Abstract
Within the last years, the use of stem cells (embryonic, induced pluripotent stem cells, or hematopoietic stem cells), Progenitor cells (e.g., endothelial progenitor cells), and most intensely mesenchymal stromal cells (MSC) has emerged as a promising cell-based therapy for several diseases including nephropathy. For patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD), dialysis or finally organ transplantation are the only therapeutic modalities available. Since ESRD is associated with a high healthcare expenditure, MSC therapy represents an innovative approach. In a variety of preclinical and clinical studies, MSC have shown to exert renoprotective properties, mediated mainly by paracrine effects, immunomodulation, regulation of inflammation, secretion of several trophic factors, and possibly differentiation to renal precursors. However, studies are highly diverse; thus, knowledge is still limited regarding the exact mode of action, source of MSC in comparison to other stem cell types, administration route and dose, tracking of cells and documentation of therapeutic efficacy by new imaging techniques and tissue visualization. The aim of this review is to provide a summary of published studies of stem cell therapy in acute and chronic kidney injury, diabetic nephropathy, polycystic kidney disease, and kidney transplantation. Preclinical studies with allogeneic or xenogeneic cell therapy were first addressed, followed by a summary of clinical trials carried out with autologous or allogeneic hMSC. Studies were analyzed with respect to source of cell type, mechanism of action etc.
Keywords: mesenchymal stromal cells, MSC therapy, renal injury, acute kidney injury, chronic kidney injury, diabetic nephropathy, polycystic kidney disease, kidney transplantation
Introduction
Renal failure is the impaired kidney function, which may lead to a systemic homeostasis disruption. Evidences show that kidney is a target organ of several diseases (hypertension, anemia, dyslipidemia, etc.), and when its physiology is compromised, it might initiate or exacerbate other pathophysiological conditions such as cardiovascular disease (1). Chronic kidney injury (CKI) is a long-term disease characterized by a decrease of glomerular filtration rate and an increase of albuminuria. CKI is associated with a higher risk of cardiovascular morbility, poor life quality, and early death, positioning CKI as health burden worldwide (2). CKI is frequently asymptomatic, and the ESRD requires dialysis or kidney transplantation (KTx), which is highly expensive for health care systems (3). In this field, cellular therapy with stem or stromal cells could potentially contribute to a better outcome of nephropathy.
Embryonic stem cells (ESC) are pluripotent cells with unlimited proliferative lifespan, derived from the inner mass of blastocysts (4). Their differentiation potential toward all cell lineages makes them highly attractive for cell-therapy approaches. However, despite the wide use of ESC in experimental settings, its clinical use is a matter of debate. As an alternative, induced-pluripotent stem cells (iPSC) were developed as differentiated cells genetically reprogrammed to induce ESC-like state, but these cells exhibit high risk of develop tumorigenicity (5, 6).
Multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells (MSC) are mesoderm derived, fibroblast-like and shuttle-shape cells under in vitro conditions (7). MSC can be isolated from a variety of adult or fetal sources like bone marrow, adipose tissue (ASC), periosteum, synovium, dental pulp, fetal tissues, umbilical cord tissue (UC), umbilical cord blood (UCB), placenta, and amniotic fluids (8, 9). Based on the MSC differentiation potential, stromal support, immunomodulatory properties and secretion of trophic factors, MSC are currently exploited in a variety of clinical settings (10) for tissue regeneration, immunomodulation, or graft improvement. Nevertheless, some of the MSC properties could change over the expansion phase in vitro. For instance, when bone marrow-derived MSC (BM-MSC) are isolated from their native tissue to culture flasks, the cells change from mostly quiescent and rounded-, actively proliferating and spindle-, to senescent and larger flattened-shape. Process, that is associated to loss of multipotency and also to DNA damage response activation (11). However, it has also been reported genetic instability in early passages, probably because of the initial adaptation of cells from their native niche to culture conditions (12). This creates a concern about a potential tumorigenic effect after MSC implantation.
The first cue of using MSC in regenerative medicine arose when Friedenstein et al. demonstrated the osteogenic potential of soft connective tissue bone marrow (BM)-derived stromal cells to form fibroblastic colonies in vitro (13–15). Heterogeneity and discordances in terminology and criteria for stromal/stem cells also spread with the increase of research in the field. Therefore, the International Society for Cellular Therapy remarked the appropriate designation as “multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells” (16).
The minimal criteria to define the human derived-MSC (hMSC) are: (1) Plastic-adherence under standard culture conditions, (2) More than 95% of the cells population must be positive for those antigens absent in most of hematopoietic cells such as CD105, CD73, and CD90. Moreover, up to 2% of the population can express CD45 (leucocytes), CD34 (hematopoietic progenitor), CD14 or CD11b (monocytes and macrophages), CD79α or CD19 (B cells), and HLA-DR (antigen presenting cell and lymphocytes), and (3) Differentiation potential to adipocytes, chondrocytes, and osteoblasts (17).
After their systemic administration, MSC move to inflammation sites, injury, and tumors to mediate healing (18). However, it also known that after intravenous delivery (IV), most of the MSC can be trapped mainly in the lungs, spleen, and liver (19–22). This diminishes the number of cells capable of homing and engrafting in the target organ. Therefore, proper imaging techniques to track and detect the specific MSC location in tissues could help to the further understanding of homing. There are several studies assessing the therapeutic potential of MSC in kidney disorders including CKI, focal segmental glomerular sclerosis, diabetic nephropathy (DN), autoimmune disease, and KTx (9). The rationale of MSC application is to cure or limit kidney diseases by the trophic factors that decrease fibrosis, promote angiogenesis, inhibit apoptosis, attenuate adverse inflammatory events by their immunomodulatory potential, and contribute to renal tissue regeneration (18, 23, 24). MSC immunomodulation generates an immunotolerant environment and reduces immune response of effector cells as monocytes/macrophages, dendritic cells, T or B cells (25–28). Paracrine effects mediated by extracellular vesicles (EVs) and exosomes further contribute to improve kidney function (23, 24).
The aim of this review is to present the results of a systematic search and analysis of the literature concerning the use of stem and stromal cells in different kidney diseases, focusing on preclinical models such as cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury (AKI), AKI induced by ischemia/reperfusion (AKI I/R), CKI, polycystic kidney disease (PKD), DN and KTx.
As MSC are the most intensely studied cell type, the review will (1) summarize relevant MSC mechanisms of action, (2) sum up imaging modalities to track stem cells and to monitor therapeutic effects in the kidney, (3) introduce the applied search strategy, and (4) present the state of the art on MSCs therapy in the treatment of the aforementioned kidney diseases (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
Graphical abstract.
MSC therapy in the treatment of kidney diseases: search strategy
Search methods for identification of studies
We searched for all studies (up to August 2017) in which animal models and clinical trials of the aforementioned diseases were treated with stem cells (Table 1). No cell type was excluded from the search. Studies with both allogeneic and xenogeneic stem cell therapy were included. For the search, the following databases were used: PubMed, Web of Science Core Collection, Cochrane Library, CINAHL, Clinical Trial Gov, and WHO ICTRP.
Table 1.
Search strategy used in the systematic reference research.
| Disease | Relevant terms |
|---|---|
| AKI induced by chemotherapy | 1: Stem cells AND |
| 2: Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) AND | |
| 3: Cisplatin | |
| AKI induced by ischemia/reperfusion | 1: Stem cells AND |
| 2: Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) AND | |
| 3: reperfusion Injury | |
| Diabetic nephropathy | 1: Stem cells AND |
| 2: Diabetic Nephropathy | |
| Polycystic kidney disease | 1: Stem cells AND |
| 2: Polycystic Kidney Disease | |
| Kidney transplantation | 1: Stem cells AND |
| 2: Kidney transplantation |
Selection and description of studies
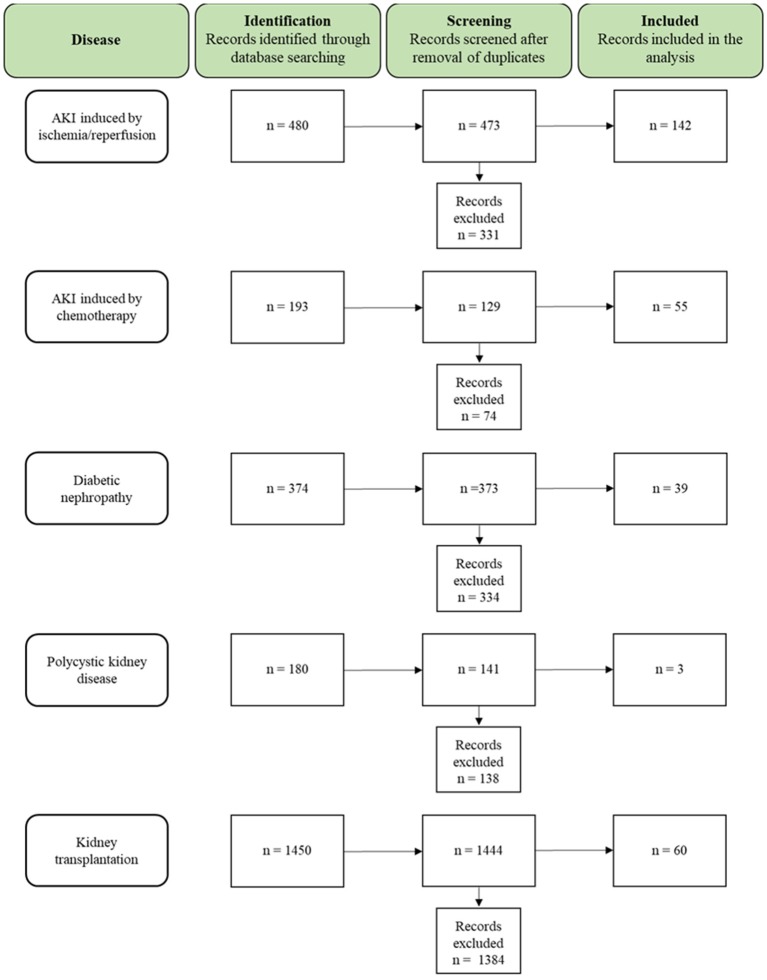
A total of 2,677 studies (AKI I/R n = 480; cisplatin induced AKI n = 193; DN n = 374; PKD n = 180; KTx n = 1450) were found through electronic searches by using the search terms (Figure 2).
Figure 2.
Flow chart summarizing the search strategy and the number of studies finally included or excluded from the analysis.
As mentioned before, the aim of this review is to give an overview of the preclinical studies and clinical trials of the aforementioned kidney diseases performed so far in the stem cell therapy field.
According to this, the inclusion criteria were:
- preclinical studies with allogeneic and xenogeneic stem cells
- clinical trials with autologous and allogeneic stem cells
All the studies were reviewed in detail and, according to the inclusion criteria, 299 studies (AKI I/R n = 142; cisplatin induced AKI n = 55; DN n = 39; PKD n = 3; KTx n = 60) were identified as relevant for the study, while 2,378 studies (AKI I/R n = 331; cisplatin induced AKI n = 74; DN n = 334; PKD n = 138; KTx n = 1384) were excluded from the analysis.
MSC modes of action
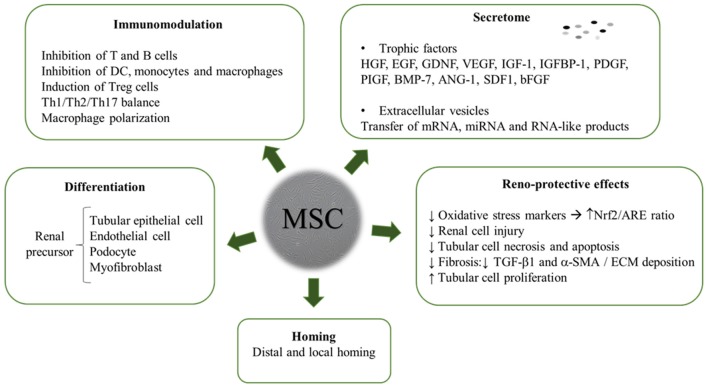
The review yielded a high number of publications, which document therapeutic efficacy of stem cell-based therapies in kidney injury. MSC mainly exert their kidney renoprotection effects through paracrine and endocrine modes of action, that include immunomodulatory, anti-inflammatory, mitogenic, anti-apoptotic, anti-oxidative stress, anti-fibrotic, and angiogenic influences (Figure 3) (29–32).
Figure 3.
MSC modes of action in kidney environment.
MSC immunomodulation
Immunomodulation emerges as key feature of MSC and refers not only to therapeutic mechanisms but also to their application as allogeneic cells. Despite expression of HLA/MHC class I and inducible expression of HLA/MHC class II, MSC present a hypo-immunogenic profile and appear to be transplantable across allogeneic/xenogeneic barriers (33). Conversely, in some studies with immunocompetent models administered with xenogeneic MSC, both humoral and cellular responses take place (34). Other allogeneic MSC animal studies suggest that a weak allogeneic immune response may be elicited (35).
Several studies claimed the lack of immune system activation after allogeneic/xenogeneic MSC administration (36). Also Le Blanc et al. suggest in vitro MSC immunosuppressive properties, but only a low number of studies support the translation in an in vivo setting (37).
On the other hand, both cellular and humoral immune responses took place in vivo after allogeneic MSC infusion, translating into a decreased engraftment (38, 39). In a study they speculate that MSC are rejected and this is a way to activate a regulatory immune response (40). Shuh et al. showed that alloantibodies were formed upon intravenous injection of allo-MSCs in rats, which facilitated complement-mediated lysis (41). Conversely, at least in the setting of graft-vs.-host-disease, immune-mediated killing of MSC was required to exert the therapeutic benefit (40).
Consequently, there is a need for further understanding on allogeneic/xenogeneic MSC infusion in the context of kidney injuries due to no consistent results and great discordances in both in vivo and in vitro settings. Some of the aspects to take into account when considering MSC treatment are MSC number of administrations, specific dosage, and interaction with immune suppression. Timing of MSC treatment is also of extreme importance given the interaction with the graft microenvironment (42). As this is a heavily debated feature, this review will specifically dissect studies using stem cell transplantation in allogeneic and xenogeneic settings.
Besides escaping immune recognition, MSC can act as immunomodulators by inhibiting lymphocyte activation and proliferation (43). MSC act on all cell types of the immune system: functional capacities of activated T cells are suppressed and a regulatory T cell (Treg) phenotype induced, monocytes are polarized to the anti-inflammatory M2 phenotype, dendritic cells maturation is impaired, likewise B and NK cell functions (44). It has been shown that M2 macrophages secrete a number of factors that mediate wound healing, sustain angiogenesis, extracellular matrix (ECM) deposition, and tissue remodeling (45).
In the setting of kidney transplantation there are several underlying mechanisms critically involved in the MSC-induced graft protection. MSC indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) secretion and Treg generation seem to prevent acute allograft rejection and induce renal allograft tolerance (46). These general features observed were also corroborated in murine animal models of kidney injury. For instance, MSC injected into the renal artery soon after reperfusion were able to sustain expression of the scatter factor system (i.e., hepatocyte growth factor, HGF) and modify cytokine network to a tolerogenic setting. MSC injection reduced IFNγ and IL-6 levels in serum, while increasing IL-10 anti-inflammatory cytokine suggesting that MSC reset the balance between T helper 1 and 2. Furthermore, MSC infusion induce Treg, which significantly prolong graft survival by Treg-dependent mechanisms and suppress the receptor tyrosine kinase in monocyte/macrophage cells, thus preventing monocyte infiltration and acute rejection. As a whole, these data suggest that MSC prevent rejection due to a shift of T cells toward an immune suppressive phenotype and the recruitment of the scatter factor system (47).
MSC secretome and extracellular vesicles
In the large variety of disease entities where MSC have been investigated, it became clear that the main mechanism of action does not involve homing and engraftment of infused cells, but rather their trophic activities which motivated Caplan to call these cells “medicinal signaling cells” (48). A number of proteins such as enzymes, cytokines and growth factors, are secreted by MSC, including also EVs, microvesicles (MVs) or exosomes. These data raise the speculation of not using MSC for injection, but rather to use their conditioned media (CM) or even EVs as drugs (see below) (49). There are multiple factors that mediate paracrine effects and confer renoprotection acting on inflammation, apoptosis and oxidative stress, such as nitric oxide, IDO, TGF-α, TGF-β, prostaglandin E2, HGF, IL-6, IL-10, VEGF, bFGF. In several studies it is claimed that the expression of proinflammatory cytokines IL1β, TNFα, IFN-γ were reduced and anti-inflammatory TGF-α, bFGF, and Bcl-2 were highly upregulated in MSC treated kidneys (50–54).
Recently, studies with EVs (MVs and exosomes) suggest their mediation to restore ATP supply by mitochondria transfer to damaged cells. In fact, Bi et al. observed that MSC derived CM not only increased tubular cell survival due to an induced proliferation and migration of kidney-derived epithelial cells in vitro but also limited renal injury in vivo (55). EVs are known to transfer mRNA, miRNA, proteins and organelles that might promote important phenotypic changes. In a glycerol-induced AKI mouse model, BM-MVs effects were assessed. The authors speculate that the MVs mRNA secretion are the final effectors of these effects. In in vivo settings, EVs were seen to accelerate the recovery of the injury of mice, demonstrating that treatment with MVs have an equal efficacy than MSC on their functional and morphological recovery (56–58).
The first requirement for in vitro biological effects of EVs is the entrance into target cells. MSC-EVs possess several adhesion molecules that are typically expressed by the MSC they are originated from (α-1, α-4, and α-5 integrins and CD44). CD44 and α-1 integrin are involved in the EV internalization within renal tubular epithelial. In vivo evidences confirm the requirement of mechanisms for organ targeting and cell uptake to achieve EV regenerative effects. Multiple studies identified the transfer of extracellular RNA as the main molecular mechanisms for EV therapeutic effects. In this context, there is both in vitro and in vivo evidence of a transfer of specific mRNA and subsequent translation into proteins in renal tubular cells. Moreover, in vitro studies indicate that MSC-EVs mediated transfer of insulin growth factor 1 (IGF-1) receptor mRNA to renal tubular cells increased cell proliferation (59, 60).
So far, two studies regarding application of MSC-EVs to patients have been published. Nassar et al. investigated the therapeutic impact of MSC-EVs in patients with CKI and not only saw significant improvements of the kidney function but TGF-β and IL-10 levels were also broadly increased (61). In addition, Kordelas et al. administered MSC-EVs in an allogeneic setting, in which EV treatment favored the status of the patients immune cells (62).
Renoprotective modes of action
Kidney fibrosis is a deposition of ECM in the renal parenchyma that leads to ESRD. ECM is normally degraded by matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) but a disadjustment in the equilibrium between MMPs and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMPs), causes an accumulation of ECM and an inhibition of degradation and matrix restoration. MSC seem to have a repressive effect on the expression of TIMPs, which would lead to the resolution of fibrosis. (63–67).
Oxidative stress is produced due to an imbalance between the production of free radicals in the mitochondrial electron transport chain, and reduced anti-oxidant defenses (68). Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are also accumulated, which lead to an upregulation of TGFβ1 and ECM proteins in glomerular mesangial cells expression, triggering mesangial expansion (69). MSC may have an antioxidative effect, thus leading to a reduction of organ oxidative damage (70). MSC avert ROS accumulation due to antioxidant upregulation and scavenging, mediated by soluble factor secretion. MSC secretion of exosomes takes part in inhibiting ROS metabolism key enzyme depletion, consequently decreasing oxidative stress injury (68, 69).
