Abstract
Aim:
The aim of this study was to give an insight into the retrospective analysis of a number of maxillofacial trauma cases reported to our institute and research center.
Materials and Methods:
The data for this study was obtained from the medical records and outpatient prescription slips of cases treated at the Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Department from 2010 to 2016. Etiology, age, gender, pattern of fracture, and surgical treatment modalities undertaken in these patients were recorded.
Results:
A total of 353 maxillofacial trauma patients with mean age of 40 years, treated at our institute were evaluated from 2010 to 2016. Mandible was the most commonly fractured bone with parasymphysis as the most frequent site. Majority of victims were males (male:female ratio of 4:1) and also in the third decade of life. This study showed that 73% patients were treated by open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF), 25.8% by intermaxillary fixation (IMF) and Stabilization of fracture mandible with acrylic splint and circummandibular wiring was done in 0.8% pediatric patients.
Conclusion:
It was concluded that road traffic accidents were reported as the leading cause of maxillofacial fractures followed by assault, falls, and familial dispute. Maxillofacial surgeons as health care providers must continue their ‘face it’ campaign to decrease the incidence of road traffic accidents. Open reduction and internal fixation remains the gold standard treatment modality.
Keywords: Dental institute, mandibular fractures, maxillofacial trauma, retrospective study, road traffic accidents
INTRODUCTION
Maxillofacial trauma is a common presentation following injury to the face. Periodic evaluation of trauma patients helps us understand the demographics and epidemiology to increase awareness and strengthening the legislation to prevent such fractures.[1] Ludhiana is the largest city in the Indian state of Punjab (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ludhiana), with an estimated population of approximately 30 lakh (www.indiaonlinepages.com/population/punjab population.html). BJS Dental College and Hospital is situated in urban estate sector which is close to highways from Chandigarh and from New Delhi to Ludhiana.
The aim of this study was to give an insight into the retrospective analysis of a number of maxillofacial trauma cases reported to our institute and research center.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The data for this study were obtained from the medical records and outpatients slips of cases treated at the Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Department in Baba Jaswant Singh Dental College and Research Institute, from 2010 to 2016. Diagnosis of maxillofacial trauma was on the basis of clinical and radiographic examination. Etiology, age, gender, pattern of fracture, and surgical treatment modalities undertaken in these patients were recorded.
Evaluation of medical records was done after permission from the concerned authority in our institute.
RESULTS
A total of 353 patients (281 males and 72 females) aged 5–70 years (mean age of 40 years) with facial bone fractures treated at our institute evaluated from 2010 to 2016. The most common cause of trauma was road traffic accidents (RTAs) followed by assault. Falls were the third and family dispute was the least common cause of trauma. Fractures were more frequently observed in 21–30 years age group. Male:female ratio was 4:1. Mandible was the most common bone to fracture with parasymphysis as the frequent anatomic location. Pattern of fractures observed is presented in Table 4.
Table 4.
Pattern of fracture
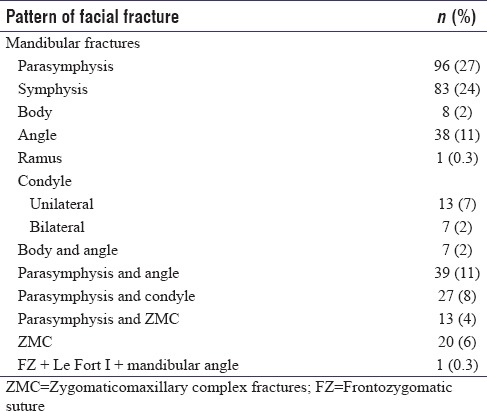
Patients were treated by open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) (259 patients, 73%) and intermaxillary fixation (IMF) (91 patients, 25.8%). Stabilization of fracture of mandible with acrylic splint and circummandibular wiring was done in three pediatric patients (0.8%) under conscious sedation by general anesthetist.
The results of this study are summarized in Tables 1–5 and Figures 1–5.
Table 1.
Etiology of trauma

Table 5.
Surgical procedures performed

Figure 1.
