3-(1,1,1-Trimethylhydrazin-1-ium-2-yl)propanoate (M, more commonly known under its commercial names Meldonium or Mildronate) co-crystalizes with sodium bromide and sodium iodide forming polymeric hydrates. Metal ions and M zwitterions are assembled into infinite layers via electrostatic interactions and hydrogen-bonded networks. These layers are connected via electrostatic attraction between halogenide ions and positive trimethylhydrazinium groups into a three-dimensional structure.
Keywords: crystal structure; 3-(1,1,1-trimethylydrhazin-1-ium-2-yl)propanoate; meldonium; sodium bromide; sodium iodide
Abstract
3-(1,1,1-Trimethylhydrazin-1-ium-2-yl)propanoate (C6H14N2O2, M, more commonly known under its commercial names Meldonium or Mildronate) co-crystalizes with sodium bromide and sodium iodide forming polymeric hydrates poly[[tetra-μ-aqua-diaquabis[3-(1,1,1-trimethylhydrazin-1-ium-2-yl)propanoate]disodium] dibromide tetrahydrate], [Na2(C6H14N2O2)2(H2O)6]Br2·4H2O, and poly[[di-μ-aqua-diaqua[μ-3-(1,1,1-trimethylhydrazin-1-ium-2-yl)propanoate]disodium] diiodide], [Na2(C6H14N2O2)2(H2O)4]I2. The coordination numbers of the sodium ions are 6; the coordination polyhedra can be described as distorted octahedra. Metal ions and M zwitterions are assembled into infinite layers via electrostatic interactions and hydrogen-bonded networks. These layers are connected via electrostatic attraction between halogenide ions and positive trimethylhydrazinium groups into a three-dimensional structure.
Chemical context
3-(1,1,1-Trimethylhydrazin-1-ium-2-yl)propanoate (M), more commonly known under its commercial names such as Meldonium or Mildronate, was introduced by Grindeks (Latvia) as an anti-ischemic medication (Liepinsh et al., 2017 ▸). The synthesis of M was originally described by Giller et al. (1975 ▸) and was improved in a number of patents and papers (Kalvins & Stonans, 2009 ▸; Kalvins et al., 2014 ▸; Silva, 2013 ▸). Recently M achieved controversial publicity as a doping agent. As a result of its inclusion in the World Anti-Doping Agency List of Prohibited Substances, it attracted the attention of pharmaceutical and forensic chemists (Görgens et al., 2015 ▸).
Binary compounds of M with various inorganic salts have been described in numerous M-related synthetic procedures (see above); their high stability was a challenge that was necessary to overcome for the preparation of pharmaceutically pure forms of M. The stability of a sodium iodide binary compound was given as an example in Silva (2013 ▸). The crystal structures of two such binary compounds, with sodium bromide (I) and with sodium iodide (II), are presented here.
Structural commentary
The labelling schemes for structures (I) and (II) are shown in Figs. 1 ▸ and 2 ▸. Molecules of (I), which crystallize in an acentric space group, have a non-crystallographic inversion centre at 0.6238 (6) 0.744 (5) 0.5001 (2). This symmetry is visible in Fig. 1 ▸; it is also demonstrated by overlay of the two chemically equivalent moieties, after inversion of one of them (Fig. 3 ▸). Both Na ions have distorted octahedral environments (coordination number 6). The coordination sphere contains an anionic oxygen atom of a monodentate carboxylic group, two pairs of bridging O atoms of water molecules (O5, O8, O9 and O10), and a terminal water molecule (atoms O6 and O7 for Na1 and Na2 respectively). The shortest Na—O separations (Table 1 ▸) correspond to the anionic oxygens O1 and O3; the longest are opposite to the bridging atoms O5 and O8 (not shown in Fig. 1 ▸, but visible in Fig. 6 ▸).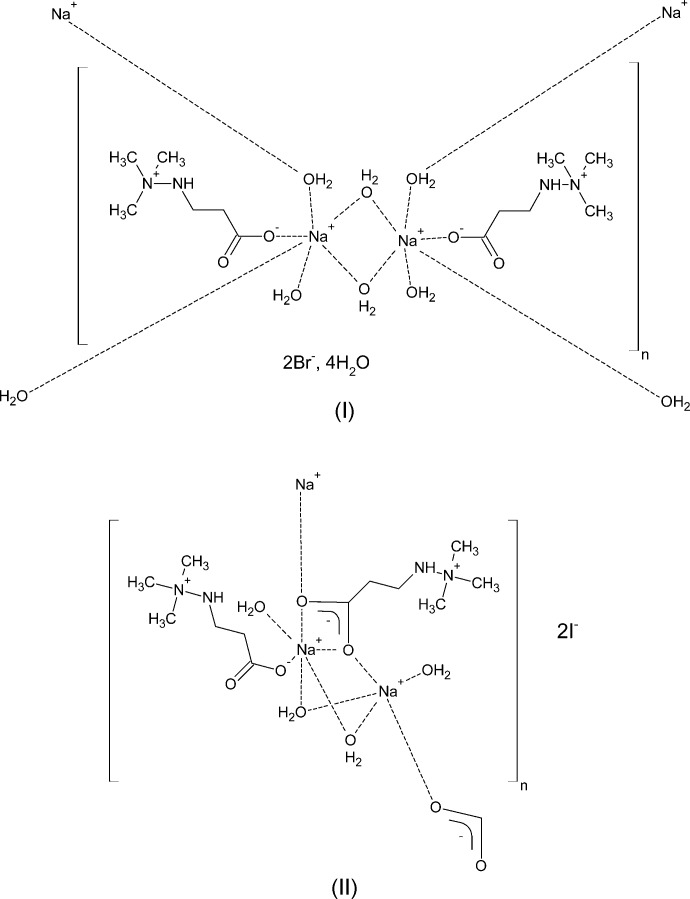
Figure 1.
Labelling scheme of the asymmetric unit of compound (I) with 50% probability displacement ellipsoids.
Figure 2.
Labelling scheme of the asymmetric unit of compound (II) with 50% probability displacement ellipsoids.
Figure 3.
Overlay of the two organic fragments in (I) after inversion. The average deviation is 0.04 Å.
Table 1. Selected bond lengths (Å) for (I) .
| Na1—O1 | 2.367 (4) | Na2—O8 | 2.364 (3) |
| Na1—O5 | 2.368 (3) | Na2—O9 | 2.361 (3) |
| Na1—O6 | 2.369 (3) | Na2—O10 | 2.449 (4) |
| Na1—O8i | 2.517 (4) | O1—C1 | 1.241 (5) |
| Na1—O9 | 2.442 (4) | O2—C1 | 1.281 (5) |
| Na1—O10 | 2.361 (4) | O3—C7 | 1.249 (5) |
| Na2—O3 | 2.359 (4) | O4—C7 | 1.282 (5) |
| Na2—O5ii | 2.543 (4) | N1—N2 | 1.471 (6) |
| Na2—O7 | 2.368 (3) | N3—N4 | 1.466 (6) |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  .
.
Figure 6.
The infinite chain of hydrated sodium ions along the [010] axis in (I).
The coordination polyhedra of the sodium ions in (II) are visibly different (Fig. 4 ▸, Table 2 ▸). Both have a distorted octahedral geometry and coordination number 6. The coordination polyhedron of Na1 contains an anionic oxygen atom O1 of a monodentate carboxylic group, atoms O3 and O4 of the bidentate carboxylic acid group, and three water molecules O5, O6, and O8. The O8 atom, which forms three bridging contacts to three different sodium ions, shows a much longer separation from Na1 than any of the other coordinated oxygen atoms (Table 2 ▸).
Figure 4.
Coordination polyhedra of the sodium ions in (II).
Table 2. Selected bond lengths (Å) for (II) .
| Na1—O1 | 2.462 (3) | Na2—O7 | 2.372 (3) |
| Na1—O3 | 2.374 (3) | Na2—O8iii | 2.569 (4) |
| Na1—O4 | 2.552 (3) | Na2—O8 | 2.510 (3) |
| Na1—O5 | 2.351 (3) | O1—C1 | 1.274 (4) |
| Na1—O6 | 2.385 (4) | O2—C1 | 1.247 (4) |
| Na1—O8i | 2.857 (4) | O3—C7 | 1.256 (5) |
| Na2—O3 | 2.315 (3) | O4—C7 | 1.264 (5) |
| Na2—O4ii | 2.431 (3) | N1—N2 | 1.478 (4) |
| Na2—O5ii | 2.373 (3) | N3—N4 | 1.476 (4) |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  .
.
The octahedral environment around Na2 in (II) (Fig. 4 ▸, Table 2 ▸) is less distorted: it consists of two bridging oxygen atoms O3 and O4 of two distinct carboxylate groups and four water oxygen atoms. The shortest distance is Na2—O3 (involving carboxylate group oxygens); the two longest again belong to the bridging O8 atoms (Table 2 ▸).
All zwitterions of M have approximately the same geometry (the two pseudo-inversion-symmetric zwitterions in the structure of (I) are nearly superimposable, Fig. 3 ▸). Both monodentate carboxylates in (I) and that in (II) have slightly elongated C—O bonds for the oxygen atom bound to the corresponding Na ion (Tables 1 ▸ and 2 ▸). These bonds are slightly longer than the corresponding bonds in M monohydrate and dihydrate [1.258 (2) and 1.2618 (9) Å, respectively; CCDC entries CCDC 1822460 and 1822463; Nazarenko, 2018 ▸). This relatively small change could be interpreted as a shift of of the anionic charge towards the sodium-bound oxygen atom. The carbon–oxygen bond lengths within the bidenate carboxylate groups in (II) are essentially identical within two standard deviations.
All N—N bond distances are around 1.47 Å (Tables 1 ▸ and 2 ▸) and are within experimental error indistinguishable from the average value [1.468 (2) Å] for known low-temperature single-crystal structures of M (CCDC 1822460–1822463; Nazarenko, 2018 ▸), but significantly shorter than the value reported for room temperature (1.49 Å; Kemme et al., 1983 ▸).
The distribution of the Hirshfeld surface electrostatic potential of the zwitterion (Fig. 5 ▸) shows that only a small area around the carboxyl oxygen atoms is negatively charged: the remaining Hirshfeld surface has positive electrostatic potential. This makes this area attractive for anions, with the N—H group of the hydrazine fragment available as a donor of an electrostatically enhanced hydrogen bond. The lone-pair density of the same hydrazine nitrogen atom is not sufficient to overcome the total positive charge of the trimethylhydrazinium fragment and does not act as a hydrogen-bond acceptor.
Figure 5.
Hirshfeld surface of the zwitterion with electrostatic potential plotted using CrystalExplorer17 (Turner et al., 2017 ▸). Red – negative, blue – positive.
