Abstract
Bacterial efflux pumps transport small molecules from the cytoplasm or periplasm outside the cell. Efflux pump activity is typically increased in multi-drug resistant (MDR) pathogens; chemicals that inhibit efflux pumps may have potential for antibiotic development. Using an in-cell screen, we identified three efflux pump modulators (EPMs) from a drug diversity library. The screening platform uses macrophages infected with the human Gram-negative pathogen Salmonella enterica (Salmonella) to identify small molecules that prevent bacterial replication or survival within the host environment. A secondary screen for hit compounds that increase the accumulation of an efflux pump substrate, Hoechst 33342, identified three small molecules with activity comparable to the known efflux pump inhibitor PAβN (Phe-Arg β-naphthylamide). The three putative EPMs demonstrated significant antibacterial activity against Salmonella within primary and cell culture macrophages and within a human epithelial cell line. Unlike traditional antibiotics, the three compounds did not inhibit bacterial growth in standard microbiological media. The three compounds prevented energy-dependent efflux pump activity in Salmonella and bound the AcrB subunit of the AcrAB-TolC efflux system with KDs in the micromolar range. Moreover, the EPMs display antibacterial synergy with antimicrobial peptides, a class of host innate immune defense molecules present in body fluids and cells. The EPMs also had synergistic activity with antibiotics exported by AcrAB-TolC in broth and in macrophages and inhibited efflux pump activity in MDR Gram-negative ESKAPE clinical isolates. Thus, an in-cell screening approach identified EPMs that synergize with innate immunity to kill bacteria and have potential for development as adjuvants to antibiotics.
Author summary
Bacteria evolved molecular machines called efflux pumps to export toxic chemicals, including antibiotics encountered in the environment. Multi-drug resistant (MDR) bacteria use efflux pumps to rapidly transport clinical antibiotics out of the cell and thereby increase the dosage at which they tolerate antibiotics. One way to combat MDR pathogens may be to reduce the activity of efflux pumps and thereby increase pathogen sensitivity to existing antibiotics. We describe an infection-based screen that identified chemicals that inhibit bacterial efflux pump activity and show that these compounds bind to and block the activity of bacterial efflux pumps.
Introduction
Human pathogens have become increasingly resistant to clinical antibiotics. Gram-negative bacterial pathogens are particularly problematic because their outer membranes are impermeable to many chemicals, and because many compounds that do enter the periplasm or cross the cellular membrane are immediately exported by efflux pumps. Multi-drug resistant (MDR) bacteria typically have increased gene copy number and/or production of efflux pumps, features demonstrated to contribute to the failure of clinical antibiotic treatment [1]. For these reasons, compounds that reduce efflux pump activity (efflux pump modulators, EPMs) are under investigation for their potential use in re-sensitizing MDR pathogens to existing antibiotics [2].
Three synthetic small molecules with EPM activity against Gram-negative bacterial pathogens have been well characterized. Phe-Arg β-naphthylamide (PAβN) was identified in a screen for compounds that increase the sensitivity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to levofloxacin, an antibiotic and efflux pump substrate [3,4]. PAβN binds AcrB, the main component of the efflux system AcrAB-TolC, a member of the RND (resistance-nodulation-cell division) family of pumps. However, this compound was not developed as an antibiotic because medicinal chemistry could not separate EPM activity from unfavorable pharmacokinetics and toxicology, possibly reflecting off-target effects [5,6]. A second series of EPMs was identified in the same screen as PAβN. These pyridopyrimidines were subjected to medicinal chemistry, and the lead compound D13-9001 has efficacy against Pseudomonas aeruginosa during infection of rats [7,8]. Finally, a screen for chemicals that increase the sensitivity of E. coli to ciprofloxacin identified the pyranopyridine MBX2319 as an EPM that targets AcrB and has activity against multiple Enterobacteriaceae [9–12]. We identified three compounds that have activity as EPMs using a different approach—an in-cell screen for small molecules that prevent the replication of the Gram-negative pathogen Salmonella enterica (Salmonella) in mammalian cells.
Results
Screen for compounds that are antibacterial and non-toxic to mammalian cells
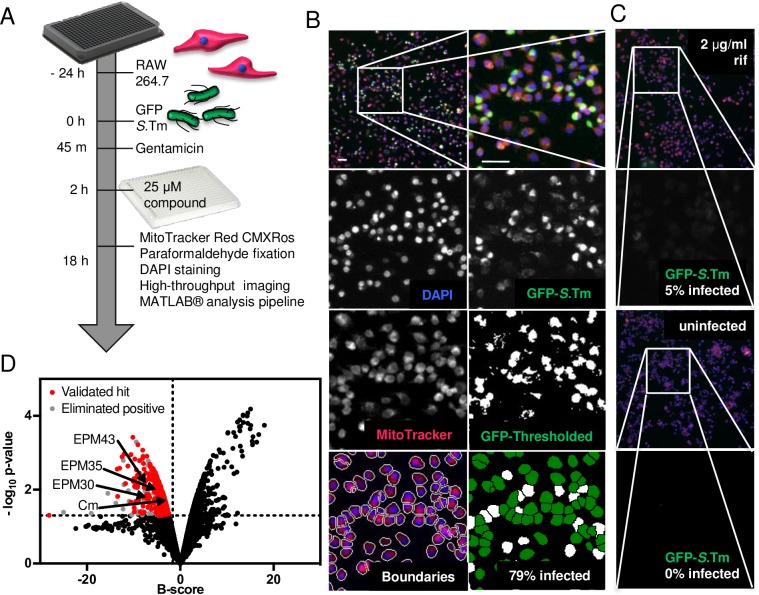
SAFIRE (Screen for Anti-infectives using Fluorescence microscopy of IntracellulaR Enterobacteriaceae) is a high-content, medium-throughput screening platform that identifies compounds active against Gram-negative bacteria within the context of host cells (Fig 1A). The platform uses fluorescence microscopy and automated image analysis to monitor Salmonella within RAW 264.7 cells, a macrophage-like cell line in which the virulent Salmonella laboratory strain SL1344 replicates 10-15-fold [13–15].
Fig 1. Screening platform (SAFIRE) used to identify EPMs.
(A) Schematic of screening methodology. (B) Representative micrographs of infected macrophages from DMSO-treated wells. Upper left is a field with 522 macrophages; remaining images are the indicated channels zoomed in on the boxed region. Scale bars are 50 μm. (C) Representative micrographs of infected macrophages treated with rifampicin [2 μg/mL] or of uninfected macrophages treated with DMSO. (D) Distribution of B-scores and p-values for 14,400 compounds from the Maybridge HitFinderTM v11 library. The locations of the three hit compounds (EPM30, EPM35 and EPM43) and of chloramphenicol (Cm), which was identified from the library, are shown.
We used SAFIRE to screen 14,400 compounds from a drug-like diversity library, the Maybridge HitFinderTM v11 [16–19]. Macrophages in 384-well plates were infected with Salmonella expressing GFP under the control of a promoter, sifB, that is induced within macrophages (Table 1) [20]. After 45 minutes, infected macrophages were treated with the antibiotic gentamicin to prevent the replication of extracellular bacteria [21]. At two hours post-infection, test compounds [25 μM] were added. The compounds remained for the duration of the experiment. At 17.5 hours post-infection, when optimal Salmonella replication was observed, cells were stained with a marker of macrophage vitality, MitoTracker Red CMXRos, to help identify compounds toxic to eukaryotic cells. Thirty minutes later, cells were fixed and incubated with DAPI to stain DNA and imaged on an automated microscope. A MATLAB-based algorithm was used to quantify bacterial infection, specifically, the percentage of infected cells. Macrophage boundaries were first established using MitoTracker and DAPI signals (Fig 1B). The percentage of infected cells was determined by setting a threshold for the GFP signal based on infected and uninfected controls; cells containing at least two GFP-positive pixels were labeled infected. The library was screened in duplicate, and well-to-well variability was addressed using B-score normalization [22–24]. Assay positives were called based on an activity threshold greater than one standard deviation below the mean B-score, and a p-value of less than 0.05 calculated using a modified t-test assuming an inverse gamma distribution of variances (Fig 1D) [23,25]. The micrographs of the 461 assay positives were manually reviewed to eliminate host-toxic and/or autofluorescent chemicals. The remaining 309 hits were retested using SAFIRE in the 96-well format and ranked based on reduction of bacterial load as determined by SAFIRE and traditional lysis and plating for colony forming units (CFU) (S1 Table). Sixty-four (85%) of the top 75 compounds, including chloramphenicol, reduced CFU by at least 25% (S1 Fig). The top 60 compounds (excluding chloramphenicol) were repurchased and validated using SAFIRE in a 96-well format; 58 repurchased compounds were active.
Table 1. Bacterial strains.
| Reference # | Species | Strain name | Antibiotic2 | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CSD1 | S. enterica1 | WT3, SL1344 | Str | [26] |
| CSD1021 | S. enterica1 | sifB::GFP | Str, Kan | [20] SDFR3 |
| CSD222 | S. enterica1 | rpsM::GFP | Str | [27] SM022 |
| ALR1268 | E. coli | RAM121 | [28] | |
| ALR1228 | S. enterica1 | mTagBFP24 | Str, Amp | [29] |
| ALR1257 | S. enterica1 | acrAB::kan | Str, Kan | This study |
| ALR1258 | S. enterica1 | macAB::kan | Str, Kan | This study |
| ALR1248 | S. enterica1 | S10801 | Str, Amp, Tet | BEI Resources (NR-22067) |
| ALC1250 | E. coli | 1101362 | Mero | BEI Resources (BAA-2340) |
| ALC1253 | K. pneumoniae | 1101160 | Mero | BEI Resources (BAA-2342) |
| ALC1251 | K. pneumoniae | ART 2008133 | Mero | BEI Resources (BAA-1705) |
| ALC1252 | Enterobacter cloacae | 1101152 | Mero | BEI Resources (BAA-2341) |
1S. enterica are serovar Typhimurium. All but S10801 are in an SL1344 background.
2 Antibiotics for growth selection: Streptomycin (Str), Ampicillin (Amp), Kanamycin (Kan), Tetracycline (Tet), Meropenem (Mero)
3 Wild-Type (WT)
4 mTagBFP2 is on pACYC177
Three compounds may modulate bacterial efflux pump activity
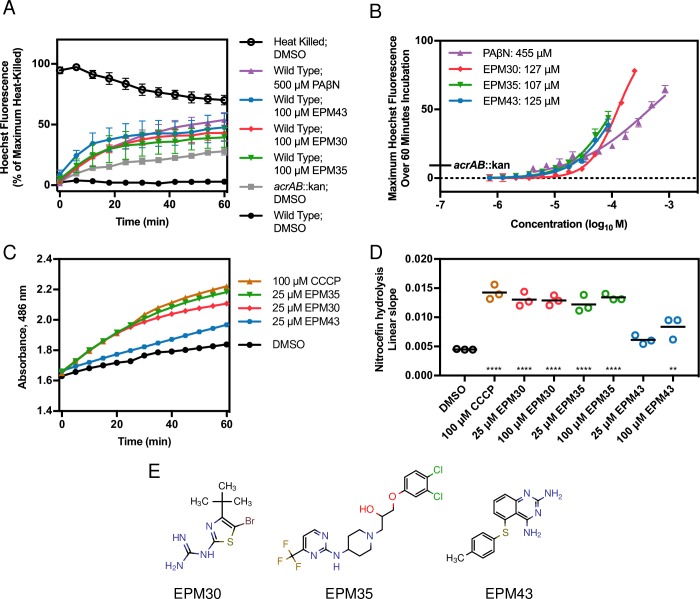
SAFIRE has the potential to identify EPMs because Salmonella requires at least two efflux pumps, AcrAB and MacAB, to replicate and/or survive within macrophages and mice [30–34]. The fluorescent dye Hoechst 33342 is an efflux pump substrate, and increased Hoechst accumulation relative to controls identifies potential modulators of efflux pumps [35]. We incubated bacteria with each of the 58 repurchased, validated hits and Hoechst 33342. As expected, heat-killed bacteria exhibited high fluorescence immediately after exposure to Hoechst because an electrochemical gradient is required to export pump substrates. Live, wild-type Salmonella demonstrated low fluorescence, and a strain lacking the AcrAB efflux pump had a modest level of fluorescence. PAβN treatment resulted in higher levels of fluorescence, as expected [35]. Under the same conditions, treatment with three of the 58 compounds (EPM30, EPM35 and EPM43) resulted in fluorescence comparable to that of PAβN (Fig 2A). Further examination revealed that the three compounds had half maximum effective concentrations (EC50s) four-fold lower than that of PAβN in the Hoechst assay (Fig 2B). These observations show that the hit compounds increase bacterial accumulation of an efflux pump substrate.
