Fig. 6.
The molecular mechanisms underlying pathological angiogenesis.
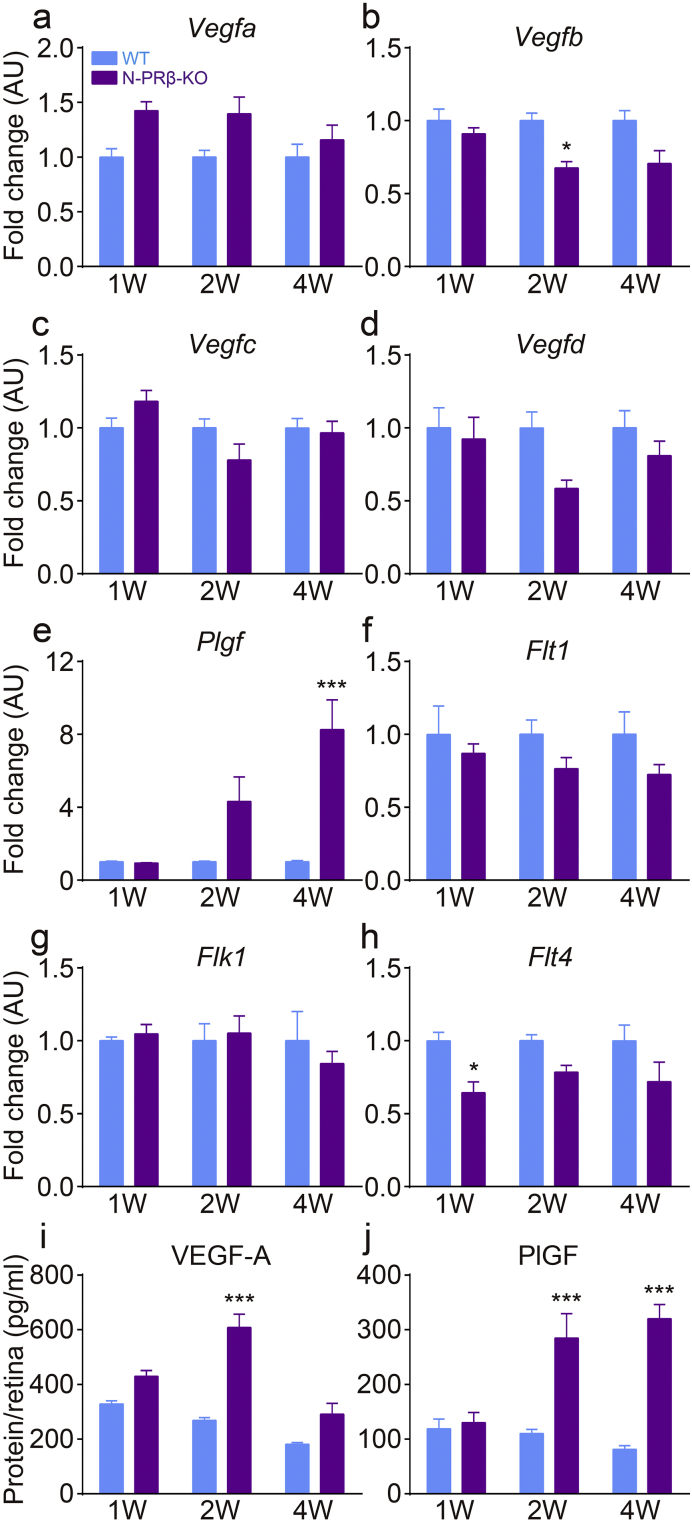
(a–e) Real-time PCR analyses of VEGF family ligands. Vegfa mRNA (a) expression in N-PRβ-KO mice tended to be higher compared to that of WT mice at 1 and 2 weeks. Plgf mRNA (e) expression in N-PRβ-KO mice was gradually upregulated from 2 weeks and was significantly higher at 4 weeks compared to the levels observed in WT mice. Vegfb (b), Vegfc (c), and Vegfd (d) mRNA levels in N-PRβ-KO mice were significantly lower or tended to be lower compared with those of WT mice at all time points. (f–h) Real-time PCR analyses of VEGF family receptors. Flt1 (f), Flk1 (g), and Flt4 (h) mRNA levels in N-PRβ-KO mice were significantly lower or tended to be lower than or comparable to levels observed in WT mice at all time points. n = 8 at the indicated time points. (i and j) ELISA results at 1- to 4-week retinas. VEGF-A expression (i) was significantly higher at 2 weeks in KO mice than WT mice, and decreased at 4 weeks. In N-PRβ-KO mice, PlGF (j) showed significantly higher expression at 2 and 4 weeks compared to the levels observed in WT mice. n = 11–15 at the indicated time points. All values represent means ± SEM. *, p < 0.05; ***, p < 0.001 vs. WT at the same time points.