MSC role in angiogenesis and vascular remodeling may comprise upregulation of pro-angiogenic and pro-survival factors. Among these, VEGF-a, IGF-1, and HGF, but also EVs may be involved (71, 72). MSC secretion of VEGF, HGF, IGF-1 together with TGF-β, stanniocalcin-1, GM-CSF, and FGF-2 seem to be involved in exerting anti-apoptotic effects (73). In MSC treated AKI mouse models, a decrease in pro-apoptotic (Bcl-xs) and an increase in anti-apoptotic molecules (Bcl-2 and Bcl-xl) have been reported (74). Anti/pro-apoptotic ratio balance is required for an enhanced renal recovery (75).
In some models of kidney disease, e.g., cisplatin-induced AKI, apoptosis of tubular cells is a key pathomechanism. MSC have been shown to provide anti-apoptotic, pro-regenerative cues, e.g., by inducing pro-regenerative/anti-apoptotic gene expression, or by transferring mRNA/miRNA to injured cells (70, 76).
Homing and hemocompatibility
It is a matter of intense debate whether migration of the cells to the injured sites is necessary to exert their therapeutic actions. In diverse kidney disease models such as AKI I/R (77, 78), cisplatin-induced AKI (79, 80), KTx (81), CKI (82), atherosclerotic renal artery stenosis (83), and DN (84) no significant evidence of cell migration to the kidney was found despite a therapeutic effect was observed. Cells show preferential accumulation in lungs, suggesting capillary engraftment and degradation thereafter (85, 86). Moreover, in an AKI I/R model, cells were no longer observed 7 days after their administration, indicating that they were cleared without any engraftment (87). Contrarily, the use of hiPSC in cisplatin induced-AKI showed extensive engraftment into the kidney that led to restoration of renal function and structure (88). Additionally, in a rat model of steptozotocin (STZ)–induced diabetes, IV injected MSC were detected in the kidney, accompanied by a reduced expression of IL-1β, IL-6, and TNFα (89). Reasons for these discrepant data might be the wide variation of MSC type used, the different administration routes, the lack of consensus on most suitable doses, the broad tracking techniques available, and of course, the use of different disease models. This indicates that more sophisticated methods are required for cell tracking (see below), or that systematic searches as provided herein, identify aspects for harmonization/standardization.
When cells are systemically administered through i.v. injection most MSC tend to accumulate in lung, spleen or liver (filtering organs) (90). Most cells infused i.v. were found to get trapped in the lung as microemboli, being potentially dangerous (91–93). It has been suggested that MSC systemical administration home to organs such as the spleen, providing additional benefits, such as a reduction of infiltrating inflammatory cells (94). MSC local infusion to the injured sites will not only deliver a higher amount of MSC to the kidney, but has also suggested MSC role in enhancing proliferation of endogenous kidney stem cells (95, 96). Nonetheless, direct intra-arterial MSC infusion has been reported to favor obstruction of the capillaries, such as microvascular occlusions (97, 98). MSC direct injection does not appear to be more beneficial compared to their systemic infusion. Further studies should be carried out, focusing on the differences regarding routes of administration considering long-term safety.
Some recent studies addressed MSC effects on hemocompatibility/thrombosis/instant blood mediated reaction and indicate that MSCs expressing tissue factor can induce thrombosis and instant blood mediated reactions. Oeller et al. suggest that selecting tissue-factor deficient or low expressing cells may improve therapeutic outcomes (99). With respect to this, clinical trial protocols have already been modified to add anti-thrombotics such as heparin or hirudin (100–103).
Our own data suggest, that MSCs do not induce platelet activation and thereby thrombus formation, but rather actively inhibit platelet activation by a CD73 activity generating anti-thrombotic adenosine (Netsch et al., submitted).
Differentiation
Another interesting subject regarding MSC therapy is whether they have the potential, once into the injured sites, to differentiate beyond the osteo-, chondro-, and adipogenic lineage. Most of the data available in this regard comes from in vitro studies being in vivo reports still scarce (104–106). Nevertheless, some studies have demonstrated a successful differentiation of MSC into kidney cells. Immunohistochemical and laser-scanning microscopy analyses revealed that BM-MSC from syngeneic GFP transgenic donors are able to differentiate into glomerular mesangial cells in C57BL/6 mice (107). Additionally, in a mouse model of AKI I/R, hASC have shown differentiation capability to renal tubular epithelial cells at early stages of injury (108). Conversely, Tögel et al. using the same model in rats, demonstrate that MSC injected via carotid artery did not differentiate toward tubular or endothelial cells, but still a therapeutic effect was found (74).
The highly contradictory data based on different models indicate that further investigation is needed to better elucidate if local communication with injured cells is required or whether the therapeutic effects observed are the result of trophic actions of MSC. Furthermore, our current understanding of cell behavior in vivo might be compromised due to limitations of imaging techniques. Therefore, improvement of existing and establishment of novel tracking and visualizing techniques is greatly needed.
MSC tracking and imaging
A central question for MSC-based therapies is: where do cells go after their transplantation? One of the limiting factors of MSC transplantation is their interaction with the microenvironment (109). Therefore, it is essential to provide information about stem cells homing, motility, migration, and allocation (110). Accordingly, the use of the microscopy for both localization and quantification of stem cells within target tissues has increased and different methodologies have been developed (111).
For MSC tracking, direct labeling of viable cells with either contrast agents (super paramagnetic iron oxide SPIO, Gd, FLI) or fluorescent dyes have been used. However, the most pronounced disadvantage of direct labeling is the decrease in signal strength as the marker decays due to cellular division. Consequently, several indirect labeling techniques, that use genetic modification of cell-reporter genes, have been developed. Green fluorescent protein-based tags (GFP, S65T, EGFP, CFP, YFP) are mostly used (112–116). The indirect labeling is more sensitive but it requires genetic engineering tools that may compromise cellular function (117).
Depending on the sample to visualize, the correct choice of microscopy is utterly important (Table 2). Optical Imaging (OI) refers to those methods that use light in the ultraviolet/near-infrared range to investigate tissues and cellular and molecular structures in living organisms (128). Fluorescence, confocal, light-sheet microscopy, and bioluminescence imaging have been used (119–127, 129). Alternatively, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is vastly used and the resulting image is dependent on the type of contrast medium (110). Over the last thirty years, live cell imaging significantly improved with the development of incubation chambers, making it possible to analyze biological events in real time (130–132). In toto imaging is now commonly used to image and track cell movements and divisions (133).
Table 2.
Description of the most commonly used microscopy for imaging.
| BrightField | Principle | Advantages | Drawbacks | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WIDEFIELD MICROSCOPY | ||||
| Sample directly hit by the white light | Easy to use | Resolution around 200 nm | (118) | |
| OPTICAL IMAGING | ||||
| Fluorescence Microscopy | Sample is illuminated by ultra-violet light to excite the fluorescent dye within the sample; Separation of emitted light from the excitation light (bright), by specific filters |
Possibility to perform experiments under physiological conditions, making unnecessary chemical fixation and, therefore, minimizing artifacts | Risk of photobleaching and quenching related to the exposure time | (119, 120) |
| Bioluminescence Imaging | Detection of light emitted from cells, in which enzymes generating light are expressed, by genetic engineering. These enzymes belong to the luciferase group | High sensitivity; Cost- effectiveness; High reproducibility; Non-invasive |
Use of genetic engineering tools (luc/neo-MSC); Low resolution; Low penetration depth; Low quantification accuracy; High light scattering |
(121, 122) |
| Confocal Microscopy | Each spot scanned by the laser, back-and-forth | Imaging completed pixel by pixel; Use of the pinhole; Final image as an ensemble of layers, much detailed; Non invasive |
Expensive; High sensitivity; Trained operators required |
(119, 123, 124) |
| Two-Photon Microscopy | Use of two low-energy photons, usually from the same laser, cooperating to cause a higher-energy electronic transition in a fluorescent molecule (usually near-infrared light is used) | High resolution; Minimized scattering light; Increased penetration depth; Reduced photobleaching Reduced Background strongly; Increased total signal-to-noise ratio |
Low penetration depth; Poor possibility of longitudinal studies |
(125, 126) |
| LightSheet Microscopy | Use of a thin plane of light, instead of a point | Very fast imaging speed; Very high resolution; Very high penetration depth (>1 cm); Reduced photobleaching; Reduced phototoxicity |
Dual side illumination not easy to be perfectly aligned in the three-dimensional space, causing a less sample focus, compared to the single side illumination | (127) |
| MRI | Principle | Advantages | Drawbacks | References |
| MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING | ||||
| Alignment of the magnetic moment from endogenous molecules (1H and 19F) into an external magnetic field | High resolution; High sensitivity of cell detection; High penetration depth; |
Low possibility of longitudinal studies; High costs; Presence of external metal disturb the analysis |
(110) | |
In the kidney setting, various different labels and visualization techniques have been applied (Table 3).
Table 3.
MSC studies using different labels and visualizing techniques.
| Cell type | WJ-MSC | ASCs | hMSC-EV | BM-hMSC | hMSC; hESC | MSC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Label | MPNPs | TMADM-03 | DiD | DiD | DiD, ICG | luc/neo-MSC |
| Species | NK | Mouse | Mouse | Rat | NK | Mouse |
| Administration route | NK | SC | IV | IP | NK | IA |
| Target organ | NK | Skin, kidney | Kidney | Arthritic joints | NK | Kidney |
| Technique | Fluorescent Microscopy | MRI | OI | OI | OI | Bioluminescence imaging |
| Reference | (109) | (134) | (135) | (136) | (137) | (138) |
- Magnetic polymeric nanoparticles to label MSC, for visualizing them by fluorescence microscopy (109).
- MRI visualization in a mouse model with ASC labeled with TMADM-03 (trimethylamino dextran-coated magnetic iron oxide nanoparticle 03) (134).
- Bioluminescence imaging as sensitive and specific in vivo cell tracking of luciferase/neomycin phosphotransferase-marked MSC (luc/neo-MSC) (138).
- Labeling of hMSC-EVs with 1,1-Dioctadecyl-3,3,3,3-tetramethylindodicarbocyanine (DiD) visualized by OI to assess biodistribution and renal localization (135). DiD and OI visualization has also been used in other studies (136, 137).
Optical tissue clearing
Bioimaging techniques have been optimized in the past with the aim to enhance imaging resolution to the subcellular level and to use them for in vivo studies. The high scattering of turbid biological tissues limits the penetration of light, light scatters, as a result of mismatch of the different refractive indexes (RIs) the image blurs and contrast decreases (139). In order to overcome this limitation, optical tissue clearing (OTC) has been introduced already in 1911 (140). Substances used within OTC can reduce the scattering of tissues and make them transparent by reducing and/or removing the main sources of scattering light (e.g., lipids from the membrane bilayer) without compromising the structure integrity. Some examples for clearing procedures are: BABB (benzyl alcohol-benzyl benzoate) (141), CLARITY (clear lipid-exchanged acrylamide-hybridized rigid imaging/immunostaining/in situ-hybridization-compatible tissue hydrogel) (142–144), PACT (passive CLARITY technique) (145), SeeDB (See Deep Brain) (146) and, recently, an Ethyl Cinnamate protocol was published (147).
Each type of tissue clearing includes four main technical steps: (1) initial treatment to eliminate pigment molecules, which may absorb tissue autofluorescence and affect the results of clearing, (2) permeabilization to assist the appropriate diffusion of the clearing solution throughout a tissue specimen (mostly using Triton X-100, other detergents or DMSO, (3) immunolabeling with different fluorescent probes specifically or unspecifically labeling target proteins, and (4) refractive matching clearing. Typical OTC substances have high refractive indices and when they permeate into the tissue replace intersticial fluid or cytoplasm, which have a lower refractive index than the surrounding tissue. By this, differences in refractive indices are reduced and light can penetrate deeper. By combining the OTC with a suitable microscopy, significant improvements in 3D tissue visualization were achieved.
It is beyond the scope of this review to summarize the major achievements in OTC, which have been already reviewed (148, 149). Here we aim to highlight the recent developments for 3D whole organ imaging which is key for monitoring stem cell/tissue interaction. By choosing the optimal clearing technique and microscopy, it is possible to visualize, track and trace, and quantify stem cells within the whole organ in 3D.
MSC therapy in the treatment of kidney diseases: state of the art
The data from the systematic reference search were stratified first according to the different disease entities, where we will briefly introduce the respective models (Figure 4). Second, the most relevant preclinical studies with allogeneic or xenogeneic (Tables 4a–c) cell therapy were analyzed and discussed in order to give an overview of the mechanisms of action mainly involved in the renoprotective activity of MSC. Lastly, a summary of the clinical trials carried out with the use of autologous or allogeneic hMSC is provided (Table 5).
Figure 4.
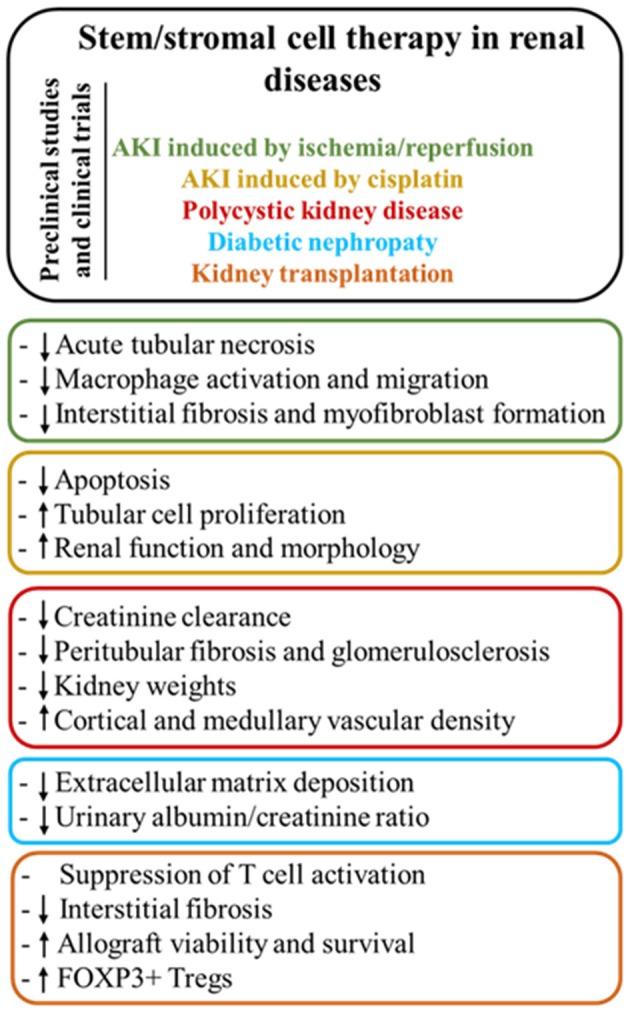
Main modes of action of stem/stromal cell therapy according to the different renal diseases.
Table 4a.
Xenogeneic MSC therapy in AKI I/R preclinical studies.
| Model | Animal/Strain | Treatment | Dose | Adm.route | Outcome | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AKI I/R | Rat SD |
hASCs | 2 × 106 in 500 μl EBM-2/1% BSA | IA (abdominal aorta) | ↓SCr, tubular damage ↓T cell infiltration in kidneys ↑Tregs |
(150) |
| AKI I/R | Rat Wistar |
hUC-MSCs hASCs |
1 x 106cells in 2 mL saline | IP | UC-MSCs more prominent renal function protection compared to ASCs treated. Amelioration of long-term renal function. ↓β-galactosidase and ↑ Klotho compared to ASCs |
(151) |
| AKI I/R | Rat SD |
hSVF hASCs |
2 x 106cells in 100 μl PBS | IR | ↑Cell proliferation ↓Apoptosis, IL-10, TNF-α |
(152) |
| AKI I/R | Mouse C57BL/6 |
hASCs | IV (tail vein) | ↑ Proliferation, tubular sox9 by release of exosomes ↓TGF-β1 |
(153) | |
| AKI I/R | Rat Wistar |
VEGF-hAFSCs | 1 x 106cells or 5 x 105cells | IA (aorta) | Treatment with higher dose: ↑ SCr, BUN, Acute tubular necrosis, hyaline cast formation. Treatment with lower dose: ↑ Proliferation, FOXP3+ cells. |
(154) |
| AKI I/R | Rat Wistar |
hUCB-MSC | 1 x 106cells | IV (tail vein) | ↓ SCr, BUN, oxidative stress. | (155) |
| AKI I/R | Mouse SCID |
h Gl-MSC hGl-MSC-EVs Progenitor cells from cortical tissue T-CD133+ cells T-CD133+ cells EVs |
1 x 105cells 400–480 x 106Evs |
IV (tail vein) | hGl-MS-EVs: more efficiently improved renal function compared to T-CD133+ EVs. hGl-MSCs: ↑ proliferation of tubular cells. RNAse treated EVs: ineffective |
(156) |
| AKI I/R | Mouse C57 BL/6 |
hERCs | 1 x 106cells | IV (tail vein) | ↓ SCr, BUN, TNF-α, IL-6, IFNγ, splenic and renal CD4+, CD8+ T cells. ↑CD4+, CD25+ Tregs and M2 macrophages |
(157) |
| AKI I/R | Mouse FVB |
Micro RNA-486-5p from hECFCs-derived exosomes | 20 μg | IV (yugular vein) | ↓SCr, BUN ↓Apoptosis ↓Neutrophil infiltration |
(158) |
| AKI I/R | Rat | hWJ-MSC-EVs | 100 μg EVs | IV (cava caudalis) | ↓Apoptosis, sNgal ↑Nrf2/ARE, HO-1 |
(159) |
| AKI I/R | Rat | hUC-MSC | 100 μg | IV (caudal vein) | ↓Apoptosis ↑VEGF ↓HIF-1α |
(160) |
| AKI I/R | Rat Sprague-Dawley |
hWJ-MSC-EVs | 100 μg | IV (caudal vein) | ↓Cell apoptosis ↓Expression of miRNA-30 |
(161) |
| AKI I/R | Mouse NOD.CB1-Prkdc scid/J |
hUC-MSC and hUC-MSC-EVs | 1 x 106in 100 μl PBS | IV (yugular vein) | ↓ SCr, tubular necrosis, oxidative stress, apoptosis. No cell persistence in kidneys. |
(30) |
| AKI I/R | Rat SD |
hUC-MSC-MVs | 30 μg | IV (cava caudalis) | ↓Collagen deposition, proliferation tubular cells. ↑HGF mRNA expression. TGF-β1, IGF-1 and EGF not affected. mRNAse treatment abolishes renoprotective effect |
(162) |
| AKI I/R | Mouse C57BL/6 |
hWJ-EPCs | 5 x 105cells | IR (subcapsular space) | Cells found in cortex at 1–2 days post AKI and in medulla and cortex 7 days post AKI. ↓ SCr, tubular necrosis and dilation ↑Microvascular density |
(163) |
| AKI I/R | Rat Wistar |
hAFSCs with renal progenitor phenotype | 1 x 106 cells in 800 μl fresh expansion media | IA (intra aorta, directed to kidney by subsequent clamping) | ↓ SCr, tubular necrosis, cast formation, macrophage infiltration, myofibroblast formation, interstitial fibrosis | (164) |
| AKI I/R | Mouse NOD.CB1-Prkdc scid/J |
hiPSCs | 1.5 x 106cells | IR (subcapsular) | ↓ SCr, BUN, tubular necrosis, interstitial fibrosis | (165) |
| AKI I/R | Mouse C57BL/6 |
hSHEDs | 1 x 106cells in 10μl PBS | IR (subrenal capsule) | ↓ SCr, BUN, infiltration of macrophages and neutrophils, MIP-2, IL-1β, MCP1 | (166) |
| AKI I/R | Rat SD |
hASCs hypoxia preconditioned | 2 x 106cellsin 100μl saline | IR (renal cortex) | ↓ SCr, BUN, apoptosis, histological injury. ↑Vascularization In hypoxia preconditioned compared to non-hypoxia preconditioned |
(78) |
| AKI I/R | Mouse C57BL/6 |
hBM-MSC | 1 x 106 | IV | Homing to kidneys ↓SCr, BUN, KIM-1 M2 macrophage polarization |
(167) |
| AKI I/R | Rat SD |
hWJ-MSC-MVs | 100 μg MVs | IV (cava caudalis) | ↓Tubular necrosis, apoptosis, CD68+ macrophages, CX3CL1, α-SMA. ↑Cell proliferation, IL-10 |
(168) |
| AKI I/R | Mouse C57BL/6 |
hUCB-MSC | 1 x 106 before AKI | IP | ↓IFN⋎ ↑VEGF ↑%Tregs |
(169) |
| AKI I/R | Rat SD |
hWJ-MSC | 2 x 106 in 500 μl serum-free medium | IV | Shifting HGF/TGF-β1 to HGF Reduction in overall kidney fibrosis |
(170) |
| AKI I/R | Mouse C57BL/6 |
hUC-MSC | 2 x 106 24 h after AKI | IV (caudal vein) | ↓Apoptosis ↑M2 macrophages |
(171) |
| AKI I/R | Rat SD |
hUCB-MSC- EVs | EVs only EVs+IFN⋎ |
IA (carotid artery) | EVs only ↓serum creatinine, urea, cute tubular necrosis. EVs+ IFNγ No ameliorative effect |
(172) |
| AKI I/R | Mouse NOD.CB1-Prkdc scid/J and FVB/NJ |
hUCB-MSC CD133+ | 1 x 106cells in 100 μl saline | IV (jugular vein) | ↑ SCr and urea, k+ and PO4, tubular injury | (173) |
| AKI I/R | Rat Wistar |
EPC-MVs | 30 μg | IV | ↑Tubular cell proliferation ↓Apoptosis, leukocyte infiltration, interstitial fibrosis. Loss or renoprotective effect when treated with RNAse, Dicer knock-down or depletion of miRNA-126 and miRNA-296 |
(174) |
| AKI I/R | Rat SD |
hBM-MSC- MVs | 30 μg | IV | ↓ SCr, BUN in acute phase, apoptosis, kidney fibrosis. Treatment with RNAse abolish renoprotective effects |
(175) |
| AKI I/R | Rat Wild type |
hMSCs from fetal membranes | 1 x 106 in 150 μl PBS MSCs only or pre-treated with butyric acid |
IR | ↓ SCr, urea, IFNγ, IL-1β, IL-1α, IL-6. ↑VEGF |
(176) |
| AKI I/R | Rat | Hepatocyte growth factor modified hUC-MSCs | Not specified | IA (carotid artery) | ↓SCr, BUN ↓Hyperemia, tubular cast formation ↓Caspase-3 ↑Tubular cell proliferation |
(177) |
| AKI I/R | Rat SD |
hUCB-MSC | 1 x 106in 500 μl saline | IA (carotid artery) | No transdifferentiation into renal cells. ↓SCr, urea, caspase-3, IL-1β |
(178) |
Table 4c.
