FIG. 3.
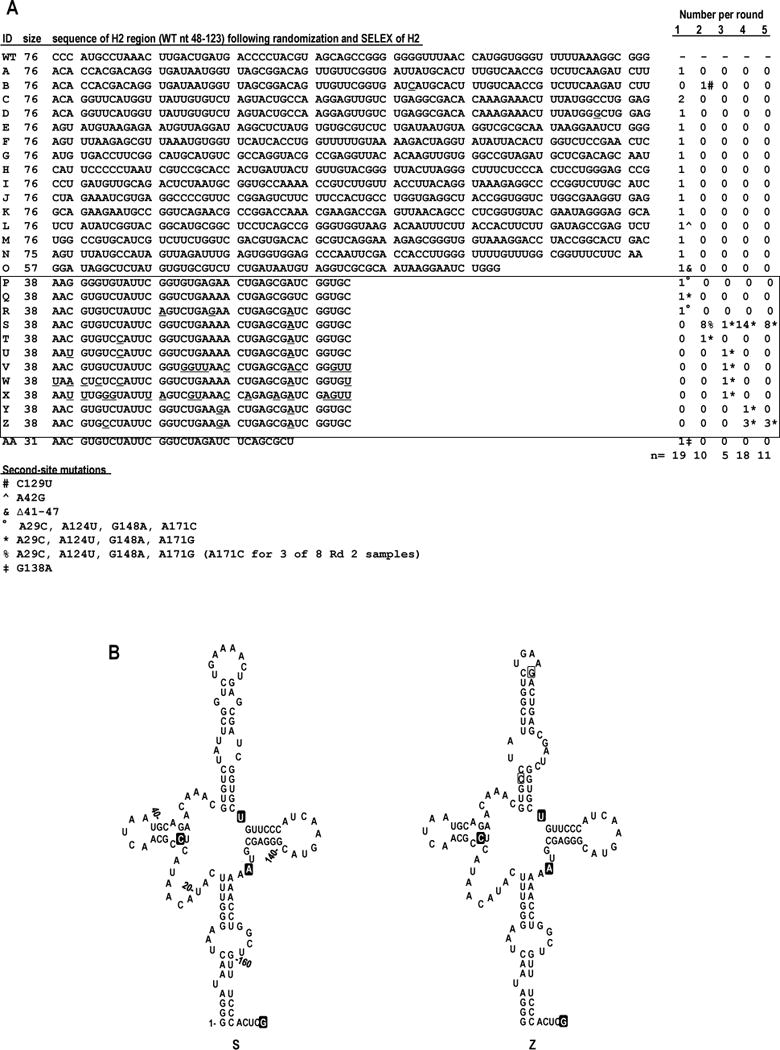
In vivo SELEX of satC76. (A) Results of five rounds of passaging satC with 76 random bases replacing H2 (satC76). Sequences related to the two nearly identical, most functional (“winning”) satCs (samples S and Z) are boxed. Underlined nt denote differences between related satC clones. Second-site mutations are identified by symbols and defined at the bottom of the figure. For reference, WT sequence for satC nt 48-123 is shown above sample A. (B) Secondary structure models for the 5′ region of SELEX winners S (left) and Z (right). Nucleotides within a filled box denote second-site mutations. Open boxed nucleotides in clone Z denote differences between S and Z.
