Introduction
Myocarditis is defined by WHO as an inflammatory disease affecting the myocardium, diagnosed by endomyocardial biopsy (EMB) using established histological, immunological, and immunohistochemical criteria; it may be idiopathic, infectious, or autoimmune (1–4). A wide variety of histological myocarditis patterns have been described according to the diverse etiologies and to the stage of the disease at the time of EMB ascertainment. Viral infections represent the most common cause in Europe and North America (5). Different viral genomes can be detected in the myocardium of patients with myocarditis and dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) using molecular techniques (6–14). When no infectious agents are identified on EMB and other known causes are excluded, autoimmune myocarditis (AMy) is the presumed etiology (15). These so-called “autoimmune myocarditis” or “virus-negative myocarditis” may occur as a distinct disease with exclusive cardiac involvement, or in the context of systemic autoimmune or inflammatory disorders with extracardiac involvement (5, 16–23).
It is likely that several etiologic types of myocarditis confluence in a common immune-mediated pathogenic process leading to chronic inflammation and tissue damage. Irrespective of triggering agents, acute inflammation may progress to subacute and chronic stages and eventually result in tissue remodeling, fibrosis, contractile dysfunction, and finally DCM (4, 6, 8, 24–29). Besides contractile dysfunction, both early myocardial inflammation and late fibrotic changes play a critical role in the development of the arrhythmic burden, which makes myocarditis one of the leading causes of sudden death (19, 27–31). Clearly, treatment interventions effectively curbing the acute inflammatory process at an early stage can prevent late cardiac remodeling and improve patient’s outcome. Emerging evidence on the pathogenic mechanisms underlying cardiac inflammation is paving the way to novel, promising treatment strategies for myocarditis.
Pathogenesis
Both autoimmune and innate inflammatory responses are involved in the pathogenesis of myocarditis and its sequelae; however, the specific contribution of either mechanism is not completely understood. As most of immune-mediated diseases, VNM is considered a multifactorial entity, with several immunologic mechanisms contributing to disease development and progression. Environmental triggers of myocardium damage lead to local inflammation and exposure of cryptic self-antigens: excessive innate and myocardium-specific immune responses ensue in genetically predisposed individuals (16, 31–35) and result in a self-sustained autoimmune or inflammatory cycle independent of the original triggering agent.
Traditionally, persistent autoimmune responses have been postulated to underlie the progression from myocarditis to DCM. Histologically, a lymphocytic infiltrate characterizes VNM, which is historically considered a CD4+ T cells mediated disease. Accordingly, transfer of CD4+ T-cells to severe combined immunodeficient mice induced the disease, while CD4+ T-cells depletion ameliorated experimental AMy (EAM). Additional immune cell-types characterizing cardiac inflammation in EAM include T-helper (Th)-1 and Th-17 cells, neutrophils, eosinophils, and monocytes/macrophages, representing a predominantly adaptive cellularity (32, 34). The role of innate immunity and auto-inflammatory mechanisms in the pathogenesis of myocarditis has traditionally received much less attention. Still, activation of the innate inflammatory response is required to prime and kick-off the adaptive immune response, and persistent inflammation is a critical cause of progressive tissue damage.
The Auto-Inflammatory Hypothesis
As most tissues, the heart exhibits a stereotyped, highly conserved response to injuries, characterized by an intense inflammatory reaction. This response, eventually leading to myocardial inflammation and heart failure (HF), is mediated by the pro-inflammatory cytokine interleukin (IL)-1, as indicated by both clinical and experimental evidence. IL-1 is an apical pro-inflammatory cytokine: two distinct ligands (IL-1α and IL-1β) with high sequence homology exert their biological activity by binding the IL-1 type-I receptor (IL-1RI), which transduces pro-inflammatory signals leading to the synthesis and expression of hundreds of secondary inflammatory mediators (35). IL-1α is produced by most epithelial cells as a fully active pro-inflammatory mediator, which is released upon cell death or stress in the case of tissue injury, thereby acting as an “alarmin.” Conversely, IL-1β is mostly produced by monocyte-macrophages as an inactive precursor and requires cleavage by an intracellular molecular complex termed “inflammasome” in order to be secreted and exert potent pro-inflammatory effects (35–38). The same cells that produce IL-1α or IL-1β also synthesize various regulatory molecules to curb excessive inflammation (35–38), including the IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra). Competitive binding of IL-1Ra to IL-1RI prevents IL-1 signaling and inhibits IL-1-mediated inflammation (35–37).