Xenogeneic MSC therapy in DN preclinical studies.
| Model | Animal/ Strain | Treatment | Dose | Adm. route | Outcome | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| STZ–T1D | Rat SD |
hUDSC-Exosomes | 100 μg exosomes | IV (tail vein) |
↓Mesangial expansion, ↓glomeruli hypertrophy ↓Casp-3, and, ↓U-ACR (↑BMP-7, ↑VEGF, ↑TGF-ß and ↑angiogenin related) |
(197) |
| STZ–T1D | Rat SD |
hUCB-MNCs | 0.5 x106 cells | IV (tail vein) |
↓ EMT markers (↓α-SMA and ↑ E-cadherin) ↓ Fractional mesangial area in glomeruli |
(198) |
| STZ–T1D | Rat Albino | hUCB-MNCs | 150 x 106 cells | IV (tail vein) | ↓ECM deposition (↓laminin expression) ↓U-ACR, ↓Arterial pressure |
(199) |
| STZ–T1D | Mouse NOD.CB17-Prkdcscid/J | hBM-MSC | 2.5 x 106 cells (twice) | IC | ↓Blood glucose ↓Macrophages infiltration, ↓Mesangial ECM deposition ↑Insulin Engraftment detected in pancreatic and renal histology |
(84) |
Table 5.
MSC clinical trials.
| Condition | ID | Title | Link | Status | Estimated Completion Date | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AKI induced by Chemotherapy | NCT01275612 | Ex-vivo expanded mesenchymal stem cells to repair the kidney and improve function in cisplatin-induced acute renal failure in patients with solid organ cancers | https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01275612 | Recruiting | March 2018 | (200) |
| T2D-DN | NCT01843387 | A Randomized, Controlled, Dose-Escalation Pilot Study to Assess the Safety and Efficacy of a Single Intravenous Infusion of Allogeneic Mesenchymal Precursor Cells (MPCs) in Subjects With Diabetic Nephropathy and Type 2 Diabetes | https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01843387 | Completed | September 2015 | (201) |
| DN | ChiCTR-ONC-17011065 | The Preliminary Clinical Trial of Treating Diabetic Nephropathy by hUCT-MSC | http://www.chictr.org.cn/showproj.aspx?proj=18779 | Not yet recruiting | June 2020 | (202) |
| DKD | NCT02585622 | Novel Stromal Cell Therapy for Diabetic Kidney Disease (NEPHSTROM Study) | https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02585622 | Not yet recruiting | December 2020 | (203) |
| ADPKD | NCT02166489 | Evaluation the Effect of Mesenchymal MSCs Transplantation in Patients With Chronic Renal Failure Due to Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease | https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02166489 | Completed | January 2016 | (204) |
| KTx | NCT02490020 | A Perspective Multicenter Controlled Study On Application Of Mesenchymal Stem Cell(MSC) To Prevent Rejection After Renal Transplantation By Donation After Cardiac Death | https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02490020 | Enrolling by invitation | December 2018 | (205) |
| KTx | NCT00497926 | Induction of Donor Specific Tolerance in Recipients of Living Kidney Allografts by Donor FCRx Infusion | https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00497926 | Active, not recruiting | March 2031 | (206) |
| KTx | ACTRN12615000678594 | Mesenchymal Stem Cells to prevent ischemia reperfusion injury in deceased donor renal transplant recipients | http://www.anzctr.org.au/ACTRN12615000678594.aspx | Recruiting | No info | (207) |
| KTx | NCT02409940 | A Randomized Trial to Elucidate Effect of Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Immune Modulation in Living Related Kidney Transplant Patients | https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02409940 | Active, not recruiting | March 2017 | (208) |
| KTx | NCT02561767 | The Efficacy and Safety of Bone Marrow-derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Kidney Transplantation From Chinese Donation After Citizen Death (DCD): A Multi-center Randomized Controlled Trial | https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02561767 | Unknown | October 2017 | (209) |
| KTx | NCT00183248 | Using Donor Stem Cells and Alemtuzumab to Prevent Organ Rejection in Kidney Transplant Patients | https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00183248 | Completed | November 2009 | (210) |
| KTx | NCT00734396 | Bone Marrow Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells for the Treatment of Allograft Rejection After Renal Transplantation | https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00734396 | Completed | December 2012 | (211) |
| KTx | NCT01649388 | Delayed Tolerance in Recipients of Living Kidney Allografts by Donor FCRx Infusion | https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01649388 | Active, not recruiting | December 2030 | (212) |
| KTx | NCT00658073 | Allogeneic Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cell Transplantation in Recipients of Living Kidney Allografts | https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00658073 | Completed | October 2010 | (213) |
| KTx | ChiCTR-ONC-11001873 | Effect of co-transplantation of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and renal transplantation in long-term outcome of allograft | http://www.chictr.org.cn/showproj.aspx?proj=7675 | No info | No info | (214) |
| KTx | EUCTR2011-001822-81-BE | Infusion of third-party mesenchymal stem cells after renal or liver transplantation: a phase I-II, open-label, clinical study | https://www.clinicaltrialsregister.eu/ctr-search/search?query=eudract_number:2011-001822-81 | Ongoing | No info | (215) |
| KTx | NCT00659620 | Mesenchymal Stem Cell Transplantation in the Treatment of Chronic Allograft Nephropathy | https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00659620 | Unknown | May 2010 | (216) |
| KTx | NCT00498160 | Induction of Donor Specific Tolerance in Recipients of Live Donor Kidney Allografts by Donor Stem Cell Infusion | https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00498160 | Active, not recruiting | December 2024 | (217) |
| KTx | CN-00448212 | Donor bone marrow derived stem cell infusion in thymus and periphery: an integrated approach to achieve tolerance in cadaver renal allograft recipient | http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/o/cochrane/clcentral/articles/212/CN-00448212/frame.html | Completed | (218) |
Table 4b.
Xenogeneic MSC therapy in Cisplatin-induced AKI preclinical studies.
| Model | Animal/Strain | Treatment | Dose | Adm. route | Outcome | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cisplatin-induced AKI | Rat NIH-Foxn1rn |
hKDCs | 106 cells in 500 μl PBS (twice) | IV (tail vein) |
↓FITC-sinistrin t1/2, sCr, serum urea, urinary albumin, tubular luminal area | (86) |
| Cisplatin-induced AKI | Mouse C57BL/6 |
hUCB-MSC | 106 cells. Early and late treatment |
IV (tail vein), IP |
Time-sensitive effect of MSCs. hUCB-MSCs early treatment: ↓BUN, apoptosis, tubular injury scores. ↑Treg. ↑anti-inflammatory and ↓pro-inflammatory cytokines Renoprotective effect addressed to immunomodulation activity. |
(31) |
| Cisplatin-induced AKI | Mouse BALB/cOlaHsd |
hUC-MSC+ATG pre-treatment |
5 x 105 cells |
IV | ↓BUN, sCr, kidney weight, in situ inflammation and oxidative stress | (179) |
| Cisplatin-induced AKI | Rat SD |
hASCs | 5 x 106 cells | IV (tail vein) |
↓BUN, sCr, oxidative stress, histological indices of injury in the renal cortex and outer medulla. | (180) |
| Cisplatin-induced AKI | Rat SD |
hASCs, hAFSCs | 5 x 106 cells | IV (tail vein) |
↓BUN, sCr, oxidative stress. ↑Regeneration and proliferation achieved with hAFSCs compared to hASCs. |
(181) |
| Cisplatin-induced AKI | Rat SD |
hAFSCs | 5 x 106 cells | IV (tail vein) |
↓BUN, sCr, oxidative stress, fibrosis. ↑Tissue regeneration. Renoprotective effect addressed to paracrine antioxidant activity. |
(182) |
| Cisplatin-induced AKI | Mouse BALB/c nude |
HIF-1α-hASCs | 105 cells per 200 μl | IV (tail vein) |
↓BUN, sCr, TNF-α, tubular damage score. ↑Antiapoptotic activity, HO-1 gene expression |
(183) |
| Cisplatin-induced AKI | Rat SD |
hASCs | 1–2 x 106 cells in 1 ml saline | IV (tail vein) |
↓BUN, sCr, apoptosis ↑Tubular cell proliferation |
(184) |
| Cisplatin-induced AKI | Mouse NOD-SCID |
RPC-hiPSCs | 5 x 105 cells |
IV (tail vein) |
↓ BUN, renal tubular damage. | (88) |
| Cisplatin-induced AKI | Mouse C3H |
hBM-MSC + pFUS pre-treatment | 106 cells |
IV (tail vein) |
↓BUN, sCr, mouse TNF-α, apoptosis, necrosis. ↑Human IL-10, mouse VEGF. M1 to M2 macrophage phenotype shift. pFUS improves MSCs homing to injured kidneys and increases the aforementioned outcome. |
(185) |
| Cisplatin-induced AKI | Rat SD |
hASCs, hAFSCs | 5 x 106 cells | IV (tail vein) |
↓sCr, tissue oxidative stress. ↑Tissue regeneration and proliferation. Renoprotective effect achieved by both cell types. An antioxidant activity is proposed. |
(186) |
| Cisplatin-induced AKI | Rat White albino |
hUCB-HSCs | 3 x 106 cells | IP | ↓BUN, sCr, TNF-α, HGF, IGF-1, VEGF, p53. | (187) |
| Cisplatin-induced AKI | Rat SD |
hUC-MSC | 2 x 106 Cells in 500 μl saline solution |
IV (tail vein) |
↓BUN, sCr, apoptosis, IL-1b, and TNF-α, inflammatory cell accumulation, kidney interstitial fibrosis. ↑Renal cell proliferation. Homing to the renal lesion site observed. EMT inhibition. |
(32) |
| Cisplatin-induced AKI | Mouse BALB/c nude | hUSSC | 105 cells in 500 μl PBS | IV (tail vein) |
No amelioration observed. No statistically significant changes in the levels of BUN, sCr, TGF-β 1, HGF, and IGF-1. Cell transplantation worsens the kidney architecture (↑ injury score) |
(188) |
| Cisplatin-induced AKI | Rat SD |
hUC-MSC-Exs, hUC-MSC- CM |
Exs: 200 μg. CM: not specified |
Renal capsule injection (both kidneys) | Exs: ↓Oxidative stress, tubuli apoptosis. ↑ Cell proliferation. No significant changes in the levels of BUN and sCr observed. CM: No notable changes observed. |
(189) |
| Cisplatin-induced AKI | Mouse C57BL6/J | hESC-MPs | 5 x 105 cells |
IV (tail vein) |
BUN, sCr, apoptosis, pro-inflammatory cytokines. ↑Anti-inflammatory cytokines, tubular cell proliferation. Cells engraftment in the kidney. |
(190) |
| Cisplatin-induced AKI | Rat SD |
hADSC, hASC-CM |
hASCs: 5 x 105 cells, hASC-CM: 4 ml |
hASCs: IV (tail vein), hASC-CM: IP |
hASCs and CM: ↓BUN, sCr, renal tissue injury, tubular apoptosis, TNF-α, NF-kB, COX2. ↑Animal survival. However, additional studies are needed to clarify if the protective effects of CM are equivalent to Ad-MSC treatment. |
(79) |
| Cisplatin-induced AKI | Rat SAS- SD |
hBM-MSC-CM | 1 ml | IV (penile vein) |
↓BUN, sCr, renal tissue injury, tubular apoptosis, IL-1β, TNFα, IL-6 and IL-1ra. ↑IL-10, animal survival |
(191) |
| Cisplatin-induced AKI | Mouse NOD-SCID |
hAFSCs | 5 x 105 cells |
IV | ↓BUN, sCr, renal tissue injury, apoptosis. ↑Animal survival. Cells engraftment in the peritubular region. Preconditioning with GDNF enhances the regenerative potential of hAFSCs. |
(192) |
| Cisplatin-induced AKI | Mouse SCID | hBM-MSC-MVs | Single dose: 10 μg. Multiple dose: 100 μg + 5 x 50 μg |
IV (tail vein) |
MVs single dose: ↓BUN, sCr. ↓↓Apoptosis. ↑Survival. MVs multiple doses: ↓↓BUN, sCr. ↓Apoptosis. ↑↑Survival. Kidney morphology restoration. |
(56) |
| Cisplatin-induced AKI | Mouse BALB/c |
hE-MSC, VEGF-hE-MSCs |
5 x 105 cells per 500 μl | IV (tail vein) |
VEGF-hE-MSC can strengthen the renoprotective effect of MSCs by antiapoptotic effect and proliferation on peritubular capillaries. | (193) |
| Cisplatin-induced AKI | Mouse BALB/c |
hUSSC-CM | No amelioration in terms of serum urea and creatinine, histopathologic examinations and physical activity score was found. | (194) | ||
| Cisplatin-induced AKI | Mouse NOD-SCID |
hUCB-MSC | 5 x 105 cells |
IV | ↓BUN, renal tubular damage, oxidative stress, apoptosis, inflammation. ↑Animal survival, tubular cell proliferation, serum HGF, kidney mRNA HGF |
(85) |
| Cisplatin-induced AKI | Mouse NOD-SCID |
hBM-MSC | 5 x 106 cells |
IP | ↓BUN, amylase, phosphorous, alanine aminotransferase, creatinine, cytokines/chemokines (MIP-2, G-CSF, KC, IL, MCP-1, PDGF, TNF-α, GM-CSF, IL-6). ↑Animal survival. |
(195) |
| Cisplatin-induced AKI | Mouse NOD-SCID |
hBM-MSC | 5 x 105 cells(500 μl) | IV (tail vein) |
↓BUN, sCr, renal tissue injury, tubular cell apoptosis, peritubular capillary changes. ↑Animal survival. |
(196) |
Acute and chronic kidney injury
AKI is a clinical syndrome characterized by rapid decline in glomerular filtration rate, resulting in retention of nitrogenous waste, mainly serum creatinine (sCr) and blood urea nitrogen (BUN) (219). It is a worldwide health concern with increasing prevalence each year affecting 45% of patients admitted to the ICU and 20% of hospitalized patients (220). AKI is associated with high morbidity and mortality due to the lack of powerful biomarkers for early detection and the limitation of fully successful therapeutic strategies (221).
In the past few years, it has been shown that patients surviving an episode of AKI have a higher risk of developing CKI. CKI leads to ESRD, where the only therapies available are dialysis or transplantation (222, 223). Both modalities have their limitations and disadvantages. While dialysis is associated with a high morbidity and mortality, patients in need for renal transplantation are mostly waiting for several years before a suitable renal allograft is available. In addition, allograft recipients also need life-long immune suppression, which increases the risk for general infections and cancer (224).
AKI induced by ischemia/reperfusion
I/R is the main cause of AKI. It is caused by a reduction of blood supply to the kidney followed by a restoration of perfusion. This decreased oxygenation produces depletion of ATP, metabolic impairment, apoptosis, production of ROS, and it is worsened during the reperfusion period, causing sterile inflammation, vasoconstriction and oxidative damage (225, 226). AKI I/R is often the result of arterial occlusion during surgery, congestive heart failure, or kidney transplantation (227). Animal models of AKI I/R have been extensively used in different species for decades. The most common procedure consists in clamping the renal artery and vein for a desired amount of time and then releasing the clamps allowing reperfusion (228).
Key to therapy is the optimal timing and dosage. Studies with BM-MSC agree that starting treatment 1 h after injury results in a better outcome, as cells are able to engraft to the kidney to a higher degree (229, 230). Interestingly, a report using human adipose stromal vascular fraction (SVF) before the induction of AKI I/R revealed an increased retention of cells in the kidney and enhanced tubular cell proliferation (152). Authors agree that the higher the dose, the worse the outcome, mostly due to cell emboli formation. The optimal cell concentration range found is 5 × 105 − 1 × 106 (164, 231).
