Abstract
Glycopeptide antibiotics inhibit the peptidoglycan biosynthesis in Gram-positive bacteria by targeting lipid II. This prevents the recycling of bactoprenol phosphate, the lipid transporter that is shared by peptidoglycan and wall teichoic acid biosyntheses. In this study, we investigate the effects of glycopeptide antibiotics on peptidoglycan and wall teichoic acid biosynthesis. The incorporation of D-[1-13C]alanine, D-[15N]alanine and L-[1-13C]lysine into peptidoglycan and wall teichoic acid in intact whole cells of Staphylococcus aureus were measured using 13C{15N} and 15N{13C} rotational-echo double resonance NMR. S. aureus treated with oritavancin and vancomycin at sub-minimal inhibitory concentrations exhibit a large reduction in D-Ala incorporation into wall teichoic acid, but without changes to the peptidoglycan cross-links or the stem-links. Thus, sequestration of bactoprenol phosphate by glycopeptide antibiotics resulted in inhibition of D-Ala incorporation into the wall teichoic acid prior to the inhibition of peptidoglycan biosynthesis. Our finding shows that S. aureus respond to glycopeptide-induced cell wall stress by routing all available D-Ala to the peptidoglycan biosynthesis, at the cost of reducing the wall teichoic acid biosynthesis.
TOC image
Introduction
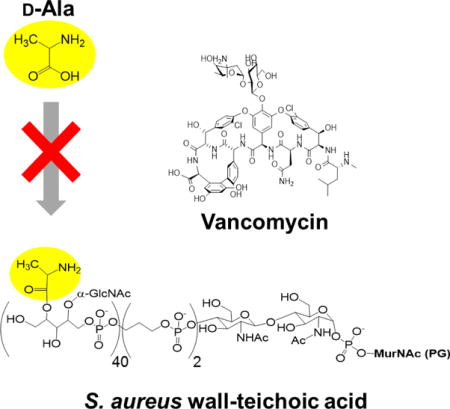
Vancomycin is a glycopeptide antibiotic used for treating acute infections by Gram-positive pathogens (Fig. 1). Vancomycin inhibits peptidoglycan (PG) biosynthesis by binding to the D-Ala- D-Ala terminus of lipid II, a PG precursor anchored to the cell membrane via the lipid transporter bactoprenol-phosphate (C55-P). Vancomycin-bound lipid II is sequestered from the transglycosylation step of the PG biosynthesis to prevent C55-P regeneration. As C55 is found in low concentration in bacteria,1 sequestration of lipid II by vancomycin results in cytoplasmic accumulation of a cytoplasmic PG precursor called Park’s nucleotide.2 In vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE), vancomycin binding to the D-Ala-D-Ala terminus of lipid II is prevented by the replacement of the dipeptide with a depsipeptide D-Ala-D-Lac, which renders vancomycin ineffective.3–4 To overcome vancomycin resistance, a structure activity relationship study of chloroeremomycin led to the discovery of oritavancin (Fig. 1).5–7 Oritavancin is a semi-synthetic lipoglycopeptide that exhibits potent activities against vancomycin-resistant pathogens including VRE and vancomycin-resistant S. aureus (VRSA).8 Oritavancin is currently a leading therapeutic agent for treating serious infections caused by multi-drug resistant Gram-positive pathogens such as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. The chemical structure of oritavancin differs from that of vancomycin with the addition of N-alkylated chlorobiphenyl side chain to the epi-vancosamine of the drug sugar (Fig 1.). In general, the modification of the glycopeptide disaccharide by the attachment of a hydrophobic side chain significantly improves the drugs’ overall efficacy and restores the activity against vancomycin-resistant pathogens. Structural characterization of these disaccharide-modified glycopeptides’ binding site in intact whole cells of S. aureus9–11 and E. faecium12 by solid-state NMR revealed that the drug hydrophobic side chain forms a secondary binding site. This secondary binding site enables the lipoglycopeptides to target the cross-linked PG-bridge structure to facilitate the binding.11 The oritavancin binding to the nascent PG interferes with the PG template recognition by transpeptidase, which is essential for efficient PG crosslinking during cell wall synthesis.13
Figure 1. S. aureus treated with disaccharide-modified glycopeptide antibiotics at sub-MICs do not readily induce ATP leakage.
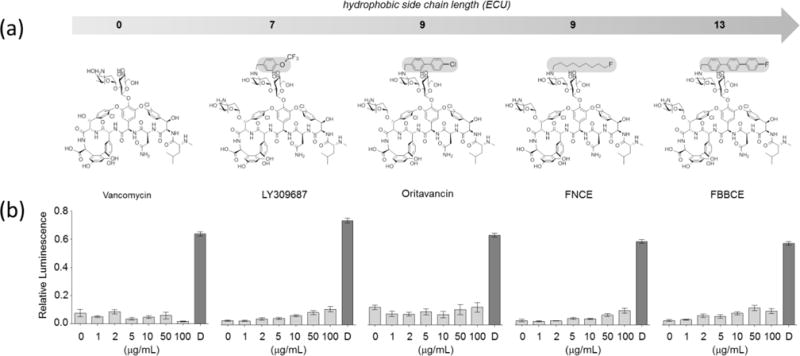
a, Chemical structures of disaccharide-modified glycopeptide antibiotics with increasing aliphatic side chain lengths (from left to right): vancomycin (no modification), LY309687 (trifluoromethoxybenzyl side chain), oritavancin (chlorophenyl-benzyl side chain), FNCE (N-9-fluorononyl side chain), and FBBCE (N-9-fluorobiphenylbenzyl side chain). b, ATP leakage was attempted in S. aureus harvested at OD660nm 1.5 by addition of glycopeptide antibiotics to final concentrations of 0, 1, 2, 5, 10, 50, and 100 μg/mL, and daptomycin (D) at 100 μg/mL. All glycopeptide antibiotics did not induce appreciable ATP leakage attributable to membrane depolarization at the concentrations tested. In comparison, daptomycin induced ATP leakage consistent with the membrane disruption. All error bars represent 95% confidence interval.
