Abstract
Although various surgical procedures have been developed for chronic rotator cuff tear repair, the re-tear rate remains high with severe fat infiltration. However, little is known about the molecular regulation of this process. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) in the intra-muscular space are origin of ectopic fat cells in skeletal muscle. We have previously shown that high-mobility group box 2 (HMGB2), which is a nuclear protein commonly associated with mesenchymal differentiation, is involved in the early articular cartilage degeneration. In this study, we addressed the role of HMGB2 in adipogenesis of MSCs and fat infiltration into skeletal muscles. HMGB2 was highly expressed in undifferentiated MSCs and co-localized with platelet-derived growth factor receptor α (PDGFRA) known as an MSC-specific marker, while their expressions were decreased during adipocytic differentiation. Under the deficiency of HMGB2, the expressions of adipogenesis-related molecules were reduced, and adipogenic differentiation is substantially impaired in MSCs. Moreover, HMGB2+ cells were generated in the muscle belly of rat supraspinatus muscles after rotator cuff transection, and some of these cells expressed PDGFRA in intra-muscular spaces. Thus, our findings suggest that the enhance expression of HMGB2 induces the adipogenesis of MSCs and the fat infiltration into skeletal muscles through the cascade of HMGB2-PDGFRA.
Subject terms: Experimental models of disease, Molecular medicine
Introduction
Recent studies have revealed a relationship between the severity of fat infiltration into skeletal muscles, as observed in ruptured rotator cuffs, and clinical outcomes1,2. Although various surgical procedures have been developed to restore cuff integrity, including bone marrow stimulation3, the re-tear rate remains high for chronic rotator cuff tear (RCT), which is associated with severe fat infiltration2. The emergence of adipocytes in muscles might be attributed to mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs)4, and the loss of mechanical stretch may initiate adipogenic pathways in pluripotent stem cell and precursor cell populations within the muscle, leading to the phenotypic changes observed with fat infiltration4.
Recently, platelet-derived growth factor receptor α (PDGFRA)-positive mesenchymal progenitors have been reported to contribute to adipogenesis in skeletal muscle and to be responsible for ectopic fat cell formation in skeletal muscle under pathological conditions5–7. In addition, PDGFRA is an MSC-specific cell surface marker, along with stem cell antigen-1 (Sca-1)8,9, which is widely accepted as a marker of stem cell enrichment in tissues10.
HMGB2 is a member of the high-mobility group box (HMGB) protein family, which also includes ubiquitous HMGB1 and embryo-specific HMGB3. These three proteins are homologous for 80% identity at the amino acid level and characterized by two basic HMG box domains followed by a long acidic tail11. As nuclear proteins, HMGB1 and HMGB2 regulate various cellular activities, including transcription, DNA replication, and repair12. They bind to transcription factors, such as steroid hormone receptors, p53, p73, LEF1, and Runx213–16, and enhance the transcriptional and recombination activities of their partner proteins. HMGB2 is detected at high levels in human MSCs, and its expression decreases during chondrogenic and osteogenic differentiation16. HMGB2 also regulates various other differentiation programs, including erythropoiesis, spermatogenesis, neurogenesis and myogenesis17–20. However, the function of HMGB2 in adipogenesis has not yet been elucidated.
The present study aimed to clarify the role of HMGB2 in MSC adipogenesis. We also investigated its role in fat infiltration into skeletal muscles following rotator cuff tear and the relationship between HMGB2 and PDGFRA during this process.
Results
Microarray analysis of adipogenesis-related markers in wild-type (WT) and Hmgb2−/− MSCs
Microarray analysis of wild-type (WT) and Hmgb2−/− MSCs identified 426 differentially expressed transcripts; 124 transcripts were decreased and 302 transcripts were increased in Hmgb2−/− MSCs as compared with WT cells. The transcriptional expressions of adipogenesis-related genes, including Ebf121, Lifr22, Lpl, Fabp4, Ppargc1a, Pparg, and Cebpa23–26 were markedly decreased in Hmgb2−/− MSCs when compared with WT cells (Table 1). Furthermore, the pathway analysis of 426 differentially expressed genes with GeneSpring demonstrated that Hmgb2 deficiency in MSCs was associated with the remarkable suppression of adipogenesis gene pathway and the PPAR signaling pathway as well as white fat cell differentiation pathway (Table 2). In contrast, the genes involved in the Wnt signaling pathway, which reportedly inhibits the adipogenesis of MSCs27, were significantly increased in Hmgb2−/− MSCs (Table 2).
Table 1.
Adipogenesis-related genes including Pparg and Cebpa were suppressed in Hmgb2−/− MSCs.
| Gene symbol | Hmgb2−/− 1 | Hmgb2−/− 2 | WT 1 | WT 2 | ave (Hmgb2−/−)/ave (WT) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hmgb2 | 32.8 | 52.4 | 1,406.4 | 2,398.2 | 0.02 |
| Lpl | 26.8 | 30.4 | 1,218.0 | 888.2 | 0.03 |
| Fabp4 | 65.1 | 135.9 | 435.2 | 1,033.7 | 0.14 |
| Pparg | 214.1 | 231.4 | 869.7 | 487.9 | 0.33 |
| Ebf1 | 114.9 | 43.6 | 269.4 | 119.1 | 0.41 |
| Lifr | 54.6 | 82.3 | 218.3 | 112.7 | 0.41 |
| Ppargc1a | 33.9 | 34.1 | 110.7 | 46.4 | 0.43 |
| Cebpa | 40.6 | 38.3 | 70.4 | 96.9 | 0.47 |
The list of genes whose expression levels were less than half in Hmgb2−/− MSCs compared to in WT MSCs.
Table 2.