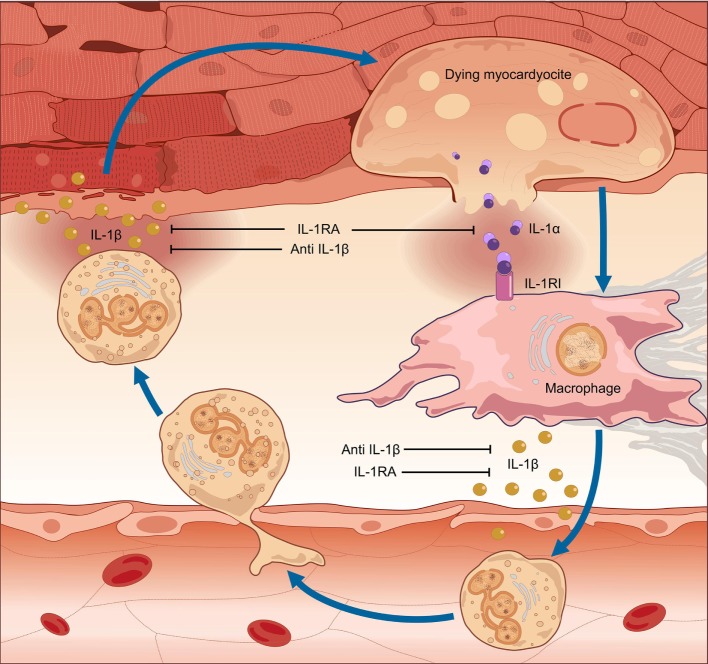
In myocarditis, IL-1α is released from the dying myocardium together with debris and other inflammatory mediators, and these in turn activate the inflammasomes in nearby cells (35–38). Runaway IL-1-mediated inflammation ensues, progressively causing apoptosis of cardiomyocytes, loss of contractile tissue, fibrosis, cardiomyopathy, HF, and arrhythmic outburst (39) (Figure 1). Intracellular aggregates of apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing CARD (ASC) and/or caspase-1, indicative of the formation of the inflammasome, can be observed in leukocytes, cardiomyocytes, fibroblasts, and endothelial-cells in EMB samples from patients with acute lymphocytic myocarditis or diagnosed as having myocarditis post-mortem (39). Of note, the number of inflammasome-containing leukocytes per-field correlated with HF severity: patients presenting with HF or with depressed left-ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) at admission, as well as those who did not experience a significant 6-month LVEF recovery, exhibited a greater number of inflammasomes and inflammasome-containing leukocytes in heart specimens. These data indicate that a stereotyped tissue inflammatory response characterized by the formation of the inflammasome is present and associated with disease severity in acute myocarditis, thus substantiating the critical role of IL-1β in both myocardial inflammation and systolic impairment.
Figure 1.
Pathogenesis of myocarditis: the auto-inflammatory hypothesis. In myocarditis, a detrimental inflammatory response leads to cardiac damage, clinically manifested with contractile dysfunction. The pro-inflammatory cytokine interleukin (IL)-1 is of pivotal importance in the pathogenesis of myocardial inflammation. Inflammation of the heart results in myocardial injury. IL-1α is released from the dying myocardiocytes, together with intracellular debris and inflammatory mediators; these in turn activate a molecular complex known as the “inflammasome,” resulting in processing and release of active IL-1β by infiltrating inflammatory cells. Runaway cardiac inflammation ensues, leading to apoptosis of cardiomyocytes and loss of contractile tissue, cardiomyopathy, and heart failure. Given the dual efficacy against myocardial inflammation and contractile dysfunction, prompt pharmacologic inhibition of IL-1 can arrest the progression of uncontrolled inflammation, thus preventing extensive tissue damage and arrhythmic complications and restoring cardiac function.
The mechanisms linking IL-1 to impaired contractile function include inhibition of L-type calcium channels, uncoupling of the β-adrenergic receptor (β-AR) from the adenylyl-cyclase (40–46), and transcriptional and posttranslational changes in phospholamban and sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase (47). IL-1 also increases nitric oxide (NO)-synthase expression leading to an increased NO activity, which mediates disruption of calcium and β-AR signaling and mitochondrial dysfunction (38, 48–50).
Experimental observations in animal models also confirm the role of IL-1 in inflammatory HF: plasma from advanced HF patients induced a significant systolic and diastolic dysfunction and reduced contractile reserve in mice following a single injection, suggesting the presence of circulating cardiodepressant factors (51, 52). Notably, administration of exogenous IL-1β to mice had comparable effects, while pre-blocking of IL-1 prevented contractile dysfunction induced by HF serum, indicating that cardiodepressant effects are IL-1-mediated (52, 53). This role of IL-1 as a cardiodepressant factor is also described in sepsis (54).
Beyond a direct cardiodepressant activity, several lines of evidence point at a central role of IL-1 signaling in the induction and development of the immune processes associated with acute myocarditis. IL-1 expression is markedly upregulated in experimental models of AMy. Coxsackievirus-induced myocarditis in mice is also characterized by heart infiltration with inflammatory cells secreting IL-1 and TNF-α (55). Persistently elevated IL-1β expression was noted in the chronic stage of myocarditis in a mouse model of post-myocarditis DCM induced by the encephalomyocarditis-virus (56). Consistently, mice deficient for IL-1RI were protected from the development of AM (57), and IL-1Ra administration or expression had beneficial effects in experimental models of inflammatory cardiomyopathy: specifically, delivery of human IL-1Ra via plasmid vectors into the hearts of experimental animals with coxsackieviral or AMy decreased myocardial inflammation and reduced mortality (58–61). These findings were paralleled by observations in humans, as increased IL-1β mRNA levels were found in EMBs from patients with viral myocarditis (57) and idiopathic DCM (58). Taken together, these evidences strongly suggest that IL-1 inhibition has the potentiality to simultaneously curb the heart inflammatory response and ameliorate myocardial contractility. Therapeutic agents specifically blocking IL-1 are available and used to treat a broad variety of autoimmune and inflammatory conditions (22, 62–65). Anakinra, the recombinant form of the naturally occurring IL-1Ra, blocks the activity of both IL-1α and IL-1β and is used to treat conditions characterized by IL-1-mediated inflammation. However, despite convincing evidence indicating a pivotal role of IL-1 in the pathogenesis of myocardial inflammation and myocarditis-related systolic dysfunction, the use of IL-1 blocking agents has been only anecdotally reported in this clinical condition.