All glycopeptide antibiotics share a common mode of action in binding to lipid II that prevents the recycling of C55-P, which is the central lipid transporter utilized by both PG and wall teichoic acid (WTA) biosyntheses. PG and WTA are two major components of the cell wall, with each contributing approximately 50% of the dry cell wall weight. WTA plays an important role in microbial pathogenesis through host attachment, colonization, infection, biofilm formation, and recruitment of penicillin binding proteins (PBPs) to the septum during cell division.14 Thus, it represents an attractive target for novel antibiotic development. Recent mode of action studies on cyclic lipopeptides that target PG biosynthesis, including plusbacin A3,15 amphomycin, and MX-2401,16–17 have shown to affect WTA biosyntheses in S. aureus. In this study, we investigate whether glycopeptide antibiotics have a hidden mode of action of inhibiting the WTA biosynthesis. We describe WTA inhibition as “hidden” because WTA is covalently attached to PG and co-integrated into insoluble cell wall,18 thus making it difficult to characterize the changes in intact whole cells using biochemical methods. Although extraction of WTA can be achieved by incubating the isolated cell wall under alkaline conditions, D-Ala attached to the ribitol-phosphate backbone of WTA via ester-links are lost during the treatment, thus making accurate quantification and composition analysis of WTA difficult and unreliable.19 In this report, we directly measured the changes to PG and WTA compositions in intact whole cells of S. aureus using solid-state NMR. Glycopeptide antibiotics were added to S. aureus during the growth at sub-minimal inhibitory concentrations (MIC). Simultaneous measure of PG and WTA compositions in vivo by solid-state NMR was crucial for determining the interplay between PG and WTA biosyntheses through the shared lipid transporter in S. aureus, and provided new insight into the potent antimicrobial activity of glycopeptide antibiotics.
Materials and methods
Bacterial growth conditions
Starter culture of S. aureus (ATCC 6538P) grown overnight in 5 mL of trypticase soy broth (TSB) was added at 1% (final volume) to 500 mL of S. aureus standard media (SASM).2, 20 Natural-abundance amino acids in SASM were replaced by L,D-[13C]Ala, or L-[1-13C]Lys and L,D-[15N]Ala, or L-[1-13C]Lys and D-[1-15N]Ala to incorporate specific 13C and 15N labels to the bridging segment of intact cells’ PG. To determine the effects of different glycopeptide antibiotics on WTA biosynthesis, vancomycin (5 μg/mL) or oritavancin (5 μg/mL) was added to the culture during mid-exponential growth phase at OD660 of 0.6. Each drug concentration was chosen to elicit a comparable growth response from S. aureus. Cells were harvested after one hour of growth with the antibiotic by centrifugation at 10,000 g for 10 min at 4 °C in Sorvall GS-3 rotor. Cell pellets were rinsed twice with 300 mL of ice-cold deionized water. Rinsed pellets were first frozen, then lyophilized.
Solid-State NMR
Experiments were performed on intact cells at 7.0 T (300 MHz for 1H, 75 MHz for 13C, and 30 MHz for 15N), and isolated cell walls at 4.7 T (200 MHz for 1H, 50 MHz for 13C, and 20 MHz for 15N) provided by 89-mm bore Oxford (Cambridge, U.K.) superconducting solenoids. The four-frequency transmission-line probe used in the 7.0-T spectrometer had a 14-mm long, 9-mm inner-diameter sample coil, while that used in the 4.7-T spectrometer had a 17-mm long, 8.6-mm inner-diameter sample coil. Both probes were equipped with a Chemagnetics/Varian magic-angle spinning ceramic stator, and the samples were spun in room temperature at 5 kHz (maintained within ±2 Hz). Radio-frequency pulses were produced by 1-kW Kalmus, ENI, and American Microwave Technology power amplifiers, each under active control; π-pulse lengths were 10 μs for 13C and 15N. Proton-carbon and proton-nitrogen matched cross-polarization transfers were at 50 kHz for 2 ms. Proton dipolar decoupling during signal acquisition was 105 kHz (for 7.0-T spectrometer) and 98 kHz (for 4.7-T spectrometer).