Pathway analysis of genes that were considerably inhibited or activated in Hmgb2−/− MSCs.
| Inhibited pathways in Hmgb2−/− MSCs | p-value | Activated pathways in Hmgb2−/− MSCs | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adipogenesis genes | 3.55E-06 | Focal Adhesion | 5.22E-09 |
| White fat cell differentiation | 4.84E-04 | XPodNet-protein-protein interactions in the podocyte expanded by STRING | 5.52E-09 |
| Retinol metabolism | 8.70E-04 | ||
| Chemokine signaling pathway | 0.00179 | PodNet-protein protein interactions in the podocyte | 8.44E-09 |
| Selenium micronutrient network | 0.00541 | Primary focal segmental glomerulosclerosis FSGS | 1.12E-07 |
| PPAR signaling pathway | 0.00655 | Focal adhesion-PI3K-Akt-mTOR-signaling pathway | 3.05E-07 |
| Oxidative stress | 0.00797 | Matrix metalloproteinases | 1.01E-06 |
| Prostaglandin synthesis and regulation | 0.00971 | Integrin-mediated cell adhesion | 2.43E-05 |
| Ovarian infertility genes | 0.00971 | IL-3 signaling pathway | 2.43E-05 |
| Focal adhesions | 0.0116 | p53 signaling | 0.0013 |
| Nuclear receptors | 0.0144 | TGF beta signaling pathway | 0.00338 |
| Tryptophan metabolism | 0.0182 | Osteoblast | 0.00595 |
| Selenium metabolism selenoproteins | 0.0215 | miRNAs involved in the DNA damage response | 0.00595 |
| S1P pathways and spinal cord injury | 0.0285 | Complement and coagulation cascades | 0.006 |
| Metapathway biotransformation | 0.029 | Alpha6-beta4 Integrin Signaling pathway | 0.00791 |
| MAPK signaling pathway | 0.015 | ||
| IL-7 signaling pathway | 0.0154 | ||
| ErbB signaling pathway | 0.0173 | ||
| Delta-Notch signaling pathway | 0.018 | ||
| EGFR1 signaling pathway | 0.0185 | ||
| PluriNetWork | 0.0228 | ||
| Hypertrophy model | 0.0232 | ||
| Regulation of actin cytoskeleton | 0.0346 | ||
| Endochondral ossification | 0.0376 | ||
| MAPK signaling pathway | 0.0408 | ||
| Wnt signaling pathway NetPath | 0.0413 | ||
| miRNA regulation of DNA damage response | 0.0423 | ||
| Kit receptor signaling pathway | 0.0456 | ||
| TFs regulate miRNAs related to cardiac hypertrophy | 0.0467 | ||
| IL-5 signaling pathway | 0.0491 | ||
| Inflammatory response pathway | 0.0492 |
Pathway analysis was performed for the 426 differentially expressed genes between WT and Hmgb2−/− MSCs. In Hmgb2−/− MSCs, adipogenesis-related pathways, such as the PPAR signaling pathway, and white fat cell differentiation-related pathways were significantly suppressed, whereas the Wnt signaling pathway was significantly enhanced.
HMGB2 Expression in MSCs during adipogenic differentiation
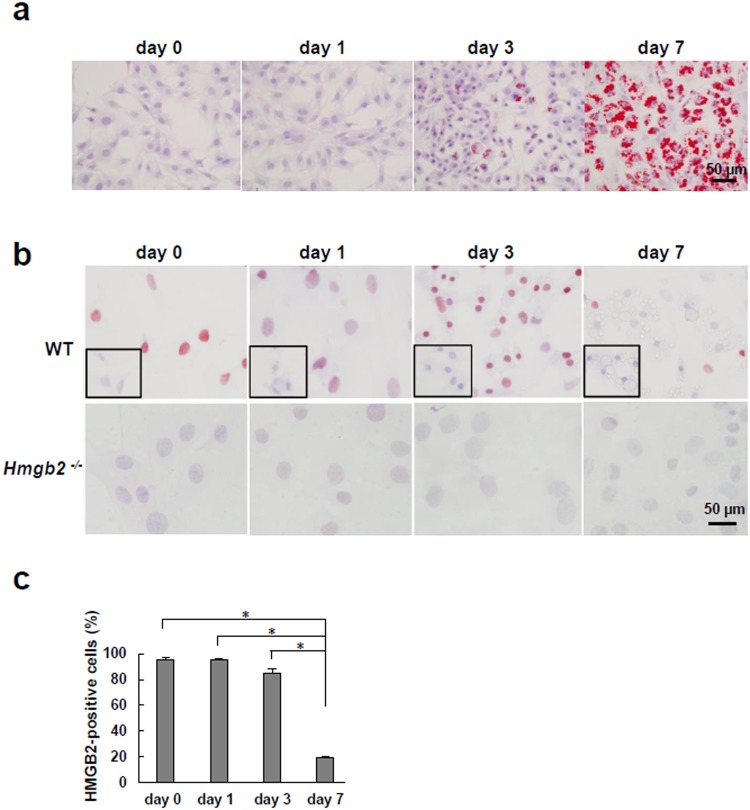
Based on the microarray data, we subsequently examined endogenous Hmgb2 expression in murine MSCs during adipogenic differentiation. Oil-red O staining showed a large increase in lipid droplets in WT MSCs on induction day 7, indicating that MSCs became mature adipocytes (Fig. 1a). During adipogenic differentiation, we found that HMGB2 was localized in the nuclei of undifferentiated WT MSCs and that Hmgb2−/− MSCs did not exhibit HMGB2 expression (Fig. 1b). On day 3, strong HMGB2 staining was observed in WT MSCs, and the number of HMGB2-positive cells was significantly reduced on day 7 (Fig. 1c).
Figure 1.
The expression of HMGB2, which was highly expressed in undifferentiated MSCs, decreased during adipocyte maturation. (a) Oil-red O staining of WT MSCs during adipogenesis (original magnification, x400, 0.237 mm2/view). (b) Immunostaining of HMGB2 in WT and Hmgb2−/− MSCs during adipogenesis. The small black boxes indicate negative controls (original magnification, x400, 0.237 mm2/view). (c) Percentage of WT MSCs positive for HMGB2. n = 3 for each time point. *p < 0.001.