AKI-I/R has a very complex pathophysiology in which several mechanisms are involved. One of the main events is apoptotic cell death of proximal tubular cells. These cells are particularly sensitive to hypoxia. An interesting study by Cantaluppi et al. demonstrated that endothelial progenitor cells (EPC)-derived MVs deliver miRNA to reprogram hypoxic proximal tubular cells into a regenerative phenotype (174). This anti-apoptotic effect mediated by miRNA transfer was also seen using hBM-MSC-MVs, in which the pre-treatment with RNAse abolished the aforementioned effect (175). Tubular cell proliferation after ischemia was also investigated in a study using hASC, in which an upregulation of SOX9 (tubular cell repair marker) was observed (153). Under physiological conditions, antioxidant enzymes present in the kidney are able to scavenge ROS. However, in AKI I/R these enzymes are overwhelmed by the massively increased production of ROS. BM-MSC are able to reduce oxidative stress by decreasing the amount of malondialdehyde, superoxide dismutase, and glutathione peroxidase in post ischemic kidney tissue (232). A similar effect was found using hUC-MSC (155). The underlying mechanism was further investigated in a study with human Wharton's jelly (WJ)-MSC-EVs in which they found that the antioxidant effect observed was the result of the Nrf2-ARE pathway activation, which regulates the expression of antioxidant proteins (159).
Another very important pathophysiological mechanism involved in AKI I/R is the so-called sterile inflammation. In this regard, ASC have shown to downregulate the expression of inflammatory cytokines and chemokines (IL-6, TNF-α, IL-1β, IFN⋎, CXCL2) and upregulate the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 (233, 234). Macrophage number and migration was reduced in a study using iPSC and hWJ-MSC-EVs where the effect was observed in terms of downregulation of MCP-1 and CX3CL1 (chemoattractant factor for macrophages) (160, 235). I/R injury eventually leads to kidney fibrosis, which is the deposition of connective tissue in the renal parenchyma. Studies using hiPSC with renal lineage and amniotic fluid-derived stem cells (AFSC) revealed a decrease in interstitial fibrosis and myofibroblast formation (164, 165). In another study using hWJ-MSC the reduction of overall fibrosis was attributed to a HGF/TGF-β shift to HGF (170).
Stem cells from diverse sources and their EVs seem to be efficiently counteracting the main pathophysiological events described for AKI I/R. However, the mechanisms underlying the beneficial effects observed are still elusive. More studies focusing not only on the outcome, but also on the mechanisms of action, are necessary previous to safely introducing MSC therapy into clinical practice. It is also noteworthy that all studies evaluated in this review focused on the acute phase of the injury, neglecting the progression of AKI to CKI. For that reason, further investigations are needed to understand the long-term effects.
AKI induced by chemotherapy
Cisplatin is a chemotherapeutic drug largely used for the treatment of several solid organ tumors and it is considered a gold standard treatment in oncology. Its nephrotoxic side effect has been widely described and reported in literature (236). Nephrotoxicity occurs in approximately 20–30% of patients treated with cisplatin due to its accumulation in proximal tubular cells where it induces apoptosis. Cisplatin has been used for decades in animal experiments in order to induce both AKI and CKI, and it represents a commonly used model to study therapeutic effects of MSC (237).
The first study involving MSC as a therapeutic approach for the treatment of cisplatin-induced AKI dates back to 2004, when Morigi et al. described the effect of allogeneic stem cell administration in a mouse model (238). In this study, BM-MSC and BM derived hematopoietic stem cells (HSC) were tested and compared, showing that only BM-MSC lead to a functional and morphological restoration of the kidney. The benefits of allogeneic MSC in cisplatin-induced AKI treatment are documented in several studies, where different cell sources, administration routes and approaches have been tested to better understand the mechanisms of action involved (55, 87, 239).
In xenogeneic studies, good results in terms of survival rate, renal function and morphology were achieved through the application of different types of hMSC, such as hBM-MSC (195, 196), hAFSC (182, 192), hESC-MP (190), hUC-MSC (32, 179, 187, 189), hUCB-MSC (31, 85). Recently, hASC have become the most widely used cell type in animal experiments, resulting in good treatment results in AKI (180, 183, 184, 186). The therapeutic effect of hASC has been demonstrated for the first time in a cisplatin induced AKI model in 2012 by Kim et al. where cells and CM were tested and both resulted in a reduction of renal tissue damage and an increase in survival rate (79). This already suggested that CM may replace cell infusion, which is of importance when considering risk/benefit ratio. Ashour et al. compared the therapeutic effect of hASC and hAFSC (181). Results show that when hAFSC were used, higher regenerative and proliferative activities were observed, compared to hASC. The authors wanted to underline that primitive MSC, such as hAFSC, have biological advantages over adult MSC and therefore should be chosen for clinical applications.
So far, the anti-apoptotic mechanism seems to be the most widely recognized in cisplatin models. Yao et al. investigated the role of apoptosis when hASC are administrated in a cisplatin-induced rat model (184). The histological analysis showed that in treated animals, the percentage of apoptotic cells was reduced and the tubular cell proliferation increased. In vitro and in vivo experiments indicated that MSC might produce specific cytokines, which are able to mediate an anti-apoptotic function through p38-MAPK, Bax, and Bcl-2 pathways. Wang et al. investigated the role of the transcriptional factor hypoxia-inducible factor subunit 1 alpha (HIF-1α) as anti-apoptotic candidate (183). HIF-1alpha has been effective in the treatment of various kidney diseases, activating downstream renal protective gene expression. Supporting this notion, genetically modified hASC overexpressing HIF-1α mediated an increased anti-apoptotic effect. The approach to genetically modify MSC has been also used in another interesting study where hESC were modified to overexpress VEGF (193). It is known that VEGF plays an important role in the renoprotective action mediated by MSC and it has been demonstrated that the VEGF-modified hESC exert a more pronounced renoprotective effect compared to the wild type ones. This results from an anti-apoptotic mechanism.
Since no cell engraftment into the kidneys was found, a possible explanation of the successful result achieved in the AKI treatment has been attributed to a possible secretion of other factors, promoted by the upregulation of VEGF, that contribute to the recovery of the kidney. High levels of VEGF were also found in a study in which the animals were treated with hUCB-MSC 1 day after induction of AKI (31). These animals showed a better outcome, which was associated with increased immunomodulatory activity and upregulation of anti-inflammatory cytokines, suggesting time dependency. Production of anti-inflammatory cytokines and anti-apoptotic proteins is also reported in another study in which a reduction of TNF-α, NF-kB, p38-MAPK, MCP-1, Bax, and caspase-3 is presented when cisplatin-induced AKI animals are treated with BM-MSC compared to the healthy counterpart (240). In animal models of cisplatin-induced AKI, MSC therapy has shown encouraging therapeutic effects, mainly involving renoprotective trophic effects. It has been largely demonstrated that the anti-apoptotic mechanism is one of the main effects mediated by MSC, even though further analyses are necessary to clarify how this is accomplished.
There is only one ongoing phase I clinical trial aiming to test the safety and efficacy of MSC to repair the kidney and improve renal function in patients with cisplatin induced AKI and solid organ cancer (200). In this study, the patients are treated with a single systemic infusion of allogeneic hBM-MSC with a 1-month follow up.
Diabetic nephropathy
One of the most costly complications arising from long-term sustained hyperglycemia is DN, which represents the most frequent cause of ESRD (more than 35% in the U.S.) (https://www.usrds.org/2017/view/Default.aspx). The onset and progression to ESRD is mostly silent and develops slowly. Abnormal kidney function is often detected only by chance after a five to ten year duration of diabetes (241–243). The pathological changes in diabetic nephropathy are well-characterized and follow a progressive pattern, where ECM deposition in the base membrane of glomeruli and tubular tissues are the main findings (244). The molecular mechanisms have been extensively studied as result of the comprehensive research of glucose metabolism and the effects of side by-product of these pathways in vitro in kidney tissues (202, 245–247). The development of diabetic animal models such as the STZ model (diabetes type 1, T1D) or leptin receptor deficient models (diabetes type 2, T2D) are essential to understand the progression that might occur in different types of diabetic patients (248).
The use of MSC to ameliorate this complication is not new. In 2006 Lee et al. demonstrated that intra-cardiac (IC) infusion of hBM-MSC had a double benefit to STZ diabetic mice by reducing mesangial matrix deposition and restoring pancreatic damage (84). The restoration of insulin secreting tissue has not been confirmed in latter studies. In a similar STZ model Ezquer et al. administered BM-MSC and observed significantly reduced glomerulosclerosis and ECM deposition, in both presence and absence of glucose normalization due to pancreatic regeneration (249–251). Similar histological end-points (such as ECM and collagen deposition reduction) support the benefits of stem cell-based therapies in this setting (252–258). Regarding functional parameters, most of the studies have reported an improvement of albuminuria in severely damaged kidneys, not only in STZ models, but also in diabetes type 2 models (259, 260).
Distinctly, Nagaishi et al. repeatedly confirmed the benefits of BM-MSC in insulin resistant and insulin depleted diabetic nephropathy models with positive outcomes using not only cells, but also CM (259). This indicates that EVs and cytokine release might be more relevant for therapeutic actions than cells themselves (197). Similarly, the immunomodulatory properties are reported and resulted in the reduction of macrophage infiltration, MCP-1 expression in tissues, and reduction of inflammatory cytokines (89, 251, 259, 261, 262). These findings clearly suggest that the metabolic environment has an important impact on the performance of MSC (by deactivation or detrimental shift of their properties). Again, further in vitro and in vivo experiments are required to answer still open questions. Interestingly, none of the studies reported signs of a host derived native immune response, even though different allogeneic and xenogeneic cell types (260, 263), and different concentrations of the same were used (84, 197–199). The positive outcome observed are similar in most of the studies, where ECM deposition, urinary albumin/creatinine ratio, and less epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) is observed.
There are currently two ongoing clinical trials, which study the safety, feasibility and tolerability of allogeneic hMSC-based interventions and the efficacy in DN patients (202, 203). Meanwhile, a completed clinical trial performed by Packham et al. in 2016 revealed no allogeneic adverse effects in patients treated with BM derived mesenchymal precursor cells compared to placebo (201). Nevertheless, the results regarding renal functional improvement were inconclusive, suggesting that larger populations and long-term studies might be needed to address this issue. Alloreactivity and the patients immune response are critical aspects to be assess before exploring the benefits reported in the literature. However, these topics are scarcely investigated in the field of preclinical research suggesting that further studies are needed.
Polycystic kidney disease
PKD is a renal disease that leads to ESRD and is the fourth most common cause of chronic renal insufficiency. The pathology can arise sporadically; however, most forms are hereditary (264). Two of the best characterized forms of PKD are: autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) that occurs typically in adults and autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD) that mainly affects infants and is associated with significant neonatal mortality and childhood morbidity (264, 265). The most likely mechanism is an alteration of the proteins signaling function within the cell and primary cilia. As a result, cells lining the renal tubules may grow and divide abnormally causing the growth of numerous cysts (266–268).
Nowadays, there are just a few therapies available for PKD patients. End-stage PKD patients usually undergo dialysis or renal transplantation. There is a strong need for more advanced therapeutic measures, due to poor life quality in long-term dialysis treatment, expensive insurance costs and increasing organ transplant waiting lists. Since the end of the last century, different types of PKD animal models have been characterized. In this context, the characteristic mutation in these animals has either been induced or developed spontaneously (269–272).
In the last years, two studies have been published that show the possible therapeutic effects of allogeneic stem cells in rats. Franchi et al. have shown that a single injection of BM-MSC isolated from healthy SD rats could improve the kidney function in PCK rats, partially restoring renal function (273). This study points out two of the potential effects of stem cells: the paracrine effects, by the release of cytokines, such as SDF1, VEGF, and HGF, and the ability of the cells, after injection, to acquire characteristics of endothelial cells, suggesting transdifferentiation of these cells. Kelly et al. instead, demonstrated that only repeated injections of primary renal tubular cells isolated from healthy SD ameliorate renal function (274). The authors have documented a clear engraftment of donor stem cells after transplantation, which leads to a decrease of total cyst volume and fibrosis and also improves vasculature, resulting in better delivery of oxygen and nutrients. The aforementioned studies have shown that MSC ameliorate renal function and limit the cysts formation in PKD animal model. Further studies should be performed in order to assess whether hMSC can also be safely applied in PKD.
Interestingly, despite the low numbers of preclinical evaluations, there is already one finished phase I clinical trial which had the aim to investigate the safety and efficacy of autologous hBM-MSC to improve the renal function in patients affected by ADPKD (204). Here, cultured BM-MSC were administrated to patients, with an 18-month follow up. Due to the limited number of samples, and lack of a control group, in this study it was not possible to demonstrate the efficacy of stem cell therapy. However, it demonstrated the safety and tolerability of IV infusion of autologous MSC. Currently, in literature there are various clinical research dedicated to safety and tolerability evaluation of MSC infusion in different pathological conditions. However, as indicated by the authors, several pathways are related with PKD progression, such as inflammation, cyst proliferation, and apoptosis. Since the mechanisms highlighting the positive effects are not yet fully clarified, it would be advised to do an evaluation of these observed mechanisms of action in relation to a long term MSC injection therapy.
Kidney transplantation
KTx is the treatment of choice for patients with ESRD providing better quality of life and increasing life expectancy. However, the long term survival of the grafts is not yet optimal (275–277). This is due to organ shortage and the subsequent access to extended-criteria and brain dead donors (278–281). Moreover, the main cause of kidney transplantation failure is the development of interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy, which is a progressive kidney dysfunction associated also with vascular occlusion and glomerulosclerosis (282, 283). Therefore, stem cell treatment arises as a possibility to create new regimes in combination with immunosuppressive drugs or to minimize the doses needed to prevent rejection while preserving renal function (9, 284).
The main points of interest regarding stem cell therapy in kidney transplantation are their competence to modulate the immune response and to reduce interstitial fibrosis. BM-MSC are able to preserve renal function, reduce interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy by decreasing T cell and macrophage activation at 24 weeks after transplantation, in a Fisher to Lewis KTx model (81). However, in a KTx model using a complete MHC discordant donor-recipient combination, the use of BM-MSC worsens transplantation outcome, causing massive infiltration, thrombotic microangiopathy and increased IL-2 and IFN-γ expression (285). As expected, the time of administration plays an important role, as in a mouse model of fully mismatched MHC, administration of recipient-derived BM-MSC 2 days after KTx caused progressive graft dysfunction and graft rejection within 20 days, but MSCs injection 1 or 7 days before KTx, prolonged graft survival by migration of the cells to the spleen causing expansion of donor specific Treg (286). Another interesting study compared BM-MSC wild-type with MSC IDO knockout. The BM-MSC wild-type were able to induce allograft tolerance by a CD4+ T cell response impairment and by increasing the percentage of FOXP3+ regulatory T cells; whereas the MSC IDO knockout were not able to induce allograft tolerance, suggesting IDO is involved in MSC immunosuppressive effect (46). The use of BM-MSC in combination with the immunosuppressant cyclosporine-A has also been tested. It shows protection of graft function, but not improvement of animal survival as strongly as cyclosporine-A treatment alone, suggesting a potential interaction between this drug and MSC (287). In an allogeneic kidney transplantation rat model, BM-MSC decrease ED1+ and CD8+ cells and are able to reduce interstitial fibrosis and TGF-β1 when administered 3 and 7 days after KTx (288, 289).
Also in an allogeneic mouse model, BM-MSC-MVs increased graft survival by decreasing the percentage of MHCII+, CD80+, and CD86+ cells. Interestingly, also in the transplantation scenario, the pre-treatment of MVs with miRNA-146a inhibitor abolished the observed beneficial effect. ASC have been tested in a fully MHC disparate rat model suggesting prolonged graft survival by decreasing CD4+/ CD8+ratio. The mechanism involved would be upregulation of tumor necrosis factor-inducible gene 6 protein (TSG-6) by ASC in vitro. This upregulation causes the suppression of allo-reactive T cells by downregulation of CD44, leading to suppression of T cell activation and infiltration into the graft (290).
So far, four clinical trials using MSC in kidney transplantation have been completed. The common factor in all of them is the use of MSC in combination with immunosuppressive drugs to minimize the doses needed and therefore, reduce the incidence of adverse effect associated with their use. In the first one, conducted by Trivedi et al. high doses of donor-derived peripheral blood stem cells were used in pediatric recipients in combination with cyclosporine-A and prednisolone. After 18 months of observation, there was 100% graft survival, sustained renal function and low incidence of opportunistic infections (218). In the second one, conducted by Reinders et al. a double infusion of autologous BM-MSC was given to allograft recipients with subclinical rejection. An inhibition of donor-specific immunity was observed in five of the six patients treated 6 months after cell infusion (211). The third one, conducted by Tan et al. autologous MSC infusion, together standard and low doses of calcineurin inhibitors were used. An additional group received IL-2 receptor antibodies and standard doses of calcineurin inhibitors. The results showed that patients receiving MSC had lower incidence of acute rejection, decreased risk of secondary opportunistic infections and improved renal function after one year, compared to the patients infused with IL-2 receptor antibody (213). In the fourth one, by Ciancio et al. donor-derived BM-MSC were infused in living-related transplant recipients. Patients were additionally treated with alemtuzumab with steroid free maintenance. This combination was unable to induce tolerance and showed suboptimal graft survival (210). Further information about ongoing clinical trials is summarized in Table 5. The clinical trials completed give an overview of possible new therapeutic regimes. However, there are several questions to which there is no consensus, such as: most suitable timing for administration (before or after KTx) and most suitable dosage. This information is vital for an appropriate translation to clinical practice. Further research is needed to elucidate the aforementioned issues as well as to assess possible synergistic or antagonistic effects of MSC with the most commonly used immunosuppressive drugs.
The results involving stem cells in kidney transplantation seem promising. However, due to the immense complexity of the mechanisms involved, the translation from animal models to clinical practice seems elusive. It would be interesting to see more studies using MSC in combination with the most common immunosuppressive drugs to assess possible synergic effects.
Conclusions
MSC are one of the mostly investigated cell types for cell based therapies. Due to their heterogeneous modes of action, they are widely studied in a variety of injuries. MSC effects seem to be mediated by immunomodulation, anti-apoptotic effect, involving secretion of paracrine and endocrine factors that act toward injury amelioration. Therefore, this review aims to highlight the latest information of MSC therapy in preclinical studies and clinical trials in diverse kidney diseases.
Although, there are multiple evidences showing that there is no consensus regarding the best administration route, dosage, timing, tissue source, and specific mode of action, due to high variances within the different kidney injury models, preclinical data suggest beneficial effects in kidney injuries.
The large complexity of the mechanisms involved, make the translation from preclinical studies to clinical trials extremely challenging. In fact, it became rapidly clear that the assumed effect does not rely on local engraftment and differentiation, but rather on trophic effects. Still, the exact mode of action is not known. Varieties of mechanisms have been postulated, varying slightly with respect to the disease entities, but still, there is no clear indication about what defines clinical efficacy. Potency assays, for instance, are still lacking to predict clinical outcomes. We fully agree with the concept proposed by Ivan Martin that a reiterative cycle is required: 1. clinical indication and proposed mechanism of action, 2. specification of the product, 3. adaptation of manufacturing, and 4. assessment of clinical efficacy in well-designed and controlled clinical trials. For optimization feed-back loops have to be implemented to learn from the results, obtained in patients, in preclinical models and corresponding in vitro correlates (11). Some clinical field appear to have already evolved, based on this “Bench to bedside and back” approach, such as graft-versus-host disease and Crohn's related perianal fistula (291–293).