Supramolecular features
In the structure of (I), the coordination polyhedra of the sodium ions are connected by common edges (a pair of bridging water molecules, O5 and O8, and O9 and O10), forming an infinite chain of ions along the [010] vector (Fig. 6 ▸). In addition to Na⋯O interactions, this chain is supported by six hydrogen bonds (Table 3 ▸): O6—H6B⋯O2, O5—H5A⋯O1, O8—H8B⋯O3, O7—H7B⋯O4, O9—H9A⋯O6 and O10—H10B⋯O7. The first four of them, connecting the anionic oxygen atoms of the carboxylic groups, are electrostatically enhanced.
Table 3. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °) for (I) .
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O5—H5A⋯O1i | 0.97 (6) | 1.79 (6) | 2.746 (4) | 172 (6) |
| O5—H5B⋯O11iii | 0.82 (6) | 2.02 (6) | 2.819 (5) | 167 (6) |
| O6—H6A⋯O4iv | 0.80 (3) | 2.06 (3) | 2.845 (5) | 165 (6) |
| O6—H6B⋯O2i | 0.82 (3) | 1.91 (3) | 2.732 (4) | 175 (6) |
| O7—H7A⋯O2v | 0.82 (3) | 2.05 (3) | 2.856 (5) | 165 (6) |
| O7—H7B⋯O4ii | 0.80 (3) | 1.94 (3) | 2.731 (4) | 169 (6) |
| O8—H8A⋯O13ii | 0.81 (3) | 2.06 (3) | 2.815 (5) | 155 (5) |
| O8—H8B⋯O3ii | 0.81 (3) | 1.95 (3) | 2.754 (4) | 168 (7) |
| O9—H9A⋯O6ii | 0.93 (6) | 1.96 (6) | 2.852 (4) | 160 (5) |
| O9—H9B⋯O13 | 0.79 (6) | 2.01 (6) | 2.772 (5) | 160 (6) |
| O10—H10A⋯O11v | 0.78 (6) | 2.00 (6) | 2.771 (5) | 167 (6) |
| O10—H10B⋯O7i | 0.90 (6) | 1.99 (6) | 2.853 (4) | 158 (5) |
| O11—H11D⋯O12 | 0.80 (3) | 1.94 (3) | 2.744 (6) | 179 (7) |
| O11—H11E⋯O2 | 0.80 (3) | 1.92 (3) | 2.719 (5) | 174 (9) |
| O13—H13A⋯O14 | 0.80 (3) | 1.95 (3) | 2.733 (6) | 170 (6) |
| O13—H13B⋯O4iv | 0.80 (3) | 1.94 (3) | 2.727 (5) | 168 (9) |
| N1—H1⋯Br1i | 0.83 (5) | 2.57 (5) | 3.379 (5) | 167 (5) |
| N3—H3⋯Br2v | 0.84 (5) | 2.57 (5) | 3.394 (5) | 169 (5) |
| O12—H12D⋯Br1i | 0.80 (5) | 2.52 (6) | 3.316 (4) | 172 (6) |
| O12—H12E⋯Br1 | 0.80 (5) | 2.49 (6) | 3.289 (4) | 177 (8) |
| O14—H14A⋯Br2i | 0.87 (7) | 2.47 (7) | 3.323 (5) | 168 (7) |
| O14—H14B⋯Br2 | 0.87 (6) | 2.41 (6) | 3.281 (5) | 175 (6) |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  ; (iv)
; (iv)  ; (v)
; (v)  .
.
Each bromide ion forms a hydrogen bond with a hydrazine N—H group. In addition, each of them forms two hydrogen bonds with neighboring water molecules (O12 and O14), thus forming two more infinite chains in the [010] direction. Water molecules O11 and O13 form bridges between the cation chain and the ‘bromide’ chains as hydrogen-bond donors; they are also acceptors of four hydrogen bonds from the water molecules O5 and O10, and O8 and O9 respectively. These hydrogen bonds connect chains into a two-dimensional network. Two more enhanced hydrogen bonds (Table 3 ▸), O7—H7A⋯O2 and O6—H6A⋯O4, also connect neighboring chains. The resulting network forms a layer in the (001) plane with the bromide ions and trimethylammonium groups forming each side (Fig. 7 ▸). These layers are bound together via electrostatic interaction of the corresponding positive and negative ions; no short intralayer contacts are visible.
Figure 7.
Packing of (I). View along the [010] axis. Sodium ions are green.
In the structure of (II), the coordination polyhedra of the sodium ions are bridged via the bidentate carboxylate group to form an infinite chain along the [001] axis (Fig. 8 ▸). The water molecule O5 provides an additional bridge, stabilizing the chain. These chains are interconnected in the (100) plane with the help of weaker (and longer by almost 0.5 Å) Na⋯O8 contacts (Fig. 9 ▸). An array of hydrogen bonds (Table 4 ▸, Fig. 9 ▸) additionally stabilizes the resulting layer. As in compound (I), both iodide ions are connected to zwitterions M via N—H⋯I− hydrogen bonds. In addition, ion I1 is an acceptor of two hydrogen bonds with water molecules (O6—H6A⋯I1 and O7—H7A⋯I1, see Table 4 ▸). In absence of neighboring water molecules, two CH groups of the trimethylammonium fragment form close contacts with the ion I2. As in structure (I), the layers are tied together by the electrostatic interaction of the corresponding positive and negative ions; no short intralayer contacts are visible (Fig. 10 ▸).
Figure 8.
The infinite chain of hydrated sodium ions along the [001] axis in (II).
Figure 9.
Chains in the structure of (II) are connected via atom O8 (in green) and a network of hydrogen bonds (dashed lines).
Table 4. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °) for (II) .
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O5—H5B⋯O1i | 0.85 (6) | 1.89 (6) | 2.741 (4) | 175 (6) |
| O7—H7B⋯O2iv | 0.91 | 1.73 | 2.629 (4) | 169 |
| O8—H8A⋯O1ii | 0.85 (6) | 2.05 (6) | 2.815 (4) | 149 (6) |
| N1—H1⋯I2 | 0.82 (6) | 2.87 (6) | 3.688 (4) | 177 (5) |
| N3—H3⋯I1v | 0.92 (6) | 2.76 (6) | 3.650 (3) | 161 (5) |
| O5—H5A⋯O7v | 0.86 (6) | 2.00 (6) | 2.846 (4) | 172 (4) |
| O6—H6A⋯I1 | 0.89 | 2.64 | 3.518 (3) | 166 |
| O6—H6B⋯O4vi | 0.89 | 1.95 | 2.825 (4) | 168 |
| O7—H7A⋯I1iii | 0.91 | 2.78 | 3.548 (3) | 143 |
| O8—H8B⋯O6iii | 0.86 (7) | 2.13 (7) | 2.989 (5) | 175 (5) |
| C3—H3A⋯I1ii | 0.99 | 3.01 | 3.920 (4) | 154 |
| C11—H11B⋯I2vii | 0.98 | 3.02 | 3.975 (4) | 165 |
| C12—H12C⋯I1vi | 0.98 | 2.99 | 3.952 (5) | 167 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  ; (iv)
; (iv)  ; (v)
; (v)  ; (vi)
; (vi)  ; (vii)
; (vii)  .
.
Figure 10.
Packing of (II). View along the [001] axis. Sodium ions are green.
Database survey
Prior to 2018, the only meldonium-related single-crystal structure in the Cambridge Structural Database (Groom et al., 2016 ▸, CSD Version 5.39) had been a crystal structure of the dihydrate form (refcode CABVOQ; Kemme et al., 1983 ▸)) measured at room temperature with no experimental positions for hydrogen atoms. Hydrates of M also were also studied using powder X-ray diffraction (Zvirgzdiņš et al., 2011 ▸; Bērziņš & Actiņš, 2014 ▸). Meldonium is closely related to betaines, a wide class of zwitterionic compounds with an onium atom that bears no hydrogen atoms and that is not adjacent to the anionic atom. The parent compound of the betaine class, N,N,N-trimethylglycine (TMG), has a very rich crystal chemistry: the CSD (Version 5.39) contains 217 different structures of its compounds. There are several known crystal structures of TMG binary compounds with potassium iodide (HIPQIG; Andrade et al., 1999 ▸), rubidium iodide (NEMKIZ; Andrade et al., 2001 ▸), potassium bromide (WIQPUH01; Andrade et al., 2000 ▸) and sodium bromide (JAZNEE; Rodrigues et al., 2005 ▸). These compounds show features similar to those of their meldonium analogs: infinite chains of hydrated alkali metal cations and layers of trimethylammonium groups. The obvious differences are the absence of N—H⋯X − hydrogen bonds and the much smaller size of the organic domain.
Synthesis and crystallization
Preparation and properties of binary compounds of M with sodium halogenides are described in detail in Giller et al. (1975 ▸) and Silva (2013 ▸). Commercial M dihydrate was received from Grindeks (Latvia) and recrystallized from propanol-2. Equimolar amounts of it were mixed with sodium iodide and sodium bromide in aqueous ethanol; subsequent slow evaporation yielded crystals suitable for single–crystal X-ray experiments. IR spectra (FTIR–ATR, cm−1) are very similar to those of M dihydrate. (I): 3399 (H2O), 1571, 1483, 1402, 1320; (II): 3350, 3180 (H2O), 1568, 1480, 1405, 1317, 1088, 816; M dihydrate: 3201 (H2O), 1577, 1484, 1404, 1320, 1090, 816.
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 5 ▸.
Table 5. Experimental details.
| (I) | (II) | |
|---|---|---|
| Crystal data | ||
| Chemical formula | [Na2(C6H14N2O2)2(H2O)6]Br2·4H2O | [Na2(C6H14N2O2)2(H2O)4]·I2 |
| M r | 678.34 | 664.23 |
| Crystal system, space group | Orthorhombic, P c a21 | Monoclinic, P21/c |
| Temperature (K) | 173 | 173 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 16.5181 (8), 5.5262 (3), 33.2605 (16) | 19.7455 (11), 11.4530 (7), 10.9733 (7) |
| α, β, γ (°) | 90, 90, 90 | 90, 92.382 (2), 90 |
| V (Å3) | 3036.1 (3) | 2479.4 (3) |
| Z | 4 | 4 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 2.76 | 2.61 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.65 × 0.13 × 0.09 | 0.3 × 0.2 × 0.07 |
| Data collection | ||
| Diffractometer | Bruker PHOTON-100 CMOS | Bruker PHOTON-100 CMOS |
| Absorption correction | Numerical (SADABS; Krause et al., 2015 ▸) | Multi-scan (TWINABS; Krause et al., 2015 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.217, 0.635 | 0.301, 0.431 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 117729, 6969, 6121 | 5475, 5475, 5012 |
| R int | 0.044 | 0.048 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.650 | 0.641 |
| Refinement | ||
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.032, 0.078, 1.03 | 0.026, 0.057, 1.17 |
| No. of reflections | 6969 | 5475 |
| No. of parameters | 380 | 286 |
| No. of restraints | 33 | 0 |
| H-atom treatment | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.71, −0.38 | 0.70, −0.55 |
| Absolute structure | Refined as an inversion twin | – |
| Absolute structure parameter | 0.250 (10) | – |
Structure (I) was was solved and refined in an achiral space group; the large Flack parameter prompted twin refinement as a two-component inversion twin [0.75 (1):0.25 (1)] with twin matrix [ 0 0, 0
0 0, 0  0, 0 0
0, 0 0  ]. Reflections in (II) were processed as a two-domain [0.668 (1):0.332 (1) ratio] non-merohedral twin with twin matrix [1.000 0.000 0.000, 0.000 −1.000 0.000, −0.146 0.000 −1.000]; domain 2 is rotated from the first domain by 180.0° about the reciprocal axis 1.000 −0.001 −0.073 or the real axis 1.000 0.000 0.002 (CELL_NOW; Sheldrick, 2008 ▸).