Fig 2. Three compounds may modulate bacterial efflux pump activity.
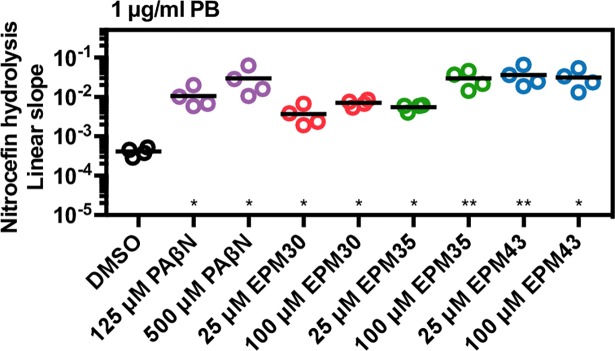
(A, B) Salmonella was incubated with Hoechst 33342 and the indicated compound. (A) Fluorescence was normalized to the maximum of heat-killed bacteria (100%). Mean and SEM from three biological replicates. (B) Maximum fluorescence over 60 minutes of exposure normalized to the maximum fluorescence of heat-killed bacteria (100%). The EC50s in the key were established using a nonlinear four-parameter fit. Mean and SEM from three biological replicates, each performed in duplicate. (C, D) Nitrocefin [100 μM] hydrolysis in a membrane-compromised E. coli strain treated with the indicated concentrations of drugs. Hydrolysis increases when efflux is blocked. (C) Absorbance 486 nm of RAM121 E. coli. Mean and SD are representative of three independent biological replicates. (D) Slope of the linear region of the A486 plot from at least three experiments. Data is normalized to A486/minute. ** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001 by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post-test. (E) Structures of the three EPMs.
We next tested the ability of the three hit compounds to inhibit efflux of nitrocefin, a chromogenic beta-lactam and known AcrAB substrate [9,36]. E. coli strain RAM121 encodes a porin with a large diameter, which allows rapid influx of nitrocefin, and the periplasmic AmpC beta-lactamase, which hydrolyzes nitrocefin and results in a color change. Carbonyl cyanide m-chlorophenylhydrazone (CCCP) is a protonophore that inhibits efflux pumps, causing increased nitrocefin hydrolysis (Fig 2C and 2D). Treatment with EPM30 or EPM35 yielded a similar result, whereas treatment with EPM43 only modestly increased hydrolysis. Thus, the three hit compounds (Fig 2E) may inhibit bacterial efflux pumps.
The three hit compounds are antibacterial against Salmonella in macrophages and epithelial cells
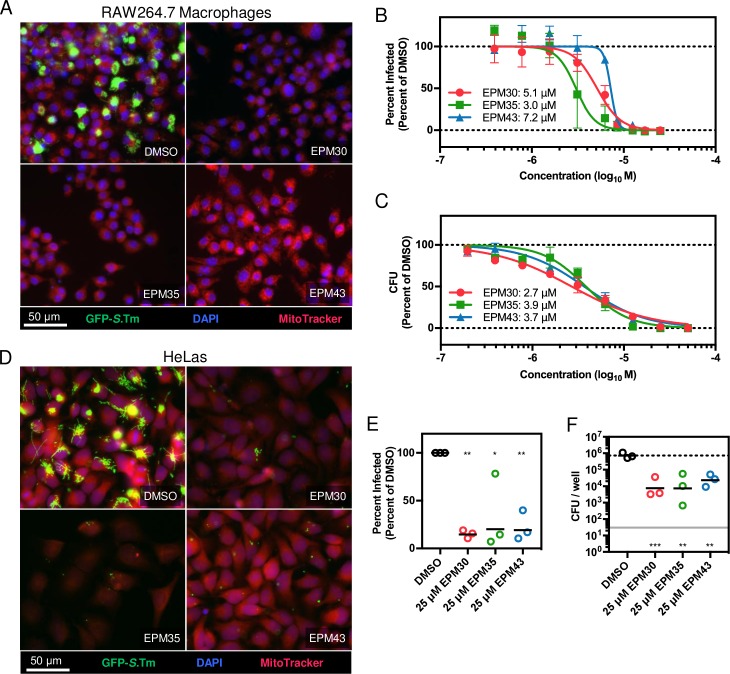
We performed a more thorough characterization of the putative EPMs regarding anti-Salmonella activity in multiple mammalian cell types. Micrographs from RAW264.7 macrophages treated with 25 μM of each compound demonstrated a significant reduction in the percentage of GFP-positive cells compared to treatment with vehicle alone (Fig 3A). The SAFIRE inhibitory concentration-50 (IC50) for the three compounds in macrophages ranged from 3 to 7 μM (Fig 3B). To establish whether reduced GFP signal correlates with bacterial killing, we quantified bacterial survival by enumerating CFU from infected cells. The IC50s for the 3 compounds by CFU ranged from 2 to 5 μM (Fig 3C). HeLa cells harboring a Salmonella-GFP expressing strain and treated with 25 μM of each compound also demonstrated a reduction in the percentage of GFP-positive cells compared to treatment with vehicle alone (Fig 3D and 3E). In primary bone marrow-derived mouse macrophages (BMDMs) all three hit compounds reduced the number of recoverable Salmonella by approximately 20-fold (Fig 3F). Finally, while the macrophage and HeLa cell culture assays require gentamicin to prevent the replication of extracellular Salmonella, we established in broth assays that the three compounds do not synergize with the antibacterial activity of gentamicin (S2 Fig). Thus, the putative EPMs inhibit bacterial replication and/or survival in at least two cell types, macrophages and epithelial cells, which are relevant to whole animal infection.
Fig 3. The three hit compounds decrease bacterial load of Salmonella in mammalian cells.
(A-C) Monitoring of bacterial load by GFP (SAFIRE) or CFU in RAW264.7 cells. (A) Representative micrographs of cells in 96-well plates infected with sifB::GFP Salmonella. Two hours after infection cells were treated with the indicated compound [25 μM] for 16 hours. (B) Dose response curve for SAFIRE and (C) CFU; keys includes IC50 values. (D-E) Monitoring of bacterial load by GFP (SAFIRE) in HeLa cells infected with Salmonella expressing rpsM::GFP and treated with the indicated compound [25 μM]. (F) Monitoring of bacterial load by CFU in BMDMs treated with compounds [25 μM]. Mean and SEM from three independent biological replicates. The nonlinear curve fitting (B, C) is constrained using uninfected cells as the minimum and DMSO-treated cells as the maximum. (E, F) * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 compared to DMSO by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post-test.
The three hit compounds reduce the survival of MDR Salmonella in macrophages
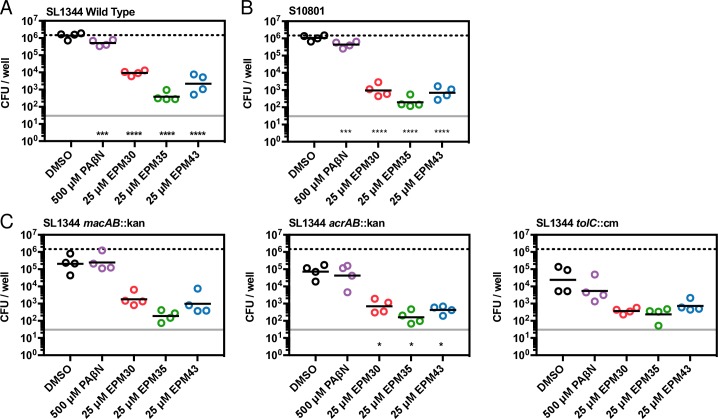
We next examined whether the bacterial load of MDR Salmonella in macrophages is reduced upon treatment of infected cells with the hit compounds. A clinical MDR Salmonella isolate (S10801) was recovered from hit compound-treated macrophages at levels 1000-fold lower than from DMSO-treated macrophages (Fig 4). These results indicate that the three compounds inhibit not only SL1344 but also an MDR clinical isolate during infection of cells.
Fig 4. The hit compounds reduce the survival of MDR Salmonella in macrophages.
Monitoring of bacterial load by CFU in RAW264.7 cells infected for two hours with the strain of Salmonella shown and then treated with the indicated compound for 16 hours, followed by macrophage lysis and plating for CFU. A) SL1344 Wild Type Salmonella, B) Clinical Salmonella isolate S10801, (C) SL1344 with macAB::kan, acrAB::kan or tolC::cm, respectively. Geometric mean of four biological replicates. Upper lines, mean CFU/well of wild-type SL1344 with DMSO treatment; lower lines, limit of detection. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001 relative to DMSO, one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post-test.
Clinical MDR isolates frequently express high levels of efflux pumps [1]. The two Salmonella efflux pumps needed for bacterial survival in cells and mice, AcrAB and MacAB, both use the TolC channel to export cargo across the outer membrane [30–34,37]. We first confirmed that Salmonella strains lacking acrAB, macAB, or tolC replicate poorly in macrophages compared to the wild-type parent strain (Fig 4). Treatment of macrophages with any of the three compounds reduced loads of wild-type bacterial below those observed in DMSO-treated cells infected with the acrAB, macAB, or tolC mutant strains. Compound treatment of the mutant strains in macrophages further reduced the levels of mutant bacteria. Given that Salmonella encodes other efflux pumps that may contribute to survival in macrophages in the absence of macAB, acrAB, or tolC [34,38,39], these data could suggest that the hit compounds target other efflux pumps.
The hit compounds inhibit energy-dependent efflux pump activity
Having established that the hit compounds are antimicrobial in mammalian cells, we returned to the analysis of their activity. While the Hoechst accumulation assay is a good first approximation of anti-efflux pump activity, quantification of export in real time based on energy (glucose) dependence is a more specific assay for pump inhibition.
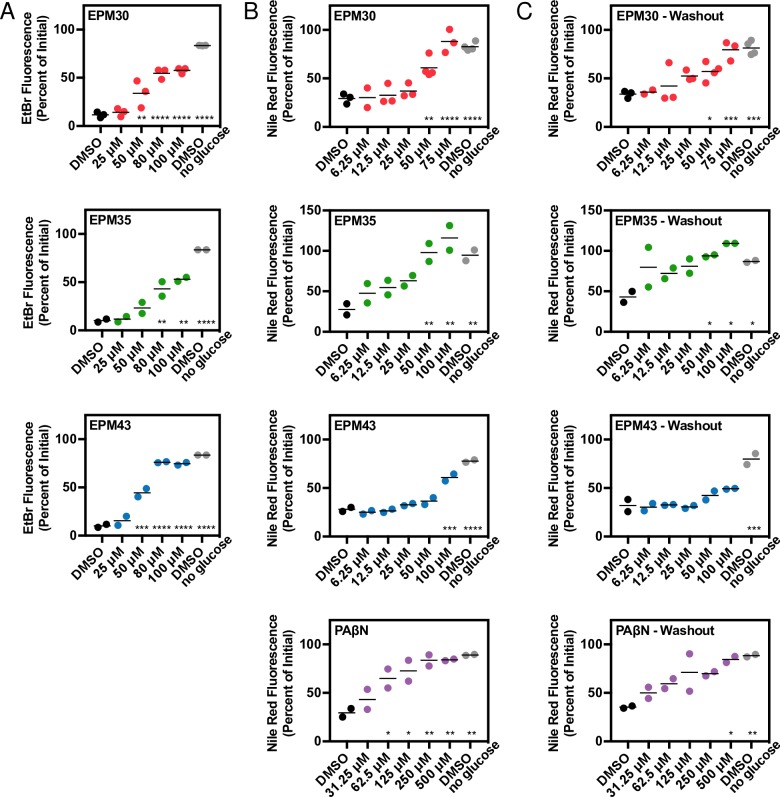
Ethidium bromide is an efflux pump substrate that fluoresces upon intercalating into DNA. We pre-loaded cells with ethidium bromide and then treated with glucose to energize the efflux pumps and stimulate export [40]. Incubation with PAβN or any of the three putative EPMs reduced ethidium bromide export upon glucose addition in a dose-dependent manner (Fig 5A; S3A Fig). A similar assay using the efflux pump substrate Nile red further demonstrated that EPM30 and EPM35 reduced pump export (Fig 5B; S3B Fig; S4 Fig). Nile red becomes strongly fluorescent upon partitioning into the cytoplasmic membrane and possibly the inner leaflet of the outer membrane but is rapidly exported [41–44]. Washout of the EPMs still reduced Nile red export, suggesting the activity of these compounds is not readily reversible (Fig 5C; S3C Fig). These observations indicate that the three hit compounds may inhibit energy-dependent efflux pump activity.
