.499 (9) |
| C15—H15C | 0.9800 | C30B—H30C | 0.9900 |
| C16—C17 | 1.394 (4) | C30B—H30D | 0.9900 |
| C16—C21 | 1.398 (4) | C31B—H31C | 0.9900 |
| C17—C18 | 1.392 (4) | C31B—H31D | 0.9900 |
| C17—H17 | 0.9500 | ||
| N2—Fe1—N2i | 180.0 | C16—C17—H17 | 119.7 |
| N2—Fe1—N3 | 90.27 (9) | C19—C18—C17 | 120.7 (3) |
| N2i—Fe1—N3 | 89.72 (9) | C19—C18—H18 | 119.6 |
| N2—Fe1—N3i | 89.73 (9) | C17—C18—H18 | 119.6 |
| N2i—Fe1—N3i | 90.28 (9) | C18—C19—C20 | 119.5 (3) |
| N3—Fe1—N3i | 180.0 | C18—C19—H19 | 120.3 |
| N2—Fe1—N1i | 89.51 (9) | C20—C19—H19 | 120.3 |
| N2i—Fe1—N1i | 90.49 (9) | C19—C20—C21 | 120.2 (3) |
| N3—Fe1—N1i | 89.95 (9) | C19—C20—H20 | 119.9 |
| N3i—Fe1—N1i | 90.05 (9) | C21—C20—H20 | 119.9 |
| N2—Fe1—N1 | 90.49 (9) | C20—C21—C16 | 121.0 (3) |
| N2i—Fe1—N1 | 89.51 (9) | C20—C21—H21 | 119.5 |
| N3—Fe1—N1 | 90.05 (9) | C16—C21—H21 | 119.5 |
| N3i—Fe1—N1 | 89.95 (9) | C23—C22—C27 | 118.9 (2) |
| N1i—Fe1—N1 | 180.0 | C23—C22—C6 | 120.9 (2) |
| C11—N3—C12 | 105.6 (2) | C27—C22—C6 | 120.2 (2) |
| C11—N3—Fe1 | 125.62 (19) | C24—C23—C22 | 120.4 (3) |
| C12—N3—Fe1 | 128.74 (18) | C24—C23—H23 | 119.8 |
| C11—N4—C13 | 107.0 (2) | C22—C23—H23 | 119.8 |
| C11—N4—C14 | 127.4 (2) | C23—C24—C25 | 120.4 (3) |
| C13—N4—C14 | 125.5 (2) | C23—C24—H24 | 119.8 |
| C5—N1—C2 | 105.2 (2) | C25—C24—H24 | 119.8 |
| C5—N1—Fe1 | 127.09 (17) | C26—C25—C24 | 119.6 (3) |
| C2—N1—Fe1 | 127.71 (18) | C26—C25—H25 | 120.2 |
| C7—N2—C10 | 105.1 (2) | C24—C25—H25 | 120.2 |
| C7—N2—Fe1 | 126.70 (17) | C25—C26—C27 | 120.0 (3) |
| C10—N2—Fe1 | 128.22 (17) | C25—C26—H26 | 120.0 |
| C10i—C1—C2 | 123.5 (2) | C27—C26—H26 | 120.0 |
| C10i—C1—C16 | 118.7 (2) | C26—C27—C22 | 120.7 (3) |
| C2—C1—C16 | 117.8 (2) | C26—C27—H27 | 119.7 |
| N1—C2—C1 | 125.7 (2) | C22—C27—H27 | 119.7 |
| N1—C2—C3 | 110.1 (2) | C28A—O1A—C31A | 109.1 (5) |
| C1—C2—C3 | 124.3 (2) | C28A—C29A—C30A | 102.9 (6) |
| C4—C3—C2 | 107.3 (2) | C28A—C29A—H29A | 111.2 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 126.3 | C30A—C29A—H29A | 111.2 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 126.3 | C28A—C29A—H29B | 111.2 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 107.0 (2) | C30A—C29A—H29B | 111.2 |
| C3—C4—H4 | 126.5 | H29A—C29A—H29B | 109.1 |
| C5—C4—H4 | 126.5 | O1A—C28A—C29A | 107.4 (6) |
| N1—C5—C6 | 125.6 (2) | O1A—C28A—H28A | 110.2 |
| N1—C5—C4 | 110.4 (2) | C29A—C28A—H28A | 110.2 |