]. Reflections in (II) were processed as a two-domain [0.668 (1):0.332 (1) ratio] non-merohedral twin with twin matrix [1.000 0.000 0.000, 0.000 −1.000 0.000, −0.146 0.000 −1.000]; domain 2 is rotated from the first domain by 180.0° about the reciprocal axis 1.000 −0.001 −0.073 or the real axis 1.000 0.000 0.002 (CELL_NOW; Sheldrick, 2008 ▸).
In the structure of (I) distances O6—H6A, O6—H6B, O7—H7A, O7—H7B, O8—H8A, and O8—H8B; O11—H11D, O11—H11E, O12—H12E, O12—H12D, O13—H13A, and O13—H13B; O14—H14A and O14—H14B were restrained to be equal with an effective standard deviation of 0.02 Å. Distances N1—H1 and N3—H3 were also restrained to be equal with an effective standard deviation of 0.02 Å; U iso(H) = 1.5U iso(N).
In the structure of (II), water molecules O6 and O7 were refined as rotating groups (AFIX 7). The positions and isotropic displacement parameters of the hydrazinium hydrogen atoms were refined.
In both structures, methylene hydrogen atoms were refined with riding coordinates and with U iso(H) = 1.2 U iso(C); methyl hydrogen atoms were refined as rotating idealized methyl groups and with U iso(H) = 1.5U iso(C). Hydrogen atoms of water molecules were refined in an isotropic approximation with U iso(H) = 1.5U iso(O).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, II. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018006977/zl2729sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018006977/zl2729Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018006977/zl2729Isup4.cdx
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) II. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018006977/zl2729IIsup3.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018006977/zl2729IIsup5.cdx
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
supplementary crystallographic information
Poly[[tetra-µ-aqua-diaquabis[3-(1,1,1-trimethylhydrazin-1-ium-2-yl)\ propanoate]disodium] dibromide tetrahydrate] (I). Crystal data
| [Na2(C6H14N2O2)2(H2O)6]Br2·4H2O | Dx = 1.484 Mg m−3 |
| Mr = 678.34 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Orthorhombic, Pca21 | Cell parameters from 9077 reflections |
| a = 16.5181 (8) Å | θ = 3.1–27.4° |
| b = 5.5262 (3) Å | µ = 2.76 mm−1 |
| c = 33.2605 (16) Å | T = 173 K |
| V = 3036.1 (3) Å3 | Needle, colourless |
| Z = 4 | 0.65 × 0.13 × 0.09 mm |
| F(000) = 1408 |
Poly[[tetra-µ-aqua-diaquabis[3-(1,1,1-trimethylhydrazin-1-ium-2-yl)\ propanoate]disodium] dibromide tetrahydrate] (I). Data collection
| Bruker PHOTON-100 CMOS diffractometer | 6121 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Radiation source: sealedtube | Rint = 0.044 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 27.5°, θmin = 3.1° |
| Absorption correction: numerical (SADABS; Krause et al., 2015) | h = −21→21 |
| Tmin = 0.217, Tmax = 0.635 | k = −7→7 |
| 117729 measured reflections | l = −43→43 |
| 6969 independent reflections |
Poly[[tetra-µ-aqua-diaquabis[3-(1,1,1-trimethylhydrazin-1-ium-2-yl)\ propanoate]disodium] dibromide tetrahydrate] (I). Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Hydrogen site location: mixed |
| Least-squares matrix: full | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.032 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0417P)2 + 2.0085P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| wR(F2) = 0.078 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| S = 1.02 | Δρmax = 0.71 e Å−3 |
| 6969 reflections | Δρmin = −0.38 e Å−3 |
| 380 parameters | Absolute structure: Refined as an inversion twin |
| 33 restraints | Absolute structure parameter: 0.250 (10) |
| Primary atom site location: dual |
Poly[[tetra-µ-aqua-diaquabis[3-(1,1,1-trimethylhydrazin-1-ium-2-yl)\ propanoate]disodium] dibromide tetrahydrate] (I). Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refined as a 2-component inversion twin |
Poly[[tetra-µ-aqua-diaquabis[3-(1,1,1-trimethylhydrazin-1-ium-2-yl)\ propanoate]disodium] dibromide tetrahydrate] (I). Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Br1 | 0.92047 (3) | −0.03168 (8) | 0.28604 (2) | 0.03549 (13) | |
| Br2 | 0.82608 (3) | 0.44931 (9) | 0.71406 (2) | 0.04007 (14) | |
| Na1 | 0.67706 (11) | 0.9937 (3) | 0.48342 (7) | 0.0182 (5) | |
| Na2 | 0.57098 (11) | 0.4989 (3) | 0.51722 (7) | 0.0186 (5) | |
| O1 | 0.73577 (16) | 0.7342 (5) | 0.43488 (9) | 0.0229 (6) | |
| O2 | 0.8552 (2) | 0.5504 (5) | 0.44213 (11) | 0.0240 (7) | |
| O3 | 0.51258 (17) | 0.7566 (5) | 0.56578 (9) | 0.0243 (6) | |
| O4 | 0.39361 (19) | 0.9443 (5) | 0.55827 (11) | 0.0226 (6) | |
| O5 | 0.63384 (19) | 1.3548 (5) | 0.45166 (9) | 0.0237 (6) | |
| H5A | 0.671 (4) | 1.481 (10) | 0.444 (2) | 0.036* | |
| H5B | 0.594 (3) | 1.388 (11) | 0.4385 (17) | 0.036* | |
| O6 | 0.78937 (18) | 1.2455 (5) | 0.49791 (10) | 0.0249 (6) | |
| H6A | 0.825 (2) | 1.210 (10) | 0.5134 (14) | 0.037* | |
| H6B | 0.809 (3) | 1.330 (9) | 0.4802 (14) | 0.037* | |
| O7 | 0.45879 (18) | 0.2480 (5) | 0.50216 (10) | 0.0255 (6) | |
| H7A | 0.423 (3) | 0.308 (9) | 0.4882 (15) | 0.038* | |
| H7B | 0.435 (3) | 0.173 (10) | 0.5193 (14) | 0.038* | |
| O8 | 0.61447 (17) | 0.1366 (5) | 0.54820 (9) | 0.0222 (6) | |
| H8A | 0.651 (2) | 0.124 (10) | 0.5642 (13) | 0.033* | |
| H8B | 0.584 (3) | 0.022 (7) | 0.550 (2) | 0.033* | |
| O9 | 0.70252 (18) | 0.6523 (5) | 0.52830 (10) | 0.0240 (6) | |
| H9A | 0.729 (3) | 0.506 (10) | 0.5247 (19) | 0.036* | |
| H9B | 0.717 (3) | 0.707 (10) | 0.5492 (19) | 0.036* | |
| O10 | 0.54562 (19) | 0.8403 (5) | 0.47200 (10) | 0.0241 (6) | |
| H10A | 0.530 (3) | 0.776 (10) | 0.4526 (18) | 0.036* | |
| H10B | 0.507 (4) | 0.945 (10) | 0.480 (2) | 0.036* | |
| N1 | 0.7581 (3) | 0.9463 (7) | 0.34771 (14) | 0.0243 (9) | |
| H1 | 0.792 (3) | 0.949 (10) | 0.3293 (16) | 0.037* | |
| N2 | 0.6865 (3) | 1.0657 (6) | 0.33042 (12) | 0.0308 (9) | |
| N3 | 0.4899 (3) | 0.5316 (7) | 0.65254 (15) | 0.0254 (9) | |
| H3 | 0.454 (3) | 0.544 (10) | 0.6701 (16) | 0.038* | |
| N4 | 0.5581 (3) | 0.3991 (7) | 0.67014 (13) | 0.0398 (10) | |
| C1 | 0.8094 (2) | 0.7177 (7) | 0.42815 (12) | 0.0180 (8) | |