Fig 5. EPMs block efflux of ethidium bromide and Nile red.
Salmonella were incubated with either ethidium bromide or Nile red without glucose, treated with compound, exposed to glucose, and then monitored for fluorescence. Data for each sample were normalized to the initial fluorescence (100%). Dose response curves are (A) ethidium bromide at 28 minutes after glucose addition, (B) Nile red at 7 minutes after glucose addition, and (C) Nile red after washout of compound 7 minutes after glucose addition. Mean of at least two biological replicates performed in duplicate. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001 compared to DMSO + glucose by one-way ANOVA and Dunnett’s multiple comparison post-test.
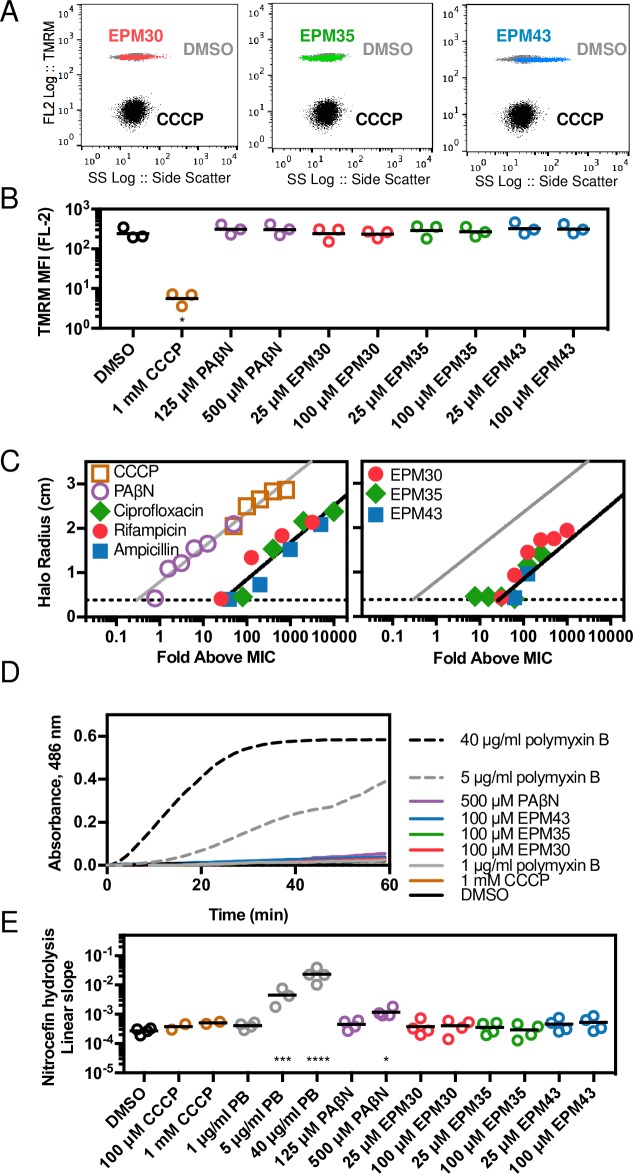
Bacterial membranes remain intact upon exposure to the three EPMs
Since efflux pumps rely upon the proton motive force or ATP to provide the energy for the transport of substrates, chemicals that disrupt the inner membrane may indirectly inhibit efflux. To establish whether the three EPMs alter bacterial inner membrane potential, we observed their effect on the incorporation of the voltage-sensitive dye tetramethylrhodamine methyl ester (TMRM). After 30 minutes of exposure to the ionophore CCCP, TMRM levels in cells were approximately 50-fold lower than upon treatment with DMSO, but treatment with any of the three EPMs did not alter TMRM signal based on analyses by flow cytometry (Fig 6A and 6B). These observations suggest that membrane potential remains intact in the presence of the EPMs. To establish whether a longer incubation with the EPMs may compromise membrane integrity, we monitored the effect of the EPMs on bacterial swimming, an energy intensive activity, over 15 hours [45] (Fig 6C; S5 Fig). Salmonella were injected into the center of soft-agar plates and 10 μl of compound was pipetted onto paper disks on the periphery [45]. Control compounds included CCCP and PAβN, which disrupts membranes over long (> 30 minutes) exposures [46–48]. Since the swimming assay also requires bacterial growth, we tested whether filters containing bacteriostatic antibiotics that are not known to disrupt membranes prevented swimming. Neither the three EPMs nor the conventional antibiotics inhibited swimming relative to their MIC, as compared to CCCP and PAβN, further suggesting that the EPMs do not interfere with bacterial energy production across the inner membrane.
Fig 6. EPMs do not disrupt bacterial inner or outer membranes.
(A,B) Salmonella treated with DMSO or EPMs [100 μM] but not CCCP [1 mM] acquire TMRM staining within 30 minutes. (A) Representative data from one of three independent experiments. (B) Median fluorescence intensity from three experiments normalized to unstained control (0). (C) Disk diffusion assays; the radius of the zone of growth inhibition after 16 hours of exposure to compound across a dose range. Black lines, semilog fit for the combined antibiotic data; gray lines, semilog fit for CCCP and PAβN; dotted lines, limit of detection (disk radius). Average of two measurements from each image captured from one experiment representative of two independent experiments. (D,E) Nitrocefin access to the periplasm as monitored by nitrocefin [100 μM] hydrolysis in the presence of the indicated concentrations of compounds. (D) Absorbance 486 nm of bla+ Salmonella normalized to bla- Salmonella. Data is representative of at least two independent biological replicates. (E) Slope of the linear region of the A486 plot from at least three experiments. Data is normalized to A486/minute. * p < 0.05, *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001 by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post-test.
A second class of chemicals that appears to interfere with bacterial efflux does so by permeabilizing the outer membrane, which allows substrates to diffuse into the periplasm [36]. We therefore tested whether exposure of bacteria with an intact outer membrane to the EPMs would enable the beta-lactam nitrocefin to enter the periplasm, as monitored by nitrocefin hydrolysis in bacteria with high expression levels of bla beta-lactamase [49]. In this assay, monitoring of absorbance showed that CCCP had no effect on nitrocefin hydrolysis, whereas polymyxin B, a pore-forming antimicrobial peptide, increased hydrolysis by 10-fold or more. The efflux pump inhibitor PAβN slightly increased hydrolysis but the EPMs did not (Fig 6D and 6E). Thus, the EPMs did not appear to increase nitrocefin access to the periplasm, suggesting they do not increase bacterial outer membrane permeability.
The three EPMs bind the efflux pump AcrB
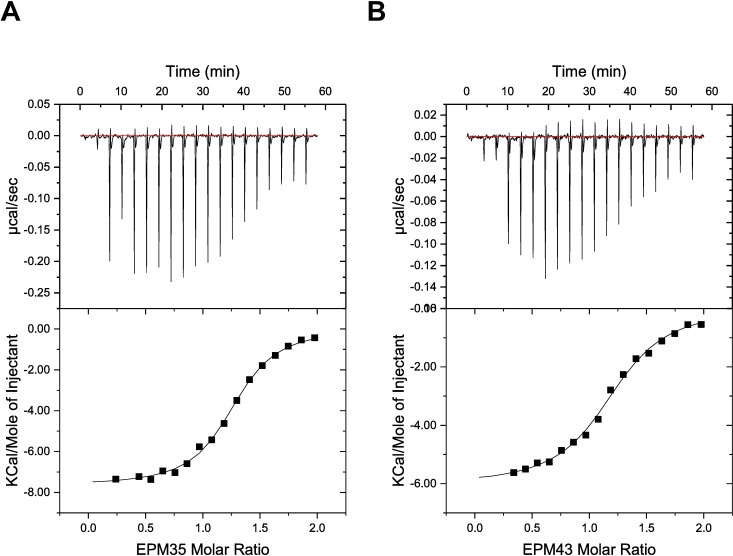
Since all three EPMs reduced Nile red or ethidium bromide export in Salmonella, well-studied substrates of the AcrAB-TolC efflux system [40,50], we established whether any of the compounds bind E. coli AcrB using isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC) [51–53] (Fig 7; S6 Fig; Table 2). The equilibrium dissociation constants (KDs) are within the micromolar range, demonstrating that AcrB is capable of binding each of the EPMs. It appears that AcrB interacts with these three EPMs using different binding mechanisms. The free energies of binding for EPM35 and EPM43 are dominated by the large negative enthalpies (ΔHs) of -7.7 and -6.0 kcal/mol, respectively. However, the binding for EPM30 is predominantly determined by its entropic contribution (-TΔS), which is -6.8 kcal/mol at 25 oC. These data suggest that the AcrB efflux pump tends to bind the EPMs with a 1:1 protein monomer-to-ligand molar ratio.
Fig 7. EPM35 and EPM43 interact with the efflux pump AcrB.
(A, B) Representative ITC for the binding of (A) EPM35 and (B) EPM43 to E. coli AcrB. Each peak in the upper graphs corresponds to the injection of 2 μL of 100 μM of the EPM in buffer containing 20 mM Na-HEPES (pH 7.5), 0.05% DDM and 5% DMSO into the reaction containing 10 μM of E. coli monomeric AcrB in buffer containing 20 mM Na-HEPES (pH 7.5), 0.05% DDM and 5% DMSO. The lower graphs show the cumulative heat of reaction displayed as a function of injection number. The solid line is the least-square fit to the experimental data.
Table 2. Binding of inhibitors by AcrB.
| KD (μM) | ΔH (cal•mol-1) | ΔS (cal•mol•deg-1) | N | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPM30 | 1.79 ± 0.37 | -1066.0 ± 46.5 | 22.7 | 1.3 ± 0.05 |
| EPM35 | 0.29 ± 0.03 | -7663.1 ± 84.4 | 4.2 | 1.2 ± 0.01 |
| EPM43 | 0.56 ± 0.06 | -6033.2 ± 106.3 | 8.6 | 1.2 ± 0.01 |
The hit compounds are not antibacterial in standard bacterial medium
To establish whether the hit compounds have minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) in broth that are similar to their IC50s in host cells (Fig 3B and 3C), we examined bacterial growth in their presence using standard rich laboratory media, Mueller Hinton Broth (MHB). The MICs of EPM30, EPM35, and EPM43 respectively were 100 μM [36 μg/mL], 400 μM [186 μg/mL], and >400 μM [113 μg/mL], for two Salmonella strains: the strain used in the SAFIRE screen (SL1344), and a clinical MDR Salmonella isolate (S10801). These broth MIC values (> 100 μM) are considerably higher than the IC50s observed in host cells (< 10 μM). Thus, the three putative EPMs may not function like traditional antibiotics and yet are potent in the context of the host cell.
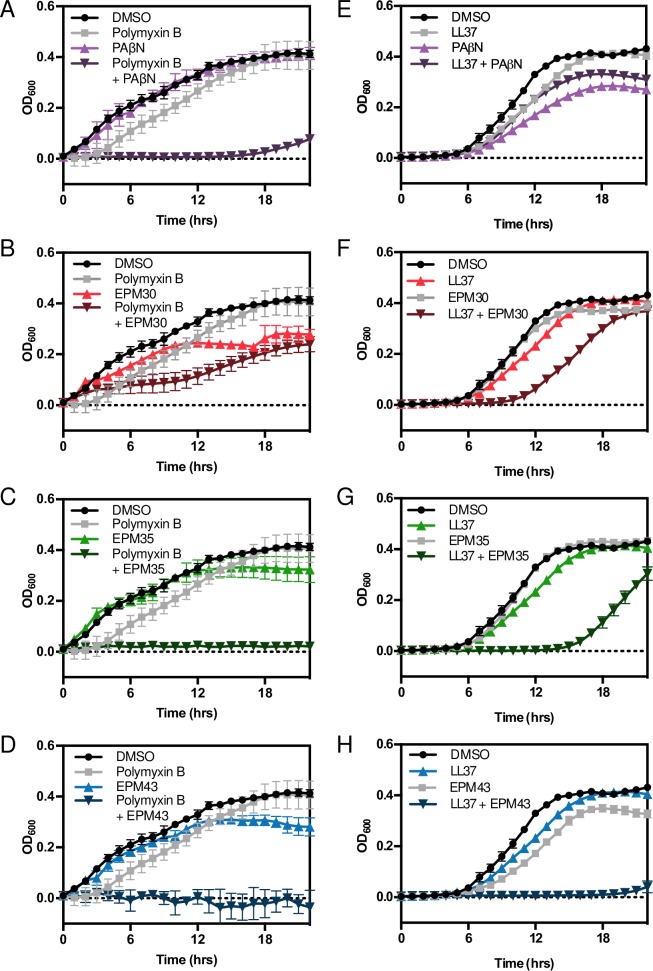
The three EPMs sensitize bacteria to antimicrobial peptides
We next addressed why the EPMs kill bacteria in mammalian cells at concentrations 10-fold lower than they inhibit efflux in broth. One possibility is that the presence of antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) within host cells plays a role. Mammalian cells constitutively express AMPs and increase AMP expression in response to infection [54,55]. We found that in broth the combination of each EPM with either the bacterial-derived polymyxin B or the human cathelicidin AMP LL37, but not individual treatments, significantly inhibited Salmonella growth; EPM35 and EPM43 display stronger synergy than EPM30 in this regard (Fig 8). These data suggest at least three possibilities: AMPs may potentiate EPM activity, EPMs may potentiate AMP activity, or both.