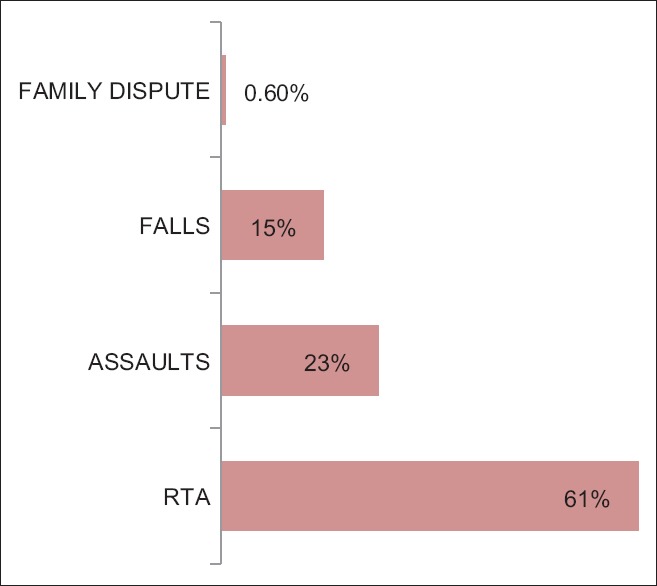
Etiology of trauma
Figure 5.
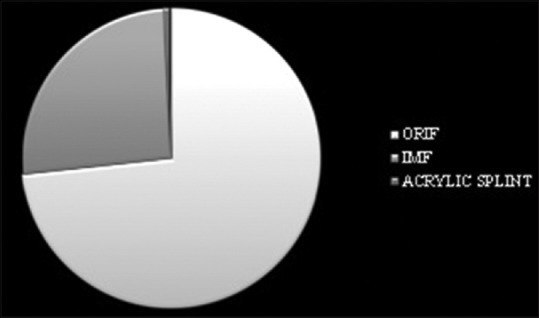
Surgical procedures performed
Table 2.
Gender distribution

Table 3.
Age distribution

Figure 2.
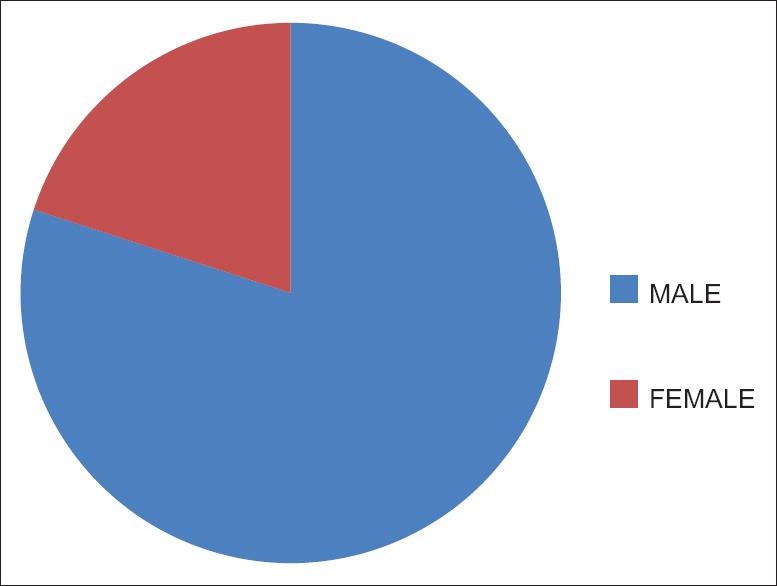
Gender distribution
Figure 3.
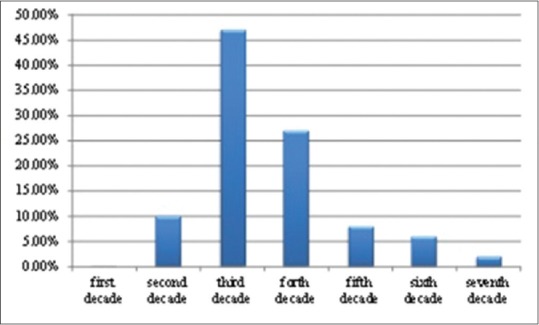
Age distribution
Figure 4.