| C2 | 0.8516 (3) | 0.9122 (8) | 0.40294 (14) | 0.0266 (9) | |
| H2A | 0.886964 | 1.009290 | 0.420772 | 0.032* | |
| H2B | 0.886701 | 0.831769 | 0.382845 | 0.032* | |
| C3 | 0.7943 (3) | 1.0812 (7) | 0.38121 (13) | 0.0240 (9) | |
| H3A | 0.751492 | 1.138148 | 0.399790 | 0.029* | |
| H3B | 0.824043 | 1.223813 | 0.370938 | 0.029* | |
| C4 | 0.6963 (4) | 1.3329 (8) | 0.32444 (18) | 0.0457 (14) | |
| H4A | 0.697253 | 1.413826 | 0.350657 | 0.069* | |
| H4B | 0.650888 | 1.394886 | 0.308527 | 0.069* | |
| H4C | 0.747182 | 1.364707 | 0.310239 | 0.069* | |
| C5 | 0.6719 (4) | 0.9498 (8) | 0.2904 (2) | 0.0416 (14) | |
| H5C | 0.719071 | 0.975629 | 0.273010 | 0.062* | |
| H5D | 0.623950 | 1.022298 | 0.277842 | 0.062* | |
| H5E | 0.663080 | 0.775844 | 0.293987 | 0.062* | |
| C6 | 0.6167 (4) | 1.0165 (10) | 0.3575 (2) | 0.0382 (14) | |
| H6C | 0.607611 | 0.841579 | 0.359257 | 0.057* | |
| H6D | 0.568050 | 1.095072 | 0.346802 | 0.057* | |
| H6E | 0.628344 | 1.080630 | 0.384387 | 0.057* | |
| C7 | 0.4383 (2) | 0.7743 (7) | 0.57220 (12) | 0.0190 (8) | |
| C8 | 0.3960 (3) | 0.5814 (8) | 0.59707 (14) | 0.0270 (9) | |
| H8C | 0.361903 | 0.662841 | 0.617476 | 0.032* | |
| H8D | 0.359465 | 0.488736 | 0.579189 | 0.032* | |
| C9 | 0.4512 (3) | 0.4059 (7) | 0.61824 (13) | 0.0244 (9) | |
| H9C | 0.419698 | 0.265265 | 0.628036 | 0.029* | |
| H9D | 0.493099 | 0.346329 | 0.599409 | 0.029* | |
| C10 | 0.5447 (5) | 0.1391 (10) | 0.6751 (2) | 0.073 (2) | |
| H10C | 0.495470 | 0.112758 | 0.691030 | 0.110* | |
| H10D | 0.591059 | 0.067082 | 0.689066 | 0.110* | |
| H10E | 0.538397 | 0.063338 | 0.648684 | 0.110* | |
| C11 | 0.5722 (5) | 0.5108 (9) | 0.7105 (2) | 0.052 (2) | |
| H11A | 0.584574 | 0.683111 | 0.707269 | 0.078* | |
| H11B | 0.617855 | 0.429848 | 0.723737 | 0.078* | |
| H11C | 0.523504 | 0.492499 | 0.727074 | 0.078* | |
| C12 | 0.6308 (5) | 0.4501 (13) | 0.6429 (3) | 0.0527 (18) | |
| H12A | 0.621070 | 0.379778 | 0.616269 | 0.079* | |
| H12B | 0.679559 | 0.377958 | 0.654625 | 0.079* | |
| H12C | 0.638291 | 0.625353 | 0.640292 | 0.079* | |
| O11 | 1.0017 (2) | 0.4552 (7) | 0.40834 (13) | 0.0284 (8) | |
| H11D | 0.999 (4) | 0.458 (11) | 0.3843 (8) | 0.043* | |
| H11E | 0.957 (3) | 0.488 (11) | 0.417 (3) | 0.043* | |
| O12 | 0.9948 (3) | 0.4654 (7) | 0.32594 (15) | 0.0441 (10) | |
| H12D | 0.973 (4) | 0.586 (9) | 0.318 (2) | 0.066* | |
| H12E | 0.975 (4) | 0.348 (9) | 0.316 (2) | 0.066* | |
| O13 | 0.7469 (2) | 0.9506 (6) | 0.59158 (13) | 0.0272 (8) | |
| H13A | 0.752 (4) | 0.933 (11) | 0.6152 (8) | 0.041* | |
| H13B | 0.793 (2) | 0.976 (11) | 0.585 (3) | 0.041* | |
| O14 | 0.7528 (3) | 0.9447 (8) | 0.67369 (14) | 0.0489 (11) | |
| H14A | 0.777 (5) | 1.077 (10) | 0.681 (3) | 0.073* | |
| H14B | 0.771 (4) | 0.817 (10) | 0.686 (2) | 0.073* |
Poly[[tetra-µ-aqua-diaquabis[3-(1,1,1-trimethylhydrazin-1-ium-2-yl)\ propanoate]disodium] dibromide tetrahydrate] (I). Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Br1 | 0.0441 (3) | 0.0355 (2) | 0.0268 (3) | −0.0014 (2) | 0.0046 (2) | −0.0016 (3) |
| Br2 | 0.0516 (3) | 0.0410 (2) | 0.0277 (3) | 0.0037 (2) | 0.0026 (3) | 0.0051 (3) |
| Na1 | 0.0180 (10) | 0.0155 (7) | 0.0211 (14) | 0.0004 (5) | 0.0014 (8) | 0.0006 (6) |
| Na2 | 0.0197 (11) | 0.0147 (7) | 0.0213 (14) | −0.0003 (6) | −0.0004 (8) | 0.0001 (5) |
| O1 | 0.0191 (14) | 0.0220 (14) | 0.0276 (15) | −0.0005 (11) | 0.0029 (12) | 0.0007 (11) |
| O2 | 0.0220 (16) | 0.0263 (14) | 0.0235 (18) | 0.0009 (13) | −0.0005 (13) | 0.0040 (13) |
| O3 | 0.0198 (15) | 0.0244 (14) | 0.0287 (16) | 0.0009 (12) | 0.0051 (11) | 0.0023 (12) |
| O4 | 0.0200 (16) | 0.0248 (14) | 0.0230 (17) | 0.0007 (12) | −0.0010 (13) | 0.0050 (13) |
| O5 | 0.0232 (15) | 0.0182 (13) | 0.0297 (16) | 0.0008 (12) | −0.0024 (13) | 0.0033 (12) |
| O6 | 0.0224 (16) | 0.0239 (14) | 0.0285 (17) | −0.0023 (12) | −0.0057 (12) | 0.0067 (12) |
| O7 | 0.0233 (16) | 0.0245 (15) | 0.0288 (16) | −0.0024 (12) | −0.0030 (12) | 0.0071 (12) |
| O8 | 0.0227 (15) | 0.0179 (13) | 0.0261 (16) | −0.0018 (11) | −0.0028 (12) | 0.0017 (12) |
| O9 | 0.0267 (15) | 0.0192 (14) | 0.0262 (16) | 0.0017 (12) | −0.0042 (13) | −0.0026 (12) |
| O10 | 0.0273 (16) | 0.0183 (14) | 0.0267 (16) | 0.0013 (12) | −0.0041 (12) | −0.0031 (11) |
| N1 | 0.030 (2) | 0.0216 (17) | 0.021 (2) | 0.0059 (16) | −0.0010 (17) | 0.0027 (15) |
| N2 | 0.046 (2) | 0.0195 (17) | 0.027 (2) | 0.0025 (16) | −0.0092 (17) | 0.0028 (15) |
| N3 | 0.031 (2) | 0.0231 (17) | 0.022 (2) | 0.0029 (16) | −0.0017 (18) | −0.0007 (15) |
| N4 | 0.061 (3) | 0.028 (2) | 0.031 (2) | 0.012 (2) | −0.021 (2) | −0.0027 (17) |
| C1 | 0.022 (2) | 0.0159 (17) | 0.0157 (19) | −0.0030 (14) | −0.0003 (15) | −0.0020 (14) |
| C2 | 0.025 (2) | 0.027 (2) | 0.028 (2) | −0.0044 (18) | −0.0001 (19) | 0.0064 (18) |
| C3 | 0.029 (2) | 0.0203 (19) | 0.023 (2) | 0.0013 (17) | −0.0015 (17) | 0.0030 (17) |
| C4 | 0.066 (4) | 0.018 (2) | 0.053 (3) | 0.002 (2) | −0.019 (3) | 0.009 (2) |
| C5 | 0.066 (4) | 0.032 (2) | 0.027 (3) | −0.004 (2) | −0.016 (3) | −0.001 (2) |
| C6 | 0.026 (3) | 0.049 (3) | 0.039 (4) | 0.004 (2) | −0.004 (3) | −0.002 (2) |
| C7 | 0.024 (2) | 0.0187 (18) | 0.0142 (19) | −0.0032 (15) | −0.0014 (15) | −0.0030 (14) |
| C8 | 0.021 (2) | 0.030 (2) | 0.030 (2) | −0.0014 (18) | 0.0002 (18) | 0.0111 (19) |
| C9 | 0.028 (2) | 0.0211 (19) | 0.024 (2) | −0.0028 (17) | −0.0043 (18) | 0.0001 (16) |
| C10 | 0.116 (6) | 0.025 (3) | 0.078 (5) | 0.003 (3) | −0.056 (4) | 0.009 (3) |
| C11 | 0.089 (5) | 0.039 (3) | 0.027 (3) | 0.004 (2) | −0.029 (3) | −0.001 (2) |
| C12 | 0.040 (4) | 0.065 (4) | 0.053 (5) | 0.017 (3) | −0.008 (3) | −0.015 (3) |
| O11 | 0.0229 (18) | 0.0383 (17) | 0.024 (2) | 0.0050 (15) | −0.0012 (15) | 0.0031 (16) |
| O12 | 0.062 (3) | 0.036 (2) | 0.034 (2) | −0.0029 (19) | −0.015 (2) | −0.0038 (17) |
| O13 | 0.0214 (17) | 0.0368 (17) | 0.023 (2) | −0.0041 (15) | −0.0035 (15) | 0.0007 (15) |
| O14 | 0.069 (3) | 0.044 (2) | 0.033 (3) | 0.008 (2) | −0.011 (2) | −0.0001 (19) |