| C6—C5—C4 | 124.0 (2) | O1A—C28A—H28B | 110.2 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 123.9 (2) | C29A—C28A—H28B | 110.2 |
| C5—C6—C22 | 118.7 (2) | H28A—C28A—H28B | 108.5 |
| C7—C6—C22 | 117.3 (2) | C31A—C30A—C29A | 100.8 (5) |
| N2—C7—C6 | 126.2 (2) | C31A—C30A—H30A | 111.6 |
| N2—C7—C8 | 110.5 (2) | C29A—C30A—H30A | 111.6 |
| C6—C7—C8 | 123.3 (2) | C31A—C30A—H30B | 111.6 |
| C9—C8—C7 | 107.3 (2) | C29A—C30A—H30B | 111.6 |
| C9—C8—H8 | 126.4 | H30A—C30A—H30B | 109.4 |
| C7—C8—H8 | 126.4 | O1A—C31A—C30A | 109.3 (6) |
| C8—C9—C10 | 106.9 (2) | O1A—C31A—H31A | 109.8 |
| C8—C9—H9 | 126.6 | C30A—C31A—H31A | 109.8 |
| C10—C9—H9 | 126.6 | O1A—C31A—H31B | 109.8 |
| N2—C10—C1i | 125.3 (2) | C30A—C31A—H31B | 109.8 |
| N2—C10—C9 | 110.3 (2) | H31A—C31A—H31B | 108.3 |
| C1i—C10—C9 | 124.3 (2) | C28B—O1B—C31B | 115.1 (11) |
| N3—C11—N4 | 111.6 (2) | C28B—O1B—O1Bii | 86.3 (9) |
| N3—C11—H11 | 124.2 | C31B—O1B—O1Bii | 147.8 (13) |
| N4—C11—H11 | 124.2 | O1B—C28B—C29B | 103.8 (11) |
| C13—C12—N3 | 109.2 (2) | O1B—C28B—H28C | 111.0 |
| C13—C12—H12 | 125.4 | C29B—C28B—H28C | 111.0 |
| N3—C12—H12 | 125.4 | O1B—C28B—H28D | 111.0 |
| C12—C13—N4 | 106.6 (2) | C29B—C28B—H28D | 111.0 |
| C12—C13—H13 | 126.7 | H28C—C28B—H28D | 109.0 |
| N4—C13—H13 | 126.7 | C28B—C29B—C30B | 102.7 (11) |
| N4—C14—C15 | 112.8 (2) | C28B—C29B—H29C | 111.2 |
| N4—C14—H14A | 106 (2) | C30B—C29B—H29C | 111.2 |
| C15—C14—H14A | 113 (2) | C28B—C29B—H29D | 111.2 |
| N4—C14—H14B | 106 (2) | C30B—C29B—H29D | 111.2 |
| C15—C14—H14B | 114 (2) | H29C—C29B—H29D | 109.1 |
| H14A—C14—H14B | 104 (3) | C31B—C30B—C29B | 102.1 (11) |
| C14—C15—H15A | 109.5 | C31B—C30B—H30C | 111.4 |
| C14—C15—H15B | 109.5 | C29B—C30B—H30C | 111.4 |
| H15A—C15—H15B | 109.5 | C31B—C30B—H30D | 111.4 |
| C14—C15—H15C | 109.5 | C29B—C30B—H30D | 111.4 |
| H15A—C15—H15C | 109.5 | H30C—C30B—H30D | 109.2 |
| H15B—C15—H15C | 109.5 | O1B—C31B—C30B | 100.4 (11) |
| C17—C16—C21 | 117.9 (3) | O1B—C31B—H31C | 111.7 |
| C17—C16—C1 | 121.7 (3) | C30B—C31B—H31C | 111.7 |
| C21—C16—C1 | 120.4 (2) | O1B—C31B—H31D | 111.7 |
| C18—C17—C16 | 120.6 (3) | C30B—C31B—H31D | 111.7 |
| C18—C17—H17 | 119.7 | H31C—C31B—H31D | 109.5 |
| C5—N1—C2—C1 | 177.7 (3) | Fe1—N3—C12—C13 | −178.97 (19) |
| Fe1—N1—C2—C1 | −2.8 (4) | N3—C12—C13—N4 | −0.1 (3) |
| C5—N1—C2—C3 | −2.0 (3) | C11—N4—C13—C12 | −0.3 (3) |
| Fe1—N1—C2—C3 | 177.45 (19) | C14—N4—C13—C12 | −176.0 (2) |
| C10i—C1—C2—N1 | 3.6 (4) | C11—N4—C14—C15 | 24.6 (4) |