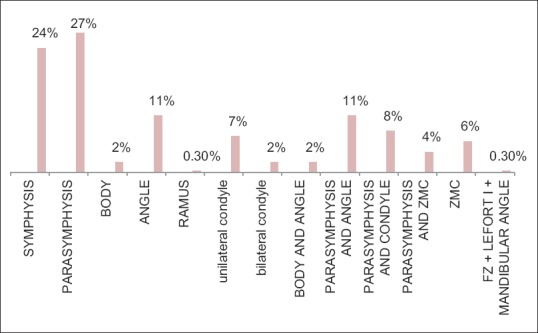
Pattern of maxillofacial fractures
DISCUSSION
Etiology
This study showed that the most common cause of facial injuries was RTAs, which was consistent with the observation in other studies in India and other countries.[2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9] While RTAs have steadily fallen in developed countries, they continue to rise with horrifying speed in the low- and middle-income countries (LMIC) of Africa and Asia. The World Health Organization has estimated that nearly 25% of all injury fatalities worldwide are a result of road traffic crashes (RTCs), with 90% of the fatalities occurring in LMIC. The reductions in RTC in developed countries are largely attributed to a wide range of road safety measures such as seat belt use, traffic calming measures, and traffic law enforcement. Therefore, there is an urgent need to get down to what the developed nations have done to reduce/prevent RTCs. Assaults and falls, respectively, were the second and the third most common cause of maxillofacial injuries in adults and children.[7,10]
Age
Similar to the findings of our study, 21–30 years was the most frequent age group involved in trauma by Obuekwe et al.[6] The low utilization of safety devices such as seat belts and air bags and the absence and nonenforcement of road traffic legislation were identified as etiological factors. The more frequent involvement of 21–30 years may be due to their increased involvement in traveling to workplace and outdoor activities.[6,7]
Gender
In the present study, male:female ratio was 4:1. Similar male predominance was seen in other studies which were done in India,[7,8,9,10] which could have occurred due to the fact that males are still the main working community and are hence more exposed to work-related stress and workplace injuries. The other causes of increased incidence of injuries in this age group and gender may be due to their risk-taking behavior along with lack of knowledge or, in the most of cases, violation of traffic rules.[11]
Pattern of facial fractures
Mandible fracture was the most common fracture observed in this study because it is the most prominent bone in the face and is often fractured more than the supported middle third of the face.[7,10] Ramdas et al.[1] in their review of maxillofacial fractures in a tertiary care center in India reported mandible as the most frequently fractured bone in most studies such as of Lida et al. in Japan, Motamedi in Iran, and Erol et al. in Turkey. Various Indian authors have documented similar findings.[1] It is known that the most common mandibular fracture location was the condyle (36%) followed by the corpus.[11] There are previous studies showing the corpus region as the most common location. Our findings are not similar to other studies[12,13,14] in this regard, demonstrating the parasymphysis as the most common region.[15,16] Fractures of the mandible were most complex with the bone fractured at more than one place. There is a saying that “like a Life Saver,” the mandible cannot be broken in only one spot.[11]
Contrary to our findings, Dube et al.[2] and Gandhi et al.[9] observed that majority of injuries are concentrated around middle third and upper third of the face. Agnihotri et al.[11] reported nasal bone as the most common site of injury. Le Fort I was the most common of the Le Fort types.[7] Ramdas et al.[1] in their review of maxillofacial fractures in a tertiary care center in India reported that cheekbone is susceptible to injury when an impact is directed laterally upon the upper face, whereas the mandible, owing to its prominent size and position, is more often affected when the impact is directed to the lower face.[1] In midface, zygomaticomaxillary complex was more frequently involved than the maxillary bone in similar studies,[1,9] whereas other studies show maxilla to be more frequently involved than zygomatic bone.[17] Midfacial fractures are often associated with head injury and polytrauma which are treated or referred to higher centers; therefore, less incidence of midfacial fracture is reported in our study.[17]
Surgical procedures performed
The face is made up of vertical and horizontal buttresses where bone is thicker to neutralize forces applied to it. Reduction and fixation of these key areas are the basis of maxillofacial reconstruction.[18]
Regarding treatment modalities, 73% of patients were treated by ORIF and IMF in 25.8% of patients, and 0.8% of pediatric patients were treated with stabilization by acrylic splint and circummandibular wiring. These findings were consistent with the studies conducted by Singh et al.[12] and Ramdas et al.[1] ORIF remains the gold standard of treatment of maxillofacial fractures.[13]
Facial bone plating remains a gold standard treatment modality[17,19,20] that was done in 259 adult patients in the present study.