ATP leakage assay
ATP-leakage assay was performed on overnight cultures of S. aureus (ATCC 6538P) grown in TSB that were harvested at OD600 of 1.5. Cells were pelleted then resuspended in phosphate buffered saline supplemented with 20 mM Ca2+. Glycopeptide antibiotics vancomycin, N‘-(p-trifluoromethoxybenzyl)chloroeremomycin (LY309687),21 oritavancin, N-(9-fluorononyl)chloroeremomycin (FNCE),9 and N-(4-(4-fluorobiphenyl)benzyl)chloroeremomycin (FBBCE)9 were added to each bacterial suspension to final drug concentrations of 0, 0.5, 1, 2, 5, 10, 50, and 100 μg/mL and the mixture incubated for 20 min at 37 °C. After the incubation, bacteria were pelleted by centrifuging and removed. Amount of leaked ATP in the supernatant was directly quantified by adding 100 μL of CellTiter-Glo® 2.0 reagent (Promega, Madison WI) to the equal volume of supernatant. After 10 min of equilibration, the luminescence given off by the mixture was measured using Fluoroskan Ascent FL Luminometer (Thermo Scientific) with the integration time of 200 ms.
Results
Disaccharide-modified glycopeptides at sub-MICs do not target membrane
Potent bactericidal activity by oritavancin and oritavancin-like disaccharide-modified glycopeptides such as telavancin has been attributed to the membrane depolarization and leakage mediated by the drugs’ hydrophobic side chains. To investigate the effect of glycopeptide antibiotics on WTA biosynthesis, it was necessary to avoid high levels of glycopeptide antibiotic concentration at which the membrane was perturbed. This critical concentration was determined by ATP leakage assay where disaccharide-modified glycopeptides with the hydrophobic side chain length, ranging from 0, 7, 9, to 13 equivalent carbon units (ECU) (Fig. 1a),9, 13 were added to an overnight culture of S. aureus.
Vancomycin, which does not have a hydrophobic side chain, failed to induce ATP leakage even at 100 μg/mL. In comparison, S. aureus treated with disaccharide modified lipoglycopeptide antibiotics, LY309687, oritavancin, FNCE (telavancin analogue), and FBBCE with the hydrophobic side chain length ranging from 7 to 13 ECU exhibited concentration dependent ATP leakages. This is because unlike vancomycin, which has a biostatic activity, lipoglycopeptides are bactericidal. Thus, during the 20 min incubation period with lipoglycopeptides, concentration-dependent bactericidal activities would account for the increased level of ATP leakage. Nevertheless, the amount of ATP leakages induced by the lipoglycopeptides are relatively low, not to the extent of daptomycin (100 μg/mL), a known membrane disrupting cyclic decadepsipeptide.22 Therefore, lipoglycopeptides including oritavancin, FNCE, and FBBCE are ineffective pore formers in comparison to the membrane-targeting antibiotic, daptomycin. The result is consistent with the solid-state NMR characterization of LY309687, oritavancin, FNCE, and FBBCE binding sites in intact whole cells of S. aureus where lipoglycopeptides are found bound to PG without partitioning to the bacterial membrane.9–11, 20, 23 For our investigation, we selected the antibiotic concentration of 5 μg/mL to add to the culture during mid-exponential growth phase at OD660 nm of 0.6. At 5 μg/mL, glycopeptide antibiotics do not target membrane, but retain activities against cell wall biosynthesis in S. aureus (Fig. 2).
Figure 2. Glycopeptide antibiotics inhibit both PG transglycosylation and WTA biosynthesis in S. aureus.
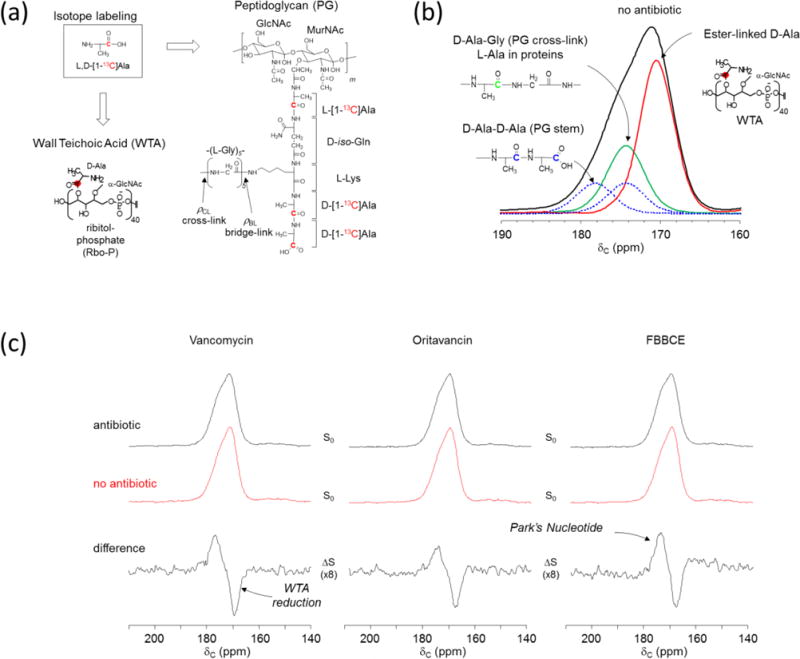
a, PG and WTA labeling by L,D-[1-13C]Ala in S. aureus. b, Deconvolution of 13C-CPMAS spectrum of intact whole cells of S. aureus with D-alanyl carboxyls at 178 ppm (blue), D-alanyl peptide carbonyls at 174 ppm (green), and ester carbonyls of WTA at 171 ppm (red). c, 13C-CPMAS spectrum of untreated S. aureus (middle, red) is subtracted from the spectrum of antibiotic treated whole cells (top, red). The difference spectra (bottom) show all antibiotic-treated S. aureus have a negative 171 ppm peak which corresponds to decreased ester-linked D-Ala incorporation to WTA. Park’s nucleotide accumulation (positive 178 ppm peak) is observed for all glycopeptide-treated S. aureus.