It should be noted that animal models are not fully able to mimic the human disease, this is why preclinical data must be taken cautiously. Autologous MSC have already been used in clinical trials and are known to have a high safety and tolerability. In our search we found several clinical trials where allogeneic MSC are used. However, there is not yet a clear understanding of how MSC act in such environment. According to the stated paracrine effect of MSC, the new trend is to test MSC EVs or CM instead of their cellular counterpart. Based on preclinical studies they have been proven efficient in ameliorating kidney diseases. Despite this knowledge, further elucidation is needed for translation to clinical trials.
The use of MSC for therapeutic purposes show encouraging results, nevertheless, the complexity of these kidney diseases, together with the animal model limitations require careful investigation. We suggest that due to our current limitations in understanding cell behavior in vivo, there is a need for novel imaging techniques (such as OTC) to open a new horizon in imaging MSC therapeutic field.
Author contributions
AT and CD manuscript writing, assembling, reviewing, editing. CG, SM, DP, DN, and CB manuscript writing. BY and NG manuscript editing and final approval. KB manuscript writing, editing and final approval.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
The help of Mr. Maurizio Grilli in supporting the literature search was highly appreciated. AT, CD, CG, CB, SM, DN, and DP are supported by the co-operative research-training group: Tissue Analytics for Stem Cell Based Diagnostics and Therapy of the Ministry of Science, Research and the Arts (MWK) Baden-Wurttemberg, Germany.
Glossary
Abbreviations
- ADPKD
Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease
- AFSC
Amniotic fluid-derived stem cells
- AKI I/R
AKI induced by ischemia/reperfusion
- AKI
Acute kidney injury
- ARE
Antioxidant response element
- ARPKD
Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease
- ASC
Adipose-derived MSCs
- ATG
Antithymocyte globulin
- BM
Bone marrow
- BUN
Blood urea nitrogen
- CKI
Chronic kidney injury
- CM
Conditioned medium
- COX2
Cyclooxigenase-2
- DiD, 1, 1-Dioctadecyl-3, 3, 3
3-tetramethylindodicarbocyanine
- DN
Diabetic nephropathy
- ECM
Extra cellular matrix
- EMT
Epithelial–mesenchymal transition
- EPC
Endothelial progenitor cells
- ESC
Embryonic stem cells
- ESC-MP
Mesenchymal-like progenitors derived from embryonic MSC
- ESRD
End-Stage Renal Disease
- EVs
Extracellular vesicles
- GM-CSF
Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor
- HGF
Hepatocyte growth factor
- HIF-1α
Hypoxia-inducible factor subunit 1α
- HLA
Human leukocyte antigen
- HSC
Hematopoietic stem cells
- IA
Intra-arterial
- IC
Intra-cardiac
- ICG
Indcyanine Green
- IDO, Indoleamine 2
3-dioxygenase
- IGF
Insulin-like growth factor
- IP
Intra-peritoneal
- iPSC
Induced-pluripotent stem cells
- IR
Intra-renal
- IV
Intra-venous
- KDC
Kidney-derived cells
- KTx
Kidney transplantation
- luc/neo-MSC
luciferase/neomycyn phosphotransferase-marked MSC
- MCP-1
Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1
- MMPs
Metalloproteinases
- MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging
- MVs
Microvesicles
- OI
Optical imaging
- PKD
Polycystic Kidney Disease
- RPC
Renal progenitor cells
- sCr
Serum creatinine
- sNGAL
Serum Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin
- STZ
Streptozotocin
- SVF
Stromal vascular fraction
- T1D
Type 1 diabetes
- T2D
Type 2 diabetes
- TIMPs
tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases
- TNF-α
Tumor necrosis factor Alpha
- Treg
Regulatory T cells
- U-ACR
Urine albumin to creatinine ratio
- UC
Umbilical cord
- UCB
Umbilical cord blood
- UDSC
Urine derived stromal cells
- USSC
Unrestricted somatic stem cells
- WJ
Wharton's jelly
- α-SMA
Alpha smooth muscle.
Footnotes
Funding. This work was funded by The Ministry of Science, Research and the Arts of the State of Baden-Württemberg.
References
- 1.Eckardt KU, Coresh J, Devuyst O, Johnson RJ, Kottgen A, Levey AS, et al. Evolving importance of kidney disease: from subspecialty to global health burden. Lancet (2013) 382:158–69. 10.1016/s0140-6736(13)60439-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Hill NR, Fatoba ST, Oke JL, Hirst JA, O'Callaghan CA, Lasserson DS, et al. Global prevalence of chronic kidney disease - A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE (2016) 11:e0158765. 10.1371/journal.pone.0158765 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Couser WG, Remuzzi G, Mendis S, Tonelli M. The contribution of chronic kidney disease to the global burden of major noncommunicable diseases. Kidney Int. (2011) 80:1258–70. 10.1038/ki.2011.368 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Martello G, Smith A. (2014). The nature of embryonic stem cells. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 30:647–75. 10.1146/annurev-cellbio-100913-013116 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Nishimori M, Yakushiji H, Mori M, Miyamoto T, Yaguchi T, Ohno S, et al. Tumorigenesis in cells derived from induced pluripotent stem cells. Hum Cell (2014) 27:29–35. 10.1007/s13577-013-0078-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Takahashi K, Yamanaka S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell (2006) 126:663–76. 10.1016/j.cell.2006.07.024 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Lindner U, Kramer J, Rohwedel J, Schlenke P. Mesenchymal stem or stromal cells: toward a better understanding of their biology? Transfus Med Hemother. (2010) 37:75–83. 10.1159/000290897 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Kern S, Eichler H, Stoeve J, Kluter H, Bieback K. Comparative analysis of mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow, umbilical cord blood, or adipose tissue. Stem Cells (2006) 24:1294–301. 10.1634/stemcells.2005-0342 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Peired AJ, Sisti A, Romagnani P. Mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy for kidney disease: a review of clinical evidence. Stem Cells Int. (2016) 2016:4798639. 10.1155/2016/4798639 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Bieback K, Wuchter P, Besser D, Franke W, Becker M, Ott M, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs): science and f(r)iction. J Mol Med. (2012) 90:773–82. 10.1007/s00109-012-0915-y [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Martin I, De Boer J, Sensebe L. A relativity concept in mesenchymal stromal cell manufacturing. Cytotherapy (2016) 18:613–20. 10.1016/j.jcyt.2016.02.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Stultz BG, McGinnis K, Thompson EE, Lo Surdo JL, Bauer SR, Hursh DA. Chromosomal stability of mesenchymal stromal cells during in vitro culture. Cytotherapy (2016) 18:336–43. 10.1016/j.jcyt.2015.11.017 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Friedenstein AJ, Piatetzky S. II, Petrakova KV. Osteogenesis in transplants of bone marrow cells. J Embryol Exp Morphol. (1966) 16:381–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Friedenstein AJ, Petrakova KV, Kurolesova AI, Frolova GP. Heterotopic of bone marrow. Analysis of precursor cells for osteogenic and hematopoietic tissues. Transplantation (1968) 6:230–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Friedenstein AJ, Chailakhjan RK, Lalykina KS. The development of fibroblast colonies in monolayer cultures of guinea-pig bone marrow and spleen cells. Cell Tissue Kinet. (1970) 3:393–403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Horwitz EM, Le Blanc K, Dominici M, Mueller I, Slaper-Cortenbach I, Marini FC, et al. Clarification of the nomenclature for MSC: the International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy (2005) 7:393–5. 10.1080/14653240500319234 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Dominici M, Le Blanc K, Mueller I, Slaper-Cortenbach I, Marini F, Krause D, et al. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy (2006) 8:315–7. 10.1080/14653240600855905 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Chen C, Hou J. Mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy in kidney transplantation. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2016) 7:16. 10.1186/s13287-016-0283-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Fischer UM, Harting MT, Jimenez F, Monzon-Posadas WO, Xue H, Savitz SI, et al. Pulmonary passage is a major obstacle for intravenous stem cell delivery: the pulmonary first-pass effect. Stem Cells Dev. (2009) 18:683–92. 10.1089/scd.2008.0253 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Iwai S, Sakonju I, Okano S, Teratani T, Kasahara N, Yokote S, et al. Impact of ex vivo administration of mesenchymal stem cells on the function of kidney grafts from cardiac death donors in rat. Transplant Proc. (2014) 46:1578–84. 10.1016/j.transproceed.2013.12.068 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Tang Y, Zhang C, Wang J, Lin X, Zhang L, Yang Y, et al. MRI/SPECT/fluorescent tri-modal probe for evaluating the homing and therapeutic efficacy of transplanted mesenchymal stem cells in a rat ischemic stroke model. Adv Funct Mater. (2015) 25:1024–34. 10.1002/adfm.201402930 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Zanetti A, Grata M, Etling EB, Panday R, Villanueva FS, Toma C. Suspension-expansion of bone marrow results in small mesenchymal stem cells exhibiting increased transpulmonary passage following intravenous administration. Tissue Eng Part C Methods (2015) 21:683–92. 10.1089/ten.TEC.2014.0344 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Aghajani Nargesi A, Lerman LO, Eirin A. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles for kidney repair: current status and looming challenges. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2017) 8:273. 10.1186/s13287-017-0727-7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Nargesi AA, Lerman LO, Eirin A. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-derived Extracellular Vesicles for Renal Repair. Curr Gene Ther. (2017) 17:29–42. 10.2174/1566523217666170412110724 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Djouad F, Charbonnier LM, Bouffi C, Louis-Plence P, Bony C, Apparailly F, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells inhibit the differentiation of dendritic cells through an interleukin-6-dependent mechanism. Stem Cells (2007) 25:2025–32. 10.1634/stemcells.2006-0548 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Gieseke F, Bohringer J, Bussolari R, Dominici M, Handgretinger R, Muller I. Human multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells use galectin-1 to inhibit immune effector cells. Blood (2010) 116:3770–79. 10.1182/blood-2010-02-270777 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Chiesa S, Morbelli S, Morando S, Massollo M, Marini C, Bertoni A, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells impair in vivo T-cell priming by dendritic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (2011) 108:17384–9. 10.1073/pnas.1103650108 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Rosado MM, Bernardo ME, Scarsella M, Conforti A, Giorda E, Biagini S, et al. Inhibition of B-cell proliferation and antibody production by mesenchymal stromal cells is mediated by T cells. Stem Cells Dev. (2015) 24:93–103. 10.1089/scd.2014.0155 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Ninichuk V, Gross O, Segerer S, Hoffmann R, Radomska E, Buchstaller A, et al. Multipotent mesenchymal stem cells reduce interstitial fibrosis but do not delay progression of chronic kidney disease in collagen4A3-deficient mice. Kidney Int. (2006) 70:121–9. 10.1038/sj.ki.5001521 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Burger D, Vinas JL, Akbari S, Dehak H, Knoll W, Gutsol A, et al. Human endothelial colony-forming cells protect against acute kidney injury: role of exosomes. Am J Pathol. (2015) 185:2309–23. 10.1016/j.ajpath.2015.04.010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Park JH, Jang HR, Kim DH, Kwon GY, Lee JE, Huh W, et al. Early, but not late treatment with human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells attenuates cisplatin nephrotoxicity through immunomodulation. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. (2017) 313:F984–96. 10.1152/ajprenal.00097.2016 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Peng X, Xu H, Zhou Y, Wang B, Yan Y, Zhang X, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells attenuate cisplatin-induced acute and chronic renal injury. Exp Biol Med. (2013) 238:960–70. 10.1177/1535370213497176 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Ankrum JA, Ong JF, Karp JM. Mesenchymal stem cells: immune evasive, not immune privileged. Nat Biotechnol. (2014) 32:252–60. 10.1038/nbt.2816 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Grinnemo KH, Mansson A, Dellgren G, Klingberg D, Wardell E, Drvota V, et al. Xenoreactivity and engraftment of human mesenchymal stem cells transplanted into infarcted rat myocardium. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. (2004) 127:1293–300. 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2003.07.037 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Kol A, Wood JA, Carrade Holt DD, Gillette JA, Bohannon-Worsley LK, Puchalski SM, et al. Multiple intravenous injections of allogeneic equine mesenchymal stem cells do not induce a systemic inflammatory response but do alter lymphocyte subsets in healthy horses. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2015) 6:73 10.1186/s13287-015-0050-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Lin CS, Lin G, Lue TF. Allogeneic and xenogeneic transplantation of adipose-derived stem cells in immunocompetent recipients without immunosuppressants. Stem Cells Dev. (2012) 21:2770–78. 10.1089/scd.2012.0176 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Le Blanc K, Tammik L, Sundberg B, Haynesworth SE, Ringden O. Mesenchymal stem cells inhibit and stimulate mixed lymphocyte cultures and mitogenic responses independently of the major histocompatibility complex. Scand J Immunol. (2003) 57:11–20. 10.1046/j.1365-3083.2003.01176.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Nauta AJ, Westerhuis G, Kruisselbrink AB, Lurvink EG, Willemze R, Fibbe WE. Donor-derived mesenchymal stem cells are immunogenic in an allogeneic host and stimulate donor graft rejection in a nonmyeloablative setting. Blood (2006) 108:2114–20. 10.1182/blood-2005-11-011650 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Badillo AT, Beggs KJ, Javazon EH, Tebbets JC, Flake AW. Murine bone marrow stromal progenitor cells elicit an in vivo cellular and humoral alloimmune response. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. (2007) 13:412–22. 10.1016/j.bbmt.2006.12.447 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Galleu A, Riffo-Vasquez Y, Trento C, Lomas C, Dolcetti L, Cheung TS, et al. Apoptosis in mesenchymal stromal cells induces in vivo recipient-mediated immunomodulation. Sci Transl Med. (2017) 9:eaam7828. 10.1126/scitranslmed.aam7828 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Schu S, Nosov M, O'Flynn L, Shaw G, Treacy O, Barry F, et al. Immunogenicity of allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells. J Cell Mol Med. (2012) 16:2094–103. 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2011.01509.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Reinders ME, Rabelink TJ, de Fijter JW. The role of mesenchymal stromal cells in chronic transplant rejection after solid organ transplantation. Curr Opin Organ Transplant. (2013) 18:44–50. 10.1097/MOT.0b013e32835c2939 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Benvenuto F, Ferrari S, Gerdoni E, Gualandi F, Frassoni F, Pistoia V, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells promote survival of T cells in a quiescent state. Stem Cells (2007) 25:1753–60. 10.1634/stemcells.2007-0068 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Mattar P, Bieback K. Comparing the immunomodulatory properties of bone marrow, adipose tissue, and birth-associated tissue mesenchymal stromal cells. Front Immunol. (2015) 6:560. 10.3389/fimmu.2015.00560 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Wise AF, Ricardo SD. Mesenchymal stem cells in kidney inflammation and repair. Nephrology (2012) 17:1–10. 10.1111/j.1440-1797.2011.01501.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Ge W, Jiang J, Arp J, Liu W, Garcia B, Wang H. Regulatory T-cell generation and kidney allograft tolerance induced by mesenchymal stem cells associated with indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase expression. Transplantation (2010) 90:1312–20. 10.1097/TP.0b013e3181fed001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Gregorini MBF, Rocca C, Corradetti V, Valsania T, Pattonieri EF, Esposito P, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells reset the scatter factor system and cytokine network in experimental kidney transplantation. BMC Immunol. (2014) 15:44. 10.1186/s12865-014-0044-1 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Caplan AI. Mesenchymal stem cells: time to change the name! Stem Cells Transl Med. (2017) 6:1445–51. 10.1002/sctm.17-0051 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Biancone L, Bruno S, Deregibus MC, Tetta C, Camussi G. Therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cell-derived microvesicles. Nephrol Dial Transplant. (2012) 27:3037–42. 10.1093/ndt/gfs168 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Erices A, Conget P, Minguell JJ. Mesenchymal progenitor cells in human umbilical cord blood. Br J Haematol. (2000) 109:235–42. 10.1046/j.1365-2141.2000.01986.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Tögel F, Weiss K, Yang Y, Hu Z, Zhang P, Westenfelder C. Vasculotropic, paracrine actions of infused mesenchymal stem cells are important to the recovery from acute kidney injury. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. (2007) 292:F1626–35. 10.1152/ajprenal.00339.2006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Uccelli A, Moretta L, Pistoia V. Mesenchymal stem cells in health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol. (2008) 8:726–36. 