Poly[[tetra-µ-aqua-diaquabis[3-(1,1,1-trimethylhydrazin-1-ium-2-yl)\ propanoate]disodium] dibromide tetrahydrate] (I). Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Na1—O1 | 2.367 (4) | N4—C12 | 1.530 (10) |
| Na1—O5 | 2.368 (3) | C1—C2 | 1.531 (6) |
| Na1—O6 | 2.369 (3) | C2—H2A | 0.9900 |
| Na1—O8i | 2.517 (4) | C2—H2B | 0.9900 |
| Na1—O9 | 2.442 (4) | C2—C3 | 1.514 (6) |
| Na1—O10 | 2.361 (4) | C3—H3A | 0.9900 |
| Na2—O3 | 2.359 (4) | C3—H3B | 0.9900 |
| Na2—O5ii | 2.543 (4) | C4—H4A | 0.9800 |
| Na2—O7 | 2.368 (3) | C4—H4B | 0.9800 |
| Na2—O8 | 2.364 (3) | C4—H4C | 0.9800 |
| Na2—O9 | 2.361 (3) | C5—H5C | 0.9800 |
| Na2—O10 | 2.449 (4) | C5—H5D | 0.9800 |
| O1—C1 | 1.241 (5) | C5—H5E | 0.9800 |
| O2—C1 | 1.281 (5) | C6—H6C | 0.9800 |
| O3—C7 | 1.249 (5) | C6—H6D | 0.9800 |
| O4—C7 | 1.282 (5) | C6—H6E | 0.9800 |
| O5—H5A | 0.97 (6) | C7—C8 | 1.519 (6) |
| O5—H5B | 0.82 (6) | C8—H8C | 0.9900 |
| O6—H6A | 0.80 (3) | C8—H8D | 0.9900 |
| O6—H6B | 0.82 (3) | C8—C9 | 1.506 (6) |
| O7—H7A | 0.82 (3) | C9—H9C | 0.9900 |
| O7—H7B | 0.80 (3) | C9—H9D | 0.9900 |
| O8—H8A | 0.81 (3) | C10—H10C | 0.9800 |
| O8—H8B | 0.81 (3) | C10—H10D | 0.9800 |
| O9—H9A | 0.93 (6) | C10—H10E | 0.9800 |
| O9—H9B | 0.79 (6) | C11—H11A | 0.9800 |
| O10—H10A | 0.78 (6) | C11—H11B | 0.9800 |
| O10—H10B | 0.90 (6) | C11—H11C | 0.9800 |
| N1—H1 | 0.83 (4) | C12—H12A | 0.9800 |
| N1—N2 | 1.471 (6) | C12—H12B | 0.9800 |
| N1—C3 | 1.468 (6) | C12—H12C | 0.9800 |
| N2—C4 | 1.499 (6) | O11—H11D | 0.80 (3) |
| N2—C5 | 1.498 (8) | O11—H11E | 0.80 (3) |
| N2—C6 | 1.489 (8) | O12—H12D | 0.80 (3) |
| N3—H3 | 0.84 (4) | O12—H12E | 0.80 (3) |
| N3—N4 | 1.466 (6) | O13—H13A | 0.80 (3) |
| N3—C9 | 1.481 (6) | O13—H13B | 0.80 (3) |
| N4—C10 | 1.463 (7) | O14—H14A | 0.87 (5) |
| N4—C11 | 1.497 (8) | O14—H14B | 0.87 (5) |
| O1—Na1—O5 | 109.25 (14) | N3—N4—C11 | 105.8 (4) |
| O1—Na1—O6 | 100.00 (12) | N3—N4—C12 | 105.9 (4) |
| O1—Na1—O8i | 160.43 (13) | C10—N4—N3 | 114.7 (4) |
| O1—Na1—O9 | 83.01 (11) | C10—N4—C11 | 109.1 (5) |
| O5—Na1—O6 | 80.32 (12) | C10—N4—C12 | 111.6 (5) |
| O5—Na1—O8i | 89.64 (11) | C11—N4—C12 | 109.5 (5) |
| O5—Na1—O9 | 167.30 (15) | O1—C1—O2 | 124.5 (4) |
| O6—Na1—O8i | 87.89 (13) | O1—C1—C2 | 119.6 (4) |
| O6—Na1—O9 | 101.22 (13) | O2—C1—C2 | 115.9 (4) |
| O9—Na1—O8i | 77.87 (13) | C1—C2—H2A | 108.7 |
| O10—Na1—O1 | 92.84 (12) | C1—C2—H2B | 108.7 |
| O10—Na1—O5 | 87.35 (12) | H2A—C2—H2B | 107.6 |
| O10—Na1—O6 | 164.52 (13) | C3—C2—C1 | 114.2 (4) |
| O10—Na1—O8i | 82.69 (12) | C3—C2—H2A | 108.7 |
| O10—Na1—O9 | 88.81 (11) | C3—C2—H2B | 108.7 |
| O3—Na2—O5ii | 160.55 (13) | N1—C3—C2 | 107.7 (3) |
| O3—Na2—O7 | 100.26 (12) | N1—C3—H3A | 110.2 |
| O3—Na2—O8 | 109.70 (14) | N1—C3—H3B | 110.2 |
| O3—Na2—O9 | 93.04 (13) | C2—C3—H3A | 110.2 |
| O3—Na2—O10 | 83.44 (11) | C2—C3—H3B | 110.2 |
| O5ii—Na2—H9A | 71.3 (14) | H3A—C3—H3B | 108.5 |
| O7—Na2—O5ii | 87.40 (13) | N2—C4—H4A | 109.5 |
| O7—Na2—H9A | 143.9 (13) | N2—C4—H4B | 109.5 |
| O7—Na2—O10 | 100.79 (13) | N2—C4—H4C | 109.5 |
| O8—Na2—O5ii | 89.11 (11) | H4A—C4—H4B | 109.5 |
| O8—Na2—O7 | 80.45 (11) | H4A—C4—H4C | 109.5 |
| O8—Na2—O10 | 166.49 (15) | H4B—C4—H4C | 109.5 |
| O9—Na2—O5ii | 82.56 (12) | N2—C5—H5C | 109.5 |
| O9—Na2—O7 | 164.42 (13) | N2—C5—H5D | 109.5 |
| O9—Na2—O8 | 87.49 (12) | N2—C5—H5E | 109.5 |
| O9—Na2—O10 | 88.67 (11) | H5C—C5—H5D | 109.5 |
| O10—Na2—O5ii | 77.55 (12) | H5C—C5—H5E | 109.5 |
| C1—O1—Na1 | 124.7 (2) | H5D—C5—H5E | 109.5 |
| C7—O3—Na2 | 124.5 (3) | N2—C6—H6C | 109.5 |
| Na1—O5—Na2i | 90.26 (13) | N2—C6—H6D | 109.5 |
| Na1—O5—H5A | 123 (3) | N2—C6—H6E | 109.5 |
| Na1—O5—H5B | 132 (4) | H6C—C6—H6D | 109.5 |
| Na2i—O5—H5A | 106 (4) | H6C—C6—H6E | 109.5 |
| Na2i—O5—H5B | 93 (4) | H6D—C6—H6E | 109.5 |
| H5A—O5—H5B | 102 (5) | O3—C7—O4 | 124.2 (4) |
| Na1—O6—H6A | 124 (4) | O3—C7—C8 | 119.3 (4) |
| Na1—O6—H6B | 120 (4) | O4—C7—C8 | 116.5 (4) |
| H6A—O6—H6B | 108 (6) | C7—C8—H8C | 108.4 |
| Na2—O7—H7A | 117 (4) | C7—C8—H8D | 108.4 |
| Na2—O7—H7B | 122 (4) | H8C—C8—H8D | 107.5 |
| H7A—O7—H7B | 105 (5) | C9—C8—C7 | 115.3 (4) |
| Na1ii—O8—H8A | 103 (4) | C9—C8—H8C | 108.4 |
| Na1ii—O8—H8B | 94 (5) | C9—C8—H8D | 108.4 |
| Na2—O8—Na1ii | 91.00 (13) | N3—C9—C8 | 108.6 (4) |
| Na2—O8—H8A | 126 (4) | N3—C9—H9C | 110.0 |
| Na2—O8—H8B | 120 (4) | N3—C9—H9D | 110.0 |
| H8A—O8—H8B | 111 (6) | C8—C9—H9C | 110.0 |
| Na1—O9—H9A | 132 (4) | C8—C9—H9D | 110.0 |
| Na1—O9—H9B | 107 (4) | H9C—C9—H9D | 108.3 |
| Na2—O9—Na1 | 91.34 (13) | N4—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| Na2—O9—H9A | 96 (4) | N4—C10—H10D | 109.5 |
| Na2—O9—H9B | 123 (4) | N4—C10—H10E | 109.5 |
| H9A—O9—H9B | 108 (5) | H10C—C10—H10D | 109.5 |
| Na1—O10—Na2 | 91.18 (13) | H10C—C10—H10E | 109.5 |
| Na1—O10—H10A | 127 (4) | H10D—C10—H10E | 109.5 |
| Na1—O10—H10B | 112 (4) | N4—C11—H11A | 109.5 |
| Na2—O10—H10A | 102 (4) | N4—C11—H11B | 109.5 |
| Na2—O10—H10B | 115 (4) | N4—C11—H11C | 109.5 |
| H10A—O10—H10B | 108 (6) | H11A—C11—H11B | 109.5 |
| N2—N1—H1 | 104 (5) | H11A—C11—H11C | 109.5 |
| C3—N1—H1 | 106 (5) | H11B—C11—H11C | 109.5 |
| C3—N1—N2 | 113.3 (3) | N4—C12—H12A | 109.5 |
| N1—N2—C4 | 114.0 (4) | N4—C12—H12B | 109.5 |
| N1—N2—C5 | 106.6 (4) | N4—C12—H12C | 109.5 |
| N1—N2—C6 | 107.7 (4) | H12A—C12—H12B | 109.5 |
| C5—N2—C4 | 108.7 (4) | H12A—C12—H12C | 109.5 |
| C6—N2—C4 | 110.1 (4) | H12B—C12—H12C | 109.5 |
| C6—N2—C5 | 109.6 (4) | H11D—O11—H11E | 107 (8) |
| N4—N3—H3 | 108 (4) | H12D—O12—H12E | 111 (9) |
| N4—N3—C9 | 113.9 (3) | H13A—O13—H13B | 102 (8) |
| C9—N3—H3 | 106 (5) | H14A—O14—H14B | 113 (8) |
| Na1—O1—C1—O2 | 99.2 (4) | N4—N3—C9—C8 | −167.1 (4) |
| Na1—O1—C1—C2 | −78.2 (4) | C1—C2—C3—N1 | −73.2 (5) |
| Na2—O3—C7—O4 | −99.5 (4) | C3—N1—N2—C4 | 43.8 (6) |
| Na2—O3—C7—C8 | 78.8 (4) | C3—N1—N2—C5 | 163.8 (4) |
| O1—C1—C2—C3 | −12.3 (5) | C3—N1—N2—C6 | −78.6 (5) |
| O2—C1—C2—C3 | 170.1 (4) | C7—C8—C9—N3 | 73.4 (5) |
| O3—C7—C8—C9 | 10.5 (6) | C9—N3—N4—C10 | −42.9 (7) |
| O4—C7—C8—C9 | −171.1 (4) | C9—N3—N4—C11 | −163.1 (5) |
| N2—N1—C3—C2 | 165.2 (4) | C9—N3—N4—C12 | 80.7 (5) |
Symmetry codes: (i) x, y+1, z; (ii) x, y−1, z.