Glycopeptide antibiotics inhibit both PG and WTA biosyntheses in S. aureus
Bactoprenol phosphate is an importance of lipid transporter for the biosyntheses of both PG and WTA. Since a small number of bactoprenol phosphate are found per bacterium,1 glycopeptide antibiotic sequestration will likely to have a profound impact on both PG and WTA biosyntheses. To monitor the effects of glycopeptide antibiotics on both PG and WTA compositions, S. aureus were grown in SASM containing 13C-labeled L,D-[1-13C]Ala. Incorporation of L,D-[1-13C]Ala into PG and WTA is illustrated in Fig. 2a. Glycopeptide antibiotics vancomycin, oritavancin, or FBBCE were added to S. aureus during the mid-exponential growth phase at OD660 of 0.6 to final concentration of 5 μg/mL. The cells were harvested after 60 min growth in the presence of antibiotic for the analysis. Figure 2b (black line) shows the 13C-CPMAS spectrum centered at 174 ppm for S. aureus grown in absence of antibiotic. The 174-ppm peak is fitted to three deconvoluted peaks: the ester carbonyls of D-[1-13C]Ala in WTA at 171 ppm (red), the peptide carbonyls at 174 ppm (green and dotted blue), and the carboxyl carbons at 178 ppm (dotted blue).13 The chemical shift and the linewidth for the peptide carbonyl carbon at 174 ppm (cross-link) was determined from the 13C{15N} REDOR difference (ΔS) spectrum of isolated cell walls of S. aureus labeled with [15N]Gly and D-[1-13C]Ala, and the carboxyl carbons at 178 ppm from the full-echo spectrum after spectral subtraction of ΔS 174 ppm. Figure 2c (top) shows 13C-CPMAS spectra of S. aureus treated with glycopeptide antibiotics. They show altered lineshapes due to the changes in D-[1-13C]Ala distribution within the cell. The changes are clearly visible in the difference spectra (Fig. 2c, bottom) obtained by subtracting 13C-CPMAS of untreated sample (Fig. 2c, red) from the antibiotic treated spectrum (Fig. 2c, top). The difference spectra of S. aureus treated with glycopeptide antibiotics all show an increase in the 178 ppm peak intensity (D-Ala carboxyl) while a decrease in the 171 ppm intensity (D-Ala esters of WTA). The increase in 178-ppm intensity is due to cytoplasmic accumulation of Park’s nucleotide, consistent with the glycopeptide inhibition of the transglycosylation step of PG biosynthesis.13 The reduced D-Ala incorporation to WTA in antibiotic-treated S. aureus suggests that all available D-Ala are routed to PG biosynthesis in effort to maintain the cell wall structure.
Oritavancin is a potent WTA biosynthesis inhibitor
To determine which biosynthesis, PG or WTA, is more affected by glycopeptide antibiotics, the double isotope-labeling scheme shown in Fig. 3a was used. This allowed a simultaneous measurement of the L,D-[15N]Ala incorporation into both PG and WTA (Fig. 3a). S. aureus were grown in SASM containing L,D-[15N]Ala and L-[1-13C]Lys in the presence of vancomycin (5 μg/mL) or oritavancin (5 μg/mL) to 13C-15N label the PG stem-link. In the S0 spectra of 13C{15N} REDOR of intact whole cells (Fig. 3b, bottom), the L-[1-13C]Lys incorporated into PG is visible as a lysyl-carbonyl carbon peak at 175 ppm. In the ΔS spectra at 1.6 ms dipolar evolution, the 13C of L-[1-13C]Lys covalently bonded to the 15N of D-[15N]Ala (PG stem-link) is dephased at 175 ppm. The ΔS 175-ppm peak intensity, which is directly proportional to the total number of stem-link in the cell wall of S. aureus, remains unchanged for S. aureus treated with glycopeptide antibiotics. This indicates that the addition of vancomycin and oritavancin at 5 μg/mL to S. aureus did not inhibit Park’s nucleotide biosynthesis.
Figure 3. Oritavancin is a potent WTA inhibitor.