Current and Future Therapeutic Perspectives
Symptomatic treatment of HF and of arrhythmias is the mainstay of treatment in myocarditis (66, 67). So far, conventional immunosuppressive drugs (steroids, cyclosporine, and azathioprine), rather than targeted treatments, have been used in order to target the pro-inflammatory mediators of the disease. Single-center randomized trials (RTs) showed some benefits in chronic VNM/DCM (68, 69), in giant-cell myocarditis (70) and in Amy (71). Recently, a single center controlled study demonstrated that combination of azathioprine and steroids can be moderately effective in the treatment of VNM refractory to standard of care (69). In the TIMIC-trial, patients with HF and biopsy-proven VNM were randomized to receive either prednisone 1 mg/kg per day for 4 weeks, followed by 0.33 mg/kg per day for 5-month plus azathioprine 2 mg/kg per day for 6 months, or placebo in addition to conventional therapy for HF. Primary outcome was the 6-month improvement in LVEF. Patients receiving prednisone plus azathioprine exhibited an improvement of LVEF and a decrease in LV volumes compared with baseline, while no patient in the placebo arm showed any improvement in LVEF. These results have been subsequently reproduced by other European observational studies (72, 73). However, a proportion of patients with myocarditis treated with current immunosuppressive strategies showed a complete lack of response, an observation indicating that some critical mechanisms of disease pathogenesis and inflammatory tissue damage are not susceptible to conventional immunosuppression.
Therapeutic IL-1 Blockade
Given the pivotal role of IL-1 in cardiac inflammation, it is expected that treatment with IL-1 blocking agents would curb inflammation and afford significant clinical benefits in patients with myocarditis. Clinical experience with specific IL-1 inhibition provides unambiguous confirmation to the role of IL-1 in human myocardial inflammation (Table 1). Specifically, in different RTs of ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) and HF, treatment with anakinra was associated with improved cardiac contractility and function. Also of note, in all these trials, anakinra treatment was associated with marked reductions in serum inflammatory markers. In the recent, massive CANTOS trial of 10,061 patients with previous myocardial infarction and C-reactive protein (CRP) > 2 mg/l, selective blockade of IL-1β with the monoclonal antibody canakinumab conferred protection against recurrent cardiovascular events (74); secondary analyses of results determined that more robust reductions in CRP after the first dose of canakinumab predicted greater clinical benefits, again confirming the role of IL-1 as driving force of cardiac and systemic inflammation (74–80).
Table 1.
Clinical experience with interleukin-1 inhibition in cardiac diseases.
| Study (reference) (year) | Population (n) | Study design | Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| VCU-ART (75) (2010)a | STEMI (10) | Double-blinded, randomized vs placebo | Anakinra treatment decreased LVESVi and LVEDVi on CMR and TTE (3 months). Trend toward decreased CRP levels correlated with the change in LVESVi and LVEDVi |
| AIR-HF (51) (2012) | HfrEF and elevated CRP levels (7) | Open-label, single-arm, non-randomized design. Anakinra 100 mg daily for 14 days | Change in aerobic capacity (peak VO2) and ventilatory efficiency (VE/VCO2) between baseline and 14 days |
| VCUART2 (76) (2013)a | STEMI (30) | Double-blind, randomized: vs placebo | No significant change in LVESVi, LVEDVi, and LVEF on cardiac MRI and echocardiography (3 months). Anakinra treatment: blunted the increase in CRP levels |
| VCUART 3 (2014) https://ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT01950299 |
STEMI (99) | Double-blind, randomized vs placebo | Results are awaited Primary endpoint: CRP levels in 14 days Secondary: change in LVESVi, LVEF, and new-onset HF (12 months) |
| CANTOS (74, 80) (2012)b | Post-myocardial infarction patients with elevated CRP (10,061) | Double-blind, randomized, multi-center, international, subcutaneous canakinumab 50, 150, or 300 mg every 3 months vs placebo. Median follow-up of 3.8 years | The 150-mg dose met the prespecified multiplicity adjusted threshold for statistical significance for a composite end point of non-fatal myocardial infarction, non-fatal stroke, or cardiovascular death. Nearly all of the risk reduction was observed in non-fatal MI. No significant difference in stroke, cardiovascular mortality, or overall mortality |
| Ikonomidis et al. (86) (2008) | Rheumatoid arthritis (23) | Double-blind, randomized cross-over trial. Anakinra 100 mg (single injection) vs placebo, baseline compared to 3 h after treatment. After 2 days, the alternate treatment was givend | Improvement of FMD, CFR, arterial compliance, resistance, longitudinal strain, circumferential strain, peak twisting, untwisting velocity, LVEF, apoptotic, and oxidative markers in CAD than in non-CAD patients |
| Ikonomidis et al. (87) (2014) | Rheumatoid arthritis + CAD (60), rheumatoid arthritis + no CAD (20) | ||
| MRC-ILA Heart Study (77) (2014)c | NSTEMI (182) | Double-blind, randomized vs placebo | Reduction in CRP levels (area-under-the-curve for CRP) over the first 7 days |
| D-HART (82) (2014) | HFpEF (12) | Double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, crossover trial: anakinra 100 mg daily vs placebo for 14 days and an additional 14 days of the alternate treatment | Improvement in peak oxygen consumption and a significant reduction in plasma CRP levels |
| D-HART2 (78) (2014) | HFpEF and elevated CRP levels (30) | 2:1 double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, single center trial: anakinra 100 mg daily or placebo for 12 weeks | Results are awaited |
| REDHART (2014) https://ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT01936909 |
HFrEF with recently decompensated HF (60) | Double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled: anakinra 100 mg daily for2 or 12 weeks or placebo for 12 weeks, follow-up of 24 weeks | Study completed. Results have yet to be published Primary outcome measure: aerobic exercise capacity (peak VO2) and ventilator efficiency at 2 weeks (follow-up = 24 weeks) Secondary: survival free of hospital admissions |
| ADHF (79) (2014) | HFrEF, acute decompensation, and elevated CRP levels (30) | Double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled: anakinra 100 mg twice daily for 3 days followed by 100 mg once daily for 11 more days | CRP reduction, greater recovery in LVEF. No difference in length of hospital stay |
| Cavalli et al. (83) (2017) | Fulminant viral myocarditis (1), life-threatening myocarditis in AOSD (1) and T-cell lymphomas (1) | Case reports | Full recovery from cardiogenic shock, rapidly amelioration of cardiac function allowing weaning from mechanical circulatory and respiratory support |
| Cavalli et al. (84) (2016) | |||
| Parisi et al. (85) (2017) | |||
| ARAMIS (ongoing) https://ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT03018834 |
Acute myocarditis (120) | Double-blinded, randomized clinical trial Phase IIb of superiority ANAKINRA 100 mg/daily subcutaneously once a day vs placebo until hospital discharge, for a maximum of 14 days, in addition to standard care: ACE and Beta-blocker for 6 months |
Results are awaited Primary outcome measures: no. of days alive free of any myocarditis complications defined as ventricular arrhythmias, HF, chest pain, ventricular dysfunction defined as LVEF < 50%, within 28 days post hospitalization |
n, number; AOSD, adult-onset Still disease; CAD, coronary artery disease; CFR, coronary flow reserve; CRP, C-reactive protein serym levels; FMD, flow-mediated reserve; HF, heart failure; HFpEF, heart failure with preserved ejection fraction; HFrEF, heart failure with reduced ejection fraction; LVEDVi, left ventricle end-diastolic volume index; LVEF, left ventricle ejection fraction; LVESVi, left ventricle end-systolic volume index; CMR, cardiac magnetic resonance; NSTEMI, non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction; ref, reference; STEMI, ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction; TTE, trans-thoracic echocardiography.