Fig 8. EPMs synergize with antimicrobial peptides.
Salmonella was grown in M9-based defined media in the presence of (A-D) polymyxin B (5 μg/ml; 1/8 MIC) or (E-H) LL37 (5 μg/ml; 1/8 MIC) and EPMs (PAβN, 500 μM; EPMs, 25 μM). Mean and SD of triplicate samples from one representative experiment of three independent biological replicates. DMSO, polymyxin B and LL37 curves repeat across graphs.
To distinguish between these possibilities, we first determined that bacterial exposure to polymyxin B concentrations high enough to allow nitrocefin access to the periplasm (5 μg/mL, Fig 6D and 6E) did not enhance the ability of the EPMs to increase Hoechst accumulation (S7A Fig). Similarly, co-treatment of polymyxin B with EPMs did not synergistically increase Nile red retention compared to polymyxin B or EPMs alone (S7B Fig). These observations suggest that the membrane-damaging activity of polymyxin B did not potentiate EPM blockage of efflux pumps. We next observed that low concentrations of polymyxin B [1 μg/mL], which do not by themselves allow nitrocefin access to the periplasm (Fig 6D and 6E), increased the rate of nitrocefin hydrolysis in a bla-expressing Salmonella strain when EPMs were present [25 μM] (Fig 9). It thus appears that EPMs potentiate AMPs with regard to both nitrocefin entry into the periplasm and bacterial growth inhibition. Therefore, EPMs may decrease the effective concentration of AMPs and, for this reason, have indirect antibacterial activity in the context of the host.
Fig 9. EPMs sensitize bacteria to outer membrane permeabilization by antimicrobial peptides.
Nitrocefin access to the periplasm in the presence of a non-permeabilizing concentration of polymyxin B [1 μg/ml] and the indicated concentrations of EPMs, quantitated as in Fig 6E. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post-test.
Two EPMs act synergistically with known AcrAB substrates in broth
We next established whether co-incubation with EPMs reduced the MIC of established AcrB substrates in the wild-type SL1344 strain and the S10801 clinical isolate. Exposure to EPM35 or EPM43 decreased by four-fold the MIC of chloramphenicol for one or both strains (Table 3). EPM35 was also synergistic with tetracycline and erythromycin. Similar effects were observed in the SL1344-derived macAB mutant strain but not in the acrAB or tolC mutant strains. These data suggest that the AcrAB-TolC efflux pump may be a relevant target for EPM35 and EPM43 with regard to antibiotic potentiation, and more importantly, that these EPMs appear to reduce the effective dose in broth of some clinical antibiotics.
Table 3. MICs (μg/mL) of AcrB substrates in combination with EPMs.
| SL1344 | S10801 | macAB::kan | acrAB::kan | tolC::cm | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tetracycline | DMSO | 2 | 128 | 2 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| 25 μM EPM30 | 2 | 128 | 2 | 0.5 | 0.5 | |
| 25 μM EPM35 | 0.5 | 64 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | |
| 25 μM EPM43 | 1 | 64 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | |
| Chloramphenicol | DMSO | 4 | 256 | 4 | 2 | |
| 25 μM EPM30 | 2 | 256 | 2 | 2 | ||
| 25 μM EPM35 | 1 | 64 | 1 | 1 | ||
| 25 μM EPM43 | 1 | 128 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Ciprofloxacin | DMSO | 0.004 | 0.016 | 0.004 | 0.002 | 0.002 |
| 25 μM EPM30 | 0.002 | 0.008 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | |
| 25 μM EPM35 | 0.002 | 0.008 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | |
| 25 μM EPM43 | 0.002 | 0.008 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | |
| Novobiocin | DMSO | 512 | 512 | 512 | 256 | 256 |
| 25 μM EPM30 | 256 | 256 | 256 | 256 | 256 | |
| 25 μM EPM35 | 256 | 256 | 256 | 256 | 256 | |
| 25 μM EPM43 | 256 | 256 | 256 | 256 | 256 | |
| Erythromycin | DMSO | 128 | 64 | 128 | 32 | 32 |
| 25 μM EPM30 | 64 | 64 | 64 | 32 | 32 | |
| 25 μM EPM35 | 32 | 32 | 32 | 32 | 32 | |
| 25 μM EPM43 | 64 | 32 | 64 | 32 | 32 | |
| Crystal Violet | DMSO | 16 | 16 | 16 | 8 | 8 |
| 25 μM EPM30 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 8 | 8 | |
| 25 μM EPM35 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | |
| 25 μM EPM43 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 |
The EPMs act synergistically with erythromycin or ciprofloxacin in macrophages
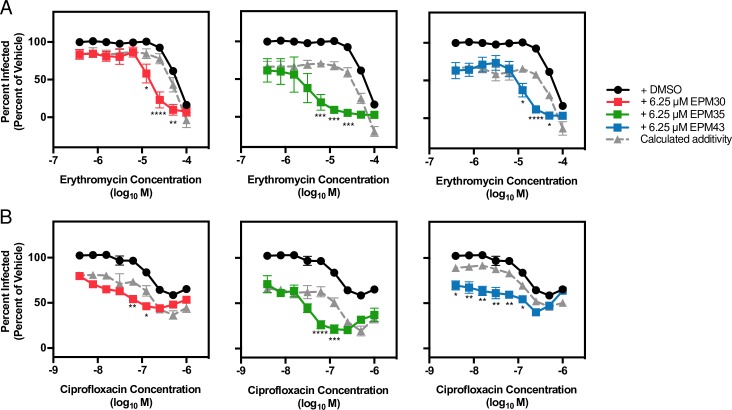
Since intracellular conditions are distinct from microbiological media, we tested whether the EPMs also synergize with AcrAB-exported antibiotics for bacterial killing in macrophages. RAW264.7 macrophages were infected with wild type Salmonella followed two hours later by treatment with antibiotic over a dose range with or without an EPM [6.25 μM]. SAFIRE analysis revealed that both erythromycin and ciprofloxacin were potentiated by the EPMs, as indicated by a difference between the co-treatment data and calculated additivity curves (Fig 10). Thus, the EPMs may reduce the effective dose of erythromycin and ciprofloxacin in macrophages.
Fig 10. EPMs enhance activity of erythromycin and ciprofloxacin against Salmonella in macrophages.
RAW 264.7 macrophages were infected with Salmonella and treated with a dose range of (A) erythromycin or (B) ciprofloxacin and with DMSO or the indicated concentration of an EPM. At 18 hours post infection samples were processed for fluorescence microscopy as described. Data were normalized to treatment with DMSO and antibiotic vehicle (100%). Key: black, DMSO; red, EPM30; green, EPM35; blue, EPM43; gray, calculated additivity of the antibiotic and the corresponding EPM using the formula (100 –([percent inhibition EPM] + [percent inhibition antibiotic])), where percent inhibition is calculated as 100 –[percent of DMSO]. Data are mean + SEM of three biological replicates. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001; **** p < 0.0001 of EPM treatment versus calculated additivity by one-way ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparison test.
EPM35 and EPM43 have anti-efflux activity in MDR ESKAPE pathogens
Six pathogens that cause the bulk of MDR nosocomial infections have been dubbed the ESKAPE pathogens: Enterococcus faecium, Staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Acinetobacter baumannii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Enterobacter species [56]. EPM35 and EPM43 significantly reduced Nile red export in MDR clinical isolates of K. pneumoniae and Enterobacter cloacae in addition to E. coli (Fig 11), suggesting these two compounds have biological relevance in MDR strains beyond Salmonella.
Fig 11. EPM35 and EPM43 block efflux of Nile red from ESKAPE MDR clinical isolates.
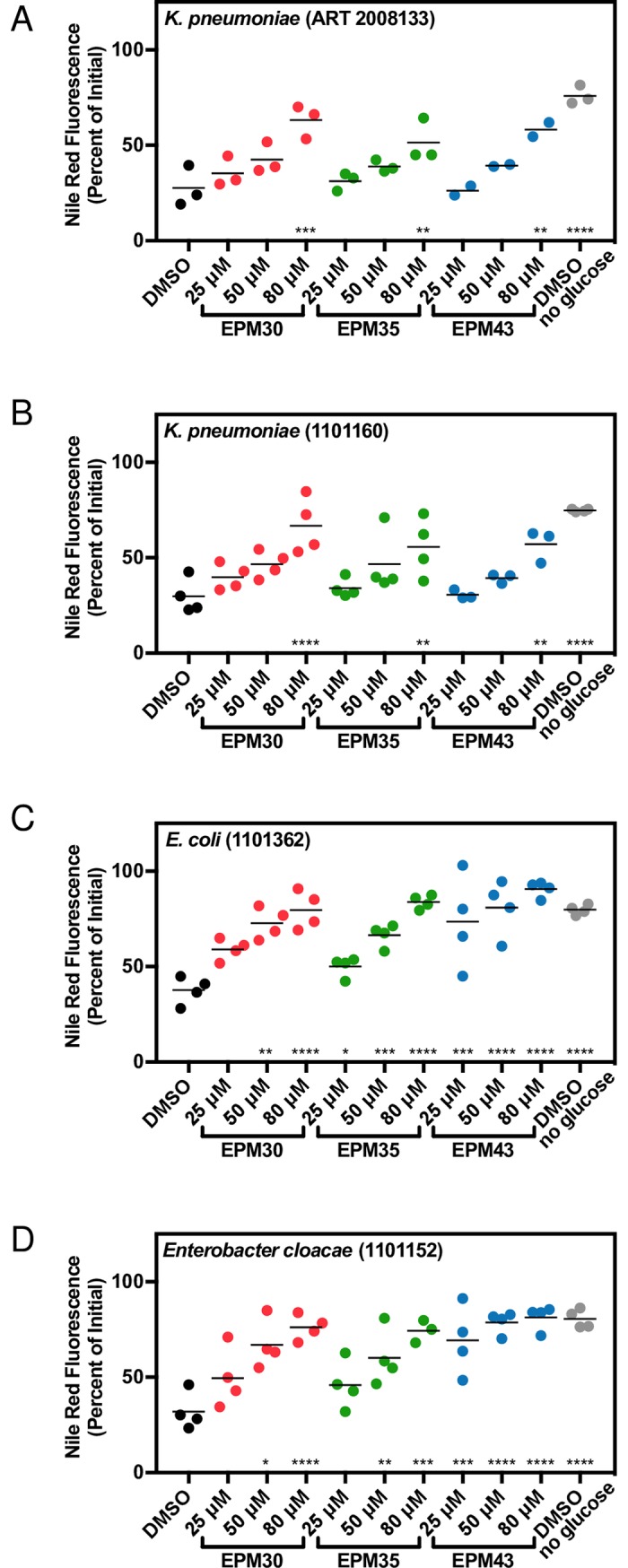
(A-D) Defined strains obtained from BEI resources were examined for Nile red retention after glucose addition in the presence of the indicated compound. Data for each sample were normalized to the initial fluorescence (100%). Dose response curves at seven minutes after glucose addition. Mean of three biological replicates performed in duplicate. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001 compared to DMSO + glucose by one-way ANOVA and Dunnett’s multiple comparison post-test.