Targeted disruption of Hmgb2 in MSCs during adipogenesis
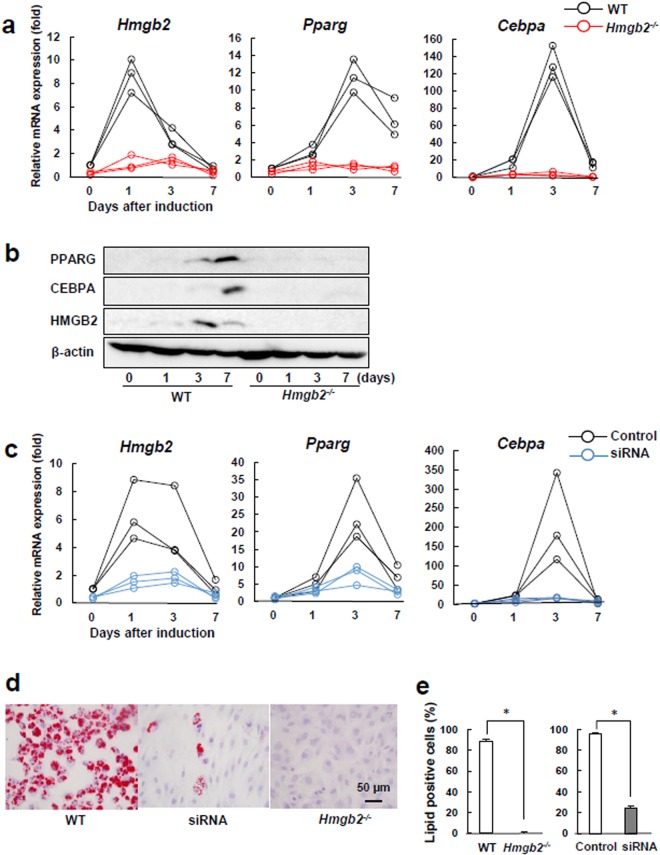
We assessed the endogenous expression of Hmgb2 and adipogenesis-related markers in WT and Hmgb2−/− MSCs. Quantitative PCR showed that the expression of Hmgb2 peaked on induction day 1, prior to the expression of the adipogenic master transcriptional regulators Pparg and Cebpa25, which peaked on day 3, and then gradually decreased (Fig. 2a). Similar to the microarray data, the Pparg, Cebpa and Hmgb2 levels were apparently decreased in Hmgb2−/− MSCs compared with WT MSCs during adipogenesis. This HMGB2, PPARG, and CEBPA expression pattern was also reflected in the western blotting results, and bands were barely detected in Hmgb2−/− MSCs (Fig. 2b). Full length blots and densitometry data are shown in Supplementary Fig. S1a,b, respectively.
Figure 2.
Hmgb2 deficiency reduced MSC adipogenic differentiation. (a) Quantitative PCR was performed to assess the Hmgb2, Pparg and Cebpa levels in WT and Hmgb2−/− MSCs during adipogenesis. (b) The expression levels in the cells at each time point in three independent experiments were determined by Western blotting of WT and Hmgb2−/− MSCs during adipogenesis. The exposure time for HMGB2, PPARG and CEBPA was 120 sec, and the time for β-actin was 2 sec. HMGB2/β-actin and PPARG/CEBPA were detected in the different part of the each gel, respectively. Representative data from three separate experiments are shown. (c) Quantitative PCR in MSCs transfected with Hmgb2 siRNA. (d) Oil-red O staining of WT MSCs, MSCs transfected with Hmgb2 siRNA, and Hmgb2−/− MSCs 7 days after adipogenic induction (original magnification, x400, 0.237 mm2/view). (e) Percentage of cells positive for lipid droplets among the WT and Hmgb2−/− cells on day 7. n = 3 for each time point. *p < 0.001.
We next sought to determine whether the attenuation of adipogenic marker expression in Hmgb2−/− MSCs was reproducible in murine MSCs following siRNA-mediated silencing of Hmgb2. We observed the transcriptional expression of Hmgb2 was reduced at approximately 63% on average after transfection of the siRNA for Hmgb2 (Fig. 2c). Furthermore, the knockdown of Hmgb2 also strongly suppressed the transcriptional expressions of Pparg and Cebpa afer adipogenic induction (Fig. 2c). On the other hand, the adipocytic differentiation of Hmgb2−/− MSCs and Hmgb2-knockdown MSCs was significantly inhibited on day 7 when compared with that of WT MSCs (Fig. 2d,e).
Correlation between PDGFRA and HMGB2 during MSC adipogenesis
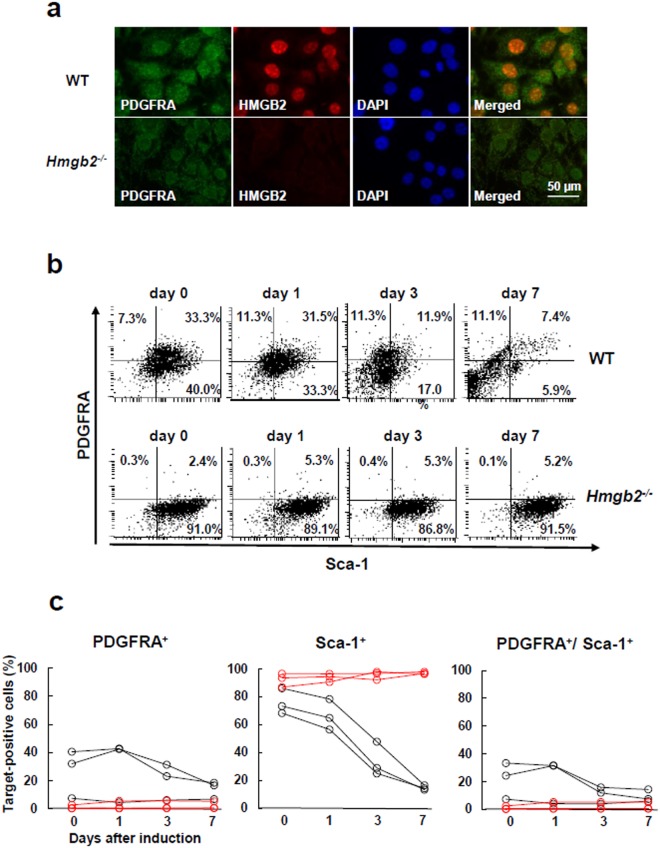
Previous studies have shown that murine bone marrow-derived MSCs express PDGERA and Sca-18,9, while they exhibit normal expressions of their related cell surface molecules under the deficiency of HMGB216. Because HMGB2 deficiency inhibited the adipogenic differentiation of MSCs, we further evaluated the effect of the deficiency of HMGB2 on the expression of PDGERA and Sca-1 during the adipogenesis of MSCs. Immunocytochemical analysis showed that both HMGB2 and PDGFRA were expressed in the nuclei and cytoplasm in undifferentiated WT MSCs, whereas PDGFRA was barely expressed in Hmgb2−/− MSCs (Fig. 3a). Flow cytometric analysis revealed that approximately one-third of WT MSCs expressed both PDGFRA and Sca-1 on days 0 and 1 after adipogenic induction (Fig. 3b,c and Supplementary Fig. S2). Thereafter, the frequency of the cells expressing both PDGFRA and Sca-1 were decreased, and less than 10% of the cells expressed these molecules on day 7 following adipogenic induction of WT MSCs (Fig. 3b,c, Supplementary Fig. S2a,b). In contrast, PDGFRA+ cells were barely detectable in Hmgb2−/− MSCs, whereas Sca-1+ cells remained upon adipogenic induction (Fig. 3b,c, Supplementary Fig. S2a,b).