aVCU-ART and VCUART2 combined showed reduction in incidence of new HF with anakinra.
bAn exploratory analysis showed a marked reduction in the incidence of lung cancer, as well as lung cancer mortality and total cancer mortality. The treatment was associated with a higher incidence of fatal infection than was placebo.
cHigher incidence of major adverse cardiac events at 12 months with anakinra.
dChronic: non randomized study: anakinra (150 mg, n = 23) vs prednisolone (+5 mg over regular dose, n = 19) for 30 days.
Besides dampening of inflammation, the beneficial effects of IL-1 blockade on cardiac function include amelioration of myocardial contractility. Early ex vivo studies with human atrial heart strips revealed that picomolar concentrations of IL-1 suppress contractile force (81). It was thus not unexpected that administration of anakinra to patients with refractory HF could improve exercise tolerance, while also dampening systemic pro-inflammatory mediators (51). IL-1 blockade with anakinra was also effective in the management of diastolic HF in a separate double-blind, placebo controlled trial (82). This direct beneficial effect of IL-1 inhibition on contractile function explains in part the near-instant clinical improvement observed in life-threatening cases of fulminant myocarditis, irrespective of the etiology (83–85). Similarly, in previous studies on patients with rheumatoid arthritis, anakinra promptly increased myocardial contractility within hours of a single dose administration (86, 87).
Given this dual efficacy on tissue inflammation and contractile dysfunction, anakinra seems a particularly attractive option for patients with inflammatory HF due to myocarditis. A double blind, randomized, phase-IIb placebo-controlled clinical trial of anakinra in patients with acute myocarditis is ongoing (ARAMIS-trial, https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03018834?term=anakinra&cond=myocarditis&rank=1). Experience is currently more limited with IL-1 blocking agents in the setting of chronic, VNM, and no clinical trials are presently evaluating this therapeutic option. However, VNM and DCM are histologically characterized by various degrees of inflammatory features, which precede and accompany fibrotic changes and drive both systolic impairment and arrhythmic complications. Prompt blockade of IL-1 can arrest the progression of uncontrolled inflammation, thus preventing fibrotic damage, curbing the arrhythmic burden, and restoring cardiac function. Also in light of a rapid onset of action and an excellent safety profile, IL-1 inhibition with anakinra represents a particularly suitable treatment option for conditions characterized by inflammatory HF, such as myocarditis with reduced LVEF.
Conclusive Remarks
The inflammatory response in myocarditis spirals into a cycle of auto-inflammation, as intracellular contents released from dying myocardiocytes trigger the activation of the inflammasome and the uncontrolled release of IL-1 from neighboring cells. Selective and prompt pharmacologic inhibition of IL-1 dampens runaway inflammation and tissue damage, thus preventing arrhythmic complications and restoring cardiac function. Dual effectiveness against myocardial inflammation and contractile dysfunction renders IL-1 blockade a suitable therapeutic option for myocarditis.