Discussion
In-cell screens aimed at identifying chemicals that prevent pathogen intracellular replication have been described. For example screens of FDA-approved drug libraries have uncovered modulators of Listeria monocytogenes or Salmonella enterica infection [57,58]. Similar screens were performed with macrophages infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis [59] or the yeast Cryptococcus neoformans [60]. There are also many reports of high-content screens aimed at identifying genetic disruptors of host-pathogen interactions [61–63]. SAFIRE adopts what we thought would be the most useful aspects of these earlier studies, including a GFP-expressing Salmonella to track the microbe, the addition of compounds after infection, automated fluorescence microscopy-based image analysis with MATLAB, and estimation of compound toxicity based on manual visualization of cell morphology and MitoTracker staining. In addition, because the SAFIRE assay includes serum, it avoids compounds that are poor candidates for drug development because of high affinity for serum proteins [64]. These features enabled us to develop SAFIRE as a medium-throughput assay useful for identifying small molecules that interfere with the host-pathogen relationship.
Pathogens require efflux pump activity to survive in host tissues, suggesting modulators of bacterial efflux may be identified with in-cell screens for pathogen survival [30,34]. Salmonella encodes nine efflux pumps [65]. The two demonstrated to be required for bacterial survival in cells and in mice are AcrAB-TolC and MacAB [30–33,39]. The first hint that several of the hit compounds may modulate bacterial efflux was the observation that treatment of wild-type Salmonella with PAβN or with any of the three EPMs allowed Hoechst to accumulate to higher levels than in vehicle-treated bacteria. We speculate that treatment with PAβN or the EPMs was more effective at raising Hoechst levels than was deletion of the acrAB::kan locus because the compounds may target other efflux pumps. We also note that EPMs are not expected to function as clinical antibiotics: EPMs have high MICs in standard broth-based assays [66]. However, EPMs are of interest because of their potential to enhance the activity of existing antibiotics and/or host antimicrobials. These properties further underscore the biology of efflux pumps and highlight the importance of looking beyond MIC assays to identify chemicals with antimicrobial activity under conditions that approximate infection.
All three of our hit compounds bind the efflux pump subunit AcrB, a subunit of the most thoroughly studied RND efflux pump. AcrB integrates into cellular membranes and captures substrates from the outer leaflet of the cytoplasmic membrane or the periplasm [67–69]. The compounds identified bind AcrB more tightly than several known AcrB substrates, such as ethidium (KD of 8.7 +/- 1.9 μM), proflavin (KD of 14.5 +/- 1.1 μM), and ciprofloxacin (KD of 74.1 +/- 2.6 μM) [70]. The chemical structures of the three compounds have some resemblance to known efflux pump inhibitors (Fig 2E). EPM30 is a small compound with an aminothiazole core, and several aminothiazole compounds have been identified that inhibit efflux [7,71]. EPM35 is a trifluoro-pyrimidine linked to a piperidine. A very similar compound was suggested to bind the AcrB substrate-binding pocket in an in silico screen [72]. EPM43 is a small quinazoline, a planar moiety which is a common drug pharmacophore. Other quinazolines have been identified as inhibitors of bacterial and fungal efflux pumps [73,74]. EPM43 itself has been identified as an inhibitor of fungal dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR), but is not known to inhibit bacterial or human DHFR [75,76]. Where on the AcrB protein the EPMs bind remains unknown. EPM35 and EPM43 potentiate multiple AcrB substrates, suggesting they bind in the hydrophobic trap [77,78]. Alternatively, the EPMs may bind outside of the substrate pocket and, for instance, disrupt AcrB folding, localization or interactions with AcrA. It is notable that the three EPMs do not behave identically in broth assays that monitor export of AcrB substrates, potentiation of antibiotics, or activity against other Gram-negative pathogens, emphasizing that they may not interact identically with AcrB and/or any other molecules they may target.
Why the three EPMs are more potent as antibacterials in mammalian cells than they are as efflux pump inhibitors in broth is not completely clear. A simple model supported by existing data is that the EPMs increase bacterial sensitivity to host AMPs by binding efflux pump subunits, thereby reducing AMP export [79] and decreasing the effective concentration of AMPs. During infection of a whole animal, endogenous AMPs, which are ubiquitous in body fluids, may synergize with EPMs, even in severely immunocompromised patients for whom innate immunity typically remains intact [80,81]. While Salmonella RND efflux pumps have not been demonstrated to export AMPs, it is nevertheless encouraging that two of the EPMs inhibit efflux in other major MDR bacterial pathogens, suggesting they may have utility beyond Salmonella. Another possible explanation for higher potency during infection than in broth is that the EPMs could accumulate in the SCV, thereby increasing the concentration of compound experienced by the bacterium within host cells. An EPM could also target the host cell and, for instance, increase production of antimicrobial mediators. Alternatively, or in addition, EPMs may interfere with other bacterial processes and/or bind targets that are not present or accessible under the broth conditions tested. To facilitate our understanding of how the EPMs function, it may be useful to identify more potent, less toxic chemical derivatives. Desirable derivatives would have efficacy in SAFIRE, potency in efflux assays, and, most importantly, resensitize MDR pathogens to clinical antibiotics by reducing the antibiotic dosage needed to treat an infection.
The work presented as a whole suggests that SAFIRE enables discovery of chemicals that interfere with the host-pathogen relationship and may have potential as lead compounds for therapeutic development. Advantages of SAFIRE-identified chemicals include that they are unlikely to be inactivated by serum and are fairly non-toxic to mammalian cells. As proof-of-principle, SAFIRE identified not only a traditional antibiotic, chloramphenicol, but also three small molecules with activity against Gram-negative bacterial pathogens. Moreover, because SAFIRE identifies compounds that decrease bacterial load within mammalian cells, the platform may single out chemicals with antibacterial activity that is facilitated by endogenous host antimicrobial peptides, which are broadly distributed across extracellular and intracellular niches. In summary, SAFIRE followed by secondary screening has the potential to identify new and previously overlooked compounds that may be useful as lead compounds for biological and/or antibacterial discovery.
Materials and methods
Ethics statement
Animal work was carried out in accordance with the recommendations in the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals of the National Institutes of Health. All protocols were approved by the University of Colorado Boulder Institutional Committee for Animal Care and Use (protocol number 2445). Euthanasia was carried out by carbon dioxide asphyxiation followed by cervical dislocation.
Bacterial strains
The wild-type S. enterica serovar Typhimurium strain, SL1344, was initially isolated from the blood of an infected calf [26]. For screening and validation in macrophages, SL1344 sifB::GFP [20] was grown in Luria-Bertani Broth (LB) with 30 μg/ml streptomycin and 30 μg/ml kanamycin to saturation overnight, diluted to an OD of 0.001 and frozen in 100 μL aliquots in 20% glycerol at -80°C. Prior to infection, aliquots were grown in 5 mL cultures of LB with 30 μg/ml streptomycin and 30 μg/ml kanamycin for 18 hours at 37°C with aeration. Bacterial strains were routinely grown in LB with antibiotics (Table 1): 30 μg/ml streptomycin, 30 μg/ml kanamycin, 50 μg/ml ampicillin, 10 μg/ml tetracycline, and/or 1.15 μg/ml meropenem. The acrAB::kan and macAB::kan strains were constructed as described [82]. S. enterica subsp. enterica, serovar Typhimurium strain S10801, NR-22067 is a multidrug resistant isolate from a calf with sepsis [83]. This strain and others as indicated (Table 1) were obtained through BEI resources, NIAID, NIH.
Cell culture
Murine macrophage-like RAW 264.7 cells and HeLa human epithelial cells were obtained from the American Type Tissue Collection. BMDMs were isolated as previously described [21]. Briefly, marrow was flushed from the femurs of 1- to 4-month-old 129SvEvTac mice (Taconic Laboratories) bred in-house. Mononuclear cells were separated using Histopaque-1083 (Sigma), washed, and directly seeded into assay plates at 1 x 105 cells/ml in complete medium supplemented with 35% conditioned media from 3T3 cells expressing MCSF. Media were refreshed three days later. After 1 week, media were replaced with 100 μL fresh media and cells were infected as described below. All three types of cells were grown in DMEM high glucose (Sigma) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum, 2 mM L-glutamine, 1 mM sodium pyruvate, 10 mM HEPES, and 50 μM β-mercaptoethanol. Cells were maintained in a 5% CO2 humidified atmosphere at 37°C. For screening, frozen aliquots of RAW 264.7 were thawed and allowed to expand for three days prior to seeding; other experiments were performed with cultures between passages four and 20.
Bacterial infections for SAFIRE and CFU plating
SAFIRE—RAW 264.7 macrophages (7 x 103 in 40 μL or 5 x 104 in 100 μL) were seeded, respectively, in 384- or 96-well black-walled glass-bottomed plates (Brooks Automation). Twenty-four hours post-seeding, bacteria in 20 or 50 μL PBS were added to a final concentration of 1 x 107 CFU/mL, conditions yielding infection of approximately 70% of macrophages at 18 hours post-infection with minimal macrophage toxicity. The sifB::GFP bacterial reporter strain was used to minimize green signal from extracellular bacteria. Forty-five minutes after bacterial addition, 20 or 50 μL gentamicin was added to a final concentration of 40 μg/mL, which did not affect intracellular infection but inhibited replication of extracellular bacteria. At two hours post-infection, 200 or 500 nL compound was added using a pin tool (CyBio) to yield a final concentration of 25 μM. Each assay plate included rifampicin and DMSO controls. In some experiments, media were removed and replaced with fresh media containing 40 μg/mL gentamicin and the indicated concentrations of drugs. At 17.5 hours post-infection, PBS containing MitoTracker Red CMXRos (Life Technologies) was added to a final concentration of 300 nM or 100 nM, for 384- or 96-well, respectively. Thirty minutes later, 16% paraformaldehyde was added to a final concentration of 1–2% and incubated at room temperature for 15 minutes. Wells were washed twice with PBS and stained for 20 minutes with 1 μM DAPI; wells were washed twice and stored in 90% glycerol in PBS until imaging. The Z’-factor of the screening platform was 0.59 and 0.48 in 96-well and 384-well plates, respectively, within published ranges for complicated cell-based screens [22,60–62].
HeLa cells—Infections of HeLa cells with Salmonella were performed as above except that 1 x 104 cells were seeded, and cells were infected with Salmonella constitutively expressing GFP from the rpsM locus because sifB::GFP is poorly expressed in HeLa cells. In addition, plates were spun for five minutes at 500 x g after addition of bacteria to enhance infection.
CFU—Infections were performed as described above, except cells were seeded in 96-well tissue culture coated plates (Greiner). At 18 hours post-infection, wells were washed three times in PBS, lysed with 30 μL 0.1% Triton X-100, diluted and plated to determine CFU.
Image acquisition, MATLAB-based screening analysis, and hit selection
High magnification images were acquired on an Olympus IX81 inverted widefield microscope (40X) or CV1000 spinning disk confocal microscope (20X). For screening, three-color images were acquired at 10X on a Cellomics ArrayScan VTI (Thermo) and exported to DIB files. At least two fields were imaged per well for all experiments, and compounds were screened in duplicate. To quantify intracellular bacterial load we developed an automated MATLAB script (“SAFIRE_ArrayScan”, “SAFIRE_OlympusIX81” and “SAFIRE_CV1000” on MATLAB File Exchange, https://www.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/). Briefly, the algorithm identifies macrophage borders via watershed segmentation using DAPI and MitoTracker. To identify bacteria, the user supplies an empirically determined GFP threshold that maximizes signal to noise based on uninfected and untreated controls. Within each macrophage, the number of pixels above the GFP threshold is counted. If more than two pixels are above the GFP threshold, the macrophage is labeled infected. The script calculates the percentage of macrophages infected in the image. Raw data for at least two images from the same well are averaged to yield one value for each well. Raw screening data were subjected to B-score normalization because we identified significant row and column effects by a method previously described [22]. To determine significance, we employed the modified one-sample t-test [23] by fitting the variances of replicates to an inverse gamma distribution [25]. The micrographs of the 461 preliminary positives were examined by the human eye to eliminate compounds that clearly destroyed the macrophages (host toxic). Assay positives were defined as having a p-value less than 0.05 and a B-score one standard deviation below the mean.