Figure 3.
HMGB2 was co-expressed with PDGFRA in undifferentiated MSCs, and Hmgb2 deficiency was associated with PDGFRA reduction. (a) Double immunofluorescence representing HMGB2 and PDGFRA expression in MSCs 1 day after adipogenic induction (original magnification, x630). (b) Flow cytometry analysis for the expressions of PDGFRA and Sca-1 during adipogenesis of MSCs. Representative data from three different experiments are shown. (c) The percentages of PDGFRA+, Sca-1+, and PDGFRA+/Sca-1+ cells in WT (black lines) and Hmgb2−/− MSCs (red lines) are plotted. n = 3 for each time point.
HMGB2 and PDGFRA expression in a rat rotator cuff tear model
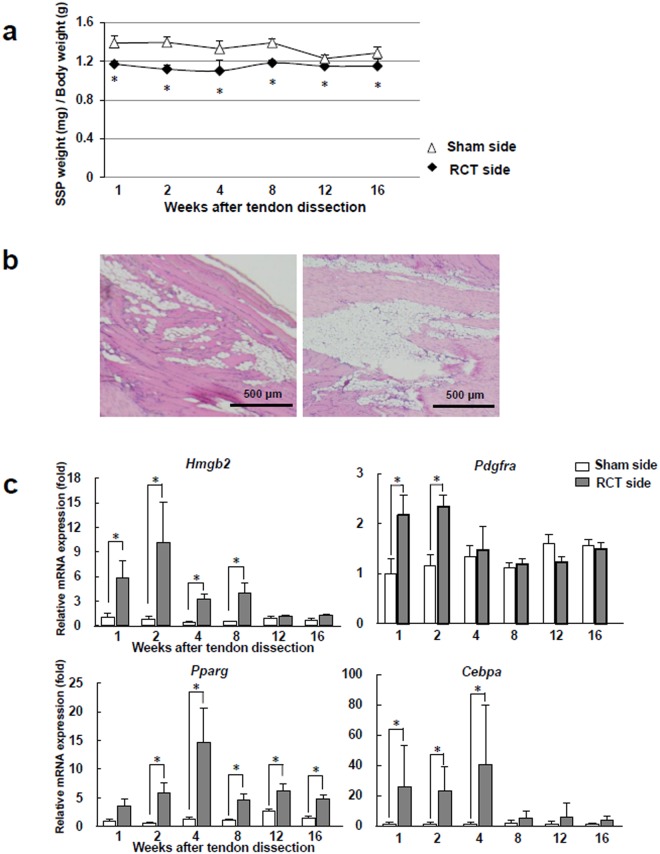
To address whether the expression of HMGB2 is associated with the ectopic fat formation in skeletal muscles, we used an RCT model in rats. As reported previously28,29, the muscles on the RCT side were atrophic with ectopic fat infiltration 16 weeks after tendon transection (Fig. 4a,b). In supraspinatus (SSP) muscles from the RCT side, the transcriptional expressions of Hmgb2, Pparg, Cebpa and Pdgfra were significantly higher than on the sham side at early time points (Fig. 4c). Furthermore, the expression of Hmgb2 transcript achieved a peak on 2 weeks after tendon transection, which preceded the transcriptional expressions of Pparg and Cebpa, whereas their expressions were gradually decreased thereafter.
Figure 4.
The expression of Hmgb2 evoked and peaked prior to that of adipogenic master regulators in rat SSP muscles after tendon transection. (a) Ratio of the SSP muscle weight to the body weight in the rat RCT model after tendon transection. (b) The representative HE images of different two SSP muscle samples from RCT side 16 weeks after tendon transection (original magnification, x40, each). (c) Quantitative PCR analysis of SSP muscles after tendon transection. n = 6 for each time point. *p < 0.05.
Immunohistochemcal analysis showed that HMGB2 was expressed in the cells in the intra-muscular spaces of SSP muscles (Fig. 5a). The average of total cell number and the ratio of HMGB2+ cells in the muscle belly were significantly increased on the RCT side on 2 weeks after tendon transection, but not on the sham side (Fig. 5b). In contrast, the expression of HMGB2 was markedly reduced in the ectopic fat cells on the RCT side 16 weeks after tendon transection, and this expression level was lower than that in the muscle belly on the sham side. Moreover, the cells in the intra-muscular spaces displayed a partial co-expression of HMGB2 and PDGFRA (Fig. 5c).
Figure 5.
HMGB2 was abundant and partially co-expressed with PDGFRA in the intra-muscular spaces of SSP muscles from rat RCT models. (a) Representative images of immunostaining for HMGB2 in SSP muscles from rat RCT models (original magnification, x400). (b) Average total cell number and ratio of HMGB2-positive cells in the muscle and ectopic fat cells 2 and 16 weeks after tendon transection. n = 6 for each time point, 0.237 mm2/view. wks, weeks after tendon transection. n = 6 for each time point. *p < 0.05. **p < 0.001. (c) Representative images showing co-expression of HMGB2 and PDGFRA (arrowheads) in serial immunostained sections (original magnification, x400).
Discussion
Muscle atrophy and fat infiltration are thought to be major factors limiting the success of RCT surgery and contributing to a higher rate of clinical failure30. The goal of this study was to identify molecular mechanisms responsible for the abnormal adipocyte differentiation and fat infiltration observed in the pathogenesis of RCT disease. Microarray analysis of bone marrow-derived MSCs from WT and Hmgb2−/− mice prompted the idea that HMGB2, which is highly expressed in MSCs16, may be important for regulating adipogenesis. Additionally, we verified that both MSCs derived from Hmgb2−/− mice and Hmgb2-knockdown MSCs with siRNA-mediated silencing derived from WT mice lost the ability to differentiate into adipocytes in vitro.
PPARG and CEBPA are major transcription factors in adipogenesis that cooperatively induce the expression of adipocyte-specific genes and are involved in the switch between proliferation and differentiation in cells26,31. Our in vitro data showed that Pparg and Cebpa were among the genes that were strongly downregulated by Hmgb2 suppression. Furthermore, we found that endogenous Hmgb2 expression in WT MSCs increased earlier than that of Pparg and Cebpa during adipogenesis. Studies in adipogenic cell lines have shown that hormonal induction of differentiation is rapidly induced by CEBPB and CEBPD, which begin to decrease coincident with a rise in CEBPA and PPARG26. CEBPB is a direct target gene of HMGB2 in senescent cells, and the knockdown of HMGB2 decreases Cebpb gene expression32; thus, HMGB2 may be an upstream factor regulating PPARG and CEBPA in MSC adipogenesis (Supplementary Fig. S3).