Author Contributions
GDL: conceived the hypothesis, contributed to the understanding of pathogenic mechanisms, clinical presentation and prognostic meaning of autoimmune myocarditis, and drafted the manuscript. GC: conceived the hypothesis, contributed to the understanding of biological effects of IL-1 and to the therapeutic usefulness of IL-1 in a broad spectrum of rheumatic diseases blockade, and critically revised the manuscript. CC: participated in previous studies focused on IL-1 blockade and myocarditis and critically revised the manuscript. MT: conceived the hypothesis and critically revised the manuscript. LD: conceived the hypothesis, critically revised the manuscript, and gave the approval of the final version.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- 1.Richardson P, McKenna W, Bristow M, Maisch B, Mautner B, O’Connell J, et al. Report of the 1995 World Health Organization/International Society and Federation of Cardiology task force on the definition and classification of cardiomyopathies. Circulation (1996) 93(5):841–2. 10.1161/01.CIR.93.5.841 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Jefferies JL, Towbin JA. Dilated cardiomyopathy. Lancet (2010) 375(9716):752–62. 10.1016/S0140-6736(09)62023-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Aretz HT, Billingham ME, Edwards WD, Factor SM, Fallon JT, Fenoglio JJ, Jr, et al. Myocarditis. A histopathologic definition and classification. Am J Cardiovasc Pathol (1987) 1(1):3–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Magnani JW, Dec GW. Myocarditis: current trends in diagnosis and treatment. Circulation (2006) 113(6):876–90. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.584532 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Caforio AL, Marcolongo R, Jahns R, Fu M, Felix SB, Iliceto S. Immune-mediated and autoimmune myocarditis: clinical presentation, diagnosis and management. Heart Fail Rev (2013) 18(6):715–32. 10.1007/s10741-012-9364-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Yajima T, Knowlton KU. Viral myocarditis: from the perspective of the virus. Circulation (2009) 119(19):2615–24. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.08.766022 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Calabrese F, Thiene G. Myocarditis and inflammatory cardiomyopathy: microbiological and molecular biological aspects. Cardiovasc Res (2003) 60(1):11–25. 10.1016/S0008-6363(03)00475-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Bock CT, Klingel K, Kandolf R. Human parvovirus B19-associated myocarditis. N Engl J Med (2010) 362(13):1248–9. 10.1056/NEJMc0911362 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Baboonian C, Treasure T. Meta-analysis of the association of enteroviruses with human heart disease. Heart (1997) 78(6):539–43. 10.1136/hrt.78.6.539 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Maisch B, Schönian U, Crombach M, Wendl I, Bethge C, Herzum M, et al. Cytomegalovirus associated inflammatory heart muscle disease. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl (1993) 88:135–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Matsumori A, Matoba Y, Sasayama S. Dilated cardiomyopathy associated with hepatitis C virus infection. Circulation (1995) 92(9):2519–25. 10.1161/01.CIR.92.9.2519 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Pankuweit S, Moll R, Baandrup U, Portig I, Hufnagel G, Maisch B. Prevalence of the parvovirus B19 genome in endomyocardial biopsy specimens. Hum Pathol (2003) 34(5):497–503. 10.1016/S0046-8177(03)00078-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kühl U, Pauschinger M, Noutsias M, Seeberg B, Bock T, Lassner D, et al. High prevalence of viral genomes and multiple viral infections in the myocardium of adults with “idiopathic” left ventricular dysfunction. Circulation (2005) 111(7):887–93. 10.1161/01.CIR.0000155616.07901.35 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Bowles NE, Ni J, Kearney DL, Pauschinger M, Schultheiss HP, McCarthy R, et al. Detection of viruses in myocardial tissues by polymerase chain reaction. evidence of adenovirus as a common cause of myocarditis in children and adults. J Am Coll Cardiol (2003) 42(3):466–72. 10.1016/S0735-1097(03)00648-X [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Rose NR. Myocarditis: infection versus autoimmunity. J Clin Immunol (2009) 29(6):730–7. 10.1007/s10875-009-9339-z [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Comarmond C, Cacoub P. Myocarditis in auto-immune or auto-inflammatory diseases. Autoimmun Rev (2017) 16(8):811–6. 10.1016/j.autrev.2017.05.021 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.De Luca G, Bosello S, Leone AM, Gabrielli F, Pelargonio G, Inzani F, et al. Life-threatening arrhythmias in a scleroderma patient: the role of myocardial inflammation in arrhythmic outburst. Scand J Rheumatol (2017) 46(1):78–80. 10.3109/03009742.2016.1157626 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Pieroni M, De Santis M, Zizzo G, Bosello S, Smaldone C, Campioni M, et al. Recognizing and treating myocarditis in recent-onset systemic sclerosis heart disease: potential utility of immunosuppressive therapy in cardiac damage progression. Semin Arthritis Rheum (2014) 43(4):526–35. 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2013.07.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.De Luca G, Bosello SL, Gabrielli FA, Berardi G, Parisi F, Rucco M, et al. Prognostic role of ventricular ectopic beats in systemic sclerosis: a prospective cohort study shows ECG indexes predicting the worse outcome. PLoS One (2016) 11(4):e0153012. 10.1371/journal.pone.0153012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Bosello S, De Luca G, Ferraccioli G. Troponin in stable ischemic heart disease and diabetes. N Engl J Med (2015) 373(20):1977–8. 10.1056/NEJMc1511645#SA4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Colafrancesco S, Priori R, Valesini G, Argolini L, Baldissera E, Bartoloni E, et al. Response to interleukin-1 inhibitors in 140 italian patients with adult-onset still’s disease: a multicentre retrospective observational study. Front Pharmacol (2017) 8:369. 10.3389/fphar.2017.00369 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.De Luca G, Bosello SL, Canestrari G, Cavalli G, Dagna L, Ferraccioli G. QTc interval prolongation in systemic sclerosis: correlations with clinical variables and arrhythmic risk. Int J Cardiol (2017) 239:33. 10.1016/j.ijcard.2017.03.088 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Campochiaro C, Tomelleri A, Cavalli G, Berti A, Dagna L. Erdheim-Chester disease. Eur J Intern Med (2015) 26(4):223–9. 