Broth antibacterial activity assays
Overnight Salmonella cultures were washed three times in PBS and diluted to an OD600 of 0.01 in MHB in 96-well flat-bottom plates. Compound was added using a pin tool (CyBio) or manually, yielding a final concentration of no more than 1% DMSO. Plates were grown at 37°C shaking and OD600 was monitored using a BioTek Eon or Synergy H1 incubator shaker microplate absorbance reader. MICs were defined as the concentration at which no growth was visually observed. The Fractional Inhibitory Concentration Index (FICI) was calculated for wells showing no visible growth (FICI = [agent A] / [MIC agent A] + [agent B] / [MIC agent B]) [84]. For experiments with polymyxin B, bacteria were grown in M9 minimal media supplemented with 100 mM Tris pH 7.4, 0.35% glycerol, 0.002% histidine, 10 mM MgCl2, and 0.1% casamino acids and 5 μg/mL polymyxin B. For experiments with LL37, bacteria were grown in M9 minimal media supplemented with 0.4% dextrose, 0.004% histidine, 1 mM MgSO4, and 5 μg/ml LL37.
Hoechst assays
Hoechst accumulation assays were performed essentially as described [35]. Briefly, overnight Salmonella cultures were washed three times in PBS and diluted to an OD600 of 0.1 in PBS with 2.5 μM Hoechst 33342 in the presence of the indicated concentrations of compounds. Fluorescence was monitored on a Biotek Synergy 2 with a 360/40 nm excitation filter and 460/40 nm emission filter. The maximum Hoechst fluorescence over 60 minutes of incubation was normalized to the signal from the equivalent number of heat-killed bacteria, after subtraction of autofluorescence signal determined from compound incubated in the absence of bacteria. EC50s were determined using a 4-parameter nonlinear fit constrained using DMSO-treated Wild-Type as the minimum and Heat Killed as the maximum (GraphPad Prism). Concentrations of PAβN used in all assays were determined by titration with the Salmonella wild-type strain in the corresponding assay.
Nile red and ethidium bromide assays
Nile red assays were adapted from an established protocol [50]. Briefly, overnight Salmonella LB cultures were washed in PBS with 1 mM MgCl2 and resuspended at an OD600 of 2.0. Cells were incubated in 10 μM Nile red for three hours at 37°C in glass tubes on a roller drum and then at room temperature standing for one hour. Cells were pelleted at 2,050 x g, resuspended in PBS with 1 mM MgCl2, and 200 μl was added to 96-well black walled plates (Greiner) with compound at the indicated concentrations. In washout experiments, after 35 minutes of incubation with compound, cells were centrifuged at 16,000 x g, resuspended in PBS with 1mM MgCl2 without compound and aliquoted into 96-well black walled plates (Greiner). During loading into plates (~ 20 minutes), bacteria effluxed some Nile red even in the absence of glucose (S4 Fig). Samples were read using a Varioskan Flash Multimode Reader at 540 nm (excitation) and 625 nm (emission) or a Biotek Synergy H1 at 560 nm and 655 nm. To activate efflux, glucose was added to a final concentration of 2 mM.
Ethidium bromide (EtBr) assays were performed similarly to Nile red assays with the following changes. Cells were incubated with 10 μM of carbonyl cyanide m-chlorophenylhydrazone (CCCP) for 15 minutes, then incubated with 10 μM of EtBr for one hour at 37°C with aeration, pelleted at 2,050 x g, aliquoted and combined with compound at the indicated concentrations in 96-well black walled plates (Greiner). Plates were monitored with a Biotek Synergy H1 at 510 nm and 600 nm.
Nitrocefin hydrolysis assays
Bacteria were subcultured to mid-log phase, washed, and combined with 100 μM nitrocefin and the indicated concentrations of drugs in 96-well plates in 200 μL [41]. Washes and incubations were performed in 20 mM KPO4, pH 7.0, 1 mM MgCl2. Absorbance (486 nm) was measured on a BioTek Eon or Synergy H1 spectrophotometer every 60 seconds for one hour. To observe efflux inhibition, E. coli RAM121 [28] were added to plates at a final OD600 of 10. This strain produces an OmpC variant with a larger pore size to allow increased influx of nitrocefin and other bulky molecules, and nitrocefin is hydrolyzed by the endogenous AmpC beta-lactamase. To measure outer membrane permeability, wild-type Salmonella harboring beta-lactamase (bla)-expressing pACYC177-mTagBFP2 [29] were added to plates at a final OD600 of 0.1.
Tetramethylrhodamine methyl ester (TMRM) permeability assays
Wild-type Salmonella harboring pACYC177-mTagBFP2 [29] were subcultured to mid-log phase, diluted to 1 x 106 CFU/ml in PBS, aliquoted into flow cytometry tubes, and treated with the indicated concentrations of compounds. TMRM was immediately added to a final concentration of 100 nM. After incubation for 30 minutes at 37°C, samples were analyzed on a CyAn ADP (Beckman Coulter) in channels FL6 and FL2. Data were analyzed using FlowJo; bacteria were gated based on side scatter and BFP signal in the FL6 channel, and the FL2 median fluorescence intensity (MFI) was calculated.
Bacterial swimming membrane permeability assays
Saturated overnight cultures were diluted to an OD600 of 0.01 in LB, and 1 μL was injected into the center of low (0.25%) agar LB plates. Ten microliters of the indicated compounds up to concentrations of 100 mM were added to sterilized Whatman paper disks (diameter 0.7 cm) placed equidistant from the plate center; solubility issues arose at concentrations above 100 mM. Plates were incubated face up at 37°C overnight; no change in halo size was observed between 14–24 hours incubation. Plates were imaged using a Gel Logic 200 imaging system, and halo radius (distance from center of disk to outermost edge of halo) was measured using ImageJ.
Isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC)
ITC was used to examine the binding of EPMs to the purified AcrB transporter. Measurements were performed on a Microcal iTC200 (Northampton, MA) at 25°C. Before titration, the protein was thoroughly dialyzed against buffer containing 20 mM Na-HEPES (pH 7.5), 0.05% n-dodecyl-μ-maltoside (DDM) and 5% dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO). The protein concentration was determined using the Bradford assay. The protein sample was then adjusted to a final monomeric concentration of 10 μM. Ligand solution consisting of 100 μM EPM30, EPM35 or EPM43 in 20 mM Na-HEPES (pH 7.5), 0.05% DDM and 5% DMSO was prepared as the titrant. The protein and ligand samples were degassed before they were loaded into the cell and syringe. Binding experiments were carried out with the protein solution (0.2 ml) in the cell and the ligand as the injectant. Two microliter injections of the ligand solution were used for data collection.
Injections occurred at intervals of 60 s, and the duration time of each injection was 4 s. Heat transfer (μcal/s) was measured as a function of elapsed time (s). The mean enthalpies measured from injection of the ligand in the buffer were subtracted from raw titration data before data analysis with ORIGIN software (MicroCal). Titration curves were fitted by a nonlinear least-squares method to a function for the binding of a ligand to a macromolecule. Nonlinear regression fitting to the binding isotherm provided us with the equilibrium binding constant (KA = 1/KD) and enthalpy of binding (ΔH). Based on the values of KA, the change in free energy (ΔG) and entropy (ΔS) were calculated with the equation: ΔG = —RT lnKA = ΔH—TΔS, where T is 273 K and R is 1.9872 cal/K per mol. Calorimetry trials were also carried out in the absence of AcrB using the same experimental conditions. No change in heat was observed in the injections throughout the experiment.
Statistics
Statistical tests were applied as indicated in figure legends using GraphPad/Prism and/or JMP software.
Supporting information
(XLSX)
The top 75 compounds as determined by SAFIRE (96-well format) are shown (purple circles). EPM30 (red triangle); EPM35 (green square); EPM43 (blue circle); chloramphenicol (gray hexagon). For comparison, antibiotic controls rifampicin, ampicillin, and ciprofloxacin are indicated with arrows (open circles).
(TIF)
Bacterial growth in MHB across a range of gentamicin concentrations was not significantly altered by the presence of an EPM, as indicated by Fractional Inhibitory Concentrations Indices (FICI) of greater than 0.5.
(TIF)
A) Ethidium bromide, B) Nile red, C) Nile red with compounds washout. Mean and SD from representative efflux assays performed twice in duplicate. Upper dotted lines, initial fluorescence for DMSO-treated cells without glucose; lower dotted lines, endpoint fluorescence for DMSO-treated cells exposed to glucose. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01 determined by t-test of slopes calculated from linear fit of 0–10 minutes (EtBr) or 0–2 minutes (Nile red) relative to buffer.
(TIF)
(A) Nile red-loaded bacteria were washed, combined with the indicated concentrations of compounds and fluorescence was immediately measured. Data shown are mean + SD. These data suggest that the discrepancies in starting fluorescence (S4B Fig) are due to the time between compound addition and the beginning of measurement (15–20 minutes). As indicated here, during this timeframe DMSO-treated cells efflux the dye even in the absence of glucose. Thus, EPM35, EPM43, and PAβN inhibit basal loss of Nile red, but treatment with EPM30 led to an immediate reduction in fluorescence. (B) Bacteria remain intact and viable after 20 minutes incubation in 75 μM EPM30, indicating the immediate reduction in fluorescence in (A) is not due to death of the bacteria. It is possible that EPM30 reduces Nile red fluorescence by quenching or by altering membrane properties, as Nile red fluorescence is highly dependent on membrane polarity, content, and dynamics.
(TIF)
Disk diffusion assay. Bacteria were injected into the center of the plate (*); 10 μl of the indicated compound (top) or vehicle was spotted onto filter paper disks. Sixteen hours later, plates were imaged. Representative images from one of three independent experiments.
(TIF)
Representative ITC for the binding of EPM30 to E. coli AcrB. Each peak in the upper graph corresponds to the injection of 2 μL of 100 μM of the EPM in buffer containing 20 mM Na-HEPES (pH 7.5), 0.05% DDM and 5% DMSO into the reaction containing 10 μM of E. coli monomeric AcrB in buffer containing 20 mM Na-HEPES (pH 7.5), 0.05% DDM and 5% DMSO. The lower graph shows the cumulative heat of reaction displayed as a function of injection number. The solid line is the least-square fit to the experimental data.
(TIF)
(A, top) Hoechst accumulation quantitated as in Fig 2. (A, bottom) The DMSO, no-polymyxin B-treated samples were subtracted from treated samples (gray bars). Assuming additivity as the null hypothesis, the sum of the 5 μg/ml polymyxin B sample and each EPM sample was calculated (white bars). No significant differences were identified between observed and calculated data, suggesting that EPMs and polymyxin B do not synergize in this assay. (B) Nile red efflux quantitated as in Fig 4 and analysis performed as in A. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001 calculated using one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post-test.
(TIF)
Acknowledgments
We thank James Orth for microscopy assistance, Xiang Wang and Wei Wang of the CU Boulder HTS Facility for expert advice, and Paul Muhlrad, Jamie Dombach and Joe Villanueva for manuscript edits. We also thank Shelley Copley for advice on data presentation and for the use of the Varioskan. We are grateful to Amy Palmer, Sarah McQuate, and Alexandra Young for the pACYC-mTagBFP2 plasmid. We also thank Helen Zgurskaya for helpful insights.
Data Availability
MATLAB scripts for SAFIRE analysis are available via MATLAB File Exchange (https://www.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/), deposited as "SAFIRE_ArrayScan”, “SAFIRE_Olympus_ix81” and “SAFIRE_CV1000”. All additional relevant data are within the paper and its Supporting Information files.