The HMGB2 mRNA and protein levels were enhanced in the early stage of adipogenesis and then gradually decreased when MSCs differentiated into mature adipocytes. This expression pattern is unique because HMGB2 expression, which is robust in undifferentiated MSCs, gradually decreases during other differentiation programs, such as myogenesis, chondrogenesis, and osteogenesis16,20. In our animal models, the transcriptional expression of HMGB2 was enhanced at the intra-muscular spaces at early stage after tendon transection, and then was barely detectable in ectopic fat cells at late stage. These phenomena led us to hypothesize that HMGB2 is prerequisite for the differentiation of MSCs during adipogenesis, myogenesis, chondrogenesis, and osteogenesis, while it is dispensable for the maintenance of the features of MSCs and their differentiated cell type. Collectively, these results suggest that HMGB2 is transiently expressed upon adipogenic induction, and that promotes the developmental process from MSCs into mature adipocytes or ectopic fat cells for the fat infiltration in skeletal muscle.
We have previously shown that MSCs exhibit normal cell surface expressions of CD44, CD29, and Sca-1 with lack of CD45, CD31, and CD34 under the deficiency of HMGB2, while they have an ability to differentiate into chondrocyte and osteocytes16,33. In contrast, Hmgb2−/− MSCs abnormally differentiate into adipocytes in terms of cell surface expressions of PDGFRA and Sca-1. These results suggest that HMGB2 is prerequisite for the differentiation of MSCs into adipocytes probably due to enhancement of the adipogenic signaling cascades.
The appearance of ectopic fat and fibrosis in skeletal muscles has been reported to be common in PDGFRA-positive cells localized in intra-muscular spaces5–7. The cells in which these phenomena originate were identified as MSCs rather than satellite cells or pericytes in the intra-muscular spaces, which are negative for PDGFRA. Based on these findings, we initially examined the expression of HMGB2 and PDGFRA in an in vitro culture model and found that both proteins were co-expressed in undifferentiated murine MSCs, followed by elimination after adipogenic maturation. Importantly, PDGFRA was notably decreased in Hmgb2−/− MSCs, which never differentiated into adipocytes, although Sca-1 was unaffected. These findings are compatible with a previous report showing that Pdgfra−/− murine MSCs cannot differentiate into adipocytes5. Thus HMGB2-PDGFRA cascade may play a key role in maintaining the pluripotency of MSCs toward the adipogenic lineage. In this context, a recent study showed that correcting the expression of HMGB2 and PDGFRA may be a potential therapeutic strategy for restoring the dysregulation of lipid metabolism in obese women with polycystic ovarian syndrome34.
A recent study showed that the population of PDGFRA-positive MSCs increased rapidly in murine SSP muscles after rotator cuff transection, and fat infiltration was reduced by PDGFR signal inhibition35. In our rat model, Pdgfra was enhanced after tendon transection, and the population of HMGB2-positive cells also increased in the SSP muscles with RCT. The co-expression of HMGB2 and PDGFRA in intra-muscular spaces was consistent with our flow cytometry data, which showed that approximately 40% of WT murine MSCs were positive for PDGFRA, although those cells were barely detectable in Hmgb2−/−. These findings indicate that HMGB2-PDGFRA-positive cells may be candidates for regulating adipogenesis as well as fat infiltration into skeletal muscles and suggest that these cells might be the origin of ectopic fat cells in ruptured rotator cuffs.
Pathway analysis of the DNA microarray suggests that Wnt signaling pathway is activated under the deficiency of HMGB2. Previous studies have shown that Wnt signaling has a key role to control the differentiation of MSCs during osteogenesis and myogenesis, and suppressing adipogenesis27,36. Furthermore, it has been reported that the changes in the activation status of Wnt signaling are observed in musculoskeletal system in response to the mechanical stimulations such as compression, tension and shearing37,38. On the other hand, the fat infiltration has been shown to suppress Wnt signal to enhance the expressions of Pparg and Cebpa in a rat RCT model38. In addition, it has been shown that the chronic tendon rupture, i.e. prolonged unloading state of muscles, often results in the highly degenerated muscles39, while continuous resistance training ameliorates muscle fibrosis and atrophy in aged mice mediated through the activation of Wnt signal40. Another studies demonstrated that mechanical stretching of muscle directly activates Wnt signaling to inhibit myoblast differentiation into adipocytes41. The interaction of HMGB2 with LEF1 enhances the Wnt/β-catenin pathway in articular cartilage15, and one possible mechanism explaining the observed modulation of LEF1-dependent transactivation by HMGB2 is that differential interactions between HMGB2 and nuclear factors affect the transcription of adipogenic genes containing LEF1-responsive elements. These findings may help elucidate the involvement of HMGB2 in the switch of MSCs to mature adipocytes or ectopic fat cells formation in the muscles.
In conclusion, we report that HMGB2 play a crucial role in regulating the adipogenesis of MSCs and fat infiltration into skeletal muscles following rotator cuff tear through the cascade of HMGB2-PDGFRA. In future studies, a better understanding of the nature of HMGB2 in the adipogenesis of MSCs may open new avenues for exploring therapeutic strategies to mediate the neutralization of its function for the ectopic fat formation in skeletal muscles with chronic tendon tears.
Methods
All animal experiments were conducted in compliance with a protocol approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Miyazaki University (no. 2015-518-4) and The Scripps Research Institute (no. 09-0130-3).
Preparation of murine MSCs and culture
Bone marrow-derived MSCs were prepared from the tibias and femurs of 6- to 8-week-old C57BL/6 J WT and Hmgb2−/− mice without sexual selection as previously reported16,42,43. At each passage during culturing the cells, cells were stained with phycoerythrin-conjugatedm mAbs to CD45, CD44 (BD PharMingen, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA), CD34 (Biolegend, San Diego, CA, USA), Sca-1, CD29, and CD31 (eBioscience, San Diego, CA, USA) and analyzed by flow cytometry to determine the phenotype of the cells16. The ability of the cells to undergo chondrogenesis and osteogenesis was assessed by quantitative PCR for Col2a1, Agc1, Col10a1, Alpl, Ibsp, Bglap, and Runx2, and confirmed by Safranin O and alizarin red S staining16. The adipogenic induction of MSCs was examined using the Poietics Mesenchymal Stem Cell Differentiation System according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Lonza, PT-3004, Basel, Switzerland), and the cells were harvested 0, 1, 3 and 7 days after induction in three independent experiments for quantitative PCR, western blotting, Oil-red O staining, immunocytochemistry and flow cytometry analyses (n = 3 for each time point).