10.1038/nri2395 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Rabb H. Paracrine and differentiation mechanisms underlying stem cell therapy for the damaged kidney. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. (2005) 289:29–30. 10.1152/ajprenal.00102.2005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Hu H, Zou C. Mesenchymal stem cells in renal ischemia-reperfusion injury biological. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. (2017) 12:183–7. 10.2174/1574888X11666161024143640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Bi B, Schmitt R, Israilova M, Nishio H, Cantley LG. Stromal cells protect against acute tubular injury via an endocrine effect. J Am Soc Nephrol. (2007) 18:2486–96. 10.1681/ASN.2007020140 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Bruno S, Grange C, Deregibus MC, Calogero RA, Saviozzi S, Collino F, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived microvesicles protect against acute tubular injury. J Am Soc Nephrol. (2009) 20:1053–67. 10.1681/ASN.2008070798 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Bruno S, Grange C, Collino F, Deregibus MC, Cantaluppi V, Biancone L, et al. Microvesicles derived from mesenchymal stem cells enhance survival in a lethal model of acute kidney injury. PLoS ONE (2012) 7:e33115. 10.1371/journal.pone.0033115 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Islam MN, Das SR, Emin MT, Wei M, Sun L, Westphalen K, et al. Mitochondrial transfer from bone-marrow-derived stromal cells to pulmonary alveoli protects against acute lung injury. Nat Med. (2012) 18:759–65. 10.1038/nm.2736 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Tomasoni S, Longaretti L, Rota C, Morigi M, Conti S, Gotti E, et al. Transfer of growth factor receptor mRNA via exosomes unravels the regenerative effect of mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. (2013) 22:772–80. 10.1089/scd.2012.0266 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Bruno S, Porta S, Bussolati B. Extracellular vesicles in renal tissue damage and regeneration. Eur J Pharmacol. (2016) 790:83–91. 10.1016/j.ejphar.2016.06.058 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Nassar W, El-Ansary M, Sabry D, Mostafa MA, Fayad T, Kotb E, et al. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells derived extracellular vesicles can safely ameliorate the progression of chronic kidney diseases. Biomater Res. (2016) 20:21. 10.1186/s40824-016-0068-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Kordelas L, Rebmann V, Ludwig AK, Radtke S, Ruesing J, Doeppner TR, et al. MSC-derived exosomes: a novel tool to treat therapy-refractory graft-versus-host disease. Leukemia (2014) 28:970–73. 10.1038/leu.2014.41 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Wynn TA. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of fibrosis. J Pathol. (2008) 214:199–210. 10.1002/path.2277 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Wynn TA, Ramalingam TR. Mechanisms of fibrosis: therapeutic translation for fibrotic disease. Nat Med. (2012) 18:1028–40. 10.1038/nm.2807 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Ali G, Mohsin S, Khan M, Nasir GA, Shams S, Khan SN, et al. Nitric oxide augments mesenchymal stem cell ability to repair liver fibrosis. J Transl Med. (2012) 10:75. 10.1186/1479-5876-10-75 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Semedo P, Correa-Costa M, Antonio Cenedeze M, Maria Avancini Costa Malheiros D, Antonia dos Reis M, Shimizu MH, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells attenuate renal fibrosis through immune modulation and remodeling properties in a rat remnant kidney model. Stem Cells (2009) 27:3063–73. 10.1002/stem.214 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Usunier B, Benderitter M, Tamarat R, Chapel A. Management of fibrosis: the mesenchymal stromal cells breakthrough. Stem Cells Int. (2014) 2014:340257. 10.1155/2014/340257 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.lv W, Booz GW, Fan F, Wang Y, Roman RJ. Oxidative stress and renal fibrosis: recent insights for the development of novel therapeutic strategies. Front Physiol. (2018) 16:105 10.3389/fphys.2018.00105 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Ezquer ME, Ezquer FE, Arango-Rodríguez ML, Conget PA. MSC transplantation: a promising therapeutic strategy to manage the onset and progression of diabetic nephropathy. Biol Res. (2012) 45:289–96. 10.4067/S0716-97602012000300010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Monsel A, Zhu YG, Gennai S, Hao Q, Liu J, Lee JW. Cell-based therapy for acute organ injury: preclinical evidence and ongoing clinical trials using mesenchymal stem cells. Anesthesiology (2014) 121:1099–121. 10.1097/ALN.0000000000000446 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Rowart P, Erpicum P, Detry O, Weekers L, Gregoire C, Lechanteur C, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cell therapy in ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Immunol Res. (2015) 2015:602597. 10.1155/2015/602597 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Kholia S, Ranghino A, Garnieri P, Lopatina T, Deregibus MC, Rispoli P, et al. Extracellular vesicles as new players in angiogenesis. Vascul Pharmacol. (2016) 86:64–70. 10.1016/j.vph.2016.03.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Meirelles Lda S, Fontes AM, Covas DT, Caplan AI. Mechanisms involved in the therapeutic properties of mesenchymal stem cells. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. (2009) 20:419–27. 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2009.10.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Tögel F, Hu Z, Weiss K, Isaac J, Lange C, Westenfelder C. Administered mesenchymal stem cells protect against ischemic acute renal failure through differentiation-independent mechanisms. J Physiol Renal Physiol. (2005) 289:31–42. 10.1152/ajprenal.00007.2005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Semedo P, Palasio CG, Oliveira CD, Feitoza CQ, Goncalves GM, Cenedeze MA, et al. Early modulation of inflammation by mesenchymal stem cell after acute kidney injury. Int Immunopharmacol. (2009) 9:677–82. 10.1016/j.intimp.2008.12.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.van Poll D, Parekkadan B, Cho CH, Berthiaume F, Nahmias Y, Tilles AW, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived molecules directly modulate hepatocellular death and regeneration in vitro and in vivo. Hepatology (2008) 47:1634–43. 10.1002/hep.22236 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Katsuno T, Ozaki T, Saka Y, Furuhashi K, Kim H, Yasuda K, et al. Low serum cultured adipose tissue-derived stromal cells ameliorate acute kidney injury in rats. Cell Transplant. (2013) 22:287–97. 10.3727/096368912X655019 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Zhang W, Liu L, Huo Y, Yang Y, Wang Y. Hypoxia-pretreated human MSCs attenuate acute kidney injury through enhanced angiogenic and antioxidative capacities. Biomed Res Int. (2014) 2014:462472. 10.1155/2014/462472 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Kim JH, Park DJ, Yun JC, Jung MH, Yeo HD, Kim HJ, et al. Human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells protect kidneys from cisplatin nephrotoxicity in rats. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. (2012) 302:1141–150. 10.1152/ajprenal.00060.2011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Yasuda K, Ozaki T, Saka Y, Yamamoto T, Gotoh M, Ito Y, et al. Autologous cell therapy for cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury by using non-expanded adipose tissue-derived cells. Cytotherapy (2012) 14:1089–100. 10.3109/14653249.2012.693157 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Franquesa M, Herrero E, Torras J, Ripoll E, Flaquer M, Goma M, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell therapy prevents interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy in a rat kidney allograft model. Stem Cells Dev. (2012) 21:3125–135. 10.1089/scd.2012.0096 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Villanueva S, Carreno JE, Salazar L, Vergara C, Strodthoff R, Fajre F, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells derived from adipose tissue reduce functional and tissue damage in a rat model of chronic renal failure. Clin Sci. (2013) 125:199–210. 10.1042/CS20120644 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Eirin A, Zhu XY, Krier JD, Tang H, Jordan KL, Grande JP, et al. Adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve revascularization outcomes to restore renal function in swine atherosclerotic renal artery stenosis. Stem Cells (2012) 30:1030–41. 10.1002/stem.1047 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Lee RH, Seo MJ, Reger RL, Spees JL, Pulin AA, Olson SD, et al. Multipotent stromal cells from human marrow home to and promote repair of pancreatic islets and renal glomeruli in diabetic NOD/scid mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (2006) 103:17438–43. 10.1073/pnas.0608249103 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Morigi M, Rota C, Montemurro T, Montelatici E, Lo Cicero V, Imberti B, et al. Life-sparing effect of human cord blood-mesenchymal stem cells in experimental acute kidney injury. Stem Cells (2010) 28:513–22. 10.1002/stem.293 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Santeramo I, Herrera Perez Z, Illera A, Taylor A, Kenny S, Murray P, et al. Human kidney-derived cells ameliorate acute kidney injury without engrafting into renal tissue. Stem Cells Transl Med. (2017) 6:1373–84. 10.1002/sctm.16-0352 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Cheng K, Rai P, Plagov A, Lan X, Kumar D, Salhan D, et al. Transplantation of bone marrow-derived MSCs improves cisplatinum-induced renal injury through paracrine mechanisms. Exp Mol Pathol. (2013) 94:466–73. 10.1016/j.yexmp.2013.03.002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Imberti B, Tomasoni S, Ciampi O, Pezzotta A, Derosas M, Xinaris C, et al. Renal progenitors derived from human iPSCs engraft and restore function in a mouse model of acute kidney injury. Sci Rep. (2015) 5:8826. 10.1038/srep08826 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Lv SS, Liu G, Wang JP, Wang WW, Cheng J, Sun AL, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells transplantation ameliorates glomerular injury in streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy in rats via inhibiting macrophage infiltration. Int Immunopharmacol. (2013) 17:275–82. 10.1016/j.intimp.2013.05.031 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Kraitchman DL, Tatsumi M, Gilson WD, Ishimori T, Kedziorek D, Walczak P, et al. Dynamic imaging of allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells trafficking to myocardial infarction. Circulation (2005) 112:1451–61. 10.1161/circulationaha.105.537480 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Schrepfer S, Deuse T, Reichenspurner H, Fischbein MP, Robbins RC, Pelletier MP. Stem cell transplantation: the lung barrier. Transplant Proc. (2007) 39:573–76. 10.1016/j.transproceed.2006.12.019 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Furlani D, Ugurlucan M, Ong L, Bieback K, Pittermann E, Westien I, et al. Is the intravascular administration of mesenchymal stem cells safe? mesenchymal stem cells and intravital microscopy. Microvascular Research (2009) 77:370–76. 10.1016/j.mvr.2009.02.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Lee RH, Seo MJ, Pulin AA, Gregory CA, Ylostalo J, Prockop DJ. The CD34-like protein PODXL and alpha6-integrin (CD49f) identify early progenitor MSCs with increased clonogenicity and migration to infarcted heart in mice. Blood (2009) 113:816–26. 10.1182/blood-2007-12-128702 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Devine SM, Cobbs C, Jennings M, Bartholomew A, Hoffman R. Mesenchymal stem cells distribute to a wide range of tissues following systemic infusion into nonhuman primates. Blood (2003) 101:2999–3001. 10.1182/blood-2002-06-1830 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Humphreys BD, Bonventre JV. Mesenchymal stem cells in acute kidney injury. Ann Rev Med. (2008) 59:311–25. 10.1146/annurev.med.59.061506.154239 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Humphreys BD, Valerius MT, Kobayashi A, Mugford JW, Soeung S, Duffield JS, et al. Intrinsic epithelial cells repair the kidney after injury. Cell Stem Cell (2008) 2:284–91. 10.1016/j.stem.2008.01.014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Walczak P, Zhang J, Gilad AA, Kedziorek DA, Ruiz-Cabello J, Young RG, et al. Dual-modality monitoring of targeted intraarterial delivery of mesenchymal stem cells after transient ischemia. Stroke (2008) 39:1569–74. 10.1161/strokeaha.107.502047 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.de Vries DK, Schaapherder AF, Reinders ME. Mesenchymal stromal cells in renal ischemia/reperfusion injury. Front Immunol. (2012) 3:162. 10.3389/fimmu.2012.00162 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Oeller M, Laner-Plamberger S, Hochmann S, Ketterl N, Feichtner M, Brachtl G, et al. Selection of tissue factor-deficient cell transplants as a novel strategy for improving hemocompatibility of human bone marrow stromal cells. Theranostics (2018) 8:1421–34. 10.7150/thno.21906 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Moll G, Rasmusson-Duprez I, von Bahr L, Connolly-Andersen AM, Elgue G, Funke L, et al. Are therapeutic human mesenchymal stromal cells compatible with human blood? Stem Cells (2012) 30:1565–74. 10.1002/stem.1111 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Stephenne X, Nicastro E, Eeckhoudt S, Hermans C, Nyabi O, Lombard C, et al. Bivalirudin in combination with heparin to control mesenchymal cell procoagulant activity. PLoS ONE (2012) 7:e42819. 10.1371/journal.pone.0042819 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Gleeson BM, Martin K, Ali MT, Kumar AH, Pillai MG, Kumar SP, et al. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells have innate procoagulant activity and cause microvascular obstruction following intracoronary delivery: amelioration by antithrombin therapy. Stem Cells (2015) 33:2726–37. 10.1002/stem.2050 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Moll G, Ignatowicz L, Catar R, Luecht C, Sadeghi B, Hamad O, et al. Different procoagulant activity of therapeutic mesenchymal stromal cells derived from bone marrow and placental decidua. Stem Cells Dev. (2015) 24:2269–79. 10.1089/scd.2015.0120 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Weng YS, Lin HY, Hsiang YJ, Hsieh CT, Li WT. The effects of different growth factors on human bone marrow stromal cells differentiating into hepatocyte-like cells. Adv Exp Med Biol. (2003) 534:119–28. 10.1007/978-1-4615-0063-6_9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Singaravelu K, Padanilam BJ. In vitro differentiation of MSC into cells with a renal tubular epithelial-like phenotype. Ren Fail. (2009) 31:492–502. 10.1080/08860220902928981 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Wong CY, Tan EL, Cheong SK. In vitro differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells into mesangial cells when co-cultured with injured mesangial cells. Cell Biol Int. (2014) 38:497–501. 10.1002/cbin.10231 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Imasawa T, Utsunomiya Y, Kawamura T, Zhong Y, Nagasawa R, Okabe M. The potential of bone marrow-derived cells to differentiate to glomerular mesangial cells. J Am Soc Nephrol. (2001) 12:1401–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Li K, Han Q, Yan X, Liao L, Zhao RC. Not a process of simple vicariousness, the differentiation of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells to renal tubular epithelial cells plays an important role in acute kidney injury repairing. Stem Cells Dev. (2010) 19:1267–75. 10.1089/scd.2009.0196 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Supokawej A, Nimsanor N, Sanvoranart T, Kaewsaneha C, Hongeng S, Tangboriboonrat P, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell in vitro labeling by hybrid fluorescent magnetic polymeric particles for application in cell tracking. Med Mol Morphol. (2015) 48:204–13. 10.1007/s00795-015-0102-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Ahrens ET, Bulte JWM. Tracking immune cells in vivo using magnetic resonance imaging. Nat Rev Immunol. (2013) 13:755–63. 10.1038/nri3531 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Waters JC. Live-cell fluorescence imaging. Methods Cell Biol. (2007) 81:115–40. 10.1016/s0091-679x(06)81007-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Tsien RY. The green fluorescent protein. Annu Rev Biochem. (1998) 67:509–44. 10.1146/annurev.biochem.67.1.509 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Sawano A, Miyawaki A. Directed evolution of green fluorescent protein by a new versatile PCR strategy for site-directed and semi-random mutagenesis. Nucleic Acids Res. (2000) 28:E78. 10.1093/nar/28.16.e78 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Scholz O, Thiel A, Hillen W, Niederweis M. Quantitative analysis of gene expression with an improved green fluorescent protein. p6. Eur J Biochem. (2000) 267:1565–70. 10.1046/j.1432-1327.2000.01170.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Griesbeck O, Baird GS, Campbell RE, Zacharias DA, Tsien RY. Reducing the environmental sensitivity of yellow fluorescent protein. Mechanism and applications. J Biol Chem. (2001) 276:29188–94. 10.1074/jbc.M102815200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Nagai T, Sawano A, Park ES, Miyawaki A. Circularly permuted green fluorescent proteins engineered to sense Ca2+. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (2001) 98:3197–202. 10.1073/pnas.051636098 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Bhirde A, Xie J, Swierczewska M, Chen X. Nanoparticles for cell labeling. Nanoscale (2011) 3:142–53. 10.1039/c0nr00493f [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Wilson M. Introduction to Widefield Microscopy [Online] (2017). Available online at: https://www.leica-microsystems.com/science-lab/introduction-to-widefield-microscopy/ [Accessed].