Funding Statement
This work was supported by the following grants from the National Institute Health https://www.nih.gov/ : GM008759 (ALR); AI121365 (CSD); AI121474 (TAN, CSD); AI114239 (EWY); AI1126453 (CSD) and a University of Colorado Innovative Seed Grant (CSD). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
References
- 1.Nikaido H, Pagès J-M. Broad-specificity efflux pumps and their role in multidrug resistance of Gram-negative bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2012;36: 340–363. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2011.00290.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Opperman TJ, Nguyen ST. Recent advances toward a molecular mechanism of efflux pump inhibition. Front Microbiol. 2015;6: 421 doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.00421 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Renau TE, Léger R, Flamme EM, Sangalang J, She MW, Yen R, et al. Inhibitors of Efflux Pumps in Pseudomonas a eruginosa Potentiate the Activity of the Fluoroquinolone Antibacterial Levofloxacin. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 1999;42: 4928–4931. doi: 10.1021/jm9904598 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Lomovskaya O, Warren MS, Lee A, Galazzo J, Fronko R, Lee M, et al. Identification and Characterization of Inhibitors of Multidrug Resistance Efflux Pumps in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Novel Agents for Combination Therapy. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. 2001;45: 105–116. doi: 10.1128/AAC.45.1.105-116.2001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Lomovskaya O, Bostian KA. Practical applications and feasibility of efflux pump inhibitors in the clinic—A vision for applied use. Biochemical Pharmacology. 2006;71: 910–918. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2005.12.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Watkins WJ, Landaverry Y, Léger R, Litman R, Renau TE, Williams N, et al. The relationship between physicochemical properties, in vitro activity and pharmacokinetic profiles of analogues of diamine-containing efflux pump inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2003;13: 4241–4244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Nakayama K, Ishida Y, Ohtsuka M, Kawato H, Yoshida K, Yokomizo Y, et al. MexAB-OprM-Specific efflux pump inhibitors in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Part 1: Discovery and early strategies for lead optimization. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters. 2003;13: 4201–4204. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2003.07.024 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Yoshida K, Nakayama K, Ohtsuka M, Kuru N, Yokomizo Y, Sakamoto A, et al. MexAB-OprM specific efflux pump inhibitors in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Part 7: Highly soluble and in vivo active quaternary ammonium analogue D13-9001, a potential preclinical candidate. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry. 2007;15: 7087–7097. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2007.07.039 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Opperman TJ, Kwasny SM, Kim H-S, Nguyen ST, Houseweart C, D’Souza S, et al. Characterization of a Novel Pyranopyridine Inhibitor of the AcrAB Efflux Pump of Escherichia coli. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. 2014;58: 722–733. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01866-13 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Vargiu AV, Ruggerone P, Opperman TJ, Nguyen ST, Nikaido H. Molecular Mechanism of MBX2319 Inhibition of Escherichia coli AcrB Multidrug Efflux Pump and Comparison with Other Inhibitors. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. 2014;58: 6224–6234. doi: 10.1128/AAC.03283-14 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Sjuts H, Vargiu AV, Kwasny SM, Nguyen ST, Kim H-S, Ding X, et al. Molecular basis for inhibition of AcrB multidrug efflux pump by novel and powerful pyranopyridine derivatives. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 2016;113: 3509–3514. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1602472113 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Nguyen ST, Kwasny SM, Ding X, Cardinale SC, McCarthy CT, Kim H-S, et al. Structure–activity relationships of a novel pyranopyridine series of Gram-negative bacterial efflux pump inhibitors. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry. 2015;23: 2024–2034. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2015.03.016 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Berghaus LJ, Moore JN, Hurley DJ, Vandenplas ML, Fortes BP, Wolfert MA, et al. Innate immune responses of primary murine macrophage-lineage cells and RAW 264.7 cells to ligands of Toll-like receptors 2, 3, and 4. Comparative Immunology, Microbiology and Infectious Diseases. 2010;33: 443–454. doi: 10.1016/j.cimid.2009.07.001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Fritsche G, Nairz M, Libby SJ, Fang FC, Weiss G. Slc11a1 (Nramp1) impairs growth of Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium in macrophages via stimulation of lipocalin-2 expression. Journal of Leukocyte Biology. 2012;92: 353–359. doi: 10.1189/jlb.1111554 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Nairz M, Fritsche G, Crouch M-LV, Barton HC, Fang FC, Weiss G. Slc11a1 limits intracellular growth of Salmonella enterica sv. Typhimurium by promoting macrophage immune effector functions and impairing bacterial iron acquisition. Cellular Microbiology. 2009;11: 1365–1381. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2009.01337.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Cremades N, Velázquez-Campoy A, Martínez-Júlvez M, Neira JL, Pérez-Dorado I, Hermoso J, et al. Discovery of Specific Flavodoxin Inhibitors as Potential Therapeutic Agents against Helicobacter pylori Infection. ACS Chemical Biology. 2009;4: 928–938. doi: 10.1021/cb900166q [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Durk RC, Singh K, Cornelison CA, Rai DK, Matzek KB, Leslie MD, et al. Inhibitors of Foot and Mouth Disease Virus Targeting a Novel Pocket of the RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase. Liu DX, editor. PLoS ONE. 2010;5: e15049 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0015049 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Mathew MD, Mathew ND, Miller A, Simpson M, Au V, Garland S, et al. Using C. elegans Forward and Reverse Genetics to Identify New Compounds with Anthelmintic Activity. Prichard RK, editor. PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases. 2016;10: e0005058 doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0005058 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Johnson JL, Ramadass M, He J, Brown SJ, Zhang J, Abgaryan L, et al. Identification of Neutrophil Exocytosis Inhibitors (Nexinhibs), Small Molecule Inhibitors of Neutrophil Exocytosis and Inflammation: DRUGGABILITY OF THE SMALL GTPase Rab27a. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2016;291: 25965–25982. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.741884 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Rollenhagen C, Sörensen M, Rizos K, Hurvitz R, Bumann D. Antigen selection based on expression levels during infection facilitates vaccine development for an intracellular pathogen. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2004;101: 8739–8744. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0401283101 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Nagy TA, Moreland SM, Andrews-Polymenis H, Detweiler CS. The Ferric Enterobactin Transporter Fep Is Required for Persistent Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium Infection. Infection and Immunity. 2013;81: 4063–4070. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00412-13 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Dragiev P, Nadon R, Makarenkov V. Systematic error detection in experimental high-throughput screening. BMC Bioinformatics. 2011;12: 25 doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-12-25 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Malo N, Hanley JA, Cerquozzi S, Pelletier J, Nadon R. Statistical practice in high-throughput screening data analysis. Nature Biotechnology. 2006;24: 167–175. doi: 10.1038/nbt1186 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Brideau C, Gunter B, Pikounis B, Liaw A. Improved Statistical Methods for Hit Selection in High-Throughput Screening. Journal of Biomolecular Screening. 2003;8: 634–647. doi: 10.1177/1087057103258285 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Wright GW, Simon RM. A random variance model for detection of differential gene expression in small microarray experiments. Bioinformatics. 2003;19: 2448–2455. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btg345 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Smith BP, Reina-Guerra M, Hoiseth SK, Stocker BA, Habasha F, Johnson E, et al. Aromatic-dependent Salmonella typhimurium as modified live vaccines for calves. Am J Vet Res. 1984;45: 59–66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Vazquez-Torres A, Jones-Carson J, Baumler AJ, Falkow S, Valdivia R, Brown W, et al. Extraintestinal dissemination of Salmonella by CD18-expressing phagocytes. Nature. 1999;401: 804–808. doi: 10.1038/44593 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Misra R, Benson SA. Isolation and characterization of OmpC porin mutants with altered pore properties. J Bacteriol. 1988;170: 528–533. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.528–533.1988 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.McQuate SE, Young AM, Silva-Herzog E, Bunker E, Hernandez M, de Chaumont F, et al. Long-term live-cell imaging reveals new roles for Salmonella effector proteins SseG and SteA: New roles for Salmonella effector proteins. Cellular Microbiology. 2017;19: e12641 doi: 10.1111/cmi.12641 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Bogomolnaya LM, Andrews KD, Talamantes M, Maple A, Ragoza Y, Vazquez-Torres A, et al. The ABC-Type Efflux Pump MacAB Protects Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium from Oxidative Stress. mBio. 2013;4: e00630-13–e00630-13. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00630-13 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Buckley AM, Webber MA, Cooles S, Randall LP, La Ragione RM, Woodward MJ, et al. The AcrAB–TolC efflux system of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium plays a role in pathogenesis. Cellular Microbiology. 2006;8: 847–856. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2005.00671.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Nishino K, Latifi T, Groisman EA. Virulence and drug resistance roles of multidrug efflux systems of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. Molecular Microbiology. 2006;59: 126–141. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2005.04940.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Lacroix FJC, Cloeckaert A, Grépinet O, Pinault C, Popoff MY, Waxin H, et al. Salmonella typhimurium acrB-like gene: identification and role in resistance to biliary salts and detergents and in murine infection. FEMS Microbiology Letters. 1996;135: 161–167. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1996.tb07983.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Wang-Kan X, Blair JMA, Chirullo B, Betts J, Ragione RML, Ivens A, et al. Lack of AcrB Efflux Function Confers Loss of Virulence on Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium. mBio. 2017;8: e00968–17. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00968-17 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Coldham NG, Webber M, Woodward MJ, Piddock LJV. A 96-well plate fluorescence assay for assessment of cellular permeability and active efflux in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium and Escherichia coli. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy. 2010;65: 1655–1663. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkq169 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Misra R, Morrison KD, Cho HJ, Khuu T. Importance of Real-Time Assays To Distinguish Multidrug Efflux Pump-Inhibiting and Outer Membrane-Destabilizing Activities in Escherichia coli. Parkinson JS, editor. Journal of Bacteriology. 2015;197: 2479–2488. doi: 10.1128/JB.02456-14 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Horiyama T, Yamaguchi A, Nishino K. TolC dependency of multidrug efflux systems in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2010;65: 1372–1376. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkq160 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Zhang C-Z, Chen P-X, Yang L, Li W, Chang M-X, Jiang H-X. Coordinated Expression of acrAB-tolC and Eight Other Functional Efflux Pumps Through Activating ramA and marA in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. Microb Drug Resist. 2017; doi: 10.1089/mdr.2017.0086 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Nishino K, Nikaido E, Yamaguchi A. Regulation and physiological function of multidrug efflux pumps in Escherichia coli and Salmonella. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)—Proteins and Proteomics. 2009;1794: 834–843. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2009.02.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Paixão L, Rodrigues L, Couto I, Martins M, Fernandes P, CCCR de Carvalho, et al. Fluorometric determination of ethidium bromide efflux kinetics in Escherichia coli. J Biol Eng. 2009;3: 18 doi: 10.1186/1754-1611-3-18 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Misra R, Morrison KD, Cho HJ, Khuu T. Importance of Real-Time Assays To Distinguish Multidrug Efflux Pump-Inhibiting and Outer Membrane-Destabilizing Activities in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 2015;197: 2479–2488. doi: 10.1128/JB.02456-14 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Greenspan P, Mayer EP, Fowler SD. Nile red: a selective fluorescent stain for intracellular lipid droplets. J Cell Biol. 1985;100: 965–973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Murata T, Tseng W, Guina T, Miller SI, Nikaido H. PhoPQ-Mediated Regulation Produces a More Robust Permeability Barrier in the Outer Membrane of Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 2007;189: 7213–7222. doi: 10.1128/JB.00973-07 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Bohnert JA, Karamian B, Nikaido H. Optimized Nile Red Efflux Assay of AcrAB-TolC Multidrug Efflux System Shows Competition between Substrates. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010;54: 3770–3775. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00620-10 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Yep A, McQuade T, Kirchhoff P, Larsen M, Mobley HLT. Inhibitors of TonB Function Identified by a High-Throughput Screen for Inhibitors of Iron Acquisition in Uropathogenic Escherichia coli CFT073. mBio. 2014;5: e01089–13. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01089-13 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Iino R, Nishino K, Noji H, Yamaguchi A, Matsumoto Y. A Microfluidic Device for Simple and Rapid Evaluation of Multidrug Efflux Pump Inhibitors. Front Microbiol. 