RCT model in rats
Thirty-six male Sprague-Dawley rats (16 weeks; 450 to 550 g body weight) underwent massive surgical rotator cuff transection as described previously28,44. After the supraspinatus and infraspinatus tendons were transected at the transition between muscles and tendons, the remaining tendons on the bone side were removed. To generate a sham surgery control, the left deltoid muscles of the rats were also split. Surgery and resuscitation were performed on a heat board and under heat lamps. After surgery, buprenorphine (0.05 mg/kg) was administered subcutaneously to control pain28, and animals were housed in normal conditions. Six rats were euthanized with intra-peritoneal overdose injection of sodium pentobarbital at each time point (1, 2, 4, 8, 12 and 16 weeks) after tendon transection, and SSP muscles were harvested for quantitative PCR and immunohistochemistry (n = 6 for each time point). The average ratio of the SSP muscle weight to the body weight was calculated at each time point and compared between the RCT and sham sides. We did not observed the mortality or complications of animals before the anticipated end point.
Microarray analysis of murine MSCs
RNA was isolated from WT and Hmgb2−/− MSCs (n = 2 each due to the financial limitation), and cRNA was prepared as described previously16. Fifteen micrograms of fragmented cRNA from each sample was hybridized to a pre-equilibrated Affymetrix chip (Affymetrix Inc., MoGene-1_0-st-v1 Santa Clara, CA, USA), which was then washed, stained, and scanned in an HP ChipScanner (Affymetrix Inc.) as described previously45. Data normalization was performed using GeneSpring (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA). All entities (number: 28,853) were filtered based on expression ranging from the 20.0 to 100.0th percentile according to the raw data (number: 22,795). The entities list was made from transcripts showing an average expression level in Hmgb2−/− per average expression level in WT ≥ 2 or ≤0.5. The overlapping rates of entities randomly selected from the entities list (n = 426) and factors in a pathway listed in GeneSpring were calculated as p-values by hypergeometric test using GeneSpring. p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. The pathways in which the overlapping factors were increased or decreased in Hmgb2−/− MSCs were considered activated or inhibited in Hmgb2−/− MSCs, respectively.
Quantitative PCR
Total RNA was extracted and reverse transcribed into cDNA as described previously46. Gene expression was analyzed using SYBR Green and a Step One Plus Real-time PCR system (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). All samples were assayed in triplicate, and the CT values were averaged. GAPDH was employed as the internal control for rat muscles, and β-actin was used as the control for murine cells. The sequences of the primers used in the study are shown in Supplementary Table S1.
Gene knockdown of Hmgb2 in murine MSCs
Murine MSCs were cultured in six-well plates (2 × 105 per well) and transfected with 100 mM small interfering RNA (siRNA) targeting HMGB2 (Integrated DNA Technologies, MMC.RNAI.N008252.3_2 nm, Coralville, IA, USA)15 or the negative control (Integrated DNA Technologies, DS Scrambled-Neg universal negative control duplex) using Lipofectamine RNAi MAX reagent (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Adipogenic induction of MSCs was initiated 24 h after transfection with siRNA or negative control in three independent experiments as described above. Only the product of Integrated DNA Technologies without fluorescent labeling worked.
Oil-red O staining
To stain adipocytes, the cells were fixed in 10% formalin, rinsed in water and 60% isopropanol, stained with Oil-red O (Wako, Osaka, Japan) in 60% isopropanol, and then rinsed in PBS. Hematoxylin was used for counter staining.
Immunohistochemistry detection of HMGB2 and PDGFRA
Rat SSP muscle samples were fixed using 4% paraformaldehyde/PBS, paraffin-embedded, and cut into 3-µm-thick sections. After deparaffinization, the slides were autoclaved at 120 °C for 15 min in 10 mM citrate buffer (pH 6.0) to detect HMGB2 and in 10 mM Tris-EDTA buffer (pH 9.0) to detect PDGFRA for antigen retrieval. After inhibition of endogenous peroxidase activity with 3% H2O2 in methanol for 15 min, the sections were preincubated for 1 h with 500 µg/ml normal goat IgG or 5 µg/ml normal rabbit IgG to block non-specific binding of HMGB2 and PDGFRA antibodies, respectively. The slides were subsequently incubated overnight at 4 °C with rabbit anti-HMGB2 (1:500 dilution, Abcam, ab11973, Cambridge, UK) or goat anti-PDGFRA (5 µg/ml, R&D, AF-307-NA, Minneapolis, MN, USA) antibodies, and normal rabbit IgG and normal goat IgG were employed as the respective negative controls. After washing with 0.075% Brij 35 (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) in PBS, the slides were reacted with an HRP-conjugated goat anti-rabbit or HRP-conjugated rabbit anti-goat secondary antibody for 1 h. The HRP sites were visualized with DAB, and hematoxylin was used for nuclear counterstaining.
For immunocytochemistry, cultured cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde/PBS and treated with Histo VT One solution (Nakarai, Kyoto, Japan) for 20 min at 60 °C. Blocking of non-specific binding of antibodies was performed as described above. The same primary HMGB2 and PDGFRA antibodies used to probe rat muscles were incubated with cells for 1 h at room temperature. An HRP-linked goat anti-rabbit secondary antibody was employed for AEC visualization of HMGB2. Alexa-488-conjugated goat anti-rabbit and Alexa-594-conjugated rabbit anti-goat secondary antibodies were subsequently added for immunofluorescence detection, followed by incubation for 1 h. DAPI (Invitrogen, D1306) was used for nuclear counterstaining.
Cell counting
During MSC adipogenesis, Oil-red O-positive cells and AEC-positive cells were manually counted as adipocytes and HMGB2-positive cells, respectively, in 10 fields of view (magnification, x400, 0.237 mm2/view) for each condition. In SSP muscles from rat models, DAB-positive cells were manually counted as HMGB2-positive cells in different 5 views containing only muscle or fat tissue (magnification, x400, 0.237 mm2/view). The views were randomly selected in different regions not to be next to each other. The ratio of Oil-red O-positive cells or HMGB2-positive cells/total cells, including hematoxylin-positive cells, was calculated.
