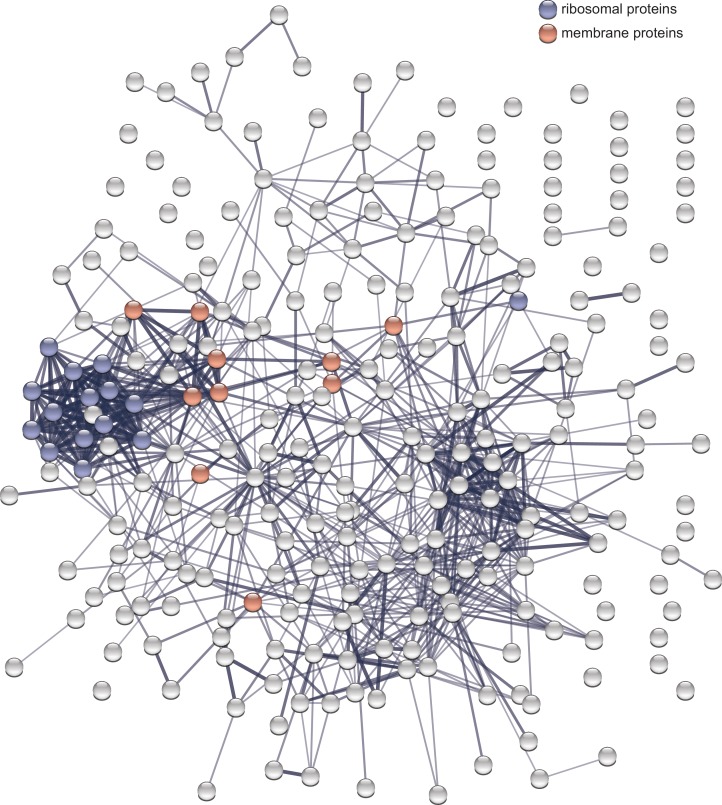
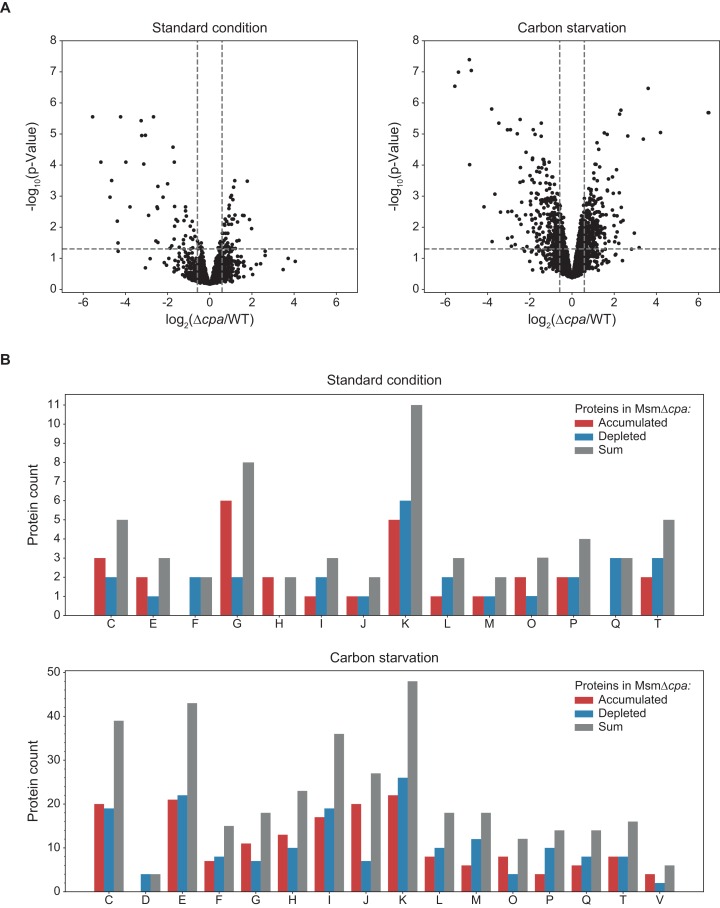
Figure 9. Label-free quantification mass spectrometry comparison of M. smegmatis WT with Δcpa proteome.
(A) Results of protein abundance comparison between the wt and the cpa-knockout strain using LFQ-MS (see Figure 9—source data 1). To filter the statistically-significant proteins, the p-value threshold was set to 0.05 (horizontal dashed line) and the fold-change threshold to 1.5 (vertical dashed lines). Under standard growth conditions (left plot), 49 proteins were found to accumulate (right side of the plot) and 45 proteins were found to be decreased (left side of the plot) in the knockout cells. Under carbon starvation (right plot), 254 proteins accumulated and 251 proteins were depleted in the knockout cells. (B) Those identified proteins for which a functional association was known or predicted, classification into functional classes using the COG classification system was carried out. Class abbreviations are as follows: C – energy production and conversion, D – cell cycle control and cell division, E – amino acid metabolism and transport, F – nucleotide metabolism and transport, G – carbohydrate metabolism and transport, H – coenzyme metabolism, I – lipid metabolism, J – translation/ribosomal structure and biogenesis, K – transcription, L – replication/recombination/repair, M – cell wall/membrane/envelope biogenesis, O – post-translational modification/protein turnover/chaperone functions, P – inorganic ion transport and metabolism, Q – secondary metabolites biosynthesis and catabolism, T – signal transduction, V – defense mechanisms. Proteins without an assigned class or assigned to class S (function unknown) were not included in the plot.