Poly[[tetra-µ-aqua-diaquabis[3-(1,1,1-trimethylhydrazin-1-ium-2-yl)\ propanoate]disodium] dibromide tetrahydrate] (I). Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O5—H5A···O1i | 0.97 (6) | 1.79 (6) | 2.746 (4) | 172 (6) |
| O5—H5B···O11iii | 0.82 (6) | 2.02 (6) | 2.819 (5) | 167 (6) |
| O6—H6A···O4iv | 0.80 (3) | 2.06 (3) | 2.845 (5) | 165 (6) |
| O6—H6B···O2i | 0.82 (3) | 1.91 (3) | 2.732 (4) | 175 (6) |
| O7—H7A···O2v | 0.82 (3) | 2.05 (3) | 2.856 (5) | 165 (6) |
| O7—H7B···O4ii | 0.80 (3) | 1.94 (3) | 2.731 (4) | 169 (6) |
| O8—H8A···O13ii | 0.81 (3) | 2.06 (3) | 2.815 (5) | 155 (5) |
| O8—H8B···O3ii | 0.81 (3) | 1.95 (3) | 2.754 (4) | 168 (7) |
| O9—H9A···O6ii | 0.93 (6) | 1.96 (6) | 2.852 (4) | 160 (5) |
| O9—H9B···O13 | 0.79 (6) | 2.01 (6) | 2.772 (5) | 160 (6) |
| O10—H10A···O11v | 0.78 (6) | 2.00 (6) | 2.771 (5) | 167 (6) |
| O10—H10B···O7i | 0.90 (6) | 1.99 (6) | 2.853 (4) | 158 (5) |
| O11—H11D···O12 | 0.80 (3) | 1.94 (3) | 2.744 (6) | 179 (7) |
| O11—H11E···O2 | 0.80 (3) | 1.92 (3) | 2.719 (5) | 174 (9) |
| O13—H13A···O14 | 0.80 (3) | 1.95 (3) | 2.733 (6) | 170 (6) |
| O13—H13B···O4iv | 0.80 (3) | 1.94 (3) | 2.727 (5) | 168 (9) |
| N1—H1···Br1i | 0.83 (5) | 2.57 (5) | 3.379 (5) | 167 (5) |
| N3—H3···Br2v | 0.84 (5) | 2.57 (5) | 3.394 (5) | 169 (5) |
| O12—H12D···Br1i | 0.80 (5) | 2.52 (6) | 3.316 (4) | 172 (6) |
| O12—H12E···Br1 | 0.80 (5) | 2.49 (6) | 3.289 (4) | 177 (8) |
| O14—H14A···Br2i | 0.87 (7) | 2.47 (7) | 3.323 (5) | 168 (7) |
| O14—H14B···Br2 | 0.87 (6) | 2.41 (6) | 3.281 (5) | 175 (6) |
Symmetry codes: (i) x, y+1, z; (ii) x, y−1, z; (iii) x−1/2, −y+2, z; (iv) x+1/2, −y+2, z; (v) x−1/2, −y+1, z.
Poly[[di-µ-aqua-diaquabis[µ-3-(1,1,1-trimethylhydrazin-1-ium-2-yl)\ propanoate]disodium] diiodide] (II). Crystal data
| [Na2(C6H14N2O2)2(H2O)4]·I2 | F(000) = 1312 |
| Mr = 664.23 | Dx = 1.779 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 19.7455 (11) Å | Cell parameters from 9932 reflections |
| b = 11.4530 (7) Å | θ = 3.1–27.9° |
| c = 10.9733 (7) Å | µ = 2.61 mm−1 |
| β = 92.382 (2)° | T = 173 K |
| V = 2479.4 (3) Å3 | Plate, colourless |
| Z = 4 | 0.3 × 0.2 × 0.07 mm |
Poly[[di-µ-aqua-diaquabis[µ-3-(1,1,1-trimethylhydrazin-1-ium-2-yl)\ propanoate]disodium] diiodide] (II). Data collection
| Bruker PHOTON-100 CMOS diffractometer | 5012 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Radiation source: sealedtube | Rint = 0.048 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 27.1°, θmin = 2.7° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (TWINABS; Krause et al., 2015) | h = −25→25 |
| Tmin = 0.301, Tmax = 0.431 | k = 0→14 |
| 5475 measured reflections | l = 0→14 |
| 5475 independent reflections |
Poly[[di-µ-aqua-diaquabis[µ-3-(1,1,1-trimethylhydrazin-1-ium-2-yl)\ propanoate]disodium] diiodide] (II). Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | 0 restraints |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: mixed |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.026 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| wR(F2) = 0.057 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0177P)2 + 4.3911P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.17 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 5475 reflections | Δρmax = 0.70 e Å−3 |
| 286 parameters | Δρmin = −0.55 e Å−3 |
Poly[[di-µ-aqua-diaquabis[µ-3-(1,1,1-trimethylhydrazin-1-ium-2-yl)\ propanoate]disodium] diiodide] (II). Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refined as a 2-component twin. |
Poly[[di-µ-aqua-diaquabis[µ-3-(1,1,1-trimethylhydrazin-1-ium-2-yl)\ propanoate]disodium] diiodide] (II). Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| I1 | 0.25574 (2) | 0.48014 (2) | 0.74401 (2) | 0.01967 (6) | |
| I2 | 0.02717 (2) | 0.01593 (2) | 0.75216 (2) | 0.02095 (7) | |
| Na1 | 0.45889 (8) | 0.30771 (15) | 0.87401 (15) | 0.0228 (4) | |
| Na2 | 0.54574 (8) | 0.37173 (13) | 0.56036 (14) | 0.0177 (3) | |
| H5A | 0.412 (3) | 0.150 (5) | 1.034 (5) | 0.048 (18)* | |
| O1 | 0.38099 (12) | 0.1816 (2) | 0.7525 (3) | 0.0205 (5) | |
| O2 | 0.29207 (14) | 0.0789 (3) | 0.8118 (2) | 0.0219 (6) | |
| O3 | 0.55979 (13) | 0.3377 (3) | 0.7678 (3) | 0.0252 (6) | |
| O4 | 0.57944 (14) | 0.3107 (3) | 0.9672 (2) | 0.0193 (6) | |
| O5 | 0.43527 (15) | 0.2101 (3) | 1.0559 (3) | 0.0212 (6) | |
| H5B | 0.418 (3) | 0.246 (5) | 1.113 (5) | 0.038 (15)* | |
| O6 | 0.42378 (16) | 0.5067 (3) | 0.8601 (3) | 0.0273 (7) | |
| H6A | 0.382266 | 0.512961 | 0.824831 | 0.041* | |
| H6B | 0.428059 | 0.568362 | 0.908724 | 0.041* | |
| O7 | 0.63392 (14) | 0.4980 (2) | 0.5020 (3) | 0.0225 (6) | |
| H7A | 0.659951 | 0.465242 | 0.444491 | 0.034* | |
| H7B | 0.662743 | 0.517998 | 0.565473 | 0.034* | |
| O8 | 0.49586 (16) | 0.4327 (3) | 0.3560 (3) | 0.0225 (6) | |
| H8A | 0.459 (3) | 0.425 (5) | 0.314 (6) | 0.049 (17)* | |
| H8B | 0.517 (3) | 0.453 (5) | 0.292 (7) | 0.06 (2)* | |
| N1 | 0.16954 (18) | 0.1758 (3) | 0.6228 (3) | 0.0167 (7) | |
| H1 | 0.137 (3) | 0.143 (5) | 0.651 (5) | 0.044 (17)* | |
| N2 | 0.13426 (15) | 0.2379 (3) | 0.5206 (3) | 0.0142 (7) | |
| N3 | 0.78736 (16) | 0.2584 (3) | 0.9016 (3) | 0.0180 (7) | |
| H3 | 0.783 (3) | 0.195 (5) | 0.850 (5) | 0.049 (17)* | |
| N4 | 0.83846 (16) | 0.2233 (3) | 0.9966 (3) | 0.0183 (8) | |
| C1 | 0.32344 (17) | 0.1332 (3) | 0.7334 (4) | 0.0155 (7) | |
| C2 | 0.29341 (19) | 0.1380 (4) | 0.6039 (4) | 0.0202 (8) | |
| H2A | 0.323168 | 0.092864 | 0.550794 | 0.024* | |
| H2B | 0.294100 | 0.220190 | 0.576042 | 0.024* | |
| C3 | 0.22141 (19) | 0.0918 (3) | 0.5852 (4) | 0.0186 (8) | |
| H3A | 0.213016 | 0.072622 | 0.497921 | 0.022* | |
| H3B | 0.216958 | 0.018875 | 0.632569 | 0.022* | |
| C4 | 0.0888 (2) | 0.3230 (4) | 0.5808 (4) | 0.0227 (9) | |
| H4A | 0.055992 | 0.280383 | 0.628483 | 0.034* | |
| H4B | 0.064620 | 0.370023 | 0.518335 | 0.034* | |
| H4C | 0.116052 | 0.374288 | 0.634871 | 0.034* | |
| C5 | 0.0924 (2) | 0.1603 (4) | 0.4372 (4) | 0.0204 (9) | |
| H5C | 0.122247 | 0.106328 | 0.395452 | 0.031* | |
| H5D | 0.067248 | 0.208076 | 0.376722 | 0.031* | |
| H5E | 0.060508 | 0.115656 | 0.484926 | 0.031* | |
| C6 | 0.1844 (2) | 0.3039 (4) | 0.4481 (4) | 0.0197 (8) | |
| H6C | 0.212631 | 0.352880 | 0.503036 | 0.029* | |
| H6D | 0.160127 | 0.353351 | 0.387941 | 0.029* | |
| H6E | 0.213223 | 0.248583 | 0.406033 | 0.029* | |
| C7 | 0.59886 (19) | 0.3209 (3) | 0.8594 (3) | 0.0149 (8) | |
| C8 | 0.67425 (19) | 0.3096 (3) | 0.8349 (3) | 0.0176 (8) | |
| H8C | 0.680210 | 0.244686 | 0.776752 | 0.021* | |
| H8D | 0.689360 | 0.382222 | 0.795342 | 0.021* | |
| C9 | 0.71953 (19) | 0.2876 (3) | 0.9479 (4) | 0.0185 (8) | |
| H9A | 0.722229 | 0.358018 | 1.000169 | 0.022* | |
| H9B | 0.701879 | 0.221932 | 0.996013 | 0.022* | |
| C10 | 0.8943 (2) | 0.1664 (4) | 0.9296 (4) | 0.0270 (10) | |
| H10A | 0.876446 | 0.097529 | 0.885963 | 0.040* | |
| H10B | 0.930579 | 0.142601 | 0.987910 | 0.040* | |
| H10C | 0.912211 | 0.221802 | 0.871014 | 0.040* | |
| C11 | 0.8123 (2) | 0.1393 (4) | 1.0886 (4) | 0.0309 (10) | |