Western blotting
Cultured cells were lysed in RIPA buffer (Sigma-Aldrich). A total of 20 µg of each lysate was separated on 12% (w/v) Tris-glycine SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis gels and transferred to PVDF membranes (Invitrogen). After the membranes were blocked in 5% skim milk, they were incubated overnight at 4 °C with rabbit anti-HMGB2 antibody (3 µg/ml, Abcam, ab6782), rabbit anti-CEBPA antibody (2 µg/ml, Abcam, ab15048), rabbit anti-PPARG antibody (2 µg/ml, Abcam, ab45036) and mouse anti-β-actin antibody (1:50,000 dilution, Sigma-Aldrich, A2228). After washing with TBS-T, the membranes were incubated for 1 h with HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit secondary antibody for targets and with HRP-conjugated goat anti-mouse secondary antibody for β-actin. Then, the protein bands were visualized by chemiluminescence using an ImageQuant LAS4000 imaging system (GE Healthcare, Japan).
Flow cytometry
Cells were suspended in ice-cold Fc Block (anti-CD16/CD32 mAb; 1 mg/ml, BD Biosciences, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA) at 5 × 107 cells/ml and then stained with APC-conjugated PDGFRA (eBioscience, 17-1401-81, San Diego, CA, USA) and FITC-conjugated Sca-1 (eBioscience, 11–5981) antibodies for 30 min on ice. Fluorescence was analyzed using a FACSCalibur flow cytometer and CELLQuest Software (both from BD Biosciences). PI (Sigma-Aldrich, P4170) fluorescence was measured to define a live cell gate.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analyses were analyzed using SPSS 21 (IBM, Armonk, NY, USA). Differences were assessed using one-way ANOVA in Fig. 1c. Because the factors did not exhibit a normal distribution based on a Shapiro-Wilk test, the differences shown in Figs 2d and 4a,c,d were assessed using Wilcoxon signed-rank tests. These results are presented as means ± SD, and p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. In Figs 2a,c and 3c, and Supplementary Fig. S1b, all the values were plotted and connected to show the range of each factor (n = 3) at each time point.
Data availability
The datasets generated and analyzed in the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Electronic supplementary material
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Ikuyo Tsuchimochi, Mie Nagata, and Waka Soma for providing technical assistance. Ayako Nakatake assisted with the microarray analysis. Junji Ide and Takuya Tokunaga (Kumamoto University, Japan) assisted with the establishment of the rat RCT models. This work was supported by MEXT KAKENHI (grant number 15K10484) and a Grant-in-Aid for Clinical Research funded by Miyazaki University Hospital and the National Institutes of Health (grant number AG007996).
Author Contributions
N.T. designed the study conception and experiments, N.T. and D.L. drafted the manuscript, D.L., N.C. and H.M. performed experiments and analyzed data, K.S., Y.H., H.K., M.L. and E.C. provided reagents, cells and information, and interpret data and the manuscript.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher's note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Change history
3/10/2020
An amendment to this paper has been published and can be accessed via a link at the top of the paper.
Contributor Information
Noboru Taniguchi, Email: nobutanigu@gmail.com.
Katsuaki Sato, Email: katsuaki_sato@med.miyazaki-u.ac.jp.
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary information accompanies this paper at 10.1038/s41598-018-28023-7.
References
- 1.Galatz LM, Ball CM, Teefey SA, Middleton WD, Yamaguchi K. The outcome and repair integrity of completely arthroscopically repaired large and massive rotator cuff tears. The Journal of bone and joint surgery. American volume. 2004;86-A:219–224. doi: 10.2106/00004623-200402000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Goutallier D, Postel JM, Gleyze P, Leguilloux P, Van Driessche S. Influence of cuff muscle fatty degeneration on anatomic and functional outcomes after simple suture of full-thickness tears. Journal of shoulder and elbow surgery. 2003;12:550–554. doi: 10.1016/s1058274603002118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Taniguchi N, et al. Bone marrow stimulation at the footprint of arthroscopic surface-holding repair advances cuff repair integrity. Journal of shoulder and elbow surgery. 2015;24:860–866. doi: 10.1016/j.jse.2014.09.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kang JR, Gupta R. Mechanisms of fatty degeneration in massive rotator cuff tears. Journal of shoulder and elbow surgery. 2012;21:175–180. doi: 10.1016/j.jse.2011.11.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Uezumi A, Fukada S, Yamamoto N, Takeda S, Tsuchida K. Mesenchymal progenitors distinct from satellite cells contribute to ectopic fat cell formation in skeletal muscle. Nat Cell Biol. 2010;12:143–152. doi: 10.1038/ncb2014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Uezumi A, et al. Fibrosis and adipogenesis originate from a common mesenchymal progenitor in skeletal muscle. J Cell Sci. 2011;124:3654–3664. doi: 10.1242/jcs.086629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Uezumi A, et al. Functional heterogeneity of side population cells in skeletal muscle. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006;341:864–873. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.01.037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Morikawa S, et al. Prospective identification, isolation, and systemic transplantation of multipotent mesenchymal stem cells in murine bone marrow. J Exp Med. 2009;206:2483–2496. doi: 10.1084/jem.20091046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Houlihan DD, et al. Isolation of mouse mesenchymal stem cells on the basis of expression of Sca-1 and PDGFR-alpha. Nat Protoc. 2012;7:2103–2111. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2012.125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Forte G, et al. Interfacing Sca-1(pos) mesenchymal stem cells with biocompatible scaffolds with different chemical composition and geometry. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2009;2009:910610. doi: 10.1155/2009/910610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Bustin M. Regulation of DNA-dependent activities by the functional motifs of the high-mobility-group chromosomal proteins. Molecular and cellular biology. 1999;19:5237–5246. doi: 10.1128/MCB.19.8.5237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Bianchi ME, Agresti A. HMG proteins: dynamic players in gene regulation and differentiation. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2005;15:496–506. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2005.08.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Boonyaratanakornkit V, et al. High-mobility group chromatin proteins 1 and 2 functionally interact with steroid hormone receptors to enhance their DNA binding in vitro and transcriptional activity in mammalian cells. Molecular and cellular biology. 1998;18:4471–4487. doi: 10.1128/MCB.18.8.4471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Stros M, Ozaki T, Bacikova A, Kageyama H, Nakagawara A. HMGB1 and HMGB2 cell-specifically down-regulate the p53- and p73-dependent sequence-specific transactivation from the human Bax gene promoter. The Journal of biological chemistry. 2002;277:7157–7164. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110233200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Taniguchi N, et al. Chromatin protein HMGB2 regulates articular cartilage surface maintenance via beta-catenin pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106:16817–16822. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0904414106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Taniguchi N, et al. Expression patterns and function of chromatin protein HMGB2 during mesenchymal stem cell differentiation. The Journal of biological chemistry. 2011;286:41489–41498. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.236984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Laurent B, et al. High-mobility group protein HMGB2 regulates human erythroid differentiation through trans-activation of GFI1B transcription. Blood. 2010;115:687–695. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-06-230094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Ronfani L, et al. Reduced fertility and spermatogenesis defects in mice lacking chromosomal protein Hmgb2. Development. 2001;128:1265–1273. doi: 10.1242/dev.128.8.1265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Abraham AB, et al. Members of the high mobility group B protein family are dynamically expressed in embryonic neural stem cells. Proteome Sci. 2013;11:18. doi: 10.1186/1477-5956-11-18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Zhou X, et al. HMGB2 regulates satellite-cell-mediated skeletal muscle regeneration through IGF2BP2. J Cell Sci. 2016;129:4305–4316. doi: 10.1242/jcs.189944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Jimenez MA, Akerblad P, Sigvardsson M, Rosen ED. Critical role for Ebf1 and Ebf2 in the adipogenic transcriptional cascade. Molecular and cellular biology. 2007;27:743–757. doi: 10.1128/mcb.01557-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Aubert J, et al. Leukemia inhibitory factor and its receptor promote adipocyte differentiation via the mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade. The Journal of biological chemistry. 1999;274:24965–24972. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.35.24965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Amri EZ, Teboul L, Vannier C, Grimaldi PA, Ailhaud G. Fatty acids regulate the expression of lipoprotein lipase gene and activity in preadipose and adipose cells. The Biochemical journal. 1996;314(Pt 2):541–546. doi: 10.1042/bj3140541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Hotamisligil GS, et al. Uncoupling of obesity from insulin resistance through a targeted mutation in aP2, the adipocyte fatty acid binding protein. Science. 1996;274:1377–1379. doi: 10.1126/science.274.5291.1377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Barak Y, et al. PPAR gamma is required for placental, cardiac, and adipose tissue development. Mol Cell. 1999;4:585–595. doi: 10.1016/S1097-2765(00)80209-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Rosen ED, et al. C/EBPalpha induces adipogenesis through PPARgamma: a unified pathway. Genes Dev. 2002;16:22–26. doi: 10.1101/gad.948702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Ross SE, et al. Inhibition of adipogenesis by Wnt signaling. Science. 2000;289:950–953. doi: 10.1126/science.289.5481.950. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Liu X, Manzano G, Kim HT, Feeley BT. A rat model of massive rotator cuff tears. Journal of orthopaedic research: official publication of the Orthopaedic Research Society. 2011;29:588–595. doi: 10.1002/jor.21266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Sevivas N, et al. Animal model for chronic massive rotator cuff tear: behavioural and histologic analysis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2015;23:608–618. doi: 10.1007/s00167-014-3441-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Burkhart SS, Barth JR, Richards DP, Zlatkin MB, Larsen M. Arthroscopic repair of massive rotator cuff tears with stage 3 and 4 fatty degeneration. Arthroscopy: the journal of arthroscopic & related surgery: official publication of the Arthroscopy Association of North America and the International Arthroscopy Association. 2007;23:347–354. doi: 10.1016/j.arthro.2006.12.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Wu Z, et al. Cross-regulation of C/EBP alpha and PPAR gamma controls the transcriptional pathway of adipogenesis and insulin sensitivity. Mol Cell. 1999;3:151–158. doi: 10.1016/S1097-2765(00)80306-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Aird KM, et al. HMGB2 orchestrates the chromatin landscape of senescence-associated secretory phenotype gene loci. J Cell Biol. 2016;215:325–334. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201608026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Dominici M, et al. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 2006;8:315–317. doi: 10.1080/14653240600855905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Xu, H. et al. PDGFRA, HSD17B4 and HMGB2 are potential therapeutic targets in polycystic ovarian syndrome and breast cancer. Oncotarget, 10.18632/oncotarget.17846 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 35.Shirasawa H, et al. Inhibition of PDGFR signaling prevents muscular fatty infiltration after rotator cuff tear in mice. Scientific reports. 2017;7:41552. doi: 10.1038/srep41552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Christodoulides C, Lagathu C, Sethi JK, Vidal-Puig A. Adipogenesis and WNT signalling. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2009;20:16–24. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2008.09.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Praxenthaler H, et al. Extracellular matrix content and WNT/beta-catenin levels of cartilage determine the chondrocyte response to compressive load. Biochimica et biophysica acta. 2018;1864:851–859. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2017.12.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Itoigawa Y, Kishimoto KN, Sano H, Kaneko K, Itoi E. Molecular mechanism of fatty degeneration in rotator cuff muscle with tendon rupture. Journal of orthopaedic research: official publication of the Orthopaedic Research Society. 2011;29:861–866. doi: 10.1002/jor.21317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Killian ML, et al. Chronic Degeneration Leads to Poor Healing of Repaired Massive Rotator Cuff Tears in Rats. The American journal of sports medicine. 2015;43:2401–2410. doi: 10.1177/0363546515596408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Horii Naoki, Uchida Masataka, Hasegawa Natsuki, Fujie Shumpei, Oyanagi Eri, Yano Hiromi, Hashimoto Takeshi, Iemitsu Motoyuki. Resistance training prevents muscle fibrosis and atrophy via down‐regulation of C1q‐induced Wnt signaling in senescent mice. The FASEB Journal. 2018;32(7):3547–3559. doi: 10.1096/fj.201700772RRR. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Akimoto T, et al. Mechanical stretch inhibits myoblast-to-adipocyte differentiation through Wnt signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;329:381–385. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.01.136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Syres K, et al. Successful treatment of the murine model of cystinosis using bone marrow cell transplantation. Blood. 2009;114:2542–2552. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-03-213934. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Meirelles Lda S, Nardi NB. Murine marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell: isolation, in vitro expansion, and characterization. British journal of haematology. 2003;123:702–711. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2141.2003.04669.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Ide J, et al. The effect of a local application of fibroblast growth factor-2 on tendon-to-bone remodeling in rats with acute injury and repair of the supraspinatus tendon. Journal of shoulder and elbow surgery. 2009;18:391–398. doi: 10.1016/j.jse.2009.01.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Spentzos D, et al. Gene expression signature with independent prognostic significance in epithelial ovarian cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22:4700–4710. doi: 10.1200/jco.2004.04.070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Taniguchi N, et al. Stage-specific secretion of HMGB1 in cartilage regulates endochondral ossification. Molecular and cellular biology. 2007;27:5650–5663. doi: 10.1128/mcb.00130-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated and analyzed in the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.