Bioresorbable implants are an area of increasing research interest for ORIF of midface and pediatric mandibular fractures.[19] However, three patients of pediatric mandibular fracture in the present study were treated with closed reduction and stabilization by acrylic splint with circummandibular wiring. Acrylic splints are easy to make, far more cost benefit, and easily accepted by patients, and they also can be used in mixed dentition. Besides, treatment can be done without open reduction, and there is no need for general anesthesia in small fractures. The stabilization of adjacent bone and tooth and minimum nonunion are among other benefits of this method. Lingual splints are more reliable than open reduction and relatively minimize the risk of morbidity and discomfort associated with open reduction. According to the above-mentioned issues and less traumatic nature of splints, some authors recommend the use of lingual splints in young patients with bone fractures.[21]
Retrospective and prospective studies in literature comparing open and closed treatments report that the surgical procedure has no superiority to the closed technique as in function, range of motion, occlusion, contour, and sensory or motional function retrieval.[22]
To avoid complications related to the traditional open techniques such as facial nerve damage and scarring and those related to the close techniques such as the lengthened maxillomandibular fixation, nonanatomical reduction, and difficulties associated with mandibular movements, the modern-day surgical techniques such as the endoscope-assisted technology again raise the question of choosing either the open or closed treatment technique.[22] However, in the present study, 91 adult patients of mandibular fractures were treated successfully by IMF.
CONCLUSION
RTAs were reported as the leading cause of maxillofacial fractures followed by assault, falls, and familial dispute, respectively. Majority of victims were adult males and also in the third decade of life. Mandible was the most commonly fractured bone with parasymphysis as the most frequent site.
The “Face-It!” campaign headed by Dr. Sanjiv Nair and his team has found widespread acclaim and helped in increasing “Road Safety Awareness” as well as awareness about oral and maxillofacial surgeons as trauma care providers.[23]
As a surgeon, we may help a few thousand patients in our lifetime, but as a researcher and entrepreneur, you can create a legacy to help millions and provide employment for thousands. We have many examples for this. This needs mentorship. I am sure we can connect culture, creativity, and entrepreneurship (Dr. David P Tauro, President AOMSI).[24]
Strengths of our study
This clinical audit emphasizes on the etiology, common age and gender involved, pattern of facial fractures, and application of novel surgical approaches as a gold standard treatment modality in oral and maxillofacial trauma patients managed in a dental teaching institute in India.
Limitation of our study
Retrospective nature is the inherent weakness of our study.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Acknowledgment
This study was presented as paper in 1st zonal AOMSI (Punjab-Haryana) conference in zirakpur on 5th october 2016 by author (Dr Paramjot kaur) of this manuscript.