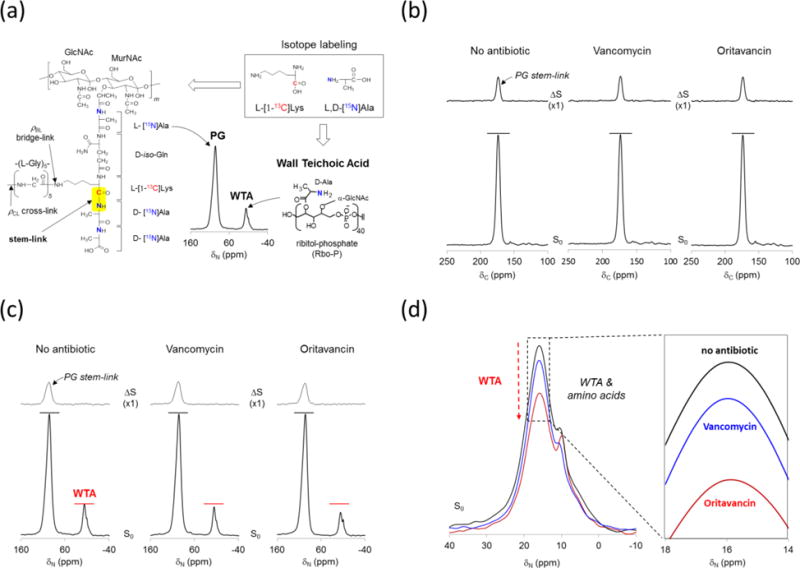
a, L,D-[15N]Ala and L-[1-13C]Lys labeling of S. aureus PG and WTA. Isotope labeled 13C-15N spin pair is predominantly found at the stem-link position of PG. 15N-CPMAS spectrum from intact whole cells of S. aureus shows D-[15N]Ala incorporated into WTA appearing at 16 ppm, and L,D-[15N]Ala into proteins and PG at 93 ppm. b, 13C{15N} REDOR spectra from intact whole cells of S. aureus grown with and without antibiotics: vancomycin (5 μg/mL), and oritavancin (5 μg/mL) following 1.6 ms dipolar evolution. The L-[1-13C]Lys incorporation to S. aureus is visible as a lysyl-carbonyl carbon at 175 ppm in the S0 spectra (bottom). In the ΔS spectra (top), only the 13C-lysyl-carbonyl carbons of L-[1-13C]Lys peptide bonded to the 15N of L,D-[15N]Ala are dephased at 1.6 ms dipolar evolution. Hence the ΔS 175-ppm intensity is directly proportional to the in situ stem-link density of the cell wall. The stem-link density of S. aureus is unaffected by glycopeptide antibiotic treatments, which indicates that D-[15N]Ala and L-[1-13C]Lys incorporations to PG are unaffected at the glycopeptide antibiotic concentration of 5 μg/mL. c, 15N{13C} REDOR spectra of intact whole cells of S. aureus at 1.6 ms dipolar evolution. In the ΔS spectra (top) 93-ppm intensity directly proportional to the stem-links in cell wall is unaffected by the glycopeptide antibiotic treatment. However, the S0 spectra (bottom) of vancomycin and oritavancin treated S. aureus show reductions in the alanyl-amine peak at 16 ppm. The 16-ppm intensity corresponds to ester-linked D-Ala in WTA, and therefore glycopeptide antibiotics inhibited D-Ala incorporation into WTA in S. aureus suggesting inhibition of the WTA biosynthesis. d, The D-alanyl-amine peak at 16 ppm from the S0 spectra are overlaid. Oritavancin shows maximum inhibition of D-Ala incorporation into WTA. Each spectra were the result of 10,000 accumulated scans.
The L,D-[15N]Ala labeling scheme allows a simultaneous measurement of the L,D-[15N]Ala incorporation into PG and WTA by 15N{13C} REDOR (Fig. 3c). In the S0 spectra, L,D-[1-15N]Ala incorporations into proteins and PG are visible as an 15N-amide at 93 ppm while the D-[15N]Ala into WTA appear as an 15N-amine at 16 ppm. In the 15N{13C} REDOR ΔS spectrum at 1.6 ms, only the covalently bonded 15N-13C spins from the PG stem-link is visible at the 93 ppm (Fig. 3c, top). The ΔS 93-ppm peak intensity is directly measure of the total number of PG stem-links, and thus it is proportional to the total number of PG stems found in each bacterium. The addition of vancomycin or oritavancin to S. aureus did not change the ΔS 93-ppm intensity. Therefore, the incorporation of L,D-[15N]Ala and L-[1-13C]Lys into PG biosynthesis is unaffected. In contrast, the D-[15N]Ala incorporation into WTA was inhibited by both vancomycin and oritavancin. The S0 spectra of glycopeptide-treated S. aureus show reduced 15N-alanyl amine intensity at 16 ppm, which corresponded to the ester-linked D-[15N]Ala found in WTA, while the 15N-alanyl amide of D-[15N]Ala (PG) remained constant (Fig. 3c, bottom). The enlarged spectral overlay of 16-ppm peaks (Fig. 3d) show a visible reduction in D-[15N]Ala incorporation into the WTA of S. aureus, when treated with glycopeptide antibiotics. Oritavancin exhibits potent inhibition of D-[15N]Ala incorporation into WTA that is approximately four times more effective than vancomycin.
Inhibition of WTA biosynthesis by glycopeptide antibiotics occurs before PG inhibition
To quantify the changes in D-[15N]Ala incorporation into WTA, S. aureus were grown in SASM containing D-[15N]Ala and L-[1-13C]Lys in the presence of alaphosphin (5 μg/mL). SASM was supplemented with the natural abundance L-Ala and alaphosphin, which is an alanine racemase inhibitor that prevents racemic scrambling of D-[15N]Ala. The addition of alaphosphin ensured that the D-[15N]Ala is incorporated into the D-Ala-D-Ala of PG stem and ester-linked D-Ala of WTA, but not into proteins. Figure 4 shows the 15N{13C} REDOR spectra of whole cell S. aureus at 1.6 ms dipolar evolution. The ΔS 93-ppm peak intensity, which is directly proportional to the total number of PG bridge-linking density, does not change with the increase in vancomycin concentration. Hence, the S0 16-ppm intensity for ester-linked D-[15N]Ala in WTA decreases by more than half for S. aureus treated with vancomycin (10 and 20 μg/mL). This indicates that vancomycin-treated S. aureus maintained D-[15N]Ala incorporation into the PG stem by routing all of the available D-[15N]Ala away from the WTA biosynthesis (Fig. 4b). Thus, vancomycin inhibition of the WTA biosynthesis preceded the PG biosynthesis in S. aureus.