2012;3 doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2012.00040 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Lamers RP, Cavallari JF, Burrows LL. The Efflux Inhibitor Phenylalanine-Arginine Beta-Naphthylamide (PAβN) Permeabilizes the Outer Membrane of Gram-Negative Bacteria. PLOS ONE. 2013;8: e60666 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0060666 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Matsumoto Y, Hayama K, Sakakihara S, Nishino K, Noji H, Iino R, et al. Evaluation of multidrug efflux pump inhibitors by a new method using microfluidic channels. PLoS ONE. 2011;6: e18547 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0018547 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Hancock RE, Wong PG. Compounds which increase the permeability of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa outer membrane. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984;26: 48–52. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Bohnert JA, Karamian B, Nikaido H. Optimized Nile Red Efflux Assay of AcrAB-TolC Multidrug Efflux System Shows Competition between Substrates. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. 2010;54: 3770–3775. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00620-10 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Bolla JR, Su C-C, Delmar JA, Radhakrishnan A, Kumar N, Chou T-H, et al. Crystal structure of the Alcanivorax borkumensis YdaH transporter reveals an unusual topology. Nat Commun. 2015;6: 6874 doi: 10.1038/ncomms7874 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Su C-C, Bolla JR, Kumar N, Radhakrishnan A, Long F, Delmar JA, et al. Structure and function of Neisseria gonorrhoeae MtrF illuminates a class of antimetabolite efflux pumps. Cell Rep. 2015;11: 61–70. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2015.03.003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Su C-C, Yin L, Kumar N, Dai L, Radhakrishnan A, Bolla JR, et al. Structures and transport dynamics of a Campylobacter jejuni multidrug efflux pump. Nat Commun. 2017;8: 171 doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-00217-z [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Park K, Elias PM, Oda Y, Mackenzie D, Mauro T, Holleran WM, et al. Regulation of Cathelicidin Antimicrobial Peptide Expression by an Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Stress Signaling, Vitamin D Receptor-independent Pathway. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2011;286: 34121–34130. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.250431 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Mineshiba J, Myokai F, Mineshiba F, Matsuura K, Nishimura F, Takashiba S. Transcriptional regulation of Î2- defensin—2 by lipopolysaccharide in cultured human cervical carcinoma (HeLa) cells. FEMS Immunology & Medical Microbiology. 2005;45: 37–44. doi: 10.1016/j.femsim.2005.01.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Rice LB. Federal Funding for the Study of Antimicrobial Resistance in Nosocomial Pathogens: No ESKAPE. J Infect Dis. 2008;197: 1079–1081. doi: 10.1086/533452 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Lieberman LA, Higgins DE. A small-molecule screen identifies the antipsychotic drug pimozide as an inhibitor of Listeria monocytogenes infection. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009;53: 756–764. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00607-08 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Ridge Y, Landini P, Thompson A. High throughput screening of a collection of known pharmacologically active small compounds for inhibitors of Salmonella invasion and intracellular replication. J Appl Microbiol. 2018; doi: 10.1111/jam.13890 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Stanley SA, Barczak AK, Silvis MR, Luo SS, Sogi K, Vokes M, et al. Identification of Host-Targeted Small Molecules That Restrict Intracellular Mycobacterium tuberculosis Growth. Ehrt S, editor. PLoS Pathogens. 2014;10: e1003946 doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003946 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Samantaray S, Correia JN, Garelnabi M, Voelz K, May RC, Hall RA. Novel cell-based in vitro screen to identify small-molecule inhibitors against intracellular replication of Cryptococcus neoformans in macrophages. International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents. 2016;48: 69–77. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2016.04.018 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Brodin P, Poquet Y, Levillain F, Peguillet I, Larrouy-Maumus G, Gilleron M, et al. High Content Phenotypic Cell-Based Visual Screen Identifies Mycobacterium tuberculosis Acyltrehalose-Containing Glycolipids Involved in Phagosome Remodeling. Deretic V, editor. PLoS Pathogens. 2010;6: e1001100 doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1001100 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Rybniker J, Chen JM, Sala C, Hartkoorn RC, Vocat A, Benjak A, et al. Anticytolytic Screen Identifies Inhibitors of Mycobacterial Virulence Protein Secretion. Cell Host & Microbe. 2014;16: 538–548. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2014.09.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Maudet C, Mano M, Sunkavalli U, Sharan M, Giacca M, Förstner KU, et al. Functional high-throughput screening identifies the miR-15 microRNA family as cellular restriction factors for Salmonella infection. Nat Commun. 2014;5: 4718 doi: 10.1038/ncomms5718 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Ghuman J, Zunszain PA, Petitpas I, Bhattacharya AA, Otagiri M, Curry S. Structural Basis of the Drug-binding Specificity of Human Serum Albumin. Journal of Molecular Biology. 2005;353: 38–52. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2005.07.075 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Andersen JL, He G-X, Kakarla P, Kc R, Kumar S, Lakra WS, et al. Multidrug Efflux Pumps from Enterobacteriaceae, Vibrio cholerae and Staphylococcus aureus Bacterial Food Pathogens. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2015;12: 1487–1547. doi: 10.3390/ijerph120201487 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Venter H, Mowla R, Ohene-Agyei T, Ma S. RND-type drug efflux pumps from Gram-negative bacteria: molecular mechanism and inhibition. Frontiers in Microbiology. 2015;06 doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.00377 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Murakami S, Nakashima R, Yamashita E, Yamaguchi A. Crystal structure of bacterial multidrug efflux transporter AcrB. Nature. 2002;419: 587–593. doi: 10.1038/nature01050 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Murakami S, Nakashima R, Yamashita E, Matsumoto T, Yamaguchi A. Crystal structures of a multidrug transporter reveal a functionally rotating mechanism. Nature. 2006;443: 173–179. doi: 10.1038/nature05076 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Nakashima R, Sakurai K, Yamasaki S, Hayashi K, Nagata C, Hoshino K, et al. Structural basis for the inhibition of bacterial multidrug exporters. Nature. 2013;500: 102–106. doi: 10.1038/nature12300 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Su C-C, Nikaido H, Yu EW. Ligand-transporter interaction in the AcrB multidrug efflux pump determined by fluorescence polarization assay. FEBS Letters. 2007;581: 4972–4976. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2007.09.035 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Costa SS, Lopes E, Azzali E, Machado D, Coelho T, da Silva PEA, et al. An Experimental Model for the Rapid Screening of Compounds with Potential Use Against Mycobacteria. ASSAY and Drug Development Technologies. 2016;14: 524–534. doi: 10.1089/adt.2016.752 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Velmurugan D. Structure Based Discovery of inhibitors for Multidrug Efflux Pump-AcrB. Ommega Internations. 2015;1: 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- 73.Chevalier J, Mahamoud A, Baitiche M, Adam E, Viveiros M, Smarandache A, et al. Quinazoline derivatives are efficient chemosensitizers of antibiotic activity in Enterobacter aerogenes, Klebsiella pneumoniae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa resistant strains. International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents. 2010;36: 164–168. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2010.03.027 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Lemoine RC, Glinka TW, Watkins WJ, Cho A, Yang J, Iqbal N, et al. Quinazolinone-based fungal efflux pump inhibitors. Part 1: Discovery of an (N-methylpiperazine)-containing derivative with activity in clinically relevant Candida spp. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters. 2004;14: 5127–5131. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2004.07.070 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Chan JH, Hong JS, Kuyper LF, Baccanari DP, Joyner SS, Tansik RL, et al. Selective Inhibitors of Candida albicans Dihydrofolate Reductase: Activity and Selectivity of 5-(Arylthio)-2,4-diaminoquinazolin. J Med Chem. 1995;38: 3608–3616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Whitlow M, Howard AJ, Stewart D, Hardman KD, Chan JH, Baccanari DP, et al. X-ray Crystal Structures of Candida a lbicans Dihydrofolate Reductase: High Resolution Ternary Complexes in Which the Dihydronicotinamide Moiety of NADPH Is Displaced by an Inhibitor. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 2001;44: 2928–2932. doi: 10.1021/jm0101444 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Zgurskaya HI, Rybenkov VV, Krishnamoorthy G, Leus IV. Trans-envelope multidrug efflux pumps of Gram-negative bacteria and their synergism with the outer membrane barrier. Res Microbiol. 2018; doi: 10.1016/j.resmic.2018.02.002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Sjuts H, Vargiu AV, Kwasny SM, Nguyen ST, Kim H-S, Ding X, et al. Molecular basis for inhibition of AcrB multidrug efflux pump by novel and powerful pyranopyridine derivatives. PNAS. 2016;113: 3509–3514. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1602472113 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Shafer WM, Qu X, Waring AJ, Lehrer RI. Modulation of Neisseria gonorrhoeae susceptibility to vertebrate antibacterial peptides due to a member of the resistance/nodulation/division efflux pump family. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1998;95: 1829–1833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Lin L, Nonejuie P, Munguia J, Hollands A, Olson J, Dam Q, et al. Azithromycin Synergizes with Cationic Antimicrobial Peptides to Exert Bactericidal and Therapeutic Activity Against Highly Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacterial Pathogens. EBioMedicine. 2015;2: 690–698. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2015.05.021 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Sakoulas G, Kumaraswamy M, Kousha A, Nizet V. Interaction of Antibiotics with Innate Host Defense Factors against Salmonella enterica Serotype Newport. mSphere. 2017;2: e00410–17. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00410-17 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Kim J, Webb AM, Kershner JP, Blaskowski S, Copley SD. A versatile and highly efficient method for scarless genome editing in Escherichia coli and Salmonella enterica. BMC biotechnology. 2014;14: 1 doi: 10.1186/1472-6750-14-1 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Daniels JB, Call DR, Hancock D, Sischo WM, Baker K, Besser TE. Role of Ceftiofur in Selection and Dissemination of blaCMY-2-Mediated Cephalosporin Resistance in Salmonella enterica and Commensal Escherichia coli Isolates from Cattle. Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 2009;75: 3648–3655. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02435-08 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Hall MJ, Middleton RF, Westmacott D. The fractional inhibitory concentration (FIC) index as a measure of synergy. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1983;11: 427–433. doi: 10.1093/jac/11.5.427 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
(XLSX)
The top 75 compounds as determined by SAFIRE (96-well format) are shown (purple circles). EPM30 (red triangle); EPM35 (green square); EPM43 (blue circle); chloramphenicol (gray hexagon). For comparison, antibiotic controls rifampicin, ampicillin, and ciprofloxacin are indicated with arrows (open circles).
(TIF)
Bacterial growth in MHB across a range of gentamicin concentrations was not significantly altered by the presence of an EPM, as indicated by Fractional Inhibitory Concentrations Indices (FICI) of greater than 0.5.
(TIF)
A) Ethidium bromide, B) Nile red, C) Nile red with compounds washout. Mean and SD from representative efflux assays performed twice in duplicate. Upper dotted lines, initial fluorescence for DMSO-treated cells without glucose; lower dotted lines, endpoint fluorescence for DMSO-treated cells exposed to glucose. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01 determined by t-test of slopes calculated from linear fit of 0–10 minutes (EtBr) or 0–2 minutes (Nile red) relative to buffer.
(TIF)
(A) Nile red-loaded bacteria were washed, combined with the indicated concentrations of compounds and fluorescence was immediately measured. Data shown are mean + SD. These data suggest that the discrepancies in starting fluorescence (S4B Fig) are due to the time between compound addition and the beginning of measurement (15–20 minutes). As indicated here, during this timeframe DMSO-treated cells efflux the dye even in the absence of glucose. Thus, EPM35, EPM43, and PAβN inhibit basal loss of Nile red, but treatment with EPM30 led to an immediate reduction in fluorescence. (B) Bacteria remain intact and viable after 20 minutes incubation in 75 μM EPM30, indicating the immediate reduction in fluorescence in (A) is not due to death of the bacteria. It is possible that EPM30 reduces Nile red fluorescence by quenching or by altering membrane properties, as Nile red fluorescence is highly dependent on membrane polarity, content, and dynamics.
(TIF)
Disk diffusion assay. Bacteria were injected into the center of the plate (*); 10 μl of the indicated compound (top) or vehicle was spotted onto filter paper disks. Sixteen hours later, plates were imaged. Representative images from one of three independent experiments.
(TIF)
Representative ITC for the binding of EPM30 to E. coli AcrB. Each peak in the upper graph corresponds to the injection of 2 μL of 100 μM of the EPM in buffer containing 20 mM Na-HEPES (pH 7.5), 0.05% DDM and 5% DMSO into the reaction containing 10 μM of E. coli monomeric AcrB in buffer containing 20 mM Na-HEPES (pH 7.5), 0.05% DDM and 5% DMSO. The lower graph shows the cumulative heat of reaction displayed as a function of injection number. The solid line is the least-square fit to the experimental data.
(TIF)
(A, top) Hoechst accumulation quantitated as in Fig 2. (A, bottom) The DMSO, no-polymyxin B-treated samples were subtracted from treated samples (gray bars). Assuming additivity as the null hypothesis, the sum of the 5 μg/ml polymyxin B sample and each EPM sample was calculated (white bars). No significant differences were identified between observed and calculated data, suggesting that EPMs and polymyxin B do not synergize in this assay. (B) Nile red efflux quantitated as in Fig 4 and analysis performed as in A. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001 calculated using one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post-test.
(TIF)
Data Availability Statement
MATLAB scripts for SAFIRE analysis are available via MATLAB File Exchange (https://www.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/), deposited as "SAFIRE_ArrayScan”, “SAFIRE_Olympus_ix81” and “SAFIRE_CV1000”. All additional relevant data are within the paper and its Supporting Information files.