REFERENCES
- 1.Ramdas S, Lingam PP, Sateesh S. Review of maxillofacial fractures in a tertiary care center in Puduchery, South East India. Ann Trop Med Public health. 2014;7:100–4. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Dube A, Rao G, Tanwar A. Pattern of Maxillofacial Injury Associated With Head Injury at a Neuro Surgical Centre: An Analysis of 250 Cases. Int J Dent Med Spec. 2014;1:2–6. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Malara P, Malara B, Drugacz J. Characteristics of maxillofacial injuries resulting from road traffic accidents – A 5 year review of the case records from department of maxillofacial surgery in Katowice, Poland. Head Face Med. 2006;2:27. doi: 10.1186/1746-160X-2-27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Gupta R, Suryanarayanan S, Sharma A, Pandya V, Sathaye S. Traumatic mandibular fractures. A pendulum towards closed reduction. World Artic Ear Nose Throat. 2010;3:1–3. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Hashim H, Iqbal S. Motorcycle accident is the main cause of maxillofacial injuries in the Penang Mainland, Malaysia. Dent Traumatol. 2011;27:19–22. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-9657.2010.00958.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Obuekwe ON, Ojo MA, Akpata O, Etetafia M. Maxillofacial trauma due to road traffic accidents in Benin City, Nigeria. A prospective study. Ann Afr Med. 2004;2:58–63. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Adeyemo WL, Ladeinde AL, Ogunlewe MO, James O. Trends and characteristics of oral and maxillofacial injuries in Nigeria: A review of the literature. Head Face Med. 2005;1:7. doi: 10.1186/1746-160X-1-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Bali R, Sharma P, Garg A, Dhillon G. A comprehensive study on maxillofacial trauma conducted in Yamunanagar, India. J Inj Violence Res. 2013;5:108–16. doi: 10.5249/jivr.v5i2.331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Gandhi S, Ranganathan LK, Solanki M, Mathew GC, Singh I, Bither S. Pattern of maxillofacial fractures at a tertiary hospital in Northern India: A 4-year retrospective study of 718 patients. Dent Traumatol. 2011;27:257–62. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-9657.2011.00996.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Brasileiro BF, Passeri LA. Epidemiological analysis of maxillofacial fractures in Brazil: A 5-year prospective study. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2006;102:28–34. doi: 10.1016/j.tripleo.2005.07.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Agnihotri A, Galfat D, Agnihotri D. Incidence and pattern of maxillofacial trauma due to road traffic accidents: A prospective study. J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2014;13:184–8. doi: 10.1007/s12663-013-0502-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Singh V, Malkunje L, Mohammad S, Singh N, Dhasmana S, Das SK. The maxillofacial injuries: A study. Natl J Maxillofac Surg. 2012;3:166–71. doi: 10.4103/0975-5950.111372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Özkaya O, Turgut G, Kayali MU, Ugurlu K, Kuran I, Bas L. A retrospective study on the epidemiology and treatment of maxillofacial fractures. Turk J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2009;15:262–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Sandhu S, Gauba ML, Kapila BK. A study of facial fractures. JIDA. 1981;53:267–9. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Motamedi MH. An assessment of maxillofacial fractures: A 5-year study of 237 patients. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2003;61:61–4. doi: 10.1053/joms.2003.50049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Kaur R, Lehl G. Retrospective analysis of maxillofacial injuries in the dental department of a medical college. Indian J Dent Sci. 2012;4:30–2. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Shah A, Nautiyal V, Gupta A, Ramola V. Trends of maxillofacial fractures in the Garhwal Himalayas at government medical college, Srinagar, Uttarakhand. Natl J Maxillofac Surg. 2016;7:80–5. doi: 10.4103/0975-5950.196139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Manson PN, Hoopes JE, Su CT. Structural pillars of the facial skeleton: An approach to the management of le fort fractures. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1980;66:54–62. doi: 10.1097/00006534-198007000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Kaur P. A review on bioresorbable materials: Application in oral and maxillofacial surgery. Int J Dent Health Sci. 2016;3:1138–56. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Bell RB, Kindsfater CS. The use of biodegradable plates and screws to stabilize facial fractures. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2006;64:31–9. doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2005.09.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Samieirad S, khajehahmadi S, Tohidi E, Pakravan M. A conservative method for treating severely displaced pediatric mandibular fractures: An effective alternative technique. J Dent Mater Tech. 2016;5:53–8. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Bayat M, Parvin M, Meybodi AA. Mandibular subcondylar fractures: A Review on treatment strategies. Electron Physician. 2016;8:3144–9. doi: 10.19082/3144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. [Last accessed on 2017 Oct 19]. Available from: http://www.aomsi.com/WebPages/newsPDFLink.aspx .
- 24. [Last accessed on 2017 Oct 19]. Available from: http://www.aomsi.com/NewsPDF/MaxFacts%20 Jan’16.pdf .