Figure 4. Vancomycin-treated S. aureus show inhibition of WTA biosynthesis preceding PG biosynthesis.
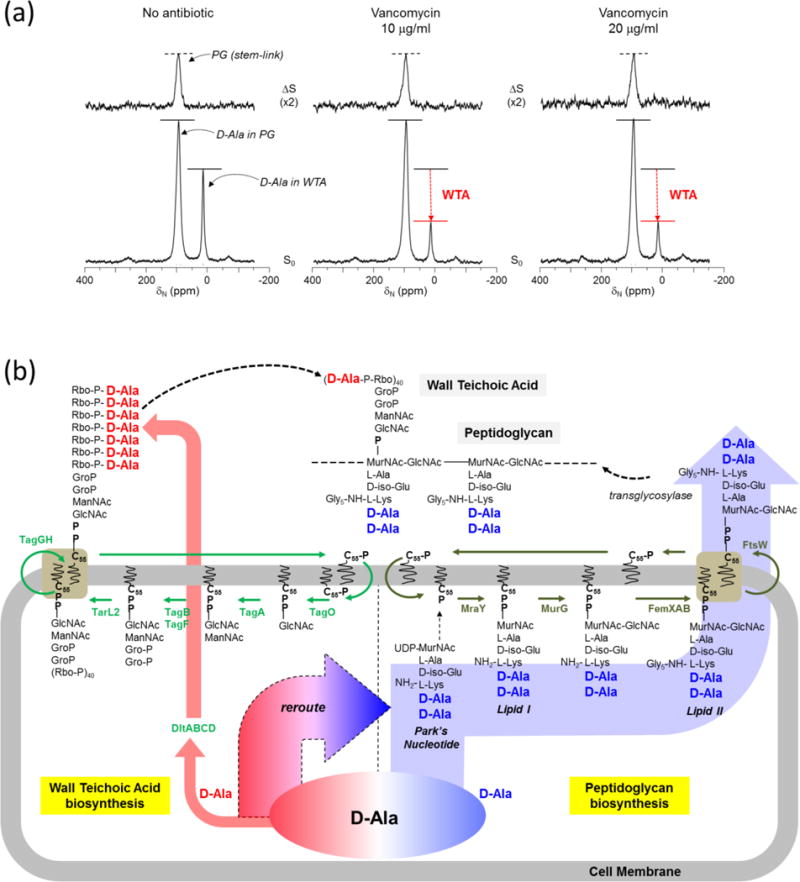
a, D-[15N]Ala and L-[1-13C]Lys labeling of S. aureus PG and WTA in presence of alanine racemase inhibitor alaphosphin (5 ug/ml). 93-ppm peak intensities in the ΔS spectra (top) of 15N{13C} REDOR at 1.6 ms show that alaphosphin improves D-[15N]Ala incorporation into PG. The addition of vancomycin did not affect the PG stem-link density; however, the S0 spectra show a large reduction in the D-[15N]Ala incorporation into WTA (16 ppm). b, Schematic representation of WTA and PG biosyntheses with bactoprenol-phosphate (C55-P) as the central lipid transporter. Glycopeptide antibiotics prevent regeneration of the lipid transporter and thereby inhibit both PG and WTA biosyntheses. However, as shown in Fig. 4a D-[15N]Ala incorporation into WTA (red arrow) was inhibited in vancomycin-treated S. aureus by rerouting all available D-[15N]Ala into maintaining the PG biosynthesis (blue arrow). Hence, the vancomycin inhibition of D-[15N]Ala incorporation into the WTA biosynthesis precedes interference of the PG biosynthesis.
The changes in the amounts of ester-linked D-Ala in WTA in comparison to D-Ala in PG are calculated by integrating the 93-ppm (D-Ala in PG) and 16-ppm peaks (D-Ala in WTA) in the S0 spectra of 15N{13C} REDOR (Fig. 4a). For S. aureus grown in the absence of antibiotics, the amount of ester-linked D-Ala found in WTA is approximately 23% of all the D-Ala found in PG. This reduces to 12% for S. aureus treated with vancomycin at 10 μg/mL. Interestingly, increased vancomycin treatment of S. aureus at 20 μg/mL does not further reduce the amount of ester-linked D-Ala in WTA, remaining unchanged at 12%. We believe that this is the minimum amount of D-Ala in teichoic acid that is required for bacteria to resume its normal cell wall biosynthesis and division. Complete removal of D-Ala from WTA and lipoteichoic acids in S. aureus has been shown to be lethal.24 Therefore, we propose that the amount of ester-linked D-Ala in WTA at of 12% (relative to all D-Ala found in PG) is the minimum amount required for S. aureus to maintain normal cell wall growth.