10.1016/j.ejim.2015.03.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Root-Bernstein R, Fairweather D. Unresolved issues in theories of autoimmune disease using myocarditis as a framework. J Theor Biol (2015) 375:101–23. 10.1016/j.jtbi.2014.11.022 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Fairweather D, Rose NR. Coxsackievirus-induced myocarditis in mice: a model of autoimmune disease for studying immunotoxicity. Methods (2007) 41(1):118–22. 10.1016/j.ymeth.2006.07.009 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Felker GM, Hu W, Hare JM, Hruban RH, Baughman KL, Kasper EK. The spectrum of dilated cardiomyopathy. The Johns Hopkins experience with 1,278 patients. Medicine (Baltimore) (1999) 78(4):270–83. 10.1097/00005792-199907000-00005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Towbin JA, Lowe AM, Colan SD, Sleeper LA, Orav EJ, Clunie S, et al. Incidence, causes, and outcomes of dilated cardiomyopathy in children. JAMA (2006) 296(15):1867–76. 10.1001/jama.296.15.1867 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kindermann I, Barth C, Mahfoud F, Ukena C, Lenski M, Yilmaz A, et al. Update on myocarditis. J Am Coll Cardiol (2012) 59(9):779–92. 10.1016/j.jacc.2011.09.074 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Caforio AL, Pankuweit S, Arbustini E, Basso C, Gimeno-Blanes J, Felix SB, et al. European Society of Cardiology Working Group on Myocardial and Pericardial Diseases. Current state of knowledge on aetiology, diagnosis, management, and therapy of myocarditis: a position statement of the European Society of Cardiology Working Group on Myocardial and Pericardial Diseases. Eur Heart J (2013) 34(33):2648a–2648d. 10.1093/eurheartj/eht210 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Pollack A, Kontorovich AR, Fuster V, Dec GW. Viral myocarditis – diagnosis, treatment options, and current controversies. Nat Rev Cardiol (2015) 12(11):670–80. 10.1038/nrcardio.2015.108 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Fabre A, Sheppard MN. Sudden adult death syndrome and other non-ischaemic causes of sudden cardiac death. Heart (2006) 92(3):316–20. 10.1136/hrt.2004.045518 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Bracamonte-Baran W, Čiháková D. Cardiac autoimmunity: myocarditis. Adv Exp Med Biol (2017) 1003:187–221. 10.1007/978-3-319-57613-8_10 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Cavalli G, Hayashi M, Jin Y, Yorgov D, Santorico SA, Holcomb C, et al. MHC class II super-enhancer increases surface expression of HLA-DR and HLA-DQ and affects cytokine production in autoimmune vitiligo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A (2016) 113(5):1363–8. 10.1073/pnas.1523482113 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Hayashi M, Jin Y, Yorgov D, Santorico SA, Hagman J, Ferrara TM, et al. Autoimmune vitiligo is associated with gain-of-function by a transcriptional regulator that elevates expression of HLA-A*02:01 in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A (2016) 113(5):1357–62. 10.1073/pnas.1525001113 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Dinarello CA. Interleukin-1 in the pathogenesis and treatment of inflammatory diseases. Blood (2011) 117(14):3720–32. 10.1182/blood-2010-07-273417 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Bujak M, Frangogiannis NG. The role of IL-1 in the pathogenesis of heart disease. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz) (2009) 57(3):165–76. 10.1007/s00005-009-0024-y [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Cavalli G, Dinarello CA. Suppression of inflammation and acquired immunity by IL-37. Immunol Rev (2018) 281(1):179–90. 10.1111/imr.12605 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Cavalli G, Justice JN, Boyle KE, D’Alessandro A, Eisenmesser EZ, Herrera JJ, et al. Interleukin 37 reverses the metabolic cost of inflammation, increases oxidative respiration, and improves exercise tolerance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A (2017) 114(9):2313–8. 10.1073/pnas.1619011114 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Toldo S, Kannan H, Bussani R, Anzini M, Sonnino C, Sinagra G, et al. Formation of the inflammasome in acute myocarditis. Int J Cardiol (2014) 171(3):e119–21. 10.1016/j.ijcard.2013.12.137 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Abbate A. The heart on fire: inflammasome and cardiomyopathy. Exp Physiol (2013) 98(2):385. 10.1113/expphysiol.2012.069021 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Van Tassell BW, Toldo S, Mezzaroma E, Abbate A. Targeting interleukin-1 in heart disease. Circulation (2013) 128(17):1910–23. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.113.003199 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Chung MK, Gulick TS, Rotondo RE, Schreiner GF, Lange LG. Mechanism of cytokine inhibition of beta-adrenergic agonist stimulation of cyclic AMP in rat cardiacmyocytes. Impairment of signal transduction. Circ Res (1990) 67:753–63. 10.1161/01.RES.67.3.753 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Liu SJ, Zhou W, Kennedy RH. Suppression of beta-adrenergic responsiveness of L-type Ca2+ current by IL-1beta in rat ventricular myocytes. Am J Physiol (1999) 276:H141–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Schreur KD, Liu S. Involvement of ceramide in inhibitory effect of IL-1 beta on L-type Ca2+ current in adult rat ventricular myocytes. Am J Physiol (1997) 272:H2591–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Liu S, Schreur KD. G protein-mediated suppression of L-type Ca2+ current by interleukin-1 beta in cultured rat ventricular myocytes. Am J Physiol (1995) 268:C339–49. 10.1152/ajpcell.1995.268.2.C339 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Combes A, Frye CS, Lemster BH, Brooks SS, Watkins SC, Feldman AM, et al. Chronic exposure to interleukin 1beta induces a delayed and reversible alteration in excitation-contraction coupling of cultured cardiomyocytes. Pflugers Arch (2002) 445(2):246–56. 10.1007/s00424-002-0921-y [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.McTiernan CF, Lemster BH, Frye C, Brooks S, Combes A, Feldman AM. Interleukin-1 beta inhibits phospholamban gene expression in cultured cardiomyocytes. Circ Res (1997) 81:493–503. 10.1161/01.RES.81.4.493 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Tatsumi T, Matoba S, Kawahara A, Keira N, Shiraishi J, Akashi K, et al. Cytokine-induced nitric oxide production inhibits mitochondrial energy production and impairs contractile function in rat cardiac myocytes. J Am Coll Cardiol (2000) 35:1338–46. 