- 119.Petty HR. Fluorescence microscopy: established and emerging methods, experimental strategies, and applications in immunology. Microsc Res Tech. (2007) 70:687–709. 10.1002/jemt.20455 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Sanderson MJ, Smith I, Parker I, Bootman MD. Fluorescence microscopy. Cold Spring Harb Protoc. (2014) 2014:pdb.top071795. 10.1101/pdb.top071795 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Lijkwan M, Bos E, Wu J. Principles of bioluminescence imaging. In: Kraitchman DL, Wu JC. editors. Stem Cell Labeling for Delivery and Tracking Using Non-Invasive Imaging. CRC Press; (2011). p. 237–52. [Google Scholar]
- 122.Kim JE, Kalimuthu S, Ahn BC. In vivo cell tracking with bioluminescence imaging. Nucl Med Mol Imaging (2015) 49:3–10. 10.1007/s13139-014-0309-x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Borlinghaus RT. MRT letter: high speed scanning has the potential to increase fluorescence yield and to reduce photobleaching. Microsc Res Tech. (2006) 69:689–92. 10.1002/jemt.20363 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Ragazzi M, Longo C, Piana S. Ex vivo (fluorescence) confocal microscopy in surgical pathology: state of the art. Adv Anat Pathol. (2016) 23:159–69. 10.1097/pap.0000000000000114 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Denk W, Strickler JH, Webb WW. Two-photon laser scanning fluorescence microscopy. Science (1990) 248:73–6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Svoboda K, Yasuda R. Principles of two-photon excitation microscopy and its applications to neuroscience. Neuron (2006) 50:823–39. 10.1016/j.neuron.2006.05.019 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Santi PA. Light sheet fluorescence microscopy: a review. J Histochem Cytochem. (2011) 59:129–38. 10.1369/0022155410394857 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Larocca RA, Moraes-Vieira PM, Bassi EJ, Semedo P, de Almeida DC, da Silva MB, et al. Adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells increase skin allograft survival and inhibit Th-17 immune response. PLoS ONE (2013) 8:e76396. 10.1371/journal.pone.0076396 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Ragazzi M, Piana S, Longo C, Castagnetti F, Foroni M, Ferrari G, et al. Fluorescence confocal microscopy for pathologists. Mod Pathol. (2014) 27:460–71. 10.1038/modpathol.2013.158 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Lichtman JW, Conchello JA. Fluorescence microscopy. Nat Methods (2005) 2:910–19. 10.1038/nmeth817 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Baker M. Cellular imaging: taking a long, hard look. Nature (2010) 466:1137–40. 10.1038/4661137a [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Coutu DL, Schroeder T. Probing cellular processes by long-term live imaging–historic problems and current solutions. J Cell Sci. (2013) 126:3805–15. 10.1242/jcs.118349 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Megason SG, Fraser SE. Digitizing life at the level of the cell: high-performance laser-scanning microscopy and image analysis for in toto imaging of development. Mech Dev. (2003) 120:1407–20. 10.1016/j.mod.2003.07.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Yukawa H, Nakagawa S, Yoshizumi Y, Watanabe M, Saito H, Miyamoto Y, et al. Novel positively charged nanoparticle labeling for in vivo imaging of adipose tissue-derived stem cells. PLoS ONE (2014) 9:e110142. 10.1371/journal.pone.0110142 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Grange C, Tapparo M, Bruno S, Chatterjee D, Quesenberry PJ, Tetta C, et al. Biodistribution of mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles in a model of acute kidney injury monitored by optical imaging. Int J Mol Med. (2014) 33:1055–63. 10.3892/ijmm.2014.1663 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Sutton EJ, Boddington SE, Nedopil AJ, Henning TD, Demos SG, Baehner R, et al. An optical imaging method to monitor stem cell migration in a model of immune-mediated arthritis. Opt Express (2009) 17:24403–213. 10.1364/OE.17.024403 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Boddington S, Henning TD, Sutton EJ, Daldrup-Link HE. (2008). Labeling stem cells with fluorescent dyes for non-invasive detection with optical imaging. J Vis Exp. 14:e686 10.3791/686 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Tögel F, Yang Y, Zhang P, Hu Z, Westenfelder C. Bioluminescence imaging to monitor the in vivo distribution of administered mesenchymal stem cells in acute kidney injury. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. (2008) 295:F315–21. 10.1152/ajprenal.00098.2008 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Fink J, Andersson-Rolf A, Koo B.-K. Adult stem cell lineage tracing and deep tissue imaging. BMB Rep. (2015) 48:655–67. 10.5483/BMBRep.2015.48.12.249 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Spalteholz W. Über das Durchsightigmachen Von Menschlichen und Tierischen Präparaten: Nebst Anhang, Über Knochenfärbung. Leipzig: Verlag von S. Hirzel; (1911). [Google Scholar]
- 141.Oldham M, Sakhalkar H, Oliver T, Allan Johnson G, Dewhirst M. Optical clearing of unsectioned specimens for three-dimensional imaging via optical transmission and emission tomography. J Biomed Opt. (2008) 13:021113. 10.1117/1.2907968 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Chung K, Wallace J, Kim SY, Kalyanasundaram S, Andalman AS, Davidson TJ, et al. Structural and molecular interrogation of intact biological systems. Nature (2013) 497:332–7. 10.1038/nature12107 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Lee H, Park JH, Seo I, Park SH, Kim S. Improved application of the electrophoretic tissue clearing technology, CLARITY, to intact solid organs including brain, pancreas, liver, kidney, lung, and intestine. BMC Dev Biol. (2014) 14:48. 10.1186/s12861-014-0048-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Tomer R, Ye L, Hsueh B, Deisseroth K. Advanced CLARITY for rapid and high-resolution imaging of intact tissues. Nat Protoc. (2014) 9:1682–97. 10.1038/nprot.2014.123 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Yang B, Treweek JB, Kulkarni RP, Deverman BE, Chen CK, Lubeck E, et al. Single-cell phenotyping within transparent intact tissue through whole-body clearing. Cell (2014) 158:945–58. 10.1016/j.cell.2014.07.017 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Ke MT, Fujimoto S, Imai T. SeeDB: a simple and morphology-preserving optical clearing agent for neuronal circuit reconstruction. Nat Neurosci. (2013) 16:1154–61. 10.1038/nn.3447 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Klingberg A, Hasenberg A, Ludwig-Portugall I, Medyukhina A, Mann L, Brenzel A, et al. Fully automated evaluation of total glomerular number and capillary tuft size in nephritic kidneys using lightsheet microscopy. J Am Soc Nephrol. (2017) 28:452–59. 10.1681/ASN.2016020232 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Richardson DS, Lichtman JW. Clarifying tissue clearing. Cell (2015) 162:246–57. 10.1016/j.cell.2015.06.067 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Seo J, Choe M, Kim S.-Y. Clearing and Labeling Techniques for Large-Scale Biological Tissues. Molecules and Cells (2016) 39:439–446. 10.14348/molcells.2016.0088 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Collett JA, Traktuev DO, Mehrotra P, Crone A, Merfeld-Clauss S, March KL, et al. Human adipose stromal cell therapy improves survival and reduces renal inflammation and capillary rarefaction in acute kidney injury. J Cell Mol Med. (2017) 21:1420–30. 10.1111/jcmm.13071 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Rodrigues CE, Capcha JM, de Braganca AC, Sanches TR, Gouveia PQ, de Oliveira PA, et al. Human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stromal cells protect against premature renal senescence resulting from oxidative stress in rats with acute kidney injury. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2017) 8:19. 10.1186/s13287-017-0475-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Zhou L, Song Q, Shen J, Xu L, Xu Z, Wu R, et al. Comparison of human adipose stromal vascular fraction and adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells for the attenuation of acute renal ischemia/reperfusion injury. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:44058. 10.1038/srep44058 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Zhu F, Chong Lee Shin OLS, Pei G, Hu Z, Yang J, Zhu H, et al. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells employed exosomes to attenuate AKI-CKD transition through tubular epithelial cell dependent Sox9 activation. Oncotarget (2017) 8:70707–26. 10.18632/oncotarget.19979 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Mori da Cunha MG, Zia S, Beckmann DV, Carlon MS, Arcolino FO, Albersen M, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor up-regulation in human amniotic fluid stem cell enhances nephroprotection after ischemia-reperfusion injury in the rat. Crit Care Med. (2017) 45:e86–96. 10.1097/ccm.0000000000002020 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.Fahmy SR, Soliman AM, El Ansary M, Elhamid SA, Mohsen H. Therapeutic efficacy of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells transplantation against renal ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Tissue Cell (2017) 49:369–75. 10.1016/j.tice.2017.04.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Ranghino A, Bruno S, Bussolati B, Moggio A, Dimuccio V, Tapparo M, et al. The effects of glomerular and tubular renal progenitors and derived extracellular vesicles on recovery from acute kidney injury. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2017) 8:24. 10.1186/s13287-017-0478-5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Sun P, Liu J, Li W, Xu X, Gu X, Li H, et al. Human endometrial regenerative cells attenuate renal ischemia reperfusion injury in mice. J Transl Med. (2016) 14:28. 10.1186/s12967-016-0782-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158.Vinas JL, Burger D, Zimpelmann J, Haneef R, Knoll W, Campbell P, et al. Transfer of microRNA-486-5p from human endothelial colony forming cell-derived exosomes reduces ischemic kidney injury. Kidney Int. (2016) 90:1238–50. 10.1016/j.kint.2016.07.015 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159.Zhang G, Zou X, Huang Y, Wang F, Miao S, Liu G, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cell-derived extracellular vesicles protect against acute kidney injury through anti-oxidation by enhancing Nrf2/ARE activation in rats. Kidney Blood Press Res. (2016) 41:119–28. 10.1159/000443413 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160.Zou XY, Gu D, Xing XY, Cheng ZL, Gong DL, Zhang GY, et al. Human mesenchymal stromal cell-derived extracellular vesicles alleviate renal ischemic reperfusion injury and enhance angiogenesis in rats. Am J Transl Res. (2016) 8:4289–99. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161.Gu D, Zou XY, Ju GQ, Zhang GY, Bao ED, Zhu YJ. Mesenchymal stromal cells derived extracellular vesicles ameliorate acute renal ischemia reperfusion injury by inhibition of mitochondrial fission through miR-30. Stem Cells Int. (2016) 2016:2093940. 10.1155/2016/2093940 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 162.Ju GQ, Cheng J, Zhong L, Wu S, Zou XY, Zhang GY, et al. Microvesicles derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells facilitate tubular epithelial cell dedifferentiation and growth via hepatocyte growth factor induction. PLoS ONE (2015) 10:e0121534. 10.1371/journal.pone.0121534 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 163.Liang CJ, Shen WC, Chang FB, Wu VC, Wang SH, Young GH, et al. Endothelial progenitor cells derived from wharton's jelly of human umbilical cord attenuate ischemic acute kidney injury by increasing vascularization and decreasing apoptosis, inflammation, and fibrosis. Cell Transplant. (2015) 24:1363–77. 10.3727/096368914x681720 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 164.Monteiro Carvalho Mori da Cunha MG, Zia S, Oliveira Arcolino F, Carlon MS, Beckmann DV, Pippi NL, et al. Amniotic fluid derived stem cells with a renal progenitor phenotype inhibit interstitial fibrosis in renal ischemia and reperfusion injury in rats. PLoS ONE (2015) 10:e0136145 10.1371/journal.pone.0136145 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 165.Toyohara T, Mae S, Sueta S, Inoue T, Yamagishi Y, Kawamoto T, et al. Cell Therapy using human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived renal progenitors ameliorates acute kidney injury in mice. Stem Cells Transl Med. (2015) 4:980–92. 10.5966/sctm.2014-0219 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 166.Hattori Y, Kim H, Tsuboi N, Yamamoto A, Akiyama S, Shi Y, et al. Therapeutic potential of stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth in models of acute kidney injury. PLoS ONE (2015) 10:e0140121 10.1371/journal.pone.0140121 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 167.Wise AF, Williams TM, Kiewiet MBG, Payne NL, Siatskas C, Samuel CS, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells alter macrophage phenotype and promote regeneration via homing to the kidney following ischemia-reperfusion injury. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. (2014) 306:F1222–35. 10.1152/ajprenal.00675.2013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 168.Zou X, Zhang G, Cheng Z, Yin D, Du T, Ju G, et al. Microvesicles derived from human Wharton's Jelly mesenchymal stromal cells ameliorate renal ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats by suppressing CX3CL1. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2014) 5:40. 10.1186/scrt428 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 169.Jang HR, Park JH, Kwon GY, Lee JE, Huh W, Jin HJ, et al. Effect of preemptive treatment with human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells on the development of renal ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. (2014) 307:1149–61. 10.1152/ajprenal.00555.2013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 170.Du T, Zou X, Cheng J, Wu S, Zhong L, Ju G, et al. Human Wharton's jelly-derived mesenchymal stromal cells reduce renal fibrosis through induction of native and foreign hepatocyte growth factor synthesis in injured tubular epithelial cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2013) 4:59. 10.1186/scrt215 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 171.Li W, Zhang Q, Wang M, Wu HY, Mao F, Zhang B, et al. Macrophages are involved in the protective role of human umbilical cord-derived stromal cells in renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Stem Cell Res. (2013) 10:405–16. 10.1016/j.scr.2013.01.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 172.Kilpinen L, Impola U, Sankkila L, Ritamo I, Aatonen M, Kilpinen S, et al. Extracellular membrane vesicles from umbilical cord blood-derived MSC protect against ischemic acute kidney injury, a feature that is lost after inflammatory conditioning. J Extracell Vesicles (2013) 2:21927. 10.3402/jev.v2i0.21927 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 173.Burger D, Gutsol A, Carter A, Allan DS, Touyz RM, Burns KD. Human cord blood CD133+ cells exacerbate ischemic acute kidney injury in mice. Nephrol Dial Transplant. (2012) 27:3781–9. 10.1093/ndt/gfs110 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 174.Cantaluppi V, Gatti S, Medica D, Figliolini F, Bruno S, Deregibus MC, et al. Microvesicles derived from endothelial progenitor cells protect the kidney from ischemia-reperfusion injury by microRNA-dependent reprogramming of resident renal cells. Kidney Int. (2012) 82:412–27. 10.1038/ki.2012.105 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 175.Gatti S, Bruno S, Deregibus MC, Sordi A, Cantaluppi V, Tetta C, et al. Microvesicles derived from human adult mesenchymal stem cells protect against ischaemia-reperfusion-induced acute and chronic kidney injury. Nephrol Dial Transplant. (2011) 26:1474–83. 10.1093/ndt/gfr015 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 176.La Manna G, Bianchi F, Cappuccilli M, Cenacchi G, Tarantino L, Pasquinelli G, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells in renal function recovery after acute kidney injury: use of a differentiating agent in a rat model. Cell Transplant. (2011) 20:1193–208. 10.3727/096368910x543394 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 177.Chen Y, Qian H, Zhu W, Zhang X, Yan Y, Ye S, et al. Hepatocyte growth factor modification promotes the amelioration effects of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on rat acute kidney injury. Stem Cells Dev. (2011) 20:103–13. 10.1089/scd.2009.0495 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 178.Cao H, Qian H, Xu W, Zhu W, Zhang X, Chen Y, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells derived from human umbilical cord ameliorate ischemia/reperfusion-induced acute renal failure in rats. Biotechnol Lett. (2010) 32:725–32. 10.1007/s10529-010-0207-y [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 179.Veceric-Haler Z, Erman A, Cerar A, Motaln H, Kolosa K, Lah Turnsek T, et al. Improved protective effect of umbilical cord stem cell transplantation on cisplatin-induced kidney injury in mice pretreated with antithymocyte globulin. Stem Cells Int. (2016) 2016:3585362. 10.1155/2016/3585362 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 180.Elhusseini FM, Saad MA, Anber N, Elghannam D, Sobh MA, Alsayed A, et al. Long term study of protective mechanisms of human adipose derived mesenchymal stem cells on cisplatin induced kidney injury in sprague-dawley rats. J Stem Cells Regen Med. (2016) 12:36–48. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 181.Ashour RH, Saad MA, Sobh MA, Al-Husseiny F, Abouelkheir M, Awad A, et al. Comparative study of allogenic and xenogeneic mesenchymal stem cells on cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury in Sprague-Dawley rats. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2016) 7:126. 10.1186/s13287-016-0386-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 182.Al-Husseiny F, Sobh MA, Ashour RH, Foud S, Medhat T, El-Gilany AH, et al. Amniotic fluid-derived mesenchymal stem cells cut short the acuteness of cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in sprague-dawley rats. Int J Stem Cells (2016) 9:70–78. 10.15283/ijsc.2016.9.1.70 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 183.Wang WW, Li ZZ, Wang W, Jiang Y, Cheng J, Lu S, et al. Enhanced renoprotective effect of HIF-1alpha modified human adipose-derived stem cells on cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury in vivo. Sci Rep. (2015) 5:10851. 10.1038/srep10851 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 184.Yao W, Hu Q, Ma Y, Xiong W, Wu T, Cao J, et al. Human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells repair cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury through antiapoptotic pathways. Exp Ther Med. (2015) 10:468–76. 10.3892/etm.2015.2505 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 185.Burks SR, Nguyen BA, Tebebi PA, Kim SJ, Bresler MN, Ziadloo A, et al. Pulsed focused ultrasound pretreatment improves mesenchymal stromal cell efficacy in preventing and rescuing established acute kidney injury in mice. Stem Cells (2015) 33:1241–53. 10.1002/stem.1965 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 186.Saad M.-A., Elhusseini F, Sobh M.-A, Ashour R, Abouelkheir M, Awad A, et al. Study of the effect of source of mesenchymal stemcells on cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury in sprague daweley rats. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation. In: Conference: 52nd ERA-EDTA Congress London United Kingdom. Conference Start: 20150528 Conference End: 20150531. Conference Publication: (var.pagings) [Online], Mansoura: (2015). p. 30. [Google Scholar]
- 187.Shalaby RH, Rashed LA, Ismaail AE, Madkour NK, Elwakeel SH. Hematopoietic stem cells derived from human umbilical cord ameliorate cisplatin-induced acute renal failure in rats. Am J Stem Cells (2014) 3:83–96. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 188.Gheisari Y, Ahmadbeigi N, Aghaee-Bakhtiari SH, Nassiri SM, Amanpour S, Azadmanesh K, et al. Human unrestricted somatic stem cell administration fails to protect nude mice from cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury. Nephron Exp Nephrol. (2013) 123:11–21. 10.1159/000353233 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 189.Dorronsoro A, Robbins PD. Regenerating the injured kidney with human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2013) 4:39. 10.1186/scrt187 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 190.Luo J, Zhao X, Tan Z, Su Z, Meng F, Zhang M. Mesenchymal-like progenitors derived from human embryonic stem cells promote recovery from acute kidney injury via paracrine actions. Cytotherapy (2013) 15:649–62. 10.1016/j.jcyt.2013.01.009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 191.Milwid JM, Ichimura T, Li M, Jiao YX, Lee J, Yarmush JS, et al. Secreted factors from bone marrow stromal cells upregulate IL-10 and reverse acute kidney injury. Stem Cells Int. (2012) 2012:392050. 10.1155/2012/392050 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 192.Rota C, Imberti B, Pozzobon M, Piccoli M, De Coppi P, Atala A, et al. Human amniotic fluid stem cell preconditioning improves their regenerative potential. Stem Cells Dev. (2012) 21:1911–23. 10.1089/scd.2011.0333 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 193.Yuan L, Wu MJ, Sun HY, Xiong J, Zhang Y, Liu CY, et al. VEGF-modified human embryonic mesenchymal stem cell implantation enhances protection against cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. (2011) 300:F207–18. 10.1152/ajprenal.00073.2010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 194.Gheisari Y, Ahmadbeigi N, Naderi M, Nassiri SM, Nadri S, Soleimani M. Stem cell-conditioned medium does not protect against kidney failure. Cell Biol Int. (2011) 35:209–13. 10.1042/cbi20100183 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 195.Eliopoulos N, Zhao J, Bouchentouf M, Forner K, Birman E, Yuan S, et al. Human marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells decrease cisplatin renotoxicity in vitro and in vivo and enhance survival of mice post-intraperitoneal injection. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. (2010) 299:1288–98. 10.1152/ajprenal.00671.2009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 196.Morigi M, Introna M, Imberti B, Corna D, Abbate M, Rota C, et al. Human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells accelerate recovery of acute renal injury and prolong survival in mice. Stem Cells (2008) 26:2075–82. 10.1634/stemcells.2007-0795 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 197.Jiang ZZ, Liu YM, Niu X, Yin JY, Hu B, Guo SC, et al. Exosomes secreted by human urine-derived stem cells could prevent kidney complications from type I diabetes in rats. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2016) 7:24. 10.1186/s13287-016-0287-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 198.Park JH, Hwang I, Hwang SH, Han H, Ha H. Human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells prevent diabetic renal injury through paracrine action. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. (2012) 98:465–73. 10.1016/j.diabres.2012.09.034 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 199.Masoad RE, Ewais MM, Tawfik MK, Abd El-All HS. Effect of mononuclear cells versus pioglitazone on streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy in rats. Pharmacol Rep. (2012) 64:1223–33. 10.1016/s1734-1140(12)70918-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 200.Remuzzi G, Perico N, Introna M, Rambaldi A, Tondini C. Ex-vivo expanded mesenchymal stem cells to repair the kidney and improve function in cisplatin-induced acute renal failure in patients with solid organ cancers (2011). [Google Scholar]
- 201.Packham DK, Fraser IR, Kerr PG, Segal KR. Allogeneic mesenchymal precursor cells (MPC) in diabetic nephropathy: a randomized, placebo-controlled, dose escalation study. EBioMed. (2016) 12:263–9. 10.1016/j.ebiom.2016.09.011 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 202.Maezawa Y, Takemoto M, Yokote K. Cell biology of diabetic nephropathy: roles of endothelial cells, tubulointerstitial cells and podocytes. J Diabetes Investig. (2015) 6:3–15. 10.1111/jdi.12255 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 203.Griffin M, Cockwell P, Maxwell P. (2015). Novel Stromal Cell Therapy for Diabetic Kidney Disease (NEPHSTROM Study). [Google Scholar]