Discussion
We show that oritavancin and other oritavancin-like glycopeptides at low concentrations can readily inhibit cell wall biosynthesis in S. aureus without membrane perturbation (Fig. 1). The potent bactericidal activity of oritavancin that was previously attributed to the hydrophobic side chain targeting the bacterial membrane does not occur at low concentrations near the MIC. Instead, we show using solid-state NMR, that vancomycin and oritavancin readily inhibit the WTA biosynthesis in S. aureus. This is crucial as the antibiotic binding to lipid II prevents the regeneration of the shared lipid transporter C55 required for the first committed step in biosyntheses of both PG and WTA (Fig. 4b). Oritavancin-treated S. aureus show rapid inhibition of WTA biosynthesis without any detectable changes to PG cross-links or stem-links, which indicates that the WTA inhibition precedes the PG inhibition. Oritavancin was approximately 4 times more active than vancomycin in inhibiting WTA biosynthesis (Fig. 3d). Although WTA itself is not required for the S. aureus viability, WTA-deficient mutants exhibit large changes to their cell morphology with increased antibiotic susceptibility, incapability to form biofilms, and diminished virulence with inability to colonize the host.25–26 Inhibition of WTA can directly impact cell division as it is required for the recruitment of PBP427 and regulation of the autolysin activity during cell growth and division.28–29 We conclude that the combination of WTA and PG inhibitions is responsible for the bactericidal activity of oritavancin. Our finding provides a new insight into the mode of action of oritavancin, which will aid the future development of this vital class of antibiotics.
Acknowledgments
We thank Drs. Richard C. Thompson and Thalia I. Nicas (Lilly Research Laboratories, Indianapolis IN) for the gift of LY309687; and Dr. Adel Rafai Far (The Medicines Company) for the gift of FNBC and FBBCE. This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health under grant number GM116130.
ABBREVIATIONS
- CPMAS
cross-polarization magic-angle spinning
- FBBCE
N-(4-(4-fluorobiphenyl)benzyl)chloroeremomycin
- FNCE
N-(9-fluorononyl)chloroeremomycin
- oritavancin
N-4-[(4-chlorophenyl)benzyl)]chloroeremomycin
- LY309687
N-(p-trifluoromethoxybenzyl)chloroeremomycin
- MIC
minimum inhibitory concentration
- PG
peptidoglycan
- REDOR
rotational-echo double resonance
- WTA
wall teichoic acid
- SASM
Staphylococcus aureus standard media
References
- 1.Brotz H, Bierbaum G, Reynolds PE, Sahl HG. The lantibiotic mersacidin inhibits peptidoglycan biosynthesis at the level of transglycosylation. Eur J Biochem. 1997;246:193–199. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1997.t01-1-00193.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Cegelski L, Kim SJ, Hing AW, Studelska DR, O’Connor RD, Mehta AK, Schaefer J. Rotational-echo double resonance characterization of the effects of vancomycin on cell wall synthesis in Staphylococcus aureus. Biochemistry. 2002;41:13053–13058. doi: 10.1021/bi0202326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Arthur M, Molinas C, Bugg TD, Wright GD, Walsh CT, Courvalin P. Evidence for in vivo incorporation of D-lactate into peptidoglycan precursors of vancomycin-resistant enterococci. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992;36:867–869. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.4.867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Billot-Klein D, Gutmann L, Collatz E, van Heijenoort J. Analysis of peptidoglycan precursors in vancomycin-resistant enterococci. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992;36:1487–1490. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.7.1487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Cooper DG, Snyder NJ, Zweifel MJ, Staszak MA, Wilkie SC, Nicas TI, Mullen DL, Butler TF, Rodriguez MJ, Huff BE, Thompson CR. Reductive alkylation of glycopeptide antibiotics: synthesis and antibacterial activity. J Antibiot. 1996;49:575–581. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.49.575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Cooper RD, Snyder NJ, Zweifel MJ, Staszak MA, Wilkie SC, Nicas TI, Mullen DL, Butler TF, Rodriguez MJ, Huff BE, Thompson RC. Reductive alkylation of glycopeptide antibiotics: synthesis and antibacterial activity. J Antibiot. 1996;49:575–581. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.49.575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Nicas TI, Mullen DL, Flokowitsch JE, Preston DA, Snyder NJ, Zweifel MJ, Wilkie SC, Rodriguez MJ, Thompson RC, Cooper RD. Semisynthetic glycopeptide antibiotics derived from LY264826 active against vancomycin-resistant enterococci. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1996;40:2194–2199. doi: 10.1128/aac.40.9.2194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Sweeney D, Stoneburner A, Shinabarger DL, Arhin FF, Belley A, Moeck G, Pillar CM. Comparative in vitro activity of oritavancin and other agents against vancomycin-susceptible and -resistant enterococci. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2016;72:622–624. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkw451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Kim SJ, Tanaka KS, Dietrich E, Rafai Far A, Schaefer J. Locations of the hydrophobic side chains of lipoglycopeptides bound to the peptidoglycan of Staphylococcus aureus. Biochemistry. 2013;52:3405–3414. doi: 10.1021/bi400054p. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kim SJ, Schaefer J. Hydrophobic side-chain length determines activity and conformational heterogeneity of a vancomycin derivative bound to the cell wall of Staphylococcus aureus. Biochemistry. 2008;47:10155–10161. doi: 10.1021/bi800838c. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Kim SJ, Matsuoka S, Patti GJ, Schaefer J. Vancomycin derivative with damaged D-Ala-D-Ala binding cleft binds to cross-linked peptidoglycan in the cell wall of Staphylococcus aureus. Biochemistry. 