| C16—C1—C2—N1 | −175.7 (2) | C13—N4—C14—C15 | −160.6 (3) |
| C10i—C1—C2—C3 | −176.7 (3) | C10i—C1—C16—C17 | 59.0 (4) |
| C16—C1—C2—C3 | 4.0 (4) | C2—C1—C16—C17 | −121.7 (3) |
| N1—C2—C3—C4 | 2.0 (3) | C10i—C1—C16—C21 | −120.9 (3) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −177.8 (3) | C2—C1—C16—C21 | 58.4 (4) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −1.0 (3) | C21—C16—C17—C18 | 0.4 (4) |
| C2—N1—C5—C6 | −178.1 (3) | C1—C16—C17—C18 | −179.5 (3) |
| Fe1—N1—C5—C6 | 2.4 (4) | C16—C17—C18—C19 | −1.2 (5) |
| C2—N1—C5—C4 | 1.4 (3) | C17—C18—C19—C20 | 1.1 (5) |
| Fe1—N1—C5—C4 | −178.10 (18) | C18—C19—C20—C21 | −0.2 (5) |
| C3—C4—C5—N1 | −0.2 (3) | C19—C20—C21—C16 | −0.6 (4) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 179.3 (3) | C17—C16—C21—C20 | 0.5 (4) |
| N1—C5—C6—C7 | −3.2 (4) | C1—C16—C21—C20 | −179.6 (3) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | 177.4 (3) | C5—C6—C22—C23 | 82.2 (3) |
| N1—C5—C6—C22 | 176.5 (2) | C7—C6—C22—C23 | −98.0 (3) |
| C4—C5—C6—C22 | −2.8 (4) | C5—C6—C22—C27 | −99.3 (3) |
| C10—N2—C7—C6 | −178.6 (2) | C7—C6—C22—C27 | 80.5 (3) |
| Fe1—N2—C7—C6 | 0.0 (4) | C27—C22—C23—C24 | −0.2 (4) |
| C10—N2—C7—C8 | −0.7 (3) | C6—C22—C23—C24 | 178.3 (2) |
| Fe1—N2—C7—C8 | 177.96 (17) | C22—C23—C24—C25 | 0.5 (4) |
| C5—C6—C7—N2 | 1.9 (4) | C23—C24—C25—C26 | −0.7 (4) |
| C22—C6—C7—N2 | −177.8 (2) | C24—C25—C26—C27 | 0.5 (4) |
| C5—C6—C7—C8 | −175.8 (2) | C25—C26—C27—C22 | −0.2 (4) |
| C22—C6—C7—C8 | 4.5 (4) | C23—C22—C27—C26 | 0.0 (4) |
| N2—C7—C8—C9 | −0.2 (3) | C6—C22—C27—C26 | −178.5 (3) |
| C6—C7—C8—C9 | 177.8 (2) | C31A—O1A—C28A—C29A | 10.8 (8) |
| C7—C8—C9—C10 | 0.9 (3) | C30A—C29A—C28A—O1A | −26.6 (8) |
| C7—N2—C10—C1i | −179.2 (2) | C28A—C29A—C30A—C31A | 31.6 (7) |
| Fe1—N2—C10—C1i | 2.3 (4) | C28A—O1A—C31A—C30A | 11.1 (8) |
| C7—N2—C10—C9 | 1.2 (3) | C29A—C30A—C31A—O1A | −26.5 (8) |
| Fe1—N2—C10—C9 | −177.34 (17) | C31B—O1B—C28B—C29B | 5.3 (17) |
| C8—C9—C10—N2 | −1.4 (3) | O1Bii—O1B—C28B—C29B | −149.7 (13) |
| C8—C9—C10—C1i | 179.0 (2) | O1B—C28B—C29B—C30B | 19.5 (16) |
| C12—N3—C11—N4 | −0.5 (3) | C28B—C29B—C30B—C31B | −36.3 (16) |
| Fe1—N3—C11—N4 | 178.81 (17) | C28B—O1B—C31B—C30B | −28.6 (17) |
| C13—N4—C11—N3 | 0.5 (3) | O1Bii—O1B—C31B—C30B | 99 (2) |
| C14—N4—C11—N3 | 176.1 (2) | C29B—C30B—C31B—O1B | 38.1 (16) |
| C11—N3—C12—C13 | 0.4 (3) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x, −y+1, −z+1; (ii) −x+1, −y+1, −z.