10.1016/S0735-1097(00)00526-X [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Schulz R, Panas DL, Catena R, Moncada S, Olley PM, Lopaschuk GD. The role of nitric oxide in cardiac depression induced by interleukin-1 beta and tumour necrosis factor-alpha. Br J Pharmacol (1995) 114:27–34. 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1995.tb14901.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Tsujino M, Hirata Y, Imai T, Kanno K, Eguchi S, Ito H, et al. Induction of nitric oxide synthase gene by interleukin-1 beta in cultured rat cardiocytes. Circulation (1994) 90:375–83. 10.1161/01.CIR.90.1.375 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Van Tassell BW, Arena RA, Toldo S, Mezzaroma E, Azam T, Seropian IM, et al. Enhanced interleukin-1 activity contributes to exercise intolerance in patients with systolic heart failure. PLoS One (2012) 7(3):e33438. 10.1371/journal.pone.0033438 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Toldo S, Mezzaroma E, O’Brien L, Marchetti C, Seropian IM, Voelkel NF, et al. Interleukin-18 mediates interleukin-1-induced cardiac dysfunction. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol (2014) 306(7):H1025–31. 10.1152/ajpheart.00795.2013 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Toldo S, Mezzaroma E, Bressi E, Marchetti C, Carbone S, Sonnino C, et al. Interleukin-1β blockade improves left ventricular systolic/ diastolic function and restores contractility reserve in severe ischemic cardiomyopathy in the mouse. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol (2014) 64(1):1–6. 10.1097/FJC.0000000000000106 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Kumar A, Thota V, Dee L, Olson J, Uretz E, Parrillo JE. Tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin 1beta are responsible for in vitro myocardial cell depression induced by human septic shock serum. J Exp Med (1996) 183(3):949–58. 10.1084/jem.183.3.949 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Lane JR, Neumann DA, Lafond-Walker A, Herskowitz A, Rose NR. Role of IL-1 and tumor necrosis factor in coxsackie virus-induced autoimmune myocarditis. J Immunol (1993) 151:1682–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Shioi T, Matsumori A, Sasayama S. Persistent expression of cytokine in the chronic stage of viral myocarditis in mice. Circulation (1996) 94:2930–7. 10.1161/01.CIR.94.11.2930 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Han RO, Ray PE, Baughman KL, Feldman AM. Detection of interleukin and interleukin-receptor mRNA in human heart by polymerase chain reaction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun (1991) 181:520–3. 10.1016/0006-291X(91)91219-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Vanderheyden M, Paulus WJ, Voss M, Knuefermann P, Sivasubramanian N, Mann D, et al. Myocardial cytokine gene expression is higher in aortic stenosis than in idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy. Heart (2005) 91:926–31. 10.1136/hrt.2004.035733 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Eriksson U, Kurrer MO, Sonderegger I, Iezzi G, Tafuri A, Hunziker L, et al. Activation of dendritic cells through the interleukin 1 receptor 1 is critical for the induction of autoimmune myocarditis. J Exp Med (2003) 197:323–31. 10.1084/jem.20021788 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Lim BK, Choe SC, Shin JO, Ho SH, Kim JM, Yu SS, et al. Local expression of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist by plasmid DNA improves mortality and decreases myocardial inflammation in experimental coxsackieviral myocarditis. Circulation (2002) 105:1278–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Liu H, Hanawa H, Yoshida T, Elnaggar R, Hayashi M, Watanabe R, et al. Effect of hydrodynamics-based gene delivery of plasmid DNA encoding interleukin-1 receptor antagonist-Ig for treatment of rat autoimmune myocarditis: possible mechanism for lymphocytes and noncardiac cells. Circulation (2005) 111:1593–600. 10.1161/01.CIR.0000160348.75918.CA [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Cavalli G, Franchini S, Aiello P, Guglielmi B, Berti A, Campochiaro C, et al. Efficacy and safety of biological agents in adult-onset still’s disease. Scand J Rheumatol (2015) 44(4):309–14. 10.3109/03009742.2014.992949 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Cavalli G, De Luca G, Dagna L. Advances in potential targeted therapies for Erdheim-Chester disease. Expert Opin Orphan Drugs (2017) 5(3):253–60. [Google Scholar]
- 64.Cavalli G, Fallanca F, Dinarello CA, Dagna L. Treating pulmonary silicosis by blocking interleukin 1. Am J Respir Crit Care Med (2015) 191(5):596–8. 10.1164/rccm.201412-2150LE [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Cavalli G, Dinarello CA. Treating rheumatological diseases and co-morbidities with interleukin-1 blocking therapies. Rheumatology (Oxford) (2015) 54(12):2134–44. 10.1093/rheumatology/kev269 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Priori SG, Blomström-Lundqvist C, Mazzanti A, Blom N, Borggrefe M, Camm J, et al. Task force for the management of patients with ventricular arrhythmias and the prevention of sudden cardiac death of the European society of cardiology (ESC). 2015 ESC guidelines for the management of patients with ventricular arrhythmias and the prevention of sudden cardiac death: the task force for the management of patients with ventricular arrhythmias and the prevention of sudden cardiac death of the European society of cardiology (ESC)endorsed by: association for European paediatric and congenital cardiology (AEPC). Europace (2015) 17(11):1601–87. 10.1093/europace/euv319 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Ponikowski P, Voors AA, Anker SD, Bueno H, Cleland JG, Coats AJ, et al. Authors/task force members; document reviewers. 2016 ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure: the task force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the European society of cardiology (ESC). Developed with the special contribution of the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur J Heart Fail (2016) 18(8):891–975. 10.1002/ejhf.592 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Frustaci A, Chimenti C, Calabrese F, Pieroni M, Thiene G, Maseri A. Immunosuppressive therapy for active lymphocytic myocarditis: virological and immunologic profile of responders versus nonresponders. Circulation (2003) 107(6):857–63. 