| H11A | 0.779170 | 0.178956 | 1.138310 | 0.046* | |
| H11B | 0.850060 | 0.111068 | 1.141379 | 0.046* | |
| H11C | 0.790487 | 0.073026 | 1.046252 | 0.046* | |
| C12 | 0.8657 (2) | 0.3300 (4) | 1.0583 (5) | 0.0290 (10) | |
| H12A | 0.883202 | 0.383425 | 0.997423 | 0.044* | |
| H12B | 0.902343 | 0.308279 | 1.116894 | 0.044* | |
| H12C | 0.829389 | 0.368612 | 1.101424 | 0.044* |
Poly[[di-µ-aqua-diaquabis[µ-3-(1,1,1-trimethylhydrazin-1-ium-2-yl)\ propanoate]disodium] diiodide] (II). Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| I1 | 0.02077 (12) | 0.02229 (12) | 0.01602 (12) | −0.00185 (10) | 0.00150 (12) | 0.00076 (10) |
| I2 | 0.01730 (12) | 0.02514 (12) | 0.02035 (14) | −0.00498 (9) | −0.00011 (13) | 0.00198 (10) |
| Na1 | 0.0199 (8) | 0.0258 (9) | 0.0226 (8) | −0.0008 (7) | −0.0001 (7) | 0.0014 (7) |
| Na2 | 0.0173 (7) | 0.0207 (8) | 0.0151 (7) | −0.0017 (6) | 0.0004 (6) | −0.0007 (6) |
| O1 | 0.0172 (13) | 0.0235 (13) | 0.0206 (13) | −0.0024 (10) | −0.0028 (11) | 0.0040 (11) |
| O2 | 0.0199 (14) | 0.0282 (16) | 0.0178 (14) | −0.0012 (12) | 0.0016 (11) | 0.0040 (12) |
| O3 | 0.0190 (14) | 0.0382 (16) | 0.0181 (15) | 0.0030 (11) | −0.0012 (12) | 0.0042 (13) |
| O4 | 0.0182 (14) | 0.0237 (15) | 0.0160 (14) | −0.0010 (12) | 0.0017 (11) | 0.0015 (11) |
| O5 | 0.0166 (15) | 0.0250 (16) | 0.0223 (16) | −0.0002 (12) | 0.0036 (12) | −0.0047 (13) |
| O6 | 0.0216 (16) | 0.0324 (18) | 0.0276 (16) | 0.0020 (13) | −0.0013 (12) | −0.0066 (13) |
| O7 | 0.0194 (15) | 0.0321 (17) | 0.0162 (13) | −0.0044 (13) | 0.0040 (11) | −0.0036 (12) |
| O8 | 0.0207 (17) | 0.0298 (17) | 0.0168 (15) | −0.0035 (13) | −0.0013 (13) | 0.0015 (12) |
| N1 | 0.0169 (18) | 0.0223 (18) | 0.0107 (15) | −0.0012 (15) | −0.0017 (13) | 0.0015 (13) |
| N2 | 0.0138 (14) | 0.0175 (18) | 0.0112 (17) | 0.0014 (14) | −0.0011 (13) | −0.0009 (11) |
| N3 | 0.0145 (17) | 0.0221 (18) | 0.0173 (17) | 0.0033 (14) | −0.0005 (13) | −0.0014 (13) |
| N4 | 0.0143 (15) | 0.020 (2) | 0.0202 (18) | 0.0029 (12) | −0.0018 (14) | −0.0014 (14) |
| C1 | 0.0142 (17) | 0.0135 (16) | 0.0188 (18) | 0.0056 (13) | 0.0015 (15) | −0.0011 (14) |
| C2 | 0.014 (2) | 0.027 (2) | 0.019 (2) | −0.0001 (17) | 0.0005 (16) | 0.0008 (17) |
| C3 | 0.0186 (19) | 0.018 (2) | 0.0184 (19) | −0.0011 (16) | −0.0020 (16) | 0.0012 (15) |
| C4 | 0.024 (2) | 0.021 (2) | 0.022 (2) | 0.0074 (18) | 0.0002 (18) | −0.0036 (17) |
| C5 | 0.021 (2) | 0.024 (2) | 0.0159 (19) | −0.0038 (18) | −0.0056 (16) | −0.0041 (16) |
| C6 | 0.018 (2) | 0.022 (2) | 0.019 (2) | −0.0033 (16) | −0.0001 (16) | 0.0030 (16) |
| C7 | 0.0135 (19) | 0.0137 (19) | 0.0176 (18) | −0.0011 (15) | 0.0006 (15) | 0.0009 (14) |
| C8 | 0.019 (2) | 0.0152 (19) | 0.0182 (18) | 0.0030 (15) | 0.0011 (15) | 0.0014 (14) |
| C9 | 0.0172 (19) | 0.019 (2) | 0.0194 (19) | 0.0007 (15) | 0.0032 (15) | 0.0012 (15) |
| C10 | 0.015 (2) | 0.034 (3) | 0.032 (2) | 0.0107 (19) | 0.0003 (18) | −0.006 (2) |
| C11 | 0.027 (2) | 0.042 (3) | 0.023 (2) | 0.006 (2) | −0.0025 (19) | 0.013 (2) |
| C12 | 0.022 (2) | 0.028 (3) | 0.037 (3) | 0.0025 (19) | −0.005 (2) | −0.011 (2) |
Poly[[di-µ-aqua-diaquabis[µ-3-(1,1,1-trimethylhydrazin-1-ium-2-yl)\ propanoate]disodium] diiodide] (II). Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Na1—Na2i | 3.325 (2) | N3—N4 | 1.476 (4) |
| Na1—Na2 | 3.977 (2) | N3—C9 | 1.490 (5) |
| Na1—O1 | 2.462 (3) | N4—C10 | 1.499 (5) |
| Na1—O3 | 2.374 (3) | N4—C11 | 1.502 (5) |
| Na1—O4 | 2.552 (3) | N4—C12 | 1.487 (6) |
| Na1—O5 | 2.351 (3) | C1—C2 | 1.518 (5) |
| Na1—O6 | 2.385 (4) | C2—H2A | 0.9900 |
| Na1—O8i | 2.857 (4) | C2—H2B | 0.9900 |
| Na1—C7 | 2.779 (4) | C2—C3 | 1.522 (5) |
| Na2—Na2ii | 3.668 (3) | C3—H3A | 0.9900 |
| Na2—O3 | 2.315 (3) | C3—H3B | 0.9900 |
| Na2—O4iii | 2.431 (3) | C4—H4A | 0.9800 |
| Na2—O5iii | 2.373 (3) | C4—H4B | 0.9800 |
| Na2—O7 | 2.372 (3) | C4—H4C | 0.9800 |
| Na2—O8ii | 2.569 (4) | C5—H5C | 0.9800 |
| Na2—O8 | 2.510 (3) | C5—H5D | 0.9800 |
| O1—C1 | 1.274 (4) | C5—H5E | 0.9800 |
| O2—C1 | 1.247 (4) | C6—H6C | 0.9800 |
| O3—C7 | 1.256 (5) | C6—H6D | 0.9800 |
| O4—C7 | 1.264 (5) | C6—H6E | 0.9800 |
| O5—H5A | 0.86 (6) | C7—C8 | 1.529 (5) |
| O5—H5B | 0.84 (6) | C8—H8C | 0.9900 |
| O6—H6A | 0.8946 | C8—H8D | 0.9900 |
| O6—H6B | 0.8873 | C8—C9 | 1.520 (5) |
| O7—H7A | 0.9110 | C9—H9A | 0.9900 |
| O7—H7B | 0.9103 | C9—H9B | 0.9900 |
| O8—H8A | 0.85 (6) | C10—H10A | 0.9800 |
| O8—H8B | 0.86 (7) | C10—H10B | 0.9800 |
| N1—H1 | 0.83 (6) | C10—H10C | 0.9800 |
| N1—N2 | 1.478 (4) | C11—H11A | 0.9800 |
| N1—C3 | 1.476 (5) | C11—H11B | 0.9800 |
| N2—C4 | 1.496 (5) | C11—H11C | 0.9800 |
| N2—C5 | 1.499 (5) | C12—H12A | 0.9800 |
| N2—C6 | 1.500 (5) | C12—H12B | 0.9800 |
| N3—H3 | 0.92 (6) | C12—H12C | 0.9800 |
| O1—Na1—O4 | 140.94 (12) | N3—N4—C10 | 105.5 (3) |
| O1—Na1—O8i | 63.43 (9) | N3—N4—C11 | 113.9 (3) |
| O1—Na1—C7 | 126.95 (12) | N3—N4—C12 | 108.8 (3) |
| O3—Na1—O1 | 109.70 (11) | C10—N4—C11 | 109.4 (3) |
| O3—Na1—O4 | 53.63 (9) | C12—N4—C10 | 108.8 (3) |
| O3—Na1—O6 | 94.48 (12) | C12—N4—C11 | 110.3 (4) |
| O3—Na1—O8i | 83.30 (11) | O1—C1—C2 | 116.7 (3) |
| O3—Na1—C7 | 26.77 (10) | O2—C1—O1 | 124.6 (4) |
| O4—Na1—O8i | 78.70 (10) | O2—C1—C2 | 118.6 (3) |
| O4—Na1—C7 | 27.00 (10) | C1—C2—H2A | 108.3 |
| O5—Na1—O1 | 92.25 (11) | C1—C2—H2B | 108.3 |
| O5—Na1—O3 | 133.27 (12) | C1—C2—C3 | 116.1 (3) |
| O5—Na1—O4 | 83.16 (11) | H2A—C2—H2B | 107.4 |
| O5—Na1—O6 | 116.18 (13) | C3—C2—H2A | 108.3 |
| O5—Na1—O8i | 70.18 (11) | C3—C2—H2B | 108.3 |
| O5—Na1—C7 | 107.91 (12) | N1—C3—C2 | 113.0 (3) |
| O6—Na1—O1 | 110.65 (11) | N1—C3—H3A | 109.0 |
| O6—Na1—O4 | 106.06 (12) | N1—C3—H3B | 109.0 |
| O6—Na1—O8i | 172.17 (12) | C2—C3—H3A | 109.0 |
| O6—Na1—C7 | 103.39 (12) | C2—C3—H3B | 109.0 |
| C7—Na1—O8i | 77.92 (11) | H3A—C3—H3B | 107.8 |
| O3—Na2—O4iii | 104.18 (11) | N2—C4—H4A | 109.5 |
| O3—Na2—O5iii | 91.51 (11) | N2—C4—H4B | 109.5 |
| O3—Na2—O7 | 108.00 (12) | N2—C4—H4C | 109.5 |
| O3—Na2—O8 | 162.13 (12) | H4A—C4—H4B | 109.5 |
| O3—Na2—O8ii | 79.78 (11) | H4A—C4—H4C | 109.5 |
| O4iii—Na2—O8ii | 175.55 (12) | H4B—C4—H4C | 109.5 |
| O4iii—Na2—O8 | 88.14 (11) | N2—C5—H5C | 109.5 |
| O5iii—Na2—O4iii | 85.36 (11) | N2—C5—H5D | 109.5 |
| O5iii—Na2—O8ii | 92.56 (12) | N2—C5—H5E | 109.5 |
| O5iii—Na2—O8 | 76.41 (11) | H5C—C5—H5D | 109.5 |
| O7—Na2—O4iii | 101.17 (11) | H5C—C5—H5E | 109.5 |
| O7—Na2—O5iii | 156.89 (13) | H5D—C5—H5E | 109.5 |
| O7—Na2—O8 | 81.63 (11) | N2—C6—H6C | 109.5 |
| O7—Na2—O8ii | 79.28 (11) | N2—C6—H6D | 109.5 |
| O8—Na2—O8ii | 87.55 (11) | N2—C6—H6E | 109.5 |
| C1—O1—Na1 | 151.3 (3) | H6C—C6—H6D | 109.5 |
| C7—O3—Na1 | 94.9 (2) | H6C—C6—H6E | 109.5 |
| C7—O3—Na2 | 149.0 (2) | H6D—C6—H6E | 109.5 |
| Na2i—O4—Na1 | 83.67 (10) | O3—C7—Na1 | 58.34 (19) |
| C7—O4—Na1 | 86.6 (2) | O3—C7—O4 | 124.2 (3) |
| C7—O4—Na2i | 124.9 (3) | O3—C7—C8 | 116.2 (3) |
| Na1—O5—Na2i | 89.48 (11) | O4—C7—Na1 | 66.4 (2) |
| Na1—O5—H5A | 105 (4) | O4—C7—C8 | 119.5 (3) |
| Na1—O5—H5B | 120 (4) | C8—C7—Na1 | 169.5 (3) |