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
Cg is the centroid of the N2/C7–C10 ring.
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C14—H14B···Cgiii | 0.99 (4) | 2.69 (4) | 3.437 (3) | 133 (2) |
Symmetry code: (iii) −x+1, −y+1, −z+1.
Funding Statement
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China grant 21371167.
References
- Adler, A. D., Longo, F. R., Finarelli, J. D., Goldmacher, J., Assour, J. & Korsakoff, L. (1967). J. Org. Chem. 32, 476–476.
- Adler, A. D., Longo, F. R., Kampas, F. & Kim, J. (1970). J. Inorg. Nucl. Chem. 32, 2443–2445.
- Allen, F. H., Johnson, O., Shields, G. P., Smith, B. R. & Towler, M. (2004). J. Appl. Cryst. 37, 335–338.
- Bruker (2014). APEX2, SAINT-Plus, XPREP and SADABS. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Fleischer, E. B. & Srivastava, T. S. (1969). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 91, 2403–2405.
- Hu, B., He, M., Yao, Z., Schulz, C. E. & Li, J. (2016). Inorg. Chem. 55, 9632–9643. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Li, J., Nair, S. M., Noll, B. C., Schulz, C. E. & Scheidt, W. R. (2008). Inorg. Chem. 47, 3841–3850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Macrae, C. F., Bruno, I. J., Chisholm, J. A., Edgington, P. R., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Rodriguez-Monge, L., Taylor, R., van de Streek, J. & Wood, P. A. (2008). J. Appl. Cryst. 41, 466–470.
- Scheidt, W. R. & Reed, C. A. (1981). Chem. Rev. 81, 543–555.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). XCIF and XP. University of Göttingen, Germany.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015a). Acta Cryst. A71, 3–8.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015b). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Takahashi, O., Kohno, Y., Iwasaki, S., Saito, K., Iwaoka, M., Tomoda, S., Umezawa, Y., Tsuboyama, S. & Nishio, M. (2001). Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn, 74, 2421–2430.
- Walker, F. A. (2004). Chem. Rev. 104, 589–615. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Xia, D., Yu, C.-A., Kim, H., Xia, J.-Z., Kachurin, A. M., Zhang, L., Yu, L. & Deisenhofer, J. (1997). Science, 277, 60–66. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018006308/qm2123sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018006308/qm2123Isup2.hkl
CCDC reference: 1839313
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report