10.1161/01.CIR.0000048147.15962.31 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Frustaci A, Russo MA, Chimenti C. Randomized study on the efficacy of immunosuppressive therapy in patients with virus-negative inflammatory cardiomyopathy: the TIMIC study. Eur Heart J (2009) 30(16):1995–2002. 10.1093/eurheartj/ehp249 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Cooper LT, Jr, Hare JM, Tazelaar HD, Edwards WD, Starling RC, Deng MC, et al. Giant cell myocarditis treatment trial investigators. Usefulness of immunosuppression for giant cell myocarditis. Am J Cardiol (2008) 102(11):1535–9. 10.1016/j.amjcard.2008.07.041 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Mahrholdt H, Goedecke C, Wagner A, Meinhardt G, Athanasiadis A, Vogelsberg H, et al. Cardiovascular magnetic resonance assessment of human myocarditis: a comparison to histology and molecular pathology. Circulation (2004) 109(10):1250–8. 10.1161/01.CIR.0000118493.13323.81 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Escher F, Kühl U, Lassner D, Poller W, Westermann D, Pieske B, et al. Long-term outcome of patients with virus-negative chronic myocarditis or inflammatory cardiomyopathy after immunosuppressive therapy. Clin Res Cardiol (2016) 105(12):1011–20. 10.1007/s00392-016-1011-z [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Caforio ALP, Malipiero G, Marcolongo R, Iliceto S. Myocarditis: a clinical overview. Curr Cardiol Rep (2017) 19(7):63. 10.1007/s11886-017-0870-x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Ridker PM, Everett BM, Thuren T, MacFadyen JG, Chang WH, Ballantyne C, et al. CANTOS trial group. Antiinflammatory therapy with canakinumab for atherosclerotic disease. N Engl J Med (2017) 377(12):1119–31. 10.1056/NEJMoa1707914 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Abbate A, Kontos MC, Grizzard JD, Biondi-Zoccai GG, Van Tassell BW, Robati R, et al. Interleukin-1 blockade with anakinra to prevent adverse cardiac remodeling after acute myocardial infarction (Virginia Commonwealth University Anakinra Remodeling Trial [VCU-ART] Pilot study). Am J Cardiol (2010) 105(10):1371–1377.e1. 10.1016/j.amjcard.2009.12.059 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Abbate A, Van Tassell BW, Biondi-Zoccai G, Kontos MC, Grizzard JD, Spillman DW, et al. Effects of interleukin-1 blockade with anakinra on adverse cardiac remodeling and heart failure after acute myocardial infarction [from the Virginia Commonwealth University-Anakinra Remodeling Trial (2) (VCUART2) pilot study]. Am J Cardiol (2013) 111(10):1394–400. 10.1016/j.amjcard.2013.01.287 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Morton AC, Rothman AM, Greenwood JP, Gunn J, Chase A, Clarke B, et al. The effect of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist therapy on markers of inflammation in non-ST elevation acute coronary syndromes: the MRCILA Heart Study. Eur Heart J (2015) 36(6):377–84. 10.1093/eurheartj/ehu272 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Van Tassell BW, Buckley LF, Carbone S, Trankle CR, Canada JM, Dixon DL, et al. Interleukin-1 blockade in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: rationale and design of the diastolic heart failure anakinra response trial 2 (D-HART2). Clin Cardiol (2017) 40(9):626–32. 10.1002/clc.22719 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Van Tassell BW, Abouzaki NA, Oddi Erdle C, Carbone S, Trankle CR, Melchior RD, et al. Interleukin-1 blockade in acute decompensated heart failure: a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled pilot study. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol (2016) 67(6):544–51. 10.1097/FJC.0000000000000378 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Ridker PM, MacFadyen JG, Everett BM, Libby P, Thuren T, Glynn RJ, et al. Relationship of C-reactive protein reduction to cardiovascular event reduction following treatment with canakinumab: a secondary analysis from the CANTOS randomised controlled trial. Lancet (2018) 391(10118):319–28. 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32814-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Cain BS, Meldrum DR, Dinarello CA, Meng X, Joo KS, Banerjee A, et al. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-1beta synergistically depress human myocardial function. Crit Care Med (1999) 27(7):1309–18. 10.1097/00003246-199907000-00018 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Van Tassell BW, Arena R, Biondi-Zoccai G, Canada JM, Oddi C, Abouzaki NA, et al. Effects of interleukin-1 blockade with anakinra on aerobic exercise capacity in patients with heart failure and preserved ejection fraction (from the D-HART pilot study). Am J Cardiol (2014) 113(2):321–7. 10.1016/j.amjcard.2013.08.047 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Cavalli G, Foppoli M, Cabrini L, Dinarello CA, Tresoldi M, Dagna L. Interleukin-1 receptor blockade rescues myocarditis-associated end-stage heart failure. Front Immunol (2017) 8:131. 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00131 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Cavalli G, Pappalardo F, Mangieri A, Dinarello CA, Dagna L, Tresoldi M. Treating life-threatening myocarditis by blocking interleukin-1. Crit Care Med (2016) 44(8):e751–4. 10.1097/CCM.0000000000001654 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Parisi F, Paglionico A, Varriano V, Ferraccioli G, Gremese E. Refractory adult-onset still disease complicated by macrophage activation syndrome and acute myocarditis: a case report treated with high doses (8mg/kg/d) of anakinra. Medicine (Baltimore) (2017) 96(24):e6656. 10.1097/MD.0000000000006656 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Ikonomidis I, Lekakis JP, Nikolaou M, Paraskevaidis I, Andreadou I, Kaplanoglou T, et al. Inhibition of interleukin-1 by anakinra improves vascular and left ventricular function in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Circulation (2008) 117(20):2662–9. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.731877 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Ikonomidis I, Tzortzis S, Andreadou I, Paraskevaidis I, Katseli C, Katsimbri P, et al. Increased benefit of interleukin-1 inhibition on vascular function, myocardial deformation, and twisting in patients with coronary artery disease and coexisting rheumatoid arthritis. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging (2014) 7(4):619–28. 10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.113.001193 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]