| Na2i—O5—H5A | 99 (4) | C7—C8—H8C | 108.6 |
| Na2i—O5—H5B | 126 (4) | C7—C8—H8D | 108.6 |
| H5A—O5—H5B | 112 (5) | H8C—C8—H8D | 107.6 |
| Na1—O6—H6A | 111.3 | C9—C8—C7 | 114.5 (3) |
| Na1—O6—H6B | 134.6 | C9—C8—H8C | 108.6 |
| H6A—O6—H6B | 105.0 | C9—C8—H8D | 108.6 |
| Na2—O7—H7A | 112.2 | N3—C9—C8 | 105.4 (3) |
| Na2—O7—H7B | 112.9 | N3—C9—H9A | 110.7 |
| H7A—O7—H7B | 106.3 | N3—C9—H9B | 110.7 |
| Na1iii—O8—H8A | 74 (4) | C8—C9—H9A | 110.7 |
| Na1iii—O8—H8B | 117 (4) | C8—C9—H9B | 110.7 |
| Na2—O8—Na1iii | 76.24 (10) | H9A—C9—H9B | 108.8 |
| Na2ii—O8—Na1iii | 136.82 (13) | N4—C10—H10A | 109.5 |
| Na2—O8—Na2ii | 92.45 (11) | N4—C10—H10B | 109.5 |
| Na2—O8—H8A | 139 (4) | N4—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| Na2ii—O8—H8A | 90 (4) | H10A—C10—H10B | 109.5 |
| Na2—O8—H8B | 129 (4) | H10A—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| Na2ii—O8—H8B | 103 (4) | H10B—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| H8A—O8—H8B | 90 (5) | N4—C11—H11A | 109.5 |
| N2—N1—H1 | 99 (4) | N4—C11—H11B | 109.5 |
| C3—N1—H1 | 112 (4) | N4—C11—H11C | 109.5 |
| C3—N1—N2 | 114.3 (3) | H11A—C11—H11B | 109.5 |
| N1—N2—C4 | 104.6 (3) | H11A—C11—H11C | 109.5 |
| N1—N2—C5 | 114.1 (3) | H11B—C11—H11C | 109.5 |
| N1—N2—C6 | 110.1 (3) | N4—C12—H12A | 109.5 |
| C4—N2—C5 | 109.3 (3) | N4—C12—H12B | 109.5 |
| C4—N2—C6 | 109.1 (3) | N4—C12—H12C | 109.5 |
| C5—N2—C6 | 109.5 (3) | H12A—C12—H12B | 109.5 |
| N4—N3—H3 | 105 (4) | H12A—C12—H12C | 109.5 |
| N4—N3—C9 | 114.7 (3) | H12B—C12—H12C | 109.5 |
| C9—N3—H3 | 109 (4) | ||
| Na1—O1—C1—O2 | −48.2 (7) | O2—C1—C2—C3 | 9.4 (5) |
| Na1—O1—C1—C2 | 134.9 (4) | O3—C7—C8—C9 | −179.1 (3) |
| Na1—O3—C7—O4 | −8.8 (4) | O4—C7—C8—C9 | −0.5 (5) |
| Na1—O3—C7—C8 | 169.7 (3) | N2—N1—C3—C2 | 102.5 (4) |
| Na1—O4—C7—O3 | 8.2 (4) | N4—N3—C9—C8 | −174.9 (3) |
| Na1—O4—C7—C8 | −170.3 (3) | C1—C2—C3—N1 | 78.7 (4) |
| Na1—C7—C8—C9 | −122.6 (14) | C3—N1—N2—C4 | −175.9 (3) |
| Na2—O3—C7—Na1 | −175.0 (6) | C3—N1—N2—C5 | 64.8 (4) |
| Na2—O3—C7—O4 | 176.2 (3) | C3—N1—N2—C6 | −58.8 (4) |
| Na2—O3—C7—C8 | −5.3 (7) | C7—C8—C9—N3 | 170.1 (3) |
| Na2i—O4—C7—Na1 | 79.9 (2) | C9—N3—N4—C10 | 164.3 (3) |
| Na2i—O4—C7—O3 | 88.0 (5) | C9—N3—N4—C11 | 44.3 (4) |
| Na2i—O4—C7—C8 | −90.4 (4) | C9—N3—N4—C12 | −79.2 (4) |
| O1—C1—C2—C3 | −173.5 (3) |
Symmetry codes: (i) x, −y+1/2, z+1/2; (ii) −x+1, −y+1, −z+1; (iii) x, −y+1/2, z−1/2.
Poly[[di-µ-aqua-diaquabis[µ-3-(1,1,1-trimethylhydrazin-1-ium-2-yl)\ propanoate]disodium] diiodide] (II). Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O5—H5B···O1i | 0.85 (6) | 1.89 (6) | 2.741 (4) | 175 (6) |
| O7—H7B···O2iv | 0.91 | 1.73 | 2.629 (4) | 169 |
| O8—H8A···O1iii | 0.85 (6) | 2.05 (6) | 2.815 (4) | 149 (6) |
| N1—H1···I2 | 0.82 (6) | 2.87 (6) | 3.688 (4) | 177 (5) |
| N3—H3···I1v | 0.92 (6) | 2.76 (6) | 3.650 (3) | 161 (5) |
| O5—H5A···O7v | 0.86 (6) | 2.00 (6) | 2.846 (4) | 172 (4) |
| O6—H6A···I1 | 0.89 | 2.64 | 3.518 (3) | 166 |
| O6—H6B···O4vi | 0.89 | 1.95 | 2.825 (4) | 168 |
| O7—H7A···I1ii | 0.91 | 2.78 | 3.548 (3) | 143 |
| O8—H8B···O6ii | 0.86 (7) | 2.13 (7) | 2.989 (5) | 175 (5) |
| C3—H3A···I1iii | 0.99 | 3.01 | 3.920 (4) | 154 |
| C11—H11B···I2vii | 0.98 | 3.02 | 3.975 (4) | 165 |
| C12—H12C···I1vi | 0.98 | 2.99 | 3.952 (5) | 167 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x, −y+1/2, z+1/2; (ii) −x+1, −y+1, −z+1; (iii) x, −y+1/2, z−1/2; (iv) −x+1, y+1/2, −z+3/2; (v) −x+1, y−1/2, −z+3/2; (vi) −x+1, −y+1, −z+2; (vii) −x+1, −y, −z+2.
Funding Statement
This work was funded by State University of New York grant .
References
- Andrade, L. C. R., Costa, M. M. R., Paixao, J., Agostinho Moreira, J., Almeida, A., Chaves, M. R. & Klopperpieper, A. (1999). Z. Kristallogr. New Cryst. Struct. 214, 83–84.
- Andrade, L. C. R., Costa, M. M. R., Pinto, F., Paixao, J. A., Almeida, A., Chaves, M. R. & Klopperpieper, A. (2000). Z. Kristallogr. New Cryst. Struct. 215, 537–538.
- Andrade, L. C. R., Costa, M. M. R., Pinto, F., Rodrigues, V. H., Paixao, J. A., Almeida, A., Chaves, M. R. & Klopperpieper, A. (2001). Z. Kristallogr. New Cryst. Struct. 216, 227–228.
- Bērziņš, A. & Actiņš, A. (2014). CrystEngComm, 16, 3926–3934.
- Bruker (2016). APEX3 and SAINT. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K. & Puschmann, H. (2009). J. Appl. Cryst. 42, 339–341.
- Giller, S. A., Eremeev, A. V., Kalvin’sh, I. Y., Liepin’sh, É. É., & Semenikhina, V. G. (1975). Chem. Heterocycl. Compd. 11, 1378–1382.
- Görgens, C., Guddat, S., Dib, J., Geyer, H., Schänzer, W. & Thevis, M. (2015). Drug Test. Anal. 7, 973–979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Groom, C. R., Bruno, I. J., Lightfoot, M. P. & Ward, S. C. (2016). Acta Cryst. B72, 171–179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Kalvins, I., Liepins, E., Loza, E., Dambrova, M., Stonans, L., Lola, D., Kuka, J., Pugovics, O., Vilskersts, R. & Grinberga, S. (2014). US Patent, US 20140088125 A1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Kalvins, I. & Stonans, I. (2009). WO Patent, WO/2009/071586.
- Kemme, A., Bleidelis, J., Kalvinsh, I. & Eremeev, A. (1983). Latv. PSR Zinat. Akad. Vestis, 2, 215–218.
- Krause, L., Herbst-Irmer, R., Sheldrick, G. M. & Stalke, D. (2015). J. Appl. Cryst. 48, 3–10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Liepinsh, E., Makarova, E., Sevostjanovs, E., Hartmane, D., Cirule, H., Zharkova-Malkova, O., Grinberga, S. & Dambrova, M. (2017). Basic & Clinical Pharmacology & Toxicology 120, 450-456. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Nazarenko, A. Y. (2018). Private communication (refcodes CCDC 1822460–1822463. CCDC, Cambridge, England.
- Rodrigues, V. H., Costa, M. M. R., Klopperpieper, A., Chaves, M. R., Almeida, A. & Agostinho Moreira, J. (2005). Z. Kristallogr. New Cryst. Struct. 220, 363–364.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). CELL_NOW. Version 2008/4. University of Göttingen, Germany.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015a). Acta Cryst. A71, 3–8.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015b). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Silva, J. (2013). Patent CA 2661357 C, 2013.
- Turner, M. J., McKinnon, J. J., Wolff, S. K., Grimwood, D. J., Spackman, P. R., Jayatilaka, D. & Spackman, M. A. (2017). CrystalExplorer17. University of Western Australia. http://hirshfeldsurface.net
- Zvirgzdiņš, A., Veldre, K. & Actiņš, A. (2011). Latvian J. Chem. 50, 64–72.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, II. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018006977/zl2729sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018006977/zl2729Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018006977/zl2729Isup4.cdx
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) II. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018006977/zl2729IIsup3.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018006977/zl2729IIsup5.cdx
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report