- 204.Makhlough A, Shekarchian S, Moghadasali R, Einollahi B, Hosseini SE, Jaroughi N, et al. Safety and tolerability of autologous bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells in ADPKD patients. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2017) 8:116. 10.1186/s13287-017-0557-7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 205.Sun Q, Hong L, Huang Z, Na N, Hua X, Peng Y, et al. Allogeneic mesenchymal stem cell as induction therapy to prevent both delayed graft function and acute rejection in deceased donor renal transplantation: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials (2017) 18:545. 10.1186/s13063-017-2291-y [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 206.Leventhal JR, Elliott MJ, Yolcu ES, Bozulic LD, Tollerud DJ, Mathew JM, et al. Immune reconstitution/immunocompetence in recipients of kidney plus hematopoietic stem/facilitating cell transplants. Transplantation (2015) 99:288–98. 10.1097/TP.0000000000000605 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 207.Irish A. Mesenchymal stem cells to prevent ischaemia reperfusion injury in deceased donor renal transplant recipients. (2015). [Google Scholar]
- 208.Rakha A, Todeschini M, Casiraghi F. Assessment of anti-donor T cell proliferation and cytotoxic T lymphocyte-mediated lympholysis in living donor kidney transplant patients. Methods Mol Biol (2014) 1213:355–64. 10.1007/978-1-4939-1453-1_29 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 209.Peng Y, Ke M, Xu L, Liu L, Chen X, Xia W, et al. Donor-derived mesenchymal stem cells combined with low-dose tacrolimus prevent acute rejection after renal transplantation a clinical pilot study. Transplantation (2013) 95:161–8. 10.1097/TP.0b013e3182754c53 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 210.Ciancio G, Sageshima J, Akpinar E, Gaynor JJ, Chen L, Zarak A, et al. A randomized pilot study of donor stem cell infusion in living-related kidney transplant recipients receiving alemtuzumab. Transplantation (2013) 96:800–6. 10.1097/TP.0b013e3182a0f68c [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 211.Reinders ME, de Fijter JW, Roelofs H, Bajema IM, de Vries DK, Schaapherder AF, et al. Autologous bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells for the treatment of allograft rejection after renal transplantation: results of a phase I study. Stem Cells Transl Med. (2013) 2:107–11. 10.5966/sctm.2012-0114 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 212.Ildstad ST. Delayed tolerance in recipients of living kidney allografts by donor FCRx infusion (2012). [Google Scholar]
- 213.Tan J, Wu W, Xu X, Liao L, Zheng F, Messinger S, et al. Induction therapy with autologous mesenchymal stem cells in living-related kidney transplants a randomized controlled trial. JAMA (2012) 307:1169–77. 10.1001/jama.2012.316 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 214.Hong J. Effect of co-transplantation of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and renal transplantation in long-term outcome of allograft (2011). [Google Scholar]
- 215.Infusion of third-party mesenchymal stem cells after renal or liver transplantation: a phase I-II open-label clinical study (2011). [Google Scholar]
- 216.Jianming T. Mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in the treatment of chronic allograft nephropathy (2011). [Google Scholar]
- 217.Ildstad ST. Induction of donor specific tolerance in recipients of live donor kidney allografts by donor stem cell infusion (2005). [Google Scholar]
- 218.Trivedi HL, Shah VR, Vanikar AV, Gera D, Shah PR, Trivedi VB, et al. High-dose peripheral blood stem cell infusion: a strategy to induce donor-specific hyporesponsiveness to allografts in pediatric renal transplant recipients. Pediatr Transplant. (2002) 6:63–8. 10.1034/j.1399-3046.2002.1o043.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 219.Bellomo R, Kellum JA, Ronco C. Acute kidney injury. Lancet (2012) 380:756–66. 10.1016/s0140-6736(11)61454-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 220.Rewa O, Bagshaw SM. Acute kidney injury-epidemiology, outcomes and economics. Nat Rev Nephrol. (2014) 10:193–207. 10.1038/nrneph.2013.282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 221.Wasung ME, Chawla LS, Madero M. Biomarkers of renal function, which and when? Clin Chim Acta (2015) 438:350–57. 10.1016/j.cca.2014.08.039 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 222.Leung KC, Tonelli M, James MT. Chronic kidney disease following acute kidney injury-risk and outcomes. Nat Rev Nephrol. (2013) 9:77–85. 10.1038/nrneph.2012.280 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 223.Chawla LS, Eggers PW, Star RA, Kimmel PL. Acute kidney injury and chronic kidney disease as interconnected syndromes. N Engl J Med. (2014) 371:58–66. 10.1056/NEJMra1214243 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 224.Bamoulid J, Staeck O, Halleck F, Khadzhynov D, Brakemeier S, Durr M, et al. The need for minimization strategies: current problems of immunosuppression. Transpl Int. (2015) 28:891–900. 10.1111/tri.12553 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 225.Carden DL, Granger DN. Pathophysiology of ischaemia-reperfusion injury. J Pathol. (2000) 190:255–66. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 226.Eltzschig HK, Eckle T. Ischemia and reperfusion–from mechanism to translation. Nat Med. (2011) 17:1391–1401. 10.1038/nm.2507 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 227.Bonventre JV, Yang L. Cellular pathophysiology of ischemic acute kidney injury. J Clin Invest. (2011) 121:4210–21. 10.1172/jci45161 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 228.Rosen S, Heyman SN. Difficulties in understanding human “acute tubular necrosis”: limited data and flawed animal models. Kidney Int. (2001) 60:1220–24. 10.1046/j.1523-1755.2001.00930.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 229.Behr L, Hekmati M, Fromont G, Borenstein N, Noel LH, Lelievre-Pegorier M, et al. Intra renal arterial injection of autologous mesenchymal stem cells in an ovine model in the postischemic kidney. Nephron Physiol. (2007) 107:65–76. 10.1159/000109821 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 230.Liu X, Cai J, Jiao X, Yu X, Ding X. Therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cells in acute kidney injury is affected by administration timing. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (2017) 49:338–48. 10.1093/abbs/gmx016 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 231.Shih YC, Lee PY, Cheng H, Tsai CH, Ma H, Tarng DC. Adipose-derived stem cells exhibit antioxidative and antiapoptotic properties to rescue ischemic acute kidney injury in rats. Plast Reconstr Surg. (2013) 132:940–51e. 10.1097/PRS.0b013e3182a806ce [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 232.Zhuo W, Liao L, Xu T, Wu W, Yang S, Tan J. Mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate ischemia-reperfusion-induced renal dysfunction by improving the antioxidant/oxidant balance in the ischemic kidney. Urol Int. (2011) 86:191–96. 10.1159/000319366 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 233.Feng Z, Ting J, Alfonso Z, Strem BM, Fraser JK, Rutenberg J, et al. Fresh and cryopreserved, uncultured adipose tissue-derived stem and regenerative cells ameliorate ischemia-reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury. Nephrol Dial Transplant. (2010) 25:3874–84. 10.1093/ndt/gfq603 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 234.Zhang JB, Wang XQ, Lu GL, Huang HS, Xu SY. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells therapy for acute kidney injury induced by ischemia-reperfusion in a rat model. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. (2017) 44:1232–40. 10.1111/1440-1681.12811 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 235.Lee PY, Chien Y, Chiou GY, Lin CH, Chiou CH, Tarng DC. Induced pluripotent stem cells without c-Myc attenuate acute kidney injury via downregulating the signaling of oxidative stress and inflammation in ischemia-reperfusion rats. Cell Transplant. (2012) 21:2569–85. 10.3727/096368912x636902 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 236.Miller RP, Tadagavadi RK, Ramesh G, Reeves WB. Mechanisms of cisplatin nephrotoxicity. Toxins (2010) 2:2490–518. 10.3390/toxins2112490 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 237.Sharp CN, Doll MA, Dupre TV, Shah PP, Subathra M, Siow D, et al. Repeated administration of low-dose cisplatin in mice induces fibrosis. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. (2016) 310, F560–68. 10.1152/ajprenal.00512.2015 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 238.Morigi M, Imberti B, Zoja C, Corna D, Tomasoni S, Abbate M, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells are renotropic, helping to repair the kidney and improve function in acute renal failure. J Am Soc Nephrol. (2004) 15:1794–804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 239.Moustafa FE, Sobh MA, Abouelkheir M, Khater Y, Mahmoud K, Saad MA, et al. Study of the effect of route of administration of mesenchymal stem cells on cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury in sprague dawley rats. Int J Stem Cells (2016) 9:79–89. 10.15283/ijsc.2016.9.1.79 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 240.Sherif IO, Al-Mutabagani LA, Alnakhli AM, Sobh MA, Mohammed HE. Renoprotective effects of angiotensin receptor blocker and stem cells in acute kidney injury: involvement of inflammatory and apoptotic markers. Exp Biol Med. (2015) 240:1572–9. 10.1177/1535370215577582 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 241.Molitch ME, DeFronzo RA, Franz MJ, Keane WF, Mogensen CE, Parving HH, et al. Nephropathy in diabetes. Diabetes Care (2004) 27(Suppl. 1):S79–83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 242.Piccoli GB, Grassi G, Cabiddu G, Nazha M, Roggero S, Capizzi I, et al. Diabetic kidney disease: a syndrome rather than a single disease. Rev Diabet Stud. (2015) 12:87–109. 10.1900/RDS.2015.12.87 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 243.Persson F, Rossing P. Diagnosis of diabetic kidney disease: state of the art and future perspective. Kidney Int Suppl. (2018) 8:2–7. 10.1016/j.kisu.2017.10.003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 244.Ponchiardi C, Mauer M, Najafian B. Temporal profile of diabetic nephropathy pathologic changes. Curr Diab Rep. (2013) 13:592–9. 10.1007/s11892-013-0395-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 245.Wendt T. Glucose, glycation, and RAGE: implications for amplification of cellular dysfunction in diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol. (2003) 14:1383–95. 10.1097/01.asn.0000065100.17349.ca [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 246.Reidy K, Kang HM, Hostetter T, Susztak K. Molecular mechanisms of diabetic kidney disease. J Clin Invest. (2014) 124:2333–40. 10.1172/JCI72271 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 247.Sagoo MK, Gnudi L. Diabetic nephropathy: is there a role for oxidative stress? Free Radic Biol Med. (2018) 116:50–63. 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2017.12.040 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 248.Betz B, Conway BR. An update on the use of animal models in diabetic nephropathy research. Curr Diab Rep. (2016) 16:18. 10.1007/s11892-015-0706-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 249.Ezquer FE, Ezquer ME, Parrau DB, Carpio D, Yanez AJ, Conget PA. Systemic administration of multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells reverts hyperglycemia and prevents nephropathy in type 1 diabetic mice. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. (2008) 14:631–40. 10.1016/j.bbmt.2008.01.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 250.Ezquer F, Ezquer M, Simon V, Pardo F, Yanez A, Carpio D, et al. Endovenous administration of bone-marrow-derived multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells prevents renal failure in diabetic mice. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. (2009) 15:1354–65. 10.1016/j.bbmt.2009.07.022 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 251.Ezquer F, Giraud-Billoud M, Carpio D, Cabezas F, Conget P, Ezquer M. Proregenerative microenvironment triggered by donor mesenchymal stem cells preserves renal function and structure in mice with severe diabetes mellitus. Biomed Res Int. (2015) 3:1–23. 10.1155/2015/164703 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 252.Wang S, Li Y, Zhao J, Zhang J, Huang Y. Mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate podocyte injury and proteinuria in a type 1 diabetic nephropathy rat model. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. (2013) 19:538–46. 10.1016/j.bbmt.2013.01.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 253.Zhang L, Li K, Liu X, Li D, Luo C, Fu B, et al. Repeated systemic administration of human adipose-derived stem cells attenuates overt diabetic nephropathy in rats. Stem Cells Dev. (2013) 22:3074–86. 10.1089/scd.2013.0142 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 254.Zhang Y, Ye C, Wang G, Gao Y, Tan K, Zhuo Z, et al. Kidney-targeted transplantation of mesenchymal stem cells by ultrasound-targeted microbubble destruction promotes kidney repair in diabetic nephropathy rats. Biomed Res Int. (2013) 2013:526367. 10.1155/2013/526367 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 255.Abdel Aziz MT, Wassef MA, Ahmed HH, Rashed L, Mahfouz S, Aly MI, et al. The role of bone marrow derived-mesenchymal stem cells in attenuation of kidney function in rats with diabetic nephropathy. Diabetol Metab Syndr. (2014) 6:34. 10.1186/1758-5996-6-34 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 256.Lv S, Cheng J, Sun A, Li J, Wang W, Guan G, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells transplantation ameliorates glomerular injury in streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy in rats via inhibiting oxidative stress. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. (2014) 104:143–54. 10.1016/j.diabres.2014.01.011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 257.Lv S, Liu G, Sun A, Wang J, Cheng J, Wang W, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate diabetic glomerular fibrosis in vivo and in vitro by inhibiting TGF-beta signalling via secretion of bone morphogenetic protein 7. Diab Vasc Dis Res. (2014) 11:251–61. 10.1177/1479164114531300 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 258.Lang H, Dai C. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 and renal fibrosis in rats with diabetic nephropathy. Arch Med Res. (2016) 47:71–7. 10.1016/j.arcmed.2016.03.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 259.Nagaishi K, Mizue Y, Chikenji T, Otani M, Nakano M, Konari N, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell therapy ameliorates diabetic nephropathy via the paracrine effect of renal trophic factors including exosomes. Sci Rep. (2016) 6:34842. 10.1038/srep34842 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 260.Nagaishi K, Mizue Y, Chikenji T, Otani M, Nakano M, Saijo Y, et al. Umbilical cord extracts improve diabetic abnormalities in bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells and increase their therapeutic effects on diabetic nephropathy. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:8484. 10.1038/s41598-017-08921-y [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 261.Jian OY, Hu G, Wen YT, Zhang X. Preventive effects of syngeneic bone marrow transplantation on diabetic nephropathy in mice. Transplant Immunol. (2010) 22:184–90. 10.1016/j.trim.2009.12.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 262.Hamza AH, Al-Bishri WM, Damiati LA, Ahmed HH. Mesenchymal stem cells: a future experimental exploration for recession of diabetic nephropathy. Ren Fail. (2016) 39:67–76. 10.1080/0886022x.2016.1244080 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 263.Yang G, Cheng QL, Liu S, Zhao JH. The role of bone marrow cells in the phenotypic changes associated with diabetic nephropathy. PLoS ONE (2015) 10:e0137245. 10.1371/journal.pone.0137245 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 264.Wilson PD. Polycystic kidney disease. N Engl J Med. (2004) 350:151–64. 10.1056/NEJMra022161 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 265.Harris PC, Rossetti S. Molecular genetics of autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease. Mol Genet Metab. (2004) 81:75–85. 10.1016/j.ymgme.2003.10.010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 266.Osathanondh V, Potter EL. Pathogenesis of polycystic kidneys. type 1 due to hyperplasia of interstitial portions of collecting tubules. Arch Pathol. (1964) 77:466–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 267.Harris PC. Molecular basis of polycystic kidney disease: PKD1, PKD2 and PKHD1. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. (2002) 11:309–14. 10.1097/00041552-200205000-00007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 268.Torra R. Autosomal dominant policystic kidney disease, more than a renal disease. Minerva Endocrinol. (2014) 39:79–87. 10.1016/S0272-6386(12)80051-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 269.Lager DJ, Qian Q, Bengal RJ, Ishibashi M, Torres VE. The pck rat: a new model that resembles human autosomal dominant polycystic kidney and liver disease. Kidney Int. (2001) 59:126–36. 10.1046/j.1523-1755.2001.00473.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 270.Neudecker S, Walz R, Menon K, Maier E, Bihoreau MT, Obermuller N, et al. Transgenic overexpression of Anks6(p.R823W) causes polycystic kidney disease in rats. Am J Pathol. (2010) 177:3000–9. 10.2353/ajpath.2010.100569 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 271.Nagao S, Kugita M, Yoshihara D, Yamaguchi T. Animal models for human polycystic kidney disease. Exp Anim. (2012) 61:477–88. 10.1538/expanim.61.477 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 272.Shoieb A, Shirai N. Polycystic kidney disease in Sprague-Dawley rats. Exp Toxicol Pathol. (2015) 67:361–4. 10.1016/j.etp.2015.02.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 273.Franchi F, Peterson KM, Xu R, Miller B, Psaltis PJ, Harris PC, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells improve renovascular function in polycystic kidney disease. Cell Transplant. (2015) 24:1687–98. 10.3727/096368914X684619 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 274.Kelly KJ, Zhang J, Han L, Kamocka M, Miller C, Gattone VH, II, et al. Improved structure and function in autosomal recessive polycystic rat kidneys with renal tubular cell therapy. PLoS ONE (2015) 10:e0131677. 10.1371/journal.pone.0131677 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 275.Haavisto A, Jalanko H, Sintonen H, Holmberg C, Qvist E. Quality of life in adult survivors of pediatric kidney transplantation. Transplantation (2011) 92:1322–6. 10.1097/TP.0b013e318237062b [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 276.Garcia GG, Harden P, Chapman J. The global role of kidney transplantation. Am J Nephrol. (2012) 35:259–64. 10.1159/000336371 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 277.Chung R, Howard K, Craig JC, Chapman JR, Turner R, Wong G. Economic evaluations in kidney transplantation: frequency, characteristics, and quality-a systematic review. Transplantation (2014) 97:1027–33. 10.1097/tp.0000000000000079 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 278.Veroux P, Puliatti C, Veroux M, Cappello D, Macarone M, Puliatti D, et al. Kidney transplantation from marginal donors. Transplant Proc. (2004) 36:497–8. 10.1016/j.transproceed.2004.02.012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 279.Hirth RA, Pan Q, Schaubel DE, Merion RM. Efficient utilization of the expanded criteria donor (ECD) deceased donor kidney pool: an analysis of the effect of labeling. Am J Transplant. (2010) 10:304–9. 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2009.02937.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 280.Nijboer WN, Moers C, Leuvenink HG, Ploeg RJ. How important is the duration of the brain death period for the outcome in kidney transplantation? Transpl Int. (2011) 24:14–20. 10.1111/j.1432-2277.2010.01150.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 281.Chen G, Wang C, Ko DS, Qiu J, Yuan X, Han M, et al. Comparison of outcomes of kidney transplantation from donation after brain death, donation after circulatory death, and donation after brain death followed by circulatory death donors. Clin Transplant. (2017) 31:e13110. 10.1111/ctr.13110 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 282.Nankivell BJ, Borrows RJ, Fung CL, O'Connell PJ, Allen RD, Chapman JR. The natural history of chronic allograft nephropathy. N Engl J Med. (2003) 349:2326–33. 10.1056/NEJMoa020009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 283.Reinders ME, de Fijter JW, Rabelink TJ. Mesenchymal stromal cells to prevent fibrosis in kidney transplantation. Curr Opin Organ Transplant. (2014) 19:54–9. 10.1097/mot.0000000000000032 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 284.Casiraghi F, Perico N, Cortinovis M, Remuzzi G. Mesenchymal stromal cells in renal transplantation: opportunities and challenges. Nat Rev Nephrol. (2016) 12:241–53. 10.1038/nrneph.2016.7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 285.Koch M, Lehnhardt A, Hu X, Brunswig-Spickenheier B, Stolk M, Brocker V, et al. Isogeneic MSC application in a rat model of acute renal allograft rejection modulates immune response but does not prolong allograft survival. Transpl Immunol. (2013) 29:43–50. 10.1016/j.trim.2013.08.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 286.Casiraghi F, Azzollini N, Todeschini M, Cavinato RA, Cassis P, Solini S, et al. Localization of mesenchymal stromal cells dictates their immune or proinflammatory effects in kidney transplantation. Am J Transplant. (2012) 12:2373–83. 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2012.04115.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 287.Zhang W, Qin C, Zhou ZM. Mesenchymal stem cells modulate immune responses combined with cyclosporine in a rat renal transplantation model. Transplant Proc. (2007) 39:3404–8. 10.1016/j.transproceed.2007.06.092 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 288.De Martino M, Zonta S, Rampino T, Gregorini M, Frassoni F, Piotti G, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells infusion prevents acute cellular rejection in rat kidney transplantation. Transplant Proc. (2010) 42:1331–5. 10.1016/j.transproceed.2010.03.079 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 289.Yu P, Wang Z, Liu Y, Xiao Z, Guo Y, Li M, et al. Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Effectively Reduce Histologic Changes in a Rat Model of Chronic Renal Allograft Rejection. Transplant Proc. (2017) 49:2194–203. 10.1016/j.transproceed.2017.09.038 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 290.Kato T, Okumi M, Tanemura M, Yazawa K, Kakuta Y, Yamanaka K, et al. Adipose tissue-derived stem cells suppress acute cellular rejection by TSG-6 and CD44 interaction in rat kidney transplantation. Transplantation (2014) 98:277–84. 10.1097/tp.0000000000000230 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 291.Hashmi S, Ahmed M, Murad MH, Litzow MR, Adams RH, Ball LM, et al. Survival after mesenchymal stromal cell therapy in steroid-refractory acute graft-versus-host disease: systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Haematol. (2016) 3:e45–52. 10.1016/s2352-3026(15)00224-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 292.Panes J, Garcia-Olmo D, Van Assche G, Colombel JF, Reinisch W, Baumgart DC, et al. Expanded allogeneic adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (Cx601) for complex perianal fistulas in Crohn's disease: a phase 3 randomised, double-blind controlled trial. Lancet (2016) 388:1281–90. 10.1016/s0140-6736(16)31203-x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 293.Bader P, Kuçi Z, Bakhtiar S, Basu O, Bug G, Dennis M, et al. (2018). Effective treatment of steroid and therapy-refractory acute graft-versus-host disease with a novel mesenchymal stromal cell product (MSC-FFM). Bone Marrow Transplant. [Epub ahead of print] 10.1038/s41409-018-0102-z [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]