2008;47:3822–31. doi: 10.1021/bi702232a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Patti GJ, Kim SJ, Yu TY, Dietrich E, Tanaka KS, Parr TRJr, Far AR, Schaefer J. Vancomycin and oritavancin have different modes of action in Enterococcus faecium. J Mol Biol. 2009;392:1178–1191. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2009.06.064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kim SJ, Cegelski L, Stueber D, Singh M, Dietrich E, Tanaka KS, Parr TR, Far AR, Schaefer J. Oritavancin exhibits dual mode of action to inhibit cell-wall biosynthesis in Staphylococcus aureus. J Mol Biol. 2008;377:281–293. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2008.01.031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Brown S, Santa Maria JP, Jr, Walker S. Wall teichoic acids of gram-positive bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2013;67:313–336. doi: 10.1146/annurev-micro-092412-155620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kim SJ, Singh M, Wohlrab A, Yu TY, Patti GJ, O’Connor RD, VanNieuwenhze M, Schaefer J. The isotridecanyl side chain of plusbacin-A3 is essential for the transglycosylase inhibition of peptidoglycan biosynthesis. Biochemistry. 2013;52:1973–1979. doi: 10.1021/bi4000222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Rubinchik E, Schneider T, Elliott M, Scott WR, Pan J, Anklin C, Yang H, Dugourd D, Muller A, Gries K, Straus SK, Sahl HG, Hancock RE. Mechanism of action and limited cross-resistance of new lipopeptide MX-2401. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011;55:2743–2754. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00170-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Singh M, Chang J, Coffman L, Kim SJ. Solid-state NMR characterization of amphomycin effects on peptidoglycan and wall teichoic acid biosyntheses in Staphylococcus aureus. Sci Rep. 2016;6:31757. doi: 10.1038/srep31757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Meredith TC, Swoboda JG, Walker S. Late-stage polyribitol phosphate wall teichoic acid biosynthesis in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 2008;190:3046–3056. doi: 10.1128/JB.01880-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Xia G, Maier L, Sanchez-Carballo P, Li M, Otto M, Holst O, Peschel A. Glycosylation of wall teichoic acid in Staphylococcus aureus by TarM. J Biol Chem. 2010;285:13405–13415. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.096172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Kim SJ, Cegelski L, Studelska DR, O’Connor RD, Mehta AK, Schaefer J. Rotational-echo double resonance characterization of vancomycin binding sites in Staphylococcus aureus. Biochemistry. 2002;41:6967–6977. doi: 10.1021/bi0121407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Kim SJ, Cegelski L, Preobrazhenskaya M, Schaefer J. Structures of Staphylococcus aureus cell-wall complexes with vancomycin, eremomycin, and chloroeremomycin derivatives by 13C{19F} and 15N{19F} rotational-echo double resonance. Biochemistry. 2006;45:5235–5250. doi: 10.1021/bi052660s. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Muller A, Wenzel M, Strahl H, Grein F, Saaki TN, Kohl B, Siersma T, Bandow JE, Sahl HG, Schneider T, Hamoen LW. Daptomycin inhibits cell envelope synthesis by interfering with fluid membrane microdomains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 doi: 10.1073/pnas.1611173113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Kim SJ, Singh M, Schaefer J. Oritavancin binds to isolated protoplast membranes but not intact protoplasts of Staphylococcus aureus. J Mol Biol. 2009;391:414–425. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2009.06.033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Santa Maria JP, Jr, Sadaka A, Moussa SH, Brown S, Zhang YJ, Rubin EJ, Gilmore MS, Walker S. Compound-gene interaction mapping reveals distinct roles for Staphylococcus aureus teichoic acids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014;111:12510–12515. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1404099111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Kristian SA, Timmer AM, Liu GY, Lauth X, Sal-Man N, Rosenfeld Y, Shai Y, Gallo RL, Nizet V. Impairment of innate immune killing mechanisms by bacteriostatic antibiotics. The FASEB Journal. 2007;21:1107–1116. doi: 10.1096/fj.06-6802com. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Kristian SA, Lauth X, Nizet V, Goetz F, Neumeister B, Peschel A, Landmann R. Alanylation of teichoic acids protects Staphylococcus aureus against Toll-like receptor 2-dependent host defense in a mouse tissue cage infection model. The Journal of Infectious Diseases. 2003;188:414–423. doi: 10.1086/376533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Atilano ML, Pereira PM, Yates J, Reed P, Veiga H, Pinho MG, Filipe SR. Teichoic acids are temporal and spatial regulators of peptidoglycan cross-linking in Staphylococcus aureus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107:18991–18996. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1004304107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Biswas R, Martinez RE, Gohring N, Schlag M, Josten M, Xia G, Hegler F, Gekeler C, Gleske AK, Gotz F, Sahl HG, Kappler A, Peschel A. Proton-binding capacity of Staphylococcus aureus wall teichoic acid and its role in controlling autolysin activity. PLoS One. 2012;7:e41415. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0041415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Schlag M, Biswas R, Krismer B, Kohler T, Zoll S, Yu W, Schwarz H, Peschel A, Gotz F. Role of staphylococcal wall teichoic acid in targeting the major autolysin Atl. Mol Microbiol. 2010;75:864